Tests for chlamydia trachomatis are necessary to confirm the presence of this infection in the body.
In case of positive results, the doctor prescribes treatment. After completion of therapy, laboratory diagnostics are performed to confirm the cure.
What tests for chlamydia exist
There are three groups of tests for chlamydia:
1. Immunological.
Aimed at identifying antigens and antibodies. Mutual fund or IFA are used.
2. Cultural method.
Sowing of chlamydia is carried out for their subsequent identification.
These bacteria are sown only on media containing living cells. These are cell lines L-929, McCoy, HeLa.
3. Molecular biological.
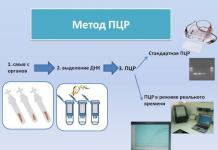
PCR is used to detect chlamydia in the smear.
Identification of a DNA fragment of bacteria is carried out.
Who needs an analysis for chlamydia
Basically, smears are taken for chlamydia if there are clinical signs indicating an inflammatory process in the lower genitourinary system. It is also necessary to be tested for chlamydia if there has been unprotected intercourse with a carrier of chlamydia.
If there are no medical or epidemiological indications, then women can be tested for chlamydia in such cases:
- miscarriage
- upcoming intrauterine manipulations (curettage, hysteroscopy, hysterosalpingography and others)
- before IVF
- impending amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling
- sexual assault
Men can be tested for chlamydia during examination for STIs when planning a pregnancy, to diagnose infertility.
In newborns, the study is carried out in the case of conjunctivitis or pneumonia.
Preparation for tests for chlamydia
- do not use systemic antibiotics for at least one, or better - two weeks
- do not apply topical treatments (creams, vaginal tablets) for 3 days
- give up intimate life for 2 days
- do not urinate 3 hours before taking urogenital swabs
- women do not use tampons for 2 days

Women are tested for chlamydia if possible in the first phase of the cycle. But you need to wait until the end of the menstrual bleeding.
How is the test for chlamydia taken?
Any biomaterial can be taken for chlamydia if PCR is used.
This could be:
- urethral scraping
- secret of the prostate
- saliva
- anal swab
- discharge of the eye
- oropharyngeal smear
Most often, swabs are taken from the urethra.
For men, they do it like this:
1. Place a tampon in the urethra to a depth of about 3 cm.
2. Rotate it inside the urethra.
3. Take out and place in a test tube.
In the same way, they take material from women. But they have a tampon inserted up to 1-2 cm.
If there is a large number of secretions, they are first removed, and only after that a smear is taken. After that, a cervical test is taken.
The external opening of the cervical canal is cleaned of vaginal discharge. Then the tampon is inserted into the canal. It is rotated for a few seconds. After that, it is taken out and placed in a test tube.
Vaginal swabs are taken without using a gynecological speculum.
A tampon is inserted into the vagina and a swab is taken from the back of the vagina.
When receiving an anal swab, the tampon is inserted into the rectum 2-3 cm.
The doctor must collect the material from all walls. At the same time, they move outward and make circular movements.
When taking oropharyngeal smears, they are taken from the pharynx and tonsils.
Purulent discharge is taken from the conjunctiva, if present. Otherwise, it is necessary to retract the lower eyelid and hold a swab over the mucous membrane towards the medial corner of the eye.
Does it hurt to take smears for chlamydia
Giving smears can be painful for men. Especially if it is a scraping for PCR.
But our clinic uses local anesthesia. Thanks to the application of a special gel, there is a loss of sensitivity in the area where the smear will be taken.
The man does not feel anything during the procedure. The anesthetic gel also contains antiseptics.
They are necessary to eliminate the risk of introducing infection into the urogenital tract.
Sowing on chlamydia
The method is based on the isolation of bacteria in a culture of living cells.
Until the 1980s, culture was the main test for chlamydia. The main advantage is close to 100% specificity. But today the method is rarely used. It is not used in routine practice.

Assign in such situations:
1. Forensic medical examination.
2. Diagnosis of chlamydia in persons subjected to sexual violence.
3. The need to assess antibiotic susceptibility.
The disadvantage of culture diagnostics is the insufficiently high sensitivity of the method. It is only 50-70%. This is due to the fact that chlamydia is very unstable in the external environment. It dies if the material is not properly transported or stored. And also in cases where the patient used local antibacterial agents before sampling the biomaterial.
After receiving the material, it is transported at a temperature of no more than 6 degrees. Then placed in the wells of the plates containing the cell layer. Incubation lasts from 2 to 3 days.
Then the resulting preparation is treated with fluorescent anti-Chlamydia antibodies and viewed through a fluorescent microscope. The result is considered positive when at least one intracellular chlamydial inclusion is detected.
Chlamydia mutual fund
Chlamydial antigens are detected.
The drug is treated with fluorescein-labeled antibodies. They stain the cytoplasm red.
Under a microscope, chlamydiae are visualized as greenish inclusions. They are elementary bodies.
Benefits of mutual funds:
- research is carried out quickly
- easy to execute
- high specificity - 98%
Minus - low sensitivity in comparison with PCR. It is only 55-75%.
The diagnostic process is manual and cannot be automated. Only smears from the urethra or cervical canal can be examined.
Any other material is not subject to research. Because at low concentrations of cells infected with chlamydia, PIF will give a false negative result.
Determination of chlamydial antigens using ELISA
ELISA-AG is based on the detection of antigens by their interaction with monoclonal antibodies.
Testing methods vary. This is direct antigen detection.
Additionally, an enzymatic application can be used, which increases the sensitivity of ELISA-AG.
Advantages:
- the process is automated, you can examine many samples in a short time
- low cost
Disadvantages:
- low specificity
- sensitivity 20-85% (indicators depend on the used test system)
- only urethral and cervical swabs can be used
ELISA-AG often gives false positive results. Because lipopolysaccharides of chlamydia are determined. Therefore, cross-reactions with LPS of other bacteria are possible.
Chlamydia blood test
ELISA is used to test blood for chlamydia.

Immunoglobulins IgG, IgA, IgM are determined. Their presence suggests that the human body has been in contact with chlamydia.
If IgA and IgM are found, then there is a recent infection. This is an acute infection.
If IgG is present, this indicates that the infection occurred at least 2-3 weeks ago.
If, at the same time, immunoglobulins A and M are not detected, this indicates that the infection is more than 2 months old. Because these antibodies quickly disappear from the blood.
While IgG is stored in it for a long time. They can remain even after the chlamydia is cured.
ELISA- insufficiently accurate diagnostic method. Therefore, it is used exclusively for screening, but not for confirming the diagnosis. The analysis is used in conjunction with other techniques. The problem is that different people have different immune responses. Some have a delayed response. Antibodies appear much later. In others, they do not develop at all, despite an active infection.
There are times when the test shows a positive result for chlamydia, but in fact the infection has long been cured. In the blood, antibodies are detected that have survived after the disease.
The best method for diagnosing chlamydia remains PCR.

Advantages of the method:
- good sensitivity and specificity
- analysis for several infections at the same time
- process automation
- the ability to examine cervical samples obtained for oncocytological screening
- non-invasive material can be used (urine, semen, etc.)
There are also disadvantages.
Due to too high sensitivity, there is a risk of contamination of the biomaterial. That is, its pollution with the ingress of other bacteria. False negative PCR results for chlamydia are rare.
Their reasons:
- destruction of chlamydial DNA due to improper transportation of material
- the presence of mutant strains of chlamydia (very rare)
Contamination of the test material may be the cause of a false positive result.
Analysis for chlamydia during pregnancy
An examination for chlamydia is often prescribed at the planning stage of pregnancy. Or after its onset in the early stages. Because chlamydia is dangerous to the fetus.
Even at the planning stage, a woman may face problems when trying to get pregnant. Because chlamydia provokes cicatricial processes in the uterus and fallopian tubes. It disrupts the migration of the ovum into the uterine cavity and prevents its introduction into the endometrium.
If pregnancy occurs, then chlamydia increases the risk of blastopathy in the first 2 weeks of embryo development. The result is his intrauterine death. Embryopathies are possible up to 12 weeks. They lead to tubal malformations.
After 12 weeks, the following pregnancy complications are possible:
- fetopathies
- chorioamnionitis
- premature birth
During childbirth, the mother can infect the baby with chlamydia. He may develop eye or respiratory inflammation.

