Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a modern diagnostic tool for a variety of infections with high accuracy. PCR analysis allows you to determine the causative agents of infectious diseases, based on their genetic material (RNA or DNA). Biological material for research can be blood, a smear from the genitals, saliva, and so on.
CONSULTATION ON THE RESULTS OF ANALYSIS or ultrasound - 500 rubles.
The PCR method was discovered in 1983. Its creator is Carey Mullis (USA), for this discovery he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Already in the first ten years, the technique has become a mandatory laboratory study all over the world, having received recognition from scientists and doctors.
Diana Medical Center offers to conduct a study using the polymerase chain reaction method in the shortest possible time and with the highest level of accuracy. Our diagnostic base meets all international standards and requirements.
What infections can be diagnosed by PCR
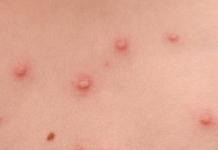
Send for diagnostics, or. Analysis PCRmakes it possible to diagnose a wide variety of infections. This group also includes hidden, asymptomatic diseases that are in the incubation period:
By using PCR methodyou can find:
- hepatitis C, B;
- ureaplasmosis of the genital organs;
- - ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, gardnerellosis;
- chlamydia of the genitals and respiratory tract;
- bacterial vaginosis;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- tuberculosis;
- salmonellosis;
- tuberculosis (pulmonary and extrapulmonary forms);
- listeriosis, tick-borne encephalitis, Lyme disease;
- , papillomavirus,;
- childhood infectious diseases detected during pregnancy and before conception - mumps, diphtheria, measles;
- HIV.
For each of the above diseases, detected by another method, it is advisable to do a PCR study. The causative agents of many infections are of several types (strains), and more accurate diagnosis makes treatment more effective. Since different types of pathogens have their own modes of transmission, an accurate identification of the pathogen helps to protect others from infection. For example, hepatitis A can be contracted through shared objects and utensils (dirty hands disease), and hepatitis C can only be transmitted through blood, medical instruments, and sexual intercourse. This is important for those who are near the patient.
The essence of the polymerase chain reaction method
The method is based on identifying the pathogen by sections of DNA or RNA. PCR is similar to forensic science, when a criminal is found by particles of skin or hair left at the scene of a crime. Because every living organism has a unique DNA or RNA structure. The method allows you to accurately identify a microorganism, even if it is present in the test material in minimal quantities.
The PCR is suitable for detecting hidden carriage, atypical, erased and other forms of infectious diseases. Diagnostics is highly accurate, so it practically does not give errors and false results. An analysis is often prescribed as an additional examination to identify a specific type of virus or microbe.
Advantages and disadvantages of the PCR method
PCR analysis is an effective diagnostic tool that allows the doctor not only to correctly determine the type of infectious agent in the patient's body, but also the number of microbes. This feature allows the PCR method to effectively detect chronic infections, for example, viral hepatitis.
The advantages of the technique are as follows:
- Versatility ... The method makes it possible to determine all currently known microorganisms, regardless of the type of material under study.
- Specificity ... PCR allows you to determine the DNA of a virus or bacteria with 100% accuracy, which does not provide any other diagnostic method.
- Sensitivity - even one tiny "fragment" of DNA or RNA can be detected and identified thanks to the fast copying reaction.
- Promptness - it is possible to make a diagnosis based on the polymerase chain reaction within a few hours after taking the biological material, which makes it possible to start treating the disease in a timely manner.
- Quantitative analysis capability ... This feature is important in identifying diseases caused by opportunistic flora (for example, thrush). The increased content of candida fungi in the body causes the disease, and the normal amount is up to 10 3 - 104 CFU / tamp. - No.
The disadvantages of PCR diagnostics are the need for high-tech equipment and highly qualified specialists. For the analysis, a special laminar box is needed, where the required temperature is maintained and the purity of the experiment is ensured.
How to pass the PCR test correctly: preparation
To understand exactly how to prepare for the upcoming PCR analysis, the patient should definitely check with his doctor what kind of biological material is planned to be taken. Preparation directly depends on this.
- Discharge from the genitals, a smear from the cervix or urethra, urine - through the study of these variants of the material by the PCR method, infections of the genital organs are effectively diagnosed.
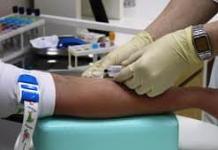
- Viral hepatitis C, HIV infection require blood collection for PCR analysis.
- Using a throat swab, you can confirm or deny the presence of infectious mononucleosis.
Smear in women
For the diagnosis of genital infections by PCR in women, as a rule, they take vaginal swab... During pregnancy, the standard rules for preparing for the PCR analysis apply.
- A couple of days before the PCR, you need to give up douching, intimate hygiene products.
- A week before the analysis for infections, it is worth stopping the use of any types of drugs, of course, if they are not included in the preparation program for the PCR analysis prescribed by the doctor.
- A couple of days before the examination, you need to start abstaining from intercourse.
