Cutaneous manifestations of syphilis are the main symptom of a sexually transmitted disease. The patient sees a rash that does not go away and goes to the doctor with it. A specialist, based on what kind of rashes a person has, will be able to conduct an initial diagnosis and determine the stage of the disease.
Body stains
As treponemas multiply in the body, certain changes occur. The appearance of a rash on the skin is the most common symptomatology. First of all, spots appear. At first, the patient notices a change in skin color in some places. They become a rich pink hue, and as syphilis progresses, they increase the area of the lesion, provoke general malaise.
Cutaneous manifestations in syphilis are classified in order to determine how long treponemas are in the body. The spots should be distinguished from other eruptions. In this case, the surface of the skin does not change. Spots with syphilis cannot peel off, they are randomly located throughout the body. The upper layer of the skin is affected, so they do not have a large depression.
Acne

A few weeks or a month after the infection, acne will begin to appear on the patient's face, body and mucous membranes.
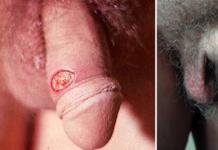
At the stage of primary syphilis, a hard chancre appears, outwardly it looks like a red spot. Then a nodule forms, over time it becomes an ulcer. The cartilaginous bottom varies in size from 1 mm to 2 cm. A week after the appearance of acne, they thicken and lymph nodes enlarge.
During secondary syphilis, acne spreads throughout the patient's body. Most of them will be observed on the face. The spread of the rash occurs when the blood contains a large number of treponemas and they begin to affect the tissues, internal organs.
New pimples will appear on the body for several months, absorbing more and more of the skin's surface.
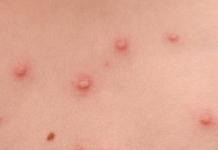
With secondary syphilis, acne is brown and rounded. They are located chaotically and have clear boundaries. The formation of abscesses indicates that syphilis is progressing successfully.
At the tertiary stage of development of syphilis, the infection affects the nervous system and the state of vital organs. Pimples become large bumps, and they are mainly located on the forehead, head and nose.
Acne during syphilis will not itch or peel off, they have a dense texture, as well as a reddish or bluish tinge. There is no pain during touching, however, crushing the rash is extremely dangerous, this will aggravate the person's condition. Without antibiotics and the selection of complex therapy, acne will not go away.
Papules
Papular eruptions have a pale pink color and a rounded shape. They should not exceed 1 cm in diameter. At first, the rash with syphilis has a smooth surface and is slightly shiny. As treponema develops, the papules begin to peel off and become denser to the touch.
Basically, the rash is located on the palms, legs and genitals. In the presence of concomitant diseases, the rash begins to itch. Due to constant discomfort, a person cannot lead a normal life, sleep disturbances and changes in the nervous system occur.
Papules on the arms and legs may be mistaken for corns by patients. The rash in these places has a denser texture and clear edges. If untreated, papules begin to peel off and crack.

White lesions occur during secondary syphilis. They are observed 6 months after infection with syphilis. The rash remains on the body for several months. In the presence of concomitant diseases or poor immunity, this period increases to a year. Treponema is not found on the affected skin areas, therefore antibiotic therapy does not affect leukoderma.
Pale areas of skin during syphilis are observed in the neck. Also, manifestations of syphilis can be found in the armpits, on the legs and arms. First, the patient develops yellow spots, then the discoloration process begins inside them. Itching, peeling, or pain is not observed in patients.
Leucoderma appears during a relapse of syphilis. Medicines do not affect its development, so the spots remain even after treatment. If rashes are found, the patient should consult a doctor as soon as possible, since changes in the cerebrospinal fluid may occur on their background. Therefore, the physician will have to monitor the patient during the treatment of the syphilitic infection and for several months after its completion.
Roseola eruptions
Roseola is observed in 70% of people suffering from syphilis. Rashes are rounded spots with jagged edges. Roseolas range in color from pale pink to crimson. Doctors draw the attention of patients that even on one part of the body there may be spots of different colors. When you press on the roseola, the stain disappears completely.
Roseola do not merge with each other and do not peel off during the progression of syphilis. In terms of their relief and consistency, the spots should merge with the skin. The diameter of roseola does not exceed 2 cm. The rashes change their color during coolness, they become more intense in color.
The rash can be located on the abdomen, back, chest and mouth. Without medication, the rash persists for 3 weeks. In the mouth, the rashes will be clearly visible, as they acquire a blue tint. The appearance of the oral cavity can be confused with sore throat, if you do not take into account the other symptoms of syphilis. Simultaneously with roseola, ulcers appear in the mouth, they are located on the vocal cords and larynx, which is why the patient's voice disappears.
Recurrence of roseolous rash occurs within 3 years after infection with a venereal disease.
Hard and weeping chancres

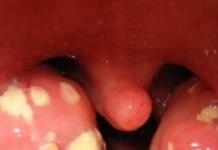
At the initial stage of the development of the disease, when treponemes begin to multiply in the body, chancres appear. They occur at the end of the incubation period and are usually observed by doctors several weeks after infection. Chancres spread on the skin and mucous membranes of the body. At the initial stage, rounded, hard eruptions with smooth edges are formed.
Chancres that are hard do not cause pain or discomfort. On palpation, it resembles cartilage, since it has a seal. Outwardly, the rash looks like an ulcer, but does not have clear edges. Small chancres are found on the mucous membranes. Large seals up to 5 cm in diameter are observed on the abdomen, thighs, genitals and extremities. Discomfort can be felt when the chancre is located on the lips.
Cutaneous manifestations contain a high concentration of treponemas, therefore, they are dangerous for healthy people. The rash heals after a few months and a scar forms in its place.
Weeping chancres occur when there are complications. Pus or lymph is released from them. When touching wet areas, burning sensation and discomfort appear.
Warts
Condyloma is a benign tumor that appears on the skin as a wart. Patients seeing them do not take the necessary measures, believing that the papilloma virus simply develops in the body. Treponemas are capable of provoking the formation of genital warts during the secondary stage of the development of the disease.
Warts appear in places where friction constantly occurs or the skin is in regular contact with fluid.
This can be the area of the armpits, anus, or genitals. Warts grow and increase in size over time. Erosion occurs on the surface, it contains a large number of treponemas. Warts vary in color from yellow to red.
In addition, the patient will exhibit concomitant symptoms:
- aching pain in the limbs;
- redness and swelling of the joints;
- thickening of the lymph nodes;
- pain in the ribs or heart;
- sleep disturbance;
- temperature rise to 39 degrees.
The presence of the listed symptoms indicates that the infection has begun to affect the organs and systems of the body.
Alopecia
At the secondary stage of the development of the disease, the rash spreads throughout the body and begins to appear on the head. Due to a violation of the condition of the skin, deformation of the hair follicles occurs, and therefore, hair loss is observed.
Baldness can be complete or partial. In this case, small rashes appear with a diameter of several millimeters.
During partial alopecia, bald patches have an uneven, rounded shape and spread unevenly throughout the head. As the pathology progresses, the foci of alopecia become larger and combine with each other.
In areas where there is no hair, redness and flaking appear. There is a risk of scarring. Alopecia begins on the temples or the back of the head, possibly the loss of a mustache and beard.
With complete baldness, skin redness and flaking is absent. The patient notices that the hair has begun to thin out in all parts of the body. In addition, a change in the structure of the hair is possible, they become more rigid and dull.
Whether hair growth will be restored depends on the characteristics of the disorder and the presence of concomitant pathologies. Timely treatment and a strong immune system can prevent alopecia during syphilis. In most cases, hair follicle activity is restored 2 weeks after the end of therapy.
Ulcers
Ulcerative formations are formed on the mobile areas of the skin. They appear in the absence of drug therapy or improperly selected medications. A chancre forms on the surface of the ulcer. Over time, it will grow and change its appearance.
With primary infection, ulcers rarely appear on the surface of the skin.
They arise against the background of aggravation of the pathological course of the disease. Ulcerations cause pain and discomfort, since the skin in this area becomes susceptible to any mechanical stress.
 Syphilitic ulcers occur in the area where treponema penetrated. They are observed one month after infection. Let's list the main features of ulceration:
Syphilitic ulcers occur in the area where treponema penetrated. They are observed one month after infection. Let's list the main features of ulceration:
- Ulcers appear on the mucous membranes of the genitals, in the mouth or anus. Their localization depends on the method of infection.
- When touching or contacting clothing, the patient may experience pain.
- The size of the ulcers does not exceed 2 cm, they have a round shape and clear edges.
- Ulcers on the surface of the skin are isolated. Multiple formations indicate a serious violation.
- Ulceration can bleed if there is a violation of the integrity of the vessels.
With the help of medicines, ulcers can be eliminated in 3-4 weeks.
Purulent wounds on the face
Purulent rashes are often confused with an allergic reaction or skin fungus, especially when they are found on the body of a newborn baby. Watery sores on the face are common in older people. Doctors strictly forbid opening them with a needle or trying to press, since there is a high risk of infection in an open wound.
Purulent formations are eliminated not only with antibiotics, but also topical preparations are used to alleviate the patient's condition. The formation of a purulent abscess obliges a person to consult a doctor as soon as possible, since it can lead to deep damage to the skin.
Is there itching with syphilis
Having found several pimples or reddening of the skin, patients begin to look for information about all kinds of sexually transmitted diseases. After reading a few paragraphs about syphilis or other pathologies, people are already starting to collect things to go to a venereal clinic.
Doctors draw attention to the fact that it is impossible to independently determine syphilis; this requires consultation of a venereologist.
A specialist, based on a survey, symptoms and examination, will be able to make a correct diagnosis. Then the doctor will take biological material for laboratory tests to confirm the presence of treponemas in the body. Visual photos in our article will help you understand whether the rash is associated with a venereal disease, but it is unacceptable to draw conclusions only on the basis of this.
If, in addition to rashes, itching is observed, then the likelihood of an infection in the body is minimal. A distinctive feature of syphilis is that the skin begins to itch only in the presence of concomitant diseases. Therefore, if the skin itches a lot, then most likely there is no treponema in the body.
Treatment of the rash is carried out in combination with therapy against syphilis. For this, antibiotics of the penicillin series are used. In order to prevent the spread of the rash, local antibacterial agents are used.
Most patients are monitored in a hospital setting to administer the drug every 3 hours. This allows you to speed up the healing process and alleviate the person's condition. In addition, during syphilis, internal organs are seriously affected, so there is a need to monitor the patient.
A rash with syphilis is one of the main manifestations of the second period of this serious illness. Such rashes have a characteristic appearance: small elements of pinkish color. There is no clear localization of such rashes, they can spread to the entire surface of the body, but are more pronounced on the skin of the thighs and shoulders.
The cause of a rash with syphilis is a disturbance in the work of small blood vessels.
On the body, a syphilitic rash usually persists for about two months and then begins to disappear. Difficulties with timely diagnosis often arise due to the fact that many people mistake such rashes for an allergic reaction, prickly heat, or signs of other mild diseases. Therefore, if a rash occurs, it is worth contacting a specialist for correct diagnosis.
If treatment is not started in a timely manner, syphilis progresses to a more severe stage, and various complications may develop, which will require long-term, complex, and often unsuccessful treatment.
Types of rash with syphilis
At the current level of medicine, syphilis is not considered a disease that in most cases ends in the death of the patient. However, its treatment should still be approached carefully and in no case should the situation be triggered. If pathology is detected in the early stages, it can be successfully treated and practically leaves no traces. But in advanced cases, it can lead to the spread of infection throughout the body, while the nervous system is most affected.
There are several types of rash with syphilis:

