Practically in every vegetable garden, a place of honor is reserved for planting potatoes, aptly nicknamed the second bread by the people. Grow your own juicy tubers and provide them to your family for winter period- an easy task, but subject to all the recommendations of agricultural technicians. One of important points in the cultivation of nightshade root crop is feeding potatoes and fertilizing the beds throughout the growing season. How to properly fertilize potato plantings to increase the tubers collected from your own plot?
Preparing the soil in fall or spring
According to experienced vegetable growers, the preparation and filling in the fall of a plot allocated for potatoes, on loams and sandy loams with matured compost or rotted manure (from one to four buckets, depending on the initial indicators of soil fertility), almost doubles the yield of tubers. In addition to organic matter in the fall, phosphorus-potassium mineral compounds are embedded in the soil during digging, for example, double superphosphate (25 g / m2) and potassium chloride (15 g / m2), as well as plant ash (200-300 g / m2). meter).
On sandy soils, fertilizers for potatoes are applied only during spring digging, and not in autumn, since all nutrient components are washed out during the winter with sedimentary and melt water.
Adding 2-3 buckets of compost or peat-manure composted mixture makes the soil more moisture-retaining and provides tubers with all the necessary compounds. Additionally, during the pre-sowing preparation of sandy soils, you need to make:
- ammonium nitrate (20 g / sq. meter);
- double superphosphate (25 gr. square meter);
- potassium magnesium (20 g / sq. meter).
Fresh manure of farm animals for any nightshade crops, including potatoes, is contraindicated. The active components of undecomposed organic matter lead not only to a decrease in yield and crop diseases (scab, rot, black leg, late blight, cercospora, etc.), but also to a deterioration in the quality of root crops.

Top dressing in the budding and flowering phase with organic and mineral compositions
The soil filled with organic matter and mineral fertilizers provides potatoes with all the necessary nutrients. However, feeding during the budding period can increase the crop yield by almost 25%. Preparation before loosening and hilling potato bushes: in the aisles, retreating 6 cm from the stems, scatter a complex composition of superphosphate, potassium sulfate and carbamide (1: 1: 1), spending 9 grams of fertilizer per plant. It is also possible to fertilize with nitrofoskoy at the rate (10 g / bush).
Gardeners who do not use mineral fertilizers on their land need high-quality humus for feeding at the rate of 2 full handfuls for each bush and plant ashes (mix first with fertile soil 1: 1). Potatoes respond well to the introduction of dry bird droppings or granular humus, which are currently not difficult to purchase in an online store or a garden specialized market.
The second feeding of potatoes is necessary in cases of slow development of the aboveground part. Thus, the plants signal the gardener about the deficiency of potash components in the soil. Preparation for flowering: planting during the beginning of flowering is fertilized with a solution of potassium sulfate (30 grams of composition per standard bucket of water), spending 1 liter per square meter. meter of beds. After irrigation with fertilizer, the hilling of the bushes is performed. These actions are needed!
Remember that a lack of potassium during the formation of tubers leads to the fact that the pulp becomes dark, and the quality of the crop deteriorates sharply.

Foliar dressing of potato plantings
After the first flowers appear on potato beds, it is recommended to dust the plantings with sifted ash daily, after moistening the tops with moisture, and preferably in the early morning, while there is still dew on the leaves. Ash pollination is not only biological foliar feeding and providing the aboveground parts of plants with additional portions of microelements, but also protection against the Colorado potato beetle.
Foliar dressing of potatoes, carried out in the budding and flowering phase of potato plantings, increases the crop yield due to the outflow of nutrients from the tops to the tubers. A single spraying with a nutrient solution (dilute 20 g of superphosphate in 10 liters of warm water, let it brew for 48 hours, spend a liter of composition per 10 square meters. 1%.

