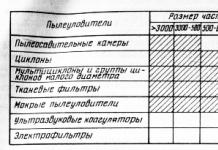
In rural areas, a personal plot is an integral part of the life of every family. So, from childhood, from spring to autumn, I was engaged in gardening work: from spring preparation of the soil, planting and sowing - to weeding with watering and, of course, to harvesting.
Plants have become my hobby. He was educated as an agronomist, but with the collapse of the USSR, collective and state farms collapsed in the village, and my profession became unclaimed. Therefore, he began to grow plants on his home acres.
In the beginning, everything was grown for their own needs and to decorate the site with ornamental plants. Subsequently, the whole family began to breed and sell planting material.

Now we are professionally engaged in the cultivation of high-quality planting material for seed potatoes. Every year we test various new varieties of potatoes. We plant more than 120 varieties, from which we select the best ones in terms of yield, taste and disease resistance - and offer them to customers.

For example, in the 2016 season, potato varieties Irbitsky, Lux, Mayak, Natasha, Sarovsky, Charodey, Alena, Fritella, Yubiley Zhukova have proven themselves well on our site.

We were one of the first to multiply and offer customers dietary varieties of potatoes with red and purple pulp: these are Cranberry, Explosion, Purple Majesty, Russian Blue, Boro.

In addition, we are interested in rare and unusual vegetable crops. For example, the amazing Vietnamese baby melon is small, about the size of a goose egg, but beautiful, fragrant and tasty. Or the cucumber Golden Vilent, which strikes with unusual fruits. They are long and white, with a length of 10 cm, they are no more than 1 cm thick and have a rare sweetish taste that children will undoubtedly appreciate.

Another popular crop is onions. We grow shallots or, as many call them, family-owned. Different types of this onion were collected from different parts of Russia: in the shape of the bulb - from round to long, in the color of the husk - from white to dark red.

We are engaged not only in vegetables, but also in fruit and berry crops. We offer amazing varieties of currants - black with berries without seeds or with berries of emerald green color.
Many varieties are striking in their properties, size and weight of berries. For example, the fruits of the red currant variety Marmeladnitsa hang on the bush until frost, without losing their qualities.
There are amazing varieties of strawberries: for example, the Dutch Panberry with white berries will decorate any table. And the dwarf Kupchikha is distinguished by a kind of large flattened berry with a strawberry aroma and a unique strawberry taste. One can say about these varieties: "When a Dutchman turns pale, the Merchant's wife turns red."

To decorate the site, we grow various ornamental shrubs. For example, the amazing Clematis burning - unpretentious, winter-hardy, originally from Siberia. The rhizome hibernates in the soil, and in the spring powerful vines-vines grow quickly up to 3 meters in height. In the middle of summer, the entire bush is covered with small, no more than 2 cm in diameter, white fragrant flowers. They are so densely arranged that the entire bush looks like one solid white cloud.

It stands out for the early flowering of Forsythia. In the spring, when there are still few colors on the shoots that have not come to life from hibernation, yellow flowers bloom on it - there are so many of them that the whole bush is painted with yellow paint.
In the middle of summer, the time comes for the flowering of the chubushnik shrub, in our area it is called street jasmine. And indeed, during flowering, a wonderful smell of jasmine emanates from it for several meters around. In our garden, there are several varieties of chubushnik - with regular and double flowers, and in the Suzdal variety, the leaves from spring to late autumn have a yellow-whitish color, which gives them a high decorative effect.
Warm summer flies by quickly in our area, and winter comes. On the long cold days, we miss our green pets so much! And so they took up indoor gardening. Now we grow indoor lemons of various varieties: from the most common (Pavlovsky, Meyer, Panderoza) to little-known varieties (Florentina, Cammune, Colored).

Next to lemons, tangerines, oranges and pomelos, pomegranates, figs, muraya and rosemary coexist well. Green pets delight us both in the garden, vegetable garden and in the house, warm the soul and give their fruits.
We offer potato planting material, seedlings and seeds of which you can purchase directly on this website. We have been sending out planting material by Russian Post for over 15 years. We have accumulated a lot of experience in packaging, so all plants reach every corner of Russia in excellent condition - from Kaliningrad to Sakhalin.
Alexander Vasilievich Lukshin, agronomist
We invite everyone to get acquainted with
Echinacea is a herbaceous perennial with high decorative and medicinal properties. It is a very popular plant among gardeners around the world.
Echinacea belongs to the Asteraceae family, it comes from North America. The name comes from the Greek word - "echinos", which means hedgehog. Most likely, this is due to its inflorescence, which, when fully ripe, becomes round and prickly.
 I want to tell you about two types of echinacea. The first is purple (Echinacea purpurea), which has been introduced into cultivation since 1692 and currently has many varieties and hybrids. It has large, exquisite purple flowers (up to 12 cm in diameter). Her flowers are located on upright rigid stems, which reach 1.5 m in height. The core of the flowers at the beginning is soft, but by the end of summer it matures and becomes prickly.
