Chlamydia is considered to be a urogenital disease that develops due to the ingestion of chlamydial infection. The bacterium appears after unprotected sexual intercourse and through personal hygiene products. That is why all people are advised to know the features of chronic chlamydia in men.
The disease in question may not present symptoms for a long time, but at the same time, it may progress. That is why the treatment of chronic chlamydia in men is carried out quite rarely. This phenomenon can be dangerous, because there is a risk of problems with the entire body.
The chronic form of the disease is diagnosed much more often than its acute stage. Due to the fact that the signs of the disease are either absent or very weakly manifested, a strong half of humanity may not even guess about the course of the pathology. If treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, then chlamydia will lead to urethritis, prostatitis or proctitis. The most terrible complication is the impossibility of having children - complete sterility. But here it is worth considering the fact that the infection can affect the joints, and the respiratory system, and vision, and the heart.
How is chlamydia spread
It is chlamydial infections that are leaders in the list of all diseases that are transmitted through sexual contact. Every year, about 2 million people aged 22 to 42 are infected with this disease. But in the modern world, statistics are "getting younger": the progression of the disease is increasingly diagnosed at the age of 14-17. It is noteworthy that people with both asymptomatic and symptomatic forms of the disease are capable of infecting a partner.
Doctors point out two main ways of transmission of infection:
- Contact form. This includes sexual intercourse and the household route. A family can become infected through dishes, bedding, unwashed hands.
- Vertical shape. This pathway is characterized by the transmission of chlamydia from mother to child. Antenatal is transmitted during pregnancy, and intrapartum is transmitted during childbirth.
The disease can remain in the incubation period for 10 to 40 days. At this time, the infection is actively spreading throughout the body: the mucous membrane of the urethra first of all suffers. If perverted intercourse has taken place, the bacteria can lodge in the rectum or mouth.
Retrograde spread is characterized by damage to the testes, epididymis and prostate gland. In addition, chlamydia affects the lymph nodes and is transmitted through the blood. In the event that additional bacteria join the infection, the disease becomes significantly more complicated and worsens.
How does chlamydia manifest
The disease begins to manifest itself on the 8-20th day after the moment of infection. In more than half of the infected, the disease is completely asymptomatic, but this does not mean that they are not dangerous for the sexual partner or family member. The main signs of chlamydia include the following:
- Increase in body temperature to subfebrile numbers: 37, 1–37, 6. Increased weakness and loss of strength.
- On the urethra, the appearance of a vitreous, watery or purulent substance mixed with mucus is noted.
- Most often observed in the morning.
- Burning and itching when urine comes out, slight turbidity.
- Inflammation of the genitourinary system can be joined by blood during sexual intercourse or during urination.
- The urethra outside swells, turns red.
- The person feels pain in the groin or lower back.

