Top dressing of tomatoes should be carried out in several stages. When preparing a site for planting tomatoes in early spring, digging up the ground, you need to add humus at the rate of 16 kg per square meter.
At the earliest stages, when planting seedlings in the ground and until ovaries appear, a pre-prepared mixture is laid in each hole. It is prepared from potassium chloride, wood ash and superphosphate and are introduced into the soil two weeks before planting. Urea can also be used to prepare the land for seedlings. It should be borne in mind that an overdose of nitrogen fertilizers can lead to the fact that the stems, leaves, shoots will actively grow, and the ovaries may not form at all. The risk of fungal infections of the plant increases. From the middle of the growing season, nitrogen fertilizers are no longer applied at all.
Feeding scheme
Regular feeding of tomatoes is necessary for two reasons:
- showers and melt water thoroughly wash out potassium and nitrogen from the soil; all types of tomatoes are intensive crops and require a lot of minerals.
As the tomatoes grow and mature, they should be fed according to the following scheme:
- after 2-3 weeks after disembarkation. Further, temporarily do not feed the culture, waiting for the strengthening of the set fruits; resume fertilization after the 2nd flower cluster appears; after the 3rd flower cluster blooms; after 12 days. The main emphasis in top dressing is on the root, since more fertilizers are always applied through the soil.
Selection of finished fertilizer
Available for sale a large number of fertilizers, which must be selected taking into account the composition of the soil on the site. Tomatoes are grown on soils of various types, but the most suitable is loose, fertile, capable of warming up well. Of the complex mineral fertilizers, Agricola, Effekton, Kemiru-Universal are recommended. Of the concentrated fertilizers, nitroammofoska is often used, produced in granules, each of which contains equal amounts of phosphorus, nitrogen and potassium.
The distribution of minerals in the soil is uniform. Nitroammofosku is bred in the amount of 2 matchboxes of fertilizer per bucket of water. Diammophos is also used.
Many gardeners believe that the most effective remedy top dressing is considered to be vermicompost, the use of which in the amount of 1 cup under each bush of a plant at any stage of growth can increase the yield by 30%.
IRRIGATION of tomatoes + FEEDING with ash. How to water the TOMATOES in the GREENHOUSE
Self-made fertilizers
Often, gardeners, using available tools at hand, prepare top dressing themselves. Many of the nutrients that tomatoes need to grow are found in regular brewer's yeast. Fertilizer is prepared in two ways: 1.
Make a solution from a package of instant yeast, 2 tbsp. l. sugar and a little warm water. After about 2 hours, the infusion is mixed with a bucket of water. Yeast fertilizer in a volume of 0.5 liters is added to the watering can. The effect is noticeable after a few days. 2.
Fertilizer is also prepared from raw yeast. A jar with a volume of 3 liters is filled with brown bread by 2/3, filled with warm water with fresh yeast dissolved in it (100 g). Leave to ferment in a warm place for a period of 3 days.
The filtered solution is mixed with water for irrigation in a ratio of 1: 10.3. To eliminate the calcium deficiency in the soil, eggshells containing calcium and magnesium are used.
To enrich the earth with these substances, it is optimal to use an aqueous infusion on crushed shells. It is necessary to withstand the solution under the lid for 2 weeks, the degree of readiness is determined by the appearance of a pungent odor.
The infusion is added to the water for irrigating tomatoes in a ratio of 1 to 3. Effective fertilizer is cow dung. You can spread it out in the beds, and when water gets on the fertilizer, the tomatoes will receive regular feeding.
For a more effective effect, manure is mixed with peat and the soil is mulched with this composition. When small fruits appear, many gardeners often use diluted chicken manure, sometimes with the addition of urea. This must be done very carefully, otherwise there is a risk of burning the plant roots. To do this, it is necessary to water the solution at some distance from the plants, 15 centimeters. Gardeners also use potassium permanganate in the form of a weak solution, which is both a fertilizer and a protective agent against diseases.
Tomatoes Early planting tomato seedlings outdoors
Foliar feeding of plants
Additional foliar feeding used to stimulate the defenses of the plant. Good results are obtained by spraying with New Ideal once a week.
During flowering, successful foliar feeding is carried out using a solution of boric acid, diluted in a ratio of 1 g per liter of water. 2-3 such sprays every 10 days help to improve fruit set. It is not surprising that tomatoes require such careful care, because the ready-to-eat vegetable is very rich in a variety of biologically active substances and has a whole range of useful properties. Tomatoes are tasty not only raw. , but also in salted, pickled, in the form of pastes and juices.
Tomatoes are powerful antioxidants that can prevent cell aging. This vegetable reduces the risk of cancer. Tomato cleanses the walls of blood vessels, preventing strokes, heart attacks, atherosclerosis. Used for varicose veins.
- Login or register to post comments
More articles about the cottage and the garden
WHAT TO FERTILIZE TOMATOES During flowering, it is advisable to shake the flower brushes so that the ripe pollen spills out from the anthers and falls on the stigma of the pistil. It is best to do this daily, in the middle of the day.
If by chance the top breaks off when transplanting tomatoes, the plant will still take root, and the side shoot will take over the role of the top. When planting overgrown seedlings, the plants must be planted at an inclination of 30-45 ° to the ground to the north.
Then the sun's rays "lift" it to a vertical position. Loosens the soil after each watering and rain.
In hot, dry weather, loosening helps to reduce the evaporation of moisture from the soil, and in rainy and cold weather it provides better gas exchange between air and soil, reduces the possibility of plant disease with fungal diseases. Irregular watering of plants in hot summer often leads to the disease of fruits with apical rot.
Tall (indeterminate) varieties are grown in one stem, in favorable weather - in two. In this case, the stepson serves as the second stem - the shoot under the first flower brush. All other shoots are removed by the stepsons.
Low-growing, early-maturing varieties can be grown without formation, but in rainy years they must be pinned and tied to stakes. The lower aging leaves are cut off in a timely manner. An accidentally thrown stub near tomato plantings can infect plants with tobacco mosaic.
When planting seedlings in the ground, before flowering, when ovaries appear and at the beginning of fruit ripening, it is useful to add potassium permanganate to the water (2 g per 10 l of water). This will have a good effect on the growth, and then on the ripening of the fruits, the tomatoes will turn out to be more sugary and resistant to late blight.
Tall varieties and hybrids are planted according to the scheme 70x70 cm, medium-sized ones - 60x60 cm and 50x50 cm, undersized ones - 50x40 cm and 50x30 cm.The stepsons break out, but in no case do they pull out, since wounds form on the plant, where fungal infection easily gets.
If the side shoots are large, it is better to remove them with a sharp knife or scissors, leaving a stump 1 cm long, which will not allow a new shoot to form. The shorter the growing season of the variety or hybrid, the fewer stepchildren are left and the denser the plants can be planted.
Tall varieties are not very sensitive to a lack of moisture, undersized varieties do not tolerate dry well. The water requirements of a tomato are highest in the flowering phase, the formation of ovaries and an intensive increase in fruit mass.
Excess water is no less harmful, which often leads to yellowing of leaves and root rot. Tomato is sensitive to chlorides, so you shouldn't fertilize the soil with potassium chloride. Better to use potassium sulfate or wood ash.
Little or no fruit set is the plant's reaction to too low or too high temperatures. The reason for the loss of ovaries and flowers can be an excess of nitrogen in the absence of phosphorus and potassium or boron and manganese.
This is more common in low light conditions. Fruit deformation and cracking are associated with fluctuations in soil temperature and moisture. When alternating planting tomatoes and white cabbage on the latter, there will be several times less leaf-eating pests.
7-10 days after planting in the ground, feed the plants with a solution of nitroammofoska (1 tbsp. Spoon per 10 l of water). 3 weeks after planting in the ground, dilute 0.5 kg of mullein and 1 tbsp in 10 liters of water. spoon of nitroammophoska, for each plant - 0.5 liters of solution.
At the beginning of the blooming of the second brush: dilute 0.2 liters of liquid chicken droppings in 10 liters of water, 1 tbsp. spoon of double superphosphate, 1 teaspoon of potassium sulfate. Under the root - 1 liter.
The next top dressing is during the blooming of the third flower brush: dilute 1 tbsp in 10 liters of water. spoon of working solution of sodium humate and 1 tbsp. spoon of nitroammophoska. For 1 m2 - 5 liters. After 12 days: dilute 1 tbsp in 10 liters of water. a spoonful of superphosphate. Top dressing bucket - per 1 m2.
The last feeding is at the end of July. In 10 liters of water, dilute 1 tbsp. spoon of nitroammophoska, superphosphate and potassium sulfate. For 1 plant - 0.5 l. They are fed when the fruits are poured.
To make the fruits sweet: dissolve 1 tbsp in 10 liters of water. a spoonful of table salt and 1 tbsp. a spoonful of potassium sulfate. For 1 plant - 0.5 l. When shedding flowers: dissolve 1 teaspoon of boric acid in 10 liters of water; when spraying, 10 liters of solution are consumed per 10 m2.
When rolling the leaves: dissolve 2 g of boric acid in 10 liters of water, pour 1 liter of solution under each plant. Exclude superphosphate from dressings, and increase the dose of potassium and nitrogen fertilizers to 30 g per 10 liters of water.
From viral diseases: dissolve in 10 liters of water 5 g of potassium permanganate, 10-15 g of boric acid. For each plant - 1 liter. If plants are damaged by viral diseases, you can try the following remedy: sand the copper wire, sharpened on one side, insert it into the plant stem (the length of the wire is 3-4 cm, 2-3 things are inserted into the stem).
It is necessary to monitor the condition of the plants and timely add the necessary nutrients to the soil. If the plants are stunted and pale in color, the tomato plants must be fed with a 1:10 mullein solution.
If the plants "fatten", they intensively increase the green mass to the detriment of fruit formation, exclude nitrogen fertilizers from fertilizing. If the leaves on the lower side acquire a purple hue, the plants lack phosphorus. Excess phosphorus causes yellowing of the leaves.
Plants dry up, and the fruits acquire a variegated color with a lack of potassium. With its excess, matte spots appear on the leaves. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers for tomatoes in a greenhouse are necessary for plants after they have adapted and started growing, until the beginning of flowering.
Then feeding with nitrogen-containing fertilizers will be necessary after the bulk of the fruits have set. Nitrogen stimulates the growth of the green mass of tomatoes, often to the detriment of the setting and development of fruits. That is why nitrogen fertilization should be applied in moderation. Also, for normal root growth and the development of fruits and seeds, phosphorus fertilizers should be applied for tomatoes in a greenhouse. Advice: you do not need to apply fertilizers containing phosphorus at temperatures below + 150C, as it is poorly absorbed and can accumulate in the soil.
Phosphorus is also poorly absorbed by plants growing on acidic soils. In order for fruits to form and develop, tomatoes need potassium, and in fairly large quantities. Potassium is also responsible for the resistance of tomatoes to various adverse factors, such as temperature fluctuations, various diseases (see.
Diseases of tomatoes in a greenhouse: their varieties and how to deal with them). If the plants lack it, then it "signals" by folding the leaves. On sandy loam and sandy soils, you need such fertilizer for tomatoes in the greenhouse as magnesium sulfate, especially for setting, growing and developing fruits.
For most modern greenhouse varieties of tomatoes, it is necessary to do foliar dressing with magnesium sulfate. Leaves of tomatoes with a lack of potassium in the soil According to recent studies, fertilizers for tomatoes in a greenhouse, especially for foliar dressing, must contain boron, copper and manganese. The fact is that copper and boron stimulate both flowering and fruiting, while manganese promotes faster ripening of fruits.
Autumn and spring preparation
In a greenhouse, the soil for tomatoes must be prepared in the fall. If such autumn preparation, then the soil will warm up well and quickly by mid-May.
So, in a few words, how to prepare the soil in greenhouses for tomatoes: During the autumn digging, if the soil is not very fertile, apply organic fertilizers such as humus or rotted manure. As an organic fertilizer, mulch that has served the season can serve. During the fall and winter, it completely decomposes and fertilizes the soil in the greenhouse well.
For 1 m2 on unfertilized and poor soils with high acidity, 600-800 g of dolomite flour, or lime, and 6-8 kg any organic fertilizers such as bird droppings, compost or manure. If the soil is well fertilized, then they are simply dug up.
- During the spring digging of soil in greenhouses from a metal profile on "rich" soils, approximately 3 kg of humus or rotted manure, sawdust per m2. If the soils are "poor", then you need to make the order 7 kg of humus, or manure and 1 glass of peat or wood ash per m2.
Important: if crops were grown in the greenhouse in the previous season, under which a large amount of fertilizer was applied, namely organic, then it is worth abandoning the introduction of humus. It must be remembered that excessive application of organic fertilizers for tomatoes in the greenhouse will promote the formation of a large number of leaves, which will impair the setting and development of fruits.
