Bacterial vaginosis or gardnerellosis in women is quite common. This is an infection that in women is caused by a special bacterium - gardnerella vaginalis. A small amount of these microorganisms is completely harmless to the body, but as soon as their number begins to increase due to a decrease in lactobacilli, the first signs of the development of gardnerellosis appear. You should not be ashamed of this female disease, because it does not belong to sexually transmitted diseases, does not depend on compliance with intimate hygiene standards, and can develop at any time in women of different ages. Even small girls who do not have a single sexual contact are capable of having a rather adult female disease - gardnerellosis.
Bacterial vaginosis or gardnerellosis in women is quite common. This is an infection that in women is caused by a special bacterium - gardnerella vaginalis. A small amount of these microorganisms is completely harmless to the body, but as soon as their number begins to increase due to a decrease in lactobacilli, the first signs of the development of gardnerellosis appear. You should not be ashamed of this female disease, because it does not belong to sexually transmitted diseases, does not depend on compliance with intimate hygiene standards, and can develop at any time in women of different ages. Even small girls who do not have a single sexual contact are capable of having a rather adult female disease - gardnerellosis.
You cannot find a female person who would have an absolutely sterile vagina. Only newborn girls do not have any microorganisms in their genitals at all, but already about a week after birth, the composition of their microflora begins to change. Before puberty, in about all, it normally has an acidity of pH 5.0.
Everything is different in the body of female adults. They constantly have various organisms in their vagina, so the acidity of the environment decreases (pH 4.0-4.5). Some of the bacteria are completely harmless and must be present in the microflora (lactobacillus), others, like gardnerella vaginalysis in women in the photo, under favorable conditions for her, becomes a real threat and leads to changes in the microflora.
Every healthy woman has a certain amount of lactobacilli in her vagina. These are her protective bodies. They regulate the level of acidity, determine the composition of microflora, and fight microorganisms that can harm health. When one day lactobacilli  lose their activity, this is immediately noticed by harmful microorganisms that were previously oppressed. This is where the time comes to come to the fore gardnerelle. Its rate in a healthy woman is about 103-105 CFU / ml, as soon as this indicator increases, there is a threat of developing gardnerellosis in the woman shown in the photo. They can develop very quickly, but they do not show any resistance. In this case, the female disease either manifests itself or subsides a little. This condition is called chronic gardnerellosis in women. During chronic gardnerellosis, bacteria go deep into the genitourinary system and move into the urethra or cervix. It can last for several years, until one day, upon accidental examination, the doctor diagnoses the disease.
lose their activity, this is immediately noticed by harmful microorganisms that were previously oppressed. This is where the time comes to come to the fore gardnerelle. Its rate in a healthy woman is about 103-105 CFU / ml, as soon as this indicator increases, there is a threat of developing gardnerellosis in the woman shown in the photo. They can develop very quickly, but they do not show any resistance. In this case, the female disease either manifests itself or subsides a little. This condition is called chronic gardnerellosis in women. During chronic gardnerellosis, bacteria go deep into the genitourinary system and move into the urethra or cervix. It can last for several years, until one day, upon accidental examination, the doctor diagnoses the disease.
Causes of gardnerella in women
An excessive increase in the number of vaginalis bacteria in women is the cause of gardnerellosis. Its amount increases significantly due to a sharp decline in the number of lactobacilli. This disproportionate relationship in the vagina between the two groups of bacteria can occur as a result of antibiotic treatment, menopause, or diabetes. It leads to dysbiosis. This is nothing more than gardnerellosis. The number of lactobacilli can be reduced when using intimate hygiene products that cause dry skin. Excessive care of the female genital organs also does not do anything good, but can cause a large number of gardnerella vaginalis in women.
Sex without a condom with a man who had previously had an affair with an infected partner and became infected also becomes the cause of gardnerellosis in a perfectly healthy woman.
