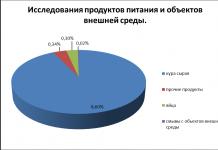
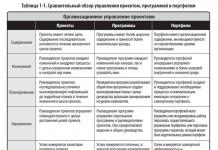
on the formation and design of the educational and methodological complex to the additional general educational general developmental program
annotation
Methodological recommendations contain general requirements for the formation of an educational and methodological complex (TMC). The recommendations present the structure, content, stages of development of the teaching materials, and also give practical advice on its design.
Compiled by: Golovacheva O. V., Methodist of the Department of Analytical and Monitoring Activities, KGBOU DO "Khabarovsk Regional Center for the Development of Creativity of Children and Youth"
Content
Introduction
Currently, in the context of modernization and improvement of the quality of the education system as a whole, the development and improvement of all its constituent parts is taking place. In these conditions, the sphere of additional education must inevitably change qualitatively and substantively, be mobile, meet the needs of children and their parents, education and society. Additional education is rightfully considered as the most important component of the educational space that has developed in modern Russian society. It is socially in demand, requires constant attention and support from society and the state as an education that organically combines the upbringing, training and development of the child's personality.
Today, with the active saturation of the educational services market with a large number of additional general educational programs, various in focus, type of activity, level of development,the role of high-quality methodological support for their implementation is growing significantly. To this endnormative documents of different levels are being developed for the active development, rethinking and updating of the principles and approaches to the organization of the educational process for additional general educational programs. Rdevelopment of softwareo-methodological support of educational institutions of preschool educationis an important direction in the implementation of the idea of quality management in education.One of the possible options for a modern solution to the problem of methodological support of educational activities in the DOD system can be the creation of a set of software and methodological materials, which can be presented in the form of an educational and methodological complex.
The creation of teaching materials by a teacher of additional education is a relevant and promising means of improving the quality of additional education.It is in the teaching and learning method that each teacher can develop a technology for determining learning outcomes for an additional general educational program.Focusing on the methodological component of professional activity, gaining experience in methodological work, first of all, is useful for the teachers themselves, since it will allow them to more easily adapt in the dynamically changing world of children's needs and interests, with lower costs, if necessary, move from one type of activity to another.
In general, the teacher's work on the design and creation of an educational and methodological complex not only allows one to systematize the experience accumulated by him as a specialist, but also contributes to the manifestation of creative activity and professional growth.
Relevance the development of methodological recommendations for the formation of teaching materials consists in the analysis, systematization, the possibility of practical application and the transfer of information to pedagogical workers about the structure, content and stages of creating an educational and methodological complex.
The purpose creationrealguidelines isdevelopment of a systematic approach to the creation of an educational and methodological complex for an additional general educational general developmental program.
The concept of the educational-methodical complex
The educational-methodical complex is an information model of a certain pedagogical system, which reflects the sides of the real educational process.EMC is designed to solve a full range of problems that arise in the educational process.The teaching and learning method should take into account all the achievements of modern pedagogical science and is intended to ensure an increase in the efficiency of the work of students and teachers through the provision and implementation of a wide range of opportunities (information, training, developmental, educational, coordinating, systematizing, stimulating, etc.).
Training and metodology complex - a system of normative and educational-methodical documentation, teaching and control tools necessary and sufficient for the high-quality implementation of additional general educational general development programs in accordance with the curriculum.
The purposeeducational and methodological complex isensuring the successful development of the program by students, providing them with pedagogical assistance and support in cognitive, creative, research and communication activities. The documents and materials included in the teaching materials characterize the methodological substantiation of the educational process for the development of an additional general educational general developmental program (DOOP), as well as specific, approved techniques, methods, technologies of its organization.
EMC is developed by the teacher of additional education (trainer-teacher) to the additional general educational program.Each teacher has the right to approach the preparation of teaching materials creatively, to develop its content at his own discretion, in accordance with the level of training of students and their educational needs.
UMC structure
UMC structure presupposes a set of didactic units reflecting a logically complete volume of educational material.
In its most general form, the educational and methodological complex of preschool education can be represented by the following components:
Explanatory note to the CMO;
Additional general educational general developmental program;
Working programm;
Individual student curriculum (if any);
Educational and methodological component for the teacher and students;
Educational component;
Performance component.
3. Content of the teaching materials:
1. Explanatory note.
The explanatory note indicates the relevance of this CMB, its conceptual foundations, a list of materials presented in the CMB (CMD information map -Appendix 2 ), information on the possible fields of application of the CMM and its potential users).
2. Additional general educational general developmental program.
The key document on the basis of which the teaching materials are developed is an additional general educational general developmental program.DOOP is the main document in which the goal, forms, content, methods and technologies for the implementation of additional education, criteria for assessing its results in specific conditions are determined in a logical sequence. An additional educational program is drawn up in accordance with federal requirements for the content and design of educational programs for additional education.
3. Work program - a regulatory document that determines the volume, content and procedure for the implementation of additional general education programs. The work program is drawn up by the teacher of additional education for the current academic year in accordance with the additional general education program he implements.
4. Individual curriculum ( IUP) is designed in accordance with the requirements of an additional general educational program implemented by the teacher. IUP is an annex to the main approvedadditional general educationlinen general developmental program.
An individual curriculum is drawn up if necessary and is not an obligatory element in the structure of teaching materials.
5. Educational and methodological component for the teacher and students . It can be:
Methodical materials on the organization of educational activities.
Methodological development of individual topics and lessons.
Tutorials– materials to ensure the implementation of the content of preschool education. These include:
reference books (encyclopedias, dictionaries, reference books, tables, databases, links, websites, etc.);
fiction;
scientific and popular science literature (scientific, popular science publications and publications, description of experiments, etc.);
periodicals;
video materials (video lectures, feature and popular science films, video recordings of classes, events, etc.);
audio materials (phonograms of musical works, audiobooks, audio recordings necessary to study this topic);
electronic means of educational purposes (virtual lectures on the topics of the educational program, demonstration models, slide presentations, virtual control and laboratory work, individual assignments, etc.);
The content of the tutorial can be:
in general for preschool education;
on separate sections;
on selected topics of preschool education.
on the formation of educational motivation among students (the use of gaming technologies, the presence of traditions, attributes, incentive systems, etc.);
on the organization of work with students who have the ability to scientific, creative, physical culture and sports activities;
monitoring the satisfaction of parents and students with the organization of the educational process;
on the effective use of the available material and technical base.
A block (module) for working with children with special educational needs (gifted children, children with disabilities, children with deviant behavior, etc.).
Didactic materials must correspond to the content of preschool education, educational goals, the level of preparedness of students, their age and individual characteristics, and sanitary and epidemiological requirements. Didactic material can be presented in the following form:
handouts for students (workbooks, test and questionnaire forms, diagnostic and creative tasks, task cards, ready-made templates and stencils, objects of animate and inanimate nature, photographs, instructional maps, technological maps), visual aids (tables, graphs, volumetric models, dummies, etc.).
6. Educational component DOOP can include:
Holidays scenarios,
Chronicle of unification,
Information materials about the team (brochures, advertisements, articles, etc.),
Creative reports,
Photo albums,
Videos,
Information about the work of the association on the Internet,
Materials for working with parents, plans for parenting meetings, etc.),
Memo, etc.
7. Performance Component includes:
I ... Availability of diagnostic material and criteria for monitoring the results of mastering pre-educational education by students:
Evaluation materials - a package of diagnostic techniques to determine the achievement of studentsplanned results.
Planned results are formulated taking into account the purpose and content of preschool education and define basic knowledge, skills, and competencies,personal, metasubject and subject results, acquired by students in the process of studying the program:
Personal results include the readiness and ability of students for self-development and personal self-determination.
Metasubject results means the methods of activity mastered by students, used by them both in the framework of the educational process and in solving real life situations.
Subject results contain a system of basic elements of knowledge, which is formed through the development of educational material, and a system of formed actions that are refracted through the specifics of the subject and aimed at their application and transformation.
Assessment of the educational results of students in pre-educational education should be variable in nature. The tools for assessing the achievements of children and adolescents should contribute to the growth of their self-esteem and cognitive interests in general and additional education, as well as diagnose the motivation of the individual's achievements.
In pedagogical practice, the diagnosis of achievementssubstantive results , as a rule, does not cause difficulties for teachers, since these results represent skills specific to a given subject area, types of activities for obtaining new knowledge within the framework of the academic subject or subject of activity. The predicted results can be standardized and modified.
The object of assessing the subject results is the ability of students to solve educational-cognitive and educational-practical tasks. Evaluation of the achievement of subject results is carried out in the form of intermediate and final certification. Federal Law "On Education" No. 273-FZ does not provide for the final certification of preschool education, but it is not prohibited to conduct it in order to establish:
Compliance of the results of mastering preschool education with the stated goals and planned learning outcomes;
Compliance of the process of organizing and implementing DOOP with the established requirements for the procedure and conditions for the implementation of programs.
Certification (intermediate and final) for preschool education can be carried out in the forms determined by the curriculum as an integral part of the educational program, and in the manner prescribed by the local regulatory act of the educational organization.
Diagnosticspersonal and metasubject the results of students cause the greatest difficulties for teachers, since they are based not on a standard, but on a social order. In these methodological recommendations to help teachers working in the system of additional education, diagnostic techniques are proposed that are quite simple and can be used in practice (Appendix 4, 5, 6). However, teachers with extensive experience in the system of additional education for children can independently develop methods for determining the level of development of students in an additional general education program.
II ... Availability of ways to track the dynamics of student development (rating system for assessing achievements, portfolios, grade books, etc.).
One of the most demanded methods is a portfolio of achievements, with the help of which it is possible to trace the dynamics of the personal development of students. The Portfolio method is not only a modern effective form of assessment, but also represents the technology of students' work, which allows solving a number of pedagogical problems:
Promotes the formation of a culture of thinking of students, the development of skills of reflective and evaluative activities (the ability to plan, organize, analyze their own activities);
Develops such qualities of students as responsibility, activity, independence and self-control.
4. Principles of design of teaching materials
Design - a complex and lengthy creative process that integrates into a single whole:
predicting desired results based on problem analysis;
putting into practice what was conceived with the subsequent adjustment of goals and objectives, comparing real and expected results. The result is the author's (at the level of a particular teacher or institution) pedagogical model or system, a mandatory feature of which is novelty.
The pedagogical essence of designCMD is based on relevant principles:
- principle of targeted and optimal selection of contenteducational material;
- principle of interdisciplinarity - work to formcontent should be comprehensive, covering allthe relationship of a specific additional general education program with subjectsrelevant educational field;
- the principle of scientific relevance - the content of leading topics should, as much as possible,meet modern achievementsrelevant fields of science;
- the principle of the priority of applied tasks - in the classroom,conducted with the aim of mastering practical skills by students, first of all, they should be involved in solving applied problems.
5. Functions of the UMK
UMK performs 3 main functions:
Learning function - ensuring the goals and objectives of mastering the content of education.
Developmental function - ensuring the possibility of using materials for the development of personal qualities, for example, perception and thinking, imagination and memory, physical development, etc.
Educational function - ensuring the orientation of the content of educational materials on the development of universal human values (love, freedom, beauty and others) in line with national cultural traditions.