- Before planting tomato seedlings in the ground, experienced gardeners recommend spilling the soil with a pink solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate). To prepare such a solution, you need to take 1 g of potassium permanganate and dissolve in 10 liters of hot water, the temperature of which should be not lower than 600С... You can also use any prophylactic drug, diluting it in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions on the package. If you have loamy or clayey soils in your greenhouse, then for every 1 m2, just before landing, you need to make another 1 tbsp. a spoonful of potassium sulfate and prestol spoons of any nitrogen fertilizer and a glass of any deoxidizer, for example, dolomite flour or ash. Then carefully dig up the soil.
When and how to feed tomatoes?
In the event that there is not enough potassium in the soil of the greenhouse, then the likelihood that the harvest will be rich is unlikely. If you apply nitrogen-containing fertilizers for tomatoes in a greenhouse, then the situation with potassium starvation can only worsen. In order to avoid various mistakes in the fertilization process, it is best to use a standard feeding scheme during the growth and development of tomatoes.
How to organize feeding and fertilizing tomatoes in a greenhouse
Many books, articles and notes have been written about how to fertilize tomatoes in a greenhouse (see Fertilizing tomatoes in a greenhouse, what fertilizers and when to use). All the many methods describing fertilization can be conventionally divided into three groups:
- using only mineral fertilizers; using only organic fertilizers; a combined method when both organic and mineral fertilizers are applied.
Let us first consider the scheme for applying mineral fertilizers, which takes into account all the needs of tomatoes for different stages development.
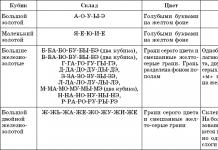
- 20 days after transplanting the seedlings into a greenhouse to a permanent place, you need to carry out the first top dressing, dissolving 1 tbsp of water in 10 liters of water. spoon nitrophoska. The second fertilization is carried out 10 days after the first feeding. For her, dissolve 1 teaspoon of potassium sulfate in 10 liters of water. 12 days after the second feeding, top dressing is carried out with a solution of 2 tbsp. tablespoons of wood ash and 1 tbsp. tablespoons of superphosphate in 10 liters of water.
For each plant, you need to use 1 liter of working solution. There is also another scheme for fertilizing tomatoes in a greenhouse using organic fertilizers. For top dressing, rotted manure or slurry is used, which are diluted in a ratio of 1: 100 (1 kg of manure per 10 liters of water), or any bird droppings. It is taken 200-250 g per 10 liters of water.
All these solutions must be insisted for at least a day, or two or three, after which they are watered at the rate of 2-3 liters per plant. The first feeding with a smaller amount of solution can be carried out immediately after planting the seedlings in the greenhouse. In the future, feeding is carried out regularly, every 10-15 days. After the tomato plants are fed, the soil under them must be mulched with treated sawdust. To do this, dissolve 200 g of urea in a bucket.
This solution is poured into three buckets of sawdust, preferably fresh. Mulch interferes with the evaporation of moisture from the soil, and also inhibits and inhibits the development of weeds. The soil covered with mulch retains heat well at night, saving the plant roots from hypothermia.
Foliar dressing
An important role in the growth and development of plants is played by foliar dressing, during which leaves and stems are sprayed with a weak nutrient solution of fertilizers, spraying it. use foliar dressing dissolved in 10 liters of water 1 teaspoon of superphosphate.In the event that the flowers of tomatoes crumble due to the heat, since pollination has not occurred, you can carry out foliar dressing with a solution of boric acid, taking 5 g (1 tsp) for 10 liters of water, or use special preparations. Foliar dressing is carried out once a month, in the evening, or on a cloudy, not sunny day.
Tomatoes are a rather demanding vegetable crop. This plant actively takes nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus and other minerals from the soil.
When seeds germinate, phosphorus is necessary to enhance the growth of plant roots, it promotes earlier flowering, ripening of tomatoes, increases productivity, sugar content and dry matter in fruits. Potassium is necessary for normal fruiting, and nitrogen in ammonia form - for the rapid ripening of fruits.
During budding, flowering and fruit formation, plants need nitrogen-potassium nutrition. If there is a lack of nitrogen or potassium, then plant growth is impaired, and this leads to a decrease in fruit and a decrease in yield. Tomatoes have high nutritional, taste and dietary qualities. An excess of nitrogen negatively affects the growth of tomatoes.
It delays fruiting, there is a high probability of plant diseases. Thus, in order to get a good harvest of tomatoes, you need to create all the necessary conditions. For this, it is worth planting tomatoes in soil prepared in advance and fed with mineral organic matter. The soil enriched with organic materials and biofertilizers is the key to a rich tomato harvest.
Recently, summer residents have been trying to abandon chemical, artificial fertilizers, preferring natural feeding. How to fertilize tomatoes, everyone chooses for himself, since there are many options.
Fertilization methods for tomatoes
Yeast is one of the best plant growth stimulants. How to feed tomatoes? The most common feeding methods are: bird droppings, ash, yeast, and others. Let's take a closer look at each of them. Yeast.
They are the best stimulant for plant growth. Recipe for making yeast fertilizer: 20 grams of yeast is diluted in 10 liters of water, left for 24 hours, the resulting solution is fertilized with plants. "Rostmoment" is a ready-made fertilizer based on yeast. It is also suitable for planting tomatoes.
This tool is the best biostimulant for the growth and further development of plants. Using this fertilizer, you can be sure of its quality. "Rostmoment" is suitable for fertilizing tomatoes that grow in pots. Ash is an excellent source of potassium and phosphorus, magnesium, sulfur, zinc and other trace elements.
Ash is added before planting seedlings in each hole. To do this, take 3 tablespoons of ash and mix it with the soil.
To enrich the soil requires 3 glasses of ash per 1 square meter. The key role in the growth of fruits is played by fertilizing the soil when planting tomatoes. Chicken droppings are a fairly valuable fertilizer. His chemical composition ahead of manure, and nutrients are kept in a rather mild form.
Feeding tomatoes with chicken manure has a prolonged effect, even after two or three years after fertilization, the soil remains nourished and has a positive effect on plants. Feeding from poultry droppings is easy to prepare.
The concentration of the solution is prepared depending on the stage at which the tomatoes grow. You can prepare the following composition: 100 g of fresh poultry droppings are added to 10 liters of water, infused for 24 hours and the plants are watered. Feeding with litter with litter is applied during soil cultivation, in the ratio of 6 kg of fertilizer per 1 sq. m. Chicken manure is not a universal fertilizer, therefore, in addition to it, it is necessary to apply other fertilizing to the soil, such as ammonium nitrate, superphosphate. For a good result, it is not necessary to use expensive fertilizers, the main thing is not to exceed the dosage and put them into the soil on time. Nitrofoska and others complex fertilizers add 0.5 teaspoon per 1 liter of water for tomato seedlings. Planting tomatoes begins with the use of superphosphate, 1 tablespoon per well. 5 days after planting, you can water the tomatoes with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
Stages of growing tomatoes in the garden
- in the fall, when digging up the soil, 4 kg are applied per 1 square m of humus or compost; in the spring, it is necessary to fill the soil with mineral fertilizers: 80 g per 1 square m of superphosphate and 20 g per 1 square m of potassium chloride; after planting the seedlings, the first top dressing is planned in 10-15 days , and the second - already at the beginning of fruiting; so that the fruits set quickly, use a 0.5% superphosphate solution or boric acid solution. The solution, which has settled, is drained and sprayed with tomatoes.
Thus, fertilizing the soil when planting tomatoes plays a key role in the growth of future fruits. Today, there are a large number of different fertilizers that can improve the quality of the fruits, the main thing is to follow the exact instructions for the dosage and the time of their introduction into the soil. With the help of top dressing, you can grow an excellent crop of tomatoes on the soil, which is not particularly fertile.
Top dressing of tomatoes should be carried out in several stages. When preparing a site for planting tomatoes in early spring, digging up the ground, you need to add humus at the rate of 16 kg per square meter.
At the earliest stages, when planting seedlings in the ground and until ovaries appear, a pre-prepared mixture is laid in each hole. It is prepared from potassium chloride, wood ash and superphosphate and is introduced into the soil two weeks before planting. soil for seedlings can also be used urea. It should be borne in mind that an overdose of nitrogen fertilizers can lead to the fact that the stems, leaves, shoots will actively grow, and the ovaries may not form at all. The risk of fungal infections of the plant increases. From the middle of the growing season, nitrogen fertilizers are no longer applied at all.
Feeding scheme
Regular feeding of tomatoes is necessary for two reasons:
- showers and melt water thoroughly wash out potassium and nitrogen from the soil; all types of tomatoes are intensive crops and require a lot of minerals.
As the tomatoes grow and mature, they should be fed according to the following scheme:
- after 2-3 weeks after disembarkation. Further, temporarily do not feed the culture, waiting for the strengthening of the set fruits; resume fertilization after the 2nd flower cluster appears; after the 3rd flower cluster blooms; after 12 days. The main emphasis in top dressing is on the root, since more fertilizers are always applied through the soil.
Selection of finished fertilizer
There are a large number of fertilizers on sale, which must be selected taking into account the composition of the soil on the site. Tomatoes are grown on soils of various types, but the most suitable is loose, fertile, capable of warming up well. Of the complex mineral fertilizers, Agricola, Effekton, Kemiru-Universal are recommended. Of the concentrated fertilizers, nitroammofoska is often used, produced in granules, each of which contains equal amounts of phosphorus, nitrogen and potassium.
The distribution of minerals in the soil is uniform. Nitroammofosku is bred in the amount of 2 matchboxes of fertilizer per bucket of water. Diammophos is also used.
Many gardeners believe that biohumus is considered the most effective means of feeding, the use of which in the amount of 1 glass for each bush of a plant at any stage of growth can increase the yield by 30%.
Self-made fertilizers
Often, gardeners, using available tools at hand, prepare top dressing themselves. Many of the nutrients that tomatoes need to grow are found in regular brewer's yeast. Fertilizer is prepared in two ways: 1.
Make a solution from a package of instant yeast, 2 tbsp. l. sugar and a little warm water. After about 2 hours, the infusion is mixed with a bucket of water. Yeast fertilizer in a volume of 0.5 liters is added to the watering can. The effect is noticeable after a few days. 2.
Fertilizer is also prepared from raw yeast. A jar with a volume of 3 liters is filled with brown bread by 2/3, filled with warm water with fresh yeast dissolved in it (100 g). Leave to ferment in a warm place for a period of 3 days.
The filtered solution is mixed with water for irrigation in a ratio of 1: 10.3. To eliminate the calcium deficiency in the soil, eggshells containing calcium and magnesium are used.
To enrich the earth with these substances, it is optimal to use an aqueous infusion on crushed shells. It is necessary to withstand the solution under the lid for 2 weeks, the degree of readiness is determined by the appearance of a pungent odor.
The infusion is added to the water for irrigating tomatoes in a ratio of 1 to 3. Effective fertilizer is cow dung. You can spread it out in the beds, and when water gets on the fertilizer, the tomatoes will receive regular feeding.
For a more effective effect, manure is mixed with peat and the soil is mulched with this composition. When small fruits appear, many gardeners often use diluted chicken manure, sometimes with the addition of urea. This must be done very carefully, otherwise there is a risk of burning the plant roots. To do this, it is necessary to water the solution at some distance from the plants, 15 centimeters. Gardeners also use potassium permanganate in the form of a weak solution, which is both a fertilizer and a protective agent against diseases.
Foliar feeding of plants
Additional foliar dressing is used to stimulate the defenses of the plant. Good results are obtained by spraying with New Ideal once a week.
During flowering, successful foliar feeding is carried out using a solution of boric acid, diluted in a ratio of 1 g per liter of water. 2-3 such sprays every 10 days help to improve fruit set. It is not surprising that tomatoes require such careful care, because the ready-to-eat vegetable is very rich in a variety of biologically active substances and has a whole range of useful properties. Tomatoes are tasty not only raw. , but also in salted, pickled, in the form of pastes and juices.
Tomatoes are powerful antioxidants that can prevent cell aging. This vegetable reduces the risk of cancer. Tomato cleanses the walls of blood vessels, preventing strokes, heart attacks, atherosclerosis.
Used for varicose veins. The iron content surpasses chicken meat, milk and fish.
- Login or register to post comments
More articles about the cottage and the garden
Tomatoes are a rather demanding vegetable crop. This plant actively takes nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus and other minerals from the soil.
When seeds germinate, phosphorus is necessary to enhance the growth of plant roots, it promotes earlier flowering, ripening of tomatoes, increases productivity, sugar content and dry matter in fruits. Potassium is necessary for normal fruiting, and nitrogen in ammonia form - for the rapid ripening of fruits.
During budding, flowering and fruit formation, plants need nitrogen-potassium nutrition. If there is a lack of nitrogen or potassium, then plant growth is impaired, and this leads to a decrease in fruit and a decrease in yield. Tomatoes have high nutritional, taste and dietary qualities. An excess of nitrogen negatively affects the growth of tomatoes.
It delays fruiting, there is a high probability of plant diseases. Thus, in order to get a good harvest of tomatoes, you need to create all the necessary conditions. For this, it is worth planting tomatoes in soil prepared in advance and fed with mineral organic matter. The soil enriched with organic materials and biofertilizers is the key to a rich tomato harvest.
Recently, summer residents have been trying to abandon chemical, artificial fertilizers, preferring natural feeding. How to fertilize tomatoes, everyone chooses for himself, since there are many options.