After the infection has occurred, the symptoms may disappear completely or partially. Such phenomena lead to the fact that the man ceases to pay attention to them or completely forgets, so he does not go to the doctor. It is this moment that leads to the fact that chlamydia becomes chronic and threatens with prostatitis, cystitis and other serious diseases.
The disappearance of signs is not evidence that the disease has receded, rather, it means that the immune system temporarily overcame it and turned it from acute to chronic. Before starting treatment, the doctor must finally make sure of the diagnosis and not confuse the problem with trichomoniasis, gonorrhea or mycoplasmosis. In addition, the symptoms of chlamydia are very similar to pathological processes in the pelvic organs.
Diagnosis and therapy of the disease in question
In order to make a diagnosis, doctors must carry out several standard procedures for this case:
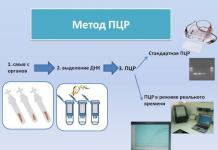
- PCR is an analysis performed by isolating the DNA of microorganisms.
- Cultural examination of the scraping taken and finding a chlamydial infection in it.
- Conducting direct immunofluorescence testing, during which the doctor uses special microscopes.
- An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, during which laboratory technicians secrete antibodies to chlamydia.
Both acute and chronic forms of the disease are treated exclusively with antibiotics. Here we are talking about the use of drugs of the tetracycline group: fluoroquinolones and macrolides.
It is these drugs that are today recognized as the most effective means for carrying out adequate therapy for the ailment in question.
In addition to the above medications, specialists can prescribe other treatment: adjusting the therapy regimen using several drugs of general action, completely relieving the patient of an unpleasant problem. This includes the Wilprafen remedy. The treatment regimen involves taking the medication for 1-2 weeks, but in the case when the disease is severely neglected, the therapy can take a whole month. 
To maintain or increase the level of immunity, doctors prescribe the intake of a multivitamin complex, a natural adaptogen or an immunostimulating substance. Along with antibiotics, you should drink medicines that include bifido and lactobacilli.
Such methods of therapy are explained by the fact that antibiotics lead to the destruction of the proper microflora in the intestine, which must be brought back to normal. For this, patients take Bifidobacterin, Linex or Lactobacterin.
In case of problems with the gastrointestinal tract, you should drink the enzymes found in Mezim, Creon, Pancreatin, Heptral or Rezalut. In addition, the patient must follow a strict diet, completely stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Both cohabitating partners should treat the disease at once, otherwise all therapeutic measures are meaningless and will not bring the desired effect.
What are the consequences of chlamydia in men
If chlamydia has not been treated for a long time or did not respond to treatment and has already developed into a chronic form, then the man's health is under great threat. He may develop the following pathological processes:

- Prostatitis. The problem is manifested by inflammation of the prostate gland, pain in the rectum, in the back, in the groin. The process of urination is slightly disturbed, and specific discharge may be released from the urethra. In addition, there is a violation of male function.
- Urethritis. Here we are talking about the appearance of itching of the urethra, frequent visits to the toilet, purulent discharge with mucus and stricture of the urethra as a result of the chronic course of chlamydia.
- Epididymitis. The phenomenon is an inflammatory process in the epididymis, characterized by an increase in temperature, edema of the epididymis. These symptoms can lead to problems with spermatogenesis and complete infertility.
- Reiter's syndrome is a chlamydial conjunctivitis and arthritis.
- Vesiculitis. The pathology is characterized by inflammation of the seminal vesicle located near the prostate. This organ is responsible for storing prostatic secretions, which are produced by the gland.
- Severe kidney inflammation.
All these phenomena and signs appear only if the treatment of chronic chlamydia in men is not carried out or does not help get rid of the problem. It must be remembered that the body always signals a pathology, and a person must be able to recognize these signals in a timely manner and contact the attending physician for a diagnosis after a complete examination.
How chlamydia affects male fertility
Almost half of infertile couples face the problem of male reproductive health. There are many reasons for male infertility, but the most popular of them are infections in the genitourinary system, transmitted through sexual intercourse and causing irreversible changes in the composition of sperm.
The inflammatory process in the urogenital tract leads to the fact that there is an overproduction of the active form of the oxygen radical by polymorphonuclear leukocytes of sperm, which threatens to stress the spermatozoa and damage the membrane in them. This phenomenon inhibits the fertilizing function of the sperm, therefore, the long-awaited pregnancy does not occur.
But it is worth considering the fact that such a pathology can lead to abnormal development of the embryo and sudden abortions. Inflammation of the prostate significantly reduces the number of active sperm and negatively affects their fertilizing function. Chronic prostatitis is characterized by an increase in ROS in the semen by several times.
Spermatogenesis suffers due to the fact that it is affected by chlamydial toxins and their products. It is chlamydia that settle on spermatozoa, leading to their adhesion, loss of mobility and natural function.
Very often in people who have been diagnosed with chronic chlamydia in men, there is a violation of the function and patency of the epididymis. In addition, pathology is observed in the process of stimulating the production of antisperm antibodies.
Chlamydia prevention measures
If a man has already recovered from a disease once, this does not mean that he can become infected with it again. To prevent this from happening, you should follow a few simple rules:
- Refrain from sexual intercourse from time to time.
- Stay faithful to a long-term partner.
- Use condoms regularly, not coils or hormonal contraception.
- Refuse to take alcoholic beverages and drugs.
- Undergo preventive examinations annually.
- Do not hide the presence of alarming symptoms from your doctor.
- Treat the genitals with special means after each dubious intercourse.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
If you are attentive to your health, do not hesitate to go to the doctor's office and follow all their prescriptions and therapeutic procedures, then you can not be afraid of dangerous complications of chlamydia, even in an advanced form.
Are you having serious POTENTIAL problems?
Have you tried a lot of tools and nothing helped? These symptoms are familiar to you firsthand:
- sluggish erection;
- lack of desire;
- sexual dysfunction.
The only way is surgery? Wait, and don't use drastic methods. It is POSSIBLE to increase the potency! Follow the link and find out how the experts recommend treating ...
What is chronic chlamydia and how is it treated?
The disease is difficult to detect because in most cases, it proceeds imperceptibly.
80% of women have no symptoms, unlike men. Their symptoms of the development of chronic chlamydia are visible at 2 weeks of development. It is a burning sensation when urinating, a white discharge from the penis. However, the presence of these signals occurs during the acute phase.
According to official data, more than 1 billion infected are officially registered in the world. The disease is a lesion by the body of the gram-negative microbe chlamydia trachomatis, which lives inside human cells.
The result of the disease is diseases of the genitourinary tract, joints, eyes, rectum, or lungs. The latter case occurs in newborns. Without treatment, the infection progresses to the second stage of chronic chlamydia, which is difficult to identify. In this case, the consequences will be sad.
For years in the body, bacteria cause a number of complications. It is possible to identify a microbe when passing tests at a regular professional examination or by passing it on for venereal diseases.
The consequences of running chlamydia will be as follows:
- pneumonia;
- bronchitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- arthritis;
- pericarditis, endocarditis.
In pregnant women, it leads to miscarriage, premature birth or undeveloped fetus. Rader's disease, when complications appear on the joints, eyes and respiratory tract, men suffer. This sometimes leads to disability.
Chlamydia is often protracted chronic appears as a result of ineffective drug treatment. Microorganisms adapt to the effects of medicinal components. A favorable environment works well for them, they begin to multiply, provoking inflammation.
Due to the fact that the pathogen is determined too late, it is detected after the onset of complications. For example, a woman becomes infertile, the cause will be salpingitis or suppuration in the fallopian tubes. Obstruction of the latter and the formation of adhesions complicate the fertilization process.
From the day of infection, the incubation stage lasts from 6 days to a month. In its early form, chronic chlamydia, namely in a fresh state, is caused by the presence of discharge with impurities of pus and an unpleasant odor at the same time.
In addition, it is noted:
- burning sensation when going to the toilet;
- pain during intercourse, sometimes with bloody leucorrhoea;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen;
- bleeding between periods;
To a lesser degree, chronic chlamydia is accompanied in all women by intoxication, low-grade fever, general malaise and weakness.
Not going to a doctor leads to ailments directly related, for example, cystitis, erosive ulceration of the cervix, colpitis, adhesions in the fallopian tubes. In this case, chronic chlamydia, its symptoms, will not manifest in any way.
Manifestations during pregnancy

Pregnant girls may notice leucorrhoea mixed with pus in an increased volume, but not always.
The latent form hides inflammation for a long time, only exacerbations reveal themselves in this way. You should not ignore this, because the sore is transmitted to the baby. Picking up her children get sick with pneumonia, otitis media and inflammation of the eye.
The constant course of the disease worsens the general condition of a woman in a position. Having given birth to a child, there is a high probability of organ infection or postpartum fever.
Causes

