For the first time they started talking about the disease back in 1879, but to this day it can be terrifying, especially if a woman was diagnosed during pregnancy.
The thing is that infection of a pregnant woman entails a lot of serious consequences and complications, until the death of the fetus.
In order to protect herself and her future baby, a woman must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations, take everything necessary, and, if necessary, immediately begin treatment.
What do you need to know?
Gonorrhea occurs in two main stages:
- Sharp when the duration of the presence of gonococci in the body is less than 2 months.
- Chronic, in which the bacterium is present in the body for more than 2 months.
There is also a more extended classification of the disease:
- latent (latent) gonorrhea, in which the disease is asymptomatic, causing an invisible blow to the body of its carrier.
This type of gonorrhea has recently been encountered more and more often and is the most dangerous, especially for a pregnant woman, since the treatment is not timely, and the infection can harm the course of pregnancy in a short period;
- chronic gonorrhea, in which local (focal) development is observed. In the place of accumulation of bacteria, scarring of tissues occurs, and, as a result, formation;
- fresh, the signs of which appear no later than 60 days after infection.
In turn fresh gonorrhea divided into:
- torpid- does not manifest itself clinically, but is diagnosed by laboratory methods;
- subacute- manifested by abundant discharge from the urethra, but the patient does not feel pain and discomfort;
- sharp- along with urethral discharge, there is a sharp pain, burning sensation and other discomfort during urination.
Varieties
By the nature of the clinical manifestation, gonorrhea is classified into:
- urogenital- affecting the organs of the genitourinary system;
- pharyngeal- localized in the oral cavity and on the pharyngeal mucosa;
- gonococcal conjunctivitis- infection of the organs of vision;
- proctitis- damage to the rectal mucosa.
As a result of infection with blood gonococci, damage to the nervous system, joints, respiratory tract can occur, as well as the development of cardiovascular pathologies.
Causes of the disease
Infection with gonorrhea can occur both during and before pregnancy. Usually, the cause of the disease is unprotected sex with a virus carrier.
Cases of infection with gonorrhea when using someone else's towels, when visiting a bathhouse together, etc. are very rare.
Gonorrhea - the program "Health with Elena Malysheva"
Diagnostics
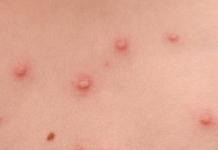
Symptoms
 In 80% of cases, gonorrhea during pregnancy is asymptomatic, minor discharge and painful sensations are often associated by women with physiological changes during bearing a child.
In 80% of cases, gonorrhea during pregnancy is asymptomatic, minor discharge and painful sensations are often associated by women with physiological changes during bearing a child.
However, the remaining 20% note the following symptoms:
- pulling;
- rapid, painful;
- vaginal discharge of varying consistency, yellow or green;
- smearing spotting, and sometimes from the genitals.
Why is gonorrhea dangerous?
For mother
The chronic course of the disease may worsen. At the same time, very there is a high probability of getting gonococci into the blood (sepsis).
Women who become infected in the second half of pregnancy are prone to developing gonococcal arthritis.
For baby
Gonococcus is not able to cause pathologies of fetal development, however the presence of bacteria "next door" is extremely unsafe.
If a woman gets infected in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy, then the gonococcus causes an inflammatory process in the uterus, and this can result in spontaneous abortion or.
When bacteria enter the body of a pregnant woman in the second 20 weeks intrauterine infection of the fetus occurs, which is manifested by sepsis (gonococcal) and an inflammatory process in the membrane of the fetal bladder (chorioamnionitis).
The latter leads to early outpouring of amniotic fluid and.
Infection of the baby can occur and during its passage through the birth canal. In this case, the eyes of the newborn are affected, which can lead to complete blindness in the future.
Girls may have genital gonorrhea. For prophylaxis, immediately after birth the eyes and genitals of absolutely all newborns are treated with a 30% sodium sulfacil solution, repeating the manipulation again after 2 hours.
Is the disease contagious?
Disease is contagious and is transmitted sexually from an infected partner and from a sick mother to her child.
Treatment
 At the first suspicion of infection with gonorrhea, a pregnant woman must consult a local gynecologist or venereologist.
At the first suspicion of infection with gonorrhea, a pregnant woman must consult a local gynecologist or venereologist.
After an external examination, the doctor will take a swab from the vagina to test for flora. If gonococci are found in the material, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment.
Medicines
When gonorrhea is detected, pregnant patients are prescribed single dose of Ceftriaxone as an intramuscular injection at a dosage of 250 mg.
Since gonorrhea often occurs in conjunction with, in addition it is recommended to take Erythromycin orally at a dosage of 500 mg... Frequency of admission - every 8 hours for 7-10 days.
With the development of gonococcal sepsis, Ceftriaxone is administered intravenously or intramuscularly, 1 g per day for 7-10 days.
If a pregnant woman is observed to the above antibiotics, carry out therapy with Spectinomycin... Spectinomycin is capable of negatively affecting the fetus, providing an ototoxic effect.
In order to prevent conjunctivitis caused by gonococci, newborns are treated with 0.5% erythromycin or 1% tetracycline ointment.
Folk remedies
Treatment of this disease traditional medicine methods are unacceptable! The destruction of the pathogen is carried out only with antibiotics and strictly under the supervision of a specialist!
The patient needs:
- exclude sexual contacts for the entire period of treatment, until complete recovery;
- observe the regimen of taking prescribed medications (without violating the time regimen and dosage);
- timely come to an appointment with a specialist to determine the degree of recovery.
After the therapy, it is necessary conduct repeated laboratory tests of the smear. This event is held three times for control.
A woman is healthy if the culture is negative within 3-4 months after drug treatment.
