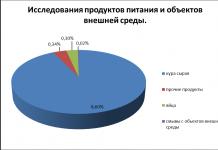
Work place is the name of the part of the workspace where the production equipment is located, with which a person interacts in the work environment.
The places where welding works are carried out are divided into permanent and temporary. Permanent (stationary) places are intended for work that is carried out in specially equipped workshops, workshops, etc. Install the welding machine protected from atmospheric influences, welder's table, manipulator, hood, etc. in a well-ventilated room with an area of at least 3 m 2. It is best if the floor is concrete and the walls of the room should not reflect welding reflections, which can be hazardous to the eyes.
Fig. 14 Layout of the welding booth:
1 - arc power source; 2 - grounding; 3 - power supply starter; 4 and 5 - forward and reverse conductive wires; 6 - table; 7 - ventilation; 8 - rug; 9 - electrodes; 10 - shield; 11 - electrode holder; 12 - chair;
13 - waste box; 14 - doorway

Fig. 15. Welder's workplace
Passages between multi-station welding units and between automatic welding installations must be at least 1.5 m; passages between single-station welding transformers or between welding generators, as well as passages on each side of the rack or table for performing manual welding - at least 1 m.The distance between the stationary welding machine and the wall or column must be at least 0.5 m, and the distance between the wall or column and the welding machine - at least 1 m. The passages between the spot and seam (roller) welding machines with the location of the workplaces opposite each other must be at least 2 m, and between the butt welding machines - at least 3 m. of the above machines with their backs to each other, the width of the aisles should be at least 1 m, and when the front and back sides are located to each other - at least 1.5 m.
For each stationary workstation during plasma and gas-plasma processing of metals,> 4m 2 should be allocated, and when working in the cabin> 3m 2.
Areas with hazardous production factors must be fenced, safety signs are maintained in accordance with GOST 12.4.026-76 *.
Depending on the dimensions of the products to be welded and the nature of the production, the welder's workplace can be located either in a special cabin, or in the workshop or directly at the assembly facility. The dimensions of the cabin must be at least 2x2 m 2.

Fig. 16. Resistance welding cabins.
The walls of the cabin are made with a height of 1.8-2 m. For better ventilation, a gap of 150-200 mm is left between the floor to the lower edge of the wall. You can use thin iron as the material for the walls of the cab, as well as plywood, tarpaulin, read with a fire retardant compound, or other fire resistant materials. The cab frame is made of metal pipes or angle steel. The cab doorway is usually covered with a tarpaulin curtain mounted on rings. Plywood and tarpaulin should be impregnated with a fire-resistant compound, for example, a solution of potassium alum.
The floor in the cab must be made of fire-resistant material (brick, concrete, cement), non-combustible and non-slip, and have low thermal conductivity.
The walls are painted in a light gray color with paints that absorb ultraviolet rays well (zinc or titanium white, yellow crown). Painting of welding shops and booths in dark colors is not recommended, as this deteriorates the overall illumination of the welding place.
Combined lighting should be provided for works of high and highest accuracy (I-III razr.), In particular, when welding and soldering materials with a thickness of 0.06 ... 0.5 mm, during flaw detection of welded seams and other similar works.
To illuminate workshops, it is necessary to use, as a rule, gas-discharge light sources: DRL, DRI lamps; for illumination of high workshops (up to 4 m) of a large area - fluorescent lamps. The use of incandescent lamps is allowed.
The illumination of the cabin must be at least 80-100 liters.
In the production rooms of welding and assembly-welding shops, the microclimate parameters should be taken in accordance with GOST 12.1.005-88 (rooms with slight surpluses of apparent heat, work of medium severity, categories IIa and IIb).
In the cold season, the permissible microclimate parameters for works IIa and IIb are respectively equal: air temperature 17 ... 23 and 15 ... 21 0 С, relative humidity< 75%, скорость движения воздуха < 0,3 и 0,4 м/с.
The cabin is equipped with local ventilation with an air exchange rate of 40 m3 / h for each worker. The ventilation suction must be positioned so that welding gases pass by the welder.