Characteristic signs of a syphilis rash
The most popular places for localization of a rash in syphilis are the scalp, the genital area and, in women, the area under the breast. There are a number of important diagnostic signs that can help distinguish a syphilis rash from a rash that appears for another reason. Syphilis can be suspected if the following points are noted:
In some cases, the appearance of syphilitic eruptions occurs against the background of a rise in temperature. Mild cold or flu symptoms may also be observed.
Treating syphilis rash
It is not possible to cure syphilis on your own at home. So you can start the disease, which will lead to serious and serious consequences. Traditional methods for the treatment of this pathology do not exist. It is possible to cope with it only with the help of specially selected medical treatment, which can only be chosen by a doctor. You should be prepared that the treatment process will drag on for a long time.
If you suspect syphilis, you should visit a venereologist. For an accurate diagnosis, you will have to pass a number of tests. A syphilis rash can be confused with the usual chickenpox, acne, allergic rashes, and more.
Treatment for syphilis should be comprehensive and include:

- taking strong antibiotics;
- a set of measures to improve the protective properties of the body;
- mandatory intake of vitamin preparations.
If the disease was detected in a timely manner, and treatment was started in a timely manner and includes the entire necessary set of measures, then in most cases the patient is fully recovered.
Rash with syphilis (photo)
1. Photo of a rash with syphilis (papular syphilis, syphilitic roseola)
Syphilis on the legs, nails; musculoskeletal disease
Medical practice regularly proves that, despite the fact that in the overwhelming majority of cases, syphilis is infected sexually, its manifestations can occur on any part of the body, including affecting the musculoskeletal system. By the way, the definition of syphilis on the legs and syphilis of the musculoskeletal system are not exact synonyms in the medical sense, since the musculoskeletal system includes a concept much wider than legs alone.
Damage to the musculoskeletal system
The most common manifestation of this sexually transmitted disease in relation to the musculoskeletal system is pain in the bones. If other symptoms of the disease can be depicted or taken a photo, then only subjective sensations and research data indicate that a person is affected by the musculoskeletal system. The pain intensifies at night, but when a person complains to a doctor dealing with problems of the musculoskeletal system, he does not find visible changes in the bones. This applies only to the primary stage of the disease, but secondary and tertiary syphilis of the musculoskeletal system is already characterized by visible damage to the bones and joints, often irreversible.

Lesion of the legs with syphilis
Manifestations of this venereal disease on the legs can occur at any stage. Syphilis on the legs, the photo shows it well, it may look like ordinary skin diseases. The primary stage is evidenced by the appearance of a chancre on the legs, a photo of which makes it possible to assume that it is most often localized on the feet or the inner side of the thigh. The secondary stage is characterized by a rash on the legs, which is of several types and indicates that treponema with blood flow has spread throughout the body, and an irreversible change in internal organs has begun. It is localized most often on the knees, less often on other parts of the legs. Tertiary signs are syphilides. they can also occur on the legs - the photos show serious lesions inherent in this period. On the legs, syphilis is easiest to notice in the secondary stage, since the rashes are characterized by extensiveness.
In most cases, the first sign that syphilis develops in the human body - a hard chancre - is located in the place where a healthy person came into contact with the causative agent of this venereal disease, and subsequently it can form anywhere, since in the absence of treatment, treponema penetrates practically to all organs or systems.
However, a hard chancre. characteristic exclusively of the primary period of the disease. Therefore, on the one hand, it seems impossible for its appearance on various parts of the body: arms, legs, abdomen, neck, face, etc. But do not forget that syphilis, unfortunately, can enter the body not only through sexual contact. Existing transmission routes suggest that contact of a healthy person with treponema can occur on absolutely any part of the body, including the legs.
The appearance of a chancre on the leg, a photo of which is not so common, is a rare phenomenon, but possible. The most likely route of transmission is through personal items, in the presence of microtrauma to the skin of the leg. The situation is complicated by the fact that a person, unaware of his contact with the causative agent of syphilis, simply does not pay attention to the chancre on the leg, especially since it develops absolutely painlessly, and after a while it disappears altogether. Unfortunately, the disappearance of the chancre on the leg does not in any way indicate the disappearance of syphilis - on the contrary, the disease is aggravated, passing into the secondary stage and further, thereby complicating the treatment and provoking consequences, often irreversible.
Symptoms of syphilis on the nails
Nails with syphilis are affected at its secondary stage. The disease can be present either directly on the nail plate, or on the surrounding tissues. If the nail plate is affected, the patient may not even notice the disease: it develops slowly, does not bring painful or unpleasant sensations. In this case, there is a risk of contamination of others (for example, when performing a pedicure or other type of nail treatment). The nail itself with syphilis becomes much thicker, more like a claw, it crumbles easily and takes on a dirty gray color. Notches, grooves can be found on the surface of the nail, and sometimes complete detachment of the nail plate is observed. If no treatment measures are taken at this stage, the nail will take on a normal appearance after a while, but this does not mean recovery from a venereal disease - it goes into the tertiary stage.
If it is not the nail itself that is sick, but the periungual integument, a roller appears, dense when pressed, red with a bluish tinge. The nail plate itself also suffers, especially if suppuration develops. The defeat can cause complete death of the nail. As a rule, all nail lesions in this disease develop simultaneously with the onset of a rash.
Skin manifestations can be a sign of primary syphilis, when the microbe multiplies directly in the focus of penetration. This forms a hard chancre.
Skin manifestations accompany the congenital form of the disease.
Erosion is similar to an ulcer, but does not have well-defined edges. This is a superficial defect that can go unnoticed. Hard chancre or erosion is most often single, but several foci may form.