The woman herself may have postpartum endometritis caused by chlamydia. Therefore, a positive test during pregnancy is the basis for treatment.
Doxycycline and fluoroquinolones are not used during gestation.
Josamycin remains the drug of choice. Azithromycin can be used.
What to do if chlamydia is found in the analysis
If the test is positive for chlamydia, treatment is required. It is a pathogenic microorganism.
Normally, it should be absent in the urogenital tract. Therefore, when the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment is carried out.
However, it should be borne in mind that the diagnosis cannot be confirmed using ELISA. Because this test is not specific enough.
Treatment can be started after the presence of chlamydia is established by PCR or culture. The therapy is carried out with antibacterial drugs. The doctor chooses them.

This may include antibiotic susceptibility data. They will be at the doctor's office if the diagnosis was confirmed by the culture method.
Re-analysis for chlamydia
Laboratory research is carried out not only for the primary diagnosis of infections. Tests for chlamydia are also done in order to check whether a person is cured.
After the course of treatment, the diagnosis is carried out in a month. PCR is used.
It is also possible to use the culture method 14 days after the therapeutic course.
According to the analyzes, one can understand whether a person has recovered from chlamydia. If the analysis is negative, then he does not need further therapy. If not, a second course is carried out. The drug is usually changed.
It is assumed that if the first course of therapy did not work, then chlamydia has a low sensitivity to the antibiotic used.
What analysis to take on chlamydia
Only the doctor decides which patient is better for taking tests. Most often, the choice is made in favor of PCR. Because this test is the most sensitive of all.
In addition, along with chlamydia, the patient is often examined for other infections. And PCR allows you to do this with a single collection of clinical material.
Cultural diagnostics are less often prescribed. Antibody blood tests are used only for screening. For example, when preparing for pregnancy.

Chlamydia antibody blood test is positive and PCR smear is negative
There are times when studies produce conflicting results. For example, a smear for chlamydia is positive, but the blood is negative.
Or, conversely, antibodies are present, but chlamydia is not detected by PCR.
What can this talk about?
With positive PCR and negative ELISA, the reason for the discrepancy is most likely a delayed immune response. Antibodies did not have time to develop at the time of taking the smear.
Probably too little time has passed since the infection. Immunoglobulins will appear later. Although PCR will already reveal chlamydia in the urogenital tract. Even if they are contained in small quantities.
In the opposite situation, when PCR does not detect bacteria, but antibodies are present, the reasons may be as follows:
1. Past illness.
2. The swab was taken not from the area of inflammation.
For example, in a woman, only the cervical canal is affected.
A smear from the urethra was examined. Or the infection is localized in the rectum, and the swab is taken from the mouth.
PCR can detect chlamydia only if the clinical material is taken correctly. That is, exactly from the place where the inflammation takes place.
As for the ELISA, it detects antibodies in the blood in any case, wherever the infection is.
Where to get tested for chlamydia
To get tested for chlamydia, please contact our clinic.
We provide the following services:
- examination of the patient and assessment of clinical symptoms
- painless swabbing
- conducting the most accurate analyzes for chlamydia
- interpretation of results
- if necessary - the appointment of treatment
- performing control analyzes
In our clinic, you can be examined for any genital infections. And if they are found, they can be treated by highly qualified doctors.
To get tested for chlamydia, contact the author of this article - a venereologist in Moscow with many years of experience.
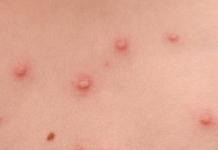
Chlamydia in women and men occurs not only as a lesion of the genitourinary system, but can also affect the eyes, lungs, and mucous membranes. To detect the pathogen, or the body's immune response to its introduction, systemic research methods are needed. One of them is a blood test for chlamydia.
Contrary to popular belief, chlamydial infection can be transmitted not only sexually, but also through household contact, within the family, especially in young children. The causative agent of chlamydia itself, Chlamydia trachomatis, is not even a bacterium, but an intermediate microorganism between bacteria and viruses.
Moreover, its extremely small size, constituting a fifth of a thousandth of a millimeter (0.2 microns), allows chlamydia in some cases to pass unhindered through the pores of mechanical contraceptive devices, which are made in violation of technical standards. Simply put, chlamydiae penetrate intact condoms.
Quite often, after a short period of severe symptoms, or a manifest form of chlamydia, which is manifested by urethritis, conjunctivitis, proctitis, cervicitis, generalization of the infection occurs, and the nature of the lesion becomes systemic. The classic triad is Reiter's syndrome, or articular - oculo - genital syndrome, with damage to large joints, eyes and genitals. But in this case, it is still possible to determine the infection with a greater probability, since the patient has pronounced complaints that fit into a certain syndromic picture.
But with asymptomatic forms of chlamydia, great diagnostic difficulties arise. with chlamydia it is uninformative, just like. In the analysis of urine, everything is also within the normal range, if the secondary bacterial and pyogenic flora did not join. Therefore, very often, and especially women, are treated for a long time and unsuccessfully by gynecologists for chronic endometritis and salpingitis, with frequent forms of ectopic pregnancy, in case of recurrent miscarriage. Men often have chronic prostatitis and other complications.
Chlamydia blood tests: PCR and immunoglobulins

This can be important in the early stages of primary infection with chlamydia, when antibodies are absent at all, or have not reached diagnostically significant titers, or in the presence of severe forms of immunodeficiency, for example, while taking hormonal drugs, immunosuppressive drugs, or during the course of HIV infection.
In addition to a blood test for chlamydia, it can determine the presence of the pathogen in any biological fluid and substrate, from discharge from the genital tract to cerebrospinal fluid. But nevertheless, before donating blood immediately, you need to take care of identifying this microorganism in the intended place of initial penetration, most often by examining the discharge from the genital tract. In women, this can be an ordinary smear, and in men, the most informative is either urethral scraping, or PCR - an analysis taken from the seminal fluid, from the ejaculate.
It is possible to determine in a blood test not only the pathogens themselves, but also to identify the body's immune response to chlamydia using or. With a picture of primary and acute chlamydia, for example, with acute urethritis in men against the background of normal tension of immunity, antibodies of the acute phase are most often detected, or already 3-5 days after the alleged infection.
Also, for an acute infection, after two to three weeks, the titer increases, usually 4 times the norm. These two tests (PCR and immunoglobulins) must be done together. In the event that you donate blood for chlamydia, but mean only donating antibodies, then when they are detected, this does not mean at all that you are sick. You could have suffered chlamydia for a long time, defeat it and recover. In this case, the circulation of antibodies of class G in an increased titer remains for life.
Indications: when to donate blood for chlamydia?