To eliminate the deficiency of nitrogen compounds in the ground, which is manifested by yellowing of the tops and a slowdown in the development of the aboveground part of the bushes, foliar dressing with ammonium nitrate or urea (20 g of fertilizer per bucket of water) will help. It is better to spray potato bushes in the budding-flowering phase. In addition to nitrogen fertilization, potatoes are responsive to foliar irrigation with a solution of micronutrient fertilizers with microelements.
Experienced gardeners recommend mowing the tops 8-9 days before harvesting potatoes. This simple agricultural technique allows you to increase the density of the peel of root crops and its resistance to damage, and also significantly reduces the risk of developing fungal diseases, especially phytophthora.
Good potato harvests! Better to work hard during the growing season of the potato plantation in order to feast on winter delicious dishes from your favorite potatoes.
Potatoes consume nutrients very intensively throughout the growing season. This is due to the fact that the root system of the plant is poorly developed, and the tubers grow large and numerous, which is why the bush constantly lacks micro- and macroelements. After harvesting, the soil also remains depleted, and if you do not apply organic and mineral fertilizers for potatoes, then the next harvest will only bring disappointment. In general, potatoes need to be fed regularly. How, when and how to fertilize potatoes? We will tell you about this in this article.
As a rule, having allocated a new plot for growing potatoes, the gardener receives the highest yields in the first 2-3 years. And the longer the site was empty, the more abundant the harvest and the larger the root crops. And all because virgin soil is rich in nutrients necessary for potatoes. But since culture consumes a lot nutrients, including from the soil, then literally in two years the land begins to deplete, which affects the amount of harvest. The situation becomes especially critical in the fall, when, after harvesting potatoes, the site becomes depleted and unsuitable for growing vegetables.
For reference: one potato bush during its growing season consumes about 20 g of phosphorus, 50 g of nitrogen and 100 g of potassium. However, it is necessary to apply these fertilizers for potatoes in much larger quantities, since some of them are consumed by weeds, and some dissolve and remain in the soil. So how much fertilizer do you need per planting meter to get a good harvest? To begin with, potatoes love complex dressings that combine different nutrients, so most often fertilizers are combined, combining organic matter and mineral mixtures.
- humus or fresh manure (it will crush until spring) - 5-6 buckets / 1 m² of soil;
- superphosphate - 30 g / 1 m² (it dissolves in the soil for a very long time, therefore it is applied only in the fall);
- phosphorus and potassium - 15 g / 1 m² (it is advisable to apply together).
You can also choose one thing: organic or agrochemicals. It is believed that organic matter is the best, one might even say an ideal fertilizer for potatoes, since it is not only a source of nutrition for the crop, but also improves the properties of the soil, enriching it with humus. With the decomposition of organic matter in the upper layer of the soil, the amount of carbon dioxide increases several times, due to which the tubers grow especially large and of high quality. With such fertilizers, even on heavy and saline soils, it is possible to achieve good yields. 
A great opportunity to enrich the soil in the fall is sowing green manure immediately after. Of course, not all plants can be sown before winter. For example, lupine seeds do not even have time to germinate before the onset of cold weather. But white mustard is what you need. To build up the green mass, she needs only 3 weeks, after which she will lie down and safely rot under the snow. In the fall, while the earth has not yet caked, it is very convenient to do a preparatory digging, and if the soil on the site has become acidic, then it's time to start restoring its balance. To reduce acidity, ash, dolomite flour or slaked lime are added to the soil. The approximate consumption rate is 200 g / 1 m².
Video "Mineral dressing"
From the video you will learn how to feed potatoes with mineral fertilizers.
Spring feeding
It is worth recalling that all top dressing should be applied to moist, not wet soil, besides, potatoes do not tolerate excessive moisture or stagnant melt water. Therefore, the primary task in the spring is to ensure drainage and removal of excess moisture. Only then can fertilization begin. The most basic nutrient for plants at the beginning of the growing season is nitrogen. It is found in huge quantities in manure, as well as in complex mineral mixtures. However, the highest yield can be achieved by combining both types of fertilizers. 
