ARVI (acute respiratory viral infection) is a group of viral diseases that mainly affect the upper respiratory tract. How is ARVI treated in children of different ages and how long does the disease last? What medications can be used without harm to the health of the child?
General information about the disease
ARVI is a widespread and numerous group of diseases that combine the following infectious processes:
- flu;
- parainfluenza;
- rhinovirus infection;
- respiratory syncytial infection, etc.
The source of infection is a sick person. The incubation period lasts from 24 to 72 hours. The virus is transmitted from person to person by airborne droplets. Particles of the virus enter the air when coughing and sneezing, after which they settle on various household items. There are known cases of human infection from birds and animals.
The population's susceptibility to ARVI is very high. Children under 3 months of age rarely get sick. Babies at this age retain specific immunity received from their mother. After the transferred infection, a persistent type-specific immunity is formed. In other words, a person becomes immune to only one specific type of infectious agent and can get sick when interacting with other types of virus.
Currently, the viral origin of almost all so-called colds has been proven. On average, every adult gets a respiratory infection 2-3 times a year. ARVI in children is somewhat more common. The peak incidence occurs during the cold season (late autumn, winter and early spring).

Main manifestations
Symptoms of ARVI in children:
- runny nose of a mucous nature;
- sneezing;
- lacrimation;
- sore throat;
- dry or moist cough;
- high body temperature;
- chills;
- headache;
- muscle pain.
When the first signs of ARVI appear, consult a doctor.
SARS symptoms are not always accompanied by an increase in temperature. In many children after the age of 3 years, the viral infection proceeds without fever and chills. Babies in the first years of life are more likely to give out a reaction in the form of high body temperature.
SARS in children can be combined with abdominal syndrome (abdominal pain, stool breakdown, nausea). If your baby has a stomach ache, you should definitely call a doctor at home. Such complications often occur against the background of a completely harmless cold and can lead to a significant deterioration in the patient's condition. A child who has a stomach ache and a runny nose should be treated only under the supervision of a doctor.
In some cases, signs of SARS may be mild or absent altogether. A child suffers an illness on his legs if he feels well enough. In this case, the baby infects the people around him and contributes to the active spread of the infection.
Symptoms of common SARS and flu are very similar. At the initial stages of the disease, even a pediatrician can find it quite difficult to distinguish one from the other. In this case, the flu is more severe and often causes serious complications, especially in children in the first years of life.
Typical flu symptoms include:
- a rapid increase in body temperature to 38–39 ° C and above;
- severe violation of the general condition;
- minimal changes in the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract (mild runny nose, moderate cough, slight sore throat);
- pain and aches throughout the body:
- pain in the region of the eyebrows.
You can treat mild to moderate flu at home, but under the mandatory supervision of a doctor. It is not recommended to give your child antiviral drugs on their own. Many drugs have restrictions on their use in childhood, as well as a large list of contraindications. Self-medication in this case can only worsen the patient's condition and lead to the development of complications.

Features of the course of the disease
How long does ARVI last without complications? On average, signs of ARVI in children (cough, runny nose, fever) persist for up to 3-7 days. The maximum severity of symptoms is observed in the first three days of illness. On the third day, there is usually a significant improvement. Full recovery occurs 7-8 days after the onset of the disease.
How long does the high temperature last? Depends on the individual characteristics of the child's body. Usually, fever with ARVI lasts 2-3 days, after which the temperature returns to normal. In debilitated and premature babies, fever can last up to 5 days.
How long does it take for the body to fully recover? Banal ARVI in children is easy enough. Already 2-3 days after recovery, the child feels well enough and can return to the usual rhythm of life. After the flu, weakness and loss of strength persist for up to 14 days.
Complications of acute respiratory viral infections in children most often occur on the 5-7th day of illness. The child's condition worsens, the temperature rises again, signs of respiratory tract damage appear:
- a strong, dry, painful cough (with tracheitis);
- severe cough with copious amounts of phlegm (with bronchitis);
- shortness of breath (with bronchitis and pneumonia).
If the child's condition worsens against the background of ARVI, urgently call a doctor!
The most common complications occur with the flu. Other respiratory infections are much easier and rarely last more than 7 days.
Complications
Viral infection in children is very insidious. Often, after an illness, various complications develop, which are not so easy to cope with. In most cases, complications are caused by the flu, the most dangerous form of respiratory infection. In children of the first years of life, undesirable consequences can occur even after a banal ARVI.
Bacterial infection
A virus entering the body significantly weakens its immune system. The virus itself may not be very dangerous. After 2-3 days, the body will develop protective antibodies and cope with the problem that has arisen. Here are just a failure in the immune system has already occurred, and against the background of ARVI, a secondary bacterial infection develops.
The forms of bacterial infection can be different:
- bronchitis;
- pneumonia;
- otitis;
- sinusitis;
- sinusitis;
- meningitis.
Bacterial complications develop on the 5-7th day of illness. In some forms of influenza, adverse effects occur as early as 2 days from the onset of the disease. The following symptoms indicate the appearance of a bacterial infection:
- high temperature persistence for more than 3 days;
- repeated rise in temperature on the 5-7th day of illness;
- a sharp deterioration in the general condition of the child;
- the appearance of a strong dry or wet cough.
ARVI in a child in the first years of life often leads to the development of complications. At risk are children who have recently been weaned and transferred to formula. Often complications arise in babies who have just started attending kindergarten. Prophylactic vaccinations delivered within the last two weeks also reduce immunity and provoke the development of a bacterial infection.

Digestive tract damage
Abdominal syndrome with ARVI includes the following symptoms:
- abdominal pain;
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea.
If a child has a stomach ache, this does not always indicate the development of serious complications. This reaction to a viral infection usually occurs in children in the first years of life. At the same time, the abdomen does not hurt very much, the nausea is moderately expressed, and the child's condition quickly returns to normal. Even if the baby is feeling well, it would be useful to call a doctor. Often, other diseases that have nothing to do with this group are masked under ARVI in children.
How long can a stomach ache with ARVI? No more than 3 days. On the third day, the child's stool should return to normal. If this does not happen, another cause of abdominal pain and diarrhea should be looked for.
The so-called "intestinal flu" has a completely different origin. This disease is caused by rotaviruses and is most common in children under 3 years of age. If the baby has a stomach ache, body temperature rises and a runny nose appears, you should definitely show the child to a specialist. often occurs with severe diarrhea and vomiting, which leads to rapid dehydration.
Does the child have loose stools and a stomach ache? Be sure to call a doctor!
It happens that signs of respiratory tract damage appear after the onset of diarrhea. First, the child has a stomach ache, and then on the 2nd or 3rd day there is a runny nose, cough, sore throat. This condition is common with rotavirus infection. It is believed that rotavirus leads to a significant decrease in immunity. Against this background, any infectious agent entering the respiratory tract can provoke the development of rather serious complications.

Diagnostics
Diagnosis of ARVI is based on the clinical symptoms of the disease. Cough, runny nose, and other typical signs allow a diagnosis to be made without additional examination. During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the condition of the skin and mucous membranes, and also palpates the abdomen. It is not possible to find out which specific virus caused the disease. It is only possible to identify the culprit of the problem in laboratory conditions.
Is it possible to identify and cure ARVI at home without the help of a doctor? Yes, but only with a mild course of the disease. There are situations in which one cannot do without consulting a specialist.
You should definitely call a doctor if:
- body temperature rises to 39 ° C and above (up to 38 ° C in children in the first years of life);
- high temperature persists for more than 3 days;
- the child has a stomach ache, vomiting or diarrhea;
- ARVI is accompanied by the appearance of a rash on the body.
ARVI treatment includes several important points.

Non-drug therapy
ARVI treatment is not only about taking medications. First of all, parents should create conditions in which the child's body can quickly recover. It doesn't matter which virus caused the disease.
The following guidelines will help you speed up your recovery.
Maintain an optimal microclimate in the room where the sick child is: air temperature 18-22 ° C, humidity 50-70%.
- Ventilate the room regularly.
- Don't forget about wet cleaning.
- Remove all objects that accumulate dust from the room (decorative pillows, carpets, stuffed animals, figurines).
- Don't force your child to eat.
- Encourage your child to drink as often as possible. Drinks should be warm, but not hot. Fruit drink, compote, weak tea will do.
- At normal body temperature and good weather, take your child for at least an hour a day.

Drug treatment
Various drugs are used to treat ARVI.
Antiviral agents
Specific antiviral drugs are used primarily in influenza therapy. A good effect has been seen from the use of Tamiflu (oseltamivir). At the moment, this is almost the only drug with proven effectiveness. Oseltamivir destroys the influenza virus and thus speeds up recovery. The drug has a large number of side effects, so it can only be used as directed by a doctor. The effectiveness of other antiviral agents against influenza is highly questionable.
An important point: antibacterial drugs for ARVI are used only with the development of complications and strictly according to the doctor's prescription. Antibiotics cannot cure a child of a typical viral infection.
Immunomodulators
Interferon inducers are drugs that stimulate the production of protective antibodies in the body and thereby increase immunity.
Important aspects of the use of interferon inducers:
- are most effective on the first day after the onset of the disease;
- shorten the period of fever by 1 day;
- can be used in children in the first years of life.
How many days do you need to take immunomodulators? Pediatricians prescribe interferon inducers for 3-5 days. Further use of these drugs does not make sense.
Antipyretic drugs
To reduce high fever in children, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used: ibuprofen and paracetamol. The dosage is determined individually and depends on the age and weight of the child.
How many days can I give my child antipyretics? No more than 3 days without a doctor's prescription. If the baby's condition does not improve, complications should be assumed. In this case, therapy can be continued in the hospital.
Local preparations
To facilitate nasal breathing with ARVI, preparations based on sea water are used ("Aqua Maris", "Salin" and others). These agents gently cleanse the nasal mucosa, preventing the transmission of infection to the lower respiratory tract. Preparations based on sea water are applied every 2-3 hours throughout the day until the child is fully recovered.
For sore throat and sore throat, local antiseptic preparations are used in the form of a spray. The choice of a specific remedy depends on the age of the child. The course of treatment is up to 7 days. If during the specified time the child's condition does not improve, you should consult a doctor.
Mucolytic (expectorant) drugs are used only for bronchitis and pneumonia. The use of these drugs for inflammation of the upper respiratory tract (nose, throat or larynx) does not make sense. The dosage and duration of admission are determined by the doctor.

Prophylaxis
Prevention of ARVI in children includes a number of measures.
- Limiting contact with sick people.
- Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
- Regular ventilation of the premises where the child is.
- Daily wet cleaning.
- Using a mask in contact with people with ARVI.
The best way to protect yourself from ARVI is to maintain your immunity at the right level. Good nutrition, deep sleep, regular walks in the fresh air and adequate physical activity better than any drugs will protect the child from infection with the virus. Helps fight infection and regularly moisturizes the nasal mucous membranes with saline solutions, especially during epidemics. To prevent drying out of mucous membranes, an optimal microclimate should also be maintained in all rooms.
Specific prevention of acute respiratory viral infections in children has been developed only for influenza. Vaccination is carried out in the fall before the start of the epidemic. The choice of vaccine will depend on the expected virus strain. You can get the vaccine at a children's clinic or a private medical center.
ARVI or acute respiratory viral infections are often called by the common name "colds". It is these diseases that prevail among diseases in children and force most often to turn to pediatricians.
What is the correct name: ARI or ARVI?
Both of these abbreviations are often found in medical records, and in certificates of a past illness, and in periodicals. Many parents do not understand if there is a difference between them, or if these are both valid names for the same disease.
Acute respiratory diseases (ARI) is the general name for the entire group of diseases of the respiratory organs of an infectious nature: both viral (ARVI) and bacterial. This means that acute respiratory viral infections are included in the group of acute respiratory infections along with bacterial inflammation of the respiratory tract.
In some cases, a disease that began as an obvious viral infection, with the addition of bacterial flora, can then be interpreted as acute respiratory infections. Both the name and understanding of the nature of the disease are sometimes important due to the different approaches to treatment.
Causes of ARVI
Symptoms and treatment of ARVI in children depend on the pathogen. SARS is caused by a whole group of viruses that differ in characteristic clinical manifestations, severity and other features. For example, influenza is one of the most severe viral infections of the respiratory tract, while rhinovirus infection is usually mild.
The following infections belong to ARVI:
- adenoviral;
- flu;
- reoviral;
- parainfluenza;
- respiratory syncytial;
- coronavirus;
- rhinovirus;
- enteroviral.