Fertilization methods for tomatoes
Yeast is one of the best plant growth stimulants. How to feed tomatoes? The most common feeding methods are: bird droppings, ash, yeast, and others. Let's take a closer look at each of them. Yeast.
They are the best stimulant for plant growth. Recipe for making yeast fertilizer: 20 grams of yeast is diluted in 10 liters of water, left for 24 hours, the resulting solution is fertilized with plants. "Rostmoment" is a ready-made fertilizer based on yeast. It is also suitable for planting tomatoes.
This tool is the best biostimulant for the growth and further development of plants. Using this fertilizer, you can be sure of its quality. "Rostmoment" is suitable for fertilizing tomatoes that grow in pots. Ash is an excellent source of potassium and phosphorus, magnesium, sulfur, zinc and other trace elements.
Ash is added before planting seedlings in each hole. To do this, take 3 tablespoons of ash and mix it with the soil.
To enrich the soil requires 3 glasses of ash per 1 square meter. The key role in the growth of fruits is played by fertilizing the soil when planting tomatoes. Chicken droppings are a fairly valuable fertilizer. Its chemical composition is ahead of manure, and nutrients are contained in a fairly light form.
Feeding tomatoes with chicken manure has a prolonged effect, even after two or three years after fertilization, the soil remains nourished and has a positive effect on plants. Feeding from poultry droppings is easy to prepare.
The concentration of the solution is prepared depending on the stage at which the tomatoes grow. You can prepare the following composition: 100 g of fresh poultry droppings are added to 10 liters of water, infused for 24 hours and the plants are watered. Feeding with litter with litter is applied during soil cultivation, in the ratio of 6 kg of fertilizer per 1 sq. m. Chicken manure is not a universal fertilizer, so it is necessary, in addition to it, to make other top dressing, such as ammonium nitrate, superphosphate, for a good result. Nitrophoska and other complex fertilizers are applied for tomato seedlings, 0.5 teaspoon per 1 liter of water. Planting tomatoes begins with the use of superphosphate, 1 tablespoon per well. 5 days after planting, you can water the tomatoes with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
Stages of growing tomatoes in the garden
- in the fall, when digging up the soil, 4 kg are applied per 1 square m of humus or compost; in the spring, it is necessary to fill the soil with mineral fertilizers: 80 g per 1 square m of superphosphate and 20 g per 1 square m of potassium chloride; after planting the seedlings, the first top dressing is planned in 10-15 days , and the second - already at the beginning of fruiting; so that the fruits set quickly, use a 0.5% superphosphate solution or boric acid solution. The solution, which has settled, is drained and sprayed with tomatoes.
Thus, fertilizing the soil when planting tomatoes plays a key role in the growth of future fruits. Today, there are a large number of different fertilizers that can improve the quality of the fruits, the main thing is to follow the exact instructions for the dosage and the time of their introduction into the soil. With the help of top dressing, you can grow an excellent crop of tomatoes on the soil, which is not particularly fertile.
Growing tomatoes in the open field
Article posted: Serg (74)
Sowing and caring for seedlings
Seeds of tomato varieties intended for cultivation in open ground, sow directly into nutrient pots, i.e. without picking. This is explained by the fact that usually for sowing seeds of open ground varieties and folk selection are used, which are not sufficiently resistant to viral diseases, especially to the tobacco mosaic virus.
When transplanting into pots, seedlings often break off small roots and infection can penetrate into the wounds of healthy plants. In addition, undersized varieties do not outgrow and remain compact until the end of planting in a permanent place, i.e. low (15-18 cm). Sowing of seeds is carried out from 1 to 25 March in cups or pots 10x10 cm in size.
They are filled with soil mixture and watered with a warm (35 -40 ° C) solution: 1 tablespoon of universal liquid fertilizer is diluted in 10 liters of water. Then, in each cup, in the center, two holes are made 1 cm deep, 1 seed is placed in each and covered with a soil mixture.
Such sowing without picking is carried out only for low-growing varieties for open ground in order to protect the seedlings from viral diseases. The sown pots are placed in a box, placed in a warm (22 - 25 ° C) bright place and carefully monitor the seedlings, which should appear after 6 - 7 days. As soon as the seedlings appear, the pots are moved one by one to a bright sunny windowsill with a temperature of 14-16 ° C during the day and 12 -14 ° C at night.
When lowering the temperature (opening the vents and window frames), it is necessary to ensure that the seedlings do not stand in a draft. This cool daytime setting will prevent the seedlings from pulling out and help the roots develop better.
Then the temperature is gradually raised during the day to 18-22 ° C, and at night to 15-17 ° C. 5-6 days after germination, the weaker plant is removed from the pot, and the strong one is left. Care for seedlings - an extremely crucial moment.
Before planting in the garden, the seedlings grow for 55 - 60 days. Watered with water in moderation, at the beginning of growth, once a week, 0.5 cups per plant. When 3 - 5 true leaves are formed, water a glass per plant. Every 10 - 12 days, the seedlings are fed.
The first time - 20 days after germination with a solution of nitrophoska (1 tablespoon is diluted in 10 liters of water), spending 0.5 cups for 2 plants. The second time is fed 10 days after the first feeding.
In 10 liters of water, 2 tablespoons of organo-mineral fertilizer are diluted, spending 1 glass of solution per plant. The third feeding (last) is carried out a week before planting seedlings in open ground.
In 10 liters of water, 2 tablespoons of superphosphate are diluted (for three days before feeding, superphosphate is infused in warm water), everything is stirred well and the seedlings are watered. It is necessary to constantly temper the seedlings at a low temperature. Starting from April, seedlings can be taken out on a balcony, veranda or left near open window frames at an air temperature of at least 10 ° C.
The first hardening for three days is carried out in the shade, since it is necessary to gradually accustom the plant to full outdoor lighting. If the seedlings are taken out on the first day in sunny weather, burns may appear from direct sunlight. In the future, the seedlings are not shaded. Transhipment of tomato seedlings. © Steve Albert When hardening the seedlings, make sure that the soil in the pots is moist, not dry, otherwise wilting and yellowing of the leaves are possible. ...
Planting seedlings in a permanent place
In the open field, a sunny place, protected from cold winds, is allocated for planting tomatoes. Unsuitable for tomatoes are low, damp areas, with a close standing of groundwater, which creates unfavorable conditions for the root system of plants.
The best precursors for tomatoes are legumes, root crops, greens.To avoid late blight, tomatoes should not be planted after potatoes and tomatoes. Preferred soils are loamy with the addition of organic and mineral fertilizers. Prepare the soil in advance at the place of planting tomatoes. © AndrewTomato beds are prepared 5 - 6 days before planting. Before digging up the soil, it must be treated with a hot (70 - 80 ° C) solution of copper sulfate or copper oxychloride.
In 10 liters of water, dilute 1 tablespoon of one or the other. The solution consumption is up to 1 - 1.5 liters per 1 m3. After that, organic and mineral fertilizers are poured onto clay and loamy soils - 3-4 kg of manure, peat and old sawdust, 1 tablespoon of superphosphate, potassium sulfate or 1 a glass of wood ash per 1 m2.
Then the bed is dug to a depth of 25 - 30 cm, leveled, watered with warm water (40 -50 ° C). They make holes, water them before planting the seedlings with an antibacterial drug. Plant the seedlings in a permanent place in the first and second decades of May.
Landing is done in cloudy weather in the morning, in sunny weather in the afternoon. At the time of planting, the seedlings should be fresh, even a slight wilting of the plants retards their growth, leads to partial loss of the very first flowers and the loss of an early harvest. Tomatoes are planted in the first and second decades of May. © Carla Seedlings are planted vertically, only the soil pot is deepened into the soil.
The stem remains uncovered with soil, and only after 15 days the plants are spud up to a stem height of up to 12 cm. Seedlings are planted in 2 rows. For medium-sized varieties (60 - 70 cm), the row spacing should be 50 cm, and the distance in the rows between plants should be 40 - 45 cm.
For low-growing (standard) varieties, the row spacing is made 40 -50 cm wide, and the distance in the row between plants is 40 cm.Immediately put pegs 50 cm high for low-growing plants and 80 cm for medium-sized plants, but the greatest effect is achieved when the plant is tied to arcs and to the stretched wire with the help of synthetic twine to a height of 1 - 1.2 m. As a result, the plant is better illuminated, ventilated and less sick.
Until the plants take root, they are not watered for 10 days after planting. After planting, if light frosts are expected, tomato plants need additional shelter, especially at night. After planting the seedlings, the bed is covered with a transparent film until warm weather (until June 5-10), then the film is not removed, but holes with a diameter of 10-12 cm are made on it throughout the film and left for the whole summer. As a result, an early harvest is obtained, the plants are free of late blight infection. If necessary, the seedlings can be tied up. © Andrew
Formation of tomato plants
The plants are shaped so that they can give 5 to 6 fruit clusters. When the plants form into one stem, all lateral shoots (stepchildren) formed in the axil of each leaf are removed on the main stem, and 5-6 fruit brushes are left on the main shoot.
A pinch is made over the last (upper) flower brush, leaving 2 - 3 leaves on it. In the case of a two-stemmed form, a stepson is left growing under the first flower brush. At the same time, 4 fruit brushes are left on the main stem and pinch the top, leaving 3 leaves, and 3 fruit brushes are left on the stepson and also pinch, leaving 2 - 3 leaves. © Andrew During the formation of a three-stemmed form, 2 - 3 fruit clusters are left on the main stem.
On the two lower stepchildren, 2 fruit brushes are left and pinching is done so that there are 2 - 3 leaves above the upper fruit brushes. In pinched and pinched plants, nutrients go to the formation and pouring of fruits, from which their size increases and ripening occurs earlier. On a formed bush, in addition to five to six fruit clusters, there should be at least 30 to 35 leaves.
First root dressing done 3 weeks after planting: 1 tablespoon of universal liquid fertilizer and 1 tablespoon of nitrophoska are diluted in 10 liters of water, consumption is 0.5 liters of solution for each plant. At the beginning of the blooming of the second flower brush, second root dressing : in 10 liters of water, dilute 1 tablespoon of universal liquid fertilizer, 1 tablespoon of superphosphate, 1 teaspoon of potassium sulfate or potassium chloride or 10 liters of water take 1 tablespoon of organo-mineral fertilizer, consumption - 1 liter of solution per plant.
Third root dressing done during the blooming of the third flower brush: in 10 liters of water, dilute 1 tablespoon of universal liquid fertilizer and nitrophoska, consumption - 5 liters per 1 m2. Fourth feeding carried out 12 days after the third: 1 tablespoon of superphosphate is diluted in 10 liters of water (consumption is 10 liters per 1 m?) or universal liquid fertilizer is used (1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water), consumption is 5 liters of solution per 1 m? Sometimes the composition of top dressing depends not only on the phase of plant development, but also on the weather: in cloudy weather, increase the dose of potassium sulfate to 1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water, and in the sun - a dose of urea of 2 tablespoons for the same amount of water, spending at this is 5 liters of solution per 1 m2. Weakly leafy and lagging plants need to be made foliar feeding, that is, sprinkle the leaves with the following solution: 1 tablespoon of urea is diluted in 10 liters of water. The best temperature for normal growth and fruiting of tomatoes is 20 - 25 ° C at night. Water the plants abundantly, in sunny weather after 6 days, in cloudy after 7-8 days at the rate of 10 -20 liters per 1 m2, depending on the air temperature.
After watering, the bed is sprinkled with sifted peat or compost with a layer of 1 - 2 cm. This does not form a crust on top, moisture remains in the soil and evaporation does not occur, which is harmful to the plant, especially in the flowering phase.
Excess moisture with a lack of heat leads to the death of the root system. Tomato in the open field. © Gina Outdoor watering is best done in the afternoon to avoid unnecessary loss of water due to evaporation. Flower shedding is often seen. This is a sign of a lack of moisture or a drop in temperature.
Plants need to be sprayed with a boron solution (1 teaspoon per 10 liters of water), spending 1 liter per 1 m2. Watering times can be determined by appearance plants - changing the color of the leaves to dark green and drooping them on hot days. In such cases, the plants are watered in 2 - 3 doses after a short period of time to gradually moisten the soil. In order for the fertilizers applied with irrigation to penetrate deeper, the soil in the row spacing is pierced with a pitchfork to the full depth of the horns.
If the soil on the site is wet, as well as a lot of atmospheric precipitation, irrigation is not carried out (fertilizers are applied in dry form). It is especially useful to use fertilizers such as "Breadwinner", "Fertility", "Bogatyr", "Signor Tomato" (1 tea spoon under the plant). July and August - the time of ripening and harvesting. In caring for tomatoes, the main thing is to accelerate the ripening of the set fruits and protect them from decay.
It is necessary to continue to remove the newly appearing stepchildren, excess leaves, pinch the tops of all fruit-bearing bushes, remove the flower brushes on which the fruits no longer have time to form. In low-growing varieties, the brushes with fruits should be turned towards the sun.