I want to tell you about two types of echinacea. The first is purple (Echinacea purpurea), which has been introduced into cultivation since 1692 and currently has many varieties and hybrids. It has large, exquisite purple flowers (up to 12 cm in diameter). Her flowers are located on upright rigid stems, which reach 1.5 m in height. The core of the flowers at the beginning is soft, but by the end of summer it matures and becomes prickly.
The second type - Echinacea strange (Echinacea paradoxa)- the only yellow echinacea in the genus. But it has a lower frost resistance than other echinaceae.
Echinacea purpurea and strange is more often grown as an ornamental plant. On their basis, modern varieties and hybrids have been created.
Over the past 10 years, breeders (primarily from Holland, Germany and America) have created several dozen varieties that differ in plant height, leaf color, size and color of inflorescences-baskets. Some varieties have fragrant buds. Varietal plants prefer fertile soil and full sun.

Echinacea grows late in spring, so it is undesirable to use them as foreground plants. But they bloom for a long time and decorate the garden in the second half of summer - from July to frost.
I have been growing Echinacea purpurea for many years. Recently I got carried away with other varieties. I was very interested in echinacea with a white color. And now on my site flaunts variety White swan (While Swan)... Plants of this variety are tall, up to 80 cm, highly decorative, with large, up to 10 cm in diameter, white flowers.
Blooms profusely and continuously from August to frost. Like all varieties of echinacea, it loves a bright place and fertile soil, where it grows well and pleases with abundant flowers.
Echinacea is, so to speak, “not a fighter,” not a conqueror. It grows for a long time in one place and does not seek to capture more space - it grows as a compact neat bush.
Echinacea is propagated mainly by seeds. I collect them when the buds-inflorescences are fully ripe and prickly. I sift them and select the fullest, ripe seeds. I store it in paper bags until spring.
It should be noted that its seeds have a reduced germination rate due to the high content of essential oils, so they germinate for a long time. I sow seeds in March-April to a depth of 0.5 cm.

For better germination, the box with seeds can be put in the refrigerator for two weeks, and then covered with foil and transferred to a warm place.
Seedlings appear in 8-14 days. During the growth of seedlings, the main thing is to observe the moisture content of the soil. Do not overfill and overdry the soil.
When the frost passes, I plant the seedlings in a permanent place according to the scheme of 30x30 cm. At first, it is advisable to shade the delicate seedlings so that they do not burn out in the sun.
Leaving is uncomplicated. During the summer, you can make 2-3 additional fertilizing with manure infusion or complex fertilizer.
I also propagate Echinacea by dividing the rhizomes. In addition, it is advisable to do this every 5-6 years, since the rhizome grows old over time and the plant feels depressed, begins to develop poorly and bloom.
I became interested in Tladiante many years ago, dreaming of acquiring this rare unusual plant with useful properties.
Doubtful tladianta(Thladiantha dubia) is the only winter-hardy perennial species among other thermophilic representatives of the genus Tladiantha, belonging to the pumpkin family.
Doubtful tladianta is a powerful herbaceous vine with edible fruits. In nature, it grows in the Russian Far East and in Northeast China.
In the works of I.V. Michurin, I read that Ivan Vladimirovich wanted to use the Tladian in selection. He planned to create perennial pumpkin crops with her participation. For example, a perennial cucumber and a perennial watermelon - it's a good idea to have such plants on your site.
I started looking for Tlandianta planting material. In one of the magazines, I came across an article by a vegetable grower from Lipetsk with the title "You will not forget the Tladian". After correspondence with the author, I managed to get several nodules of this plant, grow and propagate the tladian.
At first, I also became interested in this crop for breeding purposes, to create perennial pumpkin crops -, and. But these experiments of mine did not give any results.
Doubtful tladianta has been growing on my site for more than 20 years. The main thing that I can say about this vine is - yes, you really won't forget the tladian ...
Disadvantages and merits of dubious tladians
At first, knowing little about this vine, I assigned the best place on my site for the tladiant, where I planted its nodules. But in the end, after a few years, this plant became malicious in me.
The fact is that tladians have tuberous roots - it forms tubers in the soil, like in. This vine has yellow-skinned tubers, oval in shape. During the garden season, the roots grow in different directions from each parent plant of dubious tladians, as a result, daughter tubers are formed within a radius of up to 2 meters. And you need to be careful when digging these tubers: if even a tiny part of it remains in the soil, it will grow back into a powerful vine and give a large offspring of new tubers.
I had such a case. The dug-out tubers of the dubious tladians lay in a bucket almost all summer, dried in the sun. But as soon as they were poured onto wet soil in the fall, green shoots soon appeared.