The above features include:
- informational - providing a systematic understanding of phenomena, objects, events in science, art, production, sports, etc. in order to achieve an educational effect;
- integrating - providing students with ideas about additional sources of information on the issues under consideration;
- coordinating - ensuring the coordination of the student's actions in the use of other educational tools: encyclopedic dictionaries and reference books, annotated literature indexes, atlases, albums, popular periodicals, natural objects, computer support, etc .;
- transformational - associated with the transformation of content, taking into account age, social,national featuresstudents;
Systematizing - providing a logical and didactic sequence for the presentation of educational material;
- the rationalization function, which ensures the reduction of the resources and time of students and teachers with a high quality of educational results;
- the function of stimulating the cognitive activity of students through entertaining and problematicgiving educational material;
- the function of managing the development of the educational process due to the metered and sequential organization of the presentation of educational material;
- the function of consolidating and self-monitoring the results of activitiesstudents by setting assignments and test questions.
6. Stages of design of teaching materials
Starting work on the creation of an educational and methodological complex for an additional general educational program, the teacher needs to know all the stages of its development.
Development of an additional general education program.
Determination of the goal and objectives of the development of an educational and methodological complex.
Selection and analysis of information and methodological material:
Methodical;
Literary;
Visual;
Electronic educational resources.
Selection of material.
Systematization of the material in accordance with the educational and methodological plan and forms of conducting classes.
Creation of thematic folders (printed and electronic).
Systematization of the educational and methodological complex.
Implementation of the educational and methodological complex in practice.
Analysis of the educational and methodological complex:
Correction of the educational and methodological complex.
presentation of teaching materials materials at methodological associations, speaking at workshops, presentations of pedagogical experience, conferences, publications through publishing houses and Internet sites, participation in methodological exhibitions and professional competitions of various levels.
Since the development of an educational and methodological complex is a creative process, each teacher has the right to determine the stages of the development of teaching materials, depending on work experience, professional knowledge and skills.
7. Requirements for the creation of teaching materials
The educational-methodical complex and its components should:
provide for a logically consistent presentation of the educational material of the additional general education program;
assume the use of modern methods and technical means that allow students to deeply master the educational material and acquire skills for its use in practice;
correspond to modern scientific concepts in the subject area;
provide intersubject communications;
provide ease of use for educators and students.
In conclusion, we can identify a number of objective factors that determine the advantages of the educational and methodological complex ("pluses" of the teaching materials), which allow the teacher of additional education to more effectively solve many issues of organizing their activities.
The first "plus" - UMK allows you to keep up with the times. The use of teaching materials gives integrity to the educational process, allows the teacher to raise the organization of the pedagogical process, preparation and conduct of classes to a higher level.
Second "plus" - EMC is an important means of a more perfect organization of pedagogical work. EMC as an organic part of the teacher's activity allows him to carry out his activities in the system, feeling the components of this activity and directing them into an organically unified process of the child's personality development. At the same time, the teaching and learning method has great positive capabilities and reserves that ensure a reduction in the cost of resources and time for students and teachers with a high quality of educational results.
Third "plus" - EMC allows a teacher to fundamentally improve his skills. By mobilizing existing knowledge and experience to solve certain pedagogical problems, carrying out analysis and self-analysis of pedagogical activity in the course of work on the teaching materials, the teacher fundamentally increases his professional competence.
Fourth "plus" - EMC contributes to the teacher's creative self-realization. In general, the teacher's work on the design and creation of an educational and methodological complex not only allows one to systematize the experience accumulated by him as a specialist, but also contributes to the manifestation of creative activity and conscious professional development.
Fifth "plus" - creating favorable conditions for self-realization of students in the classroom, stimulating individual choice. The inclusion of a system of multi-level tasks in the teaching materials, taking into account the presence of students of different temperaments, types of thinking, types of memory, allows learning from the capabilities and needs of the child, thereby contributing to the intellectual and personal development of each student.
Sixth "plus" - ensuring the intensity of the development of various types of activities by children. The introduction of teaching materials into the educational process is a condition for the multifaceted activity of students in the direction they have chosen. By inviting a child to join one or another activity (communicative, play, cognitive, educational and research, etc.), the teacher of additional education provides him with the conditions for the realization of his own interests and the development of his individual abilities. The selection of variable materials by the teacher according to the levels and pace of their development allows all participants in the educational process to engage in the chosen business for pleasure and with maximum benefit for themselves.
Conclusion
The use of teaching materials gives integrity to the educational process, allows the teacher to raise the organization of the pedagogical process, preparation and conduct of classes to a higher level. EMC is an important means of a more perfect organization of pedagogical work.
By mobilizing the existing knowledge and work experience to solve certain pedagogical problems, carrying out analysis and self-analysis of pedagogical activity in the course of work on the teaching materials, the teacher fundamentally increases his professional competence.
Undoubtedly, the creation of an educational and methodological complex requires a significant amount of time on the part of the teacher, but its use will entail conscious professional development, getting more satisfaction from work.
Thus, the creative process of working on teaching materials, in which the functional role of each of its constituent components can change under the influence of many factors, can be considered as a means of improving the quality of additional education.
Bibliography:
1. Federal Law of the Russian Federation of December 29, 2012, No. 273-FZ "On education in the Russian Federation".
2. The concept for the development of additional education for children, approved by the Order of the Government of the Russian Federation of 04.09.2014, No. 1726-r.
3. Budaeva N.A. Educational and methodological complex in the system of additional education. Toolkit. -Publishing house MOU DOD DYUTS UKMO 2015.
4. Builova L.N. Methodical recommendations for the development and design of preschool education. - Moscow, 2015.
5. Builova L.N. Technology for the development and quality assessment of additional general educational programs: new time - new approaches. Toolkit. - M .: Pedagogical Society of Russia, 2015 .-- 272 p.
6. Gorskiy V.A. Educational and methodological kit as a means of software and methodological support of additional education for children, its functions and the main stages of development // Additional education. - 2009. - No. 1. - S. 29-33.
7. Dobretsova NV, Ints IG: Educational-methodical complex is a necessary part of the teacher's professional activity: educational-methodical manual: State Educational Institution "St. Petersburg City Palace of Youth Creativity" A.I. Herzen Department of Pedagogy: St. Petersburg, 2004.
8. Skuratovskaya N.A. Educational-methodical complex as a means of improving the quality of additional education // Modern Pedagogy. - 2014. - No. 12 (electronic resource).
9. Filatova M.N. Individualization and personification are topical problems of modern education. Scientific-methodical collection "Library". - 2016. - No. 1. - P. 44-80.
10. Filippova NV Assessment of the effectiveness of the additional general educational program (on the example of the work of the studio "Youth fashion" MOU DOD "Autograph" in Nerekhta, Kostroma region) // Young scientist. - 2012. - No. 5.
Annex 1
Sample title page of UMK to DOOP
Regional state budgetary educational institution of additional education "Khabarovsk regional center for the development of creativity of children and youth"
____________________________________________________
(structural subdivision)
Educational-methodical complex
to the additional general educational general developmental program __________________________
(name of DOOP)
Direction of preschool education _________________________
Age of pre-school students _____________________
Additional education teacher (trainer-teacher)
FULL NAME.
Khabarovsk
20__
Appendix 2
Information card of the educational-methodical complex for the additional general educational program
DOOP name: ______________________________________________
DOOP implementation period: ____________________________________________
Students age: ________________________________________________
Author,compiler
Year of development, compilation
Tutorials
Methodical materials
Didactic materials
Electronic resources
Diagnostic materials
Other (holiday scenarios, photo albums, pakmyatki, etc.)
Appendix 3
Scorecard (approximate)
educational and methodological complex
to the additional general education program
(for internal and external examination of the teaching materials)
DOOP name ___________________________________________________
FULL NAME. teacher ___________________________________________________
Each indicator is assessed according to a four point system:
0 - lack of materials for assessment;
1 - the materials partially meet the requirements;
2 - materials are more in line with the requirements;
3 - materials are 90% compliant with the requirements;
4 - the materials fully comply with the requirements.
The maximum number of points is 20 points.
Tutorials:Reference literature
Fiction
Scientific and popular science literature
Periodicals
Videos
Audio materials
3
Didactic materials:
Handouts for learners
Visual aids
4
Methodical materials:
Lesson plans
Control tasks
Methodical developments
5
Diagnostic materials and the criteria for monitoring the results of the development of pre-educational education students
Total points: _____________
Commission members:
1._______________________
2._______________________
3._______________________
Date of completion ______________________
Appendix 4
Individual sheet
pedagogical observation of student activities
One of the diagnostic tools is the observation method. Observations must be carried out in compulsory classes and in an informal setting, as well as during mass events throughout the school year. For pedagogical observation and analysis, it is necessary to choose the behavioral manifestations of students that characterize the child's attitude to others, peers, to activities.
The form of accumulation of pedagogical information is the "Individual sheet of pedagogical observations of the activities of students", which is filled in by the teacher. The generalized information is reflected in the summary card of observations of the students (Appendix 5).
Surname, name of the student ________________________________________
Civil responsibility (conscientiousness, orderliness, diligence, exactingness towards oneself and others)Possession of knowledge about events taking place in the country and in the world, the ability to independently highlight important state and social problems
Positive attitude towards others, manifestation of intolerance to any kind of violence (respect for nature, animals, plants)
The manifestation of one's own moral and civic position in relation to the interests of the development of the state and society
Responsible attitude to the fulfillment of public assignments
Participation in holding events with a civic focus
Social activity (purposefulness, independence, initiative, decisiveness, perseverance)
Self-expression, the desire to show your knowledge and skills during various events
Clear personal goals and their implementation
Self-organization of your educational activities
Ability to independently complete tasks
Moral culture (honesty, restraint, justice, humanity)
Possession of knowledge about the cultural and historical heritage of the country
Positive attitude towards general cultural, spiritual and moral values
Recognition of the value of cultural forms of behavior (culture of behavior with peers, culture of speech, culture of behavior with teachers, culture of behavior during offsite educational events)
Participation in cultural events
Sociability (sociability, endurance, social mobility)
Development of communication skills, cooperation in the process of carrying out various types of activities
Participation in educational and socially significant activities, activity in the process of organizing and holding events
Ability to work in a team, team
Motivation and attitude of students to the learning process
The motive for getting high marks
The desire to take a new position in relations with others, to gain respect among peers, the desire to assert oneself
The need for new knowledge and skills
Ability to subordinate your desires to consciously set learning goals
Maximum points:
Appendix 5
Summary map of pedagogical observations
for the activities of students in the children's association
Total valueThe pursuit of knowledge
Independent search for information
Ability to plan PM activities
Wed arithmetic
Self-expression
Self-organization
Self-determination
Independence
Wed arithmetic
Knowledge
Moral attitudes
Positive attitude towards others
Responsibility to the team
Participation in events
Wed arithmetic
Knowledge
Attitude
Behavior
Participation in events
Wed arithmetic
Communication skills
Organizational skills
Ability to work in a team
Wed arithmetic
Internal motives
External positive
External negative
Purposefulness
Wed arithmetic
Average
1
2
3
This technique allows you to determine the level of the student's personal development throughout the entire period of study in the additional general education program:
0-1 point - low level of personal development of students
2-3 points - average level of development
4-5 - high level of development
Appendix 6
Application form
"Determination of the level of socio-cultural development of students"
Instructions for conducting the test. Read the judgments below. Rate each judgment in relation to you on the following scale:
A - quite right, constantly;
B - relatively true, not always;
B - wrong, never.
Enter the answers (A, B or C) on the questionnaire next to the judgment number.