Diet
During treatment, the pregnant woman should exclude from the diet spicy, salty, smoked products, spices and herbs.
Complications and consequences
 There are many of them.
There are many of them.
In addition to the risk of fetal death, a woman with gonorrhea is prone to developing inflammatory diseases of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, as well as further infertility.
The advanced cases often end with the generalization of the infection: infection of the joints, blood and inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis).
Prophylaxis
Preventive measures, both for pregnant women and for other people, are the same:
- elimination of casual sex and the use of a condom. Only a condom is a barrier to infection on the way into the body;
- treatment of external genital organs with warm soapy solution and Chlorhexidine solution;
- the use of vaginal suppositories;
- when treating one of the partners, the second must necessarily pass the appropriate tests and, if necessary, also begin treatment;
- if there is more than 1 sexual partner, an annual examination by a venereologist is necessary.
Observing these rules you can save yourself and your future baby from this dangerous and very unpleasant disease.
Remember, if even the slightest suspicion arises - do not postpone a visit to a specialist... Early diagnosis and timely treatment will help avoid dire consequences.
Gonorrhea during pregnancy is dangerous to the fetus. If the disease is not cured in time, then the infection will spread to the uterine cavity and the fetus will be infected. Pathology is a serious infectious disease that is sexually transmitted.
Causes of occurrence
Gonococcus disease is provoked by microorganisms that prefer to settle on the oral mucosa and the genitourinary system. During pregnancy, gonococci attack the cervix and, as the disease progresses, move to the tubes and ovaries. The disease has a negative effect on the fetus and can cause various diseases and organ damage in it.
It can be done both sexually and by contact. The main reasons that can lead to infection:
- casual sex;
- neglect of barrier contraception;
- non-observance of hygiene rules.

Not so long ago, gonorrhea was very common, but recently there has been a slight decrease in the incidence.

Symptoms
Tripper in women often runs without symptoms, so laboratory tests are necessary to determine the presence of the disease. If you ignore gonorrhea, then it can turn into a chronic form, in which exacerbation stages will periodically occur. As soon as the immune system fails, the disease will manifest itself with renewed vigor. As you know, during pregnancy, a woman's immunity weakens significantly, which means that an exacerbation of gonorrhea will not have to wait long.
 Symptoms of gonorrhea (if any) can vary in intensity. It depends on which specific organ is affected. With an infection of the genitourinary system, a woman may experience discharge, as well as pain during intimacy and during urination.
Symptoms of gonorrhea (if any) can vary in intensity. It depends on which specific organ is affected. With an infection of the genitourinary system, a woman may experience discharge, as well as pain during intimacy and during urination.
Signs of gonorrhea with anal lesion are pain and itching during the act of defecation. With oral damage, infection of the throat and oral cavity occurs, this is accompanied by pain and inflammation. In rare cases, gonococci affect the mucous membranes of the eyes, causing eye inflammation, burning sensation, and conjunctivitis.
Diagnosis of the disease
Due to the fact that gonorrhea negatively affects the fetus, the diagnosis of pregnant women is mandatory. It is based on the following:

As for laboratory research, it is assigned:
- flora smear;
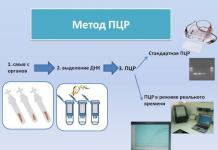
- Mutual fund method.
 with bacterioscopy, vaginal secretions can be detected no earlier than a week after the analysis, and although this research method is 95% accurate, it takes a long time to wait for an answer.
with bacterioscopy, vaginal secretions can be detected no earlier than a week after the analysis, and although this research method is 95% accurate, it takes a long time to wait for an answer.
After 2 days, the PCR results will be ready, the accuracy is almost 100%. The decoding of the mutual fund method will be ready in a day, but in this case the result will be only 75% accurate.
Therefore, today it is the fastest and most accurate diagnostic method. In addition, at the same time as gonorrhea, doctors can diagnose other genitourinary infections in a woman, for example, trichomonellosis or chlamydia.
Danger to baby and mother
The consequences for the child can be the most sad - he can die. Most often this happens if a woman was infected with gonorrhea in the first trimester of pregnancy. According to statistics, miscarriages occur in 25% of cases.
If the woman successfully delivered the baby and the birth began on time, then in this case the baby will be infected while moving along the birth canal. Since gonorrhea in children occurs in complicated forms, in order to prevent infection of the baby, a cesarean section is prescribed.

However, during gestation, a gonococcal infection harms the normal course of pregnancy. In addition to the fact that the infection can spread throughout the mother's body, it can cause gonococcal meningitis, and other diseases that pose a danger not only to the mother, but also to the child.
Any infectious disease can lead to infertility. There is a concept of secondary gonorrheal infertility, which means that after childbirth or abortion, the pathogen has penetrated the tubes and into the uterus itself, which provoked infertility. Gonorrhea can affect a woman's nervous and cardiovascular system.
Treatment during pregnancy
 After a pregnant woman has been diagnosed with gonorrhea, it is necessary to start treating the disease until it begins to progress and leads to serious ones. Treatment of gonorrhea in pregnant women is carried out in stationary conditions, the woman is prescribed antibacterial drugs, the intake of which will not have any consequences for the child:
After a pregnant woman has been diagnosed with gonorrhea, it is necessary to start treating the disease until it begins to progress and leads to serious ones. Treatment of gonorrhea in pregnant women is carried out in stationary conditions, the woman is prescribed antibacterial drugs, the intake of which will not have any consequences for the child:
- Typically, Spectinomycin and Ceftriaxone are prescribed.
- If taking these drugs for some reason is impossible (for example, in case of allergic reactions to drugs of the cephalosporin and penicillin groups), then they are replaced with Erythromycin.