A process arises against the background of unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected person, relapse and transmission to a newborn baby by passing it through the birth canal.
When it enters the body, the pathogen does not always behave actively, for years the virus sleeps in the human body, and only a few factors bring it out of the dormant form.
The circumstances are:
- stressful situations;
- weakened immunity;
- change of sexual partners;
- colds and other sexually transmitted diseases.
Chlamydia can also be pushed through by frequent douching, the installation of intrauterine devices. It is not transmitted by household means, therefore it is impossible to pick up bacterial cells by swimming in the pool or using other people's towels and linen.
It is important not to start the condition, but to carry out therapy on time. Timely treatment of chronic chlamydia will avoid serious consequences.
Diagnostics

In order to establish bacteria, it is required to undergo a diagnosis using the following methods. Examination of the smear under a microscope will show if there are leukocytes in the material.
Sowing on a nutrient medium will not only reveal the bacillus, but also help to choose the most effective antibiotics. A biopsy is taken from the tubes when the chlamydia stage in women has resulted in organ adhesions. The desired piece is carefully examined by a specialist.
Difficulties arise when the patient becomes just a carrier of the disease. That is, chlamydia does not develop, the period is delayed and even modern laboratory methods do not always show inflammation.
Treatment

After the diagnosis is made, the doctor will select the necessary treatment. It is based on the use of antibiotics, antifungal pills, and immune agents.
With a protracted course, enzyme therapy will be the way to eliminate the symptoms.
What it is?
Comprehensive struggle aimed at eliminating pathogens. The combination of the right mixtures of enzymes containing plant and animal components has a beneficial effect on the body. Enzymes are most concentrated in the focus of infection.
The scheme is individual in each case. Usually 2 anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed at once. It is necessary to take into account the factor that some medications are contraindicated for women in position.
Doxycycline, Clindamycin, Azithromycin, Rovamycin are widely used in the treatment of chlamydia in women. The first should not be consumed by pregnant women. At the time of therapy, it lasts 2 weeks, sexual intercourse is not allowed, and the partner must also be treated.
Otherwise, the risk of re-infection is high. After the antibacterial stage, chronic chlamydia, further treatment includes pro biotics, remedies for intestinal and vaginal dysbiosis.
It is important to strengthen the immune system at least a week before the start of healing. Since its weakening will not be able to give a decent rebuff to bacterial cells and no medicine will cope with its task, therefore, vitamin complexes and stimulants of the immune system will serve as an addition.
To minimize re-infection, you need to refrain from sex without a condom if you are not confident in your partner. Always have two people in therapy. Remember protecting your health is the key to a long and fulfilling life.
The chronic course of infection of the human body with chlamydia differs from the disease in its acute form in that it is asymptomatic and thus has time to cause enormous harm to the internal organs.
The absence of any characteristic manifestations or the occurrence of symptoms similar to those of other diseases leads to the fact that patients do not seek timely help from a doctor. The vital activity and reproduction of chlamydia go unnoticed for a long time, which becomes the cause of severe infection and disruption of the performance of internal organs.
The course of the chronic form of chlamydia occurs most often against the background of the absence of a clinical picture or the appearance of insignificant disturbing symptoms, which patients often take for signs of other pathologies. Chronic in women and men is also dangerous because the patient, who is not aware of the infection for a long time, spreads the infection.
It is usually possible to detect the "chronicle" of chlamydia infection during periods of exacerbation, when pathogenic agents are activated against the background of a decrease in immunity. During this time, infected men and women may notice the following symptoms:
- discharge from the urethra (in men) and vagina (in women) - more and more abundant, characterized by an unpleasant odor and a yellowish tinge;
- back pain, lower abdomen, groin;
- bloody inclusions in urine, ejaculate, vaginal discharge;
- burning, itching, discomfort, complicating the processes of urination and sexual activity;
- inflammatory processes involving various internal organs - the prostate gland and urethra in men, the cervix, urethra, glands and mucous membranes in the vagina in women.
Outside the stage of exacerbations (in the form of remission), chronic chlamydia manifests itself as a general decrease in immunity, leading to frequent infection of the patient with viral diseases. Also, patients may have the following symptoms:

- deterioration of health;
- lethargy;
- weakness;
- loss of appetite;
- increased fatigue.
If such signs occur on their own, without any other significant health problems, then this should be the reason for contacting a doctor and passing a diagnostic examination.
Reasons for the formation of a chronic form
Doctors identify the following reasons why pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply and translate the disease into the form of a "chronicle":
- lack of therapy due to the asymptomatic course of chlamydia;
- ignoring the need for treatment even with the manifestation of noticeable symptoms of the disease;
- attempts to self-medicate or receive unskilled assistance;
- late start of therapeutic effects;
- violation of the scheme of exposure or self-cancellation by the patient of the course of therapy.

Even one of the listed conditions is enough for the immunity to shake, and chlamydia got the opportunity to resume the attack on the internal organs that have not yet been infected.

Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of the chronic form of chlamydia, even if the patient has previously undergone a course of treatment and tests have not confirmed the presence of chlamydia, should be a regular measure. The only way to identify a neglected and latent disease is to be examined and tested every few months.
PCR, ELISA and culture tests can reliably confirm the lurking. The latter method not only gives the desired result with a sufficiently high accuracy, but also allows specialists to determine the sensitivity of the identified microorganisms to the effects of certain antibacterial agents, which significantly helps in prescribing the optimal treatment for chronic chlamydia to the patient.

Treatment methods
Medication course
Chlamydia must be treated in a complex manner, using a complex scheme, in which the course of drug exposure is 7-10 days, and each of them is prescribed after a break of a week. Therapy for chlamydia infection may include taking the following medications to patients:
- Rovamycin tablets (macrolide antibiotic);
- Vilprafen tablets and suspension (antibacterial drug from the macrolide group, broad-spectrum agent);
- Tetracycline tablets (antibiotics from a series of drugs of the same name);
- Clindamycin (a drug from the lincosamide group, produced in various forms).
After a course of antibiotics for patients with chronic chlamydia, doctors prescribe other medications:

- antifungal - Nystatin, Flucostat;
- bacteriophage agents (preparations containing weakened viruses capable of selectively destroying bacterial cells) - Intesti-Bacteriophage, Coliphage;
- enzyme preparations - Mezim;
- probiotic medicines - Acylact, Bifidumbacterin;
- hepatoprotectors;
- antioxidants;
- vitamin and mineral complexes, multivitamins;
- means to restore the immune system.
- iontophoresis;
- magnetotherapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- electrophoresis.
An equally important part of the fight against chronic chlamydia is the restrictions that must be observed in order for the disease to be easier to treat:
- refusal of sexual activity;
- exclusion of increased physical exertion;
- a diet with the removal of spicy and spicy foods from the diet;
- getting rid of bad habits, especially alcohol consumption.