Yes, this climbing plant can weed heavily on the site. The disadvantage of tladiants is the rapid growth of tuberous roots in the soil over long distances. But it is worth planting the tladiant tubers in any container, thus limiting their distribution, and then the plant will not "run away" anywhere. You can isolate a site with planted tladianthy tubers by digging sheets of iron or slate along its edges (to a depth of 50-60 cm).
The leaves of the tladiant are heart-shaped; they are pubescent. Therefore, when touched, the leaves stick to clothes and even just to open skin. However, there is no harm from this - the leaves of the tladiant are not poisonous and do not burn, but simply stick like Velcro.
But the dubious tladiant has not only drawbacks, but also advantages. Tladiana was named "red cucumber", and the planting material of this plant was in great demand.
Powerful shoots of dubious tladians, reaching 5 meters in length in favorable conditions, grow very quickly (several centimeters per day), forming a large green mass. Tladianta, due to its exuberant growth and rough shoots with antennae, actively rises in height and curls any support. In just a month, an overgrown liana can completely cover a vast space with greenery - cover everything that is next to it. Therefore, the tladiana is used as a way to create green arches and verticals in the garden and vegetable garden with its help, as well as cover unsightly corners of the garden with greenery. Liana blooms from July to September.
I use the tladianus as, which, with its long shoots with powerful growth, is able to quickly decorate the wall of a house, a fence, a gazebo, an arch, and figured supports of various configurations.
Just imagine how this powerful liana looks with shoots up to 5 m, hung with bright ripe fruits - "red cucumbers". And, besides, in our region this plant hibernates without problems, does not have pests and diseases.
One could say that the dubious tladiant is just a treasure for the gardener and the gardener. But not everything is so great here.
The ripe fruits of the tladiant are red, small (from 2 to 5 cm), similar to miniature cucumbers. But on top, its fruits are pubescent, and not everyone will like them. After ripening, the fruits of the tladians become sweeter, their taste is something unusual - it resembles a mixture of pumpkin and exotic plants, like baked pumpkin with notes of and.
You can use green unripe tladiant fruits in the same way as regular cucumbers.
But even with the fruiting of this vine, not everything is so successful, due to the fact that the tladiant is a dioecious plant. And in our region, local insects refuse to visit the yellow medium-sized (2.5 cm) flowers of the tladiant. Therefore, to obtain fruits, it will be necessary to carry out artificial pollination of flowers in the summer: you need to manually transfer pollen from male flowers to female ones. Widely bell-shaped male flowers of dubious tladiany with petals bent back are placed in racemose inflorescences, and flat female flowers are located singly.
Often, fruits can be set in tladiants without pollination, but there will be only a few of them on the shoots. In ripe fruits, small full-fledged seeds are formed.

In the photo: blooming tladiant; liana tladianty decorates the wall
Tladiant in medicine
Tladiant is a medicinal plant.
Ripe fruits of tladians - red "cucumbers" - normalize blood pressure.
From flowers tladiants brew healing and drink it for colds.
Tladiants tubers are also used for medicinal purposes. When boiled, their taste resembles potatoes with peas, only with bitterness. Tladiant tubers are used as a lactogonous agent (enhancing milk production in lactating women), as well as a diuretic and choleretic agent.
Reproduction and cultivation of tladiants
Tladiant reproduces quickly and easily - both by seeds and tubers.
Seeds are sown for seedlings in April, then the seedlings are planted in cups.
On site site
on the website
on the website
on the website
Weekly Free Site Digest Site
Every week, for 10 years, for our 100,000 subscribers, an excellent selection of relevant materials about flowers and garden, as well as other useful information.
Subscribe and receive!
Vegetable kitchen utensil cutter mandolin slicer fruit cutter potato ...
RUB 980.83
Free shipping★★ ★★ ★★ ★★ ★★ (4.90) | Orders (358)
Secrets of early potatoes
One of the main measures ensuring high yields of potatoes in the early stages is high-quality preparation and germination of seed tubers. The most effective methods of germinating potatoes are combined (22 days in the light and 8 days in wet sawdust) and in the light.
Sprouting potatoes
The germination time of tubers varies from 20 to 45 days and depends on the storage temperature and germination conditions (temperature, illumination, air humidity, etc.). The optimum temperature is above 10-15 degrees during the day, at least 5 degrees at night, and the air humidity is 80-90%. An increase in temperature to 20 degrees and above leads to unproductive consumption of nutrients by tubers for respiration and to excessive loss of moisture. It is very important that an elevated temperature is allowed only at the very beginning of the laying of tubers for germination: this allows you to quickly stimulate the transfer of reserve substances into shoots suitable for growth and development.
A very effective technique is sprouting with sawdust, moistened with ash infusion, sprinkled with tubers. Such germination accelerates tuberization and increases the yield of early-ripening varieties by 45-50%, and of mid-ripening ones by 110-130%.