It is also not bad during this period (from August 15), in addition to all the main dressings, additionally feed the tomatoes with the following solution: 1 teaspoon of urea, superphosphate and potassium sulfate or 2 tablespoons of nitrophosphate is diluted in 10 liters of water, spending 0.5 liters of solution per plant. The period from setting to reddening of fruits in early maturing varieties lasts 40 - 50 days. If overripe fruits are left on the plants, then the total yield decreases, and vice versa, if unripe (brown) fruits are regularly harvested, then the total yield increases much.
How to grow TOMATOES in the open field. Top dressing. Mulching.
Red fruits can be stored at a temperature of 5 - 10 ° C for 40 - 50 days, while the air humidity should be at least 80%. Fruits of a tomato ripening on a branch. © gardenfrisk beginning to turn white, and lay them for ripening. This simple technique speeds up the filling of the green fruits remaining on the bush.
Before laying for ripening, the fruits must be warmed up in order to protect them from blackening. This is done as follows: first, the tomatoes are dipped in hot water (60 - 65 ° C) for 2 minutes, then in cold water, then wiped with a soft cloth, then laid.
OCTYABRINA GANICHKINA (vegetable garden)
To speed up the maturation process, it is carried out indoors at a temperature of 18 -20 ° C. The fruits are placed in small boxes in 2 - 3 layers, removing the pedicels. A little red tomatoes are added to the boxes.
Tomatoes are perhaps the most popular vegetable crop. Despite this, many gardeners do not know exactly how to properly care for them and how to properly fertilize them during and after planting. As a result, the harvest is not as rich as we would like. Although tomatoes are quite demanding, there is really nothing difficult in caring for them. Next, we will consider the best way to fertilize tomatoes after planting and how to do it correctly.

The most important for tomatoes, both in the open field and in the greenhouse, are nitrogen, potassium, magnesium, as well as manganese, copper, boron and phosphorus. Nitrogen, for example, stimulates plant growth, and they need to fertilize tomatoes after planting in the ground until the flowers appear. It should be used more moderately during the period of fruit formation. For the good development of the root system and fruits, phosphorus is used, and in order for the plants to grow quickly and get sick less, they need a large amount of potassium. If the tomatoes miss it, the leaves will begin to curl up into a tube.


Plants that grow in sandy soils often lack magnesium, which ensures rapid growth and fruit formation. In this case, they need to be fed with magnesium sulfate. According to experts, foliar dressing of homemade tomatoes in a greenhouse must necessarily contain manganese, as well as copper and boron. It is these beneficial substances that stimulate both flowering and the formation of fruits, as well as their rapid ripening.
Preparatory work
In the greenhouse, the soil for planting tomatoes must be prepared in the fall. It was at this time that the soil must be dug up and organic fertilizers applied to it. They will not only nourish the earth, but also warm it during frosts. In winter, the soil can be fertilized with chicken droppings or manure, but in the spring, after digging, the soil must be fed with ash and rotted manure. Before planting homemade tomatoes in the ground, it is recommended to pour it with a solution of potassium permanganate. To do this, dissolve 1 gram of the solution in a bucket of hot water. If there are clay or other similar soils on the backyard, you also need to use potassium sulfate in addition.
When and what to feed?


There are several methods for fertilizing tomatoes at home:
with the use of mineral dressings;
using organic dressings;
combined.
There is also a standard system for fertilizing tomatoes in the greenhouse and outdoors. If there is no experience in such a matter, it is recommended to use it:
the first time to properly fertilize tomato seedlings about 3 weeks after planting with a tablespoon of nitrophoska diluted in a bucket of water;
the second fertilization should be carried out after 10 days with a teaspoon of potassium sulfate diluted in a bucket of water;
at the same time, plants can be treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate;
after about a week, tomatoes are treated with saltpeter at the rate of 15 grams per bucket of water;
after another week, the plants are fed with ash and superphosphate, diluted in the same amount of water.
It is worth noting that during feeding, both during planting and after planting, about 1 liter of fertilizer must be poured under each plant.
If you plan to fertilize tomatoes only with organic substances, the feeding system will be slightly different. In this case, feeding is carried out either with chicken droppings or manure, of which very little need to be taken in a bucket of water. The first feeding should take place directly at planting, and the subsequent ones - every 10 days. After the tomatoes are fertilized, the soil near them must be mulched (see photo). For this, several buckets of fresh sawdust are poured with urea diluted in water, which are subsequently placed on the ground. This allows not only to maintain optimal moisture content, but also inhibits the development of weeds.
Yeast feeding


After it became clear how often to fertilize tomatoes in the greenhouse, consider another popular fertilizing option - with yeast. Gardeners began to fertilize tomatoes with yeast a long time ago. They are used for good rooting of seedlings, as well as for abundant flowering. At home, you can use the following solution, which for young plants must be poured in half a liter, and for adults - up to 2 liters. So, to prepare the mixture you will need:
10 grams of dry yeast;
half a liter of ash;
half a liter of chicken manure;
5 tablespoons of sugar;
a bucket of water.
Foliar dressing
Fertilizing tomatoes correctly when planting and after planting also means foliar feeding. They are most needed during the period of fruit ripening. At this time, tomatoes are most often sprayed with a teaspoon of superphosphate diluted in a bucket of water. In the open field, it happens that due to the intense heat, flowers begin to crumble. In this case, gardeners recommend spraying the plants with a solution of boric acid, and this should be done exclusively on cloudy days. More detailed information on fertilizing tomatoes can be found in the video presented.
Top dressing of tomatoes should be carried out in several stages. When preparing a site for planting tomatoes in early spring, digging up the ground, you need to add humus at the rate of 16 kg per square meter.
At the earliest stages, when planting seedlings in the ground and until ovaries appear, a pre-prepared mixture is laid in each hole. It is prepared from potassium chloride, wood ash and superphosphate and is introduced into the soil two weeks before planting. soil for seedlings can also be used urea. It should be borne in mind that an overdose of nitrogen fertilizers can lead to the fact that the stems, leaves, shoots will actively grow, and the ovaries may not form at all. The risk of fungal infections of the plant increases. From the middle of the growing season, nitrogen fertilizers are no longer applied at all.
Feeding scheme
Regular feeding of tomatoes is necessary for two reasons:
- showers and melt water thoroughly wash out potassium and nitrogen from the soil; all types of tomatoes are intensive crops and require a lot of minerals.
As the tomatoes grow and mature, they should be fed according to the following scheme:
- after 2-3 weeks after disembarkation. Further, temporarily do not feed the culture, waiting for the strengthening of the set fruits; resume fertilization after the 2nd flower cluster appears; after the 3rd flower cluster blooms; after 12 days. The main emphasis in top dressing is on the root, since more fertilizers are always applied through the soil.
Selection of finished fertilizer
There are a large number of fertilizers on sale, which must be selected taking into account the composition of the soil on the site. Tomatoes are grown on soils of various types, but the most suitable is loose, fertile, capable of warming up well. Of the complex mineral fertilizers, Agricola, Effekton, Kemiru-Universal are recommended. Of the concentrated fertilizers, nitroammofoska is often used, produced in granules, each of which contains equal amounts of phosphorus, nitrogen and potassium.
The distribution of minerals in the soil is uniform. Nitroammofosku is bred in the amount of 2 matchboxes of fertilizer per bucket of water. Diammophos is also used.
Many gardeners believe that biohumus is considered the most effective means of feeding, the use of which in the amount of 1 glass for each bush of a plant at any stage of growth can increase the yield by 30%.
Self-made fertilizers
Often, gardeners, using available tools at hand, prepare top dressing themselves. Many of the nutrients that tomatoes need to grow are found in regular brewer's yeast. Fertilizer is prepared in two ways: 1.
Make a solution from a package of instant yeast, 2 tbsp. l. sugar and a little warm water. After about 2 hours, the infusion is mixed with a bucket of water. Yeast fertilizer in a volume of 0.5 liters is added to the watering can. The effect is noticeable after a few days. 2.
Fertilizer is also prepared from raw yeast. A jar with a volume of 3 liters is filled with brown bread by 2/3, filled with warm water with fresh yeast dissolved in it (100 g). Leave to ferment in a warm place for a period of 3 days.
The filtered solution is mixed with water for irrigation in a ratio of 1: 10.3. To eliminate the calcium deficiency in the soil, eggshells containing calcium and magnesium are used.
To enrich the earth with these substances, it is optimal to use an aqueous infusion on crushed shells. It is necessary to withstand the solution under the lid for 2 weeks, the degree of readiness is determined by the appearance of a pungent odor.
The infusion is added to the water for irrigating tomatoes in a ratio of 1 to 3. Effective fertilizer is cow dung. You can spread it out in the beds, and when water gets on the fertilizer, the tomatoes will receive regular feeding.
For a more effective effect, manure is mixed with peat and the soil is mulched with this composition. When small fruits appear, many gardeners often use diluted chicken manure, sometimes with the addition of urea. This must be done very carefully, otherwise there is a risk of burning the plant roots. To do this, it is necessary to water the solution at some distance from the plants, 15 centimeters. Gardeners also use potassium permanganate in the form of a weak solution, which is both a fertilizer and a protective agent against diseases.
Foliar feeding of plants
Additional foliar dressing is used to stimulate the defenses of the plant. Good results are obtained by spraying with New Ideal once a week.
During flowering, successful foliar feeding is carried out using a solution of boric acid, diluted in a ratio of 1 g per liter of water. 2-3 such sprays every 10 days help to improve fruit set. It is not surprising that tomatoes require such careful care, because the ready-to-eat vegetable is very rich in a variety of biologically active substances and has a whole range of useful properties. Tomatoes are tasty not only raw. , but also in salted, pickled, in the form of pastes and juices.
Tomatoes are powerful antioxidants that can prevent cell aging. This vegetable reduces the risk of cancer. Tomato cleanses the walls of blood vessels, preventing strokes, heart attacks, atherosclerosis.
Used for varicose veins. The iron content surpasses chicken meat, milk and fish.
- Login or register to post comments
More articles about the cottage and the garden
Planting tomato seedlings in the ground and care
To get a good tomato harvest, you need not only to grow tomato seedlings, but also to plant the plants in the ground in time. Seedlings of tomatoes are planted in the ground at different times, depending on weather conditions.
In the open- no later than May 20-25; in a closed- from 1 to 25 May. With the threat of recurrent frosts, the planted tomato seedlings take cover. In the greenhouse, you can make a second film cover.
The planted seedlings should be watered abundantly. You can mulch the ground with peat or humus. After a week, you need to give tomato seedlings first feeding with fertilizers: a matchbox of ammonium nitrate or urea in a bucket of water.
Seedlings must be planted in the ground at a distance of 40-60 cm from each other, depending on the variety. Stunted - 40 cm, medium-tall and tall - 60 cm from each other.
Care of tomato seedlings
Tomato seedlings need: systematic loosening, feeding and watering. During budding, it is advisable to sprinkle the plants with the "Ovary" solution. Before flowering, plants should be watered abundantly with warm water at the rate of 3-4 liters per bush.
At the same time, it is necessary to bring wood ash under each bush, loosen the earth and water abundantly. 3 weeks after planting, you need to spray the plant with a solution of copper sulfate (20 g per 10 l of water) or any means for the prevention of late blight. The second treatment in the same concentration, with copper sulfate - 2 weeks after the first.
As soon as the tomatoes bloom, foliar feeding is necessary (50 g of superphosphate per 10 liters of water). Throughout the growing season, tomatoes are watered abundantly with warm water; with an interval of 2-3 weeks, feed (under the root) infusion of mullein with ash.
When loosening, the tomato bushes spud. When growing tall tomatoes, the installation of plant supports is required. In order for the peduncles to be pollinated in time, active ventilation must be applied in the greenhouse - tomatoes are in great need of a draft.
Even in cool weather, when the air temperature drops to (+8 ... + 10) ° С, it is necessary to open the vents for a day. In calm weather, pollination is carried out by lightly tapping on the backwaters. It has been noticed that shedding of flowers in tomatoes can occur due to high humidity and high air temperature.
Formation of tomato bushes and pinching
It is very important to form tomato bushes correctly. Tall plants formed into one stem are better illuminated and ventilated.
To do this, it is necessary to carry out pinching, that is, remove the side shoots in the leaf axils at the initial stage of development 3-4 cm, leaving a "stump" of 0.5 cm. The stepson is not formed at this place.
At the end of August or at the beginning of September, it is advisable to pinch the tops of the plants, this will give the timely ripening of the fruits remaining on the plants. Liana varieties of tomatoes, the height of which reaches 5-6 m, are planted in the ground after 1-1.5 m, pinched, but not pinched ... Thanks to careful care, tomato plants develop effectively, and fruiting can continue until the end of September, and if the weather is favorable, until mid-October. Watch our video on the correct pinching of tomatoes.
Why tomatoes "fatten"
They say that tomatoes are fattening when stepchildren, large leaves grow rapidly in plants, the stem thickens, and the fruits themselves grow very slowly and do not have time to ripen. This usually happens if, when planting under plants, gardeners brought in too much manure instead of humus. You can cope with explosive growth as follows:
- exclude nitrogen from top dressing and focus on phosphorus-potassium dressing (40 g of superphosphate and potassium sulfate per 10 liters of water, feeding consumption 1-2 liters of solution per plant) feed “fattening” tomatoes with ash 2-3 tablespoons of ash per bush.