Fig. 17 Exhaust hood: 1- air duct; 2-gate; 3-air inlet; 4- stamped lattice; 5- visor.
When welding in confined spaces, air exhaust is carried out to the suction air duct of the workshop exhaust system. Air supply under the welder's mask is possible, equal to 110 ... 140 l / min.


Fig. 18. Air inlets built into welding torches for mechanized welding in CO 2. a, b - respectively circular symmetric and asymmetric; in-conical perforated; g - conical-slit; ----- - suction aerosol; - - - - - shielding gas.
In the organization of welding work, the correct placement of equipment is important. Multi-station units and installations, consisting of several welding units, are located in a separate room or on the area of a common production room, fenced off by permanent partitions with a height of at least 1.7 m. Welding converters during operation create noise that has a harmful effect on the human nervous system, causing a decrease attention and decreased performance. For this reason, all welding converters must be isolated in the workshop premises or taken out of the production premises, fenced off from all sides and sheltered from atmospheric precipitation.
In stationary multi-station welding installations, the connection of welding stations to the electric welding unit is carried out through a common shield, which must contain the necessary measuring instruments, protective equipment, signal lights, switches and clamps for connecting welding stations. In single-post welding, individual shields must be provided, equipped with a voltmeter and a signal lamp indicating to the welder whether there is or is no voltage in the welding circuit.
Passages between multi-station welding units and between automatic welding installations must be at least 1.5 m; passages between single-station welding transformers or between welding generators, as well as passages on each side of the rack or table for performing manual welding - at least 1 m.The distance between the stationary welding machine and the wall or column must be at least 0.5 m, and the distance between the wall or column and the welding machine - at least 1 m. The passages between the spot and seam (roller) welding machines with the location of the workplaces opposite each other must be at least 2 m, and between the butt welding machines - at least 3 m. of the above machines with their backs to each other, the width of the aisles should be at least 1 m, and when the front and back sides are located to each other - at least 1.5 m.
The term "working (welding) post" means a workplace where flame processing of metals is carried out. Work stations can be mobile or stationary.
A mobile post is used, as a rule, for manual welding, carried out in various places on the territory of the economy and in buildings, as well as during installation and on construction sites.
Gas supply of mobile work stations is carried out according to the schemes shown in Fig. 1. Cylinders for oxygen and combustible gas with appropriate editors to reduce pressure are usually used as gas supply sources.
Rice. one. Gas supply diagram of a mobile welding station: a - from cylinders; b - from an acetylene generator; 1 - oxygen cylinder; 2 - oxygen reducer; 3 - balloon with acetylene, 4 - sleeves; 5 - burner; 6 - mobile acetylene generator.
A stationary work post (Fig. 2) is designed to perform manual and mechanized work in a workshop, site or workshop.
Gas supply (gas supply) of stationary posts is carried out centrally: gas is supplied through gas pipelines to places of consumption, if the number of posts exceeds 10. With a smaller number of posts, when the arrangement of gas pipelines is irrational, gas supply from individual cylinders is allowed.

Rice. 2. Stationary work station: 1 - welding table; 2 - cover: 3 - box for storing materials; 4 - filler material: 5 - reducer for supplying oxygen to the burner (cutter), 6 - oxygen line, 7 - safety shutter, 8, 9 - hoses for supplying acetylene and oxygen. 10 - economizer; 11 - burner, 12 - water box; 13 - swivel chair.
The welding torch serves as the main tool for manual gas welding. Oxygen and acetylene are mixed in the burner in the required quantities. The resulting combustible mixture flows out of the channel of the torch nozzle at a predetermined rate and, burning, gives a stable welding flame, which melts the base and filler metal at the welding point. The burner also serves to regulate the heat output of the flame by changing the flow rate of combustible gas and oxygen.
When preparing a mobile gas welding station for work, it is necessary:
- a) check valves of cylinders with oxygen and combustible gas for serviceability;
- b) clean the thread from dirt, oil, howl;
- c) check the condition of the thread.