When a woman has her, her sexual partner must also undergo an examination and, if necessary, be treated. After the end of the procedures, the pregnant woman is prescribed physiotherapy, while the doctor should take into account the general condition of the woman.
Traditional methods and prevention
 Every woman should understand that folk remedies in the treatment of gonorrhea can be adjuncts, but in no way replace the main drug treatment. In addition, using folk remedies while carrying a child can be extremely dangerous. Therefore, if you decide to use alternative medicine, the doctor must know what you will use the funds, and allow or prohibit their use.
Every woman should understand that folk remedies in the treatment of gonorrhea can be adjuncts, but in no way replace the main drug treatment. In addition, using folk remedies while carrying a child can be extremely dangerous. Therefore, if you decide to use alternative medicine, the doctor must know what you will use the funds, and allow or prohibit their use.
Burdock enhances the effect of drugs, so you must be extremely careful with it during pregnancy. To prepare the decoction, you will need the root of the plant. It must be crushed and filled with 0.5 liters of water. Put the product on fire and boil for half an hour, then remove, close the lid and wait until it cools completely. Then strain and take 1 tbsp every hour. l. The course is 2 weeks.
The infusion of Chinese lemongrass understands immunity well. Pour in 0.5 tsp. fruits with a glass of boiling water, wait 10 minutes, and then take 3 times a day in a glass. If desired, you can add honey to the product.
There are many traditional medicine recipes that involve douching. Under no circumstances should this be done during pregnancy!
Regarding gonorrhea, they are no different from the prevention of other sexually transmitted diseases. It is unacceptable to engage in casual sex and neglect the hygiene rules in public swimming pools, saunas, solariums. If you suspect a disease, you must immediately consult a doctor and take the necessary tests. Gonorrhea while carrying a fetus harms not only your health, but also the health of your unborn baby.
Gonorrhea is a human infectious disease caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which is primarily sexually transmitted.
ICD-10 code
A54 Gonococcal infection.
A54.0 Gonococcal infection of the lower genitourinary tract without abscess formation of the periurethral and accessory glands.
A54.1 Gonococcal infection of the lower genitourinary tract with abscess formation of the periurethral and accessory glands.
A54.2 Gonococcal pelvioperitonitis and other gonococcal infection of the genitourinary organs.
A54.3 Gonococcal eye infection
A54.4 Gonococcal infection of the musculoskeletal system.
A54.5 Gonococcal pharyngitis.
A54.6 Gonococcal infection of the anorectal region.
A54.8 Other gonococcal infections.
A54.9 Unspecified gonococcal infection
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Gonorrhea is one of the most common STIs. The disease is subject to mandatory registration when detected on the territory of the Russian Federation. The prevalence of gonorrhea is significantly influenced by social, demographic and behavioral factors. In recent years, a relatively low incidence of gonorrhea has been noted, which, apparently, is due to the incomplete registration of patients due to the appeal of some patients to commercial medical institutions, insufficient examination, wide and uncontrolled use of antibiotics, and the limited use of cultural diagnostic methods.
ETIOLOGY (CAUSES) GONORRHEA
The causative agent of gonorrhea is the gram-negative diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which is a member of the Neisseriaceae family of the genus Neisseria. This is a bean-shaped coccus, the cells of which are arranged in pairs, with concave sides to each other. The size of the cocci is 1.25–1.60 µm in length and 0.7–0.8 µm in diameter.
PATHOGENESIS
Infection with gonococci causes an inflammatory process, which leads to degenerative and infiltrative changes in the organs of the genitourinary tract, rectum, oropharynx, conjunctiva. In women, it is primarily affected by the spread of the inflammatory process to the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. In the affected organ, a cellular infiltrate is initially formed, which is subsequently replaced by connective tissue.
Pathogenesis of complications of gestation
Untreated infection can spread intracanalicularly ascending with the development of amnionitis or chorioamnionitis, leading to fetal death, premature rupture of OS, premature birth. The transplacental route of transmission of gonococci has not been proven. Fetal infection is possible both antenatally (with gonococcal chorioamnionitis) and intrapartum (with the mother).
CLINICAL PICTURE (SYMPTOMS) OF GONORRHEA IN PREGNANT WOMEN
The incubation period for gonorrhea is 3 to 14 days (average 5–6 days). Chronic recurrent course is often noted. The most common diseases are urethritis, cervicitis, proctitis, salpingo-oophoritis is not excluded, which is rare. The clinical picture of gonorrhea in pregnant women has no features.
Main clinical symptoms
Among women:
Vaginal discharge;
Dysuria;
· Acyclic bleeding;
· Pain in the lower abdomen;
Dyspareunia;
Pain in the rectal area and discharge from it in the presence of proctitis.
In newborns:
Conjunctivitis;
Sepsis.
The main manifestations of the disease
Among women:
· Cervicitis;
· PID;
Urethritis;
Perihepatitis;
Bartholinitis;
Pharyngitis;
Conjunctivitis;
· Proctitis;
Disseminated gonococcal infection: arthritis, dermatitis, endocarditis, meningitis.
In newborns and infants:
Ophthalmia of newborns;
· AF infection syndrome;
· Dissemination of gonococcal infection.
Possible complications in women:
PID (endometritis, salpingitis, salpingo-oophoritis, etc.);
· Infertility;
· Ectopic pregnancy;
· Reiter's syndrome.
DIAGNOSTICS OF GORRHEA DURING PREGNANCY
Diagnostics is based on the following criteria:
· Data of anamnesis (indication of sexual contact with a sick or possibly infected partner with gonorrhea);
· Assessment of subjective and objective symptoms of the disease;
· Detection of gonococci in laboratory studies.
ANAMNESIS
Anamnesis in adults indicates an indication of sexual intercourse. When questioning, the patient reveals a possible
source of infection.