- Washing on the day of the PCR analysis is not necessary, the hygiene of the genitals is carried out the night before, only warm water is used.
- You cannot urinate a couple of hours before the test.
Smear in men
Preparing to collect a smear from the urethra for PCR is easy. It is enough to follow the rules set out below.
- 2 days before the PCR examination, you need to start abstaining from sexual relations.
- Medication is stopped approximately 7 days before the analysis, unless, of course, they were specifically prescribed by the doctor.
- Genital hygiene should be performed the night before; on the day of the PCR analysis, this should not be done.
- It is recommended not to urinate for about 2-3 hours before taking the test.
Blood test
If in the process of PCR analysis the patient's blood becomes the object of study, the rules for preparing for it are as follows.
- The optimal time to donate blood is in the morning, the test must be taken on an empty stomach (at least 8 hours of no food). Water can be drunk freely.
- Quitting alcohol one day before the PCR test, quitting smoking an hour before.
- If health allows such an option, it is recommended to stop taking medications for a while.
- Before taking blood samples, it is imperative to rest for about 20 minutes.
- On the eve of PCR studies, emotional and physical overloads are completely excluded, they can affect the results of the analysis.
How is the PCR test done?
For research, any environment is taken in which the pathogen may be located, but most often they are used:
- Blood serum or plasma - to identify a variety of pathogens - hepatitis B, C, D, G viruses, herpes, HIV, cytomegalovirus;
- Urine and prostate juice - in the diagnosis of STDs;
- Sputum, pleural fluid, bronchoalveolar lavage - for the diagnosis of pulmonary and extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis;
- Cerebrospinal fluid - for the diagnosis of infections of the nervous system;
- Amniotic fluid - to determine intrauterine infections;
- Throat swab
- to identify the causative agents of infectious mononucleosis and diphtheria;
scrapings and smears from mucous membranes for the diagnosis of STDs;
cells of the gastric mucosa and gastric juice - to identify the bacteria Helicobacter, which causes gastritis and ulcers.
With one sampling of the material, several pathogens that have entered the body can be detected at once. This versatility saves the patient from additional examinations and unnecessary expenses.
It is possible to detect and identify sections of genetic information using special reference DNA markers (primers) created for each known pathogen. The standard allows you to find "your" fragment among millions of others. If this happens, the polymerase chain reaction is triggered.

The PCR reaction makes a huge number of copies of the identified region of gene information (replication). It is important that only the DNA and RNA regions needed for the analysis are replicated. Therefore, the purity of the experiment and the ability of the personnel to handle equipment and samples are so important.
The chain reaction proceeds very quickly, after two hours the DNA section is enlarged millions of times, which makes it possible to detect and accurately identify the infection. To work with standards, test tubes are placed in a special device. With the help of the program, an algorithm is set that changes the temperature of the medium several times and affects the course of the reaction. The PCR result is visible immediately after the end of the study.
How to decode PCR analysis
Carrying out a PCR study allows not only to establish the type of infection present in the patient's body, but also to evaluate it from a quantitative point of view (the number of microbes). Deciphering quantitative PCR results plays an important role in detecting and verifying the effectiveness of treatment for a large number of chronic diseases, such as hepatitis C.
The result of the PCR analysis can be positive and negative responses.
- Negative result ... No traces of infection were detected in the biological material, which was the object of the study during the PCR analysis. As a rule, on the basis of a negative result, it can be assumed that there is indeed no infection in the body.
- Positive result. This result of the PCR analysis indicates that traces of an infectious disease are present in the patient's biological material. A positive PCR test result is characterized by a high degree of accuracy.
Sometimes infection is detected against the background of complete health and the absence of signs of the disease. Some patients believe that the analysis was done incorrectly, but the real situation is different. If the PCR showed that there is a pathogen in the body, then it really is there. It's just that infectious diseases never begin immediately after infection, having an incubation period of varying duration.
The latent period can last for a very long time, for example, in AIDS - several years, until some mechanisms push the viruses to multiply. The pathogen is determined in the body of carriers and those who have not been cured. Very often various STDs turn into a latent (latent) form. In this case, additional laboratory diagnostics may be required.
Accuracy of interpretation of PCR analysis results
The PCR method, which allows detecting a sufficiently large number of infections, is characterized by increased accuracy, sensitivity and specificity. These characteristics indicate that using a PCR study you can:
- Establish as accurately as possible the absence or presence of an infectious agent.
- Determine as accurately as possible the specific type of infectious agent (specificity).
- Identify the infection even if it is latent. We are talking about a low level of microbial DNA (sensitivity) in the patient's biological material being examined.
The advantages of the PCR method over the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and other immunological tools for detecting infection is that it is less likely to give erroneous results. That is, the decoding of the PCR analysis much less often shows the absence of infectious microbes, if they are in the patient's body.
In addition, it almost never happens that the decoding of the analysis reveals the presence of a non-existent infection in the body, that is, gives false positive results. Of course, it is still impossible to call the PCR results 100% correct, therefore it is necessary to supplement this study with other methods.