When connecting the oxygen reducer, it is necessary to clean it of oil, dirt, dust, check the thread on the nut, unscrew the working pressure adjustment screw, and visually check the serviceability of the pressure gauges. After we have checked the gearbox, we screw it to the cylinder, we check the connection for leaks. The welder stands behind the cylinder with the reducer pointing away from it and opens the cylinder valve.
When preparing the acetylene cylinder and the acetylene reducer, the cylinder valve must be cleaned of dust, oil, dirt, and the valve must be purged with gas from the cylinder. You also need to check the thread on the gearbox mounting clamp, unscrew the working gas pressure adjustment screw, clean the gearbox and inspect in the same way as for the oxygen one. It is necessary to check the tightness of the connection in the same way as the oxygen one. Also, the hoses for supplying oxygen and acetylene must be checked so that there is no gas leakage at the joints on the gearboxes and on the burner. When preparing the burner, you need to clean the mouthpiece and the entire burner from oil, dust and drops of metal adhered during the last use, check the burner for injection.
A gas welder at the workplace should have pliers, a hammer, a metal brush for cleaning the metal surface, needles for cleaning the mouthpieces and a small house for turning the workpieces. In addition, an appropriate tool (keys) is required to fasten the gearboxes, open (close) cylinder valves and fix minor burner (cutter) malfunctions detected during work.
Working welders (gas cutters) must be equipped with overalls in accordance with the established standards and protective goggles (with the density of C-3 light filters when working with cutters and C-4 when welding with an acetylene consumption of up to 2500 l / h).
When using mobile posts in closed rooms, it is necessary to provide natural or forced ventilation.
Metal products and structures are actively used in construction, shipbuilding, mechanical engineering, industry and in everyday life. Therefore, it is not surprising that the professions associated with the extraction of metal and the manufacture of metal structures are among the most important and significant specialties. The profession of an electric and gas welder, who connects metal parts into a single whole by means of welding, also belongs to such specialties. Such a specialist was and will be needed always and everywhere. Connecting metal structures is a very important job, the quality of which depends on the integrity, safety and durability of buildings, cars, ships, airplanes, household appliances, etc. Therefore, in this profession, real professionals are especially appreciated, who not only know how to use a welding machine, but are also ready to take responsibility for the quality of their work.
Electric and gas welder- a specialist who, with the help of an electric gas welding machine, welds various metal products (for example, components of metal structures, car parts, pipelines, etc.). At the same time, he can equally easily perform welding work with both electric arc and gas or plasma welding.
The workstation of an electric and gas welder can be both stationary and mobile. But in any case, the welder must have: a power source, a welding transformer, welding wires, an electrode holder, a face shield, thick (tarpaulin) protective clothing, protective shields, fire extinguishing equipment, the necessary tools, an asbestos sheet for laying in place welding.
Parts are welded on a work table. The table top is made of cast iron 20-25 mm thick. The welding station is equipped with a generator, rectifier or welding transformer.
Characteristics of works: Manual oxygen cutting and cutting of lightweight and heavy steel scrap with gasoline and kerosene machines. Manual arc, plasma, gas, automatic and semi-automatic welding of simple parts, assemblies and structures made of carbon steel. Oxygen and plasma straight and curved cutting in the lower and vertical position of the weld by metal, as well as simple and medium complexity parts made of carbon steels by hand marking, on portable stationary and plasma cutting machines. Tacking of parts, products, structures in all spatial positions. Preparation of products, units and joints for welding. Cleaning of seams after welding and cutting. Protection of the back side of the weld during welding in shielded gases. Surfacing of simple parts. Elimination of cavities and cracks in simple parts, assemblies, castings. Heating of structures and parts during straightening. Reading simple drawings. Preparation of gas cylinders for work. Maintenance of portable gas generators.