There are many options for combining them, of which the following are most often used:
- 3 tbsp. spoons of nitrophosphate, 1 glass of ash, 1 bucket of humus / 1 m²;
- 20 g of potassium sulfate, 20 g of ammonium nitrate / 1 m² - applied during plowing or after it;
- high-moor peat or compost 1 bucket, 25 g nitrophoska / 1 m²;
- 1 bucket of humus, 20 g of saltpeter, 20 g of potassium sulfate, 40 g of superphosphate and 400 g of dolomite flour - mix everything, add after plowing.
When applying mineral dressings together with organic matter, keep in mind that complex mixtures dissolve and are absorbed much faster, therefore, for early potato varieties it is better to use only agrochemicals, and for later varieties, apply organic or combined dressings. In the absence of organic matter, only mineral mixtures can be used, but in a larger volume.
Fertilization when planting
Applying dressings for each individual plant directly during the planting process is considered more economical than spreading over the site, and there is more benefit from spot application. When planting, fertilizer for potatoes is applied directly into the hole before the seed tuber is placed in it. To the frequently asked question, which fertilizer is better for potatoes when planting, one can answer that it is possible to feed both organics and agrochemistry. If organic matter is chosen, then humus and ash are considered the best here. These materials are introduced into the hole at the rate of 0.5 liters of humus and a handful of ash. Only one of these fertilizers can be applied if desired. 
Mineral mixtures are used in much smaller quantities and they should be applied strictly in the dosage specified in the instructions. Nitrofoska is introduced in 1 tbsp. spoon in each well.
Kemir's complex fertilizer is applied at the rate of 15-20 g, and before planting it should be mixed with the ground. But vegetable growers also often practice the treatment of tubers before planting with nutrient solutions of manganese (potassium permanganate), copper or boric acid. All these products kill harmful bacteria, promote rapid germination of tubers, accelerate flowering and significantly increase yields.
Root dressing
This method of feeding potatoes is considered the most effective, since it allows you to deliver nutrients quickly and directly to the roots, more precisely, root crops. Root dressing is carried out, as a rule, during each loosening before hilling. They are introduced by watering the plants, but after them the soil should be additionally moistened (watered well). The following liquid dressings are used for potatoes:

Root dressing is most beneficial during the active growing season of potatoes - in late May and early June. At other times, feeding is carried out if there is a slowdown in growth or weakening of plants. Root dressing very effective, but you should not be limited to them, because not only the roots, but also the whole plant need nutrients.
Foliar dressing
After hilling the bushes, the most suitable time for foliar dressing comes. Spraying nutrient solutions on the leaves allows you to bring nutrients to the ground part of the plants, thereby improving the condition of the tops and extending the growing season. 

You need to know that everything foliar feeding preferably in the evening, as some preparations in the sun can burn the leaves. The advantage of evening processing is that the solution dries more slowly, so that the nutrients better penetrate the stems. Remember that the main thing in dressing is not to overdo it with their quantity, and then the harvest will delight you with the level and quality.
Video "When to fertilize"
The video will show you when is the best time to fertilize your potatoes.
Svetlana
One of the most important food crops in domestic agriculture is potatoes. It is grown in large quantities throughout the country. Land fertility and climate in different regions differ markedly. Comfortable growing conditions are not everywhere, but using fertilizers for potatoes, you can achieve high yields in any area and on any soil.
One plant during the growing season consumes up to 100 g of potassium, 20 phosphorus and 50 nitrogen... Fertilizers for potatoes must be applied in much larger volumes than they consume, since some of the nutrients do not reach the plant. Useful macro- and microelements steal weeds, and part of it dissolves in the soil complex, and is removed along with the evaporating moisture.
Autumn field preparation for potatoes
Gardeners usually receive the largest potato yields when they just start developing the site, in the first years after its development. Virginia is rich in all the nutrients needed to grow this root vegetable. But gradually the land becomes poorer. Potatoes need top dressing, which is applied both during the preparation of the soil for planting and throughout the entire growing season.