Small ulcers are more common in women and are located on mucous membranes. Giant chancres up to 5 cm in diameter are localized on the skin of the abdomen, inner thighs, perineum, chin, upper limbs (hands and forearms) and are recorded mainly in men.
Chancre may be found on the lips or tongue. In the latter case, a slit-like or stellate form of the defect occurs.
One of the atypical forms of primary syphilis is chancre-panaritium. It forms on the fingers. The affected phalanx swells greatly, turns red, becomes sharply painful. A deep, irregular ulcer is visible on the skin.
Secondary syphilis
Where does the rash appear in secondary syphilis? It can occur anywhere on the body. Despite the variety of symptoms, all secondary syphilis (cutaneous manifestations) have common symptoms:
How long does it take for a syphilitic rash to appear?
A large number of items appear after the end of the primary period. This period is about 10 weeks after infection or 1.5-2 months after the onset of a hard chancre. Small bright spots or seals appear, located symmetrically. With relapses of the disease, syphilides occur in much smaller quantities, are located on a limited area of the skin, grouped into rings or garlands.
The spots are located separately from each other, do not merge or peel off. In consistency and relief, they do not differ from the surrounding skin. Their diameter ranges from 2 mm to 1.5 cm. They become more noticeable when the skin is cooled, for example, during examination. Roseola lasts up to 3 weeks without treatment, is located on the back, chest, abdomen, less often on the forehead.

Recurrent roseola rash occurs between 6 months and 3 years after infection. Very often it appears in the mouth, on the soft palate and tonsils. The rash has a red color with a bluish tinge, the elements are clearly visible against the background of a normal mucous membrane and resemble a sore throat. Sore throat, fever and other common manifestations in most cases are absent. At the same time, ulcers often appear in the oral cavity, on the walls of the larynx and vocal cords. This causes a hoarse voice.
Papules are not found on the dorsum of the hands. They are most often located on the back, back of the head, forehead and around the mouth.
How to recognize a syphilitic rash?
Acne-like rash is represented by several small conical vesicles located on a hardened base. The bubbles become crusted, which disappear after 2 weeks. Scars usually do not form.
Syphilitic ecthyma
Herpetiform syphilide
Leucoderma
For relapses of secondary syphilis, leukoderma is very characteristic. It appears six months after infection and persists for several months and even years, but sometimes disappears much faster. Interestingly, pale treponema is not found in the affected skin. This rash is resistant to treatment.
Leucoderma is observed mainly during relapses. It is resistant to treatment and can persist for a long time even after recovery. Such a lesion is often accompanied by specific changes in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Syphilitic rashes, in order: syphilitic ecthyma, plantar syphilis, leucoderma
Does syphilis rash itch?

