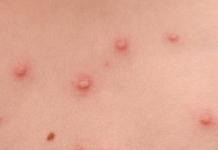
Beethoven, Baudelaire, Lincoln, Nietzsche ... Not only the level of world fame, but also the general diagnosis of "syphilis" gives us the right to mention these sonorous names in the same row. An infectious disease has been attacking humanity for centuries, regardless of ranks and titles, age and social environment. Pale treponema is to blame. A helical microorganism is recognized by monotonous curls and specific movements of a rotational-translational, wavy and flexion character. The causative agent of syphilis is reproduced in the course of transverse division into several elements, which later grow into an adult. The microorganism does not tolerate drying, prolonged exposure to high temperatures. Destroyed by ethyl alcohol. Low temperature conditions can prolong the life of pale treponema.
Morbidity
Over the past 10 years, syphilis has confidently hit records for the increase in the number of new victims. According to some reports, the army of patients with an unpleasant diagnosis has doubled over the specified period. In our country, despite the downward trend in the total number of infected persons, the incidence rate is still an order of magnitude higher than in Europe. The statistics are mostly "spoiled" by the representatives of youth leading an asocial lifestyle.
The risk of contracting syphilis increases dramatically for those who:
- prefers unprotected sex;
- seeks to replenish the "piggy bank" of contacts with unfamiliar sexual partners;
- has homosexual preferences (leading positions (about 60%) among all infected people are confidently held by men with non-traditional sexual orientation);
- is in constant contact with a sick person;
- not averse to indulge in injecting drugs.
How is syphilis spread?
Treponema pallidus lies in wait for its victims in a variety of situations and easily enters the body of a new host:
- Sexually. Any unprotected sexual intercourse is committed by the initiator at his own peril and risk. "Once" - traditional, anal or oral - is quite enough for the causative agent of syphilis to penetrate with sperm (vaginal secretions) into the blooming organism of a healthy partner and begin to actively multiply there. It does not matter how bad things are for a lover who knows how to keep his secrets. Syphilis is highly infectious at any stage of its development.
- Everyday way. Not the easiest way for a pathogen to find a new home. Pale treponema cannot exist for a long time outside the human body. However, provided that a sufficient level of humidity is maintained, the pathogen is surprisingly "survivable": if basic rules of personal hygiene are not followed, syphilis is transmitted from a sick partner to a healthy one through a kiss, the use of "one for two" unwashed toothbrush, spoon, cup. 3. By transfusion. One of the "working schemes" of infection through blood is to put a common injection syringe in a circle in the company of amateurs of experiments with narcotic substances. In practice, there are also cases when the "culprit" of the transmission of the pathogen was an unscrupulous donor, who for some reason did not pass the established procedure for testing for the presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Transplacental route. Congenital syphilis is transmitted to the infant through the mother's placenta. Often this fact becomes the cause of intrauterine fetal death. It is also likely that the newborn will become infected with breastfeeding. In the presence of such a risk factor, doctors prescribe a cesarean section and recommend switching to a regimen of artificial nutrition for the baby.
The incubation period of syphilis
I didn't think - I didn't guess, but I was already sick and contagious - this is how syphilis develops in the early stages. Usually, the first alarming signals appear 10 days after the entry of treponema into the body. However, the patient can learn unpleasant news about himself much later - in the worst case, six months later, if he takes a course of antibiotics that suppress the destructive activity of the infection.
The causative agent of syphilis is capable of producing a substance that disrupts the recognition process of the "invader" by the body's defenses. In conditions of suppression of cellular immunity, treponema actively multiplies and quickly spreads through the lymphatic tract and internal organs. From the first days of infection, there is a risk of infecting other people.
Primary syphilis
This stage lasts up to 8 weeks and leads to a noticeable enlargement of the lymph nodes and the formation of a hard chancre. In the bloodstream, there is an increase in the number of special antibodies that immobilize treponemas and form immune complexes. The body's fight against the causative agents of syphilis ends with the release of lipopolysaccharide and protein products into the blood. The destruction of tissue treponema is accompanied by a local inflammatory reaction in the form of multiple rashes on the skin and mucous membranes, which signal the onset of the second stage of syphilis.
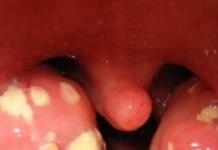
Chancre
It is formed in the foci of pale treponemas entering the body. Usually, the patient discovers a neoplasm on the skin or mucous membranes of the genitals, less often on the lips, tongue, eyelids, finger, abdomen, in the mouth, or in any other place where the pathogen penetrates. Hard chancre is erosion with well-defined rounded contours (in the shape of a saucer) of a “lacquered” red color. At the base of the neoplasm, a dense elastic seal is palpable, which does not cause pain. Recently, experts have increasingly noted the emergence of several chancre.
Clinical manifestations
A week after the formation of a hard chancre, an increase in nearby lymph nodes is noted, and inflammatory processes in the lymphatic vessels are likely. By the end of primary syphilis, almost a quarter of patients have symptoms confirming the fact of generalization of the infection: a significant increase in body temperature, nighttime headaches, discomfort in bones and joints, lack of appetite, and loss of strength.
Secondary syphilis
The approximate starting point for this stage is 2.5 months after infection. The average duration is 3 years. Within the framework of the stage, fresh (early), recurrent and latent syphilis are isolated. The formation of immune complexes is in full swing, which causes the development of inflammatory processes and provokes mass death of treponemas. Syphilis enters a latent phase lasting up to three months. However, six months after infection, the first relapse occurs. The activation of antibody synthesis becomes a response to the newly begun multiplication of pathogens. Thus, the undulating nature of the course of the disease reflects the essence of the specifics of the interaction between the causative agent of the infection and the body's immune system. The pathological process from the skin and mucous membranes passes to other organs and systems. Symptoms of intoxication are sometimes noted. The patient poses a high degree of danger to the close environment, since the risk of infection is maximum.
Fresh (early)
This period lasts from two to four months from the date of infection. It is manifested by the appearance of a rash on the skin and mucous membranes, which is a sure sign of secondary syphilis. The rashes are numerous, brightly colored, but do not bother the patient (sometimes complaints of itching are recorded in the medical history), persist for several weeks and suddenly disappear. In some cases, hair loss is noted.
Recurrent
The period of short-term "return" of a characteristic symptom of the disease: there are few groups of large rashes that form rings and arcs.
Relapses usually occur no more than four times.
Hidden
The duration of such a period is on average 3 months. External clinical manifestations are not observed. The diagnosis is possible in the presence of professional examination data (scars at the site of the former foci of rashes, enlarged lymph nodes), as well as special studies.
Tertiary syphilis
It occurs in the absence of professional treatment of the existing disease and in 25% of cases is fatal. The tertiary period (stage 3 of syphilis) stretches over decades. Most of the internal organs are affected (brain and spinal cord, liver, kidneys, stomach, intestines, genitals), as well as the nervous and cardiovascular systems. Vision and hearing deteriorate sharply. Patients experience sudden changes in mental states: from bouts of depression, paranoia to euphoria, hallucinations.
A typical cutaneous manifestation of syphilis at this stage is the formation of infectious granulomas (gum), which are subcutaneous groupings of cells in tissues in the form of nodes that develop into ulcers. Neoplasms affect not only soft tissues, but also the skeletal system, leading to irreversible deformations (for example, a sinking of the nose). The last stage of syphilis is not as contagious as the previous ones, but it is certainly the most unfavorable in terms of prognosis.
Syphilitic endarteritis (damage to the cardiovascular system)
It occurs in the first years after the illness of syphilis, develops gradually (over weeks and months) and is characterized by the simultaneous manifestation of cerebral and focal symptoms. So, the patient begins to complain of attacks of severe headache, vomiting, memory loss. The nature of the focal symptoms is due to the localization of the infectious lesion:
- Basin of the middle cerebral artery: the occurrence of hemiplegia (paralysis of one half of the body) or monoplegia (paralysis of one limb), aphasia, impaired sensitivity, apracto-diagnostic syndrome (manifested as spatial disorders) with damage to the parietal lobe.