Among other reasons involved in the appearance of gardnerella infection in women, one can single out:

Symptoms and signs of gardnerellosis in women in life and in the photo
 Not all even adult ladies know how gardnerella manifests itself in women, therefore, they do not even reveal obvious signs in time. When visiting a gynecologist, patients sometimes complain of an unpleasant odor from the vagina, which is somewhat reminiscent of the stench emanating from rotten fish. At this time, they do not even realize that these are the first signs of gardnerella in women, and such a nasty smell appeared as a result of the active decomposition of amines under the influence of anaerobic bacteria on them.
Not all even adult ladies know how gardnerella manifests itself in women, therefore, they do not even reveal obvious signs in time. When visiting a gynecologist, patients sometimes complain of an unpleasant odor from the vagina, which is somewhat reminiscent of the stench emanating from rotten fish. At this time, they do not even realize that these are the first signs of gardnerella in women, and such a nasty smell appeared as a result of the active decomposition of amines under the influence of anaerobic bacteria on them.
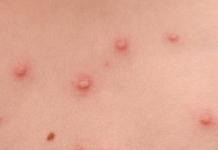
In addition to the unpleasant odor, other symptoms of gardnerellosis in women are also known. Quite often, a symptom of the disease is previously uncharacteristic discharge. Their color is not the same for everyone. It happens that the discharge is grayish-green or yellowish. Very rarely, the discharge can be white, then they are called "whites", or transparent. Their consistency resembles a cream. They stick to the walls of the vagina and hold tight to them. The number of bacteria in vaginosis increases rapidly, so the discharge becomes more and more abundant. Doctors consider such vaginal discharge to be pathological, so they will have to be dealt with immediately, reducing the amount of gardnerella in the body.
Often, vaginosis occurs against the background of inflammation of the genitourinary system. Then, to the mentioned signs of a female disease, other symptoms of gardnerella in women are added. The inflammatory process is accompanied by severe burning or itching, which becomes especially noticeable during intercourse or immediately after it.
Unreasonable irregularities in the menstrual cycle, the appearance of mucous impurities in the bloody discharge, resembling flakes of pus or pieces of cottage cheese, can also become a sign of gardnerella vaginalis.
Approximately 25 - 30% of women who had gardnerellosis had no symptoms at all in the photo. This is a common occurrence in illness, but it cannot be said that the absence of symptoms is a safer course of the disease. On the contrary, when a woman notices the symptoms of gardnerellosis or at least feels discomfort in the genital area, she goes to the clinic and tries to start treatment as soon as possible. If the disease is asymptomatic, this often happens, you can expect various complications, which will be much more difficult to cope with than with the disease detected in the early period of development.
In terms of symptoms, gardnerellosis resembles other genital infections, so a correct diagnosis can be made only after passing a smear.
Treatment of gardnerellosis in women with drugs
 Before starting treatment for gardnerellosis in women, each doctor invites his patient to undergo a diagnosis in order to exclude the presence of other microorganisms that may also be involved in the disease. The most common and accessible is the study of vaginal discharge, if any, or a smear for culture from the mucous membranes of the vagina, according to the results of which the amount of gardnerella and lactobacilli in the microflora is determined. Based on this ratio, the doctor decides how to cure gardnerellosis in a woman using topical preparations and auxiliary procedures such as baths, douching and others.
Before starting treatment for gardnerellosis in women, each doctor invites his patient to undergo a diagnosis in order to exclude the presence of other microorganisms that may also be involved in the disease. The most common and accessible is the study of vaginal discharge, if any, or a smear for culture from the mucous membranes of the vagina, according to the results of which the amount of gardnerella and lactobacilli in the microflora is determined. Based on this ratio, the doctor decides how to cure gardnerellosis in a woman using topical preparations and auxiliary procedures such as baths, douching and others.
The treatment regimen for gardnerella in a woman is based on the form of the disease, the reaction of her body to drugs, the patient's condition, and even the cause of the disease. The most effective drug in the treatment of gardnerella vaginalis in a woman is metronidazole. Let the doctor's decision in choosing pills not scare patients who have already treated trichomoniasis with this medicine, because this drug is ideal for combating many genital infections. And when the question is how to effectively treat gardnerella in women, feel free to use the drugs according to the scheme indicated by the doctor.