It is important to clarify:
The time elapsed from the moment of the last sexual contact with the alleged source of infection until the onset of symptoms of the disease;
· Results of examination of the sexual partner for gonorrhea.
PHYSICAL STUDY
It is necessary to examine the patient completely to exclude manifestations of other STIs, to assess the condition of all groups of lymph nodes. All parts of the abdomen, large vestibular and periurethral glands, urethra are palpated, bimanual vaginal examination is performed.
LABORATORY RESEARCH
Laboratory diagnostics of gonorrhea includes (table 48-8):
· Microscopy of smears stained with methylene blue and Gram;
· Cultural method. It is used to diagnose gonorrhea in pregnant women, minors, in the presence of cervicitis and PID in women. When it is carried out, the antibiotic sensitivity of the isolated gonococci is required;
· Non-cultural methods (molecular biological - PCR).
If indicated, a culture study is performed. Given the high sensitivity of gonococci to drying and temperature, inoculation is recommended to be done immediately on chocolate agar or other nutrient medium for the isolation of gonococci. If it is impossible to inoculate the clinical material on a nutrient medium for gonococci, it is necessary to use special transport media.
A combination of microscopic and cultural methods is used as a criterion for cure.
Additional use of non-cultural methods (PCR) in this case is possible no earlier than 3 weeks after the end of treatment.
Serological methods are not used to diagnose gonorrhea.
The following main areas for taking material are distinguished:
· The cervical canal of the cervix and urethra;
· Rectum when indicating anogenital contact;
· Pharynx if orogenital contact is indicated.
It is possible to take material for the detection of gonococcus and from other areas:
· Rectum and urethra, if the cervix is removed;
· Pelvic organs during laparoscopy in women with PID;
· Blood and other fluids (pus) during dissemination of the infection;
· Synovial fluid;
· Conjunctiva of the lower eyelid;
· The first portion of freely released urine (10-15 ml) for the PCR method (rarely).
SCREENING
The following are subject to examination for gonorrhea:
Women with clinical manifestations of mucopurulent cervicitis, symptoms of adnexitis;
· Persons who have had sexual contact with a patient with gonorrhea;
· Persons undergoing examination for other STIs;
· Pregnant women when registering for pregnancy;
· Pregnant women aimed at termination of pregnancy;
· Newborns with purulent conjunctivitis (if the gonorrheal etiology of the process is confirmed, parental examination is necessary).
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSTICS
Differential diagnosis of gonorrhea is carried out with cervicitis caused by other microorganisms, primarily chlamydia.
With skin lesions - with keratoderma with Reiter's disease.
With joint damage - with reactive arthritis, Reiter's disease, arthritis of a different etiology.
In the presence of symptoms of conjunctivitis - with conjunctivitis of chlamydial, viral etiology.
With meningitis in children - with meningitis of meningococcal etiology, viral lesions of the tissue and membranes of the brain.
EXAMPLE FORMULATING A DIAGNOSIS
Uncomplicated gonococcal infection of the lower urinary tract (urethritis, cervicitis).
Table 48-8. Laboratory methods for the diagnosis of gonorrhea and their features
| Sampling area | Diagnostic method | Comments (1) |
| Endocervix / urethra (in adult women) | Microscopic with Gram stain for the detection of intracellular diplococci | The sensitivity of the method is lower than when using material from the urethra in men |
| Cultural | To confirm the diagnosis (isolation and identification of Neisseria) and to conduct an antibiotic susceptibility test | |
| Non-cultural (PCR) | Only as a screening, followed by confirmation by other methods | |
| Pharynx / conjunctiva / rectum | Cultural only (microscopic with Gram stain not applicable) | Confirmation of the diagnosis (isolation and identification of Neisseria) and an antibiotic susceptibility test |
| Non-cultural (PCR) | ||
| Urine | Non-cultural (PCR) | Only as a screening followed by examination of material from the urethra and cervical canal and detection of Neisseria by other methods |
| Sepsis | Microscopic method with Gram stain for clinical materials from the urethra and cervical canal, skin rashes | Screening method. It is obligatory to study material from other localizations by the cultural method. |
| The culture method for clinical materials from the urethra and cervical canal, skin rashes, rectum, nasopharynx, cerebrospinal fluid, synovial fluid, blood | The main diagnostic method, confirmation of the diagnosis (isolation and identification of Neisseria) and an antibiotic susceptibility test | |
| Non-cultural (PCR) | As screening only followed by culture confirmation |
TREATMENT OF GORRHEA DURING PREGNANCY
OBJECTIVES OF TREATMENT
Eradication of gonococci, resolution of the inflammatory process, prevention of complications.
INDICATIONS FOR HOSPITALIZATION
Gonorrhea in pregnant women; complicated course of gonococcal infection (conjunctivitis, damage to the cardiovascular, nervous system, musculoskeletal system, etc.) require inpatient treatment.
The duration of inpatient treatment is determined by the nature of clinical manifestations and the severity of the inflammatory process and is 2–4 weeks.
NON-MEDICINAL TREATMENT
In the presence of complications, physiotherapeutic treatment methods can be used after consulting a physiotherapist, depending on the severity of the disease and the patient's condition.
MEDICINAL TREATMENT OF GONORRHEA IN PREGNANT WOMEN
Treatment of pregnant women is carried out at any gestational age in a hospital setting with antibacterial agents that do not have a pathological effect on the fetus. The choice of drug for treatment depends on the manifestations of the disease (Table 48-9).
In the absence of results from treatment, it is recommended to consider the following possible causes:
· False positive test result;
• non-compliance with the treatment regimen, inadequate therapy;
· Repeated contact with an untreated partner;
· Infection from a new partner;
· Infection with other microorganisms.