Tertiary syphilis
Congenital syphilis
Papular syphilis may present with skin infiltration. The skin thickens, turns red, swells, then peeling begins. This sign appears on the palms, soles, buttocks, as well as around the mouth and chin. The affected skin is damaged with the formation of diverging cracks. After their healing, scars remain for life. The nasal cavity and vocal cords are affected.
Syphilitic pemphigus is another typical manifestation of congenital syphilis. Bubbles with transparent contents, up to 2 cm in size, are formed on the skin, surrounded by a red rim. They always appear on the palms and soles. The bubbles do not expand or merge. At the same time, the internal organs suffer, the general condition of the child deteriorates significantly.
Syphilitic pemphigus
How to determine what causes skin changes? If rashes of unknown origin appear, you should consult a dermatologist. In many cases, the diagnosis becomes clear already upon examination.
Laboratory diagnosis of syphilis is quite difficult. It is difficult to independently interpret the results obtained, therefore, a doctor's consultation is necessary.
How to treat a syphilitic rash?
Antihistamines such as Claritin are often prescribed to prevent an allergic reaction to antibiotics.
Syphilis in women and men
Infection methods
Rarely enough, but still there are cases when syphilis is transmitted through the use of non-sterile medical instruments. A child can become infected through violent sexual contact with an infected adult. A newborn baby can become infected while in the womb of a sick mother.
Usually, the causative agent of this disease enters the body through the skin, as well as through the mucous membranes of the mouth and genitals. After entering the body, the virus enters the lymph nodes and soon spreads throughout the body.
Symptoms and course of syphilis in men
Syphilis in men
Often, a man may not even be aware of his infection. Usually, men do not pay much attention to skin rashes and other symptoms of this disease. Moreover, the signs of syphilis disappear after some time. But this speaks of the progression of the disease, rather than its cure. Taking this into account, one should pay attention to the obvious signs of syphilis (more details with the photographs of patients can be found below).
First of all, the man's foreskin thickens and swells. In addition, a clear sign is the appearance of small ulcers in the genital area, urethra and anus. Ulcers can also appear on other parts of the body. These ulcers are called chancre. They appear at the initial stage of the disease. Typically, the chancre takes a round shape from one to four millimeters in diameter. It has dense edges, is red and is painless. However, such ulcers are very insidious as they are contagious to another person. If an infection enters the ulcer, tissue necrosis may begin.
About a week after the ulcers appear, the lymph nodes swell and the temperature rises. However, the general well-being of a person remains more or less normal. At this moment, there are practically no sensations, and that is why a man does not always consult a doctor.
With the onset of the second stage of syphilis, a rash appears on the skin. At the moment, this disease is already destroying the body. If treatment is not provided to such a patient, after a few years, the systems and organs of the male body will slowly begin to refuse. At such a time, a favorable outcome of treatment is impossible. That is why, for timely treatment, tests should be taken after accidental sexual contact or at the first manifestations of the disease.
The first signs and course in women
Syphilis in women
In women, the first signs of syphilis are already noticeable a couple of weeks after infection. Ulcers appear in a woman in the area of the labia and vaginal mucosa. However, they can form on other parts of the body as well.
There are times when the disease is completely invisible. The only thing to pay attention to is the general health and lymph nodes. At the first stage of the disease, only some of the lymph nodes are enlarged. You should also see your doctor if you feel faint or unwell.
The second stage of syphilis in women is characterized by enlarged lymph nodes throughout the body. In addition, a headache appears. aches, skin rash, bone pain, and fever. The development of the disease can lead to loss of eyelashes and eyebrows. In the third stage of development of syphilis, all internal organs are affected.
Syphilis is especially dangerous during pregnancy. An infected woman can carry a child with special pathologies, which sometimes may not be compatible with life. She can also give birth to a dead baby.
The incubation period for this disease can last from three to six weeks. As already mentioned, the first sign of the disease is an ulcer, which is round in shape and can range in diameter from half a centimeter to two centimeters. This ulcer has a smooth, shiny bottom and hard edges. Then the lymph nodes in the affected area gradually increase. After two or three months, a characteristic rash appears that can be in the form of bubbles or dark red spots. Sometimes the rash can be accompanied by itching. With syphilis, a woman usually feels sore throat, malaise, and fever.
Photos of patients. What skin lesions look like
Diagnostics
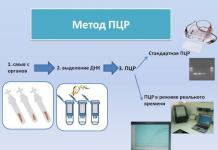
Nowadays, there are a large number of blood tests that can diagnose a disease such as syphilis. Such analyzes are based on the detection of specific antibodies. When a mass examination is carried out, the Wasserman reaction is used. However, sometimes this analysis can give false readings. In addition, to diagnose this disease, a clinical examination of the anus, genitals and skin is carried out. Also, to detect syphilis, dark-field microscopy, direct immunofluorescence reaction and polymesar chain reaction are performed.
Treatment of syphilis in men and women
The main method of treating this disease is considered to be the use of prolonged-acting penicillins, since the causative agent of syphilis can only die from exposure to antibiotics. Moreover, all sexual partners of a sick person should be treated with this method.
At all stages of the development of this disease, drugs such as erythromycin, penicillin, doxycycline and tetracycline are used. Treatment of syphilis should be prescribed by a dermatovenerologist and carried out under his constant supervision. Treatment is often carried out anonymously. After the end of treatment and complete recovery, the patient should be observed by a doctor for some time.
To prevent syphilis, you need to take precautions when dealing with other people and educate your family. If signs of the disease are nevertheless found, complex treatment should be started immediately.
Material updated 19.04.2017
Syphilis: photos, symptoms and treatment
articles are a chronic venereal disease that has been challenging humanity for many years. centuries, it is prone to a systemic course and provokes foci of the development of specific inflammation on the skin, mucous membranes and internal organs, and also affects the articular-bone system of a person.
As early as the beginning of the last century, syphilis was considered a male disease. Now, the main culprits in the spread of venous diseases are women who are indiscriminate in choosing a sexual partner and do not use personal protective equipment. It should be noted that today syphilis is most often detected in strata of society with a low sexual causative agent.
syphilis culture
The causative agent of the disease is treponema pale. The name "pale" bacterium is bad due to staining with basic dyes. It is a mobile active pathogenic gram-negative microorganism of a spiral-shaped thin curved body, moving around its own longitudinal axis. It was first discovered in the year 1905 by Hoffmann and Schaudin. Treponema pallidum is capable of developing only in an airless space, i.e. is an obligate anaerobic.
To date, there are three subspecies of the main treponemas:
Pale treponema belongs to the order of spirochetes. In length it reaches 4-14 microns in diameter, in microns - 02-05 microns. The body of this unique bacterium is covered with a mucopolysaccharide substance, which complicates the access of antibodies and phagocytes of the host.
In a live form, treponema pallidum can be detected with a microscopic infected examination of the material.
According to experts, the causative agent passes the stage of intracellular development of syphilis. After cell death, many treponemas enter the intercellular space and infect neighboring cells of their host.
artificial: on Note nutrient media, this genus of bacteria practically does not grow, and also quickly perishes human outside the body. At the same time, in the cold, their viability remains somewhat longer.
Pale treponema some are sensitive to antibiotics, and they also quickly die under the influence of disinfectants.
Ways of transmission of syphilis
The professional route of transmission of the disease is sexual. At the same time, with direct contact with a patient who is acute in an infectious form, asexual (infection) household is possible, and infection can occur through household items that are contaminated with saliva, other pus or secretions containing the pathogen. To the present, fortunately, the likelihood of domestic syphilis is negligible. This form of the disease can still be found in developing countries with a very low level of sanitary and hygienic skills of the population. Generally, children of younger age suffer from domestic syphilis.
In the event that a pregnant woman becomes infected with syphilis, due to transplacental penetration, the pathogen becomes infected with the fetus. Often this congenital ends in syphilis or the death of an unborn child.
Syphilis classification
Syphilis is of two types: congenital and acquired. Further, in accordance with the classification, the symptoms:
Syphilis symptoms
Symptoms of primary
syphilis, acquired syphilis, the average incubation period is about 30 days (less often 15-20 days or several months).
Note: the reason for a long, more latent period is the intake of infection after pale treponema of small doses of medications that inhibit the pathogen.
The first sign of primary syphilis is the appearance of a hard chancre (at the penetration site of infection). As a rule, this is localized formation on the genitals, in the area of the anus, and others on also areas of the skin and mucous membranes in particular. In membranes, it can be found in the cervical cavity, on the mouth of the uterus, in women on the nipples or on the fingers of the hands. It can be a single multiple or a formation (bipolar chancres).
Solid is a chancre, a painless, rounded, superficial erosion or ulcer that has smooth, smoothly centered, descending edges, surrounded by a healthy integument. cloth color can vary from bright grayish to red-yellow (the color of spoiled fat). Most often, the hard chancre has a smooth, shiny surface, under which exudate infected with a huge amount of treponem accumulates.
At the same time, in areas of open bodies, exudate can sometimes form and shrink crusts. At the base of the hard chancre, there is a seal that resembles ear cartilage (dense elastic infiltration). Thanks to him, this formation got its name.
On average, the diameter of the neoplasm, however, is 1 cm, which in clinical practice can be found dwarf chancres the size of a pinhead or giant chancres reaching 3-4 cm in diameter.
With an uncomplicated course, spontaneous healing of a hard chancre occurs (1-10 weeks through).
Very often, patients infected with treponema pale, due to painlessness, simply do not notice the primary signs of subjective syphilis. However, for the slit-like chancre, which is localized at the bottom of the radial fold of the anal opening, severe pain is characteristic (due to the fact that it is constantly injured during bowel movements). Also, painful sensations are caused by chancre-panaritium (a mixed consequence of infection), which forms on the nail phalanx of the index finger. If the patient has a complicated solid course of chancre (phagedenism, gangrene, phimosis, paraphimosis or), moderate pain is observed.
days 5-7 After the appearance of the first syphilitic symptom, regional lymph nodes arising on the lymph drainage pathway increase. In primary syphilis, regional lymphadenitis is characterized by an almost painless and uneven increase in some lymph nodes.
This period can last six to eight weeks. A week and a half before the end of it, specific polyadenitis develops (most of the subcutaneous lymph nodes increase). Patients develop head fever, pain, malaise, and muscle aches. This symptomatology is a sign of the mass spread of some pathogen. Infection of persons infected with treponema pallidum may develop neurotic disorders or depressive symptoms.
conditions of secondary syphilis
The secondary period without syphilis treatment lasts approximately 2 years. During this exacerbation, several times can be replaced by wave-like latent phases with a complete absence of the first.
symptoms of a rash (papules or roseola) often occur with residual manifestations of hard chancre and through. scleradenitis 1-2 months, they disappear without a trace, and the period begins early latent syphilis. After several weeks (months), a wave of generalized rashes (secondary syphilis) comes, which lasts about 1-3 months.
As a rule, over time, the latent duration of the periods increases, the elements of the rash become larger and are located in groups, and the number of rashes decreases. Most often they can be found on the lining of the oral mucosa or in the To area.
perineum of secondary recurrent syphilis is characterized by wide occurrence of genital warts, as well as loss of leukoderm and hair (violation of skin pigmentation). Sometimes pustular syphilides can be found on a sick body, which cause some subjective disorders, and soon disappear by themselves (without treatment).
Despite the fact that during this period there is a purely pale skin, symptoms of treponema, seeded all tissues and can cause various forms of meningitis, liver pathology (icteric or anicteric hepatitis), lipoid nephrosis or other kidney diseases, syphilitic gastritis. uveitis, as well as various joint and bone lesions. Along with these, serious aspects of the disturbance of the nervous system are noted (stupefaction, epileptic and paresis of seizures, as well as general cerebral phenomena).
when: Note carrying out timely anti-syphilitic treatment, lesions of the early nervous system are completely eliminated.
tertiary Syphilis symptoms
For tertiary syphilis, a long latent course is characteristic. It can appear 3-4 years later (in the complete absence of treatment, with or inadequate treatment). Most often, this form of pathology can be found in patients with chronic alcoholism, tuberculosis, or others.
In infections during the period on the skin and mucous membranes of the patient, an insignificant amount of dense infiltrates localized in the subcutaneous tissue or in deeper tissues is found. After some time, they disintegrate, and in their place painless ulcers appear, which scar only a few months or years later. It should be noted that such syphilides are not accompanied by subjective disturbances and disorders of the general condition of the patient. They contain very little of the pathogen, and therefore, they are practically not contagious.
Visceral symptoms