Content
Those who are interested in new diagnostic methods should find out what the PCR method is. Modern technical capabilities in the field of laboratory research provide the ability to detect many diseases at the initial stages. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is currently considered the most accurate and new method.
PCR analysis
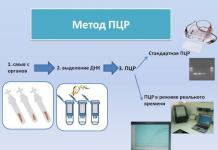
PCR analysis - what is it? This method uses the principles of molecular biology. To study the material, special enzymes are used that repeatedly and quickly copy DNA, RNA fragments of pathogens. There are different types of PCR analysis depending on the test material (blood, urine, feces, etc.). After processing, the laboratory staff compare the obtained result with the database, identify the concentration, type of pathogen.
The PCR analysis is placed in a special amplifier (device), which heats and cools the tubes with biomaterial. Temperature changes are needed to replicate the fragments. The accuracy of the result will depend on the accuracy of the temperature regime. The polymerase chain reaction method helps to identify:
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- cytomegalovirus infection;
- viral hepatitis G, C, B, A;
- sexually transmitted infections / diseases (STIs / STDs): gardnerellosis, trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis;
- herpes infection;
- oncogenic viruses;
- listeriosis;
- Helicobacter pylori infection;
- tick-borne encephalitis, borreliosis;
- tuberculosis;
- candidiasis.
Blood
At the moment, due to the novelty of the technology, the PCR blood test still has a high price. To prepare a biomaterial, you do not need to comply with certain requirements. Even changes in composition caused by physical exertion, stress, and a change in diet do not affect the study result. A PCR blood test can only spoil the intake of antibacterial agents, therefore, before taking it, it is necessary to pause between treatment and the test.
PCR blood test is the most common option for diagnosing chronic, acute infectious pathologies with a viral or atypical manifestation. Serological research methods have a certain difficulty in conducting - the determination of the presence of the pathogen is carried out by the presence of antibodies in the human body. The result could be false negative if the patient's condition did not give time for their development.
Smear
In the field of gynecology, PCR smear analysis is used to investigate the presence of infectious microorganisms. The work with the material is carried out according to the same principle as with blood: a multiple increase in the DNA fragments of the pathogen in order to easily identify it. It also helps to detect hidden infections in a woman. For the analysis, different biological fluids can be taken: saliva, sputum, urine, blood. In gynecology, for accuracy of determination, a smear from the vaginal mucosa from the cervical canal is often used.
There are certain indications for PCR. It often needs to be done to identify an antibiotic-resistant pathogen. In women, the main indications for diagnostics using this method are:
- pregnancy that is difficult;
- acute phase of STIs;
- if there is a suspicion of the transition of STIs to the chronic stage;
- search for the causes of infertility.
Kala
To detect infection, a stool PCR test may be prescribed by the doctor. In order to obtain the most reliable results after the test, you must adhere to the following rules before sampling biomaterial:
- stop taking laxatives in a few days: oils, suppositories;
- exclude medicines that give a specific color to feces, for example, with iron content.
A sterile stick and container should be used for collection. Wipe them with anything else, you do not need to rinse them. When collecting material, be careful not to touch the inside of the container with your hand. Make sure that there are no urine impurities in the feces, you can not use additional aids for bowel movements (enema). You need to collect the material on the day of delivery, 1/3 of the container volume is enough. This diagnostic method has the following advantages:

Urine
If necessary, the doctor may take urine for testing for testing. High precision makes it possible to work with any biological fluid from which it is possible to extract the DNA of the virus. To pass a PCR urine test, you need to adhere to the following restrictions before taking the material:
- stop having sex at least 1 day before the procedure;
- 3 weeks before delivery, any antibacterial treatment must be completed, because medications will smear the picture;
- you need to take the analysis on an empty stomach (liquid is also prohibited);
- you need to take the first morning portion of the material.
PCR test results
From the above, it is clear what PCR analysis is and clear advantages of this research method are visible. Another plus of this diagnostic procedure is the ease of decoding the results. Considering how much PCR analysis is done (the process itself takes about 5 hours, but the laboratory provides data after 1-2 days), this diagnostic method becomes the best option for identifying many infections. Based on the results, your doctor may tell you that the test:
- Negative - the studied material did not contain the desired pathogen.
- Positive - RNA and DNA of the pathogen were found.
Microorganisms are sometimes quantified. This is necessary for diseases that cause opportunistic pathogens. The peculiarity of these viruses is that they appear only when they are in excess and it is extremely problematic to find them by conventional research. This factor is important for the choice of therapeutic tactics in order to effectively treat viral infections, for example, hepatitis, HIV.