Tubers can be germinated in boxes installed in stacks with gaps, in foil bags with holes and in any other container. Potatoes should be packed in a layer of 2-3 tubers. With proper regulation of light, temperature and air humidity, after about a month, green, strong, short shoots form on the tubers with influxes at the base and root rudiments.
Sprouting potatoes in the light is carried out in lighted rooms, greenhouses, under sheds made of polyethylene film, as well as in open areas in boxes. Early spring sun rays largely destroy surface infection in tubers, increasing field germination and reducing disease damage to plants during the growing season. Studies have shown that sprouting potatoes in sunlight reduced the damage to sprouts by Rhizoctonia (black scab) by 19.4%, and common scab by 15.8%.
Planting potatoes
Planting should be carried out with tubers weighing at least 25-40 g without signs of disease. To obtain a very early harvest, it is better to use medium and large tubers weighing 50-70 and 70-100 g, respectively. Planting should begin when the soil at a depth of 10 cm warms up to 7-8 degrees, sprouted tubers are planted at a soil temperature of 5 degrees. It should be borne in mind that it is at this soil temperature that leaves on birches or the first dandelion flowers begin to appear, which is a signal for planting potatoes.
The planting depth of tubers depends on the planting method: in the ridges or on a flat surface with the subsequent build-up of ridges. Pre-cutting of the ridges 5-8 days before planting ensures good drying out and warming up of the soil, provokes the germination of weeds, which are easy to destroy during the planting process. Tubers should be planted into the ridges to a depth of 6-8 cm. For smooth planting, the tubers are sprinkled with a layer of soil 2-3 cm. This ensures better heating of the soil and tubers, while the seedlings will be earlier and more friendly.
Potatoes and care
Caring for early potato plantings is reduced to loosening the row spacings in order to destroy weeds, retain moisture and keep the soil loose. The first inter-row cultivation is usually carried out 5-6 days after planting, the rest - depending on the condition of the soil, the presence of weeds and weather conditions.
To protect them from frost, the seedlings are covered with soil by 3-4 cm. After frost, it is imperative to loosen the row spacings with harrowing. If the plants are still damaged by frost, it is necessary to fertilize with nitrogen fertilizers. To protect potato plants from frost and get an earlier harvest, you can use plastic wrap or spunbond. However, it must be borne in mind that under the shelter a favorable microclimate is created not only for the development of potato plants, but also for weeds.
A simple and affordable way to get an earlier harvest is to mulch the soil with peat crumb layer 3-4 cm.
Cleaning
The harvesting of early potatoes for food purposes begins when the tops are still green, the bulk of the tubers has reached a size of at least 5 cm in the largest diameter and the yield of commercial tubers is 10-12 kg / 10 sq. m. Tubers of young potatoes have a very thin and delicate skin, so it is best to transport them in a rigid container - baskets or boxes. In addition, every day you need to harvest as many potatoes as will be sold on the same day.
We need a deep "dugout"
When caring for potatoes, it is necessary to keep in mind one of its biological features: the higher the soil layer above the tuber, the more stolons the plant forms. Therefore, one of the first and constant methods of care is to create a high fertile layer over the tuber.
Helping potatoes from weeds
Immediately when the first shoots appear, they must be sprinkled with a 5-6 cm layer of soil. Potato shoots have a powerful growth force and quickly break through the filled layer. With this technique, we solve two more problems: we protect the seedlings from possible frosts and sprinkle the weed seedlings with earth. In the future, it is necessary to regularly spud potato plants with fertile and preferably moist soil, while leaving young and active leaves in the sunlight. With an ordinary placement of tubers, the height of the ridge should reach 20-30 cm, with a barrow method of planting - 30-40 cm.
The first danger to which potato seedlings are exposed is frost. They can negate all our efforts that we spent on preparing the tubers for planting. If the plants freeze, then we will get the first harvest much later than planned.
To protect the bushes, in addition to sprinkling the seedlings with dry soil, cover with film, paper caps is possible. Paradoxically, weeds will also save seedlings from low temperatures. There were cases when potato plants were badly damaged in well-weeded beds during frosts, and gave a crop two weeks later. The less weeded rows, however, remained unscathed.
If the potatoes are still frozen, you should immediately water the plants with cold water. The resulting ice crystals will melt and will not cause tissue rupture.
Water and fertilizer for potatoes
Watering the potatoes gives a tangible increase in yield. Potato plants experience the highest demand for moisture during the period of intensive crop growth - in the budding and flowering phases. Therefore, during periods with a lack of precipitation, potatoes should be watered.
Recommendations for the cultivation of early potatoes often talk about top dressing. But in fact, this technique can even have a harmful effect on the crop and, especially, on its quality. The thing is that this culture has a very short growing season. Nitrogen added to top dressing will cause an increased nitrate content in tubers. Potassium and especially phosphorus move poorly in the soil and do not have time to reach the root system of plants. So feeding will be useless. But when preparing the soil, it is necessary to apply the required amount of mineral fertilizers.