A virus carrier and a sick person are the source of infection. Viruses are released when talking, sneezing, coughing throughout the illness and infect objects around and in the air. The child becomes infected with a portion of the inhaled air. Viruses cause deep damage to the epithelial cells of the mucous membranes of the airways with a violation of their functions, the walls of blood vessels.
Susceptibility to viruses in children is high, even in a child under one year old. In the first three months, babies are protected by maternal antibodies obtained with breast milk.
The incidence is higher during the cold season. With a periodicity of 3-4 years, there are epidemics caused by a virus to which there is no immunity. SARS in children under 1 year old can cause parainfluenza viruses, enteroviruses, adenoviruses. The disease can be life-threatening in children at an early age with a severe course of viral infection and the development of complications (more often pneumonia)
Why children often get ARVI
Factors contributing to frequent ARVI in children are:
- closer contact of children in teams;
- a variety of pathogens: immunity, moreover, is not long-lasting, is developed only to one type of virus, other types and types of viruses can cause a new disease even in a child who has not fully recovered;
- insufficiently formed immune system in children under 2 years old or decreased immunity in older children under the influence of various factors;
- lack of physical activity or physical inactivity;
- the presence of chronic foci of infection;
- hypovitaminosis;
- anemia;
- insufficient care for children, allowing hypothermia, staying in wet shoes;
- insufficient hardening;
- unventilated rooms;
- lack of separation from a sick family member;
- unfavorable ecological situation;
- hereditary predisposition to respiratory diseases.
Symptoms
The incubation period of ARVI in children is short: from several hours to 3 days, depending on the type of infection, the infecting viral dose, the state of the child's defenses.

The first signs of ARVI in a child:
- anxiety or, conversely, lethargy;
- decreased appetite;
- fever with chills;
- sneezing, nasal congestion;
- dry cough;
- children in older age have a headache.
Symptoms of ARVI in children depend on the age of the child:
- In the first year of life, the child becomes capricious, restless. A stuffy nose is the reason for breastfeeding and sleep disturbance, since the baby does not yet know how to breathe through the mouth. Acute respiratory illness quickly causes shortness of breath. When a child coughs, it can vomit.
Often, high fever is poorly reduced by antipyretic drugs. Children with high fever may experience seizures. It is not uncommon for a respiratory infection to be accompanied by an upset stool.
In many children, the smell of acetone is noted from the mouth due to intoxication, the manifestation of which can also be vomiting, gray skin color.
The condition can be complicated with the development of false croup: difficulty breathing due to spasm of the glottis. It is manifested by whistling noisy breathing, pronounced anxiety, shortness of breath with difficulty breathing, a barking rough cough, a bluish tinge of the skin. Often, ARVI is complicated by pneumonia.
- In children 2-3 years old, the infection causes damage to the larynx, bronchi. clinically, this is manifested by intense coughing, hoarseness. The inflammatory process can capture the Eustachian tube and is often complicated by otitis media. Severe ear pains prevent the child from falling asleep.
SARS at this age is dangerous due to frequent serious complications: inflammation of the maxillary sinuses, inflammation of the bronchi or lungs. At high temperatures, the smell of acetone and febrile convulsions are also possible from the mouth.

The manifestations of ARVI also depend on the type of infection, each of which, in addition to general symptoms, has some peculiarities.
So, for example, the symptoms of intoxication are characteristic of influenza in the first two days (more pronounced than catarrhal phenomena):
- sharp headache;
- severe weakness;
- fever to high numbers;
- pain in the eyeballs when moving them;
- muscle pain, body aches, etc.
On the 2-3rd day, manifestations of tracheitis appear in the form of a dry annoying cough and pain along the trachea.
Parainfluenza differs in a slight increase in temperature and damage to the larynx (barking cough, hoarse voice), a relatively mild course. But in babies at an early age, laryngostenosis may develop.
Adenoviral the infection is characterized by conjunctivitis (with discharge from the eyes), inflammation of the tonsils, swollen lymph nodes. Quite often, dyspeptic manifestations in the form of loose stools and vomiting appear in children. A long course of the disease with a second wave of fever is often noted.
Rhinovirus the infection often proceeds at normal temperature and is characterized by profuse runny nasal discharge, lacrimation.
Respiratory syncytial an infection that affects the lower respiratory tract is especially dangerous for infants due to the development of bronchiolitis and interstitial pneumonia.
Hazardous symptoms requiring immediate medical attention:
- Hyperthermia: if the temperature has reached 38.5 0 C and continues to rise rapidly, not responding to antipyretic drugs. A danger sign for complications is the duration of the fever for more than 5 days.
- Violation of consciousness in a child, fainting.
- Convulsions.
- Severe headache, repeated vomiting.
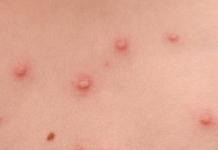
- Rash on the skin of any nature.
- Dyspnea.
- The sputum is pink in color or streaked with blood.

Complications of ARVI in children may be associated with:
- With the most viral infection:
- infectious toxic shock - a pronounced intoxication of the body caused by the action of the toxin of the pathogen;
- serous meningitis - inflammation of the meninges when viruses overcome the blood-brain barrier;
- encephalitis - inflammation of the very substance of the brain;
- hemorrhagic syndrome - increased bleeding due to damage to the vascular wall.
- With the addition of a bacterial infection:
- sinusitis;
- bronchitis;
- pneumonia;
- otitis media, etc.
Diagnostics
The doctor makes the diagnosis based on the clinical manifestations of the disease. To accurately determine the type of virus, one of the methods can be used laboratory research nasopharyngeal mucus - PCR or express immunofluorescence method. In retrospect, the diagnosis is confirmed by examining paired blood sera according to an increase in the titer of antibodies to a certain type of virus.
Treatment
ARVI treatment in children under one year old is carried out in a hospital. Children of any age are also hospitalized with a severe course of infection, with the development of a complication or with unfavorable living conditions.

How to treat ARVI in children? The most important thing is not to self-medicate. From the first day of the illness, you need to contact a pediatrician and carry out all his appointments. Only a pediatrician can determine exactly what kind of medicine is needed at a certain stage of the disease and taking into account the age characteristics of the child's body.
A typical protocol for the treatment of ARVI as a basic therapy recommends keeping bed rest during the period of fever. Create an elevated head position using a pillow. This will make breathing easier and prevent the aspiration (inhalation) of vomit in case of vomiting. The air in the room should be fresh, humidified
It is also obligatory for the child to drink plenty of water in the form of boiled water, fruit drinks, rosehip broth, tea.
You can also prepare solutions Glucosolan, Regidron, etc. Let the child drink the liquid that he likes. This will compensate for the loss of the body at an elevated temperature and prevent the thickening of phlegm in the respiratory tract. The liquid must be injected regularly, even if the child refuses, using a syringe (without a needle).
But it is not necessary to force-feed children during illness. Food should be easily digestible, mainly dairy-vegetable, fortified and age-appropriate in composition and calorie content.
Many mothers are interested in the question: how to quickly cure ARVI in a child? We must strive not for a quick cure, but for the correct treatment so as not to harm. Young children must be sick: in this way, the child's immune system "learns" to fight microorganisms and adverse factors. No treatment regimen for ARVI in children guarantees quick effect: the body itself copes with the disease, you just need to help it in this.
It is possible to cure ARVI in a child without special medications, helping the body to cope with some problems. One of these problems is nasal congestion and the inability to breathe through the nose. At the same time, it is recommended for babies to bury saline solutions bought in a pharmacy (with sea salt), or freshly prepared beetroot or carrot juice into the nose.

In babies, you can free the nasal passages with a small rubber bulb or cotton swabs (moistened with boiled water or vegetable oil). Vasoconstrictor nasal drops (children's forms of Naphthyzin, Galazolin, Protargol) can only be used with a stuffy nose in babies after 6 months. no more than 3 days, so as not to cause mucosal atrophy.
Reduction of a runny nose and cough will be ensured by inhalation - inhalation of the vapor of aromatic oils. For this purpose, the following are used: bronchicum-inhalate, tussmag-balm, balm "Doctor Theiss", etc. For this, you can add a vegetable substance to an open saucepan with hot water (2 tsp of balm for 2 liters of water). With the doors and windows closed, the child, being in this room, will inhale therapeutic vapors for about an hour.
The temperature should not be reduced to 38 0 С, it indicates the body's resistance, and viruses die with it. Temperatures up to 38 0 С should be reduced in babies up to 2 months. or if the child has febrile seizures. At temperatures above 38 ° C, you can use Paracetamol, Nurofen in an age-specific dosage, suppositories with antipyretic drugs. You can also lower the temperature with an enema with water (room temperature) or rubbing the body with the same water.

Phytopreparations can also be used in the form of medicinal herbal baths and rubbing with balms ("Doctor Theiss", Bronchicum-balm, "Doctor MOM", etc.). You can rub them into the skin 2-3 p. per day for about 5 minutes. children of any age (including newborns).
Water for healing bath should be at a temperature of about 38 0 C. A herbal preparation is added to it (20-30 ml or a strip from a tube of 10-20 cm), the duration of the bath is up to 15 minutes. When rubbing, inhaling the vapors, essential oils penetrate the body and have an anti-inflammatory, soothing effect, thin phlegm, and reduce coughing.
Cough syrups can be used from 6 months. Lozenges, lollipops, decoctions are not recommended for young children. Bronchicum syrup is not advisable for infants and children prone to allergies (it contains honey). Plantain syrup "Doctor Theiss" is prescribed for difficult sputum separation. Syrup "Doctor MOM" will help you with a convulsive dry cough. All herbal remedies should be used as directed by a pediatrician.
Antiviral drugs with ARVI, it should be used from the first hours of infection, but no later than 3 days. Recombinant (synthetic) interferon preparations (Viferon, Anaferon) are used in children of any age, they stimulate the production of interferon in the body, increase local immunity in the respiratory tract mucosa. Effective with influenza Remantadin in 1-3 days of illness (used from 7 years). Convincing data in favor of the effectiveness of other antiviral drugs in ARVI have not been obtained.