syphilis visceral lesion affects almost all organs of the patient, but most often - the cardiovascular system. Patients often complain of shortness of breath and persistent retrosternal pain. With syphilitic aortitis, the insufficiency of the mitral and aortic valve develops, and the ascending aortic section is also thickened.
Another symptom of early visceral syphilis is considered to be a lesion of the digestive tract, proceeding with disruption of the beginning.
In the liver of the secondary period, patients develop renal pathology. In this case, most often benign proteinuria, glomerulonephritis or specific lipoid nephrosis are observed.
On the part of the respiratory system, bronchopneumonia can be diagnosed, dry bronchitis or interstitial when.
pneumonia in the development of late syphilis of bones in patients diagnosed with periostitis, osteoperiostitis, osteomyelitis of flat and tubular bones, as well as syphilitic synovitis and osteoarthritis.
late Symptoms of neurosyphilis
After 10-15 years from the onset of patients, the disease reveals latent meningitis (very anti-syphilitic in stable therapy). With late diffuse meningovascular syphilis, against the background of pronounced symptoms, meningitis is noted, a lesion of the blood vessels, in which the cranial nerves are often involved, the sensitivity of the brain or spinal gum is disturbed, the sensitivity of the gum of the brain or spinal is soft (brain tumors characteristic of tertiary syphilis stage) and other neurological disorders.
Also at this stage, patients often develop a syphilitic state (psychosis of confusion of consciousness, delirious states, and hallucinosis, hallucinatory-paranoid psychoses).
Congenital today
On syphilis day, congenital syphilis is a rare enough pathology. It occurs as a result of intrauterine infection, which most often can occur when the mother is diagnosed with an early stage of syphilis. Sometimes congenital syphilis proceeds together, but, asymptomatically, in clinical practice, there are cases when the fetus reveals white pneumonia, liver damage, long bones and internal glands. Often. secretion of this condition in the VI-VII month leads to pregnancy death of the fetus. Also, a miscarriage may occur at a later date or a sick birth of a child.
The most severe congenital syphilis occurs at an early age (up to 2 years). A flabby child is born with wrinkled skin that is dirty yellow, the color is diagnosed with specific pneumonia, symptoms of syphilitic and pemphigus dystrophy (the appearance on the palms and soles of serous content with blisters). Early congenital syphilis on the background of skin lesions, pathologies of the respiratory central nervous system, pathways and organs of vision.
Late congenital syphilis is diagnosed in children 4-5 years old. At this time, a few appear on the mucous membranes and skin of the child, and lesions of the internal organs are revealed and rashes are often revealed.
osteosclerosis in patients with congenital syphilis there is no process of the xiphoid sternum, the length of the little finger is much shorter than normal ("infantile little finger"), a "gothic" (palate) high is found, and there may also be buttock dystrophy (skull-skull) and thickening of the sternal end of the right clavicle.
Diagnosis of syphilis
Diagnosis of syphilis itself includes a visual examination of the patient, collection of an epidemiological anamnesis, as well as laboratory research methods.
In laboratory practice, several techniques are used to detect syphilis:
Syphilis treatment
method The main treatment for syphilis is antibacterial present. At the moment therapy, as before, penicillin antibiotics of the series are used (short and prolonged durant penicillins or penicillin medications). In the event that, in the case of this type of treatment, or, the patient has an ineffective individual intolerance to the group of this drugs, he is prescribed drugs of the reserve group (macrolides, fluoroquinolones, azithromycins, tetracyclines, should be, etc.) streptomycins, it should be noted that at an early stage antibacterial syphilis the treatment is the most effective and complete and leads to a cure.
The attending physician in the process of treatment can adjust his scheme, and also, if necessary, prescribe a repeated course of antibiotic. Important.
therapy, the criterion of the patient's recovery is the control serological reactions.
In parallel with the antibacterial, immunostimulating therapy is prescribed to the patient. Also, non-specific treatment is mandatory (vitamin therapy, injections of biogenic stimulants, pyrotherapy and ultraviolet irradiation).
In the process, any sexual contact is prohibited from treatment, as this can lead to infection of the sexual partner or partner to re-infection of the patient.
Note: if unplanned sexual intercourse occurs without personal protective equipment (or with a violation of the condom's integrity during intercourse), experts recommend making a prophylactic injection that prevents syphilis by almost 100%.
Prevention of syphilis
After treatment, patients are required to be at the dispensary for (observation of each form of syphilis has a corresponding period, determined by the instructions). Such methods provide clear control over the successful administration of anti-syphilitic therapy. Without fail, all sexual and household contacts of the patient must be identified, sanitized and examined in order to prevent the possibility of spreading among the population of infection.
During the entire period of observation of the dispensary, patients who have undergone syphilis are obliged to abstain from sexual contact, and they are also prohibited from being blood donors.
Public preventive measures adopted Annual:
Pregnant women who have previously had syphilis and have already been removed from the register are prescribed preventive additional treatment.
Syphilis: symptoms, treatment, photos, what is it transmitted through?
Syphilis is one of the few sexually transmitted diseases that can lead to criminal liability if the surrounding people and the sexual partner become infected. In most cases, signs of the disease in women and men do not appear immediately, but some time after the direct fact of infection. This feature makes syphilis even more dangerous.
by origin - acquired and congenital.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is by no means possible to diagnose such a serious disease as syphilis “on the Internet”, simply by reading about the symptoms and treatment of the disease. You need to know that rashes and other visual changes can be copied from completely other diseases to such an extent that sometimes even doctors can make mistakes. That is why the diagnosis of the disease should be carried out according to all the standards of the polyclinic, starting with an examination by a doctor for characteristic signs and ending with laboratory tests:
examination by a dermatovenerologist. The doctor examines in detail the lymph nodes, genitals, skin and conducts a survey for the course of the disease;
detection of treponema itself or its DNA in syphilides, chancre, gum by PCR, direct immunofluorescence reaction, dark-field microscopy;
conducting serological tests: treponemal - search for antibodies of pale treponema (RIBT, immunoblotting, ELISA, RPGA, RIF); non-treponemal - search for antibodies against tissue phospholipids, treponema membrane lipids, which are destroyed by the pathogen (rapid plasma reagin test, VDRL, Wasserman reaction). It is worth noting that the result can be false positive, that is, show the presence of syphilis in its actual absence;
instrumental studies: search for gum by means of X-rays, CT, MRI, ultrasound.
Pathogen properties
The causative agent of syphilis is treponema pallidum. In the human body, treponema is capable of multiplying very quickly, which causes damage to internal organs. Among other things, there are a lot of these microorganisms on the mucous membranes. It is this property that is the reason for the high risk of transmission through sexual or household contact, for example, through personal hygiene items, common dishes and other items in common use. Treponema pallidum does not belong to infections, after having been ill with which the body gains stable immunity, therefore, if the sexual partner has had syphilis, he runs the risk of contracting it again during unprotected sexual intercourse with a sick partner.
Treponema is unstable to the effects of the external environment and dies almost instantly when boiled. When exposed, a temperature of 55 degrees destroys treponema within 15 minutes. Also, the microorganism does not tolerate drying, but in a humid environment and low temperatures, the spirochete exhibits significant "vitality":
even if a syphilitic patient dies, his corpse is capable of infecting others for another 4 days.
Modes of transmission of syphilis
Syphilis is transmitted by:
through saliva - this route of transmission is quite rare, mainly among dentists who work without protective gloves;
through household items, provided that the patient has open ulcers or decaying gum;
through mother's milk (acquired syphilis from a child);
through blood (shared shaving accessories, toothbrushes, shared syringes with drug addicts, blood transfusions);
sexual contact (anal, oral, vaginal).
In case of unprotected, accidental sexual intercourse of any kind, for emergency prevention of the disease, it is necessary to carry out the following procedure (preferably performed no later than 2 hours after intercourse): first, you must thoroughly wash the inner thighs and external genitals with soap with a solution of the antiseptic Miramistin or "Chlorhexidine". In this case, women should sprinkle the vagina with this solution, and men should inject an antiseptic into the urethra.
But it is worth noting that this method is an extremely urgent measure, which does not give one hundred percent guarantee (only 70%) and cannot be used constantly. The condom is by far the best protection against STIs, but even when using a condom with an unreliable sexual partner, emergency prevention measures should be taken. Also, after casual sexual intercourse, you should be examined by a venereologist for other infections, but it is worth remembering that to establish a diagnosis of syphilis, it is worth examining a few weeks later, because, as mentioned above, the incubation period of the disease takes just such a time.
External ulcers, erosions, papules are highly contagious. If a healthy person has microtraumas of the mucous membrane, then in contact with a patient, he risks becoming infected. The blood of a person with syphilis is contagious from the first to the last day of the disease, therefore, transmission of infection can occur not only during transfusion, but also when mucous membranes and skin are injured with manicure and pedicure tools in cosmetology or medical salons that contain the blood of a sick person.
The incubation period of the disease
After entering the human body, pale treponema is sent to the lymphatic and circulatory systems, through which it quickly spreads throughout the body. However, a person who has just become infected continues to feel good and does not observe any manifestations of the disease. From the moment of infection until the first symptoms of syphilis appear, it may take from 8 to 107 days, but on average, the incubation period takes 20-40 days.
Thus, for 3 weeks to 1.5 months after direct infection, syphilis may not manifest itself in any way, while not only external signs and symptoms are absent, but even a blood test does not reveal the disease.
The incubation period can be extended by:
taking medications: corticosteroids, antibiotics, and others;
the state of the body, which for a long time is accompanied by a high body temperature;
old age.
A reduction in the incubation period occurs in the presence of a massive infection, when at one moment a large number of treponemas enter the body.
It is worth remembering that a person, even at the stage of the incubation period, is infectious, however, at this time, infection of another person can occur only through blood.
Syphilis statistics
Syphilis in the early stages responds well to treatment, however, even despite this fact, the disease confidently ranks 3rd among STDs, second only to trichomoniasis and chlamydia.
According to international official statistics, about 12 million new patients are registered on the planet every year, while it should be borne in mind that the figures do not reflect the full scale of the incidence, since a large number of people self-medicate.
Most often people are infected with syphilis between the ages of 15 and 40, with the peak incidence falling in 20-30 years. Women are more susceptible to infection (due to the appearance of microcracks in the vagina during intercourse) than men, but recently it was men who came out on top in terms of the number of infected. This trend is explained by the increase in the number of homosexuals in the EU and the USA.
The Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation does not have a unified record of patients with syphilis on the territory of the country. In 2008, 60 cases of the development of the disease were registered per 100,000 people. At the same time, the bulk of the infected are persons without a permanent place of residence, service workers, representatives of small businesses, people who have low-paid jobs or have no regular income.
Most cases of syphilis are recorded in the Volga, Far Eastern and Siberian districts. Recently, in some regions, there has been an increase in the number of cases of neurosyphilis, which differs in that it does not respond to treatment. The number of registration of such cases increased, respectively, from 0.12% to 1.1%.
The first signs of the disease are the stage of primary syphilis
If syphilis proceeds according to the classical scenario, then the main symptoms are enlarged lymph nodes and a hard chancre. At the end of the primary period, patients are worried about the following symptoms:
an increase in the number of leukocytes in the blood;
Syphilis is a venereal disease, most often chronic, manifests itself in the form of a gradual destruction of the skin, some organs and bones, and also affects the nervous system.
The causative agent of such a common disease is pale treponema. Today, the most popular way of contracting this disease is through sexual transmission of bacteria.
Syphilis is treatable today, provided that you do not start the disease.
A sexually transmitted disease (hereinafter simply STDs) affects almost 50 out of 100,000 people a year.
The government of each country tries to contribute to a significant reduction in sickness by informing the population about prevention and methods of protection. 
Syphilis bacteria
We have known about syphilis since the beginning of the 20th century, when this disease was the most widespread, and every 5 people were infected with it.
At that time, this disease went under a more typical name for that time "French disease".
After a while, scientists summed up that this disease is bacterial in nature, and this greatly helped in its timely diagnosis and treatment.
Treponema pale even at first received such a name due to the fact that when studying it under a microscope, scientists simply could not identify it.
After all, its entire structure, in fact, had no color, it was just transparent, and at the same time it was very poorly stained by various methods.
To expose her, they used silver staining, the Gizma method and a microscope with dark lenses.
With the help of further studies over time, it turned out that treponema can function and replicate only in a living organism.