Questionnaire.
FULL NAME. student ___________________________________
Year of study, age _______________________________
Part I ... Diagnosis of cognitive need
1. I do not lose the desire to achieve the goal, even if something interferes with it.
2. I strive to acquire new knowledge, previously unknown to me.
3. Only with good knowledge can you achieve success in life.
4. A person cannot know everything, so I am not ashamed to ask the teacher questions I do not understand.
6. Learning new things for me creates a feeling of success.
7. I can independently find, analyze and select the necessary information from various sources, including using computer tools.
8. I can adequately judge the reasons for my success / failure in training, linking success with efforts, hard work, diligence.
9. I believe that education plays a primary role in the development of individuals and society as a whole.
10. I see the relationship between acquiring knowledge and future professional activity.
Part II ... Diagnostics of social activity
1. I can subordinate my actions to the set goals and not succumb to the influences of various factors that impede the achievement of the goal.
2. I am used to highlighting the main thing in business and not being distracted by outsiders.
3. I strive to cope with various difficulties on my own.
4. I reasonably plan and organize my activities, free time.
5. I can work creatively on my own initiative.
6. I like to master new types of activities, new skills.
7. I often offer my own approach to business, I strive to make any work interesting for myself and others.
8. If I get down to business, then be sure to bring it to the end.
9. I take an active part in the preparation and conduct of various events of the school, class, institution of additional education.
10. When important decisions need to be made, I act decisively.
Part III ... Diagnostics of civil liability
1. I am willing to put the public interest ahead of my own.
2. I am responsible for the affairs of the group, the class, I am worried about the overall success.
3. I want my work to be beneficial to society.
4. I am conscientious about the implementation of any business, assignment.
5. I am ready to defend my homeland, the interests of the state in case of serious danger.
6. I know the history, traditions, culture of my state.
7. I get excited when I hear songs about my homeland.
8. I know how to keep my word, if I promised something, I will definitely fulfill it.
9. It is interesting for me to take part in discussions on topical issues of the life of civil society and the state.
10. I take good care of the surrounding nature, animals, plants, etc.
Part IV ... Diagnostics of moral qualities
1. I treat adults with respect.
2. It is important for me to help a friend if he is in trouble, not expecting praise and reward in return.
3. I am ashamed if I act unfairly towards others.
4. I have shortcomings that I try to cope with.
5. I show sympathy for the guys who are failing.
6. I think that you should not allow yourself to swear at an unfair remark addressed to you.
7. I believe that there are rules of conduct in public places that must be followed by everyone.
8. I always speak the truth.
9. Appearance is an indicator of respect not only for oneself, but also for others.
10. In my free time, I enjoy going to the theater, museum, exhibition.
Part V ... Diagnostics of communicative qualities
1. I am able to maintain restraint and patience in conflict situations, accept the problem calmly, try to find a compromise solution.
2. I think it is important to understand other people, even if they are wrong.
3. In an unfamiliar company, I do not feel uncomfortable.
4. I do not feel a feeling of inconvenience or embarrassment if I have to take the initiative in order to get to know a new person, to establish contact with him, and friendly relations.
5. I easily adapt to a new team.
6. I have many friends with whom I constantly communicate.
7. It is not difficult for me to deliver a report, message, information to an audience.
8. In solving important matters, I take the initiative.
9. I take part with pleasure in holding collective events, organizing public affairs, taking responsibility for the overall result.
10. In a team I like to be in the spotlight, I feel like a significant member of the “team”.
Part VI ... Diagnostics of student motivation for cognitive activity
I am attracted by:
1. An opportunity to acquire new knowledge, skills, broaden horizons.
2. The desire to assert themselves, to gain respect among their peers.
3. The need to acquire the knowledge necessary in the future to choose a profession, the opportunity to receive initial specialized training.
4. The need for communication with peers.
5. Opportunity to develop creativity.
6. The opportunity to participate in collective affairs.
7. The ability to achieve success in certain activities, the desire to benefit society.
8. The ability to develop certain character traits in oneself: independence, activity, initiative.
9. The future depends on this: admission to an educational institution, salary, career.
10. Reward, encouragement of parents.
Processing of results.
A three-point scale is used for assessment:
Option "A" - 2 points - the student fully owns the specified skill, ability, the specified form of behavior is characteristic of him.
Option "B" - 1 point - owns it in part, shows it from time to time, inconsistently.
Option "B" - 0 points - does not own.
For each answer (option A) 2 points are awarded, for the answer (option B) 1 point is awarded, for the answer (option C) no points are awarded.
Convert your answers to the test questions into points. Write the numbers obtained in the questionnaire (table 1) in the empty box next to the answer to the questions. Calculate the results of each part of the test on the questionnaire (Table 1) by adding the scores recorded in the columns. Write the received amounts in the final cells.
Enter in table 2 "Summary table of the results of the students of the group" the test results, the results obtained from the 1st to the 6th parts from the final cells of table 1. It is calculated how many students in the group have a minimum, high, average level of socio-cultural development. Results can be converted to percentages.
Group Student Survey Results Pivot Table
Minimum level(less than 8 points)
Average level
(8-15 points)
High level
(15-20 points)
Part 1
Cognitive activity
Part 2
Social activity
Part 3
Civil responsibility
Part 4
Moral
Part 5
Sociability
Part 6
Motivation for cognitive activity
This technique allows you to reveal the strengths and weaknesses of the personality of students, to identify the level of their socio-cultural development.
The use of the methodology throughout the entire period of study in an additional general educational program will allow to record the changes in the personality of students and identify trends in personality development.
To orient educational institutions and teachers in the existing variety of educational and methodological complexes, we give a brief description of them.
Currently, there are traditional and developmental training systems in the Russian Federation.
The traditional programs include:“School of Russia”, “Primary school of the XXI century”, “School2000”, “School 2100”, “Harmony”, “Prospective elementary school,“ Classical elementary school ”,“ Planet of Knowledge ”,“ Perspective ”. Developing systems include two programs: L.V. Zankov and D.B. Elkonin - V.V. Davydov.
Below is a brief description of the above-mentioned educational and methodological complexes (TMC). More detailed information on each teaching aid can be found on the indicated sites.
Educational-methodical complex "School of Russia"
(edited by A. Pleshakov)
Publishing house "Education".
Website: http://school-russia.prosv.ru
The traditional program "School of Russia" has existed for decades. The author himself emphasizes that this kit was created in Russia and for Russia. The main goal of the program is "to develop a child's interest in knowing his country and its spiritual greatness, its significance on a global scale." A traditional curriculum allows you to carefully practice the learning skills (reading, writing, counting) that are necessary for successful high school education.
The educational-methodical course "Teaching literacy and the development of speech" by the authors of V.G. Goretsky, V.A.Kiryushkin, L.A. Vinogradskaya meets all the modern requirements of teaching children in primary school.
During the period of literacy training, work is underway to develop the phonetic hearing of children, teach initial reading and writing, expand and clarify children's ideas about the surrounding reality, enrich the vocabulary and develop speech.
In addition to the "Russian Alphabet", the set includes two types of prescriptions: prescriptions by the authors V. G. Goretsky, N. A. Fedosova and the "Miracle prescription" by V. A. Ilyukhina. Their distinctive feature is that they not only form the skills of literate, calligraphic writing, but also make it possible to correct handwriting at different stages of training and in different age groups.
For the development of the cognitive abilities of each child in the "Mathematics" course, the topics of the tasks have been updated, a variety of geometric material has been introduced, and entertaining tasks have been given that develop the logical thinking and imagination of children. Great importance is attached to juxtaposition, comparison, opposition of related concepts, tasks, clarification of the similarities and differences in the facts under consideration.
The set includes new generation textbooks and teaching aids that meet all the requirements for a modern educational book.
Publishing house “Prosveshchenie” publishes textbooks and teaching aids of the educational complex “School of Russia”.
System of textbooks "School of Russia":
1. Alphabet - V.G. Goretsky, V.A.Kiryushkin, L.A. Vinogradskaya and others.
2. Russian language - V.P. Kanakina, V.G. Goretsky.
3. Russian language - L.M. Zelenina, etc.
4. Literary reading - L.F.Klimanova, V.G. Goretsky, M.V. Golovanova and others.
5. English language - V.P. Kuzovlev, E. Sh. Peregudova, S.A. Pastukhova and others.
6. English (extended content of teaching a foreign language) - IN Vereshchagina, KA Bondarenko, TA Pritykina.
7. German language - IL Beam, LI Ryzhova, LM Fomicheva.
8. French language - A.S. Kuligina, M.G. Kiryanov.
9. Spanish - A.A. Voinova, Yu.A. Bukharova, K.V. Moreno.
10. Mathematics - MI Moro, S.V. Stepanova, S. I. Volkova.
11. Informatics - A.L. Semyonov, T.A. Rudnichenko.
12. The world around us - A.A. Pleshakov and others.
13. Fundamentals of spiritual and moral cultures of the peoples of Russia - A.V. Kuraev, DI Latyshina, MF Murtazin and others.
14. Music - E. D. Cretan, G.P. Sergeeva, T.S. Shmagin.
15. Fine arts - L.A. Nemenskaya, E.I. Koroteeva, N.A. Goryaeva.
16. Technology - N.I. Rogovtseva, N.V. Bogdanov and others.
17. Physical culture - V.I. Lyakh.

Educational-methodical complex "Perspective"
(edited by L.F. Klimanova)
Publishing house "Education".
Website: http://www.prosv.ru/umk/perspektiva
The educational-methodical complex "Perspective" has been produced since 2006. The teaching materials include lines of textbooks on the following subjects: "Literacy", "Russian language", "Literary reading", "Mathematics", "The world around", "Technology".
The educational and methodological complex "Perspective" was created on a conceptual basis that reflects modern achievements in the field of psychology and pedagogy, while maintaining a close connection with the best traditions of classical Russian school education.
EMC ensures the availability of knowledge and high-quality assimilation of program material, the all-round development of the personality of a younger student, taking into account his age characteristics, interests and needs. A special place in the UMK "Perspektiva" is given to the formation of spiritual and moral values, acquaintance with the cultural and historical heritage of the world and Russia, with the traditions and customs of the peoples inhabiting the Russian Federation. The textbooks include assignments for independent, pair and group work, project activities, as well as materials that can be used in extracurricular and extracurricular work.
The teaching materials use a unified navigation system for teachers, students and parents, which helps to work with information, organize and structure educational material, plan student activities in the lesson, organize homework, and form the skill of independent work.
The literacy course is distinguished by its communicative-cognitive and spiritual-moral orientation. The main goal of the course is the active formation of all types of speech activity: the ability to write, read, listen and speak, the development of the speech thinking of first graders, the ability to communicate and understand oneself and others. The effectiveness of the new system is ensured by educational material, selected in accordance with the level of development of the child's cognitive interests, game and entertaining exercises, structural-figurative word models that are inscribed in various communicative-speech situations. In this regard, the word is presented in a different way, namely, not only as a sound-letter complex, but as a unity of meaning, meaning and its sound-letter form.
All the conditions for a differentiated approach to students with different levels of preparation for school have been created on the pages of the teaching and learning complex "Teaching to read and write".
Teaching the Russian language is organically linked with teaching literacy and has a general focus. The peculiarity of the course is a holistic view of the language, which ensures the study of the language (its phonetic, lexical and grammatical aspects), speech activity and text as a speech work.