Antibiotics they have no effect on the virus. They are used for complications, with layering of bacterial microflora, with prolonged fever, with a high level of leukocytes in the general blood test. They use drugs of the penicillin group, cephalosporins, macrolides.
Prophylaxis
Prevention of ARVI in children includes non-specific and specific measures.
Non-specific measures include:
- good nutrition in terms of composition and calorie content;
- providing the body with vitamins;
- hardening according to an individual scheme, providing for the regularity of hardening procedures, a gradual increase in the hardening dose of exposure;
- sufficient physical activity of the child;
- daily walks in the fresh air, etc.
Specific preventive measures include influenza vaccination, the use of antiviral drugs when there is a threat of infection (Oxolinic ointment, Remantadin, Interferon).
It is unlikely that anyone will be able to avoid ARVI in a child, given the prevalence of viruses and short-term immunity after infection. It is only important to contact a pediatrician in a timely manner and follow his recommendations in order to cure ARVI in a child without allowing complications.
In contact with
classmates
It is practically the same for both a baby in the first three years of life and for older children. Many parents are interested in a logical question: is it correct to assign the same type to children under 3 years old and for those who are 3 or more? In this article, we will talk about the factors contributing to the disease and the differences in its therapy. What is the treatment regimen for children from 3 years of age and older, please read below.
There is an established opinion among doctors that the younger the child, the harder he suffers a viral infection... Therefore, if ARVI is diagnosed for the first time in a child at the age of 3, how to treat a “new” disease for him should not be solved without consulting a specialist. This is due to the not yet formed immunity and the ability to fight viruses from the outside.
On a note! In children who are breastfed, maternal immunity works, so they are less susceptible to viral diseases, and the disease is easier and faster.
 Of course, the therapy prescribed by the pediatrician must be adjusted according to the age of the child... Most drugs, including antiviral drugs, can only be used from 3 years of age. Often, doctors prescribe such drugs to children and young people, but at a lower dose.
Of course, the therapy prescribed by the pediatrician must be adjusted according to the age of the child... Most drugs, including antiviral drugs, can only be used from 3 years of age. Often, doctors prescribe such drugs to children and young people, but at a lower dose.
Anyway, but treatment of ARVI in children of all ages requires compliance with certain rules... Only then the result will be obvious already on the 3-4th day.
Treatment of children aged 3 to 9 years after consultation with the pediatrician can be done at home, except for severe cases with complications.
Treatment: general approaches
Approaches to ARVI treatment approved Clinical guidelines and are practically the same for children of all ages. The adjustment is carried out by the doctor, taking into account the severity of the disease and the characteristics of the child. Below are the basic rules of therapy.
- Treatment is prescribed only by a doctor.
- Under no circumstances do not self-medicate, prescribe antiviral drugs to your baby, and even more so antibiotics.
Remember, a parent is not a doctor. It is almost impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on external symptoms. The parental task is to observe the child and describe the symptoms to the doctor as accurately as possible.
- Do not bring down the temperature below 38.5... Of course, everything is individual: some children tolerate well, others - already at 37 degrees, they fall from their feet from weakness, become lethargic, do not respond to their parents, and it is impossible to distract or captivate.
The doctor always focuses on the fact that those parents who, when the temperature appears, immediately throw all the artillery to fight against 37.5, "do not treat, but cripple." Heat is a protective tool of the body... There is a temperature - the body is fighting viruses and bacteria.
To bring down the temperature means to condemn the body to long-term recovery. If at a high temperature the child does not express complaints, is active, he does not have neurological problems, then it is definitely better to give him more drink. Antipyretic comes in handy if the temperature continues to rise.
- Premature cancellation of drugs is unacceptable... It is not uncommon for the child to feel better, and the mother willfully cancel the treatment. In the best case, you can get a secondary infection, and in the worst case, a serious complication. Cancellation of the drug, as well as adjusting the dose, should only be dealt with by a doctor.
- Combination of daily irrigation and rinsing of the nasal cavity, as a rule, gives a positive trend in the course of the disease.
- Do not use alcohol solutions and rubbing bite as antipyretic agents... Such self-medication is fraught with burns and poisoning!
Psychological factors of the disease
 Do not forget that an important role in the course and severity of the disease, and indeed the social and psychological state of the baby plays a role in the risk of getting ARVI.
Do not forget that an important role in the course and severity of the disease, and indeed the social and psychological state of the baby plays a role in the risk of getting ARVI.
Psychologists say that the most vulnerable are children aged three years and older, who:
- lost contact with mom,
- suffer physical punishment
- do not find a response to their requests and needs, which are ignored, to which other family members do not listen,
- brought up in a family where it is permissible to yell at the child and other family members.
Children from 3 to 4 years old
This is exactly the age when the child "breaks away" from the mother and is forced to go to kindergarten (3-4 years). Preschoolers tend to be very painful about parting with their parents. often experiences a sense of fear and anxiety. In addition, the new team is the interchange of bacteria and viruses.
Few people manage to survive the adaptation period without the formula "three days in the garden, two weeks at home." Children in this group are more likely to get sick with the beginning in their life. kindergarten: whims and the manifestation of the first symptoms of acute respiratory viral infections are often associated with a change in the usual way of life.
Children from 5 to 6 years old
In this age there is a "outgrowth" of some diseases... The frequency and severity of the disease depends on how often and how severely the child was sick in the previous 2-3 years. If the treatment of the first episodes of the disease was carried out adequately, then the immune cells have undergone the correct "training" and will be able to competently respond to subsequent viral "attacks".
If the child did not go to the kindergarten and at this age first got into the children's collective, then, most likely, the incidence scenario will be similar to that according to which children of an earlier age get sick. If the adaptation is passed, but the child continues to be ill, then this may be due to an increased load on the child's body:
- developing classes and circles,
- sport sections,
- transition from kindergarten to school,
- increased requirements for the results of the baby's activity.
Sometimes a new routine is fraught with a considerable load and, as a result, ARVI, which was "helped" by overwork and stress. At this age, it is important to listen to your child.... He tells you that he does not want to go to kindergarten, goes with tears, complains about the children, the teacher, food - wait for ARVI. After all, the child subconsciously understands that getting sick is the only way to stay at home.
Children 7-8 years old (up to 9 years old inclusive)
For a long time the dependence of the disease on external factors has been proven that leave their mark on the life of a little person. Just 7 years old is the time when it is time to go to school. Children find themselves in new conditions, and this is a strong "shake-up" for the child's body, which can respond to it quite sharply. For example, fever, fever, general malaise.
Age-specific drugs
 Treatment of ARVI in children over 3 years old is based on three big whales: regimen, diet and drug therapy.
Treatment of ARVI in children over 3 years old is based on three big whales: regimen, diet and drug therapy.
During illness, it is important to try to limit the baby's motor activity, ask him to go to bed and observe bed rest. Feed only on demand... Doesn't want to eat - no need to force.
And here you need to drink a lot... It can be a variety of teas, juices, plain water.
In combination with the above actions, symptomatic therapy is carried out. Each age has its own dosage of the drug.
Antiviral
According to the instructions, these drugs are not used to treat children. The dosage is prescribed only by the pediatrician.
| The drug and its form | Dosage |
|---|---|
| Arbidol (tablets and syrup) | From two to six years - 2 scoops or 1 tablet 1 r / day; From six summer to twelve - 4 scoops or 2 tablets of 50 mg. The tablets are swallowed strictly whole. |
| Ergoferon (tablets) | Strictly for children over three years old. The tablets dissolve but are not swallowed whole. Reception should be started as early as possible at the first signs of illness. On the first day, you should dissolve one tablet every half hour. On the second day, the volume is reduced to 1 tablet 3 r / day. |
| Rimantadine (tablets, capsules) | Tablets can be taken strictly from the age of seven, 1 tablet 2 r / day. |
| Orvirem (syrup) | 3-7 years: on the first day, 3 measuring spoons are prescribed 3 r / day. On the second day, 3 h / spoon 2 r / day is enough. On the fourth day of treatment, the dose is reduced to 3 h / spoon 1 r / day. 7-10 years: 5 h / spoon 3 r / day during the course of treatment. |
| Viferon (rectal suppositories) | Viferon 1 - 150 thousand IU each are prescribed for children under 7 years old, 1 candle 2 r / day for 10 days. Viferon 2 - 500 thousand IU each for children over 7 years old, 1 candle 2 r / day. |
Important! Antibiotic therapy for ARVI is not effective. Only a complicated form of the disease gives the right to take antibiotics as prescribed by a doctor.
Antipyretic
 Before using any antipyretic, be sure to read the instructions. Many drugs in this group have age restrictions.
Before using any antipyretic, be sure to read the instructions. Many drugs in this group have age restrictions.
Candles are considered ideal for use., they are absorbed faster than others through the intestines into the blood. The syrup takes effect in half an hour. Chewable tablets are not for everyone due to the presence of chemicals that can cause allergies.
Among the most common medicines that reduce fever are the following.
Carefully! It is unacceptable to use Aspirin as an antipyretic in babies of any age group. It can only be prescribed by an ambulance or hospital doctor at temperatures above 39.5 and other life-threatening signs as an injection.
Antihistamines
Designed to reduce swelling of the mucous membranes, relieve nasal congestion, remove the possible risks of allergies.
- Erius. In the form of a syrup, it is prescribed for children according to age restrictions: 6-11 years old - 5 ml of syrup 1 r / day;
- Fenistil. Drops. For children aged 3 to 12 years, 15-20 drops of the drug are prescribed 3 r / day.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine recipes will help alleviate the child's condition. Before use, you should consult a pediatrician for contraindications.
Important! Treatment with folk remedies cannot be considered the main type of therapy. Only in combination with traditional treatment, the result will be obvious.
For children from 3 to 9 years old, the following can be applied:
- Collection for drinking based on chamomile, lemongrass, linden... Ask your little one to drink half a glass of the broth every hour and a half.
- Lemon infusion with honey and a piece of ginger... Not recommended for children with high sensitivity to honey.
- Relieve a debilitating cough will help cabbage leaf heated to room temperature... You need to spread it with a thin layer of honey and apply to the chest. Wrap up with a warm towel and leave until morning. The procedure is contraindicated at elevated body temperature.
- Rosehip decoction... Dried rose hips in the amount of 6 tablespoons must be poured with boiled water and taken 2 hours after infusion.
Useful video
Doctor Komarovsky on the treatment of acute respiratory viral infections in children:
Conclusion
- Treatment of children after 3 years of age begins with... If the child is planned to be sent to a kindergarten or school, then six months before this event, it is worth starting to prepare the baby for this event. Preparing parents is to understand that the child will inevitably start to get sick. Mild and moderate ARVI up to 8 times (some pediatricians believe that up to 12 times) per year are considered the norm for a healthy child.
- Disease therapy is based on adherence to the regimen, diet, creating conditions for proper care for the baby and symptomatic therapy.
- A doctor's consultation (at least primary) for ARVI is required... Only a doctor can suspect a child's complications or other, more serious illness. It is ideal to keep a diary of illness in order to record changes in the condition, behavior, mood and reactions of the baby to medications and “grandmother's” drugs, if parents use them as therapy.
In contact with
Most often, respiratory viral infections affect children. This happens for a variety of reasons. But the disease always brings with it not only the deterioration of the child's condition, but also excitement for the parents. After all, treating your baby like yourself will not work. They should not be given drugs for adults, and the characteristics of the disease may differ. Therefore, many parents ask themselves about ARVI in a 2-year-old child, how to treat it and how to do it right.
Temperature with ARVI in a child
In fact, it is simple to cure ARVI, it is only important not to lead to complications and not to use medications for adults. Then the baby will get rid of the disease and will feel cheerful again.
Causes of ARVI
In most cases, ARVI is caused by viruses transmitted by airborne droplets. A sick person who spreads the virus becomes the source of the disease. Such a sick person is most dangerous in the very initial stage, because sometimes it can pass without obvious symptoms. In this case, the virus is still secreted from the body and infects others.
But in the case of young children, the transmission route can also be domestic, transmitting the virus through toys or dishes. The patient coughs and sneezes, spreading particles of phlegm on various objects. When these items are used by a healthy child, infection occurs. Therefore, during epidemics, you should be careful about hygiene and monitor the environment, identifying those infected.
Incubation period
The average incubation period is about 2-5 days. It all depends on the virus and its amount in the body. In some cases, the incubation period can be reduced to several hours. A long period occurs in children with good immunity or when too little of the causative agent of the disease enters the body. Therefore, in order to identify itself, it will need a little more time for reproduction. During the incubation period, children remain sources of the disease, transmitting it to others who have come into contact with them.
ARVI forms
The forms are divided depending on the causative agent of the disease. The infection can be:
- rhinovirus,
- coronavirus,
- adenovirus,
- parainfluenza.
The rhinovirus form is most often one of the mildest and its course is the simplest. With coronavirus diseases, the child has to be sick a little longer, with more pronounced symptoms. Adenovirus infection is complemented by the symptoms of conjunctivitis, and parainfluenza has a cough and high fever in symptoms.
Complications of ARVI disease
Due to the peculiarities of the structure of the nose in infants, complications may occur with ARVI. In some cases, they spill over into more complex diseases in the form of bronchitis and pneumonia. This is due to narrower nasal passages, looser mucosa. Therefore, during inflammatory processes in the nasal cavity, edema occurs, interfering with the normal outflow of mucus and interfering with breathing.
You may notice that it is difficult for the baby to breastfeed, he refuses food and becomes restless. This affects his general condition negatively, which adds excitement to the parents.
Also, the structural features of the nasolacrimal canal help infections get from the nose into the eyes. Insufficient development of valves and a short canal lead to conjunctivitis during ARVI. There may also be a complication in the form of otitis media or sinusitis. And at very high temperatures, febrile seizures develop.
ARVI in children under 1 year old can be complicated by croup. This is an inflammation of the larynx, characterized by shortness of breath, dry barking cough. This condition is dangerous due to increased swelling and possible suffocation. Therefore, an attending physician is required who will prescribe necessary treatment.
Symptoms of ARVI in children
For all types of acute respiratory viral infections, some symptoms are characteristic, which can be well pronounced or very little:
- temperature increase,
- loss of appetite,
- anxiety and tearfulness,
- runny nose,
- cough.
With adenovirus infection, conjunctivitis always joins, causing redness and dryness of the eyes, lacrimation. Lymph nodes may also enlarge.
In some cases, with ARVI, loose stools or a small rash may join the usual symptoms. Diarrhea usually occurs at the onset of the disease, and disappears after a couple of days. The rash can appear all over the body or parts of it and disappear quickly.
In fact, an acute respiratory viral disease is not as bad as its complications. Therefore, you need to notice incomprehensible symptoms in time and immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
Usually, special diagnostic methods are not used, but a doctor will order a blood and urine test. Also, the child needs to listen to the lungs with a phonendoscope and conduct a general examination.
It is not advisable to engage in self-diagnosis and try to make a diagnosis. It should always be borne in mind that a childhood disease differs from acute respiratory viral infections in adults. Therefore, the treatment should be somewhat different.
Antipyretic drugs
When the temperature rises to 38 ° C, antipyretic drugs can be dispensed with. The body at this time is fighting the virus, producing antibodies to it. But in the case of a larger increase, it is necessary to normalize the temperature. This is especially true for children in the first year of life. It is not advisable to let them fever for a long time, it is dangerous for their health.
It is most convenient to use syrups or suppositories. There are also chewable tablets, but they can be given to children 2 years of age who have teeth. These forms of drugs are more convenient to apply to children. Syrups and chewable tablets usually begin to affect the temperature after 20 minutes, and suppositories after 30 minutes. But it is candles that are convenient in cases where children do not want to eat, and the medicine needs to be swallowed.
When choosing antipyretics, you need to understand that syrups can contain dyes and additives that cause allergic reactions. When buying a drug, be sure to pay attention to the child's age. The instructions always indicate this precisely and supplemented with the correct dosage. It is advisable to stick to it and not give the medicine to children more often than 4-5 hours after the last dose.
How to understand whether antipyretics are necessary at a temperature
There are usually two types of temperature rise. One of them is pink. In this case, the child's skin is rosy, he is quite active and plays games with pleasure. The skin is warm and slightly damp to the touch.
In this case, you should not rush to antipyretic drugs. In a child, heat transfer is quite conducive to heat production. Therefore, you can limit yourself to drinking plenty of fluids. In this case, it is important to observe the humidity and temperature conditions in the room.
With a pale fever, the child will have pale skin, his limbs will be cold, and he is lethargic and tired. In this case, heat transfer during heat production is inadequate, because peripheral blood circulation is impaired. Therefore, the temperature must be brought down without fail. You can wrap the child up and put socks on him.
It is necessary to give antipyretic drugs to children with heart disease, with a history of febrile seizures. And in the case of a child under 3 months old, it is not advisable to give him such medications without a doctor's prescription.
Fighting a runny nose
A stuffy nose prevents the child from breathing and eating normally. Therefore, symptomatic treatment should also relieve the common cold. For this, special nasal drops are used 3-4 times a day. Children under one year old need to drip them before eating. This will help loosen up the sinuses and allow him to enjoy eating in peace.
But you cannot apply all drops in a row. For children choose only children and allowed for their age. It is undesirable to use them for a long time, because they can cause partial atrophy of the mucous membrane, which will reduce its functions.
You can help the mucous membrane with moisture. This will help her to swell less, get rid of the virus faster and prevent the crusts from a runny nose from drying out. For this, inhalation is used. But for a child, it is better to purchase a special inhaler, and not use a pot of boiling water for inhalation. First of all, safety is important.
It is not advisable for children under one year old to carry out such inhalations. It is necessary to carefully examine the snot coming out of the nose. If they are thick and green, and there are bleeding cracks in the nose, then inhalation is prohibited. Also, do not do them for pain in the ears, this will lead to complications in the form of otitis media. And constantly flowing snot and a wet nose do not require inhalation at all.
What not to do with ARVI
Some adults wipe the surface of their skin with a solution of alcohol or vinegar at elevated temperatures. But children are strictly forbidden to do this. The solution can be absorbed into the skin and vaporized during inhalation. This will lead to poisoning of the body, making the disease worse. If you want to lower the temperature by rubbing, then let it be plain water.
Do not give children drugs for adults, even in the form of half a tablet or one drop in the nose. These drugs are designed specifically for the adult body, and even half the dosage can harm the baby. Treatment of ARVI in children with drugs for adults is impossible. Better it will be 3 drops in the nose or the whole pill, but just drugs for children.
When the temperature rises, the feet of children should not be steamed. At such a small age, in the first and second year of life, it is better to avoid such procedures altogether. Even warming with dry mustard in socks is not desirable. The skin of children is very delicate and the irritant in the form of mustard can lead to unpleasant consequences, especially for children under one year old.
You cannot warm up the bronchial area and apply warm compresses on them, which grandmothers like to advise so much. This helps to increase blood circulation in this place and "lower" the disease lower. In the future, this can cause complications in the form of bronchitis. It is better to use paraffin ointments, but only with a doctor's prescription.
It is not worth using honey in the treatment of children. They may be allergic to it, which will only worsen the condition.
Help with treatment
To get rid of the intoxication of the body with the waste products of viruses, you need a sufficient amount of drink. It also helps when the temperature rises. If a symptom in the form of vomiting or diarrhea has joined the ARVI, then the fluid replenishment should be constant. It is not necessary to drink large portions of liquid. It is enough to give 1 - 3 tablespoons of water every few minutes. This method will help you avoid dehydration and complications.
As a liquid, you can give plain water or a decoction of chamomile. For 1 liter of water, you need 3 teaspoons of chamomile flowers. Do not use water sweetened with honey or sugar.
It is imperative to keep the room temperature no higher than 20C and air humidity. The condition of the mucous membranes depends on this. The higher the temperature and the drier the air, the faster the mucous membranes will lose moisture. In this case, viruses will begin to multiply much faster.
Do not forget about constant airing of the room and wet cleaning. This will reduce the number of viruses, and fresh air is always good for you. If possible, it is worth taking the child out into the street. In this case, it is not necessary to go somewhere, it is enough to wrap it up and take it to the balcony. But it is better to do such walks after the condition improves.
What to do with diarrhea and vomiting
In some cases, stool disorder or vomiting is associated with the disease. In this case, it is advisable to water the child, preventing dehydration. Also use sorbents to eliminate intoxication of the body. They will help to remove some of the toxic substances.
Be sure to monitor the child's condition and use dehydration agents. Pay special attention to children under one year old. They are small and their body does not contain a large amount of fluid, while it is quickly lost. And this is a terrible complication.
For diarrhea, a special diet is prescribed. With adults, this is much clearer and easier, therefore, you should consult a doctor with a diet. Usually, children are allowed to fermented milk products, boiled vegetables and soups from them, rice and oatmeal.
Babies should not be separated from breastfeeding. This is the source nutrients and guarantees protection against infections. After all, it is able to strengthen the immune system and helps during diseases.
Preventive measures
If a sick family member is found, it is worth protecting him from communicating with the child. Ideally, he should be settled in another room until he recovers. It is imperative to ventilate the room and carry out wet cleaning three times a day. When communicating with a patient, wear a mask, and after communication, wash your hands, because viruses can be transferred from them to the child.
You should not visit public places with children during outbreaks of SARS epidemics. It is better to take a walk with them in the fresh air in the park or in the yard of the house, where you do not need to contact other people.
Knowing how to treat children, one should not neglect prevention. Therefore, you can gradually temper and try to improve immunity. For this, special preparations are used. Immunomodulators will be prescribed by a doctor, based on the characteristics of the baby and his age. The same applies to antiviral drugs, which can also be taken for prevention.
The treatment of ARVI in children should be given due attention, given how important this issue is. Firstly, in the absence of proper therapy and in case of its untimely beginning, the likelihood of serious complications increases (especially since the child's body is not yet ready to resist the disease on its own). Secondly, children sometimes have to get sick with acute respiratory viral infections up to five times a year. This disease is highly prone to spreading rapidly.
To the healing process- especially when it comes to the health of the child - cannot be approached superficially... Before using this or that medication, you should definitely consult a doctor, read the instructions for the drug, find out its indications and contraindications, and read reviews of other users on the Internet. In addition, there are certain recommendations that should be followed to accelerate recovery.