Traditional medicine cannot cure the chronic form of chlamydia to the full, however, drugs prepared according to its recipes will help speed up the cure and neutralize the effects of infection of pathogens. The main task of alternative medical means is to stimulate abundant urination, since chlamydia affected by drugs, as well as particles of dead cells of affected internal organs and drug metabolites, are excreted in the urine. The following drugs can be used for patients with illness:
- diuretic infusion of juniper fruits with horsetail grass: take 2 tsp. ingredients, mix, pour 350 ml of boiling water, let it brew and strain, then drink 1 tbsp. l. 3-4 times a day;
- diuretic collection - 1 tsp. fruits of juniper, cornflower flowers, finely chopped roots of angelica officinalis - mix everything, pour 350 ml of hot water, insist for 1 hour, strain, drink 1 tbsp. l. before every meal;
- infusion of birch leaves and horsetail - take 1 tsp. both, pour 700 ml of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, then drink ½ cup three times a day.
Alternative treatment of chlamydia should be prescribed and monitored by a doctor, since self-medication is dangerous by the development of an even more neglected form for internal organs and systems.
Prevention and risk of complications
Since chronic chlamydia is an advanced form of the disease, it is very important to take preventive measures so as not to provoke the development of infection. The main recommendation is controlled sexual activity with a minimum number of partners, the use of condoms, and the obligatory passage of regular medical examinations. Patients who have already encountered infection with chlamydia should protect their immunity, treat all diseases in a timely manner, and also strengthen their health by hardening, taking vitamins and optimal physical activity. Failure to comply with preventive recommendations leads to the risk of complications, including diseases of the reproductive system:
- in men - damage to the prostate gland, seminal vesicles and testicles, leading to impotence and obstructive infertility;
- in women - infection of the fallopian tubes, the formation of adhesions, due to which infertility occurs or, if infection occurred during pregnancy, causing irreversible damage to the fetus, miscarriage, miscarriage.
Another dangerous consequence of the chronic (neglected) form of chlamydia for patients is the spread of chlamydia throughout the body with infection and the application of severe pathologies to internal organs.
If acute chlamydia is not treated, which proceeds with vivid symptoms and can be recognized even by the patient himself, then a chronic form of the disease arises. This form of the disease is difficult to treat, since the causative agent of the disease develops immunity to some antibacterial drugs, and to those that are the basis of all therapy. If chlamydia is left unattended at this stage, then there is a high risk of damage not only to the genitourinary system, but also to the respiratory system, as well as the heart and blood vessels.
The initial infection with chlamydia occurs in the vast majority of cases through sexual contact. Moreover, the transmission of chlamydia (causative agents of the disease) can occur not only during classical sexual intercourse - the disease also spreads by airborne droplets. If, within two months from the moment of infection, the acute form of chlamydia has not been cured or at least not taken under control, then a "chronicle" develops.
Reasons for the transition of the disease to a chronic form:
- Misdiagnosis.
- The wrong choice of drugs.
- Chlamydia resistance to the drugs used.
- Patient's violation of the treatment regimen.
Often, people undergoing therapy mistake the disappearance of symptoms for a complete cure for the disease. They interrupt the treatment without "removing" the dangerous infection from the body. As a result, the disease continues to develop in a latent form, the transition to chronic chlamydia is a matter of time.
Sometimes the development of the disease occurs imperceptibly. The fact is that chlamydia, even in its acute form, is sometimes asymptomatic.
Chlamydia symptoms
Symptoms of the disease differ between men and women. At the same time, it is rather difficult to detect a disease in a chronic form without a medical examination - signs practically do not appear.
Signs of chlamydia in women
Symptoms are actively manifested only if the disease has caused a serious decrease in the level of the body's immune defense. These symptoms include:
- severe burning sensation when urinating;
- painful sensations in the lower abdomen, and they can manifest themselves both in a state of complete rest and during physical exertion;
- spotting from the vagina.
Please note that even if the discharge is without blood, it is difficult not to notice changes in their color. In addition, they are accompanied by a pungent, unpleasant odor.
A much clearer sign of chlamydia is the occurrence of other concomitant diseases:
- cervicitis;
- erosion of the uterus;
- cystitis;
- colpitis.
There is also a high likelihood of adhesions in the fallopian tubes. The worst consequences of chronic chlamydia are cervical cancer and infertility. In these cases, the symptoms are bright, and before that, the disease in the overwhelming majority of cases can be detected only at a gynecological examination or by passing tests in a laboratory.