Being wary of the side effects of metronidazole, patients will learn how to treat gardnerella in women with other drugs. You can use clion or efloran, but in their composition, the active substance is also metronidazole. Alternatively, choose drugs with clindamycin: clindamycin, dalacin.
When deciding how to treat gardnerellosis in women, doctors prescribe suppositories for the treatment. Suppositories with metronidazole are considered very effective. They create a high concentration of a drug that fights the virus in the vagina, and thereby contribute to a quick recovery by reducing the amount of the virus. In addition to treating gardnerella in women, suppositories are also effective for candidiasis, which is often found in pairs.
When choosing how to treat gardnerella in women, many opt for creams. These are also quite effective remedies that are injected into the vagina twice a day. Your doctor may recommend using creams or gels that contain metronidazole. This is a flagil or metrogil. The course of such therapy usually lasts from 5 days and can reach 10 days if a woman has chronic gardnerellosis.
As an alternative group of creams are drugs with clindamycin. Just once a day for a week, it is enough to inject dalacin into the vagina to reduce the concentration of the virus.
Although the amount of gardnerella vaginalis in a woman's body has decreased, thanks to antibiotic treatment or the use of suppositories, it is too early to talk about complete recovery until the required amount of lactobacilli in the microflora is restored. For this, the doctor prescribes drugs that contain lactobacilli.
Treatment of gardnerella in women with traditional medicine
 Since it does not belong to sexually transmitted infections, herbal preparations are quite effective in treatment. For baths, both tinctures bought at a pharmacy and decoctions of herbs prepared at home are suitable. Effective in this fight are calendula and chamomile, thyme and oak bark, wormwood and yarrow, celandine and eucalyptus, birch leaves and mint. These same herbs can be taken in the form of tea to strengthen the immune system.
Since it does not belong to sexually transmitted infections, herbal preparations are quite effective in treatment. For baths, both tinctures bought at a pharmacy and decoctions of herbs prepared at home are suitable. Effective in this fight are calendula and chamomile, thyme and oak bark, wormwood and yarrow, celandine and eucalyptus, birch leaves and mint. These same herbs can be taken in the form of tea to strengthen the immune system.
At home, you can make tampons soaked in carrot juice and apple cider vinegar. For 1 tampon, take a tablespoon of carrot juice and half of the same spoonful of vinegar. The tampon is inserted into the vagina for 20 minutes after taking hygiene procedures and douching.
Doctors recommend taking baths with salt and potassium permanganate during illness, if there is abundant discharge. This solution kills bacteria and helps to significantly reduce their number. If it is impossible to do such baths every day, you can use the same solution for tampons that are inserted into the vagina in the morning and evening. Medical workers are very wary of douching and do not recommend using them often in the treatment regimen for gardnerellosis in women, because such a procedure promotes the washing out of the beneficial microflora from the vagina, of which there is already an insufficient amount.
For the prevention of bacterial vaginosis, traditional medicine is recommended to drink tea made from sage more often.
Some consider gardnerellosis to be a frivolous female disease and wait until it goes away on its own without the use of drugs for treatment. The imbalance can recover over time and on its own if the reasons that caused it have disappeared (for example, the use of an IUD or condoms with lubricants has been discontinued), but such an independent restoration of the microflora can take a very long time. Think about whether you want to endure such fetid odors, reminiscent of illness, and communicate with your spouse, having unpleasant discharge?
Gardnerellosis, which may also be known to you as bacterial vaginosis, is one of the most common types of infectious pathology that occurs in the genital area. Gardnerellosis, the symptoms of which are predominantly relevant for women of the category of childbearing age and are manifested, first of all, in the appearance of characteristic discharge with a "fishy" odor, may, meanwhile, also occur among men.
general description
Gardnerellosis, as we have already noted, is a fairly common disease. It is caused by a bacterium corresponding to the name that enters the vaginal mucosa. An insignificant amount of these microorganisms can also be contained in the body of a healthy woman, but the manifestation of symptoms characteristic of the disease is accompanied by an excess of the concentration level in the vagina of gardnerella.