The treatment of ARVI in a child must be approached seriously and responsibly
So, the treatment of ARVI in children will be ineffective if the following recommendations are not followed:
- Drink as much liquids as possible - apart from the usual drinking water useful herbal, lemon and raspberry teas, compotes, and juices (preferably diluted).
- You should not feed the baby "by force" if he has no appetite and does not want to eat. Food should be easily digestible. In particular, one should remember about the benefits of dairy products, vegetables, fruits and cereals. Garlic is mandatory for inclusion in a therapeutic diet, since it contains phytoncides that destroy viruses.
- The room in which the sick child is located must be regularly ventilated. This will shorten the duration of the disease and avoid repeated self-infection. It is clear that while airing the baby it is better to take it to another room or dress it warmly.
- We must also not forget about wet cleaning, which helps to clean the surfaces of things and objects from viral agents that have settled on them. It's just undesirable to use chemical detergents in this case, so as not to harm children's health even more.
As a rule, it turns out to determine ARVI according to certain signs, which are sometimes difficult for adults to endure - what can we say about children (especially small ones) who suffer a lot because of:
- high temperature indicators of the body;
- severe rhinitis;
- coughing fits;
- general malaise.
Symptoms of the disease in children under 1 year old, 2,3,4,5,6,7,8 and 9 years old are, in principle, the same - only, the younger the child, the weaker his immunity (which has not yet been fully formed ) and, accordingly, it will be harder to endure the manifestations of infection. Is that small children who receive protective antibodies with breast milk are more resistant to the effects of the disease.
To reduce suffering from overly pronounced symptoms (and some of them - for example, too high a temperature - can generally lead to irreversible changes in the body, that is, are extremely dangerous to health), doctors prescribe drugs for the symptomatic treatment of ARVI.
What to give to a child with a high fever? Fever can be treated with antipyretics. In particular, children are allowed to use Panadol, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, and so on.
The cough is treated with expectorants and antitussives (you should consult your doctor before choosing the appropriate drug for the appropriate therapy, as this depends on the nature of the cough and its causes).
Antiviral agents
How to treat a child if he is sick with ARVI? Without fail, the doctor prescribes antiviral drugs in order to eliminate the immediate cause of the disease, that is, the virus.
These drugs usually contain interferon, or inhibit this protein in the human body. It is interferon that kills the infection, preventing it from multiplying.

The earlier you start ARVI treatment, the easier it will be to cope with it.
In addition, drugs activate immune defenses, both local and general, as a result of which the virus is given a worthy rebuff.
Leukocyte interferon
This medicine is presented in the form of a dry powder for dissolution in water and instillation into the nose. It is sold in ampoules.
Designed to treat and prevent flu.
At the beginning of the treatment course, a couple of drops are instilled into each of the nostrils every couple of hours.
Also helps in the treatment of viral conjunctivitis.
Viferon
The treatment regimen for ARVI in children involves the use of Viferon suppositories, which have immunomodulatory and antiviral effects.
Along with vitamins, the drug contains artificial interferon.
As for the application, it is enough to put two candles a day, while the course is 10 days.
Grippferon
Here are nasal drops, which are often prescribed to children with ARVI. They can be drunk even by babies who have not yet reached one year of age. It is advisable to start using it at the very beginning of the disease. The duration of the therapeutic course is usually 5 days.
For children under the age of three, two drops three times a day are enough.
Children, starting from 3 years old and up to fourteen years of age, should also be given a couple of drops, but already 4 times a day.
Imudon
What to give a child who is 2 or 3 years old for the treatment of ARVI? These suckable tablets are fine.
Their main action is aimed at strengthening local immunity in the oropharyngeal region.
In addition to the therapeutic function, the agent is taken for the prevention of acute respiratory viral infections in children under 3 years of age.
The medicine wonderfully copes with the inflammatory processes that accompany the infection, treats stomatitis, pharyngitis and laryngitis.
Usually 6 tablets should be sucked in a day. You do not need to chew and drink.
Derinat
How to treat a child who is 1 or 2 years old and who has a cold? The doctor may prescribe Derinat drops, which have antiviral, antifungal and antibacterial effects. They also restore damaged tissues.