- Vertebrobasilar vascular basin: the appearance of alternating syndromes (movement and sensory disorders),
loss of visual fields, bulbar syndrome (impaired swallowing and speech functions). Comatose forms of stroke with acute cerebral symptoms are possible. Repetitions of thrombotic strokes are observed.
Different vascular basins can be involved in the development of the disease. If the vessels supplying the subcortical nodes are damaged, the risk of parkinsonism, a neurological syndrome in which the patient is unable to perform voluntary movements, is not excluded.
Dorsal tabes
Desperate Boys Disease: Men suffer from this clinical variant of neurosyphilis about 5 times more often than women. The first signs of the disease appear, as a rule, in middle-aged patients 15–20 years after the entry of pale treponema into the body. The reason is a disruption in the work of the posterior parts of the spinal cord. Typical details of the clinical picture: the predominance of pain of a paroxysmal nature (in the form of an acute seizure), sensitivity disorders, distortion of the normal reaction of the pupil, impaired coordination of movements.
According to statistics, this form of syphilis is currently rare.
Damage to the musculoskeletal system
About 85% of patients diagnosed with early congenital syphilis suffer from pathological changes in the skeletal system. Osteochondritis are symmetrical and extensive.
Against the background of the development of late congenital syphilis, lesions of the skeletal system are observed more often than in secondary and tertiary syphilis, but less often than in the early congenital form and are diagnosed on average in 40% of patients. Traditionally, the pathology is localized in the region of the skull and tibia.
Organ damage
At the initial stages of the disease in the clinical picture, only individual disturbances in the work of the affected organs are noted. However, after some time, syphilis reveals its presence in more serious diagnoses, including at the level of:
- stomach: acute gastritis, the formation of characteristic ulcers and erosions;
- kidney: asymptomatic dysfunction, glomerulonephritis, nephrosis;
- hearts: cardiovascular syphilis;
- liver: various forms of hepatitis.
Diagnostics
In order to avoid the misdiagnosis of syphilis, a whole range of measures is required:
- Patient interview. The nature of complaints and the patient's lifestyle are important for identifying the nature of pathological processes. Various signs can indicate syphilis, including the types of secretions from the mucous membranes, under what circumstances "dubious" sexual intercourse took place, whether there are special preferences in sex, whether there are malfunctions in the work of internal organs.
- Inspection. The venereologist can navigate the nature of the disease by the presence of rashes, hard chancre, and enlarged lymph nodes on the patient's skin.
- Laboratory research. A reliable method of analysis for infectious syphilis is the study of the contents of the chancre, ulcers and skin rashes.
- Blood test. Reveals the presence of antibodies produced by the body to fight against the causative agent of the disease.
- Immunofluorescence reaction (RIF). The essence of the study lies in the fact that the serum of an infected patient, when interacting with injected pale treponemes in a special microscope, glows with a yellow-green light. The discharge of a healthy organism, participating in a similar reaction, does not give a luminescence.
Treatment
The patient undergoes an individual therapeutic course under the supervision of a specialist in a hospital or on an outpatient basis. In this case, sexual intercourse is completely excluded. The therapy is based on the use of antibacterial drugs. The treatment prescribed by a venereologist for primary syphilis is designed for several weeks, secondary (including late latent) - for a period of two years or more.
Syphilis, including repeated syphilis, is a curable disease. The patient must urgently go to the nearest clinic at the first suspicion of a problem.
Congenital syphilis
It is transmitted to the fetus by the transplacental method. It happens early (prenatal period, infancy and early childhood) and late (after 15 years). Requires special approaches to diagnosis and treatment.
Development mechanism
Fetal infection occurs in the fifth month of pregnancy when pale treponemas enter the placenta. The disease disrupts the work of internal organs and affects the skeletal system. The child's chances of survival are assessed as extremely low.
Some infants infected with transplacental infection survive, but the peculiarities of intrauterine development do not pass without leaving a trace.
Symptoms of early congenital syphilis
A child with this diagnosis is weakened, slowly developing mentally and physically. Syphilis in newborns is characterized by damage to the eyes, brain, skin, bones, cartilage, teeth, dysfunction of the liver, spleen, cardiovascular system.
Between the ages of 1 and 2, the following often appear:
- Skin rashes. Localized in the genital area, buttocks, larynx, face, palms. The characteristic scars located radially along the contour of the mouth will last for life.
- Rhinitis. The little patient breathes through his mouth due to inflammation caused by a rash on the nasal mucosa.
- Bone affection. Usually, swelling and soreness occurs directly in the area of infection.
In the case of latent congenital syphilis, the diagnosis is clarified using blood and cerebrospinal fluid tests.
Symptoms of late congenital syphilis
The disease manifests itself in adolescence (15–16 years) with lesions of the eyes (including up to complete blindness), inner ear, tumors in the tissues of internal organs and skin, a lunate notch along the edge of the incisors.
Among the signs of infection are also called "saber" legs, scars around the lips, "saddle" nose, "buttock" skull.
Diagnostics
The pathogen can be detected through microscopic analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid. But a negative result does not guarantee the absence of a latent form. In the presence of skin rashes, it is advisable to examine their discharge for the presence of pale treponemas.
For the final diagnosis, high-precision serological blood tests are carried out, and data from additional consultations of narrow specialists (pulmonologist, neurologist, nephrologist, ophthalmologist and others) are used.
Congenital syphilis treatment
Treponema pallidum to this day retains a high sensitivity to antibiotics. Accordingly, patients are prescribed a long course of antibiotic therapy.
Prevention of syphilis
Contrary to popular belief, condoms do not guarantee one hundred percent protection against infection, since there is a possibility of infection not only sexually, but also through domestic means. In this regard, additional personal safety measures should be taken:
- use antiseptics for full treatment of the oral cavity and genitals after intercourse is completed;
- urgently (within two hours) seek help from a venereologist if you have not protected yourself during spontaneous sex with an unfamiliar partner;
- do not neglect the basic rules of personal hygiene;
- give preference to artificial feeding of a baby whose mother is a carrier of the infection.
Can you get syphilis through a kiss? Easily! Getting rid of adversity is much more difficult. Self-medication is strictly contraindicated, since it does not lead to recovery, but it can significantly affect the course of pathological processes, which will further complicate the diagnosis. Your health should be entrusted to experienced professionals.
Latent syphilis is a condition when, in the absence of clinical manifestations of the disease, positive serological reactions are found in the patient's blood. Treatment of such patients is aimed at serological negativity (obtaining negative serological reactions) and preventing the development of relapses of the disease.
Latent (latent) syphilis occurs in patients who in the past had active manifestations of the disease that resolved on their own or under the influence of specific treatment.
In some cases, this condition is a special form of asymptomatic course of syphilis from the moment the patient is infected. A properly collected anamnesis (history of the disease) and a number of other indirect signs provide significant assistance in making a diagnosis.
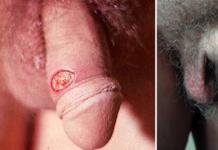
Rice. 1. Manifestations of the disease in women in the primary period of the disease - multiple hard chancre (left photo) and hard chancre in the form of indurative edema (right photo).
Current state of the problem
According to some authors, the number of patients with latent forms of syphilis in the last decade has increased by 2 - 5 times. Increasingly, it becomes difficult for a doctor to determine the timing of the disease, and the patient's sexual relations are often random. The only method for detecting syphilis in such cases is serological diagnosis.
In our country, a technique is used to actively identify patients with syphilis during preventive examinations in polyclinics and hospitals, antenatal clinics and at blood transfusion points, for which a number of treponemal tests are also used. Thanks to this work, up to 90% of patients with latent forms of the disease are detected during preventive examinations.
The reasons for the increase in the number of patients:
- a true increase in the number of patients with latent syphilis;
- improvement of methods of serological diagnostics;
- widespread uncontrolled use of antibiotics in the treatment of various diseases.
The possibility of an asymptomatic course of syphilis is now recognized.
Serological reactions in latent forms of the disease are the only criterion for confirming the diagnosis.