Table 48-9. Medicines used to treat and prevent gonorrhea
| Indications for use | Medicines of choice | Alternative medicines |
| Gonorrhea in pregnant and lactating mothers | Ceftriaxone * intramuscularly 250 mg once or |
Erythromycin inside the first 2 days 400 thousand units 6 times a day, then 400 thousand units 5 times a day (course dose 8.8 million units) or |
| Spectinomycin intramuscularly 2.0 g single dose or |
Azithromycin inside 1.0 g once | |
| Cefixime * 400 mg orally once | ||
| Conjunctivitis | Ceftriaxone * intramuscularly 1.0 g single dose | |
| Ophthalmia of newborns | Ceftriaxone * intramuscularly 25-50 mg / kg body weight (no more than 125 mg) once or intravenously 1 time per day for 2-3 days or |
|
| Cefotaxime * intramuscularly 100 mg / kg body weight once plus abundant lavage of the conjunctiva with isotonic sodium chloride solution | ||
| Prevention of ophthalmia in newborns | Silver nitrate topically 1% aqueous solution once 2-3 drops in each eye or |
|
| Erythromycin external ophthalmic ointment 0.5% single dose or |
||
| Tetracycline topical ophthalmic ointment 1% single dose | ||
| Pharyngitis | Ceftriaxone * intramuscularly 250 mg once | |
| Anorectal infection | Ceftriaxone * intramuscularly 250 mg once |
Cefuroxime intramuscularly 1.5 g once or |
| Cefodizim intramuscularly 500 mg once or |
||
| Azithromycin inside 1.0 g single dose | ||
| Complications of neonatal gonococcal infection (meningitis) | Ceftriaxone * intramuscularly or intravenously at the rate of 25-50 mg / kg body weight 1 time per day for 7 days (with meningitis - at least 10-14 days) or |
|
| Cefotaxime * intramuscularly or intravenously at the rate of 25 mg / kg body weight 2 times a day for 7 days (with meningitis - at least 10-14 days) | ||
| Prevention of gonorrhea in newborns born to mothers with this infection | Ceftriaxone * intramuscularly at the rate of 25-50 mg / kg body weight (no more than 125 mg) once or |
|
| Spectinomycin intramuscularly 40 mg / kg body weight (no more than 2.0 g) once |
Note: * Cefixime, cefotaxime, and ceftriaxone are not indicated for patients with a history of cephalosporin or penicillin allergy.
If necessary, you can use another treatment option. Therapy with the main or one of the alternative drugs is continued for at least 24–48 hours.
In order to prevent a possible concomitant chlamydial infection, treatment is simultaneously prescribed using the scheme, as in the case of chlamydial infection.
ASSESSMENT OF TREATMENT EFFICIENCY
Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment is carried out on the basis of clinical laboratory and instrumental studies confirming the eradication of the gonococcus and the resolution of the inflammatory process.
Maintaining contact persons
The examination of patients is carried out depending on the history of sexual intercourse, the severity of clinical symptoms and the expected duration of infection (in the acute course of gonorrhea - from 3 days to 3 months; with torpid and low-symptom course - 6 months).
A newborn born of a mother with gonorrhea is taken from the vulva and conjunctiva of both eyes for microscopy and culture. If gonorrhea is detected in a newborn, his parents are examined.
FURTHER INTRODUCTION
· Sexual identification is mandatory and important.
· Treatment of the sexual partner is mandatory.
· Registration: send an emergency notification to the KVD in the form 089 / ukv.
PREVENTION OF GORRHEA IN PREGNANCY
Prevention of gonorrhea includes activities common to all STIs, and is divided into primary and secondary.
Primary prevention aims to change behavior in high-risk groups in order to avoid infection. It is necessary to promote a healthy lifestyle, safe forms of sexual relations through the media, as well as in educational and medical institutions. It is necessary to talk about the clinical manifestations of genital infections, ways of infection, methods of prevention, taking into account the educational level of the audience. It is important to explain the harm of self-medication and treatment to lay people.
Secondary prevention is aimed at:
· Examination and treatment of patients with diagnosed STIs to reduce the likelihood of transmission of infection to their sexual partners;
· Reducing the risk of re-infection among sick or previously infected people;
· Effective diagnosis and, if necessary, treatment of contact persons.
All sexual partners of patients with symptoms of gonorrhea are subject to compulsory examination and treatment if they have had sexual intercourse in the last 14 days.
In the absence of symptoms of the disease in a patient with gonorrhea, all sexual partners who have had sexual contact with her in the last 60 days are subject to examination.
Specific preventive measures in newborns consist in laying erythromycin eye ointment behind the lower eyelid in the first minutes after birth.
Conducting epidemiological measures among contact persons (remediation of the epidemic focus) is carried out
together with the district epidemiologist:
· Examination and examination of contact persons;
· Assessment of laboratory data;
· Deciding on the need for treatment, its volume and timing of observation.
In case of residence of contact persons in other territories, an attire is sent to the territorial KVU.
PATIENT INFORMATION
It is necessary to exclude sexual intercourse until complete recovery, strictly observe the regimen of taking medications and visit a doctor in a timely manner to determine the criteria for cure.
FORECAST
The prognosis with timely treatment started is favorable.
Developing gonorrhea during pregnancy is one of the most serious and dangerous diseases that threatens the life of the child and the health of the mother. In the absence of appropriate treatment, gonorrhea can provoke early labor, create conditions for premature rupture of amniotic fluid, or significantly affect the health of the baby.
Why is gonorrhea dangerous in pregnant women?
The causative agent of this disease is gonococcus. Its activity provokes disturbances in the bladder, pharynx and rectum. Most often, women who suffer from gonorrhea have previously had inflammation of the fallopian tubes, ovaries or uterus. Over time, an infiltrate begins to form in the affected internal organ, which is then replaced by connective tissue.