Since chlamydial infection is very diverse, it is difficult to find two or three general criteria for prescribing tests. But, nevertheless, it is possible to identify the main symptoms in which people who are sexually active need to take blood tests for chlamydia with their subsequent decoding. These are conditions and diseases such as:
- pain and burning sensation when urinating, dysuric disorders and symptoms of urethritis;
- inflammation of the rectal mucosa, pain and burning, pain in the anus, signs of proctitis;
- chronic and difficult to treat sore throats, sore throat, symptoms of pharyngitis, especially in people who practice non-traditional forms of sexual intercourse;
- cervicitis and inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs, including those that arise during pregnancy;
- for prevention, blood tests for chlamydia can be performed with frequent and unprotected sexual intercourse, as well as with frequent change of sexual partners.
If you suspect the systemic spread of chlamydia and lesions of the bronchopulmonary system, it is necessary to conduct a study with:
- the appearance of a prolonged and persistent cough against the background of a slight increase in temperature, or subfebrile condition;
- the presence of pneumonia, which stubbornly does not want to be treated with antibiotics;
- just in the presence of prolonged and persistent fever at subfebrile numbers.
In children, the suspicion of chlamydia can be confirmed when symptoms of bronchiolitis appear. Bronchiolitis is a bronchitis with damage to the deeply located smallest bronchi, which have a large area, are the terminal section of the bronchial tree, and are directly adjacent to the alveolar section, in which gas exchange takes place. It is also important to identify possible chlamydial infection with eye damage in newborns, along with, with symptoms of treatment-resistant childhood pneumonia.
Delivery of analyzes and interpretation of results
 How to donate blood for chlamydia? And in the case of PCR, and in the study of various immunoglobulins, no special conditions for delivery do not need to be fulfilled. The main condition is at least 4 hours of fasting after a meal. Therefore, blood tests for chlamydia can be taken in the morning on an empty stomach, after a night's sleep, under normal conditions.
How to donate blood for chlamydia? And in the case of PCR, and in the study of various immunoglobulins, no special conditions for delivery do not need to be fulfilled. The main condition is at least 4 hours of fasting after a meal. Therefore, blood tests for chlamydia can be taken in the morning on an empty stomach, after a night's sleep, under normal conditions.
What test results can be obtained normally, and what is their interpretation in case of illness with various forms of chlamydia?
PCR
When performing a polymerase chain reaction in real time, a qualitative response is given, which indicates whether the pathogen is found in the blood plasma or there are no traces of it. Accordingly, in the first case, it is possible to unambiguously diagnose chlamydia infection, and in the second, it may be both the absence of chlamydia and the presence of an extremely small number of pathogens, which is below the capabilities of the method, but this is an unlikely result.
With positive PCR values, a diagnostic search is carried out in the future to determine the primary localization of the pathogen. Since the presence of chlamydia in the blood means only the fact that they have overcome the histohematogenous barrier, they could get into the blood from anywhere: from the oropharynx, from the urethra, from the anus, or from the lungs, depending on where the primary focus of the pathogen was introduced into organism.
Antibodies - immunoglobulins of classes M, G, A
In an acute process, antibodies of class M appear first in the body. This indicates an early period, or a case of exacerbation of chronic chlamydial infection. How can these two states be distinguished?
- If a high titer is combined with low titers, then this indicates the primary infection and the freshness of the infectious process;
- If a high titer of immunoglobulin M coincides with an increased titer of immunoglobulin G, then this indicates chronicity.
In some cases, a secretory blood test is performed. Their task is to protect various mucous membranes from deeper penetration of chlamydia so that they do not appear in the blood. These antibodies are also a marker of acute infection, or exacerbation of a chronic process. The term of their appearance is several days from the moment of primary infection with chlamydia. Of course, it is best to take class A immunoglobulins directly from the mucous membranes, since it is there that their concentration is highest, but they are completely determined by their peripheral blood.
After infection, the maximum value of immunoglobulins A appears within a month, and after three months their titer decreases. Facts such as reinfection and exacerbation of the chronic process again cause an increase in the titer of these antibodies. If chlamydia enters the bloodstream, the titer of these antibodies decreases, since the immune defense of the mucous membranes is broken, and in superficial forms of the disease, when the histohematogenous barrier has not yet been broken, these class A secretory immunoglobulins are produced throughout the entire period of the disease, which can be distinguished in the test results.
"Long-term" immunoglobulins of class G are called a marker of a long-term, or already transferred infection. Considering the previous data, you yourself can easily decipher the various options for their interpretation. On average, Ig G appears in the blood 2.5 weeks after the pathogen enters the body. But the activity of the immunity caused by these antibodies is unstable.
After recovery, antibodies can circulate in the blood, sometimes for years, and sometimes for a lifetime. If the chronic process proceeds with very low activity, or the patient has recovered, then their titer decreases. With exacerbations of the process, the titer increases again, and in the case of a fourfold increase in the values, we can confidently speak of the reactivation of the process.
In conclusion, it should be said about the form of issuing the test results. Many patients are accustomed to the fact that the pathology, and the interpretation of the norm, is issued in the form of a table - numerical values. This is not the case with chlamydia. PCR is a qualitative reaction that gives the answer "yes, detected" or "no, not detected." Antibodies have three options: the result is negative, doubtful and positive.
This is quite enough for diagnostics, but also in the test results a special value can be given, which is called the "positivity coefficient". This factor shows how close the patient sample results are to the thresholds at which antibodies can be detected at all. The further this coefficient is from the threshold value, the greater the reliability of the study. This coefficient can only confirm the doctor's confidence that the patient does not have a false positive reaction, since the positivity rate is quite high.
An analysis for chlamydia must be taken if suspicious symptoms appear or unprotected intercourse has taken place.
Most cases of infection occur through the sexual route of transmission, the household one is less common. The incubation period lasts 14 days, at which time chlamydia begins to multiply and infect healthy cells. The first symptoms of the disease appear after 2-3 weeks, they appear in the form of vaginal discharge in women, from the urethra in men. In half of cases, chlamydia takes a latent form and is detected when people go to the doctor with complaints of infertility.

If untreated, the disease turns into a sluggish form, women develop inflammatory changes in the fallopian tubes, endometrium, and ovaries. The formation of adhesions is the main reason for the impossibility of conception. Chlamydia in men affects the epididymis and vas deferens, leading to erectile dysfunction and infertility. What tests are performed for chlamydia?
Study types
 The rapid test can be purchased at any pharmacy and performed at home. It allows you to detect chlamydia in urine or smear. The material is placed in a special hole in the test cassette and the result is observed. The principle of action is based on the detection of lipopolysaccharide antigen. The test result often turns out to be erroneous, therefore, to confirm or refute it, you need to contact the clinic.
The rapid test can be purchased at any pharmacy and performed at home. It allows you to detect chlamydia in urine or smear. The material is placed in a special hole in the test cassette and the result is observed. The principle of action is based on the detection of lipopolysaccharide antigen. The test result often turns out to be erroneous, therefore, to confirm or refute it, you need to contact the clinic.
For cytoscopic analysis, a smear is taken from the urethra in men and from the mucous membranes of the cervix - in women. The material is placed on glass, dried and treated with methanol. By examination under a microscope, specific cellular inclusions are revealed, indicating the presence of chlamydia. This method is considered quite informative, but it can be carried out only in the acute period of infection. Chronic chlamydia can occur without the appearance of cytoplasmic inclusions, which means that the tests will have negative results.
ELISA and PIF studies are aimed at determining antibodies to chlamydia in the blood. Using this method, it is possible to determine the type of infectious agent, the stage of the disease and the nature of its course. The accuracy of the method does not exceed 60%. An analysis for chlamydia in women is prescribed both in the presence of symptoms and during the period of bearing a child or with infertility of unspecified origin.

PCR diagnostics involves decoding a small part of DNA through which chlamydia is detected. The material for analysis is a swab from the urethra or vagina. The method is highly informative and sensitive. Not only acute infection is detected, but also its latent and chronic forms. Deciphering the analysis allows you to find the cause of infertility and miscarriage. PCR is also used to assess the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy. If the analysis gives a questionable result, it is recommended to use other research methods. It is necessary to be tested for chlamydia for HIV-infected people and people suffering from tuberculosis or hepatitis.
The cultural method is considered the most informative, its accuracy is close to 100%. With its help, you can not only detect chlamydia, but also determine their sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. This is necessary to draw up the most effective therapeutic regimen.
 Bacterial culture is carried out to assess the results of treatment. The essence of the analysis consists in placing the material on nutrient media and growing microorganisms. By the nature and volume of the colony, you can determine the type of infection occurring in the body. Thus, bacterial culture and PCR methods are currently considered the most informative.
Bacterial culture is carried out to assess the results of treatment. The essence of the analysis consists in placing the material on nutrient media and growing microorganisms. By the nature and volume of the colony, you can determine the type of infection occurring in the body. Thus, bacterial culture and PCR methods are currently considered the most informative.
The rest of the methods are auxiliary and are used to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Preparation for the examination
To obtain the correct result, tests for chlamydia must be taken in a clinic, and the processing and examination of the material must be carried out in a specialized laboratory.

In children, the material is taken from the mucous membrane of the entrance to the vagina. Urine is collected in the morning, and its average portion is used for analysis. The first drops are put into the toilet, the rest into a clean container. To complete the study, you will need at least 50 ml of urine. Before collection it is necessary to wash off with water, soap or intimate hygiene products cannot be used. It is imperative to tell the specialist about all the drugs that are currently being taken.

