Reading time: 9 minutes
When visiting a urologist about suspicions of an algorithm for diagnosing a disease, a doctor begins with collecting data, for which a survey is made about the patient's complaints, rectal palpation.
But without laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods, it is not possible to accurately diagnose the disease.
When is an examination necessary?
At the initial stage of development, prostatitis passes with not pronounced symptoms, which may indicate other, often more dangerous diseases for a man.
For this reason, a complete clinical picture can be obtained only when using a set of diagnostic methods.
The grounds for prescribing a comprehensive diagnostic technique are the following complaints:
- violation of the emptying of the bladder;
- decreased sexual activity;
- repeated burning sensations in the perineal region;
- mental depression associated with dissatisfaction with sex life;
- excessive fatigue in the absence of an increase in the usual load;
- erectile dysfunction;
- repeated pain during bowel movements;
- increased frequency of urination;
- "Rate of fire" - rapid ejaculation;
- long erections at night.
What can the tests show?
Comprehensive diagnostics for prostatitis allows you to assess the condition, the presence of infectious agents in it, the presence (absence) of an inflammatory reaction, the degree of the pathogenic process.
Auxiliary examination techniques make it possible for a doctor to identify:
- the general health of the man;
- the degree of involvement of the prostate in the development of neoplasms;
- the ability of existing infectious agents to activate;
- the degree of resistance of the body to the effects of pathogenic organisms.
What tests are taken for prostatitis?
Analyzes for suspected prostatitis are conventionally classified into 2 groups:
- The main ones are bacteriological examination of urine, molecular genetic diagnostics (polymerase chain reaction analysis), computer and general analysis of prostatic fluid and urine.
- Auxiliary - a semen analysis, after which an ultrasound examination of the bladder is performed, the detection of prostate tumor markers in the blood, sonography in the form of a transrectal ultrasound examination of the prostate gland.
Manual examination - concept and procedure
Functional testing is the main examination technique among manual methods.
It is appropriate to carry out it in the absence of symptomatic signs.
The technique shows reliable results when.
One of the test methods in assessing the functioning of the prostate is a gland massage performed by the transrectal method.
The urologist has the ability to assess the degree of organ damage, the size and shape of the gland, the density and consistency of follicular tissue.
In case of acute damage to the prostate, there is a risk of damage to purulent-necrotic areas and their migration into the blood, which threatens a systemic inflammatory reaction known as "sepsis".
PSA analysis for prostatitis - concept and norm
The prostate specific antigen (PSA) index is a significant diagnostic tool used in the diagnosis of urological pathologies in the blood test.
By identifying the number of tumor markers in the blood, the analysis shows the presence or absence, and also allows you to track the level of tumor markers in a therapeutic method of cancer treatment.
A slight increase in the specific antigen of the prostate in the blood means any damage to the gland or the presence of inflammatory processes in it, accompanied by organ hyperplasia.
For this reason, a man, before donating blood for PSA analysis, should take maximum care to prevent even minimal trauma to the prostate, so as not to distort the PSA analysis.
Microtrauma can be obtained during sex, masturbation, transrectal massage, TRUS and cystoscopy.
The optimal period for abstinence from analysis after these procedures is 7-11 days.
Treatment of prostatitis, in which the value of the indicator does not exceed 7 ng / ml, occurs according to a simplified scheme.
Men over 55 years of age are required to be tested for PSA levels in the blood to prevent the development of prostatitis.
Complete blood count for prostatitis and its rate
For a general blood test, the sampling procedure takes place from a vein. The indicators for the study are the concentration of total hemoglobin, the presence (absence) of helminths, the presence of an inflammatory process.
The latter indicator is the basis for the assumption about the possibility of developing prostatitis.
A general blood test cannot suggest a diagnosis of prostatitis if the hemoglobin level in the blood does not drop below 110 g / l. The concentration of leukocytes should not exceed 9x109.
When decoding the leukocyte form of blood, attention is paid to the number of stab leukocytes, the norm of which is no more than 4.
With the development of inflammation in the prostate, ESR in the blood increases over 5 mm / h.
The excess of the norm in the indicators of the general blood test changes proportionally with the degree of development of the inflammatory process in the prostate gland: the more the indicators exceed the norm, the more the inflammation proceeds.
A referral for a general blood test is made by a urologist after examination by other diagnostic methods.