Derinat is an effective antiviral agent used to treat ARVI in children
For flu and other acute respiratory viral infections, it is necessary to take 3 drops every one and a half hours.
IRS-19
It is an effective nasal spray that strengthens local immunity. In addition to treatment, it is actively used for preventive purposes.
The drug is approved for children from the age of three.
No more than five injections are allowed per day. The course lasts until the symptoms of infections disappear. When injecting the product into the nose, you need to hold the bottle upright - the child's head should not be thrown back.
Arbidol
This drug helps the body produce the required amount of interferon. Children are usually given 50mg tablets:
- 2-6 years - one tablet a day is enough;
- 6-12 years old - you need to drink two tablets;
- everyone over the age of 12 (that is, the remedy is also suitable for treating adolescents) - 4 tablets are prescribed.
The treatment course lasts five days. At least 6 hours should pass between doses of the medicine.
Homeopathic remedies
Separately, it should be told about the benefits and effectiveness of homeopathic medicines, which are also prescribed for children.
Do these remedies help to cure ARVI in a child? Quite. In addition, one cannot fail to note their absolute safety and the absence of side effects. The most popular homeopathic remedies that can be used by children should be listed.
Oscillococcinum
This medicine is manufactured by French pharmacists. One tablet a day is enough, which is placed under the tongue and held there until it dissolves. it is best to do this a quarter of an hour before meals or an hour later.
Doctors note the possibility of allergic reactions in those who have an individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
Antigrippin (Agri)
Issued domestic manufacturer in the form of granules in a double bag (with two formulations). Differs in anti-inflammatory, sedative and antipyretic effects. Helps to cope with signs of intoxication of the body (headache, muscle aches, general malaise). Treats catarrhal symptoms (like runny nose, cough and throat pains). Does not allow complications to develop.
Among other things, this tool is used to prevent colds.

Antigrippin has anti-inflammatory, sedative, and antipyretic effects.
The medicine is taken internally, regardless of when the food is consumed. Take five pellets each time. For fever - every hour from two packets. After the temperature has subsided, two hours later. The course lasts until recovery, but should not exceed 10 days.
Aflubin
Produced by Austrian pharmacists. Performs anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating and antipyretic functions. Does not allow the development of bacterial complications, reduces the duration of intoxication.
The product is diluted in water (a tablespoon is enough) and taken at least half an hour before eating. Hold the medicine in your mouth before swallowing.
- For the smallest babies, it is enough to drink up to 8 drops a day.
- Children under 12 years of age - 24 drops a day will be enough;
- Everyone over 12 years old should drink up to 80 drops per day.
Anaferon
A drug made by a domestic manufacturer. In addition to stimulating the immune system, it successfully fights viruses.
The tablet should be resorbed: at first, take one tablet every 30 minutes, and then three pieces a day are enough.
The tool is used not only in treatment, but also to prevent infection with acute respiratory viral infections.
Influenza-Hel
Medicine from German pharmacists. Fights inflammation and stimulates the immune system. It treats flu-like conditions, including headache, fever, malaise, and loss of appetite.
It is advisable to take it already at the first signs of ARVI in a child. Three pills a day are enough, but if the case of the disease is acute, in the first couple of hours it is necessary to drink a pill every quarter of an hour.
The combination of this medication with Traumeel C, as well as with Engystol, is effective.
Influcid
Another medication from German pharmacists. Designed to increase the defenses of the child's body, fights inflammation and helps to cope with coughs.
Before swallowing the pill, it should be held in the mouth for a while. This is best done about 30 minutes before eating.

Influcid helps to strengthen the defenses of the child's body
Children under the age of 12 need to drink a pill every couple of hours (but so that they drink no more than 9 pieces per day). When the health situation improves slightly, three pieces a day are enough.
Sandra
Here is another medicine from a domestic manufacturer that will help your baby cope with ARVI.
Especially worth noting is its antipyretic effect, as well as its ability to cope with inflammatory processes.
Traumeel S
This drug is prescribed to children when the initial symptoms of viral infections appear. It is produced by a German manufacturer.
It effectively copes with tissue swelling, which is indispensable for inflammatory processes. But the remedy is useful not only as first aid, but also as a medicine that can be taken throughout the full course of treatment (up to recovery).
Enough three tablets per day. They need to be kept in the mouth until they are completely absorbed. It is best to do this before meals (half an hour), but it can also be done after meals (when at least an hour has passed).
Faringomed
This remedy, made by a domestic manufacturer, helps to alleviate the symptoms of infectious diseases, relieving people of swelling, redness and throat pain.
Children should love this medication as it comes in the form of a pleasant tasting caramel, which must be kept in the mouth until it is completely absorbed.
Viburcol
Suppositories from a German manufacturer that fight fever, soothe pain and relieve inflammation.
In the acute phase of the disease, you can use up to 6 suppositories per day. When there is an improvement, 3 candles are enough.
Babies who are not yet six months old are also allowed to use this medication, but no more than two suppositories per day.
conclusions
How and what to treat a child with ARVI, no matter how old he is, parents should learn from a qualified doctor. Trying to prescribe something on your own is not just useless, but unsafe, because instead of helping the baby, you risk harming him.

A sick child must be shown to a doctor.
As a rule, the treatment of acute respiratory viral infections should be complex, that is, along with taking various drugs, certain recommendations will need to be followed. Only in this case - with a serious and responsible approach to treatment - can we talk about the possibility of a speedy recovery.

Causes of ARVI
Get infected
SARS are transmitted
Symptoms of ARVI in a child
ARVI treatment in children
>
>
>
Herbal cough syrups
Prevention of influenza
Prevention of ARVI in children
adaptogens
How to treat ARVI in children
A happy, healthy child is the dream of most parents. The presence in the surrounding world of a variety of bacteria, viruses, which the baby encounters, becomes the cause of diseases. What does the common diagnosis of ARVI in children mean? Bronchitis, influenza, and many other diseases are designated by doctors with a mysterious abbreviation. ARVI is a large group of diseases with viral etymology, affecting the upper respiratory tract, mucous membranes. What is the difference between acute respiratory infections and respiratory infections caused by viruses?
Causes of acute respiratory viral infection in children
The diagnosis "acute respiratory disease" is the general name for the mass of diseases in children, in which the respiratory tract is affected. The causative agents are bacteria or viruses. SARS is a separate subgroup of acute respiratory infections, the impetus for the development of which are viral infections. The formation of a child's immunity begins from infancy: if a baby under one year old practically does not come into contact with a "hostile" environment, then one-year-old and older children begin to actively explore the world.

Expanding the usual boundaries of communication brings not only new knowledge, but also becomes the cause of acute respiratory diseases. What infections of a viral nature in children do doctors refer to as ARVI:
- Flu. Easily mutating, causing pandemics / epidemics, this virus is represented by three types: A (the most dangerous are atypical: "swine", "chicken"), B and C.
- Parainfluenza. This type of acute respiratory viral infection in most children affects the throat and trachea, in infants it can cause an attack of stenosis of the larynx.
- Rhinoviruses. Inflammation of the nasal passages, mucus discharge, reddened eyes are symptoms of ARVI, better known as "snot".
- Adenoviruses. They have a long incubation period, an erased form of the course, manifested periodically by a "triple bouquet": inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nose, pharynx and eye (conjunctivitis).
- Enteroviruses ("intestinal" flu). To the general deterioration of well-being, as with any types of acute respiratory viral infections, severe diarrhea and dehydration are added.
- RS (respiratory syncytial) infection. The object of action of these viruses is the lower respiratory tract - bronchi, lungs. This group of acute respiratory viral infections is characterized by: dry, tearful cough in children, rapid breathing, shortness of breath.
Infection with an infectious disease occurs by the ingestion of viruses from a sick individual, who secretes into the air the smallest particles of sputum or mucus from the nose, to a healthy one. Weakening of immunity leads to infection and the development of ARVI in children. When trying to reduce the risks, remember that the sick person remains infectious for up to 10 days after the onset of the infection.
Possible causes of ARVI in many children are:
- Decreased immunity:
- lack of vitamins;
- stressful situations;
- frequent colds.
- Visiting kindergartens, circles, schools.
- The presence of chronic / autoimmune diseases.
- Hypothermia.
- Insufficient hardening of the body.

The first signs and symptoms of the disease
For ARVI, features of the manifestation of symptoms are characteristic, depending on the type of virus. An important role is played by the seasonality of diseases: influenza, rhinoviruses, catarrh of the upper respiratory tract are constant companions of the autumn-winter period, enterovirus forms are characteristic of spring and summer, while adenovirus infection is a year-round "byaka". Common signs of ARVI in most children are:
- runny nose;
- cough;
- redness of the eyes;
- sore throat;
- irritation of the trachea.
Only a pediatrician can determine the type of viral infection and prescribe the correct treatment. However, it will be useful for mothers of children to know the features of ARVI symptoms:
- With the flu, the general symptoms of intoxication in children come to the fore: lethargy, weakness, muscle pain, "twisting" of the legs and arms. The main indicator is the rapid rise in temperature to critical indicators, the problematic nature of its "knocking down".
- Disease of the intestinal form of ARVI is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, nausea. The temperature rises to high levels, but it is easily knocked down by antipyretic drugs.
- The clinic of adenovirus infection is distinguished by the duration of catarrhal manifestations, a slight increase in temperature, general deterioration immunity.
- Other forms of ARVI proceed according to the general "pattern": the appearance of a runny nose, sore throat, cough (dry or wet). The temperature may rise up to 38 - 38.5C.

Diagnostic methods
To make the correct diagnosis, having determined the viral nature of the onset of the disease in children, the pediatrician will be helped by:
- Examination of the child. Includes:
- collection of information about the onset of ARVI symptoms;
- visual examination of the throat;
- listening to the airways;
- temperature measurement.
- Collection and analysis of laboratory research results:
- mucosal smear (PCR);
- determination of the serological reaction of the virus (RSK);
- express method for detecting the virus based on a smear of the epithelium of the nasal passages.
- Radiography (fluorography) for suspected pneumonia.
ARVI treatment in children
The reaction to the penetration of foreign bodies into the body with ARVI is an increase in temperature. Many mothers are frightened by the growing thermometer, trying to reduce the readings. This leads to a protracted recovery: at a temperature of 38 and above, the body of children begins to actively produce antibodies to the virus. The fallacy of ARVI treatment is largely due to the "initiative" of the parents, the low qualifications of the pediatrician, when antibiotics are prescribed for the common cold, viral tracheitis and other infections.