For 12 infections
To fully understand what PCR diagnostics of infections is and how effective it is, you need to know that it is capable of isolating up to 12 pathogens. The text is carried out only in a laboratory setting. For research, special enzymes are used that multiply the amount of RNA, DNA of virus fragments. PCR analysis for 12 infections can detect:
- mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- cytomegalovirus;
- hepatitis C, G, B, A;
- herpes 1, 2 types;
- Epstein-Barr virus (infectious mononucleosis);
- sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia;
- listeriosis;
- candidal infection;
- Helicobacter pylori;
- borreliosis, tick-borne encephalitis.
For hepatitis C
This diagnostic method helps to determine the presence of the virus in the blood. This gives doctors the opportunity to talk about its presence or absence. PCR analysis for hepatitis C is of two types: qualitative and quantitative. The first option indicates only its presence and may have the formulation “detected” / “not detected”. This type of test has a sensitivity of 10-500 IU / ml. This suggests that with a low content of the pathogen in the body, the analysis will not be detected.
Quantitative analysis is more accurate and will show the concentration of infection in the blood. This indicator is designated as "viral load", it is measured in the amount of viral RNA for a specific volume of blood. The decryption in different laboratories may differ. In addition to the measurement in IU / ml, the units of measurement "copy" are used. You can recalculate copies to IU using the formula: 1 IU = 4 copies. If in the decoding the value of the presence of the virus exceeds 800,000 IU / ml (or 800 * 103), this indicates a high content of the pathogen.

For tuberculosis
The test should be done in the morning. This is important in order to prevent the entire body of phlegm that has formed overnight from leaving the stomach. PCR analysis for tuberculosis is just as important as ELISA, Mantoux, tomograph. The test helps to highlight the presence of mycobacteria, the state of urine, total immunoglobulin, ESR, to determine the state of the lungs at the moment. For the accuracy of obtaining results when analyzing PCR, it must be carried out in compliance with the following rules:
- Sowing is carried out 3 times, but complete aspiration of the contents of the stomach should be carried out only in a hospital setting.
- Reveals mycobacteria by sowing the present masses in the stomach in less than 50% of diagnoses. Even when optimal conditions are obtained, an ultrasound scan is recommended instead.
- Even if the result is negative, the likelihood of developing tuberculosis with a change in ESR, immunoglobulin or other indicators cannot be completely ruled out.
- Cultures of materials for PCR are less susceptible to pathological conditions if obtained as part of a bronchoscopic examination, which excludes suspicions of TB in a child.
For HIV
For many people, this diagnosis is considered a death sentence. For this reason, after frequent sexual intercourse, a person becomes more attentive to the signals that his body gives (and sometimes comes up with them). The most reliable way to get confirmation or refutation of this disease is PCR analysis for HIV. The test can be used to identify the following possible health problems:
- Refutation / confirmation of the presence of HIV during the seronegative period.
- Determination of the genotype of HIV-1, HIV-2.
- Clarification of the description of the pathological process with a dubious result of immunoblot.
- Infection after blood transfusion.
- Determination of HIV status in children born to mothers who are carriers of the disease.
- Helps to establish monitoring of the viral load of the body.

HPV
The papillomavirus can be detected in any person, for a long time it can be in a latent state. Development provokes a weakening of the immune system, stress or emotional outbursts. An HPV PCR test helps determine the concentration of the virus in the blood. For this reason, it is recommended to carry out a quantitative determination rather than a qualitative one. This data will help predict the likelihood of developing a malignant infection.
The method for diagnosing the presence of HPV is based on the main property of PCR to isolate the virus DNA from the material. Due to the high sensitivity of the test, even small amounts of bacteria will be detected. Quantitative research opens up the possibility for doctors to determine the degree of danger of the disease, to make a forecast for the future. This diagnosis is mandatory for all men and women who have found warts in themselves. Quantitative PCR analysis will help determine what caused the development of HPV: a temporary decrease in immunity or a chronic disease.
For herpes
This type of diagnostics in microbiology helps to carry out PCR analysis for herpes with high accuracy. Copying of DNA fragments of the virus will occur only if the required gene is present in the material. In this case, a test based on the results of the conduct can indicate the presence or absence of the pathogen. It will be possible to detect it even with a low concentration in the blood.
Another plus of the PCR analysis is that it can detect a herpes viral infection immediately after infection, before the onset of clinical symptoms. You can determine the type of herpes (1 or 2), specific preparation is not required to pass the analysis, but doctors recommend that before taking blood to refuse:
- fried;
- spicy;
- alcohol;
- fatty.

During pregnancy
When carrying a child, it is very important to conduct this research in order to register the woman's condition. PCR analysis during pregnancy is one of the most effective methods for determining the presence of various diseases. It is necessary to conduct a test not only to identify pathologies, but also to determine the likelihood of infection of the child in utero. Only thanks to PCR diagnostics it became possible to identify the degree of progression, the development of many infections inside the womb.
Delivery of PCR tests
If you are interested in how a PCR analysis is taken, then each individual case should be considered, taking into account the type of biomaterial. Scraping, smear or blood sampling has its own characteristics, for example.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a high-precision method of molecular genetic diagnostics that allows you to identify various infectious and hereditary diseases in humans, both in the acute and chronic stages, and long before the disease can manifest itself.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was developed in 1983 by Carey Mullis (USA), for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993.