Decoding the results
How many days is the test for chlamydia done? On average, a negative or positive result is known after 2-3 working days, some private clinics offer an urgent research service, when the patient receives an opinion on the day the material is handed over. An exception is bacterial culture, which requires at least 5 days to obtain results.
For ELISA and PIF diagnostics, specialists use the term titer. Antibodies IgG, IgA, IgM are considered. The norm is the absence of all types of antigens:
- IgM antibodies are detected one week after infection;
- IgG - after 10 days;
- IgA - after 14-21 days.
 Doubtful are the results of IgM and IgA - up to 50, IgG - up to 100. In this case, after 1-2 weeks, the study is repeated.
Doubtful are the results of IgM and IgA - up to 50, IgG - up to 100. In this case, after 1-2 weeks, the study is repeated.
PCR is a qualitative study, therefore, the conclusion may be written "detected" or "not detected". When decoding the results of bacterial culture, first of all, the type of the causative agent of the infection is indicated, then its quantitative characteristics. They are measured in colony-forming units for a certain volume of blood or other material. One bacterial cell can give rise to an entire colony.
In conclusion, there will be a list of antibacterial drugs to which chlamydia is sensitive. If the letter R is placed next to the name of the drug, we are talking about the resistance of the bacteria to it. The S code indicates a high sensitivity of the infectious agent. In this case, the drug can be used to treat the disease.
Chlamydia can be latent, subclinical or acute. The disease contributes to the development of dangerous consequences, such as:
- infertility;
- spontaneous abortion;
- inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system and peritoneum.
Currently, there are many ways to detect chlamydia in the body, but none of them is 100 percent accurate. If the analysis is positive, additional examination methods are used. Interpretation of the results should be carried out by a qualified technician.
A blood test for chlamydia - how to take and deciphering the results. How is Chlamydia trachomatis in the blood determined?
A serious infection, more often sexually transmitted, is dangerous with serious consequences. Laboratory diagnostic methods - blood tests for chlamydia - help to identify the disease and start treating it. What features do the surveys have, how informative are all their varieties, how the results are deciphered - questions to which it is interesting to get answers.
Chlamydia trachomatis - what is it
- with unprotected intercourse;
- household way;
- during pregnancy from an infected mother to a child;
- for men, the disease is dangerous by the development of prostatitis, impotence, chlamydial pneumonia;
- in women, chlamydia provokes miscarriages, adhesions in the small pelvis, premature birth, and uterine tumors.
Chlamydia diagnosis
The disease may be asymptomatic for a long period after infection. Chlamydia is often detected in the diagnosis of other genital infections. Due to the nature of the biological cycle of the pathogen, analyzes are carried out in several ways. Laboratory diagnostics of chlamydia includes research methods:
- primary microscopic smear analysis;
- the culture method - sowing the biomaterial in a special environment - gives an accurate result;
- RIF of chlamydia - determination of the reaction of immunofluorescence - pathogens glow under a microscope, are reliable.




Chlamydia analysis
The most accurate diagnostics for detecting chlamydial infection have blood tests. They are produced according to several methods, which have their own characteristics. The main types of examination:
- Immunoassay - ELISA. By the number of antibodies Igg, Igm, Iga, it is determined which phase is currently observed in the disease - acute, chronic or remission.
- Polymer chain reaction - PCR. Detects the DNA of the pathogen, is a very reliable diagnostic method.
- having unprotected sex with a new sexual partner;
- women who have frequent ailments due to diseases of the small pelvis;
- both partners when planning pregnancy, so as not to infect the expected baby;
- women who have problems carrying a child;
- patients with unexplained causes of infertility.
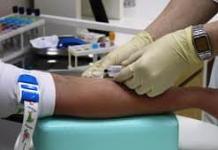
Chlamydial blood is taken from a vein. To obtain objective results, doctors recommend meeting the requirements:
- do tests no earlier than a month after antibiotic treatment;
- not have sexual intercourse in the next days before the examination;
- do not smoke half an hour before blood sampling;
- come to the study on an empty stomach;
- do not drink alcohol per day;
- do not drink water before testing;
- exclude the implementation of physiotherapy.

PCR for chlamydia
With this method of research, chlamydia in the blood is determined by the amount of DNA of microorganisms that are in the selected sample. The analysis of the polymer chain reaction - PCR - is characterized by very high accuracy and sensitivity. The result is fast and reliable. It is considered positive when there is a large number of chlamydia in the test sample - the cause of the infection is confirmed. The advantage of the method is that infections are detected with its help:
- in a latent form;
- asymptomatic;
- in the acute stage.
Chlamydia is a great danger for a woman expecting the birth of a baby. The likelihood of intrauterine infection is high. A timely diagnosis will help start treatment at an early stage and avoid serious problems. Chlamydia PCR analysis is prescribed by gynecologists to exclude infection when a pregnant woman has symptoms:
- high temperature;
- soreness in the lower abdomen;
- feeling unwell.
The PCR blood test is versatile. With its help, not only the causative agent of chlamydia is determined, but also other infections - herpes, tuberculosis, hepatitis. When decoding, there are two possible results:



- negative - indicates the absence of infection of the body;
- positive - indicates that infection has occurred, and with what type of bacteria.
ELISA for chlamydia
From the first days of infection, the body begins to produce antibodies to chlamydia in the blood. Three types of immunoglobulins, which are called Igg, Igm, Iga, stand up to protect against the disease. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay - ELISA for chlamydia not only accurately determines their presence, but states the stage in which the disease is located. This is due to the appearance of each of the antibodies at a particular stage of infection.
In the study of blood by the ELISA method, immunoglobulins are detected at the following times:
- after infection, Igm immediately appears, if the other two are absent, acute inflammation is diagnosed, it is important when examining newborns;
- a month after infection, Iga antibodies are formed, which indicate the progression of the disease;
- the appearance of Igg signals the transition of chlamydial infection to its chronic form.

Decoding the analysis for chlamydia
Interpretation of examination results has subtleties, therefore it should be carried out by qualified specialists. A blood test for chlamydia ELISA is deciphered for each type of immunoglobulin, speaks of the period of development of the infection. When determining Igm, the results are as follows:
- Positive: less than two weeks have passed since infection; if no other antibodies are found, in the presence of Igg, exacerbation of chronic inflammation.
- Negative: no chlamydia - in the absence of all immunoglobulins; when Igg is determined, the infection occurred at least two months ago.
With blood tests for the presence of Iga antibodies, the result is interpreted as follows:
- Positive: an acute stage of a chronic infection or an infection that has passed more than two weeks; infection of the child during pregnancy.
- Negative: no chlamydial inflammation; from the time of illness less than 14 days; the likelihood of infection of the fetus is low.
When decoding a test for Igg, the following results are given:
- Under normal conditions, they are absent, the value of the positivity coefficient is within the range of 0–0.99;
- Positive: Chlamydia disease or exacerbation occurred more than three weeks ago.
- Negative - in case of simultaneous absence of Iga Igm immunoglobulins: there is no chlamydia in the blood; complete recovery.
Where to get tested for chlamydia
For those who have felt the signs of illness, have had unprotected sex with a casual partner, a rapid test can be purchased at the pharmacy. With its help, the presence of chlamydia infection is quickly determined. For analysis, you need a urine or smear in women. The instructions describe the method for collecting them. The result is deciphered as follows:
- positive - requires immediate referral to a venereologist to prescribe medication;
- a negative test indicates that there is no disease at the time of the test.
You can get tested for chlamydia in the direction of a venereologist or gynecologist. It is not excluded that the patient independently turns to medical institutions if an infection is suspected. A blood test for chlamydia is carried out by the following organizations:
- antenatal clinics;
- family planning clinics;
- dermatovenerologic dispensaries;
- specialized laboratories for research.

How much does a chlamydia test cost?
You can do tests for chlamydia in clinics or specialized centers that provide such services. The cost depends on the status of the institution, the equipment available. The classification of specialists involved in decoding the results plays a role. The price of analysis for chlamydia in medical organizations in Moscow is summarized in the table:
Chlamydia analysis
The analysis for chlamydia in women and men should be given at regular intervals in order not to miss the moment of the onset of the development of the disease and to start treatment on time. Chlamydia is one of the most dangerous infectious diseases detected only by laboratory tests.

This disease is dangerous because of its asymptomatic nature, and the damage done to the body is colossal. How to protect yourself from the disease, identify it in the early stages and choose effective methods of struggle?
general information
The disease caused by the bacteria chlamydia is infectious and is called chlamydia. Such a sexually transmitted disease is one of the most common. The disease is specific. When it enters the human body, bacteria immediately proceed to active division. After 12 hours, they are able to penetrate the cells, causing their destruction.
In the female body, the infectious process initially affects the reproductive organs, gradually moving to the peritoneal region.
In men, the urinary system is affected and only then the reproductive system. Already at the first pain in the urethra, an analysis is shown for chlamydia in men.
Chlamydia can enter the body not only from the sexual partner. They are quite capable of coming from the external environment. But such cases are quite rare.
Diseases even affect the placenta, so the fetus becomes infected in utero or passing through the birth canal of a sick mother. Thus, chlamydia may appear in children. Therefore, the analysis for chlamydia in women is extremely important when planning pregnancy. Bacteria of this type can infect other organs, moving with the lymph.
The early stages of the disease do not characterize themselves in any way. The first signs are observed after years, primarily an increase in body temperature, weakness and intoxication with the products of the vital activity of bacteria. Then the symptomatic picture weakens. Chlamydia further rapidly progresses, affecting the organs of excretion and reproduction, this is expressed in constant pain in these areas and discomfort.