A general blood test is not the only and independent basis for a diagnosis.
Urine analysis for prostatitis
Semen analysis
Semen is a complex of secretions of the bulbourethral, prostate, testicles and seminal vesicles.
By the nature and composition of the secret, presented without fail by the prostate, the presence and degree of development of the inflammatory process is judged based on the leukocyte and possible erythrocyte presence.
Fragments of weakened and dead male germ cells arise in the course of pathogenic metabolic processes and immune reactions.
The inflammatory process in the prostate can also be judged by the acid-base balance of the fluid. The normal pH of the ejaculate has a slight shift towards the acidic side.
When the pH of the medium deviates from neutral to alkaline, the suspicion of an inflammatory process in the gland increases.
Prostatitis is indicated by 8 out of ten sperm cells that are dead or inactivated.
A greater percentage of gametes that are unable to fertilize an egg reveals cancerous conditions of the prostate or pathologies that have affected not only the prostate, but also the testicles of a man.
The transformed spermatozoa show abnormalities in endocrine function, the development of malignant conditions of the prostate or genetic abnormalities.
When difficulties arise with bacteriological analysis of the contents of the prostate, seeding of the ejaculate is performed.
Semen analysis is considered one of the reliable laboratory methods for detecting inflammation in the prostate gland.
For this reason and due to the high reliability of the results, the analysis of semen by urologists is often used in the diagnosis of prostatitis.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW: In acute prostatitis, the procedure is contraindicated.
Additional research methods
The main methods listed above for detecting prostatitis do not give a complete guarantee of a reliable positive result.
In order to increase the reliability of the results, several additional techniques are used, indicated above in the classification, if the infection of the prostate does not stop even after the start of the use of therapeutic methods.
Additional examination is required if symptoms of prostatitis are detected, resulting from the development of a malignant tumor in the prostate or pelvic organs.
An auxiliary technique is inevitable in the event of complications after prostatitis.
Summary of the rating of diagnostic techniques
Despite the multiplicity of the main and additional set of methods for detecting prostatitis, the effectiveness of one of them exceeds the others in terms of rating both in terms of the frequency of use and the degree of reliability of the results.
This technique is when the probe, inserted into the ampulla of the rectum, shows the consistency, size of the prostate gland, the presence of stones and calcifications in it.
If there is a suspicion of a disease, the patient is assigned tests for prostatitis, the purpose of which is to identify the presence of the disease, establish its stage and establish whether there are complications. Without a thorough examination, it is difficult to know if the prostate gland is inflamed. For this reason, prostatitis is not always diagnosed at the initial stages, although it is one of the most common urological diseases.
What does a prostate examination show?
A general analysis of blood and urine, as well as clinical examinations of the body, can determine the current state of the prostate and reveal the presence of pathogenic microorganisms.
Diagnostics also gives an idea of the severity of inflammation and the degree of tissue damage. When a man passes all the necessary tests for prostatitis, the doctor gets a complete picture of his condition, the presence of viruses and the degree of resistance of the body to viral infections.
List of tests for prostatitis
If an inflammation of the penis is suspected, a man undergoes a number of basic and additional tests. The doctor first examines the patient and asks him about the symptoms. Complaints about severe pain may indicate an acute form. If its likelihood is excluded, the doctor performs rectal palpation. This procedure allows the doctor to assess the general condition of a man and understand what tests he needs to take, except for blood and urine.
 After rectal palpation, the doctor prescribes a referral for all types of examinations. The number of tests required may differ from patient to patient. In some cases, it is enough to examine blood and urine for diagnosis, while in others a thorough examination is required.
After rectal palpation, the doctor prescribes a referral for all types of examinations. The number of tests required may differ from patient to patient. In some cases, it is enough to examine blood and urine for diagnosis, while in others a thorough examination is required.
But most often the list of diagnostic procedures looks like this:
- General analysis of blood and urine.
- Study of the secretion of the prostate gland (with suspicion of an acute form of the disease).
- MRI of the pelvic organs.
- Bacteriological culture of urine, the purpose of which is to determine the type of bacteria that caused the inflammatory process.
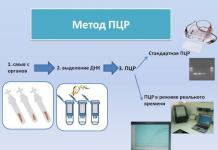
- Laboratory diagnostics by PCR method. This is a highly sensitive test that detects subtle threats in the form of latent genital infections.