Rice. 2. Manifestations of the disease in men in the primary period - a single hard chancre (photo on the left) and multiple hard chancre (photo on the right).
Forms of latent syphilis
If, from the moment of infection, syphilis takes a latent (latent) course (asymptomatic), but with positive specific serological reactions, they speak of a latent form of the disease. Latent syphilis in most cases is detected by chance when specific serological reactions are set. In some cases, the doctor manages to find out which period of the disease he belongs to:
- if the patient had a previously recorded hard chancre, but did not appear, then they speak of the latent period of primary syphilis;
- the latency period identified after the onset of secondary syphilis and in the case of recurrent syphilis refers to the secondary period of the disease;
- there is also a latent period.
Such a subdivision of the latent periods of the disease is not always possible, therefore, in venereal practice, it has been established to distinguish between early, late and unspecified latent periods.
- Diagnosis early latent syphilis installed if more than 2 years have passed since the moment of infection. In epidemiological terms, this category of patients is the most dangerous.
- Diagnosis late latent syphilis installed if more than 2 years have passed since the moment of infection.
- Latent, unspecified syphilis- this is a condition when, in the absence of anamnestic data and clinical manifestations of the disease, positive serological reactions are found in the blood of a previously untreated patient.

Rice. 3. Manifestations of the disease in the secondary period - papular syphilis on the face and palms.
Early latent syphilis
Early latent syphilis includes the period from the moment of infection up to the secondary recurrent period (on average up to two years). During this period, patients may experience manifestations of the disease of a high degree of infectiousness. With regard to them, a number of anti-epidemic measures are being taken. The main ones are:
- isolation of the patient,
- examination of sexual partners and home contacts,
- compulsory treatment (according to indications).
Who is sick
Early latent syphilis is recorded mainly in persons under the age of 40. Most of them lack control over their sex drive. They are prone to numerous casual sexual intercourse, which in an epidemic leads to the inevitable development of the disease. The absolute proof of a case of latent syphilis is the establishment of an active form of the disease in a sexual partner.
What you need to find out when interviewing
Carefully collecting anamnesis, it is necessary to pay attention to erosive-ulcerative rashes on the genitals, lips, oral cavity, skin, episodes of hair loss on the head, eyebrows and eyelashes, the appearance of age spots on the neck over the past 2 years. It is also necessary to find out whether or not the patient took antibiotics, was treated or not for gonorrhea.
Signs and symptoms of early latent syphilis
- A scar or induration on the genitals revealed during a clinical examination and often the presence of enlarged regional lymph nodes, as well as residual symptoms of polysleradenitis, may indicate a previous primary syphilis.
- In 75% of patients in the latent early period of the disease, sharply positive serological reactions (1: 160) are noted, a low titer (1: 5: 20) is noted in 20% of patients. In 100% of cases, there is a positive RIF. In 30 - 40% of cases, there is a positive RIBT. When treating concomitant diseases with antibiotics, the titers of serological reactions are reduced.
- In 1/3 of patients treated with penicillin, the Herxheimer-Jarisch reaction is observed, which is characterized by a sudden increase in body temperature, headache and muscle pain, vomiting, and tachycardia. This phenomenon is due to the mass death of pathogens. Symptoms are quickly relieved by aspirin.
- In the case of the development of latent syphilitic meningitis, an increased amount of protein is noted in the cerebrospinal fluid, (+) reactions to globulin fractions and cytosis. With specific treatment, the cerebrospinal fluid is quickly sanitized.
Treatment of early latent syphilis
Treatment of early latent syphilis is carried out according to approved instructions and is aimed at the fastest destruction of pathogens in the patient's body. With specific treatment, seroreaction negative occurs rather quickly. The extinction and complete negativity of specific serological reactions in latent syphilis are the only criteria for confirming the effectiveness of the treatment.
Timely identification of patients during the period of early latent syphilis and adequate adequate treatment have a beneficial effect on the prognosis of the disease.

Rice. 4. Manifestations of the disease in the secondary period - syphilitic roseola.
Late latent syphilis
The diagnosis of late latent syphilis is established in patients whose infection is more than 2 years old, there are no clinical manifestations of the disease and positive serological reactions are recorded. Basically, such patients are detected during preventive examinations (up to 99%), including when examining the detection of a patient with late forms of syphilis in the family (1%).
Who is sick
The disease is detected mainly in persons over 40 years of age (up to 70%). Of these, about 65% are married.
What you need to find out when interviewing a patient
When interviewing a patient, it is necessary to find out the timing of possible infection and the presence of signs indicating the manifestations of infectious syphilis in the past. Often, the anamnesis remains uninformative.
Signs and symptoms of late latent syphilis
- During the examination, it is not possible to identify traces of previously resolved syphilides. During the examination, there are no signs of specific damage to the internal organs and the nervous system.
- In the diagnosis of late latent syphilis, serological tests such as RIF, ELISA, RPGA and RITT are used. The titer of reagins is usually low and ranges from 1: 5 to 1:20 (in 90% of cases). In rare cases, high titers are noted - 1: 160: 480 (in 10% of cases). RIF and RIBT are always positive.
Sometimes serological tests have to be repeated after several months.
In patients with late latent syphilis, whose age is from 50 to 60 years, there are a number of concomitant diseases that cause the appearance of false-positive serological reactions.
- There is no Herxheimer-Jarisch reaction to the administration of antibiotics.
- Late latent meningitis is rare in these patients. In the cerebrospinal fluid, when specific meningitis is detected, a weakly pronounced inflammatory component is noted - a low cytosis and protein level, signs of a degenerative component prevail - a positive Wasserman reaction and a Lange reaction. During the period of specific treatment, the rehabilitation of the cerebrospinal fluid occurs slowly.
Treatment of late latent syphilis
Treatment of late latent syphilis is carried out according to approved instructions and is aimed at preventing the development of specific damage to internal organs and the nervous system. Patients should be consulted with a neurologist and therapist. During the period of specific treatment, the seroreaction negative occurs extremely slowly. In some cases, after a full-fledged specific treatment, serological reactions remain positive.
The extinction and complete disappearance of specific serological reactions in latent syphilis are the only criterion for confirming the effectiveness of the treatment.

Rice. 5. Manifestations of the disease in the Tertiary period - gum of the face and gummy infiltration of the hand.
Latent, unspecified syphilis
In the absence of information about the circumstances and timing of infection and the presence of positive results of serological tests, a diagnosis of latent unspecified syphilis is established. Such patients are subject to careful clinical and serological examination, often repeated. The setting of RIF, RIF-abs and RIBT, IFA and RPGA are mandatory.
You should be aware that in patients with late and unspecified syphilis, false-positive nonspecific serological reactions are often detected. Antibodies-reagins, produced against the cardiolipin antigen, appear in the blood of patients with collagenoses, hepatitis, kidney diseases, thyrotoxicosis, cancer and infectious diseases such as leprosy, tuberculosis, brucellosis, malaria, typhus and scarlet fever, during pregnancy and menstruation fatty foods and alcohol, in patients with diabetes mellitus, myocardial infarction and concussion. It is noted that the number of false positive reactions increases with age.