PCR analysis has become a kind of "gold standard" for most infections. Most specialists encounter it almost every day and cannot imagine making a final diagnosis without it. PCR often becomes the only reaction to identify active stages of the disease at those moments when other bacteriological, virological, immunological diagnostic methods do not work.
The advantages of PCR diagnostics in modern medicine:
Direct detection of the presence of the pathogen (namely, a specific region of DNA or RNA of the pathogen) in the sample under study.
High specificity allows you to determine a unique piece of DNA or RNA, characteristic of a particular pathogen, which excludes the possibility of false reactions.
The high sensitivity of the PCR method makes it possible to detect even single cells of pathogens (viruses, bacteria). The sensitivity of the PCR analysis is 10-1000 cells in the test sample (for example, the sensitivity of immunological and microscopic tests is only 103-105 cells).
Development of a universal PCR technique for the detection of various pathogens. The object for research by the PCR method is the genetic material (DNA, RNA) of the pathogen. The technique allows you to identify several pathogens from one biological sample.
Sufficiently fast obtaining of the analysis result. A complete study is carried out in 4-4.5 hours, less often a little longer.
Possibility of detecting pathogens before the onset of symptoms of the disease (preclinical diagnosis) and after a past illness (retrospective diagnosis). An example of preclinical diagnostics will be an examination during the incubation period (from the moment of infection until the patient complains), as well as latent infection (when there are no symptoms at all, but there are only laboratory data - PCR, for example). One of the important points of PCR diagnostics is PCR in archival material or biological residues, which is important for identifying a person or paternity.
Currently, PCR diagnostics is undergoing significant development. The method itself is being improved, new varieties of PCR appear again and again, new test systems for this reaction are entering the medical market. Thanks to this, the cost of PCR studies becomes more affordable for a wide range of patients every year.
What is the PCR method based on?
The basis of the polymerase chain reaction is the multiple doubling (amplification) of a certain region of DNA or RNA using enzymes in the laboratory. As a result, that amount of DNA or RNA is formed, sufficient for visual analysis. In the course of the study, only that section is copied that fits the given conditions, and only in the situation of its presence in the test sample.
For example, material for research, in which it is assumed that there are fragments of DNA or RNA of the pathogen (saliva, blood, urine, secretions from the genitals), is placed in a special reactor (amplifier). Further, specific enzymes are added to it, which bind to the DNA or RNA of the pathogen, and a copy of it is synthesized. This copying takes place in several stages according to the type of "chain reaction", and ultimately hundreds and thousands of copies can be formed from one copy of the genetic material. Then comes the analysis and comparison of the result with the available database on the structure of various pathogens. By means of PCR, it is possible not only to identify the type of pathogen, but also to give a quantitative result of the analysis, that is, how many pathogens are in the human body.
The PCR method is currently expanding the range of research opportunities: the introduction of mutations, the splicing of DNA fragments, and has become widespread in medicine, for example, to establish paternity, the emergence of new genes, etc.
What infections can be detected using PCR diagnostics
1) HIV infection (human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1 can be detected)
2) Viral hepatitis A, B, C, G (RNA-HAV, DNA-HBV, RNA-HCV, RNA-HGV)
3) Infectious mononucleosis (DNA of the Epstein-Barr-EBV virus)
4) Cytomegalovirus infection (DNA-CMV)
5) Herpes infection (DNA - herpes simplex virus HSV types 1 and 2)
6) STIs (sexually transmitted infections) - ureaplasmosis, gardnerellosis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis,
7) Tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis)
8) Oncogenic viruses - human papillomavirus infection (human papillomavirus (including its oncogenic types 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, and 59)
9) Borreliosis, tick-borne encephalitis
10) Listeriosis
11) Candidiasis (fungi of the genus Candida)
12) Helicobacter pylori infection
other
Given the range of pathogens, PCR diagnostics is actively used in gynecological, urological practice, the practice of an infectious disease specialist, in pulmonology, phthisiology, gastroenterology, hematology, oncology and others.
Material for research and the rules for its collection
The material for PCR research, in which it is possible to identify foreign DNA of bacteria or DNA or RNA of a virus, can be various biological media and human fluids: mucus, urine, blood, sputum, scraping of epithelial cells, placental tissues, blood, prostate juice, amniotic fluid, pleural fluid.
When examining for sexually transmitted infections (STIs), discharge from the genitals, a smear or scraping from the cervix, a smear or scraping from the urethra (urethra), urine is taken from men and women.
When testing for infections (herpes infections, CMVI, mononucleosis, toxoplasmosis, hepatitis B, C, HIV infection), blood is taken for PCR.
To diagnose infectious mononucleosis, CMVI, herpes infection, a swab is taken from the throat, and urine is taken for examination for CMVI. Often, for examination for damage to the nervous system, in a number of studies, cerebrospinal fluid is taken.