The main objective of the course "Literary Reading" is the formation of the personality of a younger student, acquaintance with the cultural and historical heritage and the formation of reading competence. For this, the textbook uses highly artistic texts, folklore works of different peoples. The system of questions and tasks contributes to the formation of a culture of verbal communication, the development of students' creative abilities, introduces them to spiritual and moral values, acquaints them with ethical and aesthetic norms, develops the figurative-logical thinking of students and forms an interest in a work of art as the art of words in younger students. The headings "Independent reading", "Family reading", "We go to the library", "Our theater", "The reader is a teacher", "Small and big secrets of the country of Literature", "My favorite writers" offer various forms of work with a literary work, systematize knowledge and enrich the child's practical experience, they present a system of working with a book both in lesson and in extracurricular activities.
“Teaching not only mathematics, but also mathematics” is the leading idea of the line of teaching materials in mathematics, aimed at strengthening the general cultural sound of mathematical education and increasing its importance for the formation of a child's personality. The content of the material is focused on the formation of younger schoolchildren's ability to observe, compare, generalize, and find the simplest patterns, which allows them to master heuristic methods of reasoning, their logic, develops the divergence of thinking, as the most important component of mental activity, speech culture and allows them to expand their ideas about the world by means mathematics. Much attention is paid to the development of students' numerical literacy, the formation of computational skills based on rational methods of action.
Textbooks have the same structure and consist of 3 sections: numbers and actions with them, geometric shapes and their properties, quantities and their measurement.
The leading idea of the course "The World Around" is the idea of the unity of the natural world and the world of culture. The world around us is viewed as a natural and cultural whole, man - as a part of nature, the creator of culture and its product.
The course reveals the structure of the concept of "surrounding world" in the unity of its three components: nature, culture, man. These three components are consistently considered at different socio-cultural levels of society (family, school, homeland, home country, etc.), due to which the main pedagogical approaches to mastering the subject are determined: communicative-activity-oriented, cultural-historical, spiritually-oriented.
The main objective of the subject "Technology" is to create conditions for students to gain experience in project activities from the concept to the presentation of the product. Younger schoolchildren master the techniques of working with paper, plasticine and natural materials, a designer, study the properties of various materials and the rules for working with them. This approach creates the conditions for the formation of regulatory universal educational actions in younger schoolchildren, allows the formation of specific personal qualities (accuracy, attentiveness, willingness to help, etc.), communication skills (work in pairs, groups), the ability to work with information and master the basic techniques of working in a computer.
The material in the textbooks is built in the form of a journey that acquaints students with human activities in different areas: Man and Earth, Man and water, Man and air, Man and information space.
In the textbook "Technology" a symbolic system for assessing the quality and complexity of the product is introduced, which makes it possible to form the motivation for success and self-esteem of the student.
The UMK "Perspektiva" includes:
Subject textbooks (grades 1-4)
Workbooks
Creative notebooks
Didactic materials for the student: "Reader", "The Magic Power of Words", "Mathematics and Informatics", "Fundamentals of Life Safety".
Methodological aids for teachers: lesson-based developments in subjects, additional teaching materials, calendar-thematic planning, flow charts.
Calendar-thematic planning and flow charts, which provide the teacher with effective and high-quality teaching by moving from lesson planning to designing the study of the topic, are posted on the pages of the Internet site of the UMK "Perspektiva".
Textbooks that are part of the "Perspektiva" educational complex:
1. ABC - L.F. Klimanova, S.G. Makeeva.
2. Russian language - L. F. Klimanova, S. G. Makeeva.
3. Literary reading - LF Klimanova, L.А. Vinogradskaya, V.G. Goretsky.
4. Mathematics - G.V. Dorofeev, T.N. Mirakov.
5. The world around us - А.А. Pleshakov, M. Yu. Novitskaya.
6. Technology - N.I. Rogovtseva, N.V. Bogdanova, N.V. Dobromyslova
Educational-methodical complex "School 2000 ..."
Publishing house "Juventa"
Website: http://www.sch2000.ru
 The didactic system of the activity method "School 2000 ..." offers a solution to urgent educational problems in the system of lifelong education (preschool educational institution - school - university). It is based on a continuous course of mathematics for preschoolers, primary and secondary schools, focused on the development of thinking, creative forces of children, their interest in mathematics, on the formation of solid mathematical knowledge and skills, readiness for self-development. The "Learn to Learn" program takes into account the possibility of working on this program in the context of various options for the educational plan of the educational institution (4 hours or 5 hours per week).
The didactic system of the activity method "School 2000 ..." offers a solution to urgent educational problems in the system of lifelong education (preschool educational institution - school - university). It is based on a continuous course of mathematics for preschoolers, primary and secondary schools, focused on the development of thinking, creative forces of children, their interest in mathematics, on the formation of solid mathematical knowledge and skills, readiness for self-development. The "Learn to Learn" program takes into account the possibility of working on this program in the context of various options for the educational plan of the educational institution (4 hours or 5 hours per week).
The main goal of the "School 2000 ..." program is the all-round development of the child, the formation of his abilities for self-change and self-development, a picture of the world and moral qualities that create conditions for successful entry into the culture and creative life of society, self-determination and self-realization of the individual.
The selection of the content and the sequence of studying the basic mathematical concepts was carried out in the program "Learn to learn" on the basis of a systematic approach. Built by N.Ya. Vilenkin and his students, the multilevel system of initial mathematical concepts (SNMP, 1980) made it possible to establish the procedure for introducing fundamental concepts in school mathematics education, ensuring successive connections between them and the continuous development of all content-methodological lines of the mathematics course 0-9.
The basis for organizing the educational process in the "Learn to Learn" program is the didactic system of the activity-based teaching method "School 2000", which can be used at two levels: basic and technological.
The mathematics course "Learning to Learn" for elementary school can be used in conjunction with courses in other academic subjects included in the Federal Lists of Textbooks of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation, based on the teachers' own choice. In this case, the technology of the activity method at the basic level can be used as a didactic basis for ordering the work of teachers in the conditions of variability of education.
EMC in mathematics for elementary school of the program "Learning to learn" ("School 2000 ..."
1. Mathematics - L.G. Peterson
Textbooks are equipped with teaching aids, didactic materials and a computer program for monitoring progress.
additional literature
2. Peterson L.G., Kubysheva M.A., Mazurina S.E. What does it mean to be able to learn. Study guide.-M .: UMC "School 2000 ...", 2006.
3. Peterson L.G. Activity-based teaching method: educational system "School 2000 ..." // Building a continuous sphere of education. - M .: APK and PPRO, UMC "School 2000 ...", 2007.
Educational-methodical complex "School 2100"
(supervisor - L.G. Peterson)
Balass Publishing House
Website: http://www.school2100.ru/
 In the process of teaching on EMC in accordance with the activity approach, the task of forming a functionally competent personality is realized. Using different subject content, the student learns to acquire new knowledge, to look for answers to his questions. All textbooks of the program are built taking into account the psychological specifics of the age. A characteristic feature of this educational program is the minimax principle. He assumes that the authors of textbooks and the teacher enable the student (if he wants to) to take the material to the maximum. There is redundant information in the textbooks for this, allowing the student to make personal choices. At the same time, the most important facts, concepts and connections that are included in the minimum content (FSES and program requirements) must be learned by every student. The minimum is presented to the student in the lessons of discovering new knowledge, consolidated and submitted for control. The maximum allows the student to satisfy his own personal needs and interests.
In the process of teaching on EMC in accordance with the activity approach, the task of forming a functionally competent personality is realized. Using different subject content, the student learns to acquire new knowledge, to look for answers to his questions. All textbooks of the program are built taking into account the psychological specifics of the age. A characteristic feature of this educational program is the minimax principle. He assumes that the authors of textbooks and the teacher enable the student (if he wants to) to take the material to the maximum. There is redundant information in the textbooks for this, allowing the student to make personal choices. At the same time, the most important facts, concepts and connections that are included in the minimum content (FSES and program requirements) must be learned by every student. The minimum is presented to the student in the lessons of discovering new knowledge, consolidated and submitted for control. The maximum allows the student to satisfy his own personal needs and interests.
Thus, each child has the opportunity to take as much as he can.
With the help of the problem dialogue technology used in the educational system "School 2100", schoolchildren at each lesson learn to set a goal, draw up a plan to achieve it, search for a solution, and reflect on the results of working with the text. For the formation of communicative general educational skills, the technology of working with text is used. Thus, a teacher who works according to the textbooks of the School 2100 Educational System has the opportunity to achieve new educational goals by simply delivering high-quality lessons using the technologies adopted in this system.
List of textbooks UMK "School 2100"
1. Primer - R.N. Buneev, E.V. Buneeva, O. V. Pronina.
2. Russian language - R.N. Buneev, E.V. Buneeva, O. V. Pronina.
3. Literary reading - R.N. Buneev, E.V. Buneeva.
4. English language - M.Z. Biboletova and others.
5. Mathematics - Т.Е. Demidova, S.A. Kozlova, A.P. Thin.
6. The world around us - А.А. Vakhrushev, O.B. Bursky, A.S. Rautin.
7. Fine arts - O.A. Kurevina, E. D. Kovalevskaya.
8. Music - L.V. Schoolboy, V.O. Usacheva.
9. Technology - O.A. Kurevina, E.L. Lutseva
10. Physical culture - BB Egorov, Yu.E. Grass.

Educational-methodical complex "Perspective primary school"
(scientific advisor - N.A. Churakova)
Publishing house "Akademkniga / textbook"
Website: http://www.akademkniga.ru
The teaching methodology concept is based on the humanistic belief that all children are able to learn successfully if the necessary conditions are created for them. Taking into account the age of the students makes the learning process successful. All textbooks in the kit provide teachers with opportunities to implement the regional component.
When selecting educational material, developing a language for presenting the material, developing a methodological apparatus of the kit, the following components were taken into account.
The age of the student. A first grader can be six, seven or eight years old. And this is not a problem of lowering the age of the first grader, but the problem of the simultaneous presence of older children at the lesson, which required a combination of play and educational activities throughout the first year of study.
Different level of development of the student. A student who has not attended kindergarten often comes to school with unformed sensory standards. This required solving the problem of forming sensory standards during the adaptation period of training.
Topographic affiliation of the student. The selection of material takes into account the experience of a student living in both urban and rural areas.
Different occupancy of the class. The detailed formulation of tasks, together with instructions for the organizational forms of their implementation (in a group, in a pair), allows students to study independently for a rather long time, which is important for a small and small school. A similar structure of textbooks within each subject area and a common external intrigue for all textbooks in the set help students of different age groups in the same room to be in a single educational space.
Different levels of Russian language proficiency. When developing the teaching materials "Perspective Primary School", it was taken into account that not all students speak Russian as their native language and that today's schoolchildren have a large number of speech therapy problems. The search for a solution to this complex of problems required a revision of some important theoretical positions of the Russian language, the development of special lines of orthoepic work and work with a reverse dictionary.
As a result of mastering the subject content included in the kit, each student gets the opportunity to acquire general educational skills and abilities. To master those methods of activity that meet the requirements of the state educational standard. These are, first of all, the initial skills of finding the necessary information in dictionaries, reference books, the library catalog. The system of mutual cross-references between textbooks, each of which has dictionaries specific to its educational field, gives the student the opportunity to acquire skills in working with spelling, orthoepic , reverse, explanatory, phraseological, etymological and encyclopedic dictionaries.