Rice. 6. Gummy infiltration of the buttock and areola in the tertiary period of the disease.
Latent (latent) syphilis is an asymptomatic development of a syphilitic infection that does not have any external signs and manifestations of internal lesions. In this case, the pathogen is present in the body, it is easily detected during appropriate laboratory tests and, as it becomes active, begins to manifest itself externally and internally, causing serious complications due to neglect of the disease.
The increase in the incidence of latent syphilis is due to the active use of antibiotics at an early stage of undiagnosed syphilitic infection, the symptoms of which are taken for signs of other venereal, acute respiratory or colds. As a result, syphilis is "driven" inside and in 90% of cases it is discovered by accident during medical examinations.
Latent syphilis develops for various reasons and can have several variants of the course:
- As a form of the primary period of the disease, in which infection occurs by direct penetration of the pathogen into the bloodstream - through wounds or injections. With this route of infection, a hard chancre does not form on the skin - the first sign of a syphilitic infection. Other names for this type of syphilis are headless.
- As part of the later stages of the disease, which proceed in a paroxysmal manner - with a periodic change in the active and latent phases.
- As a type of atypical development of infection, which is not diagnosed even in laboratory tests. Symptoms develop only at the last stage, when severe lesions of the skin and internal organs occur.
The development of the classic is due to the penetration of a certain type of bacteria - treponema pale. It is their vigorous activity that leads to the appearance of symptoms of syphilitic infection - characteristic rashes, gum, other skin and internal pathologies. As a result of an attack by the immune system, most pathogenic bacteria are killed. But the strongest survive and change shape, which is why the immune system ceases to recognize them. In this case, treponemas become inactive, but they continue to develop, which leads to the latent course of syphilis. When the immune system weakens, the bacteria become active and cause the disease to flare up again.
How the infection is transmitted
Latent syphilis, unlike ordinary syphilis, is practically not transmitted by household means, since it does not manifest itself as the most contagious symptom of infection - a syphilitic rash. All other routes of infection remain, including:
- unprotected intercourse of all kinds;
- breast-feeding;
- penetration of infected saliva, blood.
The most dangerous in terms of infection is a person who has been ill with latent syphilis for no more than 2 years. Then the degree of its infectiousness is significantly reduced.
At the same time, the asymptomatic course of the infection can make it hidden not only for others, but also for the patient himself. Therefore, he can be a source of infection without even knowing it and posing a great danger to those who are in close contact with him (especially for sexual partners and family members).

If latent syphilis is found in workers in those areas in which contact with a large number of people is expected, they are released from their duties for the duration of treatment with the issuance of a sick leave. After recovery, no restrictions on professional activities are established, since the bangs does not pose a danger in terms of infection.
Varieties of latent syphilis
The asymptomatic form of syphilitic infection is divided into 3 types, depending on the duration of the course of the disease. In accordance with this sign, latent syphilis is distinguished:
- early - diagnosed when a maximum of 2 years have passed since the bacteria entered the body;
- late - set after exceeding the specified 2-year period;
- unspecified - determined if the duration of infection has not been established.
The degree of damage to the body and the prescribed course of treatment depend on the duration of the course of the infection.
Early latent syphilis
This phase is the period between the initial and recurrent manifestations of the infection. At this time, the infected person has no signs of the disease at all, but he can become a source of infection if his biological fluids (blood, saliva, sperm, vaginal secretions) penetrate into the body of another person.
A characteristic feature of this stage is its unpredictability - the latent form can easily become active. This will lead to the rapid appearance of a hard chancre and other external lesions. They become an additional and most open source of bacteria, which makes the patient infectious even with normal contact.

If a focus of early latent syphilis is identified, special anti-epidemic measures are taken. Their goal is:
- isolation and treatment of the infected;
- identification and research of all persons in contact with him.
Early latent syphilis most often affects persons under 35 years of age, promiscuous in sexual intercourse. The incontrovertible evidence of infection is the identification of infection in a partner.
Late latent syphilis
This stage is determined if more than 2 years have passed between penetration into the body and the detection of a syphilitic infection. At the same time, there are also no external signs of the disease and symptoms of internal lesions, but the corresponding laboratory tests show positive results.
Late latent syphilis is almost always found during tests during a prophylactic examination. The rest of the identified are relatives and friends of the infected. Such patients do not pose a danger in infectious terms, since tertiary syphilitic eruptions practically do not contain pathogenic bacteria, and those that do exist quickly die.

Signs of late latent syphilis are not detected by visual examination, there are no complaints of deterioration in well-being. Treatment of this stage is aimed at preventing the development of internal and external lesions. In some cases, at the end of the course, the test results remain positive, which is not a dangerous sign.
Unspecified latent syphilis
In situations where the subject cannot report the time and circumstances of infection, unspecified latent syphilis is diagnosed on the basis of laboratory tests.
Clinical examination of such patients is carried out carefully and repeatedly. At the same time, false-positive reactions are often detected, which is due to the presence of antibodies in many concomitant diseases - hepatitis, renal failure, cancer, diabetes, tuberculosis, as well as during pregnancy and menstruation in women, with alcohol abuse and addiction to fatty foods.
Diagnostic methods
The absence of symptoms significantly complicates the identification of latent syphilis. The diagnosis is most often made based on the results of appropriate tests and anamnesis.
The following information is of decisive importance in compiling anamnesis:
- when the infection occurred;
- syphilis is diagnosed for the first time or the disease is repeated;
- what kind of treatment the patient received, and whether there was any;
- have you had antibiotics in the past 2–3 years;
- whether rashes or other changes in the skin were observed.
An external examination is also carried out to identify:
- syphilitic eruptions all over the body, including the scalp;
- scars after previous similar skin lesions;
- syphilitic leukoderma on the neck;
- change in the size of the lymph nodes;
- hair loss.
In addition, sexual partners, all family members, and other persons in close contact with the patient are examined for infection.
But the decisive factor for the diagnosis is the appropriate laboratory blood tests. In this case, the diagnosis can be complicated by the possibility of obtaining a false positive or false negative result.

If the test results are doubtful, a spinal tap is performed, the examination of which may show the presence of latent syphilitic meningitis, characteristic of the late latent stage.
With the final diagnosis of the disease, it is imperative to undergo examinations by a therapist and a neuropathologist. This is necessary to establish the presence or absence of concomitant (joined) pathologies.
Treatment of latent syphilis
The latent form of syphilitic infection is treated with the same methods as any type of syphilis - exclusively with antibiotics (systemic penicillin therapy). The terms of treatment and dosage of the drug are determined by the duration of the disease and the degree of damage to the body:
- with early latent syphilis, 1 course of penicillin injections lasting 2-3 weeks is sufficient, which is carried out at home (outpatient) (if necessary, the course is repeated);
- with late latent syphilis, 2 courses of 2–3 weeks each are required, while treatment is performed in a hospital setting, since this form is characterized by a high likelihood of complications.
At the beginning of treatment of the early form, an increase in temperature should appear, which indicates the correct diagnosis.
Pregnant women with latent syphilis must be hospitalized for appropriate treatment and constant monitoring of the condition of the fetus. Since the infection has an extremely negative effect on the condition of the child and can lead to his death, it is necessary to notice the frozen pregnancy in time and provide timely assistance to the woman.