- A three-glass urine sample is a specific diagnostic method (not prescribed in all cases).
General analyzes for prostatitis can provide a lot of information, but they do not always allow you to get a complete picture. So, with inflammation, ESR increases and the content of leukocytes in the blood increases. At advanced stages, the indicators deviate from the norm more than at the initial stages. But with a catarrhal form of prostatitis, the blood composition may be normal. This circumstance often leads to untimely diagnosis. The fact that a man is sick becomes known only after the analysis of urine: particles of pus appear in it.
Study of prostate secretion in men
 Biological material for study is collected in laboratory conditions. The doctor stimulates the prostate gland and collects the secreted secretion on the glass, after which he examines it under a microscope. Normally, the secretory fluid should take the form of a fern leaf. Deviations or the presence of blood particles indicate an inflammatory process.
Biological material for study is collected in laboratory conditions. The doctor stimulates the prostate gland and collects the secreted secretion on the glass, after which he examines it under a microscope. Normally, the secretory fluid should take the form of a fern leaf. Deviations or the presence of blood particles indicate an inflammatory process.
Additional examinations
Additional tests for prostatitis are prescribed only if the results of the main tests give reason to suspect that the man has other diseases, for example, inflammation of the bladder. They are also prescribed if the treatment did not bring the expected improvement or the patient has complications.
- Blood on PSA. Such tests for prostatitis are prescribed if there is a suspicion of the presence of a malignant tumor.
- Transrectal sonography (TRUS) of the prostate and seminal vesicles. It is now the most effective type of diagnosis.
- Spermogram - a study of the ejaculate in order to assess the reproductive capabilities of a man.
- Ultrasound of the bladder.
How is urine culture done?
 If the disease has passed into an advanced stage, the urine acquires characteristic changes, which are detected by laboratory research. Collection in order to carry out an analysis for prostatitis is performed in various ways, while it is important that foreign microorganisms do not get into the liquid. To diagnose inflammation of the prostate, urine is collected as follows: after the act of urination, a clean cotton pad is pressed against the urethra, into which a sufficient amount of liquid is absorbed.
If the disease has passed into an advanced stage, the urine acquires characteristic changes, which are detected by laboratory research. Collection in order to carry out an analysis for prostatitis is performed in various ways, while it is important that foreign microorganisms do not get into the liquid. To diagnose inflammation of the prostate, urine is collected as follows: after the act of urination, a clean cotton pad is pressed against the urethra, into which a sufficient amount of liquid is absorbed.
Important: before the procedure, the area around the urethra must be disinfected. This is necessary so that foreign particles and bacteria do not get into the liquid, otherwise you will have to re-study.
Also, patients donate urine using a sterile catheter in an equipped laboratory. First, the liquid is collected in a sterile container, then bacteria are inoculated there, after which a culture is grown, and only then diagnostics are performed. The patient needs to contact for the results after a while, in what terms the doctor will say.
Ejaculate analysis
 This is the most accurate and informative test. In the semen, doctors can detect non-viable and dead sperm, erythrocytes, leukocytes. The presence of agglutinins (sedentary sperm) indicates a disturbance in the functioning of the immune system. It is possible to determine the presence of inflammation by the type of reaction: it is normally acidic, but with prostatitis it is alkaline, and because of this, the sperm become lethargic and die.
This is the most accurate and informative test. In the semen, doctors can detect non-viable and dead sperm, erythrocytes, leukocytes. The presence of agglutinins (sedentary sperm) indicates a disturbance in the functioning of the immune system. It is possible to determine the presence of inflammation by the type of reaction: it is normally acidic, but with prostatitis it is alkaline, and because of this, the sperm become lethargic and die.
When diagnosing, it is often found that most of the spermatozoa (up to 75-80%) are inactive. Such a pathology indicates genetic disorders or hormonal disruptions, as well as dysfunctions of the testicles.
Semen examination is not prescribed for all men. Sometimes it is replaced by an analysis of the secretion of the prostate gland. If it does not give results, or for some reason it is difficult to collect biological material, a sperm test is carried out. These are just the main types of examinations shown for prostatitis. When there is a suspicion of concomitant diseases, complications or secondary disorders, the patient is instructed to undergo additional tests, which ones are determined on an individual basis.