Let's list the most significant fertilizers for this crop:
- potassium; phosphorus; nitrogen.
Phosphorus is of great importance for the formation of the root system and fruit setting. If the plants do not receive this substance, then the tomatoes poorly assimilate nitrogen and other essential nutrients.
Symptoms of phosphorus starvation in tomatoes are the appearance of red-purple spots on the underside of the leaves, as well as curling of the leaves along the main vein, and the ripening of fruits also slows down. When thinking about how to feed tomatoes in a greenhouse, you should remember about the high consumption of this crop of potassium. This mineral contributes to the formation of stems, as well as the assimilation and processing of carbon dioxide.
In the case of a lack of potassium, the lower leaves accumulate ammoniacal nitrogen, as a result of which they first wither, and then die off. In the photo you can see how the result of potassium starvation of tomatoes on the leaves manifests itself: Let's take a closer look at what and how to feed tomatoes in a greenhouse.
When and what feeding is carried out
The very first feeding can be done during the process of planting tomato seedlings in a greenhouse. Compost or humus is placed in the wells prepared in advance and ash is poured.
Compost, like humus, contains many minerals, and ash has a high content of various micro and macro elements that are so necessary for a tomato for normal development, growth, flowering, setting and formation and fruit. , causes "hot" discussions among gardeners. Part of the "gardening" community is of the opinion that the question of what to feed tomatoes in the greenhouse immediately after planting is generally not worth it. Such gardeners believe that the first feeding of greenhouse tomatoes should be carried out no earlier than two weeks after transplanting plants to a permanent place. Other gardeners are of the opinion that for a "injured" transplanting seedlings in a greenhouse, rather than feeding them earlier, preferably immediately after transplanting, all the better.
For the first feeding, these gardeners recommend using organic fertilizers, or the so-called "green tea". This fertilizer is easy to prepare with your own hands. For its preparation, they take a variety of herbs (various weeds, such as nettles, plantains and others), into which a bucket of liquid mullein and a glass of wood ash are added.
For infusion, take 4-5 kg of finely chopped grass for 50 liters of water, add mullein and ash, mix and leave for several days to infuse. Then the volume of the solution is brought to 100 liters. Under each bush, tomatoes are poured about 2 liters of the finished infusion.
Important: mineral dressings carried out at this time by many gardeners have a one-sided effect on plants. Some of them stimulate the active growth of green mass, others enhance flowering. If there are no organic fertilizers, it is better to feed the tomatoes with any complex mineral fertilizer. So, if you think that the soil in your greenhouse is well fertilized, then fertilizing after transplanting tomato seedlings can be skipped. Then, an approximate feeding plan will be as follows:
- The first feeding will be carried out approximately in 15-20 days after plant transplant. Mineral fertilizers are used for her, diluting them in 10 liters of water:
- 25 g nitrogen; 15 g potassium.
For each plant, 1 liter of the prepared solution is consumed.
- The next feeding is carried out at a time when the tomatoes begin to bloom en masse (see Forming a tomato bush in a greenhouse - how to do it correctly), since feeding tomatoes in a greenhouse is necessary for normal fruit setting in the future. In 10 liters of water, 1 tbsp is diluted. a spoonful of potassium sulfate, 0.5 liters of poultry manure and the same amount of liquid mullein... Each plant should receive 1-1.5 liters of the prepared solution.
If there is little or no organic fertilizers, then fertilizing can be done by dissolving 1 tbsp. spoon of nitrophoska in 1 bucket of water. For each plant, 1 liter of working solution is consumed. During the flowering of tomatoes, in order to prevent the top rot of tomatoes, it is necessary to spray the plants with an aqueous solution of calcium nitrate. To cook it 1 st. a spoonful of fertilizer is diluted in 10 liters of water.
- During the formation of ovaries, it is necessary to feed the tomatoes with a solution of 2 liters of wood ash and 10 g of boric acid, diluted in 10 liters of hot water. The prepared solution must be insisted for a day so that all elements are completely dissolved. This mixture contains a large amount of micro and macro elements that will help the crop to form more quickly. Each plant is watered with 1 liter of the prepared working solution. The last root feeding is carried out during mass and active fruiting in order to accelerate ripening and improve taste. For this root dressing, 2 tbsp is dissolved in 10 liters of water. tablespoons of superphosphate and 1 tbsp. spoon of liquid sodium humate.
In any case, there is no clear instruction on when, how often and with what fertilizers to feed greenhouse tomatoes. Every gardener, knowing what vegetable crops, were grown in the previous season and what fertilizers were used, follows an approximate feeding scheme, "adjusting" to the peculiarities of plants, the oddities of the weather and relying on their experience.
Foliar dressing
In addition to the usual root dressing of tomatoes, it is useful to use foliar dressing - spraying the stems and leaves of tomatoes. A feature of foliar dressings is that they are able to convey to the plant the substances it needs, which are lacking in the soil.
This is due to the fact that the leaves, unlike the roots, assimilate only the elements that are not enough for the plant. If the tomatoes lack some specific elements, how to feed the tomatoes in the greenhouse is solved by introducing the missing elements with foliar feeding. Spraying plants with a solution containing deficient substances very quickly gives positive results, which appear literally in a few hours.
If you introduce the same elements through root dressing, then the result can be seen only after a week or two. During flowering, thinking about how to feed tomatoes in a greenhouse, you can perform foliar feeding with a solution of boric acid and extract of wood ash.Advice: to prepare an extract from wood ash, take two glasses of ash and pour 2-3 liters of hot water.
Insist for a couple of days, after which the precipitate is filtered off. The resulting solution is brought to a volume of 10 liters with water, after which the plants are sprayed.
How to fill the deficiency of nutrients
Tomatoes signal with their appearance very clearly what elements they lack (see more Diseases of tomatoes in a greenhouse: their varieties and how to deal with them).
- with a lack of phosphorus, the stem, the lower surface of the leaves and the veins on them turn purple. If you sprinkle the plants with a weakly concentrated solution of superphosphate, then after a day the purple coloration disappears. Calcium deficiency leads to the curling of the leaf plate inward and the disease of the tomato fruit with apical rot. In this case, spraying the plants with a solution of calcium nitrate will help. If the plants lack nitrogen, the plant becomes light green or yellowish, stunted and becomes very thin. Spraying with "herbal tea" or a very weak urea solution will help to cope with nitrogen deficiency.
It may seem that feeding greenhouse tomatoes is too troublesome and unnecessary. It is enough just to fertilize the soil during spring and autumn digging, and then plant the tomato in the greenhouse.
Indeed, if the soil is not depleted and the correct crop rotation is practiced, the harvest can be obtained. But if you carefully look after the plants and quickly respond to their needs, constantly take care of them, the tomato harvest in the greenhouse can be obtained much more abundantly and of better quality. different types feeding tomatoes, you will see that you yourself can easily cope with this task.
Top dressing of tomatoes in the open field and in the greenhouse
Tomatoes grade Eupator So, two weeks have passed since you planted tomato seedlings in a greenhouse or open ground. It's time to feed the plants. Top dressing of tomatoes in the open field or in the greenhouse - is there a difference?
What types of dressings are there in general? Last years gardeners (those I know) prefer organic matter, trying to use less mineral fertilizers. Home-made cheap, but very effective "green fertilizer" is very popular.
But about him, a little below.
Types of tomato dressing
There are two types of top dressing. Root and foliar. Root feeding is used by most gardeners. It feeds the plants through the root system, that is, it is watering with a nutritious mineral or organic solution under the root.
Many people know about the foliar, but they use it less often, but in vain. Foliar is when we apply the same nutrient solution directly to the leaves of plants. This type of feeding tomatoes with mineral or organic fertilizers has a number of advantages.
First, it saves fertilizer. Because when we apply them under the plants, then a significant part of the nutrients is washed out with irrigation, during the rain, not all nutrients get to the plant.
And when we apply the solution to the surface of the leaf, then all the nutrients pass through the leaf into the plant. And this happens very quickly. Therefore, foliar feeding works much faster than root feeding.
Secondly, they use it to quickly help a plant suffering from a lack of one or another trace element. I try more often to use foliar dressing for seedlings, for plants recently planted in open ground or a greenhouse, that is, for younger seedlings. For foliar dressing, use a lower concentration of solution than for root, so as not to cause burns to the leaves.
For her, fertilizers are used that completely dissolve without sediment, which do not contain chlorine. Usually these are liquid forms of fertilizer mixtures, no matter what they are - mineral or organic.
Try to use non-chlorinated water for preparing nutrient solutions - rainwater or at least settled tap water. Both root and foliar feeding are equally useful both for tomatoes that grow in open ground and for greenhouse ones. In the first half of the growing season, it is better to alternate the plants.
In the second, go to root dressing. The greenhouse with high humidity should be ventilated more often, especially after spraying. In order for the plant to get the maximum benefit from any feeding, you need to know when - in the morning, in the afternoon, in the evening - it is better to carry them out.
When to feed tomatoes
Highly important point: if you are doing foliar or root dressing, then this should be done in the morning or in the evening. Why is that? If we are talking about foliar, then the nutrient solution should be on the surface of the leaves for as long as possible so that it can be absorbed.
And in bright sun, spraying the leaves can cause burns. This is, first of all. And secondly, the sun will quickly dry the droplets of the nutrient solution, it will not have time to be completely absorbed into the leaves.
When foliar top dressing, you should make sure that the solution falls not only on the outer side of the leaf, but also on the inner side.Under the root, water the plants with a mineral or organic solution also early in the morning or in the evening. I prefer evening watering, and my neighbor in the country watering his cucumbers, tomatoes in a greenhouse or open field only early in the morning.
The reasons also seem to be clear: water or nutrient solution that falls on the leaves during the day can cause sunburn foliage. You should not force the plant to expend energy on recovery or healing wounds.
How often should you feed
Usually they ask the question, how often should tomatoes be fertilized with mineral or organic fertilizers? The short answer is not very often. And, more precisely, I spend them, both root and foliar, in 10-15 days. That is, about 2-3 times a month. I alternate them.
Once - foliar feeding, the next time - I feed my tomatoes at the root. I do foliar feeding (spraying) in the first half of the growing season, that is, as soon as I noticed that the first fruits are full, they began to turn white, I stop feeding. And I continue to do the root during the entire growing season (development) of tomatoes. The first time you should feed the tomatoes 10-12 days after planting the seedlings.
When the flowering of tomatoes begins, do not miss the date - the number of ovaries and the harvest will depend on this. In a greenhouse or open field, fertilizing is carried out as follows. It is necessary to feed each plant individually.
If the soil under the plants is dry, then moisten the soil a little before feeding. Pour the tomatoes with clean water, the temperature of which is not lower than 20-22? C. When watering in a greenhouse, try not to get water on the leaves - there is no need for excess moisture.
Water in the morning - after that, be sure to ventilate the greenhouse. And after watering, pour half a liter of nutrient solution under each tomato bush. I try to do foliar feeding of tomatoes in the greenhouse in the morning so that the nutrient solution is absorbed by the evening. Plants should be dry at night.
How to feed tomatoes in a greenhouse or open field
For the first feeding after transplanting seedlings, I use a liquid fertilizer based on humates. This year, this is GUMI Kuznetsova (a natural elixir of fertility). For 10 liters of water - 2 tablespoons of elixir. But you can start from the range of your shops for gardeners and gardeners.
It is not bad to use Gumat-80, Gumat + 7, Gumat-Universal, Emerald, Ideal. For 10 liters of water, 1-2 tablespoons of fertilizer are enough.
To this add 1 tablespoon of an instant mineral fertilizer (for example, Fertika Universal). For each plant, 0.5 liters of solution is enough. Tomatoes in the open field or in a greenhouse are better to underfeed than overfeed. Therefore, when planting seedlings from mineral fertilizers, I use only ash and compost.
After planting - fertilizer based on humates with Fertika Universal. And that's all. The following dressings are organic only.
How to make your own organic green fertilizer
I really like the positive reaction of my tomatoes to the "green fertilizer". How do I cook it? Very simple.
There are a lot of recipes for such a "green fertilizer". It is based on mown green weeds. I have an old metal 200-liter barrel.
But it is not advised to use a metal barrel for the preparation of this fertilizer, apparently, the metal oxidation process negatively affects the quality. I don't have a plastic barrel. You know yourself that there are almost no hopeless situations.
I bought huge 300-liter plastic bags. I put one bag in another (for strength), put them inside the barrel. Fill 1/3 with water so she straightens them.
The polyethylene warmed up a little by the sun, became elastic, stretched out, the bags were tightly dressed on the outside on the edge of the barrel. I ended up with a metal barrel with a plastic liner. So, I already had a little water in the barrel, I add the cut grass there.
Experienced gardeners advise filling the barrel with mowed nettles. But I didn't have that much nettles, so I sketched an almost full (2/3) barrel of various weeds, there were also nettles.