Most often, fertilizers for potatoes are combined, combining organic matter and agrochemicals.
General recommendations for autumn application are as follows: for 1 sq.m. soil take 5-7 buckets of humus (or fresh manure, he will pereperet over the winter). In parallel, mineral fertilizers are used. , which has a long period of transition of nutrients into the soil complex, is traditionally applied in the fall, about 30 g per sq. m. Phosphorus from the composition of this fat will have time to transform into a form accessible to plants by the spring. Potassium sulfate is added together with phosphorus, at the rate of 15 g per 1 sq.
For fertilization, you can use some agrochemicals, without organic matter. This is usually done on soils infected with pests or pathogenic microflora, for which manure is a favorable habitat. In the fall, in this case, you can apply double superphosphate, and potassium sulfate, in a ratio of 1: 2, since potatoes consume more.
After harvesting the tops of the potato field, you can plant siderates. But not all. Lupine, for example, will not even have time to climb, and he will not want to, he does not like too much low temperatures... And growing is ideal. For the formation of a sufficient amount of vegetative mass, it will take three weeks. With the onset of cold weather, the siderates will fall on their own, and in the spring they can be plowed along with the soil.

When the plot is prepared in autumn period, there is an opportunity to make a deep digging of the earth, it is still loose after harvesting the potatoes, it did not have time to pack. If the soil is to be cultivated by a tractor, then it must be plowed and cultivated. When using a walk-behind tractor, the site is passed twice if the soil is clayey, and once if it is sandy. Manual digging is carried out to the full depth of the shovel bayonet. It is not necessary to break large clods - there is more chance that the cold air will get to the roots of the weeds, and they will freeze out.
If the soil on the site is acidic, then in the fall you can start restoring its normal balance. For this, dolomite flour, lime or. Application rate - 200 g per 1 sq. You can understand that the pH has changed by the appearance of sorrel, moss on the beds, as well as by the color of the soil, which turns blue when acidified.
Spring feeding
Potatoes do not tolerate stagnant melt water, and need good drainage, so the first task that must be solved in the spring, when preparing a site for planting, is to ensure the removal of excess moisture. For this, drain ditches are organized, and the site itself, if possible, is located on an elevation. If the water table remains high, when potatoes are planted, ridges or ridges are formed, on top of which they are planted. ![]()
The most important element for spring plant nutrition is nitrogen. It is found in large quantities in manure, which makes this organic compound the best fertilizer for potatoes. But the greatest increase in yield is obtained when organic and mineral fertilizers... There are many methods of their combined application, some of them are presented below. The dosage is calculated for 1 sq. soil:
- 1 bucket of humus, 1 glass of ash, 3 tbsp. nitrophosphate;
- 20 g of ammonium nitrate, 20 g of potassium sulfate, add this mixture after plowing together with green manure;
- Peat manure (or compost), 20-30 g of nitrophoska plus inter-row feeding with ammonium nitrate (20 g) and potassium sulfate (20 g).
- 7-10 kg of humus mixed with ammonium nitrate (20 g), potassium sulfate (20 g), superphosphate 30-40 g, dolomite flour - 450 g.
- If there is no organic matter, you can use tuk without additional components, for example, nitrophosphate - 5 kg per hundred square meters, or - 3 kg per hundred square meters.
When using agrochemicals in conjunction with manure, it should be borne in mind that for early potato varieties it is necessary to apply a larger amount of fertilizers than for later ones. Varieties with a short growing season simply do not have time to take all the necessary substances from organic matter. Then mineral fertilizers come to the rescue, which act much faster, and provide the necessary nutrition in full.
Micronutrient fertilizers, for example, molybdenum or copper, can be included in potato feeding, and boric fertilizers are used on soils containing lime. They help to assimilate the main nutrients, "polish" their effect on the plant organism.
Fertilization when planting
It is believed that nesting, spot application of top dressing when planting for each specific plant is much more useful and economical than spreading fertilizers over the field.