The placement of the methodological apparatus for organizing the activities of children in the classroom in the body of each textbook allows the kit to fulfill such a requirement of the Federal State Educational Standard as the formation of educational cooperation activities - the ability to negotiate, distribute work, evaluate its contribution to the overall result of educational activity.
A single system of conventions in all textbooks is designed to organize individual, pair, group and collective work.
List of textbooks of the educational complex "Perspective primary school"
1. ABC - N.G. Agarkova, Yu.A. Agarkov
2. Russian language - Kalenchuk M.L., Churakova N.A., Baikova T.A., Malakhovskaya O.V., Erisheva E.R.
3. Literary reading - Churakova N.A., Malakhovskaya O.V.
4. Mathematics - A.L. Chekin, O. A. Zakharova, E.P. Yudin.
5. The world around us - ON. Fedotova, G.V. Trafimova, S.A. Trafimov, L.A. Tsareva, L.G. Kudrov.
6. Informatics - E.N. Benenson, A.G. Pautova.
7. Technology - T.М. Ragozin, A.A. Grineva.
additional literature
1) Churakova R.G. Technology and aspect analysis of a modern lesson
Churakova N.A., Malakhovskaya O.V. A museum in your class.

Educational-methodical complex “Development. Individuality. Creation. Thinking "(RHYTHM)
(UMK "Classical primary school")
Publishing house "Drofa"
Website: http://www.drofa.ru
Educational-methodical complex “Development. Individuality. Creation. Thinking ”(RHYTHM) was created on the basis of the“ Classical Primary School ”educational complex, the main feature of which is a combination of modern approaches to solving methodological problems and proven principles of didactics, which allows schoolchildren to achieve consistently high educational results.
Educational-methodical complex “Development. Individuality. Creation. Thinking ”(RHYTHM) was revised in accordance with the Federal State Standard and supplemented with new textbooks (foreign language, the world around them, physical education). The teaching materials include programs, teaching aids, workbooks. Teaching lines for the main subjects are provided with didactic materials, tests and sets of visual aids. All EMC components are integrated into a single methodological system, have a modern layout, volumetric methodological apparatus, professionally executed illustrations.
In the subject line of the Russian language and literary reading, the native language is considered not only as an object of study, but also as a means of teaching children other disciplines, which contributes to the formation of metasubject skills. The texts and exercises contained in the textbooks expand knowledge about the native country, its nature, contribute to the education of patriotism, the development of norms and rules of behavior, traditional moral values, tolerance, and therefore the formation of the necessary personal qualities, which is the most important result of education.
In the course of studying the course of mathematics, textbooks are included in active independent and group activities, the most important result of which is the development of flexibility, criticality and variability of their thinking. The methodological apparatus of the subject line is aimed at the development of logical skills: understanding the educational problem, independent planning of one's actions to solve it, choosing the optimal methods for this.
The methodology, which is the basis of subject lines in a foreign language, is designed to form elementary foreign language communicative competence in primary schoolchildren. The principle of the dialogue of cultures, implemented in the English language course, allows the child to smoothly enter the foreign language communicative space. The German language course is aimed at the interconnected formation of all types of communication skills - listening, speaking, reading and writing. The content of foreign language courses contributes to the formation in the child of a sense of belonging to a certain linguistic and cultural community - Russian civil identity.
In the subject line of the surrounding world, the integration of natural-scientific and social-humanitarian knowledge is carried out, which lays the foundations for the formation of a holistic picture of the world, solves the problems of forming ecological thinking, a culture of a healthy and safe lifestyle, a system of national values, ideals of mutual respect, patriotism based on ethnocultural diversity and general cultural unity of Russian society.
The subject line of fine arts is focused on the aesthetic development of the individual based on the development of the best examples of the artistic heritage of the peoples of Russia and the world. It is built on the principles of the system-activity approach to learning and reflects the communicative and moral essence of art education.
The aesthetic and spiritual and moral development of students when using the subject line in music is carried out through familiarization with musical culture as the most important component of a harmoniously developed personality. The music course is built on a broad integrative basis with the subjects of the humanitarian and aesthetic cycle. It is based on the principle of the formation of universal educational actions - personal, regulatory, cognitive, communicative.
The subject line on technology and physical culture contains extraordinary methodological techniques for the formation of the necessary subject and metasubject skills, as well as personality traits of an elementary school graduate. The lines are practice-oriented and present ample opportunities for organizing educational and extracurricular activities of younger students.
UMK “Development. Individuality. Creativity, Thinking "(RHYTHM) is aimed at achieving educational results defined by the Federal State Standard, and the implementation of the" Concept of Spiritual and Moral Development and Education of a Citizen of Russia. "
Textbooks that are part of the "Classical Primary School" educational complex:
1. ABC - O.V. Jezhelei.
2. Russian language - T.G. Ramzaev.
3. Literary reading.- OV Dzhezheley.
4. English language - V.V. Buzhinsky, S.V. Pavlova, R.A. Starikov.
5. German language - N.D. Galsakova, N.I. Gez.
6. Mathematics - EI Aleksandrova.
7. The world around us - E.V. Saplina, A.I. Saplin, V.I. Sivoglazov.
8. Fine arts - V.S. Kuzin, E.I. Kubyshkin.
9. Technology.- N.A. Malysheva, O. N. Maslenikov.
10. Music - V.V. Aleev, T.N. Kichak.
11. Physical culture - G.I. Pogadaev.

Educational-methodical complex "Primary school of the XXI century"
(scientific adviser - N.F. Vinogradova)
Publishing house "Ventana - Graf"
Website: http://www.vgf.ru
The set is based on the theory of activity of A.N. Leontyev, D.B. Elkonin and V.V. Davydov. The general goal of training is to form the leading activity for this age. The goal of elementary school teachers is not just to teach the student, but to teach him to teach himself, i.e. educational activities; the student's goal is to master the ability to learn. Educational subjects and their content act as a means of achieving this goal.
The forms, means and methods of teaching are aimed at the formation of the prerequisites in the younger schoolchild (in the first half of the first grade), and then the skills of educational activity. In the course of primary education, the skills of educational activities are formed in the younger schoolchild, which allow him to successfully adapt in basic school and continue subject education in any educational and methodological package.
The leading characteristics of an elementary school graduate are his ability to think independently, to analyze any issue; the ability to build statements, put forward hypotheses, defend the chosen point of view; the presence of ideas about their own knowledge and ignorance on the issue under discussion. Hence, there are two methodological features of the EMC. So, working with the educational and methodological set "Primary school of the XXI century", the student masters a fundamentally different role - "researcher". This position determines his interest in the process of cognition. As well as increasing attention to the creative activity of students, based on the initiative and independence of each student.
List of textbooks of teaching materials "Primary school of the XXI century"
1. Primer - L.Ye. Zhurov.
2. Russian language - S.V. Ivanov, A.O. Evdokimova, M.I. Kuznetsova.
3. Literary reading - L.А. Efrosinin.
4. English language - “FORWARD” educational complex, M.V. Verbitskaya, O.V. Oralova, B. Abbs, E. Worell, E. Ward.
5. Mathematics - EE Kochurina, VN Rudnitskaya, OA Rydze.
6. The world around us - N.F. Vinogradov.
7. Music - O.V. Usacheva, L.V. School student.
8. Fine arts - L.G. Savenkova, E.A. Ermolinskaya
9. Technology - Е.А. Lutsev.
10. Fundamentals of spiritual and moral culture of the peoples of Russia (grade 4) - N.F. Vinogradov, V.I. Vlasenko, A.V. Polyakov.

The content of educational subjects of teaching materials is focused on stimulating and supporting the emotional, spiritual, moral and intellectual development and self-development of the child; to create conditions for the manifestation of independence, initiative, creative abilities of the child in various activities. At the same time, the importance of the assimilation of knowledge by children and the acquisition of skills and abilities as means of development remains, but they are not considered as an end in themselves of primary education.
In the subjects of teaching materials, the humanitarian orientation and its influence on the emotional and social-personal development of the child are strengthened. The teaching material contains content that helps the child to maintain and recreate the integrity of the picture of the world, provides him with awareness of various connections between objects and phenomena and, at the same time, forms the ability to see the same object from different sides. The main feature of this set is its integrity: the unity of the structure of textbooks and workbooks for all classes and subjects; the unity of the end-to-end lines of standard tasks, the unity of approaches to the organization of educational activities.
The textbooks and teaching aids of the educational complex "Planet of Knowledge" are published by the publishing houses "Astrel" and "AST".
The UMC includes:
1. Primer - author T.M. Andrianov.
2. Russian language - author T.M. Andrianova, V.A. Ilyukhin.
3. Literary reading - E.E.Kats
4. English language - N.Yu. Goryacheva, S.V. Larkina, E.V. Nasonovskaya.
5. Mathematics - M.I. Bashmakov, M.G. Nefedova.
6. The world around us - G.G. Ivchenkova, I.V. Potapova, A.I. Saplin, E.V. Saplin.
7. Music - T.I. Balanov.
Educational-methodical set "Harmony"
(scientific adviser - N.B. Istomina)
Publishing house "Association of the XXI century".
Website: http://umk-garmoniya.ru/
 The educational-methodological set "Harmony" implements: methods of organizing educational activities of students, associated with the formulation of an educational problem, with its solution, self-control and self-assessment; ways of organizing productive communication, which is a prerequisite for the formation of educational activities; ways of forming concepts that provide awareness of cause-and-effect relationships, patterns and dependencies at a level accessible to primary school age.
The educational-methodological set "Harmony" implements: methods of organizing educational activities of students, associated with the formulation of an educational problem, with its solution, self-control and self-assessment; ways of organizing productive communication, which is a prerequisite for the formation of educational activities; ways of forming concepts that provide awareness of cause-and-effect relationships, patterns and dependencies at a level accessible to primary school age.
The course is based on the methodological concept of purposeful and systematic work on the formation of methods of mental activity in primary schoolchildren: analysis and synthesis, comparison, classification, analogy and generalization in the process of mastering the mathematical content provided by the program.
The primer "My first textbook", intended for the course "Teaching to read and write", provides not only the mastering of elementary reading and writing by first graders, but also the development of their thinking, cognitive interests, a sense of language, the formation of phonetic hearing, spelling vigilance, speech and reading skills, an introduction into the world of children's books, as well as the accumulation of experience with an educational book.
The primer assumes the active promotion of both children who are just beginning to learn to read and those who are already at different stages of mastering the reading technique.
In general, this primer creates the conditions for the successful continuation of teaching reading and the Russian language within the framework of individual academic subjects.
The course of the Russian language, presented in the textbooks "To the secrets of our language", ensures the formation of language and speech skills in younger schoolchildren, their functional literacy, simultaneously with the formation of a whole complex of universal educational actions in them.
This is facilitated by the implementation of an activity-based approach to the organization of training, in which the development of linguistic and speech concepts, rules, work on skills goes from motivation and formulation of an educational task - to its solution and through comprehension of the necessary method of action - to the use of acquired knowledge, to the ability to control performance action and its result.
Language learning has a communicative orientation, since it is subordinated to the development of students' speech, the improvement of all forms of their speech activity.
Building literacy schoolchildren is carried out on the basis of the purposeful development of their spelling vigilance and morphographic self-control.
Course "Literary reading" presupposes the formation of the reading competence of a younger student, which is determined by the mastery of reading technique and methods of mastering a literary work, the ability to navigate in books and the acquisition of experience of independent reading activity.