Bacteria are usually transmitted sexually. As for other factors predisposing to the onset of the disease, they include pregnancy, hormonal disorders, and a number of other types of endocrine diseases. The duration of the incubation period for gardnerellosis, as a rule, is about 3-10 days.
When considering male morbidity, it can be noted that in this case, gardnerellosis occurs no less often, however, the peculiarities of the course of the disease, characterized by the practical absence of symptoms at an early stage, does not allow its timely diagnosis.
Symptoms of gardnerellosis in women
The most favorable environment for the reproduction of gardnerella is the vagina. The peculiarities of the disease in women consist in mass reproduction, which this microorganism begins to carry out, as well as in the gradual displacement of bacteria that form an environment normal for the vagina. Due to such a violation of the vaginal microbiocenosis, characteristic gynecological inflammations begin to appear.
In addition, abundant discharge of a grayish-green color of a uniform consistency and adhering to the vaginal walls begins to appear. Also, their peculiarity lies in the presence of a specific fishy smell. Among the manifestations, there is severe itching and burning in the genital area.
In particular, an increase in symptoms is noted after sexual intercourse due to the alkaline environment of the sperm. In general, it should be noted that the interaction of secretions in gardenerrellosis with any type of alkali provokes an even greater increase in the unpleasant odor. Accordingly, even the use of soap for hygienic purposes enhances this manifestation.
Neglected cases of the course of the disease often develop into or into. If the disease is relevant in pregnant women, uterine bleeding is possible. In addition, they can also rupture the membranes, and premature birth can begin. Subsequently, as a result of the disease under consideration, the newborn has a low weight, the woman in labor experiences symptoms characteristic of postpartum endometritis.
Gardnerellosis: symptoms in men
Gardnerellosis is an actual disease among men, but their symptoms are mostly absent. This is explained by the fact that gardnerella are bacteria that specifically affect the squamous epithelium, which, in turn, is located in the vagina. In men, only the first 5 centimeters of the urethra are lined with flat epithelium, which, accordingly, affects only the scaphoid fossa. Thus, the male urethra is not the environment that would provide the normal conditions conducive to the development of gardnerella.
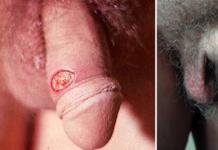
In some cases, in which gardnerellosis is accompanied by any other sexually transmitted disease, it becomes possible to diagnose it, which in other cases practically does not occur due to the characteristics of the disease. The course of gardnerellosis in men can proceed in the form of balanoposthitis. In this case, pronounced symptoms, again, are absent, however, the appearance of a characteristic unpleasant odor in the foreskin and the surface of the head becomes the determining factor for the disease.
In general, for men, it can be noted that the disease is not dangerous. The emergence of serious problems related to reproductive health is noted only in cases of reduced immunity or with a sufficiently high degree of concentration of gardnerella.
Also, medical practice indicates cases in which gardenerllosis in men led to and, as well as to inflammation of the seminal appendages (epididymitis). In any case, the listed serious complications that this disease can provoke are rather an exception to the rule. The male body copes with the causative agent of the disease within two to three days. In a number of cases, men have a carriage of the virus, which, however, excludes the urgency of the appearance of symptoms characteristic of the disease.
Diagnosis of gardnerellosis
Diagnosis of a disease in women involves the need for appropriate laboratory studies of desquamated cells of the vaginal mucosa, as well as secretions. The presence of gardnerellosis is indicated by an increased level of acidity noted in the vaginal environment, a positive result of an amine test and, of course, the presence of directly microorganisms that cause this disease.
It should be noted that a pathogenic bacterium in itself is not yet evidence of the relevance of gardnerellosis, because a small number of pathogenic microorganisms of this type, as we have already noted, is acceptable in a normal and healthy state of the body.
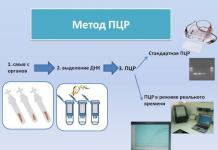
The most informative option for determining gardnerellosis in women is PCR (that is, polymerase chain reaction technology). It can also be applied in the diagnosis of a disease in men in the analysis of semen, urine and scrapings. It is noteworthy that the sensitivity of this method is almost 100%.