Why do potato tubers turn black
Boiled potatoes often darken. This is most often due to the unbalanced application of fertilizers.
If darkening is observed from the umbilical end (this is the place of attachment of the tuber to the stolon), then the plants were overfed with potassium. As a result, the concentration of chlorogenic and citric acids increased, which, oxidizing in air, impart a dark color to the pulp. The situation is corrected by introducing carbamide at a dose of 1 kg per hundred square meters.
If the entire surface of the tuber darkens, waterlogging of the soil and an increased content of nitrogen are to blame. Phenolic compounds are formed in tubers, which are also oxidized by air. Therefore, it is necessary to observe the measure when applying nitrogen fertilizers - their dose should not be higher than 2 kg per hundred square meters.
Proper preparation of potato tubers
To get a rich potato crop, you need to protect the plants from pests and protect them from disease. This is best done when preparing tubers for planting and when the first shoots appear.
Wireworm Fight
Among the enemies of potatoes, the most common in recent years are the larvae of click beetles, or the so-called wireworms. They can, with an average number of 6-8 pieces per 1 sq. m damage up to 65% of tubers. This usually manifests itself in the form of moves made in the tubers and the yellow worms present there. The harmfulness of larvae is manifested mainly in the second half of summer with the beginning of the formation of tubers.
Scientific research has established. that the most effective method in the fight against this pest is dressing the tubers before planting. Studies at the Institute of Plant Protection of Belarus showed that as a result of treating tubers with dressing agents, their damage by wireworms decreased by 60-87%, and the yield increased by 25-50%.
For use in summer cottages and household plots, the drug "Kruiser" is recommended. It is used in a dose of 20 ml per 1 liter of water. For 100 kg of tubers, 1 liter of the prepared solution is required.
"Trojan horse" for the Colorado potato beetle
In addition, potato plants, especially early ones, are the most tasty prey for the Colorado potato beetle. Now there are many effective means of protecting potatoes from this pest. An example of this is the drug "Troy" and its analogue "Prestige Chameleon". These are preparations of complex action. They act against wireworms, all kinds of ticks and caterpillars, and also have a preventive and curative effect against late blight and other fungal diseases. They can be used to treat tubers before planting, which reliably protects potato plants from pests and diseases for the entire growth period. In addition, in the future, plants can be sprayed with solutions of these drugs.
The drug "Prestige Chameleon" is used as follows: 10 g of the product must be dissolved in 600-800 ml of water and treated with 25-30 kg of planting material using a sprayer. When processing with a working solution, the tubers are thoroughly mixed.
Prevent late blight on potatoes
The most dangerous disease is late blight. Early potatoes are especially susceptible to it. For prevention, it is very important to process potato plantings as early as possible - when full shoots appear. In more detail, the conditions for the use of drugs are indicated on the packaging of drugs, we will limit ourselves here to general information.
It is best to carry out the treatment with contact drugs mixed with systemic fungicides (doses are given in g or ml of the drug per 10 liters of water and per 1 hundred square meters of area):
- "Acrobat MC" -2;
- Ridomil Gold MC - 2.5;
- "Ordan" -2.5.
All subsequent treatments are carried out only with contact fungicides:
- Abiga Peak - 30;
- "Azofos, ps" - 40-60;
- "Azofos, k.s." - 60-70;
- Pennkoceb (tridex) -16;
- "Kuproksat" - 50;
- "Polyazophos (PKS-2)", "Polyazophos-1 (PKS-2 + K)" - 40-70;
- "HOM-k" -30.
The second treatment is carried out after 8-10 days. The average number of treatments is 3-4.
New products that are effective on potatoes have appeared in the retail network: the complex preparation "Marshal" (2 g per 10 l of water), the biological preparation "Fitosporin M" (5 g per 10 l of water).
Colored potatoes
For several years I have been fond of growing various varieties of potatoes, and recently among them there have been specimens with colored pulp - purple, blue and even red.
I started with Linzer Blau with a purple and unclassified look with pink flesh. Now my assortment has increased a little: I purchased and tested several new color varieties, which I would like to briefly tell you about.
"Foreigners" varieties of potatoes with colored pulp
Cranberry Red(red cranberry) - medium early variety, oval tuber with a smooth red skin and pink-red flesh. Possesses a good, pleasant taste, does not discolor during cooking.
All red(all red) is a mid-season variety with a delicate red skin and flesh. Its characteristic feature is drought tolerance. The tubers have a pleasant nutty flavor.
Explosion(explosion) is a new early maturing high-yielding variety. The tubers have a blue pulp. Resistant to diseases.