A woman in position should be regularly tested and be observed by a doctor throughout the entire period of gestation. If you follow these requirements, then gonorrhea can be detected in the early stages. The sooner the disease is detected, the less likely it is to develop negative consequences for the child or mother.
An untreated violation can lead to:
- poor work of internal organs;
- late miscarriage;
- infection of amniotic fluid;
- the occurrence of placental insufficiency;
- infection of the child.
How dangerous gonorrhea turns out to be directly depends on when the infection occurred.
If this happened even before the moment of fertilization, then most likely gonorrhea will acquire a latent form, and then become a chronic disorder. Chronic gonorrhea is more difficult to treat and is dangerous because the fetus can gain a foothold outside the uterus.
The causes of gonorrhea
Most often, women contract gonorrhea through sexual contact. There is also a risk of contracting gonococci through the household route. This can happen when the rules of personal hygiene are violated, that is, using someone else's underwear, a washcloth or a towel will be enough to get such a violation.
Symptoms of gonorrhea do not appear immediately. The incubation period ranges from 3 days to several weeks. With the development of the chronic form of the disease, other disorders are also observed, such as proctitis, cervitis, salpingo-oophoritis, etc.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in pregnant women
Gonorrhea during pregnancy has practically no distinctive features. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the symptoms begin to manifest themselves sharply, since the influence is also exerted on the baby.
The situation is aggravated by the fact that, against the background of the development of concomitant diseases, a woman may not pay attention to their cause, especially if she does not consult a doctor during this period. The acute course of the disorder is accompanied by a high body temperature and other signs of intoxication.
With a recurrent course, all symptoms can be blurred, which greatly complicates the identification of the disease.
 There are no significant differences in gonorrhea during pregnancy. The only complication that can occur against the background of reduced immunity is the emergence of several infectious agents at once. In this case, the following symptoms will occur:
There are no significant differences in gonorrhea during pregnancy. The only complication that can occur against the background of reduced immunity is the emergence of several infectious agents at once. In this case, the following symptoms will occur:
- Burning or aching pain when urinating.
- Discomfort in the vagina, itching is possible. This is due to the fact that the microflora in the body is disturbed.
- Discharge from the genitals. They will have a thick consistency and white color.
- Lack of pleasure during sex. On the contrary, this process will be unpleasant for a woman.
- Unpleasant sensations in the area where the rectum is located.
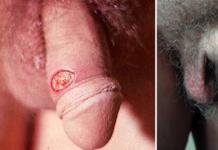
In the photo on the right, you can see how the process of infection of an infant occurs during the development of gonorrhea.
If you notice at least one of the signs listed above, then you should immediately seek help from a doctor and conduct additional research to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for gonorrhea during pregnancy
Before proceeding to the appointment of medications, the doctor will definitely carry out a diagnosis, during which he will assess the current condition of the patient.
A mandatory survey is carried out with regards to sexual intercourse and the time of possible infection. In addition, a smear is taken for flora and gonorrhea; during a woman's pregnancy, the doctor determines his rate independently. The level largely depends on what stage of development the baby is at and whether the expectant mother has concomitant diseases. A swab is taken from the rectum, cervix and pharynx. If leukocytes are found in the smear, then the previously established diagnosis is confirmed. In addition, blood, urine and mucous secretions are analyzed.
When a disease is detected, patients are prescribed a course of antibiotics.
The most popular of these is ceftriaxone. A single dose of the drug in the form of an injection is recommended, the dosage should not exceed 250 mg.
Often, the treatment of gonorrhea during pregnancy is carried out taking into account chlamydia and other disorders that have developed simultaneously with gonococci. In this case, a course of erythromycin is prescribed, in duration it should not exceed 10 days. This drug is taken orally every 8 hours, but the doctor may prescribe a different dosage regimen.
Also, immunomodulators and medications are required to maintain the normal state of the placenta.
Drug-free treatment
Any traditional method of treatment will be of little effect in the fight against gonorrhea. Usually, doctors, when drawing up a treatment plan, in addition to drugs, prescribe certain herbs or homeopathic remedies that are auxiliary. In this case, their use is useless. It should be understood that it is extremely dangerous to make a decision on this matter on your own.
- exclude all sexual contact;
- follow the medication regimen in order to notice the effect of therapy;
- be seen by a doctor to track the dynamics of recovery;
- adhere to proper nutrition and exclude the consumption of spicy, salty, smoked and fatty foods.
How well the therapy works and the main remedy for treatment is assessed based on the test results. A woman is considered healthy if, 3 months after therapy, gonococci were not found.
Consequences of gonorrhea for pregnant women
The most negative consequence that a pregnant woman can experience is a miscarriage.
The high probability of negative consequences increases with infection in the first trimester of pregnancy. However, properly selected therapy and medical supervision help to avoid this in 75% of cases.
If it is possible to avoid premature birth, then the baby can become infected with gonorrhea when passing through the birth canal. In this case, doctors decide to have a cesarean section in order to prevent negative consequences.
During the period of gestation, gonococci negatively affect the condition of the baby, and problems with its stabilization may arise. In pregnant women, against the background of the disease, immunity deteriorates, which makes it vulnerable to other pathologies. Pathogens in such a situation quickly enter the bloodstream and begin to rapidly spread throughout the body.
The deterioration of health can be affected by arthritis, pharyngitis and miningitis caused by gonococci.
The consequences of gonorrhea for the fetus
 Infant gonorrhea can occur during pregnancy or during childbirth. If an infection enters the uterus at an early stage of fetal development, serious defects may appear. However, even the successful course of the first trimester of pregnancy does not guarantee that health problems of the child will not arise later.