Fertilizers can be applied directly to the hole. For example, if the choice fell on organic matter, then a 700 gram can of dry humus and 5 tablespoons are added to each hole. ash (a handful that fits in the hand of an adult).

And when using agrochemicals, you can adhere to the following scheme: put 1 tablespoon in each well. nitrophosphate and 0.5 cups of bone meal.
For local application when growing potatoes, you can use ready-made fertilizers, for example, Kemiru. This mineral dressing is added to the wells during planting, in the amounts indicated in the instructions for use.
Root dressing
This type of dressing is usually done before hilling the bushes, after slightly loosening, so that the components of the nutrient mixtures can more easily get to the roots of the plant. After fertilization, you should always water the plantings abundantly.
- . Despite the aggressiveness of this fertilizer, it can be used even in fresh, diluting in a ratio of 1:10, and spilling the grooves between the rows of potatoes with this suspension.
- . A tablespoon of urea is dissolved in 10 liters of water, and the bushes are poured under the root with this solution, after slightly loosening, but before the first hilling. The application rate for one plant is 0.5 l.
- . In a bucket of water (10 l), dissolve a liter of fresh cow dung, ferment, spill the aisles.
- Herbal infusion. Prepared from any types of weeds growing on the site. They soak in a barrel of water, wait for the infusion to ferment, dilute to obtain the color of weakly brewed tea, water the potatoes in the evening, along the perimeter of the hole. It is advisable not to touch the stem. It is best to carry out this feeding of potatoes in June, when the plant is actively consuming nitrogen.
- Mineral fertilizers. For root dressing of potatoes, various agrochemicals are used, for example, a solution of ammonium nitrate (20 g per 10 liters of water). You can use a mixture of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers in a 1: 1: 2 ratio by dissolving about 25 g of the mixture in 10 liters of water.
Foliar dressing
Potatoes need nutrients throughout the growing season. Starting soil fertilization alone is not enough, since not all macro- and microelements get directly to the cultivated crop, a significant part of them is scattered due to various reasons.
Foliar feeding is a good processing method that allows you to bring nutrition directly to the plant itself. It is best done after weeding the potatoes, in the evening, so as not to burn the leaves. With this method of applying fertilizers, they enter the plant organism much faster, and activate metabolic processes in it, significantly spurring its growth, development of the root system and, accordingly, significantly improving the quality and quantity of the crop. There are many types of potato feeding that have worked well. Some of them are presented below: 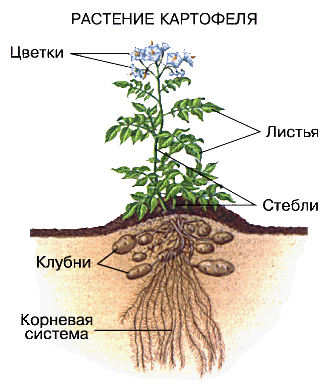
Urea
The following doses are recommended: water - 5 l, urea - 100 g, potassium monophosphate - 150 g, boric acid 5 g. You can include trace elements in the fertilizer - boron, copper, manganese, zinc and cobalt in minimal dosages, no more than 1 g per 10 l.
The first top dressing based on urea is carried out two weeks after full germination in the entire field. The working solution for it is diluted 2 times. The following dressings are carried out with the same composition, but undiluted. An interval of two weeks must be observed between them. Continue processing until the onset of flowering potatoes.
Phosphoric
At the end of the flowering of potatoes, about a month before harvesting, foliar feeding (especially of mid-season and late varieties) with superphosphate infusion (100 g of superphosphate per 10 liters of water - for spraying 10 sq. M.) Gives good results. Phosphorus, applied as leaf dressing, increases productivity and at the same time increases the starchiness of potato tubers.
Humates
Planting can be started from the appearance of the 4th leaf on the plant, with the periods between processing - 2 weeks. You can use, for example, Humate + 7, the application rate is 3 liters per hundred square meters, the working solution is 2 g per 10 liters.