In pulmonology, the material is sputum, pleural fluid.
When examining for intrauterine infections - amniotic fluid, placental tissue.
Preparation for the delivery of material and PCR diagnostics
Almost all patients who undergo PCR diagnostics have the right to count on a reliable, accurate and quick result, which depends to a large extent on the laboratory's capabilities and the professionalism of the laboratory assistant. At the same time, many do not think that this very reliability largely depends on ourselves, namely, on the recommendations of the attending doctor, lifestyle and the correctness of the sampling of material. When sampling material, conditions are required that exclude contamination (contamination) of the material and, accordingly, call into question the objectivity of the analysis.
Correct preparation for the delivery of the material is not particularly difficult. There are the following recommendations of doctors for patients:
1) not to live sexually the day before the delivery of the material;
2) blood for research is given in the morning on an empty stomach (do not eat, do not drink);
3) when giving urine, the first morning portion is collected in a clean, sterile container.
The timing of the readiness of the PCR analysis
 The final result is ready in 1.5-2 days after the delivery of the material. In some cases, the result is ready on the very first day.
The final result is ready in 1.5-2 days after the delivery of the material. In some cases, the result is ready on the very first day.
Decoding of PCR results
Negative the PCR result indicates that no traces of infectious agents were found in the test material at the time of delivery. Most of the cases show the absence of the infection that was tried to be found in the test sample.
Positive the PCR result indicates the detection of traces of infection in the biological sample under study. With great accuracy, a positive result indicates the presence of infection at a given time.
There are situations when PCR is positive, but it is impossible to talk about an active infection - this is the so-called "healthy carriage" without clinical symptoms of the disease, which does not require treatment, but requires dynamic observation by a doctor. It is observed more often in a number of viral infections (HPV, CMVI, EBV infection, herpes infection and others) in materials such as saliva, scraping of the cervical canal, urethra, that is, from a local focus. However, we must not forget that transmission of infection from carriers to healthy people is possible, as well as a transition to a chronic form of the disease with activation of the process is possible. If PCR is positive in blood, then this is no longer a carrier and requires specific treatment.
The quantitative result of PCR is assessed only by the doctor individually for a particular infection separately and does not have general gradations. Based on the quantitative PCR result, the doctor can determine the degree of infection activity and set the stage of the disease, which will certainly affect the course and doses of prescribed drugs.
One of the last worrying questions: how accurate is PCR diagnostics?
There are 3 definitions for PCR analysis:
1. Accuracy (with a high degree of probability, detection or absence of infection is possible).
2. Specificity (accuracy of detecting a specific infection).
3. Sensitivity (even with a low content of the genetic material of pathogens in the test sample, the infection will be detected).
Polymerase chain reaction practically does not give false positive results (that is, there are no positive samples where there is no infection). False negative results are rare (more often this is due to the absence of an active infection in a person at the moment). For example, latent infection, chronic infection with no activity.
Infectious disease doctor N.I. Bykova
Video about why and how to take a PCR test for infections
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is an achievement of molecular biology, one of the main methods of clinical laboratory diagnostics of the late 20th and early 21st centuries, bringing enormous benefits in various fields of medical science.
Thus, even if not the living virus itself is lost among the millions of cells of the human body, but only a particle of its DNA, then PCR, if nothing interferes with it, will probably cope with the task and report the presence of a "stranger" with a positive result. This is the essence of PCR and its main advantage.
Advantages and disadvantages
The highest requirements are imposed on the laboratory performing PCR diagnostics in terms of equipment, test systems and the qualifications of medical personnel. This is a high-tech laboratory with an arsenal of highly sensitive and highly specific reagents, so it has no particular drawbacks. Is it something that gives a positive result in the absence of clinical manifestations and thereby puts the doctor in front of a dilemma: is it worth starting treatment or not?

The doctor observing the patient begins to doubt the reliability of the test results, since he does not see any signs of the disease. But still, given the high sensitivity of the PCR system, it should be remembered that it detects the pathogen even in the preclinical stage, and a positive result in this case is more an advantage than a disadvantage. Based on this, the attending physician must himself decide on the appropriateness of therapy, taking into account other arguments "for" and "against".
The advantages of diagnostics using polymerase chain reaction are obvious:
- High specificity reaching 100%, due to the presence in the selected sample of particles of nucleic acids inherent in a particular organism, but alien to humans;
- High performance, because PCR is a high-tech automated technique that makes it possible to conduct testing on the day of sampling and thus relieve the patient of unnecessary worries;
- PCR, working on one sample, is able to carry out several studies and about find multiple pathogens if she has such a task. For example, when diagnosing chlamydial infection, where PCR is one of the main methods, along with chlamydia, neisseria (gonococcus), the causative agent, can also be detected. Moreover, this does not negatively affect the reliability of the results;
- PCR testing you is dangerous microorganisms in the incubation period, when they have not yet managed to inflict tangible harm on the body, that is, early diagnosis warns of the future development of the pathological process, which makes it possible to prepare for it and take it fully armed.