Infant gonorrhea can occur during pregnancy or during childbirth. If an infection enters the uterus at an early stage of fetal development, serious defects may appear. However, even the successful course of the first trimester of pregnancy does not guarantee that health problems of the child will not arise later.
At about 4 months of pregnancy, the risk of infection in the membranes increases. This, in turn, will provoke chorioamnionitis. With this violation, inflammation of the membranes that envelop the baby occurs.
Complications of gonorrhea can cause placental insufficiency or hypoxia in the baby. At the final stage of pregnancy, there is a risk of developing polyhydramnios. At the same time, the amniotic fluid exceeds the norm and the child cannot develop normally in such conditions. After 30 weeks of gestation, there is a risk of premature outpouring of water, which will inevitably lead to infection of the baby.
Childbirth with gonorrhea
An infection transferred during gestation is not an indication for a cesarean section. If complications have been avoided, and the child feels normal, then childbirth takes place naturally. Doctors insist on surgery only when the fetus is infected and the water leaves early.
Caesarean is done even if the pathology was detected immediately before childbirth. In this case, it will not be possible to avoid infection of the baby, and it is simply impossible to quickly cure the gonorrhea. Symptoms of intoxication of the body will complicate the birth process and can provoke negative consequences in the form of injury to the baby.
Doctor Komarovsky in one of his programs focused the attention of women that it becomes necessary to carry out a cesarean if there is evidence. Many people think that surgery is much worse than a natural birth, but it often helps prevent health problems for the baby and mother.
Regardless of whether the mother's disorder has been completely cured or not, doctors should especially carefully monitor the baby's condition in the postpartum period. A woman who has given birth also needs to be periodically tested to make sure that there is no chronic gonorrhea.
Gonorrhea is one of the most serious sexually transmitted infections. A disease that is not cured in time can spread in the uterine cavity and cause infection of the fetus. How does gonorrhea manifest in pregnant women?
In this article, you will learn:
Causes
The cause of the onset of the disease is most often intercourse, not protected by contraceptives.
When a gonococcus pathogen enters the mucous membrane of a microorganism on the genitals.
Also, infection can occur during the birth of a child, through the infected genital tract of the mother. The disease proceeds at a rapid pace and is accompanied by pronounced ones.
Symptoms of the disease:
- when urinating, sharp painful sensations appear;
- discharge of pus from the genital tract;
- the onset of fever.
Untimely treatment of the disease or the complete absence of therapy, threatens damage to many internal organs of the mother and fetus
The causative agent of gonococcus in gonorrhea in pregnant women affects:
- uterus;
- bladder;
- kidneys.
In men, in addition to the kidneys and bladder, the testes, their appendages and the vas deferens are affected.
Often the result of gonorrhea is infertility in both women and men. The causative agent of gonorrhea - gonococcus can provoke inflammation of other organs.
Gonococcus provokes inflammation:
- tissues with glandular or columnar epithelium;
- rectum;
- the appearance of conjunctivitis;
- inflammation of the pharynx.
In women in position, the microorganism affects the cervix in the first place, then spreads to the fallopian tubes.
Ultimately, the ovaries are damaged. In newly born babies, gonorrhea can cause conjunctivitis.
The causes of gonorrhea can be:
- not using condoms;
- promiscuous sex;
- violation of personal hygiene.
Based on the causes of gonorrhea, it can be avoided by following simple rules of personal hygiene with control of sexual intercourse.
Infection options in pregnant women
In many ways, gestational gonorrhea is similar to that outside of pregnancy, but there are a number of typical features. In medicine, the course of gonorrheal infection is conventionally divided into three stages, differing in clinical manifestations. It:
- Fresh infection and infection, current in acute or subacute, less often torpid (sluggish) form.
- Chronic gonorrhea with few and few symptoms.
- Latent (or in another way) latent infection that does not have any manifestations other than the presence of microbes.
Fresh form of gonorrhea will be diagnosed in cases where up to two months have passed since the moment of infection. In this case, the acute form is understood as pathology in situations where the symptoms are pronounced and gradually increase during the first two weeks from the moment of intimacy without protection. At subacute the symptomatology does not increase so sharply and is not so pronounced.
Most dangerous torpid form of gonorrhea, especially in pregnant women. With her, the signs of infection are very scanty or practically absent, so the woman does not worry about anything, she bears the baby without going to the doctor for help and without proper treatment. This leads to the fact that the infection gradually flows into chronic form... It is much more difficult and longer to treat it than an acute infection.
Latent form during pregnancy it is rare and this is due to the fact that she does not have pronounced symptoms, but at the same time forms significant problems in the genital area and disrupts the process of conception, leading to infertility. This is usually formed due to the formation of adhesions in the area of the fallopian tubes, which form obstacles for the meeting of eggs and sperm. And besides, such a woman is a constant source of infection for sexual partners.
Gonorrhea during pregnancy: consequences for women
Gonorrhea refers to an insidious ailment and is dangerous for a woman at any stage of her life. In a pregnant woman, this disease can lead to the following problems:
- the threat of termination of pregnancy;
- placental insufficiency;
- septic miscarriage;
- premature outpouring of water;
- premature birth;
- chorionic amnionitis (inflammation of the placenta + fetal membranes).
Gonorrhea during pregnancy is most often hidden and painless. The changes in a woman's health are attributed to the physiological characteristics of pregnancy, ignoring a visit to a specialist.
Only a third of expectant mothers report pain in the lower abdomen or "bad" discharge. Most women do not worry at all, but in vain!
In addition to the possible serious complications of this disease, the presence of gonorrhea increases the likelihood of even more dangerous diseases, including HIV.