When a similar symptomatic picture appears, you need to immediately pass the appropriate analysis. An analysis for chlamydia during pregnancy is also extremely necessary, because with an illness there is a threat of infection of the fetus. This study has several varieties, differing in cost and accuracy. Diagnostics can be carried out for all biomaterials of the human body. Laboratory research is also carried out using various techniques.
How are tests for chlamydia in women and men taken?
There are many variations of methods from where you can take a sample for analysis. The main methods of studying biomaterials for the presence of chlamydia in the body:
- Independent express test. This research method is the most affordable; the test can be purchased at a pharmacy. This study is based on the paper chromatography method. In the presence of chlamydia in the patient's biomaterial, the test acquires a rich characteristic color. It is advisable to carry out such a test several weeks after intercourse. In the early stages, this manipulation is impractical to apply, since the bacteria do not manifest themselves in any way. This test is not informative enough, but a positive test is a reason to contact a specialist for further research and find out how accurate the test was.
- General smear from the urethra or female genital tract. The manipulation is carried out by a gynecologist or urologist. The fence is carried out with a special medical brush. Material is taken from the prostate or urethra in men, in women from the genital tract. The result is known in two days. The advantage of such research is simplicity and accessibility. The accuracy does not exceed 20%.
- Immunofluorescence reaction (RIF). The biomaterial is taken from the urethral cavity, which is further subject to staining and microscopy. For such a study, a sufficient amount of biomaterial is required, the accuracy is higher than 60% percent. The disadvantage is the impossibility of taking from the child. If this study is done correctly, then it is most informative.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). This laboratory study allows you to clarify the presence and staging of the disease. For this, blood is taken from a vein or material from the urethra. A few hours before the procedure for collecting material, you must refrain from urinating. The accuracy of this study is more than 50%, this method is used in tandem with others. The procedure can be easily carried over by both adults and children. This is another plus that makes the procedure universal.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). This research is the most accurate. The disadvantages of such diagnostics are: the high cost and labor intensity of the method. Not every medical institution is able to purchase the necessary equipment. Biomaterials are secretions, portions of urine, endometrial tissue.
- Cultivation method. This method is ideal. With its help, you can make sure of the presence or absence of pathogens in the body and choose the right therapy. This analysis takes time: the cells are placed on a Petri dish with a growth medium, incubating for a week. The procedure reveals chlamydia in an adult and a child. The norm of the analysis is no growth of colonies on the medium.
How to get tested correctly
Preparation for analysis:
- If you need to donate blood for such a study (from a vein), then it is necessary to perform the manipulation on an empty stomach, otherwise the study may be unreliable. In order to improve accuracy, it is necessary to reduce the consumption of fat-containing and fried foods 2 days before the check, it is preferable to eliminate alcohol altogether. In addition, it is preferable not to smoke on the day of the procedure;
- When passing urine, you must refrain from sexual intercourse. Collect morning urine, take the first portion for research. This increases the accuracy at times;
- If it is necessary to take material from the genital and urinary tract, then 2 days before the manipulation it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse. And it is recommended not to use the toilet a few hours before the procedure. It is preferable for girls to collect material on the 1st day after the end of menstruation;
- Analysis for chlamydia in women. In the fairer sex, a smear or layer is taken from the cervix, vagina and urethra;
- Analysis for chlamydia in men. In the stronger sex - from the urinary canal. In some cases, seminal fluid is used for research;
- Sometimes it becomes necessary to take for analysis the articular fluid produced by the synovial formation. To take these samples, the required joint is punctured. The doctor must maintain sterility during the procedure.
How much analysis is done
Each type of research requires a certain period of time. The time spent on the analysis depends on the accuracy of the method, the complexity of the procedure and the qualifications of the specialist. Express methods are done in a few seconds, but they do not differ in accuracy. The most reliable studies are time consuming.

Analysis decoding
Only a specialist (biologist, doctor) is able to unambiguously disassemble the results of the analysis. But you can independently study the methodology of the procedure and the possible results. The most reliable studies to date are ELISA and PCR analyzes.
The results of laboratory research depend on the duration of the bacteria in the body. There are several stages found in laboratory tests:
- Latent stage - IgM (appear after 5 days after infection, the peak of concentration occurs on the 10th day);
- the second stage - IgA (detected after 10 days after infection);
- third stage of the disease. - IgG (appear after 15–20 days after infection).
All measurements are carried out in titers. They show the ratio of antibodies produced to the volume taken for analysis. These measurements do not fit into the analysis form, there you can only observe the final conclusion of the laboratory assistant: a positive analysis, doubtful or negative.
Observing the rules of personal hygiene and a decent sex life, you can protect yourself from such diseases. And at the first sign, you need to see a doctor.
Analyzes for chlamydia: types, preparation, decoding
Chlamydial infections are a group of infectious diseases caused by chlamydia. Bacteria of this kind affect the organs of the genitourinary, respiratory, cardiovascular, visual, musculoskeletal systems.
Indications for analysis for chlamydia
Examination for chlamydia is indicated in the following cases:
- preventive examination;
- signs of a genital infection;
- planning pregnancy;
- a history of complicated pregnancy;
- obstetric registration;
- inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary organs;
- absence of pregnancy for 2-3 years of regular sex life;
- monitoring the effectiveness of therapy for chlamydia;
- persons whose sexual partners have chlamydia.
Types of tests for chlamydia
Due to the fact that chlamydia is often asymptomatic, laboratory diagnostics plays an important role as part of a preventive examination. Tissue samples, blood, urine and other biological fluids can serve as material for research on chlamydia.
Chlamydia diagnosis is carried out in several directions.
Culture analysis
Study of biomaterial by inoculation, isolation of the culture of the pathogen and determination of its sensitivity to antibiotics. Chlamydia isolate is used to infect sensitive cells. Then a growth medium is added to them, which contains an antibiotic. Infected cell cultures are incubated at +36 ° C for five days. Antibiotic susceptibility is determined depending on the suppression of infection. Sowing on chlamydia is used to assess the effectiveness of antibacterial treatment; the disadvantages of the method include the laboriousness of the process and the duration of preparation.
Cytological examination of a smear
The method is informative only in acute forms of the disease. Epithelial scrapings serve as clinical material for research. During the study, the biomaterial is exposed to fixing agents and staining. Under the influence of reagents, preparations are detected under a light microscope.
The results of the study are individual for different types of infection, only a doctor should deal with their interpretation and determination of the nature of the treatment.
Immunofluorescence reaction (RIF)
Identification of chlamydial antigens using a fluorescent microscope. The method is based on the property of antibodies to differ from each other in the brightness of the glow, while the inclusions of chlamydia stand out against the background of the cytoplasm of the cells. This method is not sensitive enough in the asymptomatic course of the disease.
Immunoassay (ELISA)
A method based on the detection of specific antibodies to chlamydia in the test samples. Allows you to determine the phase of the disease, to evaluate the effectiveness of antibacterial treatment. Thus, the production of IgM antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis is a marker of the acute stage of the process. With the progression of the disease and its transition to a chronic form, IgA antibodies appear, then IgG.
The decoding of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is presented in the table.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
A method for detecting DNA fragments of the pathogen, which allows you to confirm the presence of a foreign microorganism in the body with an accuracy of 90-95% and determine what kind of microorganism it is. Samples of tissue, blood, urine, and other biological fluids can be taken for analysis. In women, an epithelial scraping is taken from the vagina, urethra, cervix. In men, a smear from the urethra, prostate secretions, ejaculate are used. If the eyes are affected, scraping from the conjunctiva is examined. To exclude rheumatic lesions of the osteoarticular system, the articular fluid is examined.
Special devices are used - amplifiers for DNA multiplication. When the amount of DNA is sufficient, it is determined whether the sample contains DNA fragments characteristic of the infectious agent. Evaluation is carried out by electrophoresis or using labeled DNA fragments. Normally, the genetic material of chlamydia is not found.
Chlamydiae are intermediate between viruses and bacteria.
The PCR result can be positive or negative. A quantitative assessment in dynamics allows one to determine the activity of the pathogen and the effectiveness of the therapy.
Express diagnostics
Chlamydia can be identified using an integrated approach. It is important to consider how much analysis is done. As a rule, after receiving the results of PCR (usually ready 4 days after delivery), additional studies are prescribed - culture culture and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The results of the study are individual for different types of infection, only a doctor should deal with their interpretation and determination of the nature of the treatment.
Preparation for analysis for chlamydia
How do you take the material for research and how to hand it over correctly?
A blood test for chlamydia is performed using venous blood, which is taken in the morning on an empty stomach.
Preparation for the study includes abstinence from alcohol, fatty and salty foods, smoking for a day. Before taking a biological sample from the urethra, it is recommended not to urinate for several hours.
Before a culture study, it is necessary to stop taking antibiotics and uroseptic drugs for 30 days. In immunocytological studies, antibacterial drugs are canceled in 14 days.
On the eve of PCR, women are advised to abandon douching, hygiene procedures with antibacterial soap, and the use of vaginal suppositories. Before collecting material, men need to stop using medications to increase potency.
Tissue samples, blood, urine and other biological fluids can serve as material for research on chlamydia.
Chlamydia and chlamydia
Three types of chlamydia infect humans - C. trachomatis, C. Psittaci and C. pneumoniae. The localization of the pathological process depends on the type of bacteria. The urogenital form of chlamydia is caused by Chlamydia trachomatis.
According to the characteristics of the genetic material, there is a similarity with mycoplasma, ureaplasma and haemophilus influenzae.
- sexual- with unprotected sexual intercourse;
- vertical (from mother to newborn baby)- infection of the fetus through the placenta during pregnancy or during childbirth;
- contact-household- through common household items, kisses.
The significant prevalence of chlamydial infection is due to the asymptomatic nature of the course of the disease. The appearance of the first clinical signs and the development of symptoms (vitreous discharge from the urethra, itching, pain and stinging during urination, temperature drops, signs of intoxication) depends on the state of immunity. After a while, the symptoms of chlamydia usually disappear, the disease becomes chronic with periods of exacerbation. This form of infection is called persistent.
For express diagnostics, immunochromatographic tests are used, the action of which is based on the use of fluorescent markers, while the presence of chlamydia DNA in the sample is determined already in the reaction tube.
Chlamydia in the body causes many complications, including urethritis, prostatitis, endometritis, salpingo-oophoritis, pneumonia, conjunctivitis, joint diseases, damage to the cardiovascular system. Chlamydia trachomatis can cause infertility in men and women, miscarriage, and the development of chlamydia in children.
YouTube video related to the article:
Education: Rostov State Medical University, specialty "General Medicine".
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
The life expectancy of left-handers is shorter than that of right-handers.
The person taking antidepressants will, in most cases, be depressed again. If a person coped with depression on his own, he has every chance to forget about this state forever.
The first vibrator was invented in the 19th century. He worked on a steam engine and was intended to treat female hysteria.
More than $ 500 million a year is spent on allergy drugs in the United States alone. Do you still believe that a way to finally defeat allergies will be found?
74-year-old Australian resident James Harrison has donated blood about 1000 times. He has a rare blood group whose antibodies help newborns with severe anemia survive. Thus, the Australian saved about two million children.
It used to be thought that yawning enriched the body with oxygen. However, this opinion has been refuted. Scientists have proven that yawning, a person cools the brain and improves its performance.
In the UK, there is a law according to which a surgeon can refuse to perform surgery on a patient if he smokes or is overweight. A person must give up bad habits, and then, perhaps, he will not need surgery.
People who are used to regularly eating breakfast are much less likely to be obese.
Studies have shown that women who drink several glasses of beer or wine per week have an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
Falling off a donkey is more likely to break your neck than falling off a horse. Just do not try to refute this statement.
The weight of the human brain is about 2% of the total body weight, but it consumes about 20% of the oxygen entering the blood. This fact makes the human brain extremely susceptible to damage caused by lack of oxygen.
An educated person is less susceptible to brain disease. Intellectual activity promotes the formation of additional tissue that compensates for the diseased one.
Many drugs were initially marketed as drugs. Heroin, for example, was originally marketed as a cough medicine for children. And cocaine was recommended by doctors as anesthesia and as a means of increasing endurance.
Human blood "runs" through the vessels under enormous pressure and, if their integrity is violated, is capable of shooting at a distance of up to 10 meters.
Human bones are four times stronger than concrete.
It would seem, well, what could be new in such a hackneyed topic as the treatment and prevention of influenza and ARVI? Everyone has long known as the old "grandmother's" methods, that.
Types of analyzes for chlamydia and their decoding