The diagnosis of "prostatitis" in men is not always easy to make, especially at the very beginning of the disease or if the disease occurs in men without symptoms. In any case, it is necessary to undergo an examination and pass all the necessary tests to determine the form of the disease and the severity.
To confirm the diagnosis of a disease of the prostate gland, it is worth passing certain tests.
Forms of the disease
Prostatitis can manifest itself in several forms: Forms of the disease Types of tests Preparation for testing and their results
- sharp;
- bacterial;
- chronic.
Chronic prostatitis is a syndrome of chronic pelvic pain that is asymptomatic. Diagnosis of acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis is primarily carried out on the basis of questioning the patient about complaints and symptoms, examination, examination of a urine culture sample before and after massage of the prostate gland. It is important to distinguish prostatitis from other diseases. Therefore, the diagnosis should be carried out by an experienced specialist, it is he who chooses which tests to appoint a man. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome is a more difficult diagnosis in men, in part because the pathology is poorly understood. Diagnosis is often based on exclusion of other urological conditions (eg, urinary dysfunction, bladder cancer). Asymptomatic prostatitis can be an accidental "find" in a patient who comes to the doctor with other urological problems.
Types of analyzes
So, let's talk in more detail about what is the diagnosis of prostatitis and what methods are available for men to diagnose "prostatitis" and determine its type. Initially, your doctor will ask you about the history of your symptoms. It is imperative to mention here anything that bothers you or seems strange and does not happen as before. Evaluation of the patient includes a digital rectal examination. Despite the simplicity of this method, an experienced physician can gain valuable information about the prostate. Today there are many modern technological methods due to which the diagnosis is carried out accurately, more aesthetically and not so unpleasant for men. For example, diagnostics using ultrasound (ultrasound), computed tomography. However, they cost money and take time. Finger examination is the simplest and cheapest method that can be used in any situation, but it is not as informative as ultrasound and CT.

Diagnostics using ultrasound is carried out accurately, more aesthetically and not so unpleasant for a man.
But, one way or another, all patients are tested for a complete and final examination. The most common ones are:
- A blood test (can be from a finger or from a vein), in which the doctor will look primarily at indicators of the presence of inflammation, the number of leukocytes in the blood (white blood cells) and ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate). Also, blood counts are checked for an allergic reaction in the body, since inflammation of the male gland is sometimes allergic in nature. It is important to conduct a biochemical examination of the blood (from a vein) and monitor the parameters of electrolytes, including blood urea nitrogen and creatinine, this is necessary, especially in patients with urinary retention or obstruction.
- You also need to take a urine test before and after treatment. In the urine, the specialist looks at the number of leukocytes and bacteria, whether there are oval fat bodies and macrophages in the analysis. Urine culture can be used to identify pathogens, if any. E. coli is the most common pathogen.
- Analysis of the secretion taken from the prostate. It is taken for biochemical and cytological research to determine the cellular and biochemical composition, bacterial culture is also done and the sensitivity to antibiotics is determined.
- A urine culture helps to determine the type of bacteria that caused the development of acute prostatitis.
- PCR - diagnostics. This type of analysis consists of checking urine for hidden types of infections.
Preparation for the delivery of tests and their results
Before you get tested, you need to prepare for this. There are special measures that should be followed in order for the analyzes to be reliable. You do not need to limit yourself to drinking, the regimen should be normal. The exception is alcohol, coffee and juices 8 hours before the blood test.
If it is necessary to pass a urine test, it must be collected correctly and the container must be clean. Before handing over, you should carry out a personal hygiene procedure.
Before passing the secretion of the prostate, the doctor should massage the gland. Before such a procedure, it is necessary to abstain from sexual activity for several days.

Analyzes help the specialist to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Urine shows the rate and amount of protein, leukocytes, glucose and bacteria. There should be no glucose in the urine, its presence indicates diabetes mellitus. The norm of leukocytes in men should not exceed 0-3. In a secret taken from the prostate, the specialist pays attention to leukocytes, epithelial cells. The norm of leukocytes is 10, if the indicator is higher, this means that the man has an inflammation of the gland, that is, prostatitis. The microflora of the secret shows the presence of bacteria, and crystallization shows the presence or absence of chronic prostatitis. Normal crystallization should look like a fern leaf pattern. Otherwise, the pattern is damaged or crystals are absent altogether. This indicates the presence of prostatitis.