Symptomatic treatment
ARVI treatment should be started after a mandatory consultation with a local pediatrician. While waiting for the doctor's visit, create optimal conditions for the fastest recovery: bed rest, proper nutrition - diet and plenty of drink, a clean, ventilated nursery room. What medicines will help level the symptoms of ARVI in children:
- Antipyretic drugs: "Panadol", "Paracetamol" in the form of syrups (1 scoop for children under 3 years old), tablets. The daily dosage for children is 60 mg per kg of body weight, a single dose is 15 mg / kg.
- Solutions for washing the nasal passages: "Salin", "Aquamaris". No less effective will be the "home" version of the saline solution. You can achieve the required concentration by dissolving a teaspoon of sea / table salt in a glass of boiled water.
- Vasoconstrictor drops: "Snoop", "Nazivin" help to restore nasal breathing, drying the mucous membrane. Small children with ARVI are perfect for "Protargol" with silver proteinate or "Compound drops", produced in pharmacies by order of the parents. The duration of use for ARVI should not exceed 3-5 days.
- Cough medicines. A light, moist cough indicates an upper respiratory tract infection with acute respiratory viral infections. Mucolytic drugs: "Cough tablets", "Mukaltin" should be taken in a dosage of 1 tablet half an hour before meals 4 times / day.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. "Ibuprofen", "Nise", "Nurofen" are distinguished by their complex action: they reduce rheumatic syndrome, lower temperature, remove inflammation and swelling. The dosage depends on age and weight. The maximum allowable rate of nimesulide is 5 mg, ibufen is 20 mg per 1 kg of body weight.

Etiotropic therapy
The viral etymology of the disease in children involves the use of drugs, the action of which is aimed at strengthening the antiviral defense of the body, as well as fighting bacteria if a bacterial infection has joined the ARVI:
- Antiviral drugs: Acyclovir, Arbidol. Available in tablet form. In the first days of the disease, the dosage is: 1 tablet (2 mg) 5 times a day. Children under 2 years of age are prescribed half the dose. For children under 5 years of age, in the treatment of ARVI, candles "Viferon" with vitamins C, E, which have complex antiviral and immunostimulating effects, are recommended.
- Antibiotics "Biseptol", "Amoxiclav", "Clarithromycin" are effective in the presence of a bacterial infection, accompanied by a cough; "Ampicillin", "Flemoxin Solutab" cope well with sore throats, bronchitis, pneumonia. The dosage is selected by the doctor individually for the child in accordance with the instructions.
- Stabilizing agents. The action of the drugs "Fenistil", "Loratidin" is aimed at reducing the manifestation of the allergic effect in children with ARVI. Dosage for children under one year old - 10 drops up to 3 times a day, up to 3 years old - 15 drops, over - 20 drops.

Folk remedies
The centuries-old recipes of traditional healers will help to alleviate the condition of the baby with a viral infection:
- Vitamin teas. The herbal collection, prepared from equal parts of chamomile, lemongrass, linden, will perfectly cope with the intoxication of the body in children with ARVI. Dosage - half a glass of broth every 1.5-2 hours.
- Lemon honey infusion. A slice of lemon, a teaspoon of honey and a tiny piece of ginger, filled with boiled water, will increase the child's immune forces.
- Cabbage leaf. Spread a thin layer of honey heated to the body temperature of a sick baby and apply it to the chest at night, wrapping it with a towel. Moist, easily expectorant cough, improvement of health, normalization of breathing - the results of the procedure.

Homeopathy
The use of the principles of homeopathic treatment is characteristic of the remedies available in most pharmacy chains. Effective drugs for specific symptoms of acute respiratory viral infections, prescribed by doctors to children, are:
- Aflubin. It has a prophylactic effect that increases the body's immune response as a result of a monthly intake of viruses and colds during the season. The first days (1-3) should be taken up to 8 times / day, gradually reducing the number of doses to three per day. Dosage: a drop - for children under one year old, up to 4 - for children up to 5 years old, 5-9 drops at a time for school-age children.
- Oscillococcinum. Perfectly fights the flu at the initial stage of the disease. Effective in the "elimination" of the residual effects of acute respiratory viral infections. For admission, children are advised to dilute the tablet in water (up to 100 ml). One dose should be taken when the first symptoms appear. The second tablet, diluted with water, must be drunk in small portions (one teaspoon) every quarter of an hour.
Possible complications after ARVI in a child
Antibiotic therapy for a viral infection, increased treatment with antipyretic drugs, as well as its absence, sometimes become the causes of complications in children. What are the possible consequences of ARVI:
- Respiratory tract infections complicated by bacterial lesions of their lower part: pneumonia, bronchitis, purulent tonsillitis in children.
- Laryngitis, tracheitis are dangerous for newborn babies, children under one year old. The small lumen of the baby's larynx closes with stenosis, causing breathing problems. In such cases, the child should be treated in a pediatric hospital.
- Chronic rhinitis, otitis media, proliferation of adenoid tissue in children are the consequences of the adenoviral form of ARVI.
- Taking medications in excess dosages, lack of proper treatment, transfer of ARVI by a child "on his feet" often become the reasons for the addition of secondary infections, causing diseases of the kidneys, liver, nervous system, Gastrointestinal tract.

Prevention of influenza and other respiratory viral infections
Preventive measures aimed at:
- Strengthening the body's immune defenses. The intake of vitamin and mineral complexes for children before the autumn season of colds and viruses will stimulate the creation of a reliable "barrier" to infections.
- ARVI prevention. A contrast shower, walking barefoot, regular airing, exercise and physical activity will help strengthen the child's defense mechanisms at home.
- Development of immunity to certain influenza strains. Vaccinations given in early autumn promote the production of antibodies to a particular type of virus.
- During epidemics of SARS, mothers with children should avoid crowded crowds. For preschool children and schoolchildren, it is advisable to limit the attendance of entertainment centers, shops, circles.
Video: how and what to treat a child with ARVI - Dr. Komarovsky
Popular wisdom that colds with the help of pills can be cured in a week, and by providing proper care, drinking and diet - in 7 days, is not far from the truth. In children, most ARVIs proceed in the classical form: snot, cough and fever accompany up to 90% of viral infections. Why you shouldn't force-feed a child in case of illness, how to help the baby's body cope with a cold faster, you will find out by watching the video below.
What should be the treatment for ARVI in children 2-3 years old with weakened immunity?