Signs of chlamydia in men
Representatives of the stronger sex even tolerate the acute form of chlamydia asymptomatically in 45-47% of cases. The chronic form most often proceeds without any signs at all. At the same time, a man remains a potentially dangerous carrier of infection for his sexual partners. If symptoms do appear, they look like this:
- the temperature rises to 37.5, especially in the morning and evening hours;
- there is increased fatigue and general muscle weakness;
- the first drops of urine when visiting the toilet are unclear, and the process of urination is accompanied by a burning sensation;
- in the morning there are vitreous and purulent discharge from the urethra;
- the urethra is slightly swollen and becomes reddish;
- with ejaculation, bloody impurities in the semen are possible.
All these symptoms can be vivid in the chronic form of the disease, but they appear in short periods of time, most of the course of the disease does not bother a man. But there is one exception - with chronic chlamydia, the stronger sex almost continuously feel unpleasant sensations in the lower back.
If women have a large "set" of concomitant diseases, then in men they are limited to cystitis and prostatitis.
Chlamydia treatment regimen
The treatment regimen for the disease in both men and women is based on suppressing the activity of the infection and on its complete elimination from the body through the use of antibiotics. In this case, the treatment of the chronic form of the disease is longer and more difficult, since the causative agent of the disease has already managed to develop immunity to certain medications.
Treatment in men
Before starting therapy, the doctor conducts a study of the activity of chlamydia, and also assesses the general condition of the body:
- the ability of the immune system to resist microorganisms;
- the presence or absence of diseases of the liver, pancreas, kidneys and gallbladder (it is through these organs that antibacterial components are released from the body);
- whether there is a microbiocenosis of the gastrointestinal tract.
The general condition of the genitourinary system is also assessed. After that, analyzes are carried out to establish the characteristics of chlamydia in each specific case of the disease.
After that, the doctor prescribes antibacterial drugs. These may include:
- tetracyclines: "Dorix" (from 11 748 rubles),"Unidox Solutab" (340 rubles), "Vibramycin" (about 950 rubles);
- fluoroquinolones: "Lomflox" (469 rubles), "Rovamycin" (from 1,089 to 1,634 rubles), "Ofloxacin" (from 31 to 194 rubles), "Levostar" (357 rubles);
- macrolides: "Sumamed" (from 219 to 1 114 rubles), "Wilprafen" (from 540 to 686 rubles), "Hemomycin" (from 143 to 304 rubles).