Analyzes for prostatitis help the specialist make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Additional examinations for prostatitis:
- Ultrasound examination - an examination of the bladder is underway.
- CT diagnostics.
- Sonography of the prostate and seminal vesicles.
- Spermogram, if a man cannot conceive a child, and he has prostatitis. This will help to understand how the disease affects fertilizing ability.
- PSA blood test - performed if there is a suspicion of prostate cancer.
Analyzes and thorough diagnostics help specialists to make an accurate diagnosis, determine the form of prostatitis and prescribe effective treatment.
Prostatitis is a male disease that is too often overlooked. Many patients do not pay attention to alarming symptoms, or try to get rid of them with folk remedies. Due to the indifference of loved ones or his own shyness, a man can bring even minor inflammation provoked by hypothermia to a chronic state.
Prostatitis is the most insidious male disease with indistinct, extensive symptoms. It is almost impossible to recognize it in the early stages without additional diagnostics, therefore, analyzes are very important in this case. They are carried out in order to accurately diagnose the disease, determine its stage and the severity of the symptoms of inflammation.
On the basis of clinical examinations, the most appropriate and effective method of treating the patient is also selected for health reasons.
So, what tests are taken for suspected prostatitis? What role do they play in the diagnosis and treatment of pathology?
Accurate diagnosis is the basis for effective treatment
It is known that the more accurately the diagnosis is made, the easier it is for the doctor to choose the necessary treatment for the patient. Prostate examinations and tests themselves largely determine the drugs that will be effective in each case.
They also allow you to accurately determine the culprit, contributing to the development of inflammation of the prostate gland, and choose the right treatment tactics.

The study of the prostate implies a complex of clinical procedures carried out in order to determine the general condition of the organ, the presence of inflammation in it, the main microorganism that caused its stage of tissue damage.
Clinical examinations also provide the attending physician with additional information about the patient's general health, the absence or presence of tumors, viruses in the body, and the response of the immune system to them.
When is it necessary to get tested for prostatitis?
All patients who come with complaints of unbearable pain in the groin area and difficulty urinating should immediately be tested for inflammation of the prostate. In most cases, men are treated with the acute phase of the disease.
Chronic prostatitis is less pronounced, and therefore often goes unnoticed.
Check if you can answer yes to the following questions:
- sometimes urination is accompanied by a burning discomfort;
- the stream of urine is interrupted, comes out unevenly and irregularly;
- You have noticed strange whitish clots in your urine;
- periodically you experience slight difficulties with urination, but then they disappear;
- You often feel false urges, or notice that you have begun to go to the toilet more often;
- bowel movements are accompanied by difficulty or even pain;
- You suffer from sexual disorders;
- You have difficulty ejaculating or ejaculating too quickly. The orgasm has become weak, sometimes it is uncomfortable;
- at night you cannot sleep normally due to frequent urge and / or prolonged erection;
- You have become nervous and irritable. Your relatives, friends and colleagues also notice it;
- You get tired much faster.
Even one affirmative answer is enough to start worrying about your health. If prostatitis is suspected, it is necessary to undergo examination as soon as possible. Some forms of this disease are almost asymptomatic, manifesting themselves only in the most advanced stages. Early identification of a threat will protect you from unpleasant consequences, and also reduce the risk of prostate adenoma.
Mandatory research
You should contact a specialist as early as possible. Then you will be able to go through all the stages of the examination and get the most accurate diagnosis.
Knowing what tests are taken if you suspect an inflammation of the prostate, you can plan the time in advance and carry out all the necessary procedures faster.
To establish the cause of the damage to the tissues of the prostate gland, a comprehensive examination is carried out. The obtained indicators are compared, and on their basis the final diagnosis is made.
Common Methods

A blood test for prostatitis in men is of paramount importance, as is a urine test. These tests are done with virtually any infection screening. In case of revealing prostatitis in men, they help to establish the following factors:
- the presence of infectious agents;
- abnormal behavior of bacteria;
- the presence of primary signs of leukocytosis;
- the presence of protein secretions in the urine;
- the speed of movement of erythrocytes.
These data are important for the prompt determination of the degree of the disease. They can indicate the presence of an inflammatory process, help characterize the intensity of inflammation and determine the extent of the lesion.