Must know: device and principle of operation of serviced electric welding machines and apparatus for arc welding of alternating and direct current, gas welding and gas-cutting equipment, gas generators, electric welding machines and semiautomatic devices, oxygen and acetylene cylinders, reducing devices and welding torches; rules for the use of used burners, reducers, cylinders; methods and basic techniques of tacking; forms of cutting a seam for welding; rules for ensuring protection when welding in shielded gas; types of welded joints and types of seams; rules for preparing the edges of products for welding; types of grooves and designation of welds in the drawings; basic properties of electrodes used in welding, welding metal and alloys, gases and liquids; allowable residual gas pressure in cylinders; purpose and brands of fluxes used in welding; purpose and conditions for the use of instrumentation; causes of defects during welding and methods of their prevention; gas flame characteristic; scrap dimensions according to the state standard. (decree of 15.11.1999 No. 45)
This profession has specific, so-called occupational diseases:
· electrophthalmia- photoophthalmia, which occurs as a result of exposure to a powerful stream of ultraviolet rays, which are absorbed by the cells of the body and cause chemical changes in them. Such irradiation is possible in the presence of an electric arc (for example, with a short circuit, electric welding), which is a source of intense radiation not only of visible light, but also of ultraviolet and infrared rays. ( Russian encyclopedia of labor protection: In 3 volumes - 2nd ed., Revised. and add. - M .: Publishing house of NTs ENAS, 2007 .)
· Pneumoconiosis- a group of lung diseases caused by prolonged inhalation of industrial dust and characterized by the development of a fibrotic process in them)
- Silicosis- occupational lung disease caused by prolonged inhalation of dust containing free silicon dioxide. It is characterized by diffuse proliferation of connective tissue in the lungs and the formation of characteristic nodules). (Anthracosis of the lungs // Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary: In 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional). - SPb., 1890-1907.)
· Poisoning (manganese, fluorine, chromium, lead).
CERTIFICATION CARD
workplace under working conditions N ____
_______19756 electric and gas welder ________________
(profession, employee position)
Name of company: LLC "GAZPROM TRANSGAS UFA"
Organization address ________________________________________________
Department name _______________________________________
Site name (office, sector) __ welding
The number and numbers of similar jobs (RM) 3
Line 010. Issue ETKS, KS Issue 2, § 61_
Line 020. Number of employees:
on one RM _____________
on similar RM ____________
of them women 0
Line 030. Assessment of working conditions:
according to the degree of hazard and (or) hazard of factors of the working environment and labor process
| The name of the factors of the working environment and the labor process | Working conditions class | |
| Chemical | 3.2 | |
| Biological | - | |
| APFD | ||
| Acoustic | Noise | |
| Infrasound | - | |
| Airborne ultrasound | - | |
| Ultrasound pin | - | |
| General vibration | - | |
| Local vibration | - | |
| Non-ionizing radiation | - | |
| Ionizing radiation | - | |
| Microclimate | ||
| Lighting | - | |
| The severity of labor | 3.2 | |
| Labor tension | ||
| Air ionic composition of air | - | |
| General assessment of working conditions | 3.3 |
Trauma safety ______2 (valid) ____________________________________
(class of working conditions
on injury safety)
According to the provision of PPE ____corresponds to ______________________________________
(workplace corresponds
(does not meet) the requirements
provision of PPE, PPE is not provided)
Depending on the type of robot being performed, the size of the product and the type of production, the welder's workplace can be organized in different ways. It can be a stationary welding booth or a temporary welding station for the installation or manufacture of a large-sized product or structure.
If the product to be welded is small and is manufactured in large batches, then the workplace is organized in stationary welding cabins with dimensions for one welder at least 2.0 * 2.5 m, at least 2.0 m high.To better ventilate the cabin due to natural air movement , its walls are not brought to the floor by 200 ... 250 mm. In the doorway, a tarpaulin curtain is hung on rings. The walls of the cab are made of fire-resistant material, usually metal. From the inside, a fire-resistant coating or light-colored paint is applied to the walls, which gives a matte surface that excludes glare. General and local exhaust ventilation is required. A power source for the welding arc, a switch or a magnetic starter is installed in the cabin to connect it to the power supply network. If a welding transducer is used, then it is installed outside the cabin in a room with good sound insulation.