Literary reading training is also aimed at:
enrichment of the spiritual and moral sphere of junior schoolchildren, the formation of ideas about good and evil, justice and honesty, respect for the culture of the peoples of multinational Russia;
mastering universal learning activities
improvement of all types of speech activity, the ability to build a monologue statement and conduct a dialogue;
development of creative abilities;
fostering an aesthetic attitude to the art of words, interest in reading and books, the need for communication with the world of fiction;
broadening the reader's horizons.
Mathematics course presented in the textbook, in the process of mastering the program material, purposefully forms all types of universal educational actions (ULE) among students. This is facilitated by: the logic of constructing the content of the course, a variety of methodological methods for organizing the educational activities of younger students, a system of educational tasks aimed at performing various types of actions by students.
In the process of studying the course, children acquire: mathematical knowledge, skills and abilities provided by the course program, and learn to use them to describe the surrounding objects, processes, phenomena, assess quantitative and spatial relationships; master the skills: to build reasoning; argue and correct statements; distinguish between justified and unfounded judgments; identify patterns; establish causal relationships; analyze various mathematical objects, highlighting their essential and non-essential features, which will ensure their successful continuation of mathematical education in basic school.
Features of the content of the course "The World Around" are: the integrative nature of the presentation of natural science, social science and historical knowledge; purposeful formation of UUD in the development of subject knowledge and skills.
The study of the surrounding world is aimed at:
the formation of younger schoolchildren of a holistic picture of the world of the natural and socio-cultural world, environmental and cultural literacy, moral, ethical and safe norms of interaction with nature and people;
mastering a complex of subject knowledge, skills and universal educational actions for the successful continuation of education in basic school;
development of skills to observe, analyze, generalize, characterize objects of the surrounding world, reason, solve creative problems;
upbringing of a citizen who loves his Fatherland, who realizes his belonging to it, who respects the lifestyle, customs and traditions of the inhabiting peoples, striving to participate in environmental and creative activities.
The main course presented in the textbooks "Technology", is a subject transformative activity that allows you to integrate conceptual (speculative), visual-figurative, visual-effective components of cognitive activity.
The main features of the course "Fine Arts":
acquaintance of schoolchildren with the figurative language of the visual arts as the basis for the emotional and ethical development of the surrounding world;
communicative orientation of training, ensuring the education of the basic visual culture of the individual and the primary development of visual means of visual communication;
an activity-based approach to the study and further practical development of graphic, design and decorative-artistic activities;
problem-based learning, when the teacher, without prompting the final answer, asks questions that help students come to the right solution themselves;
the formation of methods of cognitive activity and the development of interest in the field of artistic development of the world, the enrichment of the child's sensual and practical creative experience.
Music course, presented in the textbooks "To the heights of musical art", has the following features:
development of the musical thinking of schoolchildren through the development of various genres of music;
selection of musical material with a focus on the masterpieces of the world musical art, which helps the child to form a holistic idea of musical culture according to its reference samples;
formation along with the song type of musical thinking at the symphonic level;
the methodological principle of “recreation” of the masterpieces of the world musical art, which consists in the fact that the integral perception of the work is preceded by the stage of its “creation” by the child through the passage of the main stages of the composer's path;
the creation by schoolchildren of the independence of music as an art form capable of conveying the feelings and thoughts of people by their own means as a result of acquaintance with musical images of various genres of music and disclosure of the multifaceted connections between music and life.
The purpose of the textbooks "Physical culture" is the formation of the foundations of a healthy lifestyle among students, the ability to communicate and interact with peers, plan their own activities, distribute the load and rest in the process of its implementation, analyze and objectively evaluate the results of their own work, evaluate the beauty of physique and posture, and perform motor actions technically correctly.
The publishing house "Association of the XXI century" publishes textbooks and teaching aids of the educational complex "Harmony".
To communicate with colleagues and exchange experience in the educational system "Harmony", a social network has been created - www.garmoniya-club.ru
The UMC includes:
1. Primer - author M.S. Soloveichik, N.S. Kuzmenko, N.M. Betenkova, O.E. Kurlygina.
2. Russian language - by M.S. Soloveichik, N.S. Kuzmenko.
3. Literary reading - by O.V. Kubasov.
4. Mathematics - by N. B. Istomina.
5. The world around us - by O.V. Poglazova, N.I. Vorozheikin, V.D. Shilin.
6. Technology - by N.M. Konysheva.
7. Fine arts - (publishing house "Yakhont"), author: T.A. Koptseva, V.P. Koptsev, E.V. Koptsev.
8. Music - (publishing house "Yakhont"), authors: M.S. Krasilnikova, O. N. Yashmolkina, O. I. Nekhaeva.
9. Physical culture - (publishing house "Yakhont"), authors: RITarnopolskaya, BI Mishina.
EXPLANATORY NOTE ON THE PERSPECTIVE CMD
The educational-methodical complex (hereinafter TMC) "Perspective" has been published by the publishing house "Prosveshchenie" since 2006, annually replenished with new textbooks. The teaching and learning complex "Perspective" includes lines of textbooks on the following subjects: "Literacy", "Russian language", "Literary reading", "Mathematics", "The world around", "Technology".
The complex was created in parallel with the development of the Federal State Educational Standard for primary general education, the requirements of which found their theoretical and practical embodiment in the textbooks of the UMK "Perspektiva".
The conceptual basis of the teaching materials reflects modern achievements in the field of psychology and pedagogy, while maintaining a close connection with the best traditions of classical Russian school education. UMK "Perspektiva" was created within the walls of the Federal Institute for the Development of Education of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation, which is headed by the head of the Department of Personality Psychology at Moscow State University, Academician A.G. Asmolov. Under his leadership, theoretical and methodological materials were developed, which are the backbone components of the Federal State Educational Standard and focused ondevelopment of the student's personality on the basis of mastering universal educational actions. The authors of the UMK "Perspektiva" and, at the same time, the developers of the Federal State Educational Standard, are such famous scientists, teachers and methodologists as L.F. Klimanova, V.G. Dorofeev, M.Yu. Novitskaya, A.A. Pleshakov, S.G. Makeeva, N.I. Rogovtseva and others.
Methodological framework the new complex is the system-activity approach. In this regard, in the textbooks of the UMK "Perspective", tasks aimed at including children in activities are built into a system that allows building the learning process as two-way:
learning as a means the formation of universal educational actions and personal qualities of primary schoolchildren
learning as a goal- obtaining knowledge in accordance with the requirements for the results of mastering the basic educational program of the Federal State Educational Standard.
EMC ensures the availability of knowledge and high-quality assimilation of program material, the all-round development of the personality of a younger student, taking into account his age characteristics, interests and needs. A special place in the UMK "Perspektiva" is given to the formation of spiritual and moral values, acquaintance with the cultural and historical heritage of the world and Russia, with the traditions and customs of the peoples inhabiting our homeland. The textbooks include assignments for independent, pair and group work, project activities, as well as materials that can be used in extracurricular and extracurricular work.
The quality of knowledge assimilation is determined by the variety and nature of the types of universal actions. That is why the planned results of the Federal State Educational Standard determine not only subject, but metasubject and personal results. In this regard, all programs of the teaching and learning complex "Perspective" are focused on the planned results of primary general education and are a tool for achieving them. In the chapters that follow, specific examples will illustrate the capabilities of the Perspektiva CMM in the context of the formation of a CFM.
The main goal of the UMK "Perspektiva" is the all-round harmonious development of the personality (spiritual and moral, cognitive, aesthetic), realized in the process of mastering school subject disciplines.
The main tasks of the UMK "Perspektiva" are:
general cultural development- the formation of a holistic picture of the world (image of the world) on the basis of the integration of cultural experience in the unity of scientific and figurative-artistic forms of knowledge of the world;
personal development- the formation of the identity of a citizen of Russia in a multicultural multinational society; value-moral development of a student, which determines his attitude to the social world and the natural world, to himself; readiness for personal choice and taking responsibility for it; the ability for equal cooperation based on respect for the personality of another person; tolerance for the opinion and position of others;
cognitive development- development of cognitive motives, initiative and interests of the student on the basis of the connection between the content of the academic subject and the life experience and the system of values of the child; harmonious development of conceptual-logical and figurative-artistic thinking; formation of readiness to act in new, non-standard situations; development of the creative potential of the individual;
formation of educational activities- the formation of the ability to learn, independently acquire new knowledge and skills, organizing the assimilation process; development of the ability for self-improvement;
development of communicative competence- the ability to organize and carry out joint activities; exchange information and interpersonal communication, including the ability to understand a partner.
WORKING PROGRAM IN RUSSIAN LANGUAGE
EXPLANATORY NOTE
The program was developed on the basis of the federal state educational standard of primary general education, the Concept of spiritual and moral development and upbringing of the personality of a citizen of Russia, the author's program of L.F. Klimanova, T.V. Babushkina, as well as the planned results of primary general education.
In the system of subjects of an elementary general education school, the subject "Russian language" implements two main goals:
1) cognitive (familiarization with the main provisions of the science of language and the formation on this basis of sign-symbolic perception and logical thinking of students);
2) sociocultural (the formation of the communicative competence of students: the development of oral and written speech, monologue and dialogical speech, as well as the skills of literate, error-free writing as a demonstration_
the body of the general culture of a person).
Modern teaching of the Russian language is not limited to familiarizing students with the language system and its rules, the formation of elementary speech skills. This subject plays an important role in the formation of the foundations of civic identity and worldview, the formation of the foundations of the ability to learn and the ability to organize their activities, spiritual and moral development and education of younger students.
A feature of the subject is its close relationship with literary reading, which ensures the implementation of the main tasks of the content of the subject area "Philology":
● formation of initial ideas about the unity and diversity of the linguistic and cultural space of Russia, about language as the basis of national identity;
● development of dialogical and monologic oral and written speech;
● development of communication skills;
● development of moral and aesthetic feelings;
● development of abilities for creative activity.
General characteristics of the course
A distinctive feature of the Russian language course is the communicative and cognitive basis, which is common with the literary reading course. The content of these two courses has a pronounced communicative-speech and cognitive orientation, covering three aspects of learning the native language: the language system, speech activity and literary text, which ensures the implementation of the system-activity approach in teaching.
The course program provides a holistic study of the native language in primary school through the implementation of three principles:
1) communicative;
2) cognitive;
3) the principle of personal orientation of learning and creative activity of students.
The communicative principle provides for:
● comprehension and implementation of the main function of the language - to be a means of communication;
● development of the ability to navigate in communication situations (to understand the purpose and result of communication between interlocutors, to control and correct their speech depending on the communication situation);
● acquaintance with various communication systems (oral and written, speech and non-speech);
● formation of an idea of the text as a result (product) of speech activity;
● development of students' desire (need) to create their own texts of various styles: business (note, letter, announcement, etc.), artistic (story, poem, fairy tale), scientific and educational;
● organization of educational (business) communication (communication as a dialogue of the teacher with children and with each other) using the formulas of speech etiquette and spiritual and moral communication style based on respect, mutual understanding and the need for joint activities.