During the treatment period, all contacts of the patient are significantly limited. He is forbidden to kiss, have sex in any form, use common utensils, etc.
The main task of the treatment of early latent syphilis is to prevent the development of the active stage, in which the patient becomes a source of infection. Treatment of the late involves the elimination of complications, especially neurosyphilis and neurological lesions.
To assess the results of treatment, indicators are monitored:
- titles, which are reflected in the analysis results and should decrease;
- cerebrospinal fluid, which should return to normal.
Normal indicators of all laboratory studies with antibiotic therapy with penicillin of early latent syphilis usually appear after 1 course. If they are late, it is not always possible to achieve them, and regardless of the duration of therapy. Pathological processes in this case persist for a long time, and regression is very slow. Often, to accelerate recovery in late latent syphilis, preliminary therapy with bismuth preparations is first carried out.
Forecast for life
The results of treatment, the duration and quality of further life of a patient with latent syphilis are largely determined by the duration of the course of the infection and the adequacy of its treatment. The sooner the disease is detected, the less harm it will have time to inflict on the body.
The following pathologies often become complications of late latent syphilis:
- paralysis;
- personality disorder;
- loss of vision;
- destruction of the liver;
- heart disease.
These or other negative consequences of infection can lead to a significant reduction in life expectancy, but the results are always individual.
If latent syphilis is detected in a timely manner and proper treatment is carried out, a person can be completely cured. Then the disease will not affect the duration and quality of life in any way. Therefore, at the slightest suspicion, you should immediately seek medical help.
In the video, the doctor talks about modern methods of treating syphilis.
Syphilis can also occur in a latent form.
This variant of the course of the disease is called latent syphilis. Latent syphilis from the moment of infection takes a latent course, is asymptomatic, but blood tests for syphilis are positive.
In venereal medicine, it is customary to distinguish between early and late latent syphilis: if a patient contracted syphilis less than 2 years ago, they talk about early latent syphilis, and if more than 2 years ago, then about late.
If it is impossible to determine the type of latent syphilis, the venereologist makes a preliminary diagnosis of latent unspecified syphilis; during the examination and treatment, the diagnosis can be clarified.
The possession of treponemal syphilitic infection in a latent form is not observed in all patients, in 75% of cases after infection at the end of the incubation period, the period of the first manifestations of the disease begins.
In some patients, after infection for years, the infection is present in the body, however, there are no clinical symptoms of the disease. This flow is called latent.
Currently, leading experts in the field of medicine and science believe that several factors affect the rate of development of the disease and the frequency of cases of transition to the latent course of the disease.
First of all, this is the state of the immune system, the frequency of taking medications, antibiotics during the period of infection and concomitant pathology.
It has been proven that taking any antibacterial drugs for syphilis lengthens the incubation period of the syphilitic system for different periods for each patient.
When the first signs of the disease appear, which can be extremely similar to a cold or flu-like condition, taking antibiotics can become a real reason for the transition of the disease into latent syphilis, which will not appear for months.
Common syphilis develops when pale treponemes, the causative agents of this disease, enter the human body. During their activity, the patient develops symptoms of syphilis: a rash, bumps, gum, and so on.
At the same time, the patient's immunity does not stand aside: as with any infection, it secretes antibodies (protective proteins), and also sends cells of the immune system to the breeding sites of bacteria.
Thanks to these measures, most of the pale treponemas die. However, the most tenacious bacteria remain, which change their shape so that the immune system no longer recognizes them.
In the cystic form, pale treponema cannot be active, but it can multiply
This type of "disguised" pale treponema is called cystic forms or L-forms. In this form, pale treponema cannot be active, but it can multiply.
As a result, when the immune system "loses its vigilance", secretly multiplied bacteria enter the bloodstream and repeatedly harm the body.
The same thing happens with the wrong treatment for syphilis. If the antibiotic is chosen incorrectly or in the wrong dose, not all pale treponemas die - the survivors disguise themselves and remain invisible until better times.
Definition and causes of occurrence
The diagnosis of latent syphilis in clinical practice is made if the patient after sexual intercourse does not have specific symptoms on the mucous membranes and skin, there are no visible lesions of internal organs, but the results of laboratory tests reveal antibodies to pallidum spirochete.
Diagnosis of this form of syphilis is considered the most difficult, since patients do not have the slightest suspicion of infection. Usually, pathology is detected during examination for another disease.
In addition, the strains of treponema pale are so insidious that they disguise themselves as chlamydia or gonorrhea, and with a special cunning of the pathogen, patients develop signs indicating stomatitis, bronchial asthma, sore throat, but not syphilis.
The reason for the development of latent syphilis in patients, experts in the overwhelming majority of cases, put attempts to self-medication with a persistent unwillingness to go to doctors after casual sexual intercourse.
There are few people who, having felt a sore throat or a severe runny nose, decide that this is the result of accidental sexual intercourse, and immediately consult a doctor.
Most begin to heal on their own, being completely confident in their actions and knowledge of medicine. And the most dangerous thing is to be treated with antibiotics.

Illiterate and uncontrolled intake of antibacterial drugs leads to the formation of new strains that are insensitive to drugs. And in the case of syphilis, the transformation of pale treponema into a cyst state, which allows it to survive an unfavorable period without loss and harm to the colony.
As a result, the disease is not treated, but passes into a latent form, which is several times more dangerous.
One of the main reasons for the prevalence of latent syphilis among ordinary people is the illiteracy of people and their inadequate attitude towards their health.
The fact is that a person, suspecting he has a cold or the initial stage of development of sore throat, without prior consultation with a specialist begins to take antibiotics uncontrollably.
But these medications hide the main symptoms of syphilis. In other words, syphilis is not cured, but healed and proceeds in a latent form.

Classification
The main classification of latent syphilis identifies such forms as:
- Early - diagnosed if 2 years have not passed since the moment of infection;
- Late - set if more than 10 years have passed since the moment of infection;
- Unspecified (ignored, unknown) - recorded if the infection time cannot be determined;
- Congenital - diagnosed in children who are infected with sick mothers, but do not have characteristic symptoms.
In addition, latent syphilis can have forms that are an active component of the latent course after inadequate therapy, these are:
- Primary, developing without any symptoms in patients who started treatment in a timely manner, but did not receive effective therapy;
- Secondary, developing with secondary syphilis, in the complete absence of characteristic symptoms;
- Tertiary, given to patients who have undergone the active third phase of syphilis.
Early latent syphilis
Early latent syphilis in clinical practice is considered the most dangerous form of the disease. The patient, unaware of his condition, infects the people around him. And what is most unpleasant is that not only sexual partners, but also loved ones living nearby can be infected.
It is possible to establish the presence of a disease of this form only during a routine examination or during examination for another disease. A blood test for Wasserman's reaction is necessarily prescribed for any examination or hospitalization of patients with various pathologies.
This allows you to identify some forms of latent syphilis. But the analysis of the serological reaction does not always give accurate results, so patients must pass other tests as well.
When examining patients with suspected early latent syphilis, seals and enlargements of the lymph nodes are often revealed, and short-term skin rashes are also possible, which did not cause concern, due to their transience.
Quite often, the nervous system suffers from the early latent form. In patients, violations of the walls of blood vessels and the lining of the brain are noted.
Late latent syphilis
Late latent syphilis is placed if more than 2 years have passed since the moment of infection. This form differs in its safety for those around the patient.
Late latent syphilis does not give skin rashes, but significantly destroys internal organs and negatively affects the functioning of the nervous system.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, late latent syphilis is found in elderly people with symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, myocarditis, or coronary heart disease.
Indicators of late latent syphilis are such manifestations as:
It should be noted that the latent form of syphilis is divided into several subspecies:

- early latent syphilis;
- late;
- unspecified.
Usually, the early form of latent syphilis is detected within 2 years after infection. This form is considered the most dangerous, since an infected person poses a danger to the people around him.
After all, not only his sexual partners can become infected with this disease, but also people living with him under the same roof.
This disease is mainly found during medical examinations or during the examination of a patient who has complaints of a completely different disease. The Wasserman reaction is carried out, however, this study does not always give an accurate answer, therefore the patient is subjected to a number of other additional laboratory and clinical examinations.
During a clinical examination, a patient's body is often found to have enlarged and somewhat compacted lymph nodes. During the consultation, patients suddenly begin to recall that at a certain period of time, rashes appeared on their bodies, which disappeared by themselves.
All these symptoms indicate the presence in the patient's body of the causative agent of latent syphilis.
In some cases, early latent syphilis affects internal organs, such as:
- liver;
- stomach;
- thyroid;
- joints.
The central nervous system can also be affected by late latent syphilis. The nervous system, in particular the lining of the brain and the walls of blood vessels, is affected within 5 years after the moment of infection.
Syphilis is divided into several periods of the course of the disease:
- initial, or incubation;
- primary;
- secondary;
- tertiary.
Each period is subdivided into sub-periods. Latent syphilis refers to the secondary period of the course of the disease.
Secondary is divided into three types:
The early one appears 10 days after the person has become infected. It is dangerous that a person, not knowing himself, infects the people around him.
Such syphilis often turns into active, in which a large number of rashes appear, there are many treponemas in them, due to which a person becomes infected.
To find out about latent syphilis, you need to go through the necessary research, so you can find out that you are running a dangerous disease in a latent form, which is transmitted by contact and everyday life.
The patient is immediately isolated from others until his body completely gets rid of harmful bacteria.
A person learns about the late form of syphilis after 2 years. Such patients are not dangerous to others, they do not become infected.
But latent syphilis is dangerous in that it is often diagnosed at a late stage, when it is in the active phase, it can affect the internal organs, the nervous system, tubercles, low-infectious gums appear on the skin.
Often the doctor cannot say for sure when a person became infected and how long latent syphilis lasts.
Symptoms and signs of latent syphilis
The latent form of syphilis has no visually visible symptoms and signs. This latent syphilis is dangerous for sexual partners, for the immediate environment (the likelihood of infection in a household way), for the unborn child (if syphilis is in a pregnant woman).