The optimum temperature for the reproduction of this bacterium is the body temperature of a living organism, 37 ° C; under the same optimal conditions, it divides every day.
Thanks to these data, a new method of treatment was created: a forced increase in body temperature to the maximum mark, while using the malaria virus.
Thus, it was easier for the patient to tolerate the manifestations of the underlying disease.
What does syphilis look like?
Treponema pale, getting into the body of each of us, passes the incubation period, which can last from 1 week to 1.5 months.
At this time, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, so that we may not even guess who lives inside us.
With a simple examination during the incubation period, syphilis may not be found, all indications will be within normal limits.

During such a period, there is a high probability that one person carrying this disease in himself in the incubation phase and, not suspecting that he is a carrier, can transmit it sexually to his partners.
The disease begins to manifest itself after the expiration of the incubation period, when primary syphilis occurs.
The first signs of the disease appear on the skin, in the form of a rash, hard dark brown spots (ulcers), as well as on the genitals, in the oral cavity (namely on the mucous membrane of these organs).
Transmission routes
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease (STD). Transmission is ensured during traditional intercourse, during anal and oral sex, even if the carrier has syphilis in the incubation phase.
After the incubation period, a small ulcer will appear at the site of the passage of the bacterium pale treponema, which will only grow if measures are not taken to treat the disease.

When caring for a patient, infection is possible in contact with his personal belongings and the carrier itself.
With this method of infection, signs of syphilis will initially appear on the skin of the legs and hands, and after that chancre will form on the genitals.
This sexually transmitted disease can be transmitted, like everything else, through the blood. When reusing syringes, razors and other personal hygiene items.
Difference of syphilis by gender
As for women, after an asymptomatic period (about a month after syphilis has entered your body), the time for the manifestation of the disease in all its glory comes.
The first sign is the appearance of ulcers in the mouth, on the labia or anus. An ulcer (chancre) manifests itself in the form of a response of our immunity to the invasion of harmful bacteria.
Chancre is an inflammatory area of the skin or mucous membrane, usually round in shape, with a flat base.

At first, the growth on the skin will not show painful spasms, but later a rash on different parts of the body and mucous areas will surely add to it.
The course of syphilis in men is no different from the manifestations of the disease in women. Most often in men, syphilis first appears on the penis, its base and head.
But, despite this, ulcers (chancres) can also occur in the above places (mouth, anus).
The subsequent treatment regimen is not divided according to genital characteristics; for men and women, the treatment is the same.
From the birth of syphilis to chronic illness
Not many with the capabilities of modern medicine go through all the existing stages of the development of this disease.
With the latter stage, a person can live from 10 to 20 years, followed by death. Let's take a closer look at each stage of this disease.
Incubation period
Duration up to six months. During this period, there are no visible manifestations on the body or in the body itself. If the infection occurs several times in different places, then this period is reduced to 7-14 days.

This stage is prolonged due to the person taking strong immunoprotective drugs, for example, antibiotics for influenza.
For the end of the incubation period, you can take the appearance of an ulcer on the skin, followed by inflammation of the lymph nodes.
In the case when the penetration of syphilis bacteria occurred directly through the blood, then syphilis bypasses the primary stage and immediately goes into the second.
Primary syphilis
Symptoms of primary syphilis include the following:
- The appearance of ulcers on the skin and mucous membranes. Initially, it will not cause any problems and complaints. In the future, it will acquire a more bluish or even purple hue, which will mean an inflammatory process that will entail pain;
- After 7 days, inflammation begins in the lymph nodes and in the vessels around the previously manifested ulcers. Inflamed nodules are growths with swelling around the chancre. If the chancre is located in the mouth, then swelling of the tonsils and throat is possible, which makes it difficult to breathe and swallow saliva. The onset of these symptoms make it difficult to walk, defecate, eat, and more.
The transition to the second stage of syphilis can be considered the manifestation of a syphilitic rash on visible parts of the body.

Modern medicine can diagnose such a disease after the first signs appear.
For this, modern medicine uses specialized analyzes:
- ELISA is a qualitative and quantitative immunological method for the isolation of almost all combinations, molecules and viruses;
- PCR is one of the biological methods that allows you to increase the density of our DNA in one sample of genetic material.

These diagnostic methods can only be prescribed by your personal therapist or venereologist.
The cost of such tests will not hit your pocket hard, but it will certainly allow you to confirm or deny a previously made diagnosis.
But do not forget that such analyzes will give a result and show an accurate picture only at the primary stage of the disease.
Primary syphilis is characterized by the appearance of chancre (ulcers) of different diameters on the skin, by its nature it is hard and follows as a response of the immune system to the penetration of harmful bacteria into your body.

Places of its manifestation: the oral cavity (on the tongue with syphilis can also be covered with ulcers), fingers, anus, genitals.
He does not particularly worry, which most often does not contribute to an early visit to specialists in the clinic. This is followed by the development of chancre and inflammation of the lymph nodes near its site of localization.
Concomitant symptoms are: frequent and severe dizziness, fever, painful condition.
When infected with treponema pallidum through the blood, after the incubation period, the second stage follows or the disease passes into a latent stage.