Nettle infusion
Potatoes need nitrogen, potassium, calcium, iron, which are contained in this fertilizer. It is very simple to prepare the infusion - together with the tops, they are poured with water, and kept warm until complete fermentation. After that, the working solution is filtered, diluted and treated with the potato field, at intervals of 10 days.
Video: mineral nutrition of potatoes
Disease and pest control
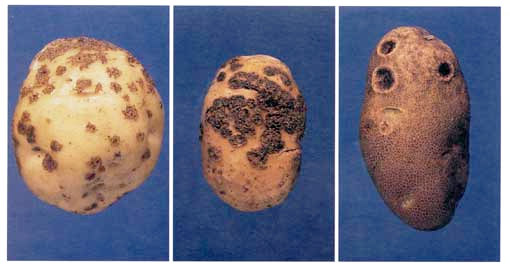
When growing potatoes, many gardeners traditionally limit themselves to fighting the Colorado potato beetle, and finding spots, ulcers, rot on root crops, they say that potatoes are sick. Many do not delve into the reasons for what is happening, believing that this is the influence of weather factors. In fact, this is far from the case. This plant has many diseases and pests. Potatoes need protection measures against various negative factors throughout the growing season.
Preventive measures
It is always better to prevent a problem than to heroically fight its consequences later. Therefore, in the spring, special attention should be paid to protecting potatoes from common diseases and insect pests. The measures taken will greatly help to preserve the harvest and improve its quality indicators.
Protection during the growing season

You can also mulch potatoes using sawdust for this. Under them, a favorable breeding environment will be created for insects that destroy Colorado beetles, for example, ladybugs.
Dealing with the consequences
- Before harvesting potatoes, it is necessary to remove diseased bushes from the field, and cut off the tops of healthy ones, otherwise the spores of the fungus can get from the stems onto the tubers, infecting them.
- Diseased potatoes can be eaten by removing the affected areas.
- Seed material must be prepared for storage before harvesting. For a safe wintering, potatoes need good drying in the sun and forced landscaping.
Video: growing potatoes - seminar "Good harvest at minimal cost"
When we plant potatoes on an area where there was previously virgin soil, the harvest is excellent without any fertilizers. But if we inherit a dacha from our grandmother, where for forty years active gardening has been going on with digging, weeding and other delights, you simply cannot grow good potatoes.
For all its apparent simplicity, potatoes consume a huge amount of minerals every year. One plant per season "draws" from the soil 50 grams of nitrogen, 100 grams of potassium and 20 grams of phosphorus. So it is necessary to feed, especially on poor soils. How to fertilize potatoes? When is the best time to fertilize potatoes? Let's figure it out ...
By and large, we all understand that it is possible to fertilize areas intended for growing potatoes both in the spring before planting and in the fall after harvesting. Fertilize when it suits you, as the saying goes.
Fertilizers for spring plowing
Before the spring digging of a plot for potatoes, the greatest effect is given by the combined use of organic and mineral fertilizers. The combinations can be different:
Option 1. 10 kilograms of humus, 20 grams of ammonium nitrate, 20 grams of potassium sulfate, 40 grams of superphosphate, 450 grams of dolomite flour per 1 square meter.
Option 2. 7 kilograms of compost, 30 grams of nitrophoska, 20 grams of potassium sulfate, 20 grams of ammonium nitrate per 1 square meter.
Option 3. 1 bucket of humus, 3 tablespoons of nitrophoska, 1 glass of ash per 1 square meter.
Option 4. If they grow on the site, then together with the incorporation of green mass, it is enough to add 20 grams of ammonium nitrate, 20 grams of potassium sulfate per 1 square meter.
Option 5. With a shortage of organic matter, complex fertilizers are applied: nitrophoska at the rate of 5 kilograms per hundred square meters or nitroammofoska (3 kilograms per hundred square meters).