In addition, in order to avoid misunderstandings that sometimes arise during diagnostics, PCR also protects itself by the fact that its results can be recorded (photograph, computer) in order to use them for expert purposes, if necessary.
A negative result is considered normal in PCR responses. indicating the absence of fragments of foreign nucleic acids, a positive response will indicate the presence of infection in the body, digital values mean the state of the virus and its concentration at the time of testing. However, the full decoding of the analysis is carried out by a doctor who has completed special training on the topic of "PCR". Trying to interpret the results on your own does not make any sense, since it is possible, which is likely to happen, to misunderstand and start worrying in advance.
What is PCR “afraid” of, what can it do and how to prepare for it?
As in any other research, sometimes test results turn out to be false positive or false negative where PCR is no exception. This can happen in the following cases:
- Violations of the technological process at one of the stages of the reaction;
- Failure to comply with the rules for the collection of material, its storage or transportation;
- The presence of impurities in the material.
This suggests that the PCR diagnosis of infections must be approached carefully, carefully and accurately, otherwise the samples of the material may change their structural structure or completely collapse.

Stages of PCR diagnostics. False results can give violations at any stage of the study.
PCR diagnostics of infections belongs to the category of "gold standards" among other laboratory methods, so it can be used to search for causative agents of many diseases that, at first glance, have nothing in common:
- Tuberculosis of various localization, pneumonia (including atypical, caused by chlamydia);
- Childhood infections (measles rubella, mumps, measles);
- Diphtheria;
- Salmonellosis;
- Zoonotic infectious disease - listeriosis (the disease is characterized by a variety of symptoms with damage to the lymph nodes, central nervous system, internal organs);
- Diseases caused by the penetration of the Epstein-Barr virus (infectious mononucleosis, etc.);
- Oncological pathology provoked by papillomavirus infection (HPV and its types);
- Borreliosis (Lyme disease, tick-borne encephalitis);
- Helicobacter pylori infection, the causative agent of which is the Helicobacter pylori microbe living in the human stomach. It has been proven that Helicobacter pylori causes the development of cancer of the stomach or duodenum;
- and almost everything.
PCR diagnostics of sexually transmitted infections is of particular importance, since the diseases caused in this way often proceed for a long time without any clinical manifestations, but during pregnancy they begin to intensify and, thus, threaten the health and even the life of the child. They behave similarly and. Some of them ("sticky") also refer to STIs, so the latter require more detailed consideration. The reader will be able to familiarize himself with the most popular techniques in the following sections of the article.
How to prepare properly in order to get a reliable result?
Immediately, we note that preparation for PCR is quite simple, requiring no special efforts on the part of the patient. You just need to complete three simple tasks:
- Not have sexual intercourse 24 hours before taking the test;
- To take and analyze blood from a vein, you need to come on an empty stomach; by the way, you cannot drink either;
- You should donate urine at night (in the morning - in a sterile jar, purchased the day before at the pharmacy).
PCR can work in any biological environment
The PCR method does not differ "bloodthirstiness", therefore, it accepts any biological environment containing the alleged infectious agent. the choice - what needs to be taken for research, remains with the doctor.

Thus, in search of a pathogen, in addition to a blood test (although it is also suitable and in most cases is taken in parallel with another material), you can use:
- (discharge of the urogenital tract);
- Scraping of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, conjunctiva, nasopharynx, genital tract (in women they are taken from the cervix and vagina, in men - from the urethra);
- Saliva;
- Sperm;
- Prostate juice;
- Placental tissue and amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid);
- Urine sediment (after centrifugation), for example, to detect some STIs and Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- Sputum and pleural fluid for the same purpose;
- Exudates;
- Cerebrospinal fluid in case of suspicion of an infectious lesion of the central nervous system;
- Biopsy material (biopsy) taken from the liver, duodenum, stomach, etc.
To the above, I would like to add that there will be enough material for testing in all cases, even in scrapings and secretions, since PCR testing does not require large volumes, a few microliters are enough for analysis, which are usually taken into an Eppendorf microtube and sent to study.
Diseases and the use of PCR
HIV and polymerase chain reaction
Usually, when passing an anonymous examination in case of positive results of immunoblotting, the diagnosis is repeated again. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is prescribed additional studies:
- Determination by means of immunological reactions of the absolute values of the number of CD 4 lymphocytes (immunocompetent cells - T-helpers or helpers), which the infection affects in the first place, after which they lose their basic properties and cannot distinguish between "ours" and others. " They mistake the RNA of the virus circulating in the blood plasma for normal cells of the body and do not react to them;
- Detection of viral RNA by PCR and calculation of the concentration of viral particles in order to establish the stage, severity of the pathological process and prognosis, taking into account these data... Of course, the word "norm" does not exist in this regard, since the reaction is always positive, and decoding of digital values is in the competence of the doctor.
PCR and hepatitis
 The PCR method can detect pathogens, most often the test is used to diagnose C hepatitis, which is poorly determined by other methods.