All blue(all blue) is a mid-late variety. Tubers are medium in size, showy blue with purple flesh, well kept, good taste. The structure of the pulp allows it to be subjected to all types of culinary processing. To maintain the color, it is important that the potatoes do not boil over.
Boro- mid-season variety. The tubers have a blue flesh and a bronze sheen rind. Used raw for salads.
Domestic varieties of potatoes with colored pulp
Currently, many breeding institutions are working to create varieties of potatoes with colored pulp. In Russia at the Institute. A.G. Lorkha, which is located in the Moscow region, was created and is already widely spreading a mid-season variety with purple pulp Lilac. Round-oval tuber weighing 70-80 g. Productivity is average, good keeping quality.
From the latest novelties of Russian breeders - the Raspberry variety with red pulp, which does not lose its color during cooking and has a good taste.
Results of the experiment
I did not create special conditions during testing of colored potato varieties, I did everything as usual. When planting in the holes, I apply a mineral complex fertilizer, during the season I carry out weeding, hilling and watering.
The soil on my site is black soil with light loam. On it, the colored varieties did not show good yields, there were an average of 7-8 tubers per bush, and of a small size. Only Explosion produced good large potatoes, which, by the way, looked more like red beet roots.
At the same time, the colored varieties are considered to show good yields on fertile and more breathable soils with light texture. Plants develop poorly at high temperatures and lack of moisture.
What is the use
Why do we need potatoes with such pulp? Of course, purple or red puree is exotic, but is it necessary to engage in complex breeding work for such an effect?
The main value is the increased content of antioxidants, which is associated with the pigment substances anthocyanins. In our body, they are not synthesized, they come only with food. Anthocyanins bind free radicals, increase immunity and prevent premature aging of cells in the human body.
In order not to lose the color of the pulp, potatoes of colored varieties must be boiled in a peel in salted water.
GROWING EARLY POTATOES - TIPS FOR GARDENERS AND GARDENERS
The potato is young, but very early
Someone just takes out potatoes for planting from the basement, while others are already laying out young crumbly potatoes on plates. Some plant hectares, while others plant in pots. The only pity is that you can't cook it right in the pan.
I have been planting early potatoes since 1970. She was forced by need, she became a widow very early, and she had three children in her arms. My husband and I lived for a long time in the Stavropol Territory, and when she was left alone with her children, she moved to her homeland - to the Smolensk region. There they gave me 14 acres of land, so to speak, lifting. I developed them and began to plant potatoes, the seeds were first given by relatives, and then my own appeared. My salary at that time was 90 rubles (for comparison: an engineer received 210 rubles). And the children had to be fed, clothed, that's when in the spring I decided to sell potatoes in the market. On a weekend early in the morning I went to the market, and by 12 o'clock my potatoes were already sorted out! This is how potatoes feed me all my life.
I plant it very early, I take out March from the basement. 2-3 buckets of potatoes, washed in a weak solution of potassium permanganate and laid out to dry in fruit boxes with ventilation holes. From time to time I spray with water and sprinkle with ashes. On April 26, I am already planting potatoes in the furrows, and they emerge three weeks earlier than others. The first time I dig potatoes on June 18, the second time - on June 22 and take a bucket to my family, on this day my daughter has a birthday, for the holiday there is always fresh young potatoes on the table. And the third time I dig for my birthday, July 1, but I constantly dig it all summer.
I plant potatoes in the ground in the spring without applying manure. In the fall, immediately after harvesting, I plant mustard on a potato bed, I do not mow it before winter, but dig up this bed with lodged mustard in the spring, make holes for potatoes and put a pinch of fertilizer for potatoes in each hole, then a little earth, potatoes on top and on it a handful of onion peels. Then I fall asleep with earth. If the ground is dry, then I water it after planting. I huddle twice a season.
After planting, I sprinkle the rows of potatoes with ash to scare off the Colorado beetles. And during the summer I sprinkle ashes twice more, maybe that's why last year Colorado didn't attack my potatoes at all. I never throw away onion husks, I collect all winter, and in spring it goes to the potato ridge.
Last year, she planted potatoes at a record early, on the third day after Easter, that is, on April 23. On June 18, I dug for the first time. Onion peel potatoes are clean and even. When I brought it to my relatives, my grandson said to me: "Grandma, no one has potatoes yet, you probably grow them on the balcony!" And I answered him: “You know, granddaughter, who gets up early, God always gives, but under a lying stone and water does not flow. Learn to get up early and work, then you will always have potatoes early! "
© Z. V. Krasnikova
Straight in pots and buckets
I plant early potatoes in buckets, pans - and the result is always satisfactory. I use Red Scarlett. But the potatoes in the bags let us down, the experiment ended in failure. This is an option for the lazy. Oily green tops have grown, but there are no ovaries. But here's what I'm interested in: have our Russian sellers really lost their conscience? After all, they sell seed potatoes for big money. Last spring, it cost 30 rubles per 1 kg. They tried to convince me that the variety is very good, I bought it, and as a result, there was not even a single sprout, so I threw it all in the trash. 1,500 rubles went down the drain. But for us, pensioners, this is a lot of money! In general, anything can happen: both good and bad.