The cognitive principle suggests:
● mastering the language as the most important instrument of human cognitive activity and as a means of knowing the world through the word;
● development of thinking of primary schoolchildren based on "two wings of knowledge": figurative and abstract-logical thinking, development of intuition and imagination;
● gradual assimilation of the most important concepts of the course from the visual-practical and visual-figurative level to the assimilation of concepts in an abstract-logical, conceptual form;
● comprehension of the concept of "culture", ensuring the integrity of the content of teaching the Russian language, helping to identify the ways of the formation of the studied concept (from its cultural and historical origins, where the subject of activity is combined with its function, to the final result of the activity, that is, to the formation of one or another concepts);
● mastering the processes of analysis and synthesis in the structure of mental actions (comparison, classification, systematization and generalization) and in the general process of cognition;
● comprehension of language as a sign system of a special kind and its substitutional function;
● consideration of a word as a complex linguistic sign, as a two-sided unit of language and speech;
● formation of semantic, not vocal reading; the object of attention of students becomes both the sound side of the word and its meaning, meaning;
● stage-by-stage assimilation of the language from the disclosure of its lexical and semantic side (meaning of words) to the assimilation of the sound-alphabetic and formal-grammatical (abstract) form.
The principle of personal orientation of learning and creative activity provides:
● awakening the child's desire to learn and gain knowledge;
● formation of ideas about the book, native language and classical literature as a cultural and historical value;
● development of interest in learning a language and creative activity due to the logic of its assimilation, built “from the child”, and not “from the science of language” (the latter provides students with only the final results of cognitive activity, recorded in the form of ready-made abstract concepts suitable for memorization, since the way of their formation is not revealed);
● acquaintance and development of basic values based on the traditions of national culture and providing students with a spiritual and moral basis for behavior and communication with peers and adults;
● creative self-realization of the individual in the process of studying the Russian language and working with a work of art through the creation of his own texts.
The implementation of these principles makes it possible to most fully provide not only the "instrumental basis of students' competence" (a system of knowledge, skills and abilities), but also the spiritual and moral development of the individual, the acquisition of social experience.
Studying the Russian language on the basis of these principles creates real conditions for the implementation of the activity approach, thanks to which the subject content unfolds "from the child", becomes accessible and interesting for students.
The initial stage of learning the Russian language is literacy training. The main attention during this period is given to the study of written speech and the development of the phonemic hearing of children. In parallel with the development of written forms of verbal communication (the ability to read and write), there is an improvement in oral forms of communication (the ability to listen and speak). Therefore, the key concept in the content of teaching literacy is "communication", which is not considered statically, but unfolds in the form of activities proceeding in the cultural and historical plane - from the origins of the process of communication among people (in written form) to the development of writing at the modern level.
After teaching literacy, a separate study of the Russian language and literary reading begins.
The study of a systematic course of the Russian language provides:
● conscious mastery (at a level accessible to children) the native language as a means of communication and cognition for free use in various communication situations;
● development of communication and speech skills (writing and speaking, listening and reading), functional literacy and intellectual abilities of students;
● formation of a respectful attitude to the language, its richness, depth and expressiveness; development of interest in the native language, its study;
● formation of the style of speech communication of students, based on respect for the interlocutor and his opinion;
● familiarizing students with the spiritual and moral values of the Russian language and national culture.
The communicative-cognitive orientation of the course and the system-activity approach implemented in it aim younger students at the joint study of the language system (phonetic, lexical, grammatical units) and understanding the ways of functioning of these linguistic units in oral and written speech, in various communication situations and various texts.
The content of the course covers a fairly wide range of information related to different aspects of the language. Students get acquainted with the phonetic composition of the word, with the division of the word into syllables and significant parts, with the main parts of speech and their most important forms, with various types of sentences, with members of sentences, learn the spelling rules. The program assumes an acquaintance of students with the lexical meaning of a word (without a term), with the polysemy of words and synonymy.
Teaching the Russian language on the basis of this Program has a personality-oriented character, since it is built taking into account the level of development of the child's interests and his cognitive capabilities. So
linguistic concepts are not given in a finished form (or on an explanatory and illustrative basis), but unfold as a process of obtaining them, and in the future - as an activity to assimilate them.
The cognitive orientation of the Program ensures the assimilation of the language as the most important instrument of human cognitive activity, as a means of cognition of the surrounding world and the development of verbal thinking.
The Program attaches great importance to the study of language as a sign system, since it allows you to pay attention to the interaction of the semantic (content) and formal aspects of speech, which fundamentally changes the system of language learning. An appeal to the semantic side of the language creates conditions for the harmonious development of figurative and logical thinking. At the same time, the speech activity and functional literacy of children increase, interest arises and a respectful attitude to the native language, its richness and expressiveness appears, the speech thinking of students develops.
The program provides not only for acquainting children with sign-symbolic activity, but also for mastering the basics of the thought process, analysis and synthesis, which are present in the most important mental operations (comparison, classification, systematization and generalization).
The main content lines of the Program include:
● basics of linguistic knowledge: phonetics and orthoepy, graphics, word composition morphemics), grammar (morphology and syntax);
● spelling and punctuation;
● development of speech.
The content of the Program and approaches to the study of the Russian language have a number of features. So, the study of the composition of a word is preceded by exercises on word formation. Another feature of this Program is the approach to studying parts of speech, changing the attitude of students to the word. If, when studying vocabulary, students deal with a single word and its meaning, then when mastering grammar they work with a whole group (class) of words that have common characteristics. It is not so much the function of naming that is important here as the function of generalization, the development of which is necessary for the development of abstract-logical thinking (the way of forming concepts).
Spelling and punctuation rules are considered in parallel with the study of phonetics, morphology, morphemics and syntax.
In order for the study of grammar to become the most important element in the development of speech and thinking of students, and not to train their memory, the content includes the formation of skills to classify (group) words on different grounds (semantic and formal grammatical). These learning skills help students distinguish between the features of working with a word with its specific meaning in vocabulary and with the abstract (generalized) meaning of words in grammar.
This approach leads students to an independent conclusion that the whole class of words has common characteristics (grammatical meaning, i.e., the meaning of objectivity, gender forms, number and case in nouns, etc.).
In this course, the study of parts of speech is built in stages: from vocabulary to grammar through various levels of classification and generalization of words.
Awareness of the differences between the grammatical (generalized) and lexical (single) meaning of a word allows you to get away from the formal study of grammar.
The course has changed the approach to the study of proposals . The sentence is considered as the main communicative unit of the language. First, an idea of the sentence as a whole is formed (semantic and intonational completeness, the connection of words in the sentence). Then children learn to classify sentences by intonation (exclamatory - non-exclamatory), by the purpose of the statement (narrative, interrogative, incentive). After they have gained experience in observing the sentence in various speech situations, definitions of concepts are introduced.
The program focuses on creating conditions for the development of regulatory learning activities that bring order and orderliness to any activity and form the basis of learning activities. Skills are formed to set a goal, determine the sequence of actions, control, correct and evaluate them. The program provides for the development of calligraphy skills - a kind of graphic "gymnastics", where writing samples are used, the writing of generalized elements of letters, their connections in words, rhythmic and tempo writing of words and sentences is practiced, an installation is given for the calligraphic writing of letters, their connections, self-control and mutual verification are carried out.
A separate, very important element of the Program is familiarity with the dictionary. It is assumed that younger students will be familiar with different dictionaries: spelling, explanatory, encyclopedic, a dictionary of synonyms and antonyms.
The section "Development of speech" provides not only the enrichment of the vocabulary, the improvement of the grammatical structure of speech (in oral and written form), the development of various types of work with the text, but also the formation of ideas about speech in general, about speech communication, about the means of communication (verbal and non-verbal The study of a systematic course of the Russian language begins with a generalization of the initial information about speech communication and language as a means of communication, obtained during the period of literacy training.
The program focuses on the development of skills to accurately and clearly express your thoughts in speech, to solve a particular speech problem in the process of communication (to approve, explain, express surprise, confirm the interlocutor's thought, etc.), to keep the content of speech and its form in the field of attention expressions.
In addition to general ideas about the text, students receive the first information about various types of texts (narration, description, reasoning), begin to comprehend the role of the word in a literary text, work with the title and draw up a plan (with the help of a teacher), observe the stylistic features of artistic and scientific cognitive texts.
Consideration of language as a means of communication in specific communicative-speech situations and texts (scientific, business, artistic) helps children to present the language in a holistic manner, which increases motivation in learning their native language.
Place of the course in the curriculum
Only 675 hours are allocated for the study of the Russian language in elementary school.
In the first grade - 165 hours (5 hours a week, 33 academic weeks), of which 115 hours
(23 academic weeks) is allocated for teaching writing during the period of literacy training and 50 hours (10 academic weeks) for Russian language lessons.
In grades 2-4, 170 hours are allocated for Russian lessons (5 hours a week, 34 academic weeks in each class).
Course learning outcomes
The program ensures that primary school graduates achieve the following personal, metasubject and subject results.
Personal results
1. Formation of the foundations of Russian civic identity, a sense of pride in their Motherland, the Russian people and the history of Russia, awareness of their ethnic and national identity. Formation of the values of the multinational Russian society, the formation of humanistic and democratic value orientations.
2. Acceptance and development of the social role of the student, the development of motives for learning activities and the formation of the personal meaning of learning.
3. Development of independence and personal responsibility for their actions based on ideas about moral norms.
4. Development of ethical feelings, benevolence and emotional and moral responsiveness, understanding and empathy for the feelings of other people. Understanding the importance of a positive communication style based on peacefulness, patience, restraint and goodwill.
5. Formation of aesthetic needs, values and feelings.
6. Development of skills of cooperation with adults and peers in different social situations, the ability not to create conflicts and find ways out of controversial situations.
Metasubject results
1. Ability to plan, control and evaluate educational activities in accordance with the task and the conditions for its implementation, to determine the most effective ways to achieve the result.
2. The ability to accept and maintain the goals and objectives of educational activities, to find the means of its implementation.
3. Ability to engage in discussion of creative and exploratory problems, to learn ways to solve them.
4. Ability to understand the reasons for the success / failure of educational activities and the ability to act constructively even in situations of failure.
5. Mastering the initial forms of self-observation in the process of cognitive activity.
6. Ability to create and use symbolic models for solving educational and practical problems.
7. Using various methods of searching (in reference sources and open educational information space - the Internet), collecting, processing, analyzing, organizing, transferring and interpreting information in accordance with communicative and cognitive tasks.
8. Mastering the skills of semantic reading of texts of various styles and genres in accordance with the goals and objectives. Conscious building of speech utterance in accordance with the tasks of communication, compilation of texts in oral and written form.
9. Mastering the following logical actions:
● comparison;
● analysis;
● synthesis;
● classification and generalization by generic characteristics;
● establishment of analogies and cause-and-effect relationships;
● construction of reasoning;
● assignment to known concepts.
10. Willingness to listen to the interlocutor and conduct a dialogue, to recognize the possibility of the existence of different points of view and the right of everyone to have their own. Ability to express your opinion and argue your point of view and assessment of events. Ability to actively use dialogue and monologue as speech means for solving communicative and cognitive tasks.
11. Determination of the common goal of joint activities and ways to achieve it; the ability to agree on the distribution of functions and roles, to exercise mutual control, to adequately assess their own behavior.
12. Willingness to constructively resolve conflicts, taking into account the interests of the parties and cooperation.
perspective Basic educational program
Program " Perspective " in accordance with the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard, contains the following sections: explanatorynote; planned ... primary school working onUMK « Perspective "... To the teacher working onUMK « Perspective " publishing house "Education" ...