Treatment of gardnerellosis
The treatment provided for gardnerellosis in women is in itself complex. This, in turn, provides for a therapy focused on reducing the total number of microorganisms, as well as colonizing the vaginal area with valuable lactobacilli with a general increase in immunity inherent in the body. Pathogenic bacteria are destroyed mainly using local antibiotic therapy. To strengthen the immune system, immunomodulators are used.
The most difficult, as, in fact, and a long stage of treatment for women is the colonization of beneficial bacteria in the vaginal area. In this case, eubiotics saturated with live bacteria are applicable. To determine the effectiveness of treatment, special control tests are used, carried out at intervals of several weeks.
As for the treatment of men, it is carried out at the local level, and there is no need for antibiotic therapy.
To avoid re-infection, therapy should be given to both partners. During the period of treatment, it is strongly recommended to avoid unprotected sex using barrier methods of contraception.
To diagnose the disease and prescribe the appropriate therapy, it is necessary to contact several specialists: a gynecologist, a urologist and a microbiologist.
Gardnerellosis is a disease during which disorders in the genitourinary system occur in both women and men. The causative agent of this disease is an aerobic pathogenic microorganism. In medicine, the female disease in question is called a little differently, namely, bacterial vaginosis. But in each individual case, this disease develops in different ways, affecting various organs of the reproductive system. We will discuss this disease in more detail below.
Gardnerella is a small microorganism. This organism constantly resides in the female vagina and genitourinary organs. Therefore, the detection of gardnerella in a smear is not considered an indicator to diagnose gardnerella. As a rule, the diagnosis can be made in cases where clinical symptoms were found at the same time.
Gardnerellas begin to develop actively after a person has local immunity decreases... This usually happens in the following cases:
- In the presence of a concomitant infectious disease
- During and after taking antibacterial medicines
- After taking medications that lower a person's immunity, such as glucocorticosteroids
- With frequent change of sexual partners
- With diabetes mellitus
- If a person is very addicted to sweets
Gardnerella can be transmitted during intercourse. But the disease can develop only after the failure of dysbiosis in the genital tract and with their loss of beneficial microflora, which loses its own protective function.
Symptoms in women:
Approximately 1/4 of all girls and women are considered carriers of this disease. Moreover, the disease itself may not develop in them, since these carriers have an ideal tension of the immune system.
The rest of the women develop certain clinical symptoms. The main ones are:
- A watery discharge that is grayish-white in color is periodically released from the vagina
- This discharge has an unpleasant odor that often smells like rotten fish.

- During the examination, the doctor may notice how this discharge is evenly distributed over the entire surface of the vagina.
Gardnerellas very often provoke the occurrence of other infectious diseases. These bacteria induce endometritis that develops after childbirth or after an abortion.
Symptoms in men:
The disease is characterized by slightly different symptoms than in women. Often, bacteria provoke the onset of chronic urethritis or chronic prostatitis.

Sometimes these microorganisms can cause the appearance of balanoposthitis. All these forms of manifestation of the disease have certain symptoms.
- Discharge has an unpleasant fishy odor
- The discharge itself is viscous and sticky.
- The head of the male organ becomes very sensitive, it acquires a reddish tint
With a pronounced failure of the immune system, the disease will surely begin to progress. It can even lead to damage to the organs of the genitourinary system.
Treatment of gardnerellosis in women and men
If timely diagnostics and qualified therapy were carried out, there is a chance for a complete recovery and prevention of complications. It is possible that a relapse may occur after treatment.
Through therapy, it is possible to eliminate all the causes of the onset of the disease and its symptoms. Plus, you can normalize the state of the microflora of the woman's vagina.
- At the initial stage, doctors carry out antibiotic therapy. They reduce acid-base levels.
- Depending on the indications, doctors may prescribe an immunomodulator, estrogen, or a drug that has an antihistamine effect. During unpleasant symptoms, the patient is prescribed an anesthetic.