Pediatricians believe that normally a child aged 1 to 5 years can get sick no more than 6 times a year. This does not create a serious burden on the body and "trains" the immune system to respond correctly to harmful microbial attacks. But if the baby is sick more often and is harder to tolerate ARVI, there may be problems with immunity. These children need special treatment and prevention during the flu and cold season.
The main danger is that children who are often ill have a higher risk of complications and the addition of a secondary infection - fungal or bacterial. To prevent this, parents need to be especially careful about their baby. You should call a doctor as soon as you notice alarming symptoms:
- temperature rise to 38.5 degrees and above,
- runny nose and watery eyes,
- shortness of breath due to nasal congestion
- redness of the throat
- cough, perspiration, complaints of pain when swallowing,
- lethargy and refusal to eat.
All manifestations of ARVI are due to the fact that pathogens enter the cells lining the respiratory tract and damage them. This causes irritation of the mucous membranes, inflammation occurs. If this process is not stopped in time, a 2-3-year-old baby may develop otitis media, sinusitis, bronchitis or pneumonia. Therefore, you should not hesitate - you must definitely seek help from a specialist!
The main thing is not to make mistakes.
Treatment of ARVI in children 2 years old is prescribed by a pediatrician. Parents should always remember this in order not to make typical mistakes. So what shouldn't be done categorically?
- Self-medicate, especially when it comes to the use of antibiotics and antiviral drugs. Such medications can only be prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the symptoms and condition of the child.
- Reduce the temperature if it is below 38.5 degrees. Fever is a natural defense reaction of the body, and it is not recommended to suppress it without good reason. You can take an antipyretic if the baby does not tolerate temperature well or suffers from a neurological disease. In other cases, it is better to give the baby more to drink.
- Rub the child with vinegar or alcohol, put mustard plasters and cans, use herbs. These products, in the wrong concentration, can cause burns or provoke allergic reaction... In the treatment of ARVI in children 2-3 years old, chamomile and fennel can be safely used, but only if they are not allergic.
- Stop taking medications as soon as the baby feels better. In this case, the treatment will be incomplete. The virus threat will not pass, but will become less active. The result will be a return of the disease a few days after the apparent recovery.
- Ignore the risk of secondary infection. Under the influence of viruses, the nasopharyngeal mucosa is damaged and becomes more vulnerable to bacterial and fungal attacks. Therefore, the treatment of ARVI in children 3 years old must be supplemented with drugs with a reparative effect. Only healthy mucous membrane does not allow the infection to spread lower into the respiratory tract!
ARVI in a child 2 years and 3 years old: how to treat? Complex therapy will help
Treatment of ARVI in children 2-3 years old should be comprehensive and include taking several drugs of different spectrum of action as prescribed by a doctor. Derinat is often prescribed by pediatricians to alleviate the symptoms of the disease and to combat its causes. It comes in the form of:
- nasal drops - have no contraindications, except for individual intolerance, are allowed for use from the first day of life;
- spray - intended for irrigation of a sore throat in children from 3 years of age.
You can start using Derinat at any stage of the disease. The drug acts in several directions at once and helps:
- destroy pathogens - viruses, bacteria, fungi,
- strengthen the immune defense and "close" the entrance gate of the infection,
- restore damaged mucous membranes of the nasopharynx due to reparative properties.
In addition, Derinat reduces the risk of complications, which is especially important in the treatment of ARVI in frequently ill children 2-3 years old. Take care of the health of your beloved babies and be healthy yourself!
ARVI in children. Causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
Acute respiratory diseases (ARI), known as colds, account for more than half of all childhood illnesses. Two-thirds of visits to a pediatrician are associated with colds. This is due, firstly, to the infectious nature of acute respiratory infections, which can quickly spread in a team, and secondly, to the variety of microorganisms that cause diseases: most acute respiratory infections are caused by viruses. The ARIs caused by viruses are called acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI). These include influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus, enterovirus and other infections. The incidence of ARVI is constantly high; in winter, children get sick more often. Almost every year there is an increase in the incidence of influenza, which is called an epidemic.
Real epidemics occur periodically every 3-4 years, when a type of pathogen appears against which most people have no immunity.
For the overwhelming majority of patients, only severe forms of the disease and complications that easily arise in children (pneumonia) pose a threat to life. The most severe among all SARS is the flu. SARS and flu usually end in recovery.
Causes of ARVI
Get infected children from patients who secrete viruses during the entire illness (7-10 days) and virus carriers.
SARS are transmitted by airborne droplets: droplets of sputum containing viruses, when the patient sneezes and coughs, infect the surrounding air, as well as objects and things. Infection is facilitated by close communication with the patient, poor ventilation of the room, violations of sanitary and hygienic standards.
Susceptibility to ARVI and influenza is high in children of all ages, including newborns. Children in nurseries, kindergartens, schools are especially often sick. Frequent recurrent diseases occur due to the fact that immunity after suffering ARVI is developed only against one virus, that is, it corresponds to each pathogen. Infection with another type of virus leads to a new disease, even if the child has not yet recovered from the previous one. In children of the first year of life, colds with the same frequency are caused by influenza viruses, parainfluenza, adenoviruses. There is an opinion that newborns and children in the first two to three months of life, especially those who are breastfed, are less susceptible to colds due to the presence of immune protection transmitted by the mother. However, it must be taken into account that hereditary and congenital diseases of the respiratory tract, unfavorable environmental factors, inadequate child care, violation of the feeding regime and rules, the presence of colds in family members increase the risk of a child's illness.
Symptoms of ARVI in a child
The manifestations of acute respiratory infections in children of the first year of life, regardless of the type of virus, have common features. As a rule, the state of health worsens: anxiety appears, the child cries more often, he loses interest in the environment, sleep is disturbed, appetite disappears - all this is due to the development of viral intoxication, swelling of the mucous membranes and nasal congestion, "stuffing" of the ears and painful sensations in them. The child's temperature rises, often quite significantly (above 38-38.5). Against this background, lethargy, weakness, and seizures may develop. Frequent signs of ARVI are rapid breathing (shortness of breath), runny nose, sore throat and chest pain, perspiration, and coughing. All these manifestations of colds are due to the fact that viruses penetrate the cells lining the respiratory tract, irritate the mucous membrane and develop inflammation in different parts of the respiratory tract.
In young children, acute respiratory viral infections, especially influenza, are more severe and often cause severe complications. There is a very high risk of developing inflammation of the ear (otitis media), maxillary sinuses (sinusitis), inflammation of the bronchi and lungs (bronchitis, pneumonia). These diseases, in turn, determine the formation of a contingent of so-called frequently ill children.
ARVI treatment in children
Patients with mild and moderate forms of ARVI are treated at home. The indications for hospitalization are:
1. Severe ARVI, the presence of complications (pneumonia, croup - regardless of the degree of stenosis, etc.).
2. Children under 1 year of age and from 1 to 3 years old.
3. Epidemiological and material conditions: from closed children's groups, unfavorable housing conditions not provided with care, etc.
Basically, children should get sick at an early age, so they train their immune systems to deal with harmful influences. environment... But it is worth worrying about a decrease in immunity when the doctor took your child to the group "often and long-term ill children." The term "frequently ill children" is used to describe children with frequent acute respiratory illnesses. Currently, this category includes children with acute respiratory infections:
> under the age of 1 more than 4 times a year,
> at the age of 1 to 5 years - 5-6 per year,
> at an older age - more than 4 diseases per year
The term "long-term ill children" is used in children whose cold lasts more than 2-3 weeks with each episode of illness.
In order to prevent such complications, it is important to start the correct treatment as early as possible, when the first signs of a cold appear. However, parents' independent choice of over-the-counter drugs is a big tactical mistake. Only a doctor can correctly assess the child's condition, diagnose and prescribe the necessary treatment, taking into account the characteristics of infancy, the course of the disease and the action of the recommended remedies.
Every mother needs to remember that a rise in temperature, a change in the child's behavior, refusal to eat, the appearance of signs of a cold is a reason for consulting a doctor. You can call a doctor at home by calling the registry, on weekends you can always call the doctor on duty. If the child's temperature is higher than 38.5-39.0, does not get confused by the usual children's antipyretic drugs, or shortness of breath, noisy, shortness of breath joins, the child does not respond to stimuli, or convulsions appear - do not hesitate, urgently call an ambulance.
After consulting a doctor, you can start treating your child with safe and effective measures at the same time. These include the use of plant substances (phytopreparations). The pharmacies offer a wide selection of simple herbal preparations based on the herb thermopsis, thyme; roots of ipecac, licorice, marshmallow; pine buds, linden; eucalyptus leaves, coltsfoot, plantain, etc. Modern combined herbal preparations are very popular: bronchicum (cough syrup, balm, inhalate, bath extract), Doctor Theiss (cough syrup, balm), Doctor MOM (cough syrup, ointment), Tussamag (balm , cough syrup) and others. Combined preparations, which include simple herbal substances, are more effective, have optimal healing properties and are well tolerated. They can be used in the form of rubbing (rubbing), baths, inhalations, and also taken orally in the form of a cough syrup. Dosage forms such as decoctions, drops, elixirs, lozenges, lozenges, capsules are not prescribed for young children.
Modern drugs-immunomodulators have proven themselves well in the treatment and prevention of colds in children. They noticeably activate the immune response of the child's body to infection, due to which the duration of the disease is halved on average, the cold itself is noticeably easier, and the risk of complications is reduced to zero. Immunomodulators are effective, as a rule, if you start taking them from the first signs of acute respiratory infections, no later than the 3rd day of illness.
ARVI treatment at home
In addition to the use of drugs, there are a number of measures that can alleviate the condition of a sick child. Every mother should be able to carry out this or that procedure at home. First of all, in case of acute respiratory infections, it is necessary to raise the head end of the bed or put a pillow under the child's head, as regurgitation, increased salivation may occur, and with a cough and a runny nose - sputum and mucus from the respiratory tract. With a low head position, there is a risk of aspiration (inhalation) of the discharge and the development of suffocation. In addition, the elevated position of the head relieves the difficulty of breathing with a cold. The air in the room should be moderately humid and warm. Ventilate the room often, but not with a sick child.
Bed rest is prescribed until the temperature normalizes and the acute symptoms of ARVI subside (for 6-7 days). The child needs to be given an additional amount of fluid, since with fever there is an increased loss of it with sweat, breathing and physiological secretions. Food should be age-appropriate in calories and food ingredients, but mechanically and chemically gentle, moderately warm with limited sodium chloride, with sufficient vitamin content. A dairy-plant diet with the inclusion of fruits and vegetables is more commonly used. Children should be given water more often, giving tea with 5% sugar, compote, cranberry juice. During the period of convalescence, food should not differ from physiological, but be enriched with vitamins. Many children during the period of illness and for several days after it refuse to eat in the previous regime, in this case it is impossible to insist, the additional load on the digestive organs can slow down the healing process. Let the baby eat what he wants and how much he wants. After a complete recovery, the appetite will be restored.
When the first signs of a cold appear in young children, treatment can be started with rubbing, therapeutic baths and compresses. It must be remembered that these procedures can be carried out only at a body temperature not higher than 38 ° C and in the absence of damage and skin diseases. A temperature that does not reach this limit does not require special treatment: it indicates that the body is fighting the infection on its own. At temperatures above 38 ° C, non-drug treatments can be used. They will help to reduce the temperature of wiping with warm water: the child is covered with a sheet, the leg is opened, quickly wiped, put under the sheet, opened another, wiped, closed, and so on. Small enemas with room temperature water (20-30 ml) are also effective. In the absence of effectiveness from the procedure from medicines, it is safest for a child to use paracetamol from temperature in an age-specific dosage and form. At least 2 hours should pass between doses of the medicine.
Rubbing the skin of the chest, back, neck, legs and feet can be carried out using bronchicum-balsam, eucalyptus balsam "Doctor Theiss", ointment "Doctor MOM", tussamag-balsam and others. Rubbing into the skin is carried out for 5-7 minutes 2-3 times a day and always at night, at the end of the procedure, the child should be wrapped in flannel or soft wool. Rubbing is recommended for children of all ages, starting from birth.
Healing herbal baths are also indicated for children of any age. For children under one year old, a water temperature of about 38 ° C is recommended, this temperature must be maintained during the entire bath, that is, 10-15 minutes. The required volume of the herbal preparation is dissolved in water: bronchicum bath with thyme (20-30 ml), eucabal balm (a 10-20 cm long strip of balm is squeezed out of the tube). Repeat the bath daily if necessary. After the bath, the child should be wrapped up and put to bed. In case of excessive sweating, it is necessary, some time after taking a bath, to carefully change the child's clothes into warm, dry clothes.
Compresses on the chest are made using any vegetable oil: the child is wrapped in a soft cloth moistened with oil heated in a water bath, after which thin polyethylene is applied, then a cotton or woolen pad, and all this is fixed on the chest with a bandage or kerchief. Compresses are made for a period of at least 2 hours, they can be repeated up to 2-3 times a day.
The therapeutic effect of rubbing, medicinal baths and compresses is due to the content of aromatic (essential) oils in herbal preparations. During the procedure, they freely penetrate the skin into the blood and lymph and have a healing and calming effect: the child's general well-being and heart function improve. In addition, when taking herbal baths, aromatic vapors penetrate the respiratory tract, contributing to the restoration of normal breathing.
Bronchicum-balm, eucalyptus balm “Doctor Theiss”, ointment “Doctor MOM”, tussamag-balm for colds contain eucalyptus, camphor, coniferous (pine) and nutmeg oils. They relieve inflammation, thin phlegm, eliminate obstacles to its excretion, improve breathing, and reduce coughing. In addition, when heated to body temperature, essential oils become volatile and have a healing effect also when inhaled. Thanks to the double effect, rubbing in balms and ointments is an emollient for colds.
Difficulty in nasal breathing with ARVI and influenza disturbs the child, interferes with sucking in infants, interferes with sleep. In young children who cannot blow their nose, it is easiest to remove mucus from the nasal passages with a rubber bulb, but this requires caution and skill, you can clean the nose with soft cotton swabs moistened with sterile vegetable oil or boiled water. If the child knows how to blow his nose, then each nostril must be cleaned in turn, pinching the other, otherwise the infection can get into the eyes and ears. The weak effect of medications for the common cold is most often associated, on the one hand, with the fact that the wrong medication is used, and, on the other hand, that it is premature to expect a result immediately after the first injection. Nasal drops, according to the mechanism of local action, refer to vasoconstrictor agents that relieve swelling of the inflamed mucous membrane and thereby improve the passage of air through the nose, therefore, such drops should be used only with congested nasal breathing. Naphthyzinum or galazolinum, the most commonly used for this purpose, have children's forms, but require caution and strictly controlled dosage, since frequent instillation of these drugs leads to irritation of the epithelium of the upper respiratory tract and even atrophy of the mucous membrane. To wash off microbes from the mucous membrane, it is better to use pharmacy saline solutions, including sea salt, at any stage of the common cold.
Another group of local agents used to treat rhinitis has a detrimental effect on the causative agent of the disease - viruses and microbes. These are various sprays, a solution of protargol, a large number of complex drops and ointments that have a combined vasodilator, decongestant and disinfectant effect.
To reduce a runny nose and cough, it is advisable to use inhalations - inhalation of vapors of plant substances containing aromatic oils; they get directly into the respiratory tract, envelop and moisturize them, relieve irritation, cough. For inhalations are used: bronchicum-inhalate containing aromatic oils of eucalyptus, pine needles, thyme; ointment "Doctor MOM", eucalyptus balm "Doctor Theiss", tussamag-balm and other means. For newborns and infants, inhalation is carried out in a special way: with the help of evaporation from an open container (pan) of hot water with a herbal substance dissolved in it. In this case, the windows and doors of the kitchen (or other room where the waking or sleeping child is located) must be tightly closed. The proportions of the solution for inhalation: for 2-2.5 liters of hot water 2-3 teaspoons of balm, inhalate or ointment. The child should be in this room and inhale vapors for 1-1.5 hours.
The combination of baths, rubbing and inhalation leads to a speedy recovery. Correct rubbing, baths, compresses and inhalations with the help of herbal substances cannot harm the health of the child. However, these procedures must be agreed with the doctor, just like taking cough syrups by mouth.
Herbal cough syrups prescribed for infants from 6 months. Shake syrups before use. Store them in a cool, dark place. Here are the characteristics of some syrups:
Bronchicum is a cough syrup (contains thyme, rose hips, honey and other substances), it is prescribed by mouth for 0.5 teaspoon 2-4 times a day. It is undesirable to use syrup in the first months of life, since it contains honey. When taking bronchicum syrup on the 3-5th day, the cough softens, it becomes more rare.
"Doctor Theiss" - cough syrup with plantain, is applied orally by 0.5 teaspoon every 2-3 hours (with a night break). Recommended for coughs with difficult sputum separation.
"Doctor MOM" - herbal cough syrup (contains licorice, basil, saffron), applied orally 0.5-1 teaspoonful 3 times a day. Especially recommended for perspiration, irritable, convulsive cough.
Tussamag - cough syrup (contains thyme extract), used from 9-12 months, 0.5-1 teaspoon 3 times a day. It is especially indicated for dry coughs.
All herbal substances at home are used as directed by a doctor and only for the treatment of mild colds in young children. Severe ARVI, suspected complications require inpatient treatment.
Prevention of influenza
Prevention of influenza is carried out with the help of specific vaccine prophylaxis. The vaccination time must be prior to the onset of the influenza epidemic, as vaccines are designed to address circulating influenza viruses during a given season. Special vaccines are used for young children, schoolchildren, adults and the elderly. Rarely there is a reaction to the vaccine in the form of short-term malaise, fever. It proceeds much easier than the disease, and one should not be afraid of it. Immunity is formed only against the flu, so a vaccinated child may well get sick with another viral disease.
Anyone with the flu should be isolated from healthy people. You will say that it is difficult to isolate a child. And you will be right. After all, he constantly needs something. In order to minimize the risk of infection, put a 6-layer gauze bandage on the sick person if it is SARS or flu. Change the dressing for a new one every 3 hours. It is good to ventilate the room where the patient was, and regularly carry out wet cleaning. For everyone who comes into contact with a sick flu, it is recommended that interferon be instilled into the nose for a week, aflubin, arbidol, ascorbic acid or dibazol can be given. Adults are advised to take rimantadine in a prophylactic dose, arbidol. It is useful for children over 1 year old to prescribe algire.
The category of preventive measures also includes hardening, restorative procedures, full summer rest, healthy image life: adherence to the daily routine, regular walks, age-appropriate sleep, the use of fresh fruits, garlic and onions.
It should be noted that smoking by parents is harmful to the child, since the tobacco smoke that the child inhales has a harmful effect on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract and promotes inflammation.
Very interesting is the use of inhalations using essential oils - aromatherapy to protect against infections. Place an icon lamp in the middle of the room, drip fir or eucalyptus oil on a saucer and light a candle. Gradually evaporating, the molecules of the odorous antimicrobial substance will do their job. It is even better to all this, at night, each family member to eat a clove of garlic.
Prevention of ARVI in children
One of the topical issues in the autumn-winter period is the prevention of respiratory infections in children of different ages.
Non-specific prophylaxis involves the use of both general and special means and methods (drugs and procedures that increase non-specific resistance to infectious agents and antiviral drugs). Non-specific seasonal immunocorrection during an influenza epidemic or local outbreaks of other acute respiratory infections is complemented by emergency (according to epidemic indications) prevention, which is carried out with antiviral drugs.
Non-specific prevention of influenza and ARVI in preschool children.
The most time-consuming method, although more gentle for the body, is to increase the nonspecific resistance of the child's body, the so-called nonspecific prophylaxis, which includes a whole range of measures.
First of all, these are tempering procedures, ranging from the most affordable - foot baths or walking barefoot to visiting the pool and classes in health centers. When hardening, the following principles should be adhered to:
Hardening procedures can only be performed on healthy children; contraindications are febrile conditions, a period of early convalescence after acute respiratory infections, diseases with serious dysfunctions of the cardiovascular, respiratory, nervous systems;
- start with low doses of hardening effects, followed by their gradual increase, for example, daily reducing the temperature of water for foot baths or herbal tincture for gargling by 1 degree;
- to use the effect on the body of various environmental agents - water, air, ultraviolet rays;
- carry out the procedures regularly, alternating between weaker and stronger hardening agents throughout the hardening period;
- strive to create positive emotions during the procedures.
Of paramount importance is complete nutrition, rich not only in proteins, but also in vitamins. In the best way is the intake of multivitamins.
Complex vitamin preparations Vetoron and Vetoron-E (orally from 5 years old, 3-4 drops, from 7 years old - 5-7 drops once a day, or in capsules from 6 years old, 5-80 mg once a day).
Vitamins C, A and group B should be widely used in age-related dosages. The optimal ratio of these vitamins is contained in the preparations "Geksavit", "Revit", "Dekamevit" and "Undevit". They are recommended to be taken in age-specific dosages 2-3 times a day after meals for a course of 20-30 days.
In the cold season, children are advised to use rosehip syrup, 1 teaspoon per day.
The recognized means of enhancing nonspecific resistance are adaptogens- harmless biologically active substances of plant or animal origin, capable of restoring impaired body functions. Many biologically active additives (BAA) are such drugs. As a rule, adaptogens are prescribed during periods of seasonal overvoltage of the adaptive mechanisms of the body - in autumn and spring. In relation to acute respiratory infections, these drugs have a fairly pronounced protective effect. Long-term use (for 1-2 months) of adaptogens is not accompanied by any side effects, but one should remember about possible individual intolerance and the presence of contraindications for some of them, therefore it will be necessary to consult a pediatrician on this matter.
The most popular adaptogens are extracts from the roots of Eleutherococcus and ginseng, tincture of aralia, preparations of echinacea, seaweed (Fitolon), pine and spruce needles ("coniferous tablets-lesmin"), honey ("vitamedin"), as well as adaptogens of animal origin : from royal jelly - "apilak", mussel hydrolyzate - "viramid", from maral antlers - "pantocrin", etc.
Schemes for the use of the main adaptogens:
Immunal - 5-10 drops orally (1-3 years), 10-15 drops (from 7 years) 3 times a day;
Echinacin - 5 ml orally (up to 3 years), 10-15 ml (from 4 years) 2 times a day;
Dr. Theiss - Echinacea tincture - orally from 1 year old - 10-20 drops 3 times a day;
Echinacea Hexal - orally, 5-7 drops from 12 years of age and older, 2 times a day.
Eleutherococcus extract - 1-2 drops per year of life, 2 times a day for 25-30 days.
Aralia tincture - 1-2 drops per year of life 1 time per day 30 minutes before meals for 2-3 weeks.
For the specific prevention of diseases of bacterial etiology in frequently ill children with reduced resistance, it is proposed to use vaccine-type immunomodulators containing antigenic determinants of the most common bacterial pathogens of respiratory infections.
To address issues of emergency prevention, great importance is attached to drugs that have a quick protective effect against all pathogens of acute respiratory infections. As means of emergency prophylaxis, irrigation of the oral cavity with decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, calendula, sage, etc.), Kalanchoe juice, garlic and onion (diluted 20-30 drops per glass of water), as well as local bacterial immunocorrectors ( Imudon, IRS-19).
Taking into account the common causes of the occurrence and the factors contributing to the development of the disease means being able to prevent the disease in advance. Currently, the pharmaceutical market offers a huge selection of drugs for the treatment and prevention of acute respiratory infections in children. But only their competent use will help to achieve the desired result.
Etiology
The presence of pathogens in the body does not always indicate a disease. It is also necessary to simultaneously influence provoking factors. The latter are air temperature (that is, not only hypothermia, but also overheating of the body), air humidity (with dry air, the risk of infection is more likely than with humid air). Emotional and physical stress also contributes to the development of the disease, as there is a decrease in the body's defense systems.
Clinical manifestations
Viruses have properties such as epitheliotropy, vasotropy, lymphotropicity. This means that viruses mainly infect mucous membranes, blood vessels and lymphoid tissue (lymph nodes). These properties determine the entire clinic and symptoms.
But most often, when talking about acute respiratory infections, parents mean a cough and a runny nose. This is not entirely correct. Of course, the nose and oral cavity, being the gateway for infection, are the first to be affected, which misleads the parents.
There are the following syndromes for acute respiratory infections in children.