Symptoms of latent syphilis can occur in a person, according to the signs of some other diseases:
- body temperature rises to 38 degrees, for no apparent reason and regularly;
- unreasonable weight loss;
- psychological disorders depression, apathy;
- a state of weakness throughout the body;
- enlargement and hardening of the lymph nodes.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The course of latent syphilis has practically no effect on the health status of patients. But, there are several signs by which patients may suspect the consequences of the vital activity of treponema pale.
If a person has noticed symptoms such as:
- regular increase in body temperature;
- enlargement and hardening of the lymph nodes;
- overwhelming weakness;
- a feeling of apathy towards everything around;
- unreasonable weight loss.
As well as obvious signs of a violation of the nervous system, which means it is worth thinking about the reasons for this condition. These may not be sexually transmitted diseases, but there may also be the consequences of rash sexual intercourse, the result of which was infection with treponema pale, and the development of latent syphilis.
The diagnosis of latent syphilis is a rather complicated process. The doctor can be confused by the patient's secrecy, symptoms indicating other diseases and false positive test results.
A detailed history is of great importance, according to the results of which it is possible to reveal not only the presence of suspicious sexual intercourse, but also the appearance in the past of patients with erosion on the genitals or the oral cavity, taking antibiotics associated with a disease with suspicious symptoms, and much more.
Serological blood tests are mandatory. Indicators ELISA, RIBT, RIF, and other specific tests help to identify the presence of pale treponema.
A consultation with a neurologist, gastroenterologist and proctologist must be appointed to confirm or exclude damage to internal organs and disorders of the nervous system.
In practice, one has to deal with patients in whom the presence of syphilis is established only on the basis of positive serological reactions in the absence of any clinical data (on the skin, mucous membranes, on the part of internal organs, nervous system, musculoskeletal system) indicating the presence in the patient's body of a specific infection. Many authors cite statistical data, according to which the number of patients with latent syphilis has increased in many countries. For example, latent (latent) syphilis is detected in 90% of patients during preventive examinations, in antenatal clinics and somatic hospitals. This is explained by both a more thorough examination of the population (i.e., an improvement in diagnostics), and a true increase in the number of patients (including due to the widespread use of antibiotics by the population for intercurrent diseases and the manifestation of syphilis, which are interpreted by the patient himself not as symptoms of a venereal disease, but such as the manifestation of allergies, colds, etc.).

Latent syphilis is divided into early, late and unspecified.
Latent late syphilis (syphilis lateus tarda) is epidemiologically less dangerous than the early forms, since when the process is activated, it manifests itself either by damage to the internal organs and the nervous system, or (with skin rashes) by the appearance of low-contagious tertiary syphilides (tubercles and gummas).
Symptoms and Diagnosis
In the diagnosis of the latent form of syphilis, the following data can help:

Before starting treatment for the latent form of syphilis, it is very important for a person with suspicion of this disease to undergo a full diagnosis. To do this, he needs to provide the venereologist with complete information about the sexual partners.
The doctor also needs to determine the presence of isolated erosions in the genital area, mouth or on the skin.
When diagnosing a disease, it is important to take into account the patient's age and lifestyle.
When diagnosing, it is very important to examine not only the patient himself, but also his sexual partner. Thus, early latent syphilis can be detected. The main confirmation of the presence of the disease is serological tests.
Diagnosis of the latent form of syphilis is carried out using the following serological methods:
Treponema pallidum immobilization reaction (RIBT)... For this analysis, the patient's blood serum and a suspension of pale treponemas are used. They mix them up and watch how the treponemes behave. Getting into the blood of a person sick with syphilis, treponemas are motionless. And getting into the blood of a healthy person, they are active, they swim for a long time, they are ready to infect. The accuracy of this testing is 95%.
Diagnosing latent syphilis is not an easy task for a doctor, as there is the possibility of a false positive reaction to syphilis.
- Indirect hemagglutination reaction (RPHA). For this analysis, special erythrocytes are prepared with antigens of the causative agent of syphilis. These red blood cells are mixed with the patient's serum. If the patient is sick with syphilis, then the red blood cells stick together.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). A special enzyme is added to the prepared blood serum of the patient. If the serum changes color, then the patient is considered to be sick with syphilis.
- RIF (reaction of immunofluorescence). The presence of pale treponema is indicated by a specific glow.
It helps in determining the presence of the syphilis virus in the blood and the unusual type of pale treponema itself. Under the microscope, you can see that pale treponema has the appearance of a spiral.
The size of the curls decreases towards the end of the treponema, the intervals between the curls increase. Movement in liquid media is slow and graceful.
A feature of pale treponema is its ability to maintain its spiral shape even under the pressure of its environment.
For elderly people, treatment for syphilis on the basis of serological methods alone is not prescribed. They undergo additional examinations by a neurologist, ophthalmologist and otolaryngologist.
The definition of syphilis in pregnant women deserves special attention. During pregnancy, all women donate blood for syphilis three times.
When a disease is detected, specific therapy is carried out taking into account the duration of pregnancy and the stage of the disease. If syphilis is left untreated, there is a high likelihood of infection of the fetus, the formation of birth defects, miscarriage or premature birth.
The venereologist collects information about sexual partners, there were earlier cases of single erosions in the genitals, in the mouth, on the skin, whether a person took antibiotics for similar diseases like syphilis.
The age, sex life of the patient is taken into account. After examining the patient, they notice scars, seals that remain after syphiloma. It is also often observed that the lymph nodes are enlarged, lymphadenitis develops.
It is important that not only you but also your partner are examined, perhaps the whole problem is in him, so early syphilis can be detected. The diagnosis is confirmed on the basis of a serological test.
The patient has elevated reagin titers. If a person has taken antibiotics, the level of reagins may decrease.
Sex partners who have an advanced form of syphilis often do not have different symptoms at all.
It is very difficult for a doctor to accurately diagnose latent syphilis, false-positive reactions can be observed due to the fact that a person has had bronchitis, malaria, chronic cystitis, tonsillitis, pyelonephritis, cirrhosis, hepatitis, pulmonary tuberculosis, rheumatism.
The patient must take all tests for latent syphilis several times, they must be repeated after a somatic illness in order to eliminate the chronic infection in time.
Where to get tested for latent syphilis and who to contact?
It is no coincidence that the latent course of syphilis is the cause of the epidemiologically dangerous and rapid spread of the disease. Prevention of infection consists not only in medical examinations, but also in the timely access to doctors if there is a suspicion of infection with syphilis.

Treatment
Treatment of latent syphilis is selected by a venereologist after a thorough examination and confirmation of the diagnosis. Early latent syphilis cures quickly enough, after several courses of antibiotic therapy. Late latent syphilis and other forms require a more complex treatment regimen.
Therapy for latent syphilis is accompanied by attacks of fever and severe internal discomfort. This is the result of effective destruction of treponema pallidum.
After the detection of latent syphilis, treatment cannot be postponed for a day, since the insidious latent form can entail serious consequences.
According to the existing instructions and treatment regimens for syphilis, all patients with early latent syphilis are subjected to the same treatment. In cases where, by history or confrontation, it is possible to establish the age of the infection, the outcome of the disease can be predicted (naturally, the shorter the duration of the disease, the more favorable the prognosis and outcome of therapy).