The PCR method can detect pathogens, most often the test is used to diagnose C hepatitis, which is poorly determined by other methods.
The hepatitis C virus (RNA-containing) in its behavior in the human body resembles HIV. Wedging into the genome of liver cells (hepatocytes), he stays there waiting for his time, which may come even in 2 years, even in 20 years, so doctors called him "affectionate killer". Hepatitis C leads to the formation of a malignant process in the hepatic parenchyma, which manifests itself in the later stages. The immune system does not notice all these events, mistaking the virus for the hepatocyte. True, antibodies to the virus are produced in some quantities, but they do not provide a decent immune response. For the diagnosis, ELISA for hepatitis C is not very informative, since it indicates that the virus has left traces, and whether it left itself is unknown. Cases of self-healing are known in HCV, while antibodies against the virus remain and continue to circulate for life (immunological memory). PCR noticeably outstrips the formation of antibodies and can detect a viral particle already after 1-1.5 weeks, while antibodies can appear in the interval from 2 months to six months
PCR diagnostics in case of suspicion of rampant hepatitis C virus in the human body is the most optimal research method, because only it is able to recognize the presence of a "affectionate enemy" in the patient's blood or liver biopsy.
However, sometimes there are cases when the antibodies are positive, and the PCR result is negative. This sometimes happens when the amount of the virus is very low or when it is "dormant" in the liver without going into the bloodstream. In order to still find the truth, a repeated analysis is taken from the patient, or even more than one.
Human papillomavirus infection
If self-healing does not occur, it can also, without showing itself, persist for a long time in the host's body, who does not even suspect about it, since no PCR has ever been done, and there were no symptoms of the disease. However, the presence of papillomavirus infection, albeit latent, is far from indifferent to human health, where certain types of virus that cause cancer (types 16, 18) are especially dangerous.
More often, the female half of the population suffers from HPV, since the virus loves the female genital area more, and especially the cervix, where some types of viruses contribute to the development of dysplastic processes, and then cervical cancer, if dysplasia is not treated and the virus is given free rein. So, the polymerase chain reaction will detect viral DNA, and then indicate the "bad" or "good" (oncogenic or non-oncogenic) type settled in the woman's body.
Other STIs and TORCH infections
 Obviously, the polymerase chain reaction can find any foreign structure consisting of nucleic acids, so this test is suitable for detecting all STDs and TORCH infections, however, it is not always used. Why, say, conduct such expensive studies to detect or gonococcus, if there are more affordable and cheaper ones?
Obviously, the polymerase chain reaction can find any foreign structure consisting of nucleic acids, so this test is suitable for detecting all STDs and TORCH infections, however, it is not always used. Why, say, conduct such expensive studies to detect or gonococcus, if there are more affordable and cheaper ones?
TORCH infections and STIs are so interconnected that it is sometimes difficult to determine to which group a particular pathogen should be attributed. In general, it can be difficult to understand them, since these are quite diverse groups of microorganisms that can be sexually transmitted always or only under certain conditions (immunodeficiency), and may be of interest only during pregnancy, due to the possible negative effect on its course and on the fetus.
PCR is the main method for detecting hidden infections
The development of clinical manifestations is based on different pathogens, which can only be found by PCR, which is its main task sometimes together with ELISA, and sometimes as the only confirmatory test, especially if there are no symptoms of the disease. Such a difficult situation can be created by a polymicrobial infection, which, in addition to obvious pathogens, also includes opportunistic pathogens.
Ureaplasma is often considered paired with mycoplasma. And this is no accident. These species, like chlamydia, are not classified as viruses or bacteria, they live inside cells and belong to STIs, although their presence in a healthy body is also far from uncommon. So, in order to distinguish a healthy carrier from a sick person, special methods are needed, where PCR is considered the most reliable, since, due to the peculiarities of the structure and behavior of these microorganisms, other studies are ineffective.
As for (type 1, 2) and, which also belongs to herpes viruses (type 5), the situation here is also ambiguous. The infection rate of the world's population is approaching 100%, therefore, in this case, identification of the virus and its dose is very important, which especially plays a role in pregnancy, because for an adult, a virus that has taken root in his body often does not cause any trouble and does not give signs of the disease.
Therefore, such an examination prescribed by a doctor should not be ignored, because in some cases the polymerase chain reaction is a mandatory and necessary method of laboratory diagnostics that can protect not only a woman, but also a small, unborn man from serious complications.
In conclusion, I would like to note that such a wonderful method as PCR has been serving humanity for more than 30 years. At the same time, the tasks of the test are not limited to the search for pathogens of infectious diseases. The polymerase chain reaction, born on the basis of molecular biology, is inextricably linked with genetics, it successfully used in forensic science for personal identification, in forensic medicine to establish paternity, in veterinary medicine, if the animal clinic has the ability to purchase expensive equipment, as well as in other areas (industry, agriculture, etc.).
Video: PCR - the essence and application