Study of the secretion of the prostate gland
This procedure must be completed as quickly as possible. It will take a little longer to get results, but at the end you will almost certainly know if you are suffering from prostatitis or not.
Only patients who do not suffer from the acute phase of the disease will be able to hand over the secret for testing. Material for research is excreted from the urethra by stimulating the prostate gland, which is strictly prohibited in advanced stages of inflammation.
Some forms of chronic prostatitis can prevent secretions from leaving the body naturally. In this case, a portion of the material is excreted from the urine.
An in-depth study of the secretion provides accurate information about the status of inflammation and the condition of the prostate tissue. Combining the results with data on general methods allows you to establish an error-free diagnosis.
Ejaculate research

The indicators obtained in the study of seminal fluid give information similar to studies of the secretion of the prostate gland. This is a mandatory examination for patients who are unable to identify a secret for diagnosis.
Prostatitis is diagnosed by comparing total leukocyte counts and suspicious single erythrocyte neoplasms.
The general condition of the seminal fluid can also tell a lot about the course of prostatitis.
Particularly important features include:
- a change in the acidity of the medium (the nature of the reaction becomes alkaline);
- decrease in sperm concentration;
- a significant number of sperm unsuitable for fertilization.
MRI and computed tomography
A patient at any stage of prostatitis can undergo these high-tech procedures. Research helps to study in detail the course of the disease and analyze the development of inflammation.
Magnetic resonance imaging is not used as an independent method, but it is extremely useful in clarifying the diagnosis and forming a complete picture of the disease. Knowing how the lesion developed, the doctor will be able to choose the most effective drugs.
Computed tomography practically does not differ in the spectrum of the obtained data from MRI. Some patients are unable to undergo magnetic resonance imaging for individual reasons. Computer examination is suitable for everyone. Plus, it delivers near-instantaneous results that you can work with immediately.
Other additional diagnostic methods
Sometimes the doctor is not able to conduct classical studies that allow to accurately determine the specifics of the disease. In such extreme conditions, the patient has to rely on the experience of a specialist.
The type and stage of prostatitis are determined in this case by a traditional manual examination. Massage of the prostate gland, despite the "retardation", allows you to establish many important signs of the disease (for example, an increase in the size of the prostate, pain when pressed, etc.).
If the patient shows signs of acute prostatitis, such an examination is not performed. However, in most cases, men suffering from prostatitis are faced with an abundance of analytical procedures available. If an infection is suspected, appropriate studies are necessarily carried out: if the infectious pathogen is left unattended, the disease will not be cured.
Many procedures make it easier for the urologist to make a diagnosis with maximum confidence.
Additional studies of urine sampling can become a source of valuable information about a patient with an acute course of the disease who is unable to pass the "standard" tests.
Sowing blood allows you to completely eliminate the likelihood of bacterial infection - or, conversely, to isolate harmful bacteria.
Brief transcript
Urine test results. Leukocytes in urine in men should normally be no more than 3. If ketone bodies are present, diabetes mellitus may develop. The presence of blood is also unacceptable.
In PCR diagnostics, erythrocytes should not be in the field of view. If there is even a small amount, then there was a prostate injury. Also, the presence of red blood cells indicates prostate cancer.
The results of the study of prostate juice. The number of leukocytes does not exceed 12. Erythrocytes and epithelium should be single. The rest of the indicators should be absent.
When examining the ejaculate, leukocytes should be in large quantities, there is no mucus. Normally, the volume can be 2 ml. Normal sperm in the amount of 50% of the total.
The volume of the prostate gland is looked at by ultrasound and TRUS. Its density is estimated. Seminal vesicles are normal up to 5 cm.
Useful video
Prostatitis is the most insidious male disease with indistinct, extensive symptoms. It is almost impossible to recognize it in the early stages without additional diagnostics, therefore, tests for prostatitis are very important. They are carried out in order to accurately diagnose the disease, determine its stage and the severity of the symptoms of inflammation.
On the basis of clinical examinations, the most appropriate and effective method of treating the patient is also selected for health reasons. What tests are recommended for men with suspected prostatitis? What is their role in the diagnosis and treatment of pathology?