From above I threw about 1 kg of wood ash, half a bucket of chicken droppings, added 2 liters of milk "store" whey (natural, they say, 1 liter is enough), a pack of baker's yeast (100 g). She added water almost to the top. This recipe was taken long ago from the book "Reasonable Agriculture" by Yu. I. Slashchina.
He calls this solution an infusion of microbial organisms. The author recommends adding mash instead of yeast - 3 liters of non-chlorinated water, insist 150 g of sugar for 2-3 days. The solution ferments in the barrel very actively and the stench, sorry for the details, is not the most pleasant.
And you need to mix the fertilizer at least once a day. All this is insisted for 1.5-2 weeks. Then I take out the fermented grass.
When it dries up, I put it under the zucchini. Why for zucchini - I don't know. Somehow it happened from the very beginning. The courgettes are very grateful. You can try using this mulch on other plants; the nutritional infusion in the barrel is just over half.
I fill up the barrel to the top. I take a ready-made infusion (500 ml), add it to a watering can (6 liters), water tomatoes, cucumbers, eggplants, pumpkins - half a liter of solution per bush. Yes, I almost forgot. The effect will be better if the soil under the plants is moist.
That is, before root feeding, be sure to water the tomatoes in the open field or in a greenhouse. I really like the result of such organic feeding - the plants are always green, they look healthy, they tolerate bad weather well, they grow very quickly, a lot of fruits are tied and, it seems to me, they began to hurt less , that is, their immunity has increased. This solution can be used for root and foliar feeding. Foliar is usually carried out on young plants planted in open ground or in a greenhouse.
Watering at the root - every 10-12 days. I have enough of this solution for a long time. But everything, of course, depends on the number of planted plants. If I feel that the "green fertilizer" is not enough, then after less than half of it remains in the barrel, I fill the barrel with new grass.
I don't add anything else except water. I wait 10-15 days - the new nutrient solution is ready. This "green fertilizer" works well against late blight.
At least, it seems to me that after I started using it, there were almost no cases of phytophthora on the leaves, fruits. Last year (2013), only a few fruits of tomatoes (5 pieces) growing in the open field were thrown from one bush.
I did not notice any signs of late blight on the rest of the bushes, but this garden year (2014) began with rainy weather. The humidity in the greenhouse and in the garden is high.
To prevent late blight on tomatoes, powdery or downy mildew on cucumbers, zucchini, I additionally process the plants with a solution of whey (1 liter per 10 liters of water), to which I add 10 drops of iodine. This solution is especially beneficial for tomatoes.
Iodine helps to increase the number of ovaries, and whey has a depressing effect on pathogenic fungi. To prevent late blight on tomatoes, alternate treatments. Once with a solution of whey, and the other with a solution of Fitosporin.
This drug not only protects tomatoes from late blight, it also feeds plants with bioactivated microelements, especially its new modification - Fitosporin-M. Sometimes I skip lactic acid treatment, but be sure to replace it with Fitosporin solution, which well suppresses the development of fungal and bacterial diseases on plants. Do not forget that moisture, high humidity in greenhouses or in the garden during a rainy period have a beneficial effect on the development of phytophthora, others fungal, bacterial diseases.
Be sure to process your seedlings, do not wait for the first signs of the disease. If the disease has begun to manifest itself, then it is already too late and practically useless to fight it. So, the answer to the main question.
What fertilizers, what top dressing are the best for tomatoes? Mineral or Organic? I would answer this way.
How to feed tomatoes after planting in the ground
Greetings, dear friends!
We will talk about how to feed tomatoes after planting in the ground in this article.
Tomatoes are quite demanding on nutrients and respond well to fertilization.
In late autumn, when plowing a plot planned for planting tomatoes, 5 kg of humus (rotted manure) or garden compost are applied for each square. meter, and in the spring the site is filled with mineral fertilizers: double superphosphate (80 mg / sq. meter) and potassium chloride (10 mg / sq. meter). It is advisable to close up wood ash at the rate of 2-2.5 cups per sq. meter, both in autumn and spring.
During the vegetative period of tomato development, in order to improve the growth and development of plants, as well as in order to maximize the yield of the crop, it is necessary to make 4 root dressings of plantings. The main dose of fertilizer is applied through the soil when the necessary nutrients are absorbed by the plant root system. At each stage of the growing season of tomatoes, they require certain chemical elements.
The composition of top dressing depends on the fertility of the soil, climatic conditions, the mass of hanging fruits on the plants. In cool and cloudy summers, the dose of potassium in nutritional compositions should be increased (+ 25% of the recommended), and, on the contrary, reduced in dry hot summers.
Root dressing of tomatoes planted in the open field
1. Spend on the twentieth - twenty-second days after planting tomato seedlings in the beds. Recommended composition of the solution (introduction of organic matter and mineral fertilizers): dilute liquid mullein (half a liter) and 15 ml of nitrophoska in a bucket of water. Consumption - half a liter for each bush.
2. The feeding time is approximately twenty days after the first ( best moment for the second feeding - budding of the second brush of color). Irrigation composition: chicken manure (0.4 kg), superphosphate (1 tbsp. Spoon), potassium sulfate (1 tsp.) In a standard bucket of water. Consumption - 1 liter for each plant.
3. Feeding time - approximately 1-2 weeks after the second, when the third cluster of tomatoes begins to bloom. Composition for irrigation (fertilizing with mineral fertilizers): nitrophoska (15 ml) and potassium humate (15 ml) per bucket of water. Consumption - 5 liters for each square meter of your garden.
4. The feeding time is 11-14 days after the third. At this stage, plants only need a superphosphate solution: a tablespoon of the composition for 10 liters of pure water. Consumption - a bucket per square meter. meter.
Foliar dressing of tomatoes
Irrigation of tomato tops or fine dispersion of the nutrient composition on the leaves gives good results, improving plant growth, development of leaf apparatus and young shoots, as well as helping to prevent shedding of color. The main
the advantage of such fertilization is that nutrients applied directly to the leaf apparatus are absorbed by plants much faster. Spraying of plantings is carried out 1-4 times during the growing season.
1. This composition is suitable for both open field and greenhouse plants. 15 g of urea and 1 g of potassium permanganate crystals (potassium permanganate) are added to a bucket of water. The prepared solution is enough for irrigation of 60-70 bushes.
2. In a dry summer, when due to the heat there is a massive shedding of color, that is, pollination does not occur, it is recommended to fertilize with an aqueous solution of boric acid, which is prepared in the following proportion: 1 teaspoon of crystals per bucket. In addition to this composition, specialized preparations are sometimes used, for example, "Ovyaz".
The optimal time for foliar dressing of tomatoes is evening, always in dry weather. Treatment with composition in the given time days is most expedient, since the solution dries longer on the tops and fruits and, accordingly, brings more benefits. The abundant summer dew that falls out early in the morning contributes to the fullest assimilation of the nutrients remaining in the evening by plants.
Now you know how to feed tomatoes after planting in the ground... Remember that root and foliar dressing is especially important if the soil for tomatoes has not been previously enriched with organic matter and minerals. See you, friends!
Site news to your email! Enter your Email
ayatskov1.ru
Growing tomatoes in the open field. My garden, vegetable garden. Piggy bank of country experience.
- 5.2 Pollination of tomatoes
Hello dear friends!
We continue the tomato theme. After reading the previous article, I hope you learned something new about tomatoes, about the variety of varieties of this wonderful plant, about how to prepare tomato seeds and the timing of their planting, about caring for seedlings.
In this article, we will discuss how to grow an excellent tomato harvest on our summer cottages, subject to planting plants in open ground.
So, the topic of our today's article is - growing tomatoes in the open field.
Preparing the soil for tomato princes
For a rich harvest, we need, first of all, to find a good place for our pets. Tomato plants love indirect sun and will thrive in sunny but sheltered areas.
- The best predecessors of tomatoes are carrots, cucumbers and onions. And if you plant your favorites next to strawberries, both cultures will benefit from this. The yield of tomatoes and fragrant berries will increase several times, and the fruits will become larger.
But the places where potatoes, eggplants and peppers grew should be avoided by tomatoes. Pathogens of various diseases can accumulate in these areas.
Our country is huge. And the quality of the soil is different in all regions (even in different fields). And tomato princes are very demanding and whimsical to the land. Therefore, we need to find out the quality of the soil in our garden.
◊ Check the acidity. A pH test can be purchased from any garden department. The lower the indicator, the higher the acidity. Neutral ground has a score of 7.0.
- Tomatoes need soil with acidity values between 6.0 and 7.0.
In the case of a lower indicator, we add lime to the soil (0.5-0.8 kg per square meter), if the level is higher, sulfur in the same amount.
◊ We estimate the amount of nutrients. Analysis for the presence of trace elements can be ordered and carried out in special laboratories. This is very useful information for gardeners.
It is necessary in order for the cultivation of tomatoes in the open field to take place without losses and to please with a rich harvest.
| Nitrogen | Phosphorus | |
| Has an effect on the health of tomato leaves. With a lack of it, the tomato will have yellowed, sluggish leaves. | This substance gives tomatoes strength and health. It increases the immunity and resistance of plants to diseases. With a lack of potassium, tomatoes do not grow well and look stunted. | Helps strengthen the root system and regulates seed formation. With its lack, tomatoes give sick, unripe fruits. |
| If there is a nitrogen deficiency, add fishmeal, compost or inorganic substances such as calcium nitrate, ammonium sulfate or sodium nitrate to the soil. | To compensate for the lack of potassium, supplement the soil with sand, granite dust or wood ash (bucket per square meter). | Add superphosphates, compost, and bone meal to the soil to raise phosphorus levels. |
♦ Compost- ideal for soil preparation. It also attracts many earthworms, which do an excellent job of loosening the soil and, in turn, attract and create favorable conditions for the parthenogenesis of beneficial bacteria.
Prepare the land for growing tomatoes in the open field need to start back in autumn period after thorough cleaning of all previous plant residues. We dig the area selected for plants to a depth of 30 cm.
- Autumn top dressing of the soil. To a depth of 20-25 cm, we apply organic (bird droppings, humus, peat or compost 5 kg per sq. M) or mineral fertilizers (potassium salt 20-25 g, superphosphate 40-50 g per sq. M.).
- Spring top dressing. To a depth of 15-20 cm, we introduce a mixture of 1 kg of poultry manure, 1.5 kg of wood ash and 20-25 g of ammonium sulfate per sq. m. Or mineral dressing (superphosphate 55 g, ammonium nitrate 20 g and potassium chloride 15 g per sq. m).
For a successful growing tomatoes the earth must be thoroughly dug up 2-3 times (preferably with a pitchfork) and harrowed. Tomato plants and humus will like it.
But it is better to refuse manure (tomatoes, having tasted manure fertilizers, begin to actively grow their tops, while the growth of fruits fades away).
- If the soil does not warm up enough, you can cover the area with black film or plastic. The black color perfectly attracts the light of the sun and absorbs it, warming up the soil underneath.
On the prepared site, 5-6 days before planting, we form ridges (width 100-120 cm, height 15-20 cm) in the north-south direction. This will help to achieve uniform illumination of the seedlings.
Maintain a distance between the ridges of about 70 cm (for all varieties).
Growing tomatoes in the open field
As soon as the spring frosts come to an end (usually it is the end of May - the beginning of June), we will plant young tomatoes in the open ground.
It is ideal to carry out this procedure on a cloudy, gloomy day. If it's sunny outside, wait for the evening.
Plant young shoots in two rows with a distance between them for classic planting:
- For undersized boles and determinant species (row spacing 40-50 cm, between plants 30-35 cm).
- For medium-sized ones (row spacing 50-60 cm, between tomatoes 40-45 cm).
Square-nesting fit
This method will greatly facilitate the care of our tomatoes (it will become easier to loosen them), and the plants themselves will create the most favorable living conditions: it will improve the absorption of nutrients and increase the illumination. As a result, we will achieve a good harvest. We plant it according to the following scheme:
- Standard and determinant varieties: 70x70 cm, 2-3 plants for one nest.
- Early maturing species with a spreading bush: 70x70 cm, a couple of plants in one hole.
- Mid and late ripening: 70x70 cm, 1 bush in one nest. Or 90x90 cm (100x100 cm) - 2 plants each.
Ribbon-nest landing
This method of growing tomatoes in the open field makes it possible to place more bushes in one area. It becomes easier for them, crowded in one hole, to withstand bad weather conditions.
As it grows, weaker shoots thin out.
- With this method, irrigation furrows are cut every 140 cm. Plants are planted on both sides of the furrows (from a row of 60 cm, in the row itself after 70 cm, a couple of bushes in one nest).
Focus on the final growth of the bush. Ideally, for good development, one tomato should be given about 0.3 sq. m.
On average, for a plot of 100 sq. m. will need approximately 340-420 early tomatoes, and late and medium varieties 240-290 pieces.
Getting started disembarking
First of all, you need to moisten the soil well in pots or boxes with seedlings. This will help to easily remove them from the container and prevent accidental damage to the root system.
Prepared holes for growing tomatoes in the open field should have a depth of 10-15 cm.
We water them (a bucket of water for 8-10 holes) and apply mineral fertilizers mixed with humus (proportion 1x3).