Antifungal agents are sometimes used to treat chronic chlamydia. Among them are "Fluconazole" (from 32 to 298 rubles), "Pimafucin" (from 163 to 534 rubles).
Treatment in women
The general principle of therapy does not differ from the "male" version - taking antibiotics. But there are still a number of differences. Ladies should take more "lethal" doses of drugs, since the infection takes root in their bodies better, which means that resistance to antibacterial drugs is much higher. In this case, the therapy itself is somewhat longer.
Basic remedies for the treatment of chronic chlamydia in women:
- "Wilprafen" (once a day, 2 grams for 14 days). Price from 540 to 686 rubles;
- "Rovamycin" (3 units 3 times a day for a week). Price from 1,089 to 1,634 rubles
- "Tetracycline" (one and a half grams once a day for 14 days). Price from 77 to 80 rubles.
Such a drug as "Clindamycin" is especially effective. price from 184 to 595 rubles... It is taken according to the scheme 3-4 times a day, 0.3 grams for 7 days. At the same time, sometimes one dose is enough to completely eliminate all symptoms, but, of course, this does not mean complete elimination of the disease itself, so the course of therapy should not be interrupted.
Women tolerate this disease much worse than men. Therefore, for a complete recovery after a cure, it is necessary to take a course of taking medications to increase the resistance of immunity, as well as vitamin complexes. Sometimes doctors recommend physical therapy along with taking antibacterial agents. In addition, after completing the course of treatment, you should undergo an additional examination for infections concomitant with chlamydia.
Chronic chlamydia sometimes leads to such sad consequences as infertility and cervical cancer. Treatment is complicated by the fact that at the advanced stage of the disease, the symptoms rarely manifest themselves, so that the ailment can only be identified in a clinical setting. You can find out about the causes and course of this disease by watching this video.
Chronic chlamydia in women is an advanced stage of the disease resulting from the lack of adequate treatment in acute course.
If the acute form of the disease has a number of characteristic symptoms, then in the chronic one they are practically absent. This makes diagnosis difficult and leads to complications.
Infection methods
What is chronic chlamydia in women? It is a common sexually transmitted disease. Affects women and men.
In half of all cases, chlamydial infection is transmitted through unprotected intercourse with an infected sexual partner.
Risk factors
When the causative agent of the disease, chlamydia, enters the woman's body, the symptoms do not appear immediately.
With a strong immune defense, the infection remains latent for a long time. However, under the following favorable conditions, it is activated and causes characteristic manifestations:
- suffered colds, acute respiratory viral infections;
- accession of other sexually transmitted infections;
- stressful conditions;
- weakening of the immune system;
- promiscuous sex life with different partners.
With one of these factors, the progression of chlamydia begins, provided that it was infected earlier. If untreated, it becomes chronic.
Reasons for the transition to another stage
The main reason for the transition of the disease to a chronic form is the lack of treatment for the acute stage due to the fact that there are no symptoms. Often, infection with an infection passes completely unnoticed by a woman and does not manifest itself.
The second most common cause is misdiagnosis of the disease and inappropriate therapy. If during the examination the doctor did not detect chlamydia or mistook it for another disease, then the treatment will have no effect. In the meantime, the disease will acquire a chronic stage.
Further - the resistance of chlamydia to the effects of drugs. Lack of comprehensive treatment or improperly selected funds contribute to the development of immunity in pathological microorganisms.
Another reason is the woman's non-compliance with the doctor's recommendations for taking medications. Skipping a pill, stopping the use of antibiotics and other medications on your own leads to complications. It may seem that the disease has receded, but it is not.
Chronic chlamydia in women: what are the symptoms?
The chronic course of the disease, in contrast to the acute one, is even more difficult to replace. However, with a serious decrease in immune defense, the following symptoms are possible:
- Abundant with an unpleasant odor.
- Blood elements in the discharge.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Pain, burning and cramps when using the toilet.
In the absence of treatment at this stage, the development of concomitant diseases of the organs of the reproductive system is possible:
- adhesion process in pipes;
- cervical erosion;
- colpitis;
- cervicitis;
- cystitis.
Often, the detection of chlamydia occurs during a planned visit to a gynecologist, when the doctor diagnoses an inflammatory process in the organs of the reproductive system.
In pregnant women
Chlamydia in pregnant women often has a latent course. The disease does not manifest itself with any signs and only with an exacerbation there are pulling pains in the abdomen, mucous discharge from the vagina containing pus.
Effects
Early detection of chlamydia can be quickly treated with proper therapy. If more than two months have passed since the moment of infection, the disease becomes chronic.
Chronic chlamydia affects the functioning of the respiratory system, intestines, musculoskeletal system, genitourinary, cardiovascular systems.
The development of the following diseases can become a complication:
- bronchitis;
- pneumonia;
- conjunctivitis;
- arthritis;
- proctitis;
- pericarditis;
- endocarditis, etc.
One of the most severe consequences of pathology is Reiter's syndrome. It is characterized by large-scale damage to the body, which affects the genitourinary system, joints and eyes.
On the video about chlamydia
Treatment
When using antibiotics. The choice of a drug and a treatment regimen takes into account individual indicators, the state of the body, the duration and symptoms of the disease. Therapy has its own characteristics in pregnant women. In the position, antibacterial drugs are mostly prohibited from taking.
For chlamydia, antibiotics are prescribed:

The duration of the treatment course depends on the selected type of antibacterial drug and its combination with other drugs as part of complex therapy.
The doctor must take into account the possible complications of chronic chlamydia, examine the woman for concomitant infections and inflammatory diseases, and supplement the treatment if necessary.
With chlamydia, vaginal candidiasis or thrush often occurs, which contributes to a violation of the microflora. In this case, probiotics or suppositories with lactobacilli are prescribed.
In the treatment of chronic chlamydia, the sexual partner must be treated.
Chronic chlamydia in women is a disease that is often asymptomatic. With a weakened immunity, discharge begins, an inflammatory process in the organs of the reproductive system. Treatment is long-term. For a complete recovery, you need to complete the entire course and follow the doctor's recommendations.