The cabin should have a workbench rack with a locksmith's tool (hammer, chisel, vise, etc.), a sealed box for electrodes, since sometimes the electrodes are stored for more than two hours after unpacking. To bake the electrodes, a drying cabinet or oven is required, which, depending on the workload of the welders and the welding conditions, can be installed one at several posts. If the welder must use assembly and welding devices or a pneumatic tool, then compressed air is supplied to the cab. The cab should contain a metal welder's table and a chair with a height-adjustable seat.
Welder's tables are made with a stationary local smoke exhaust. This is a table CCH-1 with a built-in ventilation unit without filtration, as well as tables CCH-2 and CCH-3 that require workshop ventilation wiring and a general air purification system. The smoke is sucked up from them. These tables do not completely remove smoke from the welder's breathing zone. More efficient are tables with a combined ventilation unit, in which the tabletop is made in the form of a grate, and the smoke exhaust is carried out downward by a built-in fan and upward - to the side
autonomous smoke exhauster. The built-in filter provides the degree of air purification from smoke and aerosols up to 99.96%.
When welding large-sized products from the outside of the product in the workshop, it is necessary to enclose the welder's workplace with personal shields from other workplaces, aisles, resting places, etc. The requirements for the shields are the same as for the walls of the cab. Power supplies, a portable shelf or cabinet for tools and electrodes should be located inside the enclosure. At such welding stations, it is also mandatory to use local exhaust ventilation. It can be a flexible plastic pipe up to 5 m long with a wire screw ring inside, connected to a centrifugal fan equipped with a filter. It is convenient to use an energy-saving machine with a sensor in the form of a current clamp, which turns on the fan only when the arc is burning and turns it off after a specified time after its extinction.
The welder's workplace should be well lit. When working in cabins, at assembly sites, and especially inside containers, the main attention should be paid to electrical safety, strictly observe the current norms and rules for grounding arc power supplies, chokes, switch housings, welding tables. Inside the tanks, the welder must work with a safety observer.
In addition to traditional arc power supplies, transformerless AC inverter sources are starting to be used for manual arc welding. With sufficient power, they have small dimensions and weight. For example, the inverter of the Swedish company ESAB provides a welding current of 5 ... 250 A, has a mass of 20 kg and dimensions of 450 * 350 * 300 mm.
Electrode holder- this is the main tool of the welder. It must be safe, durable, must reliably and quickly fix and release the electrode without significant efforts of the welder, have a low weight, protect the welder's hand from the heat of the arc, the heated electrode and from live parts of the welding circuit. Electrode holders are pliers, with a lever clamp, screw and snap-on type. Depending on the strength of the welding current, the electrode holders are divided into three types: for current strength up to 125 A; 125… 315 A and 315… 500 A. The electrode change time should not exceed 4 s; without repair, the electrode holder should withstand 8000 electrode clamps.
Welding wires - serve to supply current from the power source to the electrode holder and the product. The electrode holder is connected to a flexible PRGD or PRGDO wire with copper conductors, or to APRGDO aluminum conductors. The length of the flexible wire is 2-3 m. The flexible wire is connected to a cable with a copper or aluminum core KRPT, KRPG (med.); AKRPT (al.). The wires are connected with couplings or soldering. The total length of the wire is not more than 30 m, due to a voltage drop in the welding circuit. The wire leading to the product may be less flexible, but insulated with PRG. The diameter of the wire is chosen according to the amperage used for welding.