- Turn over the container with seedlings, grasp the trunk of the tomato with your middle and forefinger and remove it from the container.
- Tear off the leaves of the seedlings, leaving only 2-3 leaves on top (this will stimulate root growth).
- Place the plant with the root clod vertically in the hole and cover with compost. In this case, the stem of the tomato should remain open. Only the roots or a pot of soil are placed in the ground.
- Press down firmly around the plant and cover the compost with dry soil.
- After planting, we mulch the soil (for this, mowed, slightly withered grass, sawdust, straw or newspaper leaves are suitable). The mulch layer should be about 10 cm high.
When the planting of tomatoes in the ground is over, we will leave them alone for 8-10 days. During this period, the plants take root and master in a new place.
Do not water them yet. But you need to be prepared for freezing. To do this, immediately after planting, we will cover our young tomatoes with transparent film.
It will remain until the threat of frost disappears (for the middle zone, this usually happens by June 5-10). Holes with a diameter of 10 cm can be made in the film. This will reduce the risk of late blight infection.
After 10 days, we water the seedlings and at the same time plant a new one in the place of the deceased. The first hilling when growing tomatoes in the open field can be done two weeks after planting the seedlings.
In the future, we will huddle the plants as they grow.
How to tie tomatoes
Place pegs 50-80 cm high above the rows with planted tomatoes (depending on the growth of the bush).
The pegs are placed on the north side, retreating from the stem about 10 cm. We will tie each bush to them with a washcloth or twine.
Plants begin to tie up when they have 4-5 true leaves. In total, 3-4 garters are produced during the growth period of a tomato.
Plants are tied up only under a brush with fruits. This allows them to be well lit and receive more heat and sunshine, which speeds up and increases yields.
The fruits, not in contact with the ground, are less susceptible to pest attacks and are better protected from diseases.
Tapestry method
For medium-sized plants, large-fruited and richly fruiting, it is best to use trellises, not garters.
This method of growing tomatoes in the open field makes it easier to care for the plant, harvest, and also lengthen the fruiting period of tomatoes. Plants are less likely to develop fungal infections. This method allows you to more effectively use a plot of the garden (especially when it is small in size).
To do this, install pillars about 1.2-1.5 m high in the rows (the more often the posts are driven in, the stronger the structure will be).
Drive carnations onto the posts every 20-25 cm. Attach horizontal slats to them with twine or wire.
When the tomato seedlings start to grow (this will happen two weeks after planting), gently tie the brush of the plant to the slats with a soft twine or cord. Continue tying them as they grow, every 15-20 cm.
- This method is ideal when growing tall tomatoes in greenhouses (we will talk more about caring for greenhouse giants in another article).
With the trellis method, further care for the plants will be very simple: timely tying of fruiting shoots and their stepchildren to the slats.
Care when growing tomatoes in the open field
|
Operation |
Advice |
|
| Grassing tomatoes (or shaping) | It is necessary to remove side shoots constantly, starting from an early age of the plant. By the time the fruit ripens, there should be no stepsons. | They must be removed before the shoots reach 3-5 cm in length. It is best to do this in the morning. In the southern, sunny regions, you can not completely remove the stepsons, just do not tie them up. But in the north, this operation is required (leave only 2-3 stems for each bush). In extreme heat, this procedure cannot be carried out. |
| Top dressing tomato | Once every 10 days. The first time we feed tomatoes two weeks after planting. | The first feeding with a solution of mullein (1x10) or chicken manure (1x20). We make repeated dressings with mineral fertilizers (nitrofoska 60g + water 10l). Quantity: before flowering, 1 liter for each bush, after flowering for 2-5 liters. |
| Watering tomatoes | Abundant, but rare watering. | Water the tomatoes once a week in the spring and early summer. In warm summer, limit yourself to one watering every 2-3 days. Water the root bushes in the evening. |
| Spraying | We spray every week, alternating the compositions of the liquid. First spraying immediately after planting in open ground (Bordeaux liquid). | Alternate between Bordeaux liquid and homemade onion tincture. |
How to pinch tomatoes. When removing the stepchildren, do not pull them out, but gently break them out, grabbing them with your index and thumb, and gently pull them to the side and break them off.
If they have grown too large, cut with a sharp knife or razor. First of all, get rid of the stepchildren growing under the brushes (otherwise the tomato can shed the ovary).
For the best yield when growing tomatoes outdoors, pinch the tops of all the shoots with fruits at the end of summer.
Also remove excess flower brushes where the fruit has failed to form.
Preparation of Bordeaux liquid. In water, extinguish quicklime (100 g) and add water (about 5 liters). In another container, dissolve in a small amount of hot water copper sulfate(100 g) and add 5 liters of water.
Then pour the vitriol solution into the slaked lime. The correct liquid will have a sky blue tint.
Just in case, measure the alkaline reaction with an indicator ( bordeaux liquid must be neutral or slightly alkaline).
- Any iron objects can be used to check. If the metal is covered with a layer of copper, you made a too acidic solution. More lime needs to be added. But do not overdo it, otherwise the liquid will lose its beneficial qualities.
Preparation of onion tincture. Grind onion and garlic (100 g each) with a meat grinder. Transfer the mixture to a 3-liter glass container and fill it ¾ with water. We close and insist for 3 days.
Shake it periodically. At the same time, pour bird droppings (200 g) in a plastic bucket with water and set to infuse. Both mixtures are mixed and filtered before use.
For top dressing when growing tomatoes in the open field, it is useful to use fermented nettle and ash.
Also, a couple of times in the fruiting season, feed the plants with microelements (crush 5 tablets and stir them in ½ l of water, then add another 10 l of water). Consumption of 1 liter for each bush.
Banana fertilizer. We are preparing a natural, very healthy top dressing, enriched with calcium and phosphorus. This remedy is made from banana peels.
- Cover the oven tray with food foil. Put the banana peel on top of the skin with the outside side down (so that it does not stick). Place the tray in the oven.
- After roasting and cooling it, grind the peel into flour and place it in an airtight bag.
Sprinkle banana flour on the soil near the plant roots once every two weeks.
To get an excellent harvest of tomatoes, you need to do more than just water and feed them correctly. They need pollination.
Pollination of tomatoes
Tomato is a self-pollinating plant. When growing tomatoes outdoors, these plants create a lot of high-quality pollen, which is also enough for neighboring flowers.
To help with pollination, attract insect helpers (bees, bumblebees).
To do this, plant bright annual melliferous plants between the tomatoes: rapeseed, coriander, basil and mustard. By the way, these crops also improve the taste of the fruits themselves.
But it is not always possible for a tomato to self-pollinate. There can be many reasons:
- Lowering the temperature at night (below + 13 ° C). Under such conditions, the deformation of the anther occurs.
- The daytime temperature is too high (above + 30-35 ° С). In the heat, the flowers fall off, and the pollen grains die.
- Features of the structure of the pistil of some large-fruited varieties (it protrudes outward and the pollen does not fall on the stamens). Or the pestle is too wide.
In such cases, we need to help our tomatoes to pollinate. You can tilt down the buds with a protruding pistil and shake the flower slightly. Or it is easy to knock on a trellis or a flowering brush.
- The best time for artificial pollination is 10-14 hours, at a temperature of + 22-27 ° C. The ideal air humidity is not more than 70%. Repeat the pollination procedure after 4 days.
Immediately after pollination, water the tomatoes or spray over the flower (so that the pollen sticks to the pistil). The last flowers to appear are usually empty and underdeveloped. It is better to remove them immediately.
Secrets of growing tomatoes. An amazing tomato has one peculiarity - it is completely unpretentious.
And it can bear fruit even if your care is limited only to watering and weeding.
But the tomato is very responsive. And the more carefully you take care of the plants, the more harvest they will give you.
But don't overdo it in your quest to please him. The golden rule for growing tomatoes is that everything is good in moderation!
Caring for tomatoes should be within reasonable, competent limits!
Now, my dear friends, you know how to grow our precious tomatoes outdoors. Next, we have to learn about growing tomatoes in a greenhouse and about the possible difficulties (diseases and pests) when growing them.
And I also suggest watching a short video with several useful tips for growing tomatoes.
See you soon, dear friends!
syperdacha.ru
Fertilizer for cucumbers and tomatoes (tomatoes): in a greenhouse, open field
The first condition for obtaining a high yield of tomatoes and cucumbers is fertile soil. Naturally, every year the earth, giving us a generous harvest, loses many useful microelements, therefore, to replenish reserves, fertilizers for cucumbers and tomatoes should be regularly applied. Usually, the soil is fertilized before planting, during its process and after planting vegetables.Basic requirements for growing
Cucumbers are a very demanding crop of soil fertility; for active growth, a nutritious habitat should be provided that will help ensure an excellent harvest. The best soil for the development of cucumbers is a light loamy soil with a neutral reaction, enriched with humus.
For cucumbers, it is best to use fractional (partial) fertilization, since the plants require a large amount of nutrients, however, excess minerals can also affect negatively. Deciding on fertilizers is not an easy task, because, depending on the stages of development, various trace elements and minerals should be introduced.
How to fertilize cucumbers
Some gardeners prefer organic fertilizers, others prefer mineral fertilizers related to agricultural chemistry. To tell the truth, with the right approach: compliance with the dosage and time of use, both will be effective. For those vegetable growers who are just getting acquainted with the cultivation of this crop, it would be best to use complex mineral fertilizers, for example, Agricola, Kemira Lux, etc. The manufacturer's label contains all comprehensive information about the periods of use and recommended dosages.
If you are an experienced gardener and have some idea of fertilizers, then you can safely add potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen to the soil, as an independent element, focusing on the need for cucumbers in a particular period of growth.
You can determine the deficiency of any element by the appearance of the plant:
- Foliage color from light green to light green - lack of nitrogen.
- The leaves are rounded, curled downwards - calcium deficiency.
- A light border appears around the leaf blade - a lack of potassium.
- Too lightened veins on the foliage - not enough magnesium.
1 top dressing - 14 days after planting in the ground.
2 times - during the flowering period.
3 introduction - during the ripening of the fruit.
4 times - feeding is carried out to prolong fruiting.
The use of mineral compounds:
- For the first fertilization, it is better to use root dressing, for this, when loosening the soil, distribute over the garden bed, 5 g of ammophos per 1 sq. M.
- The second feeding can be carried out both root and foliar.
- Root - dilute 30 g of ammonium nitrate and superphosphate each, and add 20 g of potassium nitrate - to 10 liters of water.
- Foliar (spraying) - dilute 2 tablespoons of superphosphate in 10 liters of water.
- For the third fertilization, root top dressing is carried out. In a ten-liter bucket, dilute 50 g of urea or 2 liters. Potash nitrate.
- The fourth foliar dressing - for 10 liters of water - dilute 15 g of urea and spray the beds with cucumbers with the resulting solution.
Application of organic fertilizers
- In the first feed, slurry is used (8 l of water / 1 l of slurry).
- For the second, ash is suitable as a fertilizer (1 tbsp ash / 10 l of water). Stir and apply under plant roots.
- For the third fertilizer, the Gummi preparation is best suited (10 l of water - 2 l of the preparation).
It is necessary to stop the introduction of various dressings 2 - 3 weeks before the planned harvest.
Tip: When choosing fertilizers for growing cucumbers in a greenhouse, choose those that do not contain nitrate nitrogen.
Basic requirements for growing tomatoes
Fertilizers for tomatoes can be purchased ready-made, or made on your own.
The main rule when growing tomatoes is compliance with optimal dosages when using fertilizer for tomatoes, because an excess of organic additives (manure, chicken droppings), mineral nitrogen fertilizers can lead to negative consequences... Preference should be given to phosphorus-potassium compositions, potassium sulfate will also be useful ash.
Tomatoes, unlike cucumbers, prefer slightly acidic soils over neutral compounds.
When growing tomatoes, you should remember what absolutely must not be done:
- Over-fertilize the soil with organic fertilizing.
- When planting seedlings in the soil, add manure or bird droppings to the holes (the plants will grow, and not into the fruit ovary).
- Use mullein fertilizer more than 3 times per season.
- It is recommended to apply urea under the plants, it is recommended to apply this fertilizer only once at the initial stage of the growing season, as a foliar dressing.
- It is not recommended to change fertilizers for tomatoes. Best option, choose one of the complex mineral compositions (for example, ammophos, diammophos, nitroammophos, etc.) and use it together with organics, adhering to strictly defined dosages. Before choosing a fertilizer for tomatoes, take into account the peculiarity of the soil.
How to fertilize tomatoes
- The first feeding of tomatoes occurs at the beginning of June, 1 liter of fertilizer mixture is applied under each bush:
- 10 liters of water.
agro-biz.ru
In recent years, gardeners have preferred organic fertilizing, trying to add less chemical fertilizers to the soil.
Home-made cheap, but very effective "green fertilizer" is very popular. But about him, a little below. So, two weeks have passed since you planted tomato seedlings in a greenhouse or open ground. It's time to feed the plants. Types of dressings
There are two types of top dressing. Root and foliar.
Most gardeners use root dressing. This is feeding the plant through the root system, that is, watering it with a nutrient solution under the root.
Many people know about the foliar, but they use it less often, but in vain.