- The next therapeutic stage of treatment is the restoration of the microflora in the vagina. A few days after the antimicrobial treatment ends, the patient is prescribed eubiotics.
- Since the treatment is considered complex, it is strictly forbidden to exclude at least one of the possible stages.

The very same therapeutic course is controlled by laboratories and research. It will end after absolutely all the symptoms have been eliminated, the patient will stop complaining, and his tests will show normal indicators.
Treatment of the disease in men requires an integrated approach. During it, measures are taken that destroy the pathogen and increase the immune system at the same time.
This disease requires immediate treatment, requiring preventive medical and household measures.
Gardnerellosis treatment: drugs
The main treatment of gardnerellosis, as a rule, is carried out with the help of drugs, which include the active ingredient metronidazole. The drug can be applied topically (gels, suppositories) or orally (using tablets).
- Due to their own action against strong anaerobic microorganisms, the following drugs are considered the most effective drugs: "Metronidazole" and "Klion".
- In addition, doctors often prescribe drugs that contain doxycycline, clindamitacin, levofloxacin, and azithromycin.
- Since antibiotics can often cause fungal infections, to prevent them it is necessary to use the following drugs: "Flucostat", "Pimafucin".
- During treatment, it is recommended for women to use medications that normalize the vaginal microflora. For example, "Vagilak" or "Atzilakt".
Treatment of pregnant women practically does not differ from the treatment of ordinary women. Still, there are slight differences. For example, metronidazole is prohibited in the first three months of pregnancy. In addition, it is advisable to use drugs that have a local effect, but not oral.

You should be aware that the human immune system cannot comprehensively fight the disease. Therefore, there is every chance of contracting this disease even during treatment. That is why doctors advise to use condoms during therapy or to abstain from intimacy for some time.
If a condom breaks during intercourse, you need to carry out thorough hygiene and use a local antiseptic, for example, Miramistin.
Gardnerellosis: suppositories for treatment
Gardnerellosis occurs in women, as a rule, in the following cases:
- after prolonged use of drugs, antibiotics
- after frequent douching
- and also those representatives who use spermicides
Such situations greatly disrupt the microflora of the vagina and spread pathogenic bacteria in it. Very often, when contacting a doctor with a complaint of itching and severe discharge, women describe the medicines that they have already used during the treatment of thrush. After all, the symptoms of this disease are very similar to the symptoms of gardnerellosis. However, this disease is more common than candidiasis. And their treatment is different.

During treatment, special pills are mainly used. But there are also candles that contain the same ingredients.
The required dose and time of the treatment period with such drugs is prescribed only by the attending doctor. You can never carry out the treatment yourself. There are situations when after the first course the patient is not completely cured. If this happens, then the doctor prescribes a second course. At the same time, he corrects it.
The most common suppositories that are prescribed during the treatment of the disease are:
- "Metronidazole-suppositories"
- "Metrowagin"
During therapy, it is important to consider the following point: these drugs cannot be combined with alcoholic beverages.
Chronic gardnerellosis: treatment
Chronic gardnerellosis is an infectious disease that does not cause inflammatory changes, but develops the development of dysbiosis in the vagina. This disease is believed to be the result of a decrease in the number of Dederlein rods. It also develops due to pathogenic microbes.
Chronic gardnerellosis in a woman can develop for several reasons:
- The patient does not monitor her own health
- She does not visit the gynecologist on time
- Patient hides complaints during doctor's visit
- The disease develops and becomes chronic due to improper treatment
- Due to non-compliance with the doctor's advice
- The woman's sexual partner is not involved in the treatment

During the treatment of the chronic form of the disease, a combination of several variants of drugs and their administration are used.
- Systemic treatment: the medicine is taken intravenously or through the mouth
- Local treatment: creams or gels are used, which contain metronidazole, as well as suppositories
After the end of the treatment course, a smear is taken from the patient in order to assess the effectiveness of re-therapy. If during such treatment strictly follow all the instructions of the doctor, take the correct medications, then the course itself will be no more than 7 days. The doctor may also prescribe an immunomodulator and vitamins, which will strengthen the protective qualities of the human body.