Shields and masks serve to protect the welder from metal spatter, sparks and radiation. The welder holds the shield in his hand, the mask is put on the head and frees the welder's hand for manipulating the part. The best designs cover not only the face, but also the neck and the welder's hand holding the shield. The visor and mask have a viewing window with a light filter that traps hazardous arc radiation. The outside of the filter is protected by replaceable transparent glass from metal splashes. A distinction is made between attenuating constant density filters, attenuating variable density filters and filters with two optical density zones. Constant density light filters have dimensions of 100 * 150mm, additional glass of lower density is 100 * 160mm. the optical density of the filters varies from 3 to 13. The set includes diopter glasses (1.0 ... 2.5). Light filters with varying optical density allow you to carry out assembly, tuned and welding work without lifting the shield. Without an arc, the light filter is transparent, and when it is ignited in a time of less than 0.01 s, its optical density automatically increases to the nominal. The operation of such devices is based on the properties of liquid crystals to change their optical density under the influence of external influences. The electric power supply of such light filters is autonomous, from batteries; their service life can be increased due to solar batteries. Light filters with two zones of optical density can be made either in the form of one glass, the upper part of which is lighter than the lower, or of two glasses with different optical polarity. Lighter glass is located in a narrow strip above the dark, working glass; it is designed to control the adjustment movements of the electrode, manipulate the part. On the side surfaces of the welder's mask, windows are sometimes made with tinted glasses, which more than double the field of view. The welder can see potentially hazardous objects.
For work in especially harmful conditions, the welder's mask can be equipped with a forced air supply system. It consists of a micro-fan, a filter element, an accumulator unit, and connecting hoses. The system is attached to the welder's belt from the back. Air is captured in the clean area and blown to the welder for breathing under the shield.
Overalls for the welder are made of thick tarpaulin or cloth. Overalls should not have open pockets. Shoes must have a dull top. Welding gloves must be made of leather, thick tarpaulin or asbestos fabric. When working in closed vessels, the welder must use dielectric overshoes and a rubber mat tested for electrical breakdown.
GOA POU
Lipetsk Industrial and Construction College
Training element
Profession 01/15/05 Welder (electric and gas welding works)
Organization of the electric welder's workplace
Teacher of special disciplines T.A. Merkulova
Lipetsk
Target:
Having studied this educational element, you will be able to organize the workplace of an electric welder.
Work place an electric welder is a section of the production area assigned to a worker or a team, equipped in accordance with the requirements of the ongoing technological process with certain equipment, tools, fixtures, etc.
Equipment, tools, fixtures, accessories
Welding machine
Welder's table
Chair
Metal brush
Chisel
Hammer
Screw clamp
Electrode holder
Welding mask
Related tutorials and tutorials:
Safety rules for welding
Electrical safety rules
Fire safety rules
Eye protection rules
Respiratory protection regulations
Signs of attention:
Fire safety rules
Safe working practices when working with a tool
Mandatory use of personal protective equipment
The places where welding works are carried out are divided into:
- permanent - (stationary) places are intended for work that is carried out in specially equipped workshops, workshops, etc.
- temporary.
Working cabin

Organization of a stationary workplace for an electric welder
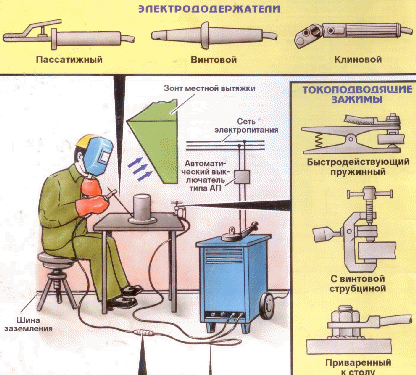
The floor in the cab must be made of fire-resistant material (brick, concrete, cement). The walls are painted in a light gray color with paints that absorb ultraviolet rays well (zinc or titanium white, yellow crown). The illumination of the cabin should be at least 80-100 lux. The cabin is equipped with local ventilation with an air exchange rate of 40 m3 / h for each worker. The ventilation suction must be positioned so that welding gases pass by the welder.
Parts are welded on a work table. The table top is made of cast iron 20-25 mm thick. The welding station is equipped with a generator, rectifier or welding transformer.
Welding wires are used to supply current from the welding machine or transformer to the electrode holder and the workpiece to be welded. The electrode holders are supplied with a flexible insulated wire PRG (flexible rubber wire) or PRGN (flexible rubber neurite wire), woven from a large number of copper, annealed and tinned wires with a diameter of 0.18-0.2 mm.