N. Romandina Kursk region
What prevents you from planting potatoes early? It is obvious. The fact that the soil has not yet warmed up properly. There is a popular way. Scatter coal dust directly over the snow. The sun will heat up the black particles - and the snow will melt earlier.
The earliest potato?
Now eating early potatoes in June is not a problem, all supermarkets are overwhelmed with them.
But its taste leaves much to be desired. So we thought: can we ourselves grow the harvest of the “second bread” so that it will be put on the table at the beginning of summer? How to do it? I would like an agronomist to answer my question, preferably from a nearby area.
Vera Andreevna SHILOVA, Udmurtia, Glazov
The choice of planting material
To obtain an early harvest of potatoes - in the second half of June - it is necessary to select a variety with a growing season from germination to the formation of full-fledged tubers in 50-65 days. Of course, such an early variety must be adapted to the region. You can learn this from reference books or consult with local gardeners in the market, who are the first to start selling potatoes. So, the well-known early Borodyansky pink variety gives stable yields regardless of weather conditions, has excellent taste, but is susceptible to diseases.
Always try to place 3-4 varieties, because it is impossible to predict the weather of the coming season. And it so happens that last year the variety showed itself to be high-yielding, and the next year it may fail.
One of the new products that has proven itself well in our area is the early Colette variety. It stands out for its good yield and, most importantly, for its excellent taste. The high-yielding German variety Bellarosa with large tubers has shown itself well. Although it is early, its tubers are perfectly stored. Our Siberian variety Alena is not inferior to the German. It has beautiful, slightly elongated tubers with red skin and white flesh.
The variety Meteor, created by scientists from the Lorkh Institute from the Moscow Region, lives up to its name: it ripens super fast and at the same time gives a good yield. The tubers are large, the skin and flesh are yellow.
El Moon-do remains the leader in taste of foreign varieties. Its tubers, after boiling, taste as if butter were added to them. But the Impala variety can be recognized as the most productive with large tubers and a large number of them under the bush. For three seasons we are pleased with the German variety with the Russian name Natasha. These early potatoes are distinguished by good yields, disease resistance, excellent palatability and attractive tubers.
Hussar on a "horse"
The new Gusar variety of breeders from Belogorka (Leningrad region) was bred with the participation of six different types of wild potatoes, famous for their "indifference" to various diseases. Hussar is resistant to cancer, nematodes, viral diseases, alternaria, rhizoctonia, scab, however, in relation to late blight it has average indicators. The cultivar also tolerates drought well, does not attract the Colorado potato beetle and is even able to resist weeds to some extent. Tubers are attractive, short-oval, yellow, light cream flesh. The taste is good. Tubers have a long dormant period, at a temperature of 3-5 degrees Celsius they can be stored without germination for up to 7 months.
Preplant preparation of early potatoes
After choosing a variety, you need to prepare the tubers, and it is better to start this in the second half of March - early April. They should weigh between 60 and 120 g on average - no larger than a chicken egg. Large potatoes are not suitable for planting, and I do not use chopped as planting material at all. Excess wounds on the tuber always carry an additional risk of infection with viruses, bacteria, fungi, even with careful processing of the sections. The planting material must be carefully examined, while all tubers with noticeable various sores are immediately removed.
After that, it is advisable to treat the potatoes with drugs for the prevention of diseases. Currently, there are a lot of different means intended for this purpose, including such well-known ones as "Maxim" and "Prestige", which I used until I made a discovery for myself quite by accident: it turns out that we have developed an excellent drug in Russia. "TMTD-plus". It is effective in treating tubers against various bacterial, viral and fungal diseases of potatoes. "Additive" plus means that an immunomodulator and other substances are introduced into the composition of the drug, which significantly affect the increase in germination energy, and, consequently, on the acceleration of germination, increase in yield and drought resistance. It is a pity that it is sometimes difficult to acquire this product, it is not available in all stores, but imported fungicides are present in almost every outlet for gardeners.
The second drug that I really liked was Mival-Agro. It is a complex biological plant growth regulator based on living silicon. After one treatment of the planting material, success is ensured for the entire season. The drug is packed in a capsule
ly, you need to dilute one in 0.5 liters, and this amount is enough to spray 50 kg of seed potatoes. The same preparation is used to treat seedlings in the phase of 3-5 true leaves or during the budding period of plants. The solution for these purposes is prepared in the same way as for the treatment of tubers before planting. The drug significantly increases germination and germination energy, stimulates root formation, increases resistance to unfavorable growing conditions: sudden temperature changes, spring return frosts, heat and drought. It also restores the development of plants after damage (hail, low temperatures), increases yields up to 25-30%, improves product quality.