Second stage
The main signs of the second stage of syphilis include:
- The skin around the chancre is dotted with spots reaching up to 1.1 cm in diameter. Such a rash can grow over time and, increasing its area, turn into large spots. In this case, it is flat pink or red up to 5 cm in diameter, flat with conical growths along the entire diameter, or purulent acne can form with syphilis. How such symptoms of syphilis look like, you can easily find photo reports on the World Wide Web;
- With the appearance of lesions on the skin, the central nervous system begins to suffer, mainly: vision, memory, attentiveness, ease and smoothness of movements. Responding quickly and taking action to treat syphilis can stop further damage to the nerves, but not repair them;
- One of the last symptoms of the second stage is hair loss. First the head: split hairs appear, then they become much thinner, and then they simply fall out. Even after intensive and timely treatment, the hairline is not restored.
Its specialists are subdivided into 4 successive phases:
- Early phase - begins after 2 months from the day of infection, lasts up to 14 days. During this period, our immunity begins to actively respond to the release of toxins from syphilis bacteria, that is, multiple ulcers appear on the body. The main blow falls on the internal organs, the central nervous system and bone tissue. Concomitant symptoms: body temperature up to 38 ° C, cough, painful condition, rhinitis, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes. Inflammation of the lymph nodes, no pain, mild or complete hair loss.
- Latent phase - begins 2 months after infection. Throughout its life, Treponema pallidum bacteria can be stopped by the human immune system. The chancre no longer spreads throughout the body, and the rash is no longer observed. But this is not the end, each of us should know that in the fight against this difficult disease, the return of syphilis is always possible.
- Latent phase - during this period, a global renewal of the primary symptoms of the disease is possible. This is possible with severe stress, colds, injuries, or simply inadequate nutrition throughout the day. In this case, absolutely all the symptoms are repeated, starting from the primary stage with a new formation of chancre.
- Primary neurosyphilis - usually this period occurs no earlier than 2 years after the disease. Its main destructive effect affects the central nervous system, brain, heart, liver, bones and joints of the human skeleton. An accompanying symptom is necessarily meningitis. In the vessels of the brain, pressure increases, which leads to frequent and severe headaches. With damage to the central nervous system, abilities such as memories, attentiveness, simplicity and ease of movement begin to weaken. Such changes are not returning to the norm.
Third stage
It is also divided into several phases:
- Latent permanent syphilis - the period of manifestation up to 20 years. It often happens that people who are carriers of syphilis at this stage are not even aware of the development of such a disease within themselves. After the next resumption of the disease, when the immune system simply cannot cope, a person may receive lifelong disability or everything may end in death;
- Tertiary form - during this period, almost the entire body suffers. There is an active formation of purulent tumors in the vessels of the brain. It is not uncommon for such tumors to attract many other bacteria in the process, which subsequently lead to gangrene and abscess.
- The final stage - lasts from 10 to 20 years and leads to a serious degree of disability with subsequent death. Complete damage to the central nervous system, paralysis, mental disorder, brain and bone tumors.
Attention, abnormal!
After the incubation period, the time comes for the formation of ulcers and, accordingly, the disease enters the first stage.
But, despite the presumptive outcome for each phase, abnormal phenomena on the skin are possible.
Based on this, unforeseen manifestations are divided into several categories:
- Damage to the vessels of the skin that occurs near the syphilitic chancre. This symptom changes the color of the penis, scrotum of men and of the female genitals, to a darker one with a blue tint. The woman is characterized by a more frequent occurrence of syphilis on the lips. I often confuse it with other gynecological inflammatory processes. However, only syphilis is inherent edema, which, when diagnosed, will not show any particular deviations from the norm, but the person will have inflamed lymph nodes.
- Idiopathic syphilis is an inflammation that causes pale treponema on the three main fingers of the hand. Pieces of skin peeling off at the lesion sites, which leads to small blood loss, more like a recent moderate burn.
- Syphilitic amygdalitis is an inflammation of the submandibular or cervical tonsils. With this anomaly, the structure of the amygdala itself does not change, only there is an inflammatory process that makes it difficult to swallow saliva and food. All accompanying symptoms are more like a sore throat (fever, sick condition, pain when swallowing), but in our case, inflammation is present only in one amygdala.
From birth side by side with danger
Syphilis can be transferred from mother to child during pregnancy, which negatively affects the fetus even during the prenatal period.
Modern medicine has identified the main indicators that can be used to judge that syphilis affected intrauterine growth:
- Institutional keratitis is an inflammation of the outer globe of the mucous membrane of the eye and eyeball. This can be seen as significant redness and suppuration of the eyes. After completing the course of treatment, traces of surgery will remain on the eyeball, and a leukoma (white mesh) will appear on the eyes. Usually, such changes still attract a significant decrease in vision, pain and watery eyes.
- Chronic hearing loss - during intrauterine growth, the fetus is actively attacked by treponema pallidum, as a result of which hearing loss is one of the main symptoms of a woman's transmission during pregnancy of syphilis;
- Hutchinson's teeth are the unfinished development of dental tissue during pregnancy in the fetus. In this case, the teeth have an unpleasant appearance, they can grow rarely, and are not completely covered with enamel. And all this leads to their early destruction.