Welding wires
It is not recommended to use a wire longer than 30 m, as this causes a significant voltage drop in the welding circuit. The wires must be securely fastened. Insulated in places of damage.
!Connect the wires using couplings.

Electrode holder selection


Electric holders are used to fix the electrode and supply current to it during manual electric arc welding. Their main characteristics are given in table.
Rated welding current, A
Cycle time, min
The ratio of the duration of the working period to the duration of the cycle,%
Weight, kg
Electrode diameter, mm
Section of the connected welding wire, mm 2
0,35
0,50
0,70
1,5...3
2...6
4...10
The live parts of the electrode holders must be reliably isolated from accidental contact with the workpiece to be welded or the welder's hands. The insulation resistance must be at least 5 Mohm. The handle insulation must withstand a test voltage of 1500 V at a frequency of 50 Hz for 1 min without breakdown. The excess of the temperature of the outer surface of the handle at the nominal operating mode should not exceed 55 ° C. Electrode holders must have sufficient mechanical strength.
!Electrode holders must allow the possibility of gripping the electrode in at least two positions: perpendicular and at an angle of at least 115 ° to the axis of the electrode holder. The design of the electrode holder should provide a time for changing the electrode no more than 4 s.
Means of protection .
Electric welder mask.



Masks should be made of special plastic that is resistant to high temperatures and high humidity, practically does not deform, does not deteriorate from splashes of molten metal. There are no metal protruding parts in the design of the shields, which excludes the welder's injury from electric shock.
!For work in closed containers or in confined spaces where it is impossible to use a hood, special masks with air supply are used
 A special light filter is inserted into the visor or helmet, held by a frame measuring 120 x 60 mm.
A special light filter is inserted into the visor or helmet, held by a frame measuring 120 x 60 mm.
Do not use random colored glasses, as they cannot reliably protect the eyes from the invisible rays of the welding arc, which cause chronic eye disease.
!Protective filters have different densities and are selected depending on the strength of the welding current.
Welding method
Filter types
Current strength
Metal arc welding
S-3
P-4
S-5
S-6
S-7
S-8
15-30
30-60
60-150
150-275
275-350
350-600
In modern “chameleon” masks, the darkening of the glass is automatically adjusted depending on the brightness of the arc.


Ventilation
During welding, harmful substances are emitted into the air, such as: nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxides, fluoride compounds. The task of the exhaust ventilation is to remove harmful gases as efficiently as possible, and the supply ventilation must compensate for the exhaust, diluting the harmful to the maximum permissible concentrations. From this point of view, the best work tables for the welder are tables with exhaust gases and dust to the side or downward.

The efficiency of local suction of harmful impurities that are released during the welding process from the welder's breathing zone largely depends on the maximum approximation
exhaust intakes to the place of arc burning.
!
Special clothing
Requirements for special clothing: the suit must be made of heat-resistant fabric (tarpaulin, suede), the jacket must be worn for release, the pockets must be inside, the boots must be high, no nails, made of non-combustible material, gloves (leggings) made of non-combustible materials of sufficient length so that the material does not fly in when overhead welding, a headgear that protects the neck.

3 green
2. Can I use specials. coarse calico clothes?
1. No
2. Yes
3. When it's hot outside.
3. Can the cooker hood be located under the ceiling?
1. Yes
2. No
3. In exceptional cases.
4. How do you choose electrode holders?
1. By design
2. Depending on the amperage
3. For convenience
5. Choose the glass number when welding at 120A
1.P-3
2.P-4
3.P-5
Practical task:
Organize a locksmith's workplace for filing.
References
1. Chernyshov G.G. Welding business. Welding and cutting metalsPublishing CenterAcademy 2013
2.Yukhin N.A. Tutorial Gas welderPublishing CenterAcademy 2009
3. Ovchinnikov V.V. Tutorial Manual Electric Welder (Covered Electrode Welding)Publishing CenterAcademy 2010
4. INTERNET - resource