4.18. Educational-methodical complexes: goals and principles of creation, structure and content
Training and metodology complex can be created for a specialty (educational specialty), profession, subject, topic, lesson, account. class. EMC provides two-way teaching and learning, includes components to ensure teaching and learning processes in their unity.
The structure of the CMB may include the following components:
Means of regulatory support ( regulatory documents, technical documentation, PKH, typical account. programs and plans)
Means of educational and methodological support (methodology of teaching subjects, method, recommendations).
Means of education (educational editions, TSO, electrical, audiovisual media, etc.).
Controls:Means of lesson, thematic, intermediate, final control.
The initial principles for the creation of the teaching materials are as follows:
Integrity principle... It lies in the fact that the teaching and learning method acts as an organic part of the projected ped. System, ensuring the implementation of all its basic functions: image, educational, developing.
The principle of economy... It means the creation of optimal conditions for the intensification of educational and production work and the provision of the necessary amenities, contributing to the development of versatile ways of studying.
The principle of openness and accessibility... It means constant optimization, modernization and expansion of the components of the complex and free access to it, if necessary, by all teaching staff in order to borrow advanced experience. The implementation of the principle is ensured by the creation of an open databank on the components of teaching materials at the ur-not republic.
The principle of informatization... It assumes information communication based on the use of computer telecommunication technologies.
The principle of continuity... Assumes the creation of a teaching and learning method based on the use of the accumulated experience of previously developed tools.
The principle of autonomy... It consists in granting the right to each teacher to form his own version of the layout of the teaching materials.
The locality principle... Assumes independence in the development and manufacture of individual components of the UMK.
UMK should issue the following. f-tion: 1-act as a mandatory component of the educational process; 2-combine into a single whole various normative, educational and programmatic documents, the means of educational and methodological support, training and to-la, subordinating them to the goals of training, education and development; 3-way to motivate and activate self-learning and cognitive learning, individualization and differentiation of teaching. v. and development; 4-provide intensification of the image-th process; 5-allow to objectively evaluate the progress and results of training .; 6-disclose the requirements for the content of the image, contributing to the implementation of the image of the standard; 7-to increase the visibility of teaching., To make the teaching accessible to the student. material; 8 is an independent source of information; 9-yavl-sya middle control-ia cognizing the d-yu study; 10-to provide an increase in the efficiency of the uch-th d-ti study in the educational process; 11-serve the accumulation of ped. experience, to stimulate the development of the creative potential of ped collectives; 12 development of cognition and creativity of learning.
A CMM component, as an integral part of an integral system, in contrast to a separate component, must meet the following requirements: be necessary, ensuring the stability of the system; be interconnected and interdependent with other components; have only a characteristic form (book, flat, volumetric, etc.); carry a certain functional load in solving educational problems; correspond to the age characteristics of students, their educational qualifications.
4.19. Control - identification, measurement and evaluation of ZUN ob-Xia.
Role control: to prevent the formation of erroneous skills, to draw generalizing conclusions about the method of communication, to determine the level of training of students, to evaluate their work, to change the methods of communication, the presence or expectation of control stimulates the learning of actions by learning, is an additional motive for their learning to work -ty.
Requirements: 1) K-l should wear a regular character. 2) K-l should cover the maximum number of students per unit of time. 3) The volume of controlled material db is small, but sufficiently representative, so that by the degree of its assimilation / non-assimilation, possession / non-possession of them, one can judge whether they have appropriated the necessary knowledge. and um-me.
Functions counter: 1. Upbringing: the impact on the mental characteristics of the student (development of will, memory,). 2. Correction: correction occurs after K., 3. Feedback function: allows the teacher. manage uch pr-som, act meaningfully and provide the system with reinforcement. 4. Stimulating: mainly associated with the mark.
Forms: Oral f. way to generate fast reaction to the question of developing the memory of the student.
Pisman... counter: they can cover all students at the same time; it is much more convenient to process letters. Developing more effectively. logical thinking, teaches you to be exact in the answers.
Frontal- allows you to observe the basic rules to-la - regularity and max. study coverage per unit of time. The advantage keeps the whole team in tension, their attention is focused, their thoughts are concentrated. Yavl. a more perfect form of verification.
Individual j. In the process and. because there is a communication "teacher - student". The disadvantage is the forced passivity of the group during a significant part of the lesson.
Diagnostics- clarification of the circumstances of the course of the didactic. process, precise definition of its result. Diagnostics incl. in itself to-l, checking, evaluating, accumulating statistical data, analyzing them, identifying dynamics, trends, predicting further developments. D. is designed to: optimize the individual learning process; ensure the correct definition of learning outcomes and reduce to mini-mistakes when transferring students from one study group to another, when sending them to various courses and choosing a specialization of training.
Kinds control: Current control, carried out on the basis of an involuntary form of attention. In the lesson, the students do not know that they are being controlled. Lecturer also notes how much new material is learned in the lesson.
The final control, including both thematic and periodic control. Topic k. Is usually held at the end of the study of the topic. Periodic to. is carried out after mastering a large volume of material.
Counter methods: checking the knowledge and skills of students (oral, written, practical); ongoing observations are carried out throughout the training process. without allocating special time for them and is carried out at any stage of the assimilation process. K-l contains an assessment (process) and a mark (as a result of the assessment, expressed in points).
Testing : designed to assess the success of mastering specific knowledge and individual sections of academic disciplines, and more objective an indicator of learning than the score T = TK (test task) + E coupon.
Types (Bespalko):
Identification (answer yes or no)
To discriminate (choice of answer from options a.b.c)
For classification (connection by arrows of the figure and text to this figure)
Substitutions (insert missing word)
Copies (define, list steps)
Test typical task
Creative task.
According to the form of the tests, they can be individual and group, oral and written, blank, subject, hardware and computer, verbal and non-verbal.
4.20. A software lesson in training workshops is carried out according to an operational-complex system. The essence of this system is that all labor techniques and methods of performing work are divided into a number of complexes. Each complex includes 3-4 labor. operations and complex work, the cat is performed using these operations. That. The software process includes the study of techniques, operations and their multiple repetition, that is, their consolidation. Therefore, the software process can be divided into 2 periods: 1-operational (the main goal of software is to form the skills of learning to qualitatively produce basic labor techniques and their combinations that make up the operation), 2-performance of complex works ( the goal is to form the skills of students, to combine the studied operations in a specific technological process of performing educational and production work, the development of speed and precision skills, labor planning skills) Makienko identified the following types of industrial training lessons: ; - implementation of complex work; - lesson control. The didactic structure of the lesson is determined by didactic tasks. Allocate sl. didactic tasks:
1 Motivation of student activities. Target setting. Updating basic knowledge.
2 Formation of practical knowledge, techniques and methods of action.
3 Application of practical knowledge, techniques and methods of action
4 Control of practical knowledge, techniques and methods of action
The methodological substructure is determined by the goals of the software lesson, the type of lesson. The methodological substructure of the lesson is determined by:
Teaching methods, - methodological techniques and their content, - teaching aids, - forms of organizing student activities
The logical-psychological substructure is determined by the logic of mastering the educational material: perception, awareness, memorization; comprehension of educational material, generalization, systematization. Depending on the type of instruction, the software lesson is divided into 3 stages: 1 introductory instruction, 2 current (self-study), 3 final.
MODERN CMD AS A MEANS OF FORMATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF LEARNING ACTIVITIES (08/26/2015)
Friauf L.N., physics teacher
MBOU "Selective school"
Recently, there have been changes in society in the idea of the goals of education and the ways of their implementation. The school should not only equip with knowledge, skills and abilities, but form UUD for the use and application of this knowledge, skills and abilities in any life situation.
The main purpose of the teaching materials
is the spiritual-moral, cognitive, aesthetic development of the personality, realized in the process of mastering school subject disciplines.The formulation of the tasks of the teaching and learning method assumes that the theoretical knowledge acquired by the child, the cultivated attitude to educational activity should become one of the means of personality formation.
A set of textbooks for the main
and middlegeneral education "Vertical" is an integral system built on unified psychological, pedagogical and conceptual foundations. EMC of all subject lines provide sustainable motivation for adolescents to learn, the implementation of subject, metasubject and personal results indicated in the Federal State Educational Standardmain common and middleeducation, the formation of universal educational actions as the basis of the ability to learn and readiness for self-development.The educational and methodological complex should include a system of teaching aids that meet state education standards. This complex usually includes a basic textbook, a workbook and several additional teaching aids, which have an essential teaching function - not only to expand and deepen subject knowledge, but also to actively contribute to the formation of universal learning actions (ULE). Such a complex can be supplemented by interactive software products.
Universal learning activities
- these are generalized actions that open up the possibility of a broad orientation of students, both in various subject areas and in the structure of the educational activity itself, including the students' awareness of its target orientation, value-semantic characteristics.The entire teaching and learning method should be understood by the teacher and students, first of all, as a program of educational intellectual activity, originally incorporated in the textual content and tasks for it. For the formation of universal educational actions in modern conditions, the dominant role is played not so much by textbooks as by correctly selected additional teaching aids. Thus, the teaching and learning method simultaneously performs the functions of a carrier of the content of education and the functions of designing the educational process, focused primarily on the development of the student himself.
In practice, the school textbook remains the leader. It is almost the only stable teaching tool, and there are not so many additional teaching aids among additional teaching aids that would provide independent purposeful guidance of the cognitive activity of students. The teaching and learning method should ensure the assimilation of all components of the content of education (knowledge, reproductive and creative skills, value system). The system of tasks for additional teaching aids should expand the apparatus for mastering the textbook and purposefully organize the educational activities of students. The use of teaching materials should be technological and provide for the possibility of saving study time.
Tasks play the most important role in teaching materials. They can be conditionally divided into the following groups:
Text comprehension tasks (what the text says, what the text says about it).
Tasks for training memory (reproduction of terms, facts, fragments of text).
Assignments for the definition of concepts.
Tasks for generalizing concepts or excluding a concept from a number of similar ones in meaning.
Tasks for the reproductive application of knowledge: perform practical work according to the instructions, solve a problem according to a model, explain a fact familiar from similar situations, etc.
This approach to the preparation of tasks allows you to take into account most of the manifestations of intellectual and practical activity (analytical, synthetic, comparative, systematizing, etc.) both at the reproductive and creative levels.
The educational-methodical complex has the function of organizing teaching methods. In this case, this function is implemented in the form of a task system. The methodological apparatus of the complex actualizes such educational actions as the acceptance and awareness of the goal of the teaching, the implementation of the action specified in the task, the verification of the result of the action. The tasks themselves in their own formulations, starting with the words -
select, correlate, connect, define, analyze, find common etc. perform, on the one hand, setting functions, orienting students to the implementation of specific operations, and on the other hand, they present, in the form of techniques, the specific content of education that must be mastered - methods of choice, correlation; establishing links; the ability to define concepts, analyze, generalize, etc.Consequently, the teaching materials, with the help of assignments, questions and tasks of various types, formulated in accordance with specific learning goals and having either separate functions or their combination, should ensure the management of students' activities in the formation of the UUD. The formation of these skills will become an objective sign of mastering subject (special) and non-subject (applied) content. The result of such assimilation is:
conscious implementation of the necessary actions;
a certain degree of freedom of the student in the application of the formed skills both in a familiar and in a new situation.
Thus, the role of the educational-methodical complex and its system of tasks consists in the formation of both specific-subject and supra-subject skills, manifested at the reproductive and creative levels of mastering the content of education.