Trace elements can be included in the fertilizer mixture, for example: copper (0.5 grams copper sulfate per 1 square meter) and molybdenum (0.1 grams of ammonium molybdenum per 1 square meter). They help the absorption of essential macronutrients.
All fertilizers are usually applied superficially. They are simply scattered over the soil surface, and then embedded to a depth of 20-25 centimeters when plowing, digging or loosening with a flat cutter.
Fertilizing the hole when planting

The second method of fertilizing in the spring is even easier and even more effective - all fertilizers are applied directly to the hole along with the planting of the tuber. Fertilizers in the planting hole can be applied both organic and mineral.
Organic option: Five tablespoons of ash and a 700 gram can of dry humus in each well.
Mineral option: 1 tablespoon of nitrophosphate in each well or 15-20 grams complex fertilizer"Kemira Potato".
Top dressing potatoes in summer
If in the spring they were late with fertilizers, did not have time, or by the appearance of the plants it is clear that they do not have enough nutrition, they help out feeding. You can feed potatoes until mid-July, it is not worth it longer, otherwise the plants will gain extra green mass, and the tubers will be “forgotten”. Any dressing is best done after watering or rain.
Root dressing of potatoes

First feeding carried out at the beginning of the growth of the tops. It is needed if the potato stalks are thin and pale green.
Usually it is applied just before the first hilling.
The first feeding option. 1 teaspoon of urea (or ammonium nitrate) + 1.5 cups of humus per 1 running meter of potato strip.
The second option for feeding. 3 grams of superphosphate, 3 grams of chloride or potassium sulfate, 2 grams of urea or ammonium nitrate for each bush.
The third option for feeding. 10 grams of nitrophoska per plant.
The fourth feeding option. 10 grams of dry bird droppings for each bush or watering the grooves between potato rows with chicken droppings in a 1:10 ratio.
Fifth feeding option. Two handfuls of humus per bush.
Sixth feeding option. 1 tablespoon of urea in 10 liters of water. The consumption rate for one plant is 0.5 liters.
Seventh feeding option.
Eighth feeding option. 20 grams of ammonium nitrate per 10 liters of water. The consumption rate for a bush is 0.5 liters.
Ninth feeding option. 1 liter of mullein per 10 liters of water. The aisles are watered with this solution.
As you can see, there are plenty of variations of the first feeding so that everyone can choose the most suitable one for their garden.
The first feeding option. 1 teaspoon of potassium sulfate and 3 tablespoons of ash per 1 running meter of potato strip.
The second option for feeding. 30 grams of potassium sulfate per 10 liters of water per 10 square meters.
The third option for feeding. Two handfuls of ash are mixed with the same amount of soil and added under each bush.
Third feeding done during flowering to accelerate the formation of tubers. To do this, dissolve 2 tablespoons of a spoonful of superphosphate and 1 glass of mullein in 10 liters of water. Introduce 0.5 liters of the resulting solution under each bush.
Foliar dressing of potatoes

Someone likes to water, but someone is more convenient to spray. If you belong to the second group, then you, undoubtedly, better pay attention to foliar feeding that is sprayed directly over the leaves of plants. Such dressings quickly deliver nutrients "to the address", activating the metabolic processes of the plant.
Nitrogen-potassium feeding. For 5 liters of water, 100 grams of urea, 150 grams of potassium monophosphate, 5 grams of boric acid are taken. You can also add trace elements - boron, copper, manganese, zinc and cobalt in a dosage of no more than 0.5 grams per 5 liters.
Such feeding is carried out two weeks after germination. Repeat if necessary. With this solution, potatoes can be sprayed before flowering at two-week intervals.
Supporters of organic farming spray potato plots with fermented nettle infusion or solutions of gummates.
Phosphate feeding. At the very end of the flowering of potatoes, to increase the yield and starchiness of tubers, potato bushes are sprayed with an extract of superphosphate: 20 grams of fertilizer are poured with 10 liters of warm water and insisted for two days, stirring occasionally. The consumption rate of this infusion: 1 liter per hundred square meters.