Foliar is when we apply a nutrient solution directly to the leaves of plants. This type of feeding has several advantages. First, this top dressing saves fertilizer. Because when we apply fertilizers for plants in the soil, then a significant part of the nutrients is washed out with irrigation, during the rain, not all nutrients get to the plant.
And when we apply the solution to the surface of the leaf, then all the nutrients pass into the leaf. And this happens very quickly. Therefore, foliar feeding works much faster than root feeding. Secondly, such feeding is used to quickly help a plant suffering from a lack of one or another trace element. I try to use more foliar dressing for seedlings, for plants recently planted in open ground or a greenhouse, that is, for younger seedlings.
For foliar feeding, lower concentrations of the solution are used than for root, so as not to cause burns to the leaves. For her, fertilizers are used that completely dissolve without sediment in water and that do not contain chlorine. Usually these are liquid forms of fertilizer mixtures. Try to use non-chlorinated water for preparing nutrient solutions - rainwater or at least settled tap water.
When to feed tomatoes
A very important point: if you are doing foliar feeding or root feeding, then this should be done in the morning or in the evening. Why is that? If we are talking about foliar feeding, then the nutrient solution should be on the surface of the leaves for as long as possible so that it has time to be absorbed. And in sunny weather, spraying the leaves can cause burns. This is, first of all. And secondly, the sun will quickly dry the droplets of the nutrient solution and it will not have time to be completely absorbed into the leaves. When foliar top dressing, care should be taken that the solution falls not only on the outside of the leaf, but also on the inside.
Watering plants with a nutrient solution under the root is also necessary early in the morning or in the evening. I prefer evening watering, and my neighbor in the country watering his tomatoes or cucumbers only early in the morning. The reasons also seem to be understandable: water or nutrient solution that gets on the leaves during the day in sunny weather can cause burning of the foliage. You should not force the plant to expend energy on recovery or healing wounds.
How often should you feed
Usually the question is asked, how often should you feed tomatoes? The short answer is not very often. And, more precisely, I carry out top dressing, both root and foliar, in 10-15 days. That is, about 2-3 times a month. I alternate them. Once - foliar feeding, next time - I feed my tomatoes at the root.
I do foliar dressing (spraying) in the first half of the growing season, that is, as soon as I noticed that the first fruits have poured, they began to turn white, I stop feeding. And I continue to make the root throughout the growing season (development) of tomatoes.
The first time you should feed the tomatoes 10-12 days after planting the seedlings in a greenhouse or open ground. When the flowering of tomatoes begins, do not miss the timing of feeding - the number of ovaries and the yield will depend on them.
In a greenhouse or in the open ground, feeding is carried out as follows. It is necessary to feed each plant individually. If the soil under the plants is dry, then moisten the soil a little before feeding. Pour the tomatoes with clean water, the temperature of which is not lower than 20-22 ° C. When watering in a greenhouse, try not to get water on the leaves - there is no need for excess moisture. Water in the morning - after that, be sure to ventilate the greenhouse. And after watering, pour half a liter of nutrient solution under each tomato bush.
I try to do foliar feeding of tomatoes in the greenhouse in the morning, so that by the evening the nutrient solution is absorbed into the leaves. Plants should be dry at night. How to feed tomatoes
For the first feeding after transplanting seedlings into a greenhouse or open ground, I use a liquid fertilizer based on humates.
This year it is GUMI Kuznetsova (natural elixir of fertility). For 10 liters of water - 2 tablespoons of elixir.
But you can start from the range of your gardening and gardening shops. It is not bad to use Gumat-80, Gumat + 7, Gumat-Universal, Emerald, Ideal. For 10 liters of water, 1-2 tablespoons of fertilizer are enough. Add 1 tablespoon of instant mineral fertilizer (for example, Fertika Universal) to this.
For each plant, 0.5 liters of solution is enough.
It is better to underfeed tomatoes than to overfeed. Therefore, when planting seedlings in open ground or a greenhouse from mineral fertilizers, I use only ash and compost. After planting - fertilizer based on humates with Fertika Universal. And that's all. The following dressings are organic only.
How to make your own organic green fertilizer
I really like the positive reaction of my tomatoes to the "green fertilizer". How do I cook it? Very simple. There are a lot of recipes for such a "green fertilizer". Its basis is mown green weed.
I have an old metal 200 liter barrel. But it is not advised to harvest this fertilizer in a metal barrel, apparently, the metal oxidation process negatively affects the quality. I don't have a plastic barrel. You know yourself that there are almost no hopeless situations. I bought huge 200-liter plastic bags. I put one bag in another (for strength) and placed them in the barrel. Filled 1/3 with water so that the water straightens them. In the sun, the polyethylene warmed up a little, became elastic, stretched out and the bags were tightly dressed on the outside on the edge of the barrel. I got a metal barrel with a plastic liner.
So, I already had a little water in the barrel, I add the cut grass there. Experienced gardeners advise filling the barrel with mowed nettles. But I didn't have that much nettles, so I sketched out an almost full (2/3) barrel of various weeds, including nettles. From above I threw about 1 kg of wood ash, half a bucket of chicken droppings, added 2 liters of milk "store" whey (natural, they say, 1 liter is enough) and a pack of baker's yeast (100 g). I added water almost to the top.
This recipe was read long ago in the book "Reasonable Agriculture" by Yu.I. Slushchina. He calls this solution an infusion of microbial organisms. The author recommends adding mash instead of yeast - 3 liters of non-chlorinated water, insist 150 g of sugar for 2-3 days.
The solution in the barrel wanders very actively and the stench, sorry for the details, is not the most pleasant. And you need to mix the fertilizer at least once a day. All this is insisted for 1.5-2 weeks. Then I take out the fermented grass. It dries up in the sun and I put it under the zucchini. Why for zucchini - I don't know. Somehow it happened from the very beginning. The courgettes are very grateful. You can try using this mulch on other plants.
A little more than half of the nutritional infusion in the barrel is obtained. I fill up the barrel to the top. I take a ready-made infusion (500 ml), add it to a watering can (6 liters), water tomatoes, cucumbers, eggplants, pumpkins - half a liter of solution per bush. Yes, I almost forgot. The effect will be better if the soil under the plants is moist. That is, before root feeding, be sure to water the tomatoes.
I really like the result of such feeding - the plants are always green, they look healthy, they tolerate bad weather well, they grow very quickly, a lot of fruits are tied and, it seems to me, they began to hurt less, that is, their immunity increased.
This solution can be used for root and foliar feeding. Foliar is usually carried out on young plants planted in open ground or in a greenhouse. Watering at the root - every 10-12 days.
This solution is enough for me for a long time. But everything, of course, depends on the number of planted plants. If I feel that the "green fertilizer" is not enough, then after less than half of it remains in the barrel, I fill the barrel with new grass. I don't add anything else except water. I wait 10-15 days - the new nutrient solution is ready.
This "green fertilizer" works well against late blight. At least, it seems to me that after I started using it, there were almost no cases of phytophthora on the leaves and fruits. Last year (2013), only a few fruits of tomatoes (5 pieces) growing in the open field were thrown from one bush. On the rest of the bushes, I did not notice any signs of phytophthora.
But this garden year (2014) started with rainy weather. The humidity in the greenhouse and in the garden is high. And in order to prevent the appearance of late blight on tomatoes, powdery or downy mildew on cucumbers, zucchini, I additionally process the plants with a solution of milk whey (1 liter per 10 liters of water), to which I add 10 drops of iodine. This solution is especially beneficial for tomatoes. Iodine helps to increase the number of ovaries, and whey has a depressing effect on pathogenic fungi.
For the prevention of late blight on tomatoes, alternate treatments. Once with a solution of whey, and the other with a solution of Fitosporin. This drug not only protects tomatoes from late blight, it also feeds plants with bioactivated microelements, especially its new modification - Fitosporin-M. Sometimes I skip lactic acid treatment, but be sure to replace it with Fitosporin solution, which well suppresses the development of fungal and bacterial diseases on plants.
Do not forget that moisture, high humidity in greenhouses or in the garden during a rainy period have a beneficial effect on the development of phytophthora, other fungal, bacterial diseases. Be sure to process your seedlings, do not wait for the first signs of the disease. If the disease has begun to manifest itself, then it is too late to fight it and it is practically useless.
secretdachi.ru
Top dressing of tomatoes during flowering | LS
Everyone knows that tomatoes that are grown in their garden are much tastier than those that are sold in stores and markets. In order for the harvest to please with its abundance, and the tomatoes to be large, juicy and tasty, the plants need to be provided with proper care and conditions for good development.
For good growth, tomatoes need nutrition, because the more abundant the harvest, the more nutrients it takes from the soil. That is why plants need periodic feeding.
Tomatoes also do not like an excess of fertilizers. The imbalance of certain substances in the soil can cause a delay in development, disease, or shedding of ovaries in a plant.
Feeding tomatoes with yeast
- Ordinary nutritional yeast can act as a top dressing for tomatoes. They contain many of the substances that these plants need. You can fertilize tomatoes 2 times a season. To prepare the product, take 1 sachet of instant yeast, mix with 2 tbsp. l. sugar, warm water (a small amount), then insist all for a couple of hours and mix with 1 bucket of water. Such a composition is used when watering plants as follows: 1 watering can of water will need 0.5 liters of solution. The effect will be visible after 3 days: the tomatoes grow quickly, and the leaves and stems become stronger.
- Another way to prepare yeast top dressing: fill a 3-liter glass jar 2/3 with brown bread, add 100 gr. raw yeast (diluted with water in advance). Pour everything with warm water, close the lid and put in a large saucepan (the solution will pour out of the container during fermentation). The mixture should ferment for at least 3 days. After it, you need to strain and water the tomatoes in the following proportion: for 10 liters of water 1 liter of solution.
Top dressing of tomatoes in the open field during flowering
Many novice gardeners do not know exactly what products should be used to fertilize tomatoes during flowering. Caring for seedlings in the open field requires a lot of time and effort. Top dressing is used in cases where the seedlings were planted in, which was not fertilized in advance.
Usually, the seedlings develop for about 2 months and throughout this time the plants need nutrition. Particular attention should be paid to the period of formation of the ovary of flowers and the flowering itself. At this time, you can use both simple mineral fertilizers, such as urea, superphosphate, ammonium nitrate, and complex ones, designed specifically for tomato seedlings - diammophos, nitroammofosk, kemir, etc.
It is convenient to use special nutrient boxes and pots that are filled with a substrate, a soil mixture with the necessary organic substances. You can use mullein solution or chicken droppings as fertilizers, and during flowering, it is useful to sprinkle the inflorescences themselves with boron solution.
An element like phosphorus important at all stages of development and formation of tomatoes. It is responsible for the correct development of the roots and helps to activate the processes of fruit set. The first feeding should be done 21 days after planting the seedlings. To do this, you need to make a solution: for 10 liters of water, 0.5 kg of liquid mullein and 1 tbsp. l. nitrophosphate.
The next feeding is done during the blooming of the brushes with flowers. To do this, it is better to use ready-made fertilizers for tomatoes during flowering, for example, such as Senior Tomato - 1 tbsp. l. this drug must be diluted in 10 liters of water. Can be used mineral fertilizer Tomato master.
Top dressing of tomatoes in the greenhouse during flowering
Tomatoes that are grown in greenhouse conditions, as well as those that grow in open ground, need regular feeding. You can fertilize such seedlings from the very beginning of development, immediately after the first leaves have formed. It is best to choose a top dressing for these purposes, which includes many different nutrients.
During the flowering of tomatoes, you need to carefully use fertilizers that contain nitrogen. Dose the use of vermicompost, granular compost and other organic fertilizers. They can certainly be used, but the effect will be weak.
Tomato care: pinching
In order for the tomatoes to give large fruits and accelerate growth, it is necessary to carry out the formation of the plants themselves. It consists in getting rid of the side trunks that grow between the sheets, they are also called stepchildren.
The very first pinching is done 3 weeks after planting the seedlings. During this time, the tomatoes reach a size of 7 cm.After this procedure should be carried out regularly. You need to break out the branches with your thumb and forefinger. You cannot pull them out, otherwise wounds will form that take a long time to heal, through them fungal infections can enter the plant. If the pinching was done with some delay, then the shoots must be cut off with a sharp knife, not forgetting to leave 1 cm near the trunk.
What can happen if the tomatoes are not fed?
- If you refuse to feed, the leaves of the plant will suffer first. They will lose their shape, begin to curl at the very beginning of growth, and may fall off. This is often due to an excess of nitrogen in the soil, and its lack manifests itself in yellowing of the foliage, its stuntedness and dropping. The most important thing is not to confuse these symptoms with exposure. low temperatures and lack of moisture.
- It is also necessary to feed tomatoes in greenhouse conditions with phosphorus, because due to its lack, the plant can acquire a purple color. But if the leaves grow normally, then the deficiency of the substance is considered the norm.
- Lack of calcium is less common. It is formed more often when cultivating a crop in greenhouse conditions and manifests itself in the form of apical rot on the bushes themselves. Fertilizing seedlings is necessary in small quantities, but often. It is best to use complex fertilizers.