Gardnerellosis: treatment with folk remedies
This disease can be cured at home with medicinal herbs and plants. Medicines are very easy to prepare. After them, a positive result appears quickly enough. If you are affected by this problem, you can use one of our recipes.
First recipe.
- Medicinal chamomile - 200 g
- Sage - 200 g
- Calendula - 200 g
Cooking process:
- Mix all ingredients
- Fill them with water (2 L). Boil over low heat and boil for 30 minutes
- Cool the finished composition
- Use a douche

Second recipe. For this recipe, stock up on the following ingredients:
- Dry medicinal chamomile - 50 g
- Boiling water - 500 ml
Cooking process:
- Steam chamomile in boiling water
- Set the resulting composition aside for about an hour.
- Strain
- Use to douche
Third recipe:
- If you have gardnerellosis, try oak bark
- To do this, take 100 g of raw materials, fill it with boiling water (500 ml)
- Boil the composition for about 30 minutes, then strain
- For douching, take 250 ml of the product
- Douche them 2 times a day.
The fourth recipe. For this recipe, stock up on the following ingredients:
- Elecampane root - 50 g
- Wormwood - 30 g
- Licorice roots - 30 g
- Raspberry leaves - 30 g
Cooking process:
- Stir all ingredients
- Steam them with boiling water (1 L)
- Leave for 9 o'clock
- Use the resulting composition for douching 2 times a day.

The fifth recipe. If you want to strengthen your own body and saturate it with useful substances, we advise you to use this recipe:
- Take Calendula (50g)
- Pour boiling water over it (500 ml)
- Set aside the composition until it cools completely.
- Drink warm tea throughout the day
Sixth recipe. For this recipe, stock up on a pinch of these ingredients:
- Chopped badan root
- Clover flowers
- Eucalyptus leaves
- Tansy flowers
- Bearberry leaves
- Grushanka
- Leaves of mother-and-stepmother
- Mint
- Yasnotkoy
Cooking process:
- Mix all ingredients
- Take 1 tablespoon of the composition, pour boiling water (500 ml)
- Drink the resulting remedy every day for 1 tbsp. before meals 3 times
Treatment of gardnerellosis with metronidazole
Usually, during the treatment of gardnerellosis, doctors prescribe metronidazole to patients, since this drug is considered the best and most effective. This medicine exists both for local use (suppositories or vaginal tablets) and for systemic use (tablets or capsules plus suppositories).
If treatment with metronidazole is not performed on time, then the number of lactobacilli begins to actively decrease. As a result, microorganisms multiply rapidly.

During the illness, as a rule, there is severe itching in the genital area and an unpleasant burning sensation. And this disease can also cause pain with intimacy.
- Metronidazole Gel is used for topical treatment. The drug must be injected into the inside of the vagina. The introduction is made for about 5 days, 2 times a day.
- Metronidazole tablets are suitable for the systemic therapy of the disease. The drug 0.5 g is applied orally for at least 7 days, 2 times a day. Note that when taking pills, you should not drink alcohol at all.
If we talk about side effects, then, as a rule, they occur very few during intravaginal use than during systemic use. You should know and understand that no medicinal product gives a complete guarantee that there will be no relapse. Therefore, it is advisable not to refuse preventive visits to the treating doctor.
Treatment of gardnerellosis during pregnancy
After a disease was discovered in a pregnant woman, the doctor prescribes therapy for her. This is generally a gentle treatment when compared to a non-pregnant woman. It is impossible to completely eliminate gardnerellosis during pregnancy, since the disease can only be cured with antibiotics. And as we know, such drugs are strictly prohibited for pregnant women.
Therefore, therapeutic measures against this disease are reduced to the use of local procedures. Complete treatment of the disease in the vagina is carried out only after the woman has given birth to a child.
The main task of the doctor in such an interesting period is as follows: he carefully monitors the number of microorganisms in the female body in order to prevent the unexpected appearance of the inflammatory process. During a regular examination for this disease, the doctor examines the woman in the gynecological chair a couple of times a month.