Accurate diagnosis is the basis for effective treatment
It is known that the more accurately the diagnosis is made, the easier it is for the doctor to choose the necessary treatment for the patient. Examination of the prostate, directly analyzes largely determine the drugs that will have an effect in each case. They also allow you to accurately identify the culprit, contributing to development, and choose the right treatment tactics.
What analyzes can tell?
 The analysis of the prostate implies a complex of clinical examinations carried out in order to determine the general condition of the organ, the presence of inflammation in it, the main microorganism that caused its stage of tissue damage.
The analysis of the prostate implies a complex of clinical examinations carried out in order to determine the general condition of the organ, the presence of inflammation in it, the main microorganism that caused its stage of tissue damage.
Clinical examinations also provide the attending physician with additional information about the patient's general health, the absence or presence of tumors, viruses in the body, and the response of the immune system to them.
When is the examination necessary?
It is recommended to undergo a clinical examination of the prostate gland when symptoms such as:
- easy difficulty urinating;
- sexual dysfunction;
- burning sensation in the urethra and perineum;
- unpleasant sensation during bowel movements;
- the presence of floating filaments in the urine;
- increased urge to urinate;
- intermittent urination;
- accelerated ejaculation;
- long nocturnal erections;
- decreased potency;
- increased fatigue;
- mental depression, anxiety.
If at least one of these signs bothers you, you need to urgently consult a urologist and undergo a comprehensive examination for prostatitis.
Basic analyzes
 What tests are taken for prostatitis? The main ones include a general analysis of urine and blood, bacterial culture of urine, analysis of urethra secretion, PCR diagnostics, computed or magnetic resonance imaging. Additional tests include a blood test for PSA, spermogram, transrectal sonography of the prostate and seminal vesicles, ultrasound of the bladder.
What tests are taken for prostatitis? The main ones include a general analysis of urine and blood, bacterial culture of urine, analysis of urethra secretion, PCR diagnostics, computed or magnetic resonance imaging. Additional tests include a blood test for PSA, spermogram, transrectal sonography of the prostate and seminal vesicles, ultrasound of the bladder.
They are prescribed if the pathogens in the prostate are not completely destroyed, if the treatment is ineffective, if there are suspicions of other pathologies of the bladder and prostate, if abscesses develop.
Remember that palpation of the prostate always reveals its inflammation in the early stages, therefore, it is imperative to pass the tests prescribed by a specialist, even with comforting forecasts.
More details about the role of each specific analysis.
General analysis of blood and urine
 Research is carried out on a special laboratory automatic analyzer. A blood test allows you to identify other pathologies associated with the urinary system. It is considered one of the most important ways to diagnose the causes of urinary flow obstruction, since it allows you to determine with extreme accuracy the causes of stagnation in the urethra and the state of the urinary organs.
Research is carried out on a special laboratory automatic analyzer. A blood test allows you to identify other pathologies associated with the urinary system. It is considered one of the most important ways to diagnose the causes of urinary flow obstruction, since it allows you to determine with extreme accuracy the causes of stagnation in the urethra and the state of the urinary organs.
A general blood test for prostatitis allows you to assess the bacterial content of urine, assess its transparency, color, organic and inorganic components, the presence of inclusions and prescribe adequate treatment.
Analysis of the secretion of the urethra and prostate
Analysis of the secretion of the urethra and prostate is a microscopic examination of the fluid produced by the organs, which makes it possible to identify inflammation and assess its severity. Materials for analysis are obtained by massage of the prostate: by pressing on the canal, a liquid is applied to the glass for further research. The deviation of the secretion indicators indicates changes in the prostate gland.
Computed and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are technologies that allow an examination of the prostate without harm to the body. They allow you to better study soft tissues, to determine how developed the inflammation process is, to identify seals and deformations of tissues, congestion and the reasons for their appearance.
Additional methods
Additional analyzes for inflammation of the prostate include:
- Transrectal sonography is a study that allows an accurate assessment of all sizes of the prostate gland, including the volume of malignant tumors. Analyzes for prostate adenoma and cancer must include this type of study.
- A blood test for PSA is the identification of a substance produced by prostate cells in a man's blood. This test is considered a tumor marker for prostate cancer.
- Ultrasound of the bladder is a study that allows you to assess the shape of the organ, external and internal contours, and the contents of the bladder.
These analyzes for prostatitis will allow not only to identify the stage and type of pathology, but also to select the optimal methods and means of treating the patient.