If a woman has undergone a course of treatment and got rid of pale treponema, then the child will still have a chronic weakened immune system.
But with incorrect and untimely treatment, the child after birth will definitely have external deviations.
Breastfeeding in the presence of syphilis is strictly prohibited for mothers, milk with the bacteria of treponema pallidum automatically flows to the child, causing only harm.
A woman after treatment for syphilis can have children, but for a more accurate conclusion, you need to get a referral from your physician for the two main tests described above.
Disease treatment methods
Since the middle of the 20th century, the treatment of this STD has been carried out with antibiotics, mainly using penicillin or analogues based on it. Since treponema pale is simply not adapted to this type of antibiotics.
With this method, syphilis is treated in the initial stages, before the transition to the stage of neurosyphilis.
After that, antibiotic treatment is continued, injecting them with injections, and the method of forcibly increasing the patient's body temperature is used.
At the onset of the third stage, patients with syphilis are placed in a special hospital, and subsequent treatment is carried out using highly toxic doses of drugs, which are based on a substance - bismuth.
If a person is found to have an initial phase of syphilis, compulsory treatment of all his sexual partners in the last three months is necessary.
All personal belongings of the patient and things that he used in everyday life are subject to forced disinfection.
During the primary stage, the immediate elimination of a person in the hospital is not required; it is quite possible to do with outpatient treatment.
If the patient has already addressed the second stage of the disease, then he will be immediately admitted to the hospital.
Otherwise, self-medication can do more harm and only give treponema a pale vessel for ideal development.
According to statistics from the Ministry of Health, in the Russian Federation there are 30 syphilis patients per 100,000 inhabitants. These figures are not indicative, since a large number of infected people do not go to doctors for treatment. Thus, the risk of infection remains high.
A little about syphilis
Syphilis Is a sexually transmitted infection. The causative agent of this disease is treponema pale, which is a bacterium that is capable of movement.
How does syphilis appear on the skin?
Syphilitic manifestations are very diverse and cause difficulties in the differential diagnosis of syphilis with other skin diseases. The morphological elements that appear on the skin in syphilis vary depending on the stage of the process.
The incubation period of this disease is on average from 2 weeks to 2 months. Shortening of terms occurs in people with reduced immunity who have had infectious diseases, with a history of cancer, tuberculosis, HIV infection.
During these periods, the pathogen is in the human body, but its concentration is insufficient for the onset of symptoms of the disease. There are no manifestations on the skin.
After the specified time period, when the accumulation of pale treponema occurred, the stage of primary syphilis develops. It is characterized by a single but most contagious skin manifestation - chancre.
Formed, as a rule, in the place of penetration of pale treponema (with genital contact - in the genital area, with oral - genital contact - in the mouth, in the lips, etc.).
Chancre is formed in several stages:
- the formation of a spot of small size, pink-red;
- the formation of an erosive defect;
- compaction of the bottom by erosion, color change to bright red. Erosion is covered with a transparent or brown film.
With timely treatment or, on the contrary, the transition to the next stage of syphilis, the chancre again goes into the stage of the spot, and then completely disappears. As a rule, such a neoplasm does not cause discomfort in an infected person. A slight itching may occur in the area of erosion.
Among the diseases that are predominantly sexually transmitted, syphilis occupies a special place. One of the main causes of this disease is the promiscuity of sexual intercourse, while a syphilitic rash, the symptoms of which are pronounced, becomes a kind of "gift" received not for too diligent behavior. The peculiarity of the disease also lies in the fact that complete disposal of it is possible only at the initial stages of its course. Irreversible consequences become when the brain disease is affected, while the treatment becomes almost impossible.
general description
The statement that syphilis is exclusively a sexually transmitted disease is not entirely true. The fact is that it is possible to become infected with it in everyday life if the infection directly enters the bloodstream through scratches or wounds on the body, it is also possible when using toilet items (towel, washcloth) belonging to the patient. In addition, infection with syphilis can occur through blood transfusion, it can be syphilis and congenital. Basically, the rash is located in the foci in the area of the hair and steps, as well as on the palms. In addition, in women, it is also localized under the mammary glands; for both sexes, its concentration can be located in the genital organs.
After 3-4 weeks from the moment of infection, the place in which the introduction of pale treponema, the causative agent of the infection of this disease (which is mainly the genitals), takes place, acquires signs indicating primary syphilis.
Primary stage symptoms
Signs of primary syphilis are the appearance of a small red spot that turns into a tubercle after a few days. The center of the tubercle is characterized by gradual tissue necrosis (its death), which ultimately forms a painless ulcer, framed by hard edges, that is, a hard chancre. The duration of the primary period is about seven weeks, after the beginning of which, after about a week, all lymph nodes undergo enlargement.
The end of the primary period is characterized by the formation of many pale treponemas, causing treponemal sepsis. The latter is characterized by weakness, general malaise, joint pain, fever and, in fact, the formation of a characteristic rash, which indicates the onset of a secondary period.
Secondary stage symptoms
The secondary stage of syphilis is extremely diverse in its own symptomatology, and it is for this reason that in the 19th century, French syphilidologists called him "the great ape", indicating, thereby, the similarity of the disease at this stage with other types of skin diseases.
Signs of a general type of secondary stage of syphilis are the following features of the rash:
- Lack of subjective sensations (soreness, itching);
- Dark red color of the rash;
- Density;
- Clarity and correctness of roundness or roundness of outlines without their tendency to possible merging;
- Peeling of the surface is not expressed (in most cases, its absence is noted);
- Spontaneous disappearance of formations is possible without subsequent atrophy and scarring stage.
Most often, the rash of the secondary stage of syphilis is characterized in the form of its manifestations (see photo of syphilitic rash):
- This manifestation of this stage of syphilis is the most common. Indicates its occurrence that the spread of pale treponema occurred throughout the body. A characteristic manifestation in this case is roseola (spots) in a mild inflammatory form. Initially, the color is pale pink, the outlines of the rashes are indistinct, the shape is oval or round. Their size is about 1-1.5 cm in diameter, the surface is smooth. There is no draining of roseola, nor do they rise above the skin surrounding them. There is no propensity for peripheral growth. Often, localization is concentrated in the area of the lateral surfaces of the trunk and abdomen.
- This type of rash is formed in the form of nodules (papules), their shape is round and hemispherical, the consistency is dense elastic. The size can reach the size of a lentil, while reaching the size of a pea. The first days of appearance are characterized by the smoothness and shine of the surface of the papules, after which it begins to peel off until a scaly border forms along the periphery, by analogy with Biett's collar. As for the localization of papules, it does not have clear areas of concentration, respectively, they can form anywhere. Meanwhile, there are also localization environments "favorite" by them, which include the genitals, anus, soles and palms.
- This form of formations is a common manifestation of papular syphilis. It is expressed in the formation of thickened nodules similar to calluses with a sharp limitation from the skin surrounding them. Their surface is smooth, the shade is erythematous-brown or lilac-red. The growth of papular elements leads to their cracking in the center, which leads to the formation of a flaky border along the circumference. Often, patients with this form of syphilis are mistaken for ordinary calluses, which does not lead to a timely visit to a doctor.
- This form of rash is also quite common in the secondary stage of syphilis. Wide warts are vegetative-type papules, the formation of which occurs on the basis of weeping papules, which tend to merge and hypertrophy. Often their accompanying feature is the formation of a deep infiltrate, covered with a white bloom of the stratum corneum, in the presence of a characteristic serous discharge. Quite often, wide warts are the only manifestation characteristic of the secondary period. Most often, rashes are localized in the anus, therefore it is often necessary to distinguish them from genital warts (anal warts) and from hemorrhoids.
- Today it is extremely rare, but it is also impossible to exclude the possibility of this type of rash. Not so long ago, syphilitic leukoderma was such a specific manifestation of syphilis that it was named no less striking - "the necklace of Venus." Its manifestation is characterized by the formation of oval light rounded foci against the background of brownish-yellowish darkening of the skin. The most common areas of localization of syphilitic leukoderma are the lateral surfaces of the neck, in some cases - in the region of the anterior chest surface, as well as in the region of the upper limbs and armpits.
- This rash occurs as rose-colored spots that form along the mucous membrane of the mouth and throat, as well as in the upper palate. The affected area is characterized by the acquisition of a stagnant red surface color, in some cases it can give off a copper tint. The surface is generally smooth, the outlines of the formations are clear. They are also characterized by the absence of subjective sensations, however, some cases are marked by the occurrence of difficulty in swallowing. In the process of secondary syphilis, especially at the time of relapse of the disease, syphilides formed in the mucous membranes can act as almost the only clinical manifestation of the disease. In addition, their presence is extremely important from an epidemiological point of view, because they contain a huge number of pathogens of this infection.
- Syphilitic alopecia. The main manifestation is baldness, which provokes the formation of a large number of foci of a characteristic rash. In this case, the hair falls out so that in appearance it can be compared with moth-eaten fur.






In general, considering the rash, it can be noted that with syphilis it can be of a completely different type of character. A severe course of syphilis provokes the appearance of pustular (or pustular) syphilis, which can manifest itself in the form of a rash, and a rash characteristic of.
Secondary recurrent syphilis is characterized by fewer and fewer rashes that occur with each new form of recurrence. The rashes themselves, in this case, acquire ever larger sizes, characterized by a tendency to their own grouping into rings, ovals and arcs.
Secondary, untreated syphilis becomes tertiary.
Tertiary stage symptoms
This stage of the disease is characterized by an insignificant amount of pale treponema in the body, but it is sensitized to their effects (that is, allergic). This circumstance leads to the fact that even with a small number of treponemas, the body responds with a peculiar form of anaphylactic reaction, which consists in the formation of tertiary syphilides (gum and tubercles). Their subsequent disintegration occurs in such a way that characteristic scars remain on the skin. The duration of this stage can be decades, which ends with a deep damage to the nervous system.
Dwelling on the rash of this stage, we note that the tubercles are smaller when compared with gummas, moreover, both in their size and in the depth at which they occur. Tuberous syphilis is determined by probing the thickness of the skin with the identification of a dense formation in it. It has a hemispherical surface, the diameter is about 0.3-1 cm. Above the tubercle, the skin becomes bluish-reddish. Bumps appear at different times, while grouping into rings.
Over time, necrotic decay forms in the center of the tubercle, which forms an ulcer, which, as we have already noted, leaves a small scar after it heals. Given the uneven maturation of the tubercles, the skin is characterized by the originality and variegation of the overall picture.
Gummy syphilis is a painless dense knot that is located in the middle of the deep skin layers. The diameter of such a knot is up to 1.5 cm, while the skin above it acquires a dark red hue. Over time, the gum softens, after which it opens, releasing a sticky mass. The ulcer, which was formed at the same time, without the necessary treatment, can exist for a very long time, but at the same time it will increase in size. Most often, such a rash has a solitary character.
Syphilitic rash treatment
Treatment of the rash is carried out in conjunction with the treatment of the underlying disease, that is, the syphilis itself. The most effective method of treatment is the use of water-soluble penicillins in it, which allows maintaining a constant required concentration of the required antibiotic in the blood. Meanwhile, treatment is possible only in a hospital setting, where the drug is administered to patients for 24 days every three hours. Penicillin intolerance provides for an alternative in the form of a backup type of medication.
An additional important point is also the exclusion of diseases that have arisen against the background of syphilis. For example, syphilis often increases the risk, because in general it provokes a sharp decrease in the body's immune defense. Accordingly, the appropriate solution is to carry out a full course of treatment that helps to eliminate any type of pathogens present.
If you suspect a syphilitic rash, you should immediately contact a dermatovenerologist or venereologist.