When decorating a house with flowers, we think about how well it will live among living plants. But if they delight us not only with their beauty, but also are medicinal or fruitful, this is doubly pleasant. I'll tell you about a plant that will beautifully decorate your windowsill with its creeping stems and bring you, no, not fruits, but sugar. True, not in the form of sugar familiar to everyone for tea, but in the form of a sweet substance that is contained in its leaves. One of these plants is the well-known stevia, which is native to Paraguay. It contains more than twenty glycosides of varying degrees of sweetness, which are 300 times more sweet than sugar beet sucrose. In addition, it is a low-calorie vegetable, that is, it can be consumed by those with diabetes. Stevia is also rich in vitamins, especially B group, and micronutrients. Yes, stevia is 300 times sweeter than sugar, but this plant has not justified itself. It has a sweet taste, but at the same time there is a strong herbaceous aftertaste. In addition, this sweetness does not go into solution, and when brewing, for example, tea, it does not become sweet from the addition of stevia, and if you chew its leaves, a strong pleasant sweet taste is felt at first, but soon it turns into bitterness. However, I think that soon stevia will be replaced by another sugar plant, the best in its qualities - lipia. Sweetness with vitamins Sweet lippia belongs to the vervain family. Her homeland is Nicaragua. Actually, lipia has several species that are widespread in the tropics. One species - creeping lipia - grows as an invasive plant in the south of our country and is a weed, but this species does not contain sweet glycosides. And only sweet lipia has long been used by Indians and other peoples as a sweetener. Lippia is 500 times sweeter than sugar, moreover, it is low in calories and rich in vitamins, microelements that help remove radionuclides and heavy metals, restores blood composition, its biologically active substances normalize metabolism, stop inflammatory processes and caries. Support her Lippia is an original plant. Its leaves a little resemble nettle, but they do not burn, and if you touch them, they emit a unique sweet aroma. She prefers to grow in a creeping form, and the shoots, in contact with the ground, quickly take root, so it is advisable to put supports for her and tie up the shoots so that they grow up and do not crawl along the ground. In favorable conditions, the lipia blooms profusely and for a long time, her flowers are very small, less than a millimeter in diameter, collected in inflorescences on long pedicels in the leaf axils. The flowers are self-pollinating and, under favorable conditions, form seeds even in central Russia, if flowering and ripening occurs at a stable temperature of at least +15 degrees and the duration of daylight hours at least 12 hours. Lippia is a tropical plant and grows well at an optimal temperature of + 23-25 degrees, absolutely does not tolerate frost. We propagate the houses ourselves by cuttings Lipia propagates by seeds and cuttings. The seeds are very small, so they are sown in a light substrate, slightly sprinkled with earth, covered with foil and placed in a warm place. Seeds sprout for a long time, about a month. Seedlings grow slowly at first, and only after the appearance of 3-4 true leaves, growth accelerates. While the seedlings are small, they are demanding on lighting and moisture. Over time, having got stronger, they grow well and tolerate drought. Even if the plant is very dry, it is worth watering it - and it quickly comes to life. It is easier to propagate this plant by cuttings. It is enough to cut off a piece of a branch and put it in water for a week, and it will give a good lobe of roots. Lippia itself reproduces well, as soon as the shoot touches the ground, it immediately takes root. I grow the lipia as follows: in winter, the plant is at home on the window in a flower pot. She looks good, decorating the interior with her curving shoots. In the spring, at the beginning of May, I cut the cuttings, root them in water and plant them in separate cups. At the end of May, when the threat of frost passes, I plant the seedlings in open ground according to the 20x20 cm scheme. The fact is that in the bright sun the plant is strongly oppressed, the leaves acquire a bronze tint. The planted seedlings quickly take root and give a strong increase. I put pegs next to the stems and tie up the shoots so that they do not spread along the ground. If sugar is bad for you ... And now the most important thing for the sake of which we grow lipia is the procurement of raw materials. The content of the sweetener in the aerial part is very dependent on the living conditions and the age of the plant. The sweetest leaves on the central part of the shoots, grown at a moderate temperature of about +25 degrees and with a moderate application of nitrogen fertilizers. With a lack of light and heat, the content of the sweetener in the leaves decreases, less of it in old leaves. Shoots that have not yet begun to lignify are cut off for raw materials, and dried in the shade, like any grass. Subsequently, the dried herb can be added to tea or homemade preparations. It is difficult to imagine the life of a modern person without sugar, but if it is contraindicated due to illness, it is even more difficult. Plants that have a sweet taste but do not contain sugars will help us out. When applying, please put an envelope with your address in the letter.
Alexander Vasilievich Lukshin, 431370, Mordovia, Elniki, st. Zarechnaya, 263, sot. Tel. 89053780288