Treatment of the latent form of syphilis should be started only after the diagnosis has been confirmed. It is carried out using antibiotics of the penicillin group.
If the treatment began at the initial stage of the development of the disease, then somewhere by the end of the second course of therapy, an improvement is noticeable. It is much more difficult to treat more neglected forms.
A significant increase in body temperature at the beginning of the course of treatment speaks only of the effectiveness of therapy. Fever is a sign that harmful microorganisms are being destroyed at a rapid rate. Over time, this unpleasant symptom also passes.
After completing the course of treatment, it is necessary to continue to undergo full examinations with a doctor. It is very important to carry out serological control and this will last until the indicators of this analysis return to normal.
The treatment regimen for latent syphilis is to prevent the transition of the disease to a severe form.
When infected for less than two years, treatment of early latent syphilis is aimed at eliminating the transition of syphilis to a secondary form and eliminating the epidemiological danger to others, family members and partners.
In cases where the patient has been infected for more than two years, and doctors determine late latent syphilis, treatment is aimed at eliminating all pathologies of internal organs and preventing the most severe complications - neurosyphilis, heart attacks and strokes.
The main treatment for syphilis is systemic antibiotic therapy with penicillins, or drugs of other groups for allergies and insensitivity to treponemas.
Depending on the severity of organ damage, manifestations of symptoms from the heart and nervous system, a treatment regimen is also formed. In addition, drugs are used to correct the protective properties of the immune system.
Treatment of latent syphilis should take place according to a scheme that should correspond to the type of disease and the timing of its infection.
Syphilis is a long-term healing disease. Latent syphilis is treated according to the same rules and schemes as other forms of syphilis. All family members must undergo an examination and carry out a complex of treatment for prevention.
Treatment of latent syphilis is carried out with drugs of the penicillin group:
- the drug benzathine penicillin - 1 time per day for 3 days (for the early stage);
- benzylpenicillin sodium salt - 2 times a day, the course of treatment is 28 calendar days. After 2 weeks, a second course of treatment is carried out.
In case of allergy to penicillin, macrolides, fluoroquinolones and tetracyclines are administered to the patient. Also, in the treatment of the disease, in addition to antibiotics, vitamins and immunostimulants are attributed to the patient. If necessary, the patient is prescribed extracts of medicinal herbs: echinacea, eleutherococcus, aralia.
Treatment of syphilis today is practiced by 2 methods of treating this disease, this is a continuous method and a course method.
Complex therapeutic therapy consists of the reception:
- antibiotics;
- general strengthening drugs;
- symptomatic drugs;
- multivitamins;
- probiotics.
At the time of therapy, the patient is prescribed food, in the diet of which protein foods predominate and a restriction in the consumption of fats and carbohydrates.
During this period, smoking and drinking alcohol is contraindicated, and it is also necessary to reduce physical stress on the body.
How to treat syphilis while carrying a baby? Women during the period of bearing a child are treated only with antibiotics of the penicillin group. Penicillins do not affect the intrauterine development of the fetus.
How to treat syphilis while breastfeeding? At the time of treatment, it is necessary to stop breastfeeding or, if absolutely necessary, limit treatment to the minimum duration and doses.
Stress, depression and insomnia will negatively affect the treatment of the disease.
People who refuse treatment for latent syphilis, or have not completed the entire course of treatment with medications, lose their health, which will already be restored.
The consequences of syphilis in the female body can be:
- developing syphilitic gangrene;
- infectious syphilitic vaginitis;
- syphilitic infectious endocervicitis of the cervix.
The consequences of syphilis in the male body can be:
- syphilitic balanitis;
- syphilitic balanoposthitis of the glans penis;
- phimosis and paraphimosis of the foreskin;
- syphilitic infectious gangrene of the head of the penis;
- phagedenism of the penis.
Therapy of latent early syphilis is carried out according to the same treatment methods as the usual forms of this disease. With a correct, adequately selected treatment regimen, the ailment can be completely cured.
Therapy of latent late syphilis is much more difficult, since both internal organs and the brain, due to a long illness, have undergone structural changes that are difficult to treat.
Treatment for latent syphilis is the same as for other forms. Any syphilis is treated only with antibiotics, and the dose and timing depend on the duration of the disease.
During treatment, patients undergo a course of injections (most often penicillin). With early latent syphilis, 1 course of injections is carried out, which is several weeks, with late syphilis, 2 courses are carried out with a duration of 2 to 3 weeks.
Early latent syphilis is most often treated at home (outpatient). Treatment of late latent syphilis is most often carried out in a hospital (in a hospital), because with an advanced disease, the risk of complications is much higher.
In addition, regardless of the stage of the disease, pregnant women with syphilis are necessarily sent to the hospital. Syphilis is dangerous for an unborn child: the fetus can become infected and even die, and in this case a frozen pregnancy will develop. This will eventually lead to miscarriage or stillbirth.
During the treatment of latent syphilis (as well as its other forms!), The patient is prohibited from any sexual intercourse, kissing, the use of common hygiene items or utensils.
Latent syphilis is no better than manifested syphilis and is very dangerous if left untreated! Therefore, it is important to be attentive to your health - if you suspect a sexually transmitted infection, immediately contact a specialized doctor. If the treatment of latent syphilis is started on time, it is completely curable.
Today, the treatment of syphilis is not difficult for doctors. But one point should be understood.
When they talk about the treatment of latent syphilis, they mean the fight against infection, but not the consequences of syphilis: bone deformities, cardiovascular disorders, disorders of the nervous system.
At the current stage of the development of medicine, this cannot be done.
In the treatment of latent syphilis, antibacterial drugs are used. The therapy regimen is selected individually, taking into account the stage of the disease and concomitant pathology.
Additionally, drugs are prescribed that raise immunity, since syphilis weakens it.
Approximate treatment regimens for latent syphilis are presented in the table:
Taking any medications is possible only after consulting a doctor. Self-medication is unacceptable! The frequency of taking medications and the duration of therapy are determined by the attending doctor.
It is important to prevent the disease in time before it gets complicated. During treatment, they prevent the development of neurosyphilis, protect somatic organs from various types of damage.
The latent form of syphilis is treated with antibiotics of the Penicillin group. At first, the patient's body temperature rises sharply, this indicates that the disease has worsened.
Whether the treatment is effective or not, serological studies will help to find out whether the cerebrospinal fluid has returned to normal. A negative serological reaction should be observed, this indicates a successful treatment. The late form is best treated with bioquinol.
Complications of latent syphilis for the body
Latent syphilis is also dangerous for its possible serious complications. Untimely treatment of this disease can lead to an even greater spread of the infection throughout the body and damage to internal organs.
If there is a temporary improvement, the disease continues to progress in its development.

Complications of the early form of syphilis are as follows:
- the strongest damage to the optic and auditory nerves occurs, which leads to blindness and deafness;
- the functionality of many internal organs is disrupted.
If the late form of syphilis is not treated, then:
- sclerosis of lung tissue;
- suppurative process in the lungs.
Preventing syphilis is one of the most effective ways to avoid infection, and choosing a partner should be careful and very careful. It is recommended to use protective equipment in any case.
If, nevertheless, contact occurs, after intercourse, the contacting areas should be treated with an antiseptic or antibiotic. Also, do not use general hygiene products.
Be healthy!
When people hide their infection with syphilis, try to treat themselves, or do not know about latent syphilis in the body and do not undergo drug treatment, the infection spreads to the internal organs and tissues of the whole body and begins to destroy the healthy state of organs and systems.
As a result, the body weakens, and the person loses efficiency. Periodically, there is an improvement in the general condition, but this improvement does not come for long.
Complications of the latent form of syphilis at an early stage:
- early development of neurosyphilis, which damages the optic nerve, leads to blindness. And also the auditory nerve, which causes deafness;
- in men, the testicles are affected, and their fertility is destroyed;
- the internal organs of the human body and systems are destroyed.
Complications of the latent form of syphilis at a late stage:
- aortic valve pathology;
- pathology of the walls of the aorta, which causes the expansion of some of its sections;
- sclerosis of lung tissue, chronic stage of pulmonary suppuration.
Complications that can turn a healthy person into a disabled person:
- deformation of the palate and inability to eat;
- destruction of the nose, which makes it impossible to breathe normally;
- destruction of bone tissue, which constrains movement.
Complications and prevention
Latent syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease that is more than 90 percent transmitted through sexual contact.