- Catarrhal syndrome. There is nasal congestion, mucous, transparent, sometimes greenish discharge from the nose, cough.
- Respiratory Syndrome- cough, pain, burning in the throat and chest, signs of respiratory failure.
- Intoxication syndrome. There is weakness, lethargy, muscle pain, aches throughout the body, fever, and lack of appetite.
- Abdominal Syndrome. Most often occurs in young children. Young children complain of abdominal pain of different nature and intensity.
- Hemorrhagic syndrome. It is characterized by the appearance of a punctate red rash on the skin, the presence of rashes on the oral mucosa and pharynx.
All symptoms can manifest themselves in varying degrees of severity, and not all of the above signs will necessarily be present.
Based on the presence of symptoms and the degree of their severity, there are three degrees of severity of acute respiratory infections: mild, moderate and severe.
It is also necessary to point out that with an increase in body temperature in many children, especially in small children, there are those that occur only against the background of a high temperature.
Diagnostics
There are no specific tests for the general diagnosis of acute respiratory illness. Usually it is exhibited without the use of laboratory and instrumental research methods, that is, often only on the basis of clinical data.
But in any case, parents need to seek qualified medical help. Only a doctor will be able to make a diagnosis indicating the form and severity of acute respiratory infections and, accordingly, prescribe the necessary therapeutic measures.
During the examination, patients complain of a lack of strength, mood, that they have a headache and a stuffy nose, and cough worries. Very often in young children, the body temperature rises to high numbers. Clear, sometimes greenish or yellow discharge from the nose and respiratory tract is noted.


Cough is the most common symptom of acute respiratory infections. It occurs when the cough receptors are irritated, which are most in the nasal cavity and pharynx. In case of untimely and inappropriate treatment, "the infection slides down," that is, complications arise in the form of bronchitis, pneumonia and respiratory failure.
When examining the mucous membrane of the oropharyngeal cavity, redness of the posterior pharyngeal wall is observed, sometimes with a transition to the mucous membrane of the palate and cheeks. There may be a rash in the form of vesicles (vesicles with transparent contents) on the mucous membrane of the palate and pharynx. Mucus draining down the back of the pharynx is very often noticeable (a manifestation of a "posterior" rhinitis).
Auscultation will help to suspect the presence of pathological processes in the lower respiratory tract. Further, if necessary, the organs of the chest are assigned.
Laboratory methods are usually not addressed immediately, but 3 - 4 days after the initial treatment. The indication for the delivery of a clinical blood test and a general urine test is the persisting body of the child, the ineffectiveness of the prescribed drugs and the early detection of possible complications. In the analysis of blood, the following picture is observed: acceleration of ESR, leukocytosis, or (there may be both options), a decrease in hemoglobin level is possible. In the analysis of urine, in the absence of complications, pathological changes may not be.
With protracted processes, as well as when treatment is ineffective, an additional biochemical blood test is prescribed. In the latter, C-reactive protein is determined, and in a hospital setting, the level of procalcitonin is also determined, an increase in which indicates 100% bacterial inflammation.
Treatment
The key point in the treatment of acute respiratory infections in children is the use of an integrated approach. It is also important that a qualified pediatrician treats the child; self-medication is not permissible. Below are the general principles treatment.
- Treatment of children with acute respiratory infections begins with a regimen, which should be bed or semi-bed, depending on the severity of the condition.
- The room should be ventilated frequently.
- The optimum temperature regime is 18 - 22 ° С.
- It is advisable to isolate the child, and use separate dishes for feeding to prevent reinfection.
- An abundant warm drink is recommended, especially when the body temperature rises. Drink preferably non-acidic and unsweetened drinks. Low-fat broths, compotes, fruit drinks, unsweetened tea are best suited. The diet should exclude spicy and spicy foods.
- Drug treatment begins with etiotropic drugs. In most cases, these are antiviral and antibacterial drugs. For infants, such forms of release are used as suppositories for rectal use (for example, Viferon and Genferon light) and drops (). For young children, you can already use antiviral drugs in the form of syrups (Orvirem) or chewable tablets (Anaferon). Antibiotics are presented for children in the form of a powder for the preparation of suspensions.
- Symptomatic treatment includes:

- antitussive drugs (Erespal, Sinekod);
- expectorants (Ambroxol, ACC);
- antipyretic and pain relievers (, Nurofen);
- vasoconstrictor (Nazivin, Otrivin);
- antihistamines (Zodak, Claritin).
In addition, for the treatment of rhinitis and, before taking the above drugs, rinsing of the nasal cavity and pharynx with saline is prescribed in order to mechanically remove microbes and improve the absorption of drugs (AquaLor, Aquamaris).
About antihistamines. It is advisable to prescribe them when taken simultaneously with preparations containing herbal ingredients, for example, when taking Tonsilgon, or when setting Viferon suppositories (based on cocoa butter). This reduces the risk of allergic manifestations.
In addition, physiotherapy procedures can be used to treat ARVI in children. For example, ultraviolet irradiation of the throat and nose, UHF and electrophoresis of the chest, inhalation. Of course, doctors are extremely careful with regard to physiotherapy. Due to the immaturity of the body, electrical procedures are not recommended for young children, but inhalation is possible from birth.
Prophylaxis
Prevention of acute respiratory infections in children includes several points:
- first of all, it is an active lifestyle, walking in the fresh air, avoiding hypothermia and overheating of the body, adequate sleep, good nutrition, hardening the body, massage;
- the child plays an important role;
- some drugs used for treatment are also used for prophylaxis (for example, Anaferon), but according to different dosage regimens;
- in relation to frequently ill children, for prophylaxis, 4-6 months courses of taking the appropriate drugs are used (Ribomunil,).
Conclusion
In conclusion of the topic, I would like to add about self-treatment ARVI in children. Many parents, without waiting for a qualified assessment of the condition, begin to treat the child themselves. This is fraught with dangerous consequences for such a seemingly simple disease. Uncontrolled intake of antipyretic and analgesic drugs hides possible complications. Only a doctor, when called at home, in a clinic or in a hospital, will adequately assess the child's health and prescribe a suitable treatment.