There are a number of diseases transmitted through sexual intercourse if safety rules are ignored. Their appearance, if the diagnosis is not timely, is fraught with complications. Conducting research allows you to choose the right therapeutic treatment regimen.
Features of pathology and types of analyzes
Chlamydia infection can occur in three ways:
- The main route of infection is unprotected sex.
- Infection through household items is possible.
- The vertical path is the infection of a child with chlamydia during childbirth, when the infection is transmitted from a sick mother.
The development of pathology begins at the moment when chlamydia in women in the body multiplies to a certain amount. The main danger in this case is the reproductive system - when infected with chlamydia, infertility and a number of equally serious problems can develop. When infected with chlamydia, adhesions form, miscarriages and premature birth in women in position, possible oncological problems in relation to the uterus. In men, chlamydia provokes the formation of prostatitis and impotence, chlamydial pneumonia may appear.

When chlamydia enters the body, it is very difficult to identify the disease at an early stage of development. Even a large number of chlamydia is not a guarantee of pronounced symptoms. Pathogens are able to live inside cells for a long time without manifesting themselves in any way. Quite often, chlamydia is discovered by accident during a routine inspection. At the same time, the methods for determining pathology, taking into account the characteristics of the disease, are rather complicated, in addition, chlamydia occurs as an independent disease or it may be accompanied by other infections. General examination of biomaterials at diagnosis is insufficient. There are several modern methods that determine the presence of a disease, including:
- Rapid testing, which is good because it allows you to conduct independent research at home.
- Microscopic analysis for chlamydia, when selected biomaterials are examined by multiple magnification.
- Bacteriological culture, when blood or a smear is placed in a specially prepared medium.
- The RIF immune fluorescence response is an analysis for chlamydia, during which pathogenic pathogens glow under a microscope.
- An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is also called an ELISA for chlamydia. Focusing on the amount of Igm, Iga and Igg antibodies, the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay determines the stage of development and the severity of the course of the disease
- Polymer chain reaction, it is also PCR for chlamydia, allows you to identify the DNA of the causative agent of the disease and is the most reliable diagnostic method.
Fact. Quite often, several methods are used to determine pathology at once. The combined approach allows for greater reliability, tests for chlamydia are prescribed depending on the history of each individual patient.
Which research is preferable
Each study has its positive and negative aspects. Express tests are distinguished by increased convenience - there is no need for trips to the laboratory, the result appears quickly, with chlamydia, contrast staining of the control strips occurs. The method is based on immune chromatography, however, such an analysis for chlamydia will show the result only after 14 days have passed since the moment of unprotected intercourse. At the same time, such testing cannot be trusted completely and unconditionally.
Professional diagnostics for the presence of chlamydia is carried out in medical institutions, for which women need to visit a gynecological office. The specialist can take swabs for examination from the cervix or the vaginal mucous layer. Biomaterials are examined at multiple magnifications under a microscope.

An ELISA test for chlamydia allows you to determine whether the body has antibodies to pathogens. Their presence in the analysis, even if there are no pathological microorganisms, suggests that a person had had chlamydia at one time. ELISA analysis can be either qualitative or quantitative. Carrying out according to the first option determines the presence or absence of the desired substance and gives an unambiguous result. When decoding according to the second method, the chain of reactions is more complex and allows you to determine the concentration of antibodies in the blood, demonstrating the development of the infectious process. The advantages of the method include:
- High sensitivity even at low concentrations of the analyte.
- Specificity, ensuring the reliability of the result - with a positive value, it can be concluded that the putative antigens were found.
- Due to the high level of manufacturability of the analysis for chlamydia ELISA, the impact of the human factor is minimized, respectively, the percentage of correct results increases, and the possibility of error decreases.
- High reliability of the data obtained during the delivery of biomaterials due to the release of reagents in the industrial sector.
Despite the high accuracy of this method, it has certain disadvantages. The specialist must correctly assume the nature of the disease in women, while the ELISA does not directly find the pathogen, but only shows the presence of antibodies. Another negative point is the cost of the study, which does not belong to cheap ones; accordingly, the appointment, conduct of the study and its decoding must be trusted by experienced doctors.
Let's consider what bacteriological inoculation is. In the culture method, the selected biological material is placed in containers with an artificially created nutrient medium, growing colonies of pathological microorganisms in it. Plus research - the ability to determine the quantitative composition of chlamydia in the blood and its sensitivity to antibiotics for the development of an effective therapeutic regimen.
The analysis of PCR deserves a separate consideration.
Proven fact. If we compare which of the studies is the most reliable, the polymerase chain reaction demonstrates a sensitivity of 99%.
PCR research
As practice shows, a general analysis of urine and blood does not give a complete picture. In research, one can only note the presence of inflammation or the presence of pathological microorganisms without specifying their nature. When carrying out the polymerase chain reaction, the biomaterial is taken from the focus, in the case of chlamydia it is:
- vaginal area;
- urethra and uterine cervix;
- ejaculate and prostate secretions;
- a blood test, urinalysis is done.
The study can select sections of RNA or DNA of chlamydia that have entered into a polymerase reaction, contributing to their development and rapid growth. After that, it is not difficult to make a diagnosis. The overall picture demonstrates the complete safety of the method under consideration and the absence of specific preliminary preparation. On the part of doctors, the use of special efforts is also not required, although patients are interested in how much such research is being done. Usually, the required results in time can be obtained several days after the analysis.