Frequent consequences of gonorrhea for women in labor are postpartum complications, manifested in inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
In the chronic form of gonorrhea, adhesions form in the woman's tubes, which leads to infertility. causes severe abdominal pain. Also chronic tube pathology is. Adhesions of the peritoneum as a pushing factor of an ectopic pregnancy.
Women with gonorrhea have a 3 times higher risk of developing endometritis
Childbirth with gonorrhea is carried out in special observational departments, in compliance with the rules of the sanitary and hygienic regime (to avoid cross-infection of other women).
Danger to baby and mother
The consequences for the child can be the most sad - he can die. Most often this happens if a woman was infected with gonorrhea in the first trimester of pregnancy. According to statistics, miscarriages occur in 25% of cases.
If the woman successfully delivered the baby and the birth began on time, then in this case the baby will be infected while moving along the birth canal. Since gonorrhea in children occurs in complicated forms, in order to prevent infection of the baby, a cesarean section is prescribed.
However, during gestation, a gonococcal infection harms the normal course of pregnancy. In addition to the fact that the infection can spread throughout the mother's body, it can cause gonococcal meningitis, pharyngitis, arthritis and other diseases that pose a danger not only to the mother, but also to the child.
Any infectious disease can lead to infertility. There is a concept of secondary gonorrheal infertility, which means that after childbirth or abortion, the pathogen has penetrated the tubes and into the uterus itself, which provoked infertility. Gonorrhea can affect a woman's nervous and cardiovascular system.
Methods for treating gonorrhea (gonorrhea) during pregnancy
At the moment, there is only one method of treating such a disease - it is taking antibiotics. This infection has a clearly pronounced infectious nature, which cannot be cured without taking them.
When treating gonorrhea during pregnancy in women, it is necessary to pass all the necessary and recommended tests, according to which the doctor prescribes individual antibiotics specifically for your body.
When contracting an infection (gonorrhea) during pregnancy, most women can have serious problems, including miscarriage, and even fetal death, or postpartum infections.
There are also a number of possible complications, namely:
- chorioamnionitis;
- placental insufficiency;
- miscarriage;
- infection of the membranes of the membranes;
- infection of amniotic fluid.
Symptoms of a gonococcal infection in pregnant women:
- Specific purulent vaginal discharge;
- Sore urination;
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Burning;
- Soreness of the lower abdomen;
- Increased body temperature.
During pregnancy, there is a high risk of infection of the fetus, as a result of which the child may develop gonococcal conjunctivitis, as well as gonorrhea of the genitourinary tract (it develops exclusively in girls).
It is important: Pregnant women should treat gonorrhea exclusively in a hospital, as this is a high risk for fetal development.
I trimester... If the infection occurred at the first stage of pregnancy, then there is a high probability of inflammation of the uterus, its membranes, which can lead not only to interruption, but also to underdevelopment of pregnancy.
II trimester... If a woman is infected during the second stage of pregnancy, then the infection cannot enter the uterus, since she will not be allowed to do this by the membranes of the fetal bladder. Therefore, the risk of miscarriage is significantly low, but this leads to placental insufficiency, which causes a lack of oxygen and a lack of nutrients.
Gonococcus does not cause major malformations in the development of the fetus, but this does not mean that the infection is so safe.
Diagnosis of gonococcal infection during pregnancy is as follows:
- Gonococcus smear.
- Examination of the throat cavity for gonococcal pharyngitis.
Treatment of gonococcal infection in women during pregnancy is carried out by prescribing drugs that restore the body's immune system. Antibiotics are prescribed, a vitamin restoring complex is prescribed.
The treatment of such an infection in pregnant women is dealt with by a venereologist and a gynecologist. The safest drugs for pregnant women are drugs made on the basis of penicillin and antibiotics - cephalosporins.
Prevention of infection during pregnancy, of course, is the exclusion of sexual intercourse, as well as timely treatment if the disease is detected.
Treatment of gonorrhea in women who are expecting a baby
After the diagnosis of gonorrhea, treatment of pregnant women is carried out in a hospital, regardless of the gestational age.
Patients are prescribed a course of antibacterial drugs that do not pose a threat to the health of the expectant mother and her baby.

Most often, doctors use ceftriaxone and spectinomycin. Erythromycin and azithromycin are used as a substitute for these drugs.
It should be noted that cefixime, cefotaxime and ceftriaxone are not prescribed for patients with a history of allergic reactions to cephalosporins, as well as drugs of the penicillin group.
For the prevention of concomitant chlamydial infection, drugs are prescribed that are used to treat it. A prerequisite for effective treatment of gonorrhea is the examination and treatment of the second sexual partner.
Non-drug treatment includes physical therapy, which is carried out after consultation with the attending physician and taking into account the general health of the patient.
Prevention of gonorrhea for mother and child
A woman can infect her baby during childbirth. 40% of these children develop gonococcal ophthalmia. This is an eye infection. This condition requires treatment. Babies are prescribed ceftriaxone. It is used at 25-50 mg per kg, but not more than 125 mg per administration. The drug is administered once a day, for a course of 3 days.
Treatment is necessarily carried out with the participation of a neonatologist. Therapy is prescribed in any case if the child was born to an infected mother. And it doesn't matter if he has signs of a gonococcal infection.
But if there are no symptoms, then ceftriaxone is administered 1 time, not three times. This treatment is called prophylactic. Topical medications can also help prevent gonorrhea in newborns.
0.5% erythromycin ointment or 1% silver solution is prescribed.
The use of silver nitrate reduces the risk of ophthalmia by 4-5 times. Without prevention, it develops in 40-50% of children born to mothers infected with gonorrhea.
With prophylaxis, the risk is reduced to 10% or less. Prevention of congenital gonorrhea in girls and boys also consists of treating the mother. Therapy can be performed late in gestation, shortly before delivery.