Fertilizing potato beds in the fall

Those who care about every minute in the spring prefer to fertilize the land for potatoes in the fall. This option has many advantages: some phosphorus fertilizers (for example, superphosphate) do not immediately transform into forms that are easily digestible for plants, and by spring they are just transformed. Fresh manure, too, cannot be put directly into the hole, but with autumn application it will just have time to overheat.
If it is tight with manure and humus, a green fertilizer called green manure helps out. After harvesting, all the beds are sown with green manure plants, an ideal option for potatoes is oil radish and others. Before the onset of cold weather, green manures will have time to gain enough green mass, and by the next season they will already be in the soil as useful organic matter. By the way, for those who use (or want to try) the no-till technology of growing potatoes, rye is perfect as a green manure for potatoes.
The potato crop is very susceptible to soil conditions. Fertilizers for potatoes in autumn are necessary in the same way as in spring, because for this crop it is the main factor in increasing yields and acquiring immunity against diseases. Also, taste and taste depend on the quantity and quality of fertilizers. appearance grown fruit.
1 Biological features of potatoes
The composition of the soil, its appropriate saturation with the required amount of nutrients affects the final result. In addition to fertilizers, the growth of potatoes is influenced by weather conditions, varietal characteristics of the crop, cultivation technology, and so on. The listed features are important, but some importance should be given to the composition of the soil.
Potatoes belong to herbaceous plants family of nightshades. The root system of this vegetable does not penetrate far into the soil; it develops in the surface layer. Thus, this arrangement of roots may seem unfortunate just because the plant receives nutrition in a small space. But with such an arrangement of the root crop, it becomes possible to apply fertilizers directly to the tubers, spending the preparations sparingly. The development of tubers and the green part of the plant requires a large number of nutrients.
A perennial tuberous potato plant is quite responsive to certain types of fertilizers. First of all, organic feeding is necessary for the vegetable. The main representatives of organic matter are straw manure and peat-manure composts. These valuable products are responsible for soil fertility, they effectively help to increase yields. Fertilizing the soil with organic compounds must be carried out in accordance with specific instructions.
In the fall, it is necessary to lay food for autumn plowing. Fertilization during this period helps to increase the yield several times, does not take up precious time during the spring work. During the winter, the organic matter introduced in the fall will rot and later be better absorbed by young potato tubers. Manure or compost fertilizer is spread over the entire plot before plowing. Agronomists believe that for 1 m² of land, it is enough to use from 5 to 10 kg organic fertilizers... The amount of compost or manure required is largely dependent on the initial state of the soil.

Manure contains a wide variety of trace elements.
The main ones are nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium and calcium. Regular introduction of this composition into the soil improves its physical condition: the soil becomes loose, breathable, gradually filled with humus.
In addition to the listed organic fertilizers, you can use chicken manure. It is also rich in phosphorus and nitrogen, which the plant prefers. This top dressing should be used in smaller doses than manure.
V last years green manure plants are increasingly used as organic additions to the soil. It is the cleanest and cheapest fertilizer. They are engaged in the landing of such plantings at the end of summer, and in the fall the green mass is shallowly buried. The best siderates can become alfalfa, clover, vetch. On the good side, rye and oats showed themselves.

Mineral fertilizers chosen for autumn use should contain a small amount of nitrogen. Most often, packages with dressings for winter have the designation "autumn". Using mineral fertilizing, it is worth remembering: it is better not to feed a piece of land than to overfeed.
The combined use of mineral and organic fertilizers is the right solution for providing nutrients to potatoes. To get a high-quality food vegetable, it is necessary to use more effectively an increased proportion of organic matter and an average proportion of mineral products.
In order to correctly decide what additives to add in the fall for the spring, it is worth considering the peculiarities of the land plot. It is important to remember that the feeding process must be regular, then the soil will not become scarce.