Preventive methods for syphilis are:
- constant sexual partner;
- using a condom during sexual intercourse;
- douche with antiseptics after sexual intercourse that was not protected by a condom;
- when planning a pregnancy, mandatory examination of both partners;
- refrain from sex at the time of drug treatment with antibiotics;
- healthy lifestyle;
- properly balanced nutrition;
- observance of intimate hygiene;
- regular examination by a gynecologist, urologist and venereologist;
- maintain a healthy immune system at all times.
In order to avoid various infections, some rules must be followed.
- Be selective in the choice of sexual partners.
- Use condoms for sex.
- Use only your own personal hygiene items.
- Do not hope for false positive results, but consult a doctor at the first sign of illness.
Remember that getting sick with syphilis is not only a private matter of a citizen. If a person knows about his illness with syphilis, he hides it and infects another, then he may be criminally liable.
Post Views: 2 258
Many sexually transmitted infections do not show symptoms for a long time. Among those, and latent syphilis - a sexually transmitted disease, which patients learn about by chance examination. However, the disease can be diagnosed according to certain criteria.
Syphilis is the causative agent
The causative agent of the disease is treponema pale. The microorganism belongs to spirochetes; under a microscope it looks like a spiral-shaped bacterium. On average, the structure has 8-14 turns, and the total length does not exceed 14 microns. With the latent course of a disease such as syphilis, the causative agent of the infection is in an inactivated state for a long time, forming cysts, L-forms.
Such modifications of treponema are able to stay for a long time in the regional lymph nodes, cerebrospinal fluid of an infected person. Under favorable conditions for the pathogen (decreased immunity, chronic diseases), treponema is activated and an active stage develops with a characteristic clinical picture and symptoms.
Syphilis - routes of transmission
To prevent infection, each person must understand how treponema pallidus is transmitted. The main route is sexual, with unprotected intercourse. However, it is impossible to completely exclude the possibility of transmission of the pathogen by the household route, when using the same hygienic accessories and cutlery with the patient. The penetration of the pathogen occurs through the mucous membranes, on the surface of which there are micro-abrasions and cracks. Among the rare ways of infection, venereologists call:
- transfusion (transfusion of infected blood and components to the patient);
- transplacental (during pregnancy and childbirth, from mother to child).
What is latent syphilis?
Hearing a similar term, patients often ask doctors whether there is latent syphilis and what kind of disease it is. The definition of "latent syphilis" is customary to designate a form of the disease in which there are no clinical manifestations, symptoms and signs of the disease, but the results of laboratory tests indicate the presence of the pathogen in the body. More often, changes in the blood are noticeable already 2 months after infection. Immediately from this time, the countdown of the duration of the latent period of syphilis begins.
In most cases, the detection of pathology occurs by chance, during the delivery of tests, which are mandatory for a preventive examination (blood on RW). In women, a gynecologist can suspect a disease during the next examination. However, in practice, the latent form of syphilis is detected when diagnosing changes in internal organs (heart, liver, thyroid gland, musculoskeletal system).

Is latent syphilis contagious?
Many people mistakenly assume that the absence of signs of illness is the main criterion for absolute health. For this reason, a common question arises: is latent syphilis transmitted? Venereologists claim that infection with this type of syphilis is possible. However, the transmission of the pathogen occurs in only two ways:
- with contaminated blood;
- during sexual intercourse.
It should be noted that the risk of infection is maximum during the first two years after the development of the disease. When diagnosing a disease in a sexual partner at this time, doctors advise to refrain from sexual intercourse and also undergo a comprehensive examination. Early diagnosis and timely initiation of therapy determine a successful outcome.
Latent early syphilis
The term "early syphilis" is customary to designate the period of illness, which corresponds to the time from primary infection to recurrent secondary syphilis. Doctors talk about early syphilis when two years have not passed since the infection. Patients at this stage do not have manifestations of the disease, but they pose a potential epidemic hazard.
At any time, the early latent form of syphilis is able to enter the active phase, which appears with skin rashes and general symptoms of intoxication. The elements of the rash contain a large number of pale treponemas, the release of which can cause infection of those in contact with the infected person. It is worth noting that early latent syphilis occurs more often in patients under 40 years of age who are promiscuous.
Late latent syphilis
Late latent syphilis is recorded 24 months or more after infection. With the transition of the disease into the active phase, symptoms and clinical manifestations of tertiary syphilis are observed. With this form, the internal organs and the nervous system are always damaged (neurosyphilis). At the same time, low infectious tertiary syphilides, tubercles, gummas can be observed on the skin. If their integrity is violated, it is possible to isolate pale treponemas, infecting others in contact with the patient.

Latent congenital syphilis
It is rarely diagnosed in children. Infection comes from an infected mother. In this case, the woman herself can get sick before pregnancy or during the process of carrying a child. The pathogen enters the fetus through the umbilical vein or through the lymph gaps. Pathological changes in the organs and tissues of the unborn baby can be registered at 5-6 months of gestation, during an ultrasound scan.
However, more often the latent form makes itself felt in early childhood. Prior to this, the detection of pathology is possible by serological studies, analysis of biological material (cerebrospinal fluid). Often, the indication for a comprehensive examination of a child is the detection of a positive one in the mother in the postpartum period or during pregnancy.
Latent, unspecified syphilis
The diagnosis of unspecified syphilis is made if the patient has no information about the possible timing of infection. At the same time, doctors also find it difficult to determine the duration of the disease. Patients are assigned a set of serological studies, during which, based on the morphological forms of treponemas, assumptions are made regarding the type of disease. Unspecified syphilis in the latent course can give false positive nonspecific serological reactions, therefore, they are repeated before the final diagnosis.
Latent syphilis - signs
Symptoms of latent syphilis do not make themselves felt for a long time. On the mucous membranes and skin, ulcers, rashes are not observed, however, changes can be recorded in the internal organs, the nervous system, and the musculoskeletal system. Among the indirect signs of an early form of latent syphilis, doctors call:
- A history of rashes, the nature of which could not be diagnosed earlier.
- STI treatment, previously.
- The presence of an active form of syphilis in a sexual partner.
- Inflammatory reactions in the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid.
It is customary to highlight indirect signs indicating a late stage:
- degenerative changes in the spinal fluid;
- positive result of serological tests.
In addition, the following phenomena may indicate syphilis:
- a prolonged increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees of unknown origin;
- an increase in peripheral lymph nodes (no pain);
- weight loss;
- general weakness, depressed mood.
Diagnostics of the latent syphilis
How to identify latent syphilis in a specific situation - doctors determine depending on the nature of suspicions, indirect signs. The final diagnosis is made on the basis of a comprehensive assessment of the research results obtained. Among the main diagnostic methods:
- Indirect hemagglutination reaction (RPHA)- prepared erythrocytes are mixed with the patient's serum. If the result is positive, the cells stick together.
- (IFA)- a special enzyme is added to the patient's serum sample, which changes color in case of a positive result.
- RIF (immunofluorescence reaction)- a characteristic glow is present in the sample of the patient's biomaterial.
How to treat latent syphilis?

When treating latent syphilis, the main goal is to eliminate the cause of the disease. It takes more time to eliminate the consequences (deformation of bones, violation of the nervous system, heart), and some of them are no longer amenable to correction. Treatment of late latent syphilis is based on the use of antibiotics, which are selected taking into account the stage of the pathology. Above is a table that indicates the treatment regimen for late late syphilis, with the names of drugs and dosages. However, it should be borne in mind that all appointments are carried out only by a doctor.