With the help of the polymerase chain reaction, it is possible to detect even the presence of single pathogenic microorganisms, after which specific conditions are created for them in the process of research. The growth and formation of the DNA of pathogens in the biomaterial occurs. Then, various analytical markers are added to the resulting sample - they help to determine the presence or absence of DNA in the smear.
Despite all the positive qualities of the method, it is capable of causing a certain complexity and mainly due to its high cost. In addition to the price, the total
patient dissatisfaction causes:
- The impossibility of conducting an analysis in a regular clinic at the place of residence. PCR is a high-tech method that requires the use of expensive reagents and modern equipment.
- Chlamydia, as a rule, is not detected in the early stages of development by the PCR method; this approach works when an inflammatory process develops in the body.
- In some cases, the decoding of a blood test can show a false positive or false negative result, respectively, additional verification is necessary to confirm the data obtained.
When and how is the sampling of biomaterials carried out
Even in the absence of obvious symptoms that can indicate the presence of pathological pathogens in the body, there are a number of situations in which it is necessary to donate blood for chlamydia:
Now about how to take a blood test for chlamydia, collect urine or prepare for the collection of biological materials. Before conducting an inspection, you need to prepare in a certain way. 48 hours before the gynecologist deals with smears, their selection and examination, you will need to give up sexual intercourse. The period for which it is necessary to abandon the use of intimate hygiene products with chemical constituents is 72 hours before the study.

For 7 days, they stop using vaginal sprays, suppositories, tablets. If you are taking a smear, douching, washing and going to the toilet before the procedure is prohibited. The material is taken three days after the end of menstruation, making scrapings in the vagina, urethra, uterine cervix using a probe. To obtain a reliable decryption, some rules should be taken into account:
- No smears are taken during your period.
- PCR is not carried out for a month after the end of the intake of antimicrobial drugs, to which pathogens are sensitive.
- In the case of blood donation, the biomaterial is taken on an empty stomach, fried and fatty foods are removed from the menu 24 hours before it.
- Refuse to take all pharmaceuticals.
- Blood is taken from a vein.
- If urine testing is required, collect the first morning urine using a sterile pharmacy container or clean container.
- It is necessary to carry out hygiene of external organs; during urine collection, the entrance to the vagina is closed with clean cotton wool to prevent pathological secretions from entering the liquid.
Important! If the listed rules are violated during the analyzes, the risk of incorrectly deciphering the results obtained and developing an erroneous therapeutic scheme increases.
Decoding of the obtained results
It should be understood how responsible the process is to decipher the analyzes, on which both the diagnosis and treatment depend. Donated blood, urine, and other biomaterials have certain "normal" indicators according to analyzes, from which they are repelled in the research process. With the deciphering of the PCR results for the person who passed the tests, everything is quite simple - here they operate with only two concepts, the result can be either negative or positive. In the first case, chlamydia is absent in the provided samples, in the second it is present. At the same time, there are many subtleties, absolutely everything can be taken into account only by a professional doctor.
The results of ELISA analyzes look somewhat different, as can be seen from the provided table:

As you can see, the norm is negative IgG and IgM readings. In the second line, the indicators can also be attributed to the norm - in any case, treatment at this stage of the development of the disease is not required. The last two options indicate a pathology in the body.
Another table can be compiled into which possible quantitative expressions will be summarized. When analyzing for chlamydia, the decryption can demonstrate the following results:
How to take a blood test for chlamydia
Chlamydiae are specific bacteria, the vital activity of which is possible mainly in the structures of the human urogenital tract.
As a result of infection with chlamydia, the infectious disease chlamydia develops.
It refers to sexually transmitted diseases.
Infection with these pathogenic microorganisms occurs through sexual contact.
With direct contact of the mucous membranes of the genitals during unprotected sex with an infected person.
Chlamydia is often asymptomatic.
Therefore, a laboratory test is carried out to diagnose the disease.
Studies that are carried out to diagnose chlamydia
Laboratory diagnostics of the infectious process of the structures of the urogenital tract caused by chlamydia includes several specific studies.
Chlamydia blood test
Determination of specific antibodies to chlamydia using ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay).
They appear in the blood in the presence of an infectious process in the structures of the urogenital tract.
It is the ELISA that the venereologist has in mind when he prescribes a blood test for chlamydia to a patient.
Antibodies G and M are determined by a blood test for chlamydia.
PCR for chlamydia - a smear in the material of which the DNA of chlamydia is determined.
Cultural bacteriological study for chlamydia.
The material is sown (a smear from the urethra, in women also from the vagina and cervix) on a special nutrient medium.
If a colony of microorganisms grows on it, the species of bacteria is determined.
As well as their sensitivity to the main groups of antibiotics. This is a fairly long-term research method, its result can be obtained no earlier than a few days after the analysis.
How long does a blood test for chlamydia take?
In a modern laboratory, which is equipped with special diagnostic equipment and reagents for ELISA, the analysis is usually performed within 1-2 days.
If a person donated blood in the morning, then the results can be obtained by the end of the next working day.
Currently, chlamydia is not only a medical problem, but also a social one, primarily actively affecting a woman's ability to get pregnant and give birth to a child.
In cells, they persist until favorable conditions occur, later causing a chronic inflammatory process. Self-treatment of chlamydia leads to a chronic course of the disease. Chlamydial infection can coexist with other infections. The modern analysis for chlamydia in women is based on laboratory research.
These include:
- express tests;
- microscopy;
- linked immunosorbent assay;
- analysis for the reaction of immune fluorescence;
- complement binding assay;
- bacteriological inoculation.
In order to maximize the effectiveness of diagnostics, methods are combined depending on the most suitable for the history of a particular patient. Several diagnostic methods are often used. The development of modern medicine today allows you to check your body for the presence of chlamydia.
You can do an express test yourself, which you can buy at a pharmacy. It is based on the method of immune chromatography. If an infection is present, the two test strips are colored in a contrasting color. A rapid test should be done no earlier than two weeks after unprotected sexual intercourse. In the early stages, chlamydia may not manifest itself in any way. You cannot trust the results of the mini test one hundred percent.
When the slightest hint of infection appears, a woman should urgently visit a gynecologist and get tested. The microscopy method is based on taking a smear from the mucous membrane of the vaginal walls, cervix and examining it. The analysis of immunoenzymes does not recognize the infection itself, but the presence of antibodies to it. An analysis for chlamydia in women reveals the stage of the infection. The PCR method is very sensitive - up to 99%, but quite financially and labor-intensive.
The results are ready no earlier than in a day. Chlamydia disease is not only a medical, but also a social problem that affects reproductive function. It is difficult to diagnose the infection due to its sluggish nature. The infection may not appear for a long time and may be revealed by chance during a routine medical examination and laboratory research.
note
Chlamydia can affect entire organ systems. The infection negatively affects the ability to carry a child, often develops a secondary disease.
 The cultural method consists of introducing biological material onto dishes with a nutrient medium and growing chlamydial colonies on them. This type of examination makes it possible to determine the quantitative composition of the colonies of the forming units and check their sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs. And this, in turn, allows you to correctly prescribe drug treatment.
The cultural method consists of introducing biological material onto dishes with a nutrient medium and growing chlamydial colonies on them. This type of examination makes it possible to determine the quantitative composition of the colonies of the forming units and check their sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs. And this, in turn, allows you to correctly prescribe drug treatment.
During pregnancy, chlamydia infection becomes the root cause of fetal infection and, as a result, its possible loss. Diagnosis of chlamydia infection in our time has become much more accessible thanks to many advanced methods of microbiological and immunological types of analyzes. The material for the study of a pregnant woman is discharge from the urethra, vagina and cervix. The material is taken with a sterile cotton swab.
Blood sampling is also taken. For a blood test, it is taken in the morning on an empty stomach from a vein. During the period of gestation, depending on the gestational age, it is possible to diagnose near the fetal waters. All samples for analysis are taken during the examination of a woman by a gynecologist. Detection of chlamydia infection in a woman carrying a fetus gives indications for examination and treatment of all the patient's sexual partners.
Its useful to note
Testing for chlamydia in a pregnant woman is extremely important because of the possibility of serious fetal developmental disorders.
What tests are taken for chlamydia in women
There can be many reasons for being tested for chlamydia in women:
- strange discharge from the genitals;
- a feeling of discomfort, soreness in the pelvic organs;
- recognition of infection in a sexual partner;
- accidental unprotected sexual intercourse;
- planning pregnancy;
- infertility;
- natural incomprehensible termination of pregnancy;
- prevention.
If you find any of the listed symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor and be tested for chlamydia in women. A neglected form of the disease can negatively affect the fate of a woman, deprive her of the joy of motherhood.
It is necessary to prepare for the examination by a gynecologist:
- Two days before the examination, you need to interrupt sexual intercourse.
- Refuse 3 days before the examination from the use of any chemical means of intimate hygiene.
A week before the examination, stop using vaginal suppositories, vaginal tablets and sprays.
- Provide personal hygiene of the external genitalia.
- For the purity of the analysis, douching is strictly prohibited.
- It is forbidden to wash away on the day of the examination, which is necessary for the cleanliness of the sampling of the material.
- Do not urinate 3 hours before the gynecologist's appointment.
- Choose comfortable clothes so that you can easily take off your underwear (pants, skirt, underwear).
 For examination for the presence / absence of chlamydia, it is worth making an appointment with a doctor. It is important that the sampling of the material is carried out not by a nurse, but by a doctor. Otherwise, the probability of detecting an infection drops by half. For the study in the morning on an empty stomach, blood is taken from the patient's vein.
For examination for the presence / absence of chlamydia, it is worth making an appointment with a doctor. It is important that the sampling of the material is carried out not by a nurse, but by a doctor. Otherwise, the probability of detecting an infection drops by half. For the study in the morning on an empty stomach, blood is taken from the patient's vein.
A smear is taken in the gynecologist's office. The smear is taken on the fourth day after the end of menstruation. Material for analysis is taken from the vagina, urethra, cervix with cotton swabs. Scrapings are performed with a probe. After scraping, a woman may feel pain when urinating, slight spotting is possible. This is fine. In municipal gynecology, the analysis for chlamydia is handed over free of charge in the direction of a doctor. In private clinics, the cost of testing for the presence / absence of infection in women varies approximately in a single pricing policy.
The price is formed from the cost of expenses for materials for inspection, depreciation of equipment, rent of space and staff salaries. When choosing a laboratory, the patient should take into account the reputation of the medical center or laboratory conducting the examinations.
The approximate cost of CVD PCR for chlamydia varies from 250 to 300 rubles, sowing for chlamydia - 1800-2100 rubles, blood sampling for chlamydia from 500 to 750 rubles. It is important to know that the absence of clinical manifestations of the presence of infection does not mean its absence at all, therefore, the importance of modern and comprehensive diagnosis of chlamydia should not be underestimated.
A blood test for chlamydia allows you to identify pathogenic microorganisms with high reliability and prescribe the correct treatment. The indications for the study are the presence in patients of signs of an inflammatory disease of the genital organs, deterioration of health, pain syndrome that occurs when urinating. A blood test in laboratory conditions is carried out using different methods. To obtain accurate results, you must familiarize yourself with the rules for sampling the material.
How to prepare for the test for chlamydia and how to take it correctly
There are a number of rules that must be followed when preparing for the test:
- Two days before the sampling of the biomaterial, the patient must exclude alcoholic beverages, spicy and fatty foods from the diet. Abstinence from sexual activity is an important requirement.
- If a man or woman is being treated with antibacterial drugs, the study is not done. The doctor should be sure to notify about the treatment being carried out and familiarize him with the list of medications.
- Do not smoke for several hours before taking blood.
- The recommended time for submitting the material is early morning.
- As with the clinical type of serum testing, tests for chlamydia are performed on an empty stomach.
Chlamydia blood test
Chlamydia pathogens are diagnosed by different methods. The choice of the type of examination is determined by the attending physician. In some cases, a specialist prescribes a comprehensive examination with a smear. The delivery of urine for analysis is rarely prescribed.
Blood test methods
Currently, the following methods are used to detect an infectious sexually transmitted disease:
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which is characterized by high accuracy of results;
- an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay that allows you to determine the phase of the disease and establish an accurate diagnosis by detecting antibodies;
- immunofluorescence reactions carried out using fluorescence microscopy.
Explanation of the results of the passed tests
The results of analyzes carried out by the method of polymerase chain reaction are indicated by the words "not detected" and "detected". Thus, doctors judge the presence or absence of antibodies to chlamydia. The polymerase test is not highly accurate, and in some cases, if there is a sign of the disease, the patient is recommended to undergo a number of other diagnostics.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays are expressed as titers.
A negative result means that an antibody was found in the blood in single values or not at all.
Factors affecting test results
 Laboratory tests show inaccurate results for the following reasons:
Laboratory tests show inaccurate results for the following reasons:
- Taking antibacterial drugs is capable of distorting the analyzes. For a correct study, the body must completely remove the drug. The patient is obliged to notify the attending physician about taking medications!
- Blood should only be drawn on an empty stomach. Eating food will cause high levels of fat particles and increased turbidity in the samples, which greatly complicates the research process.
- Alcohol and smoking also contribute to bias in research results. That is why, one day before the delivery of the material, it is necessary to give up alcohol and tobacco.
- Doctors do not recommend carrying out physiotherapy procedures and apparatus research on the eve of blood sampling.
- Menstrual bleeding and pregnancy are also monitored by specialists.
- Repeated tests for chlamydia, carried out in different laboratories, often show different results. It is advisable to take secondary tests at the same clinic.
When should you get a blood test for chlamydia?
A blood test for chlamydia is required in the following cases:
- when another infectious sexually transmitted disease is detected;
- if the partner has sexual intercourse with another person;
- if one of the couple has symptoms of chlamydia;
- if abnormal discharge or inflammatory processes in the female reproductive system are detected during a gynecological examination;
- when a partner is diagnosed with an infectious sexually transmitted disease;
- when having sexual intercourse with a new partner without using a condom;
- with the appearance of discomfort during urination, pain in the lumbar region and abdomen;
- with subfebrile condition, when the temperature is kept within 37-37.4 degrees for a long period;
- when identifying previously such pathogenic microorganisms as ureaplasma and mycoplasma.
How do you submit material for research?
Currently, chlamydia is defined in several ways:
- To carry out an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, blood is taken from patients (from a vein), scraping (from the urethra, cervix). Blood tests, like the general type of serum examination, must be taken correctly. The procedure is recommended to be carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. If the material for analysis is taken from the urethral canal, then one and a half hours before the procedure, it is necessary to refrain from the urethra.
- The method using the immunofluorescence reaction requires the study of the secretory fluid taken from the urethral canal. To carry out such a study, a sufficient amount of biological material is required, which is stained with special means, and then studied under a microscope.
- To carry out the polymerase reaction, not only blood is used, but also secretions from the cervix and urethral canal, urine, and endometrial tissue.
- To carry out the culture method, a specially prepared medium is required, in which the removed cells are placed. The material for the study is also secretory fluid taken from the urinary canal or cervix.
Decoding the results - norms and deviations

Interpretation of the tests takes about three days. Currently, a number of clinics provide paid services, thanks to which it is possible to get results in your hands in a couple of hours.
Identification of the causative agent of the disease using the culture method requires a longer period of time. The decryption includes the following data:
- name of the type of pathogen;
- indicators of the concentration of microorganisms and the norm - CFU / ml;
- a list of antibacterial drugs that are most effective (if infection has occurred).
If antibiotic therapy gives a positive result in a short time, there is a high probability of receiving false positive tests when diagnosing a patient, which is associated with the presence of single cells of pathogens.
The decision to retest is made by the attending physician.
Obtaining a false negative result is possible if a small amount of time has passed after getting a genital infection: the immune system did not have time to develop antibodies. The results can be transmitted incorrectly also in the case when the rules for the storage of the collected biomaterials were not followed.
The deviation and development of the inflammatory process in the body is indicated by the results of more than 103 CFU / ml.
The price of the issue
The price for diagnostic services and analyzes depends on two factors:
- Clinic status. State medical institutions carry out research free of charge. Frequent hospitals offer advice from a specialist for an amount of $ 7 or more.
- Survey method. The assay using the polymerase reaction is inexpensive. The cost is $ 5. Culture research costs about $ 17.
Where to get tested
Currently, renowned laboratories offer services for the detection of chlamydial infection. Analyzes can be taken at Invitro, Citylab, Sinevo, CMD. These medical institutions are equipped with modern equipment and offer quality service.
Check with the laboratory workers about the time of preparation of analyzes and the rules for passing the material.
It is important to find out where the sampling will be from, indicate the age of the patient (adult or child).