When such an examination is carried out, the woman passes in advance analyzes of the flora, plus for bacterial inoculation. If signs of inflammation are found, she is prescribed a certain local drug, for example, douching, suppositories, and so on. If a disease is detected a couple of weeks before childbirth, a special preparatory process is carried out.
As a rule, treatment is divided into stages.
- The first stage - the doctor prescribes antimicrobial drugs that eliminate negative microflora
- The second stage is the restoration of the fermented milk environment of the vagina
Basically, gardnerellosis in pregnant women disappears after preventive measures are taken to cleanse the microflora and douching. This, of course, is possible, but only if the disease arose precisely during pregnancy or in the absence of its complications.
Based on the foregoing, it is safe to say that a disease such as gardnerellosis can be stopped in almost all cases. The main thing here is the timely detection of this disease and the prevention of its overflow into a chronic form. Numerous reviews of women who have had a similar ailment indicate that modern methods of treatment are very effective if all the prescriptions of the attending physician are followed. Take care of yourself!
Video: Treatment of gardnerellosis in women
Gardnerella (bacterial vaginosis) is a fairly common gynecological disease that develops as a result of an increase in the concentration of the bacteria Gardnerella vaginalis in the vagina. A small amount of these bacteria is in the vaginal microflora of every healthy woman, but only an imbalance of lactobacilli and gardnerella leads to the appearance of symptoms of the disease.
The most common causes of bacterial vaginosis
Gardnerella is characterized by an increase in the concentration of the microorganism Gardnerella vaginalis in the vagina.- Promiscuous sex life;
- constant wearing of panty liners;
- violation of the rules of intimate hygiene during menstruation (untimely change of pads and tampons);
- violation of hormonal balance in the body during puberty and during pregnancy;
- wearing tight-fitting synthetic underwear;
- long-term use of antibacterial drugs;
- immunodeficiency states.
Symptoms of gardnerellosis
The main and, perhaps, the only sign of the disease is abundant discharge from the genital tract, which has a uniform consistency, a grayish-whitish or yellowish color and an unpleasant odor resembling the smell of rotten fish. In half of the cases, in sick women, an inflammatory process in the vagina (vaginitis) is attached. In this case, itching and burning sensation in the vagina appears, which can increase with urination and during intercourse.
When such discharge appears, you should contact your gynecologist for examination. Do not self-medicate, in most cases it turns out to be ineffective. Meanwhile, gardnerellosis can be complicated by vaginitis, colpitis and other gynecological diseases that will require more complex and long-term treatment.
Gardnerellosis in men
The onset of gardnerellosis as a disease in men is impossible. However, the ingress of the bacteria Gardnerella vaginalis into the urethra during intercourse, especially in men with reduced immunity, can lead to the development of urethritis, which, in turn, manifests itself with characteristic symptoms (itching, burning, pain in the urethra during urination). In men with a normal immune status, gardnerella, getting into the genitourinary tract, does not cause any pathological processes. Nevertheless, a man can be a carrier of gardnerella, therefore, with recurrent bacterial vaginosis in women, it is recommended to undergo an examination of her sexual partners.
Treatment of gardnerellosis
 For the treatment of gardnerellosis, drugs are used that have a detrimental effect on the pathogen microorganism, and then drugs containing beneficial microorganisms - lactobacilli.
For the treatment of gardnerellosis, drugs are used that have a detrimental effect on the pathogen microorganism, and then drugs containing beneficial microorganisms - lactobacilli. Treatment of the disease includes two successive stages. Moreover, the second stage without the first will be absolutely ineffective.
1. The first stage is necessary to suppress the excessive growth of opportunistic flora, which includes the bacterium Gardnerella vaginalis. For this purpose, antibacterial drugs (metronidazole, clindamycin) are prescribed, in most cases they are used topically in the form of gels and suppositories, less often in tablet form. The course of antibiotic therapy lasts 7-10 days.
2. The second stage is much more difficult than the first one. It consists in the colonization of the vagina with normal microflora (lactobacilli). Before starting the use of drugs with lactic acid bacteria, it is recommended to pass an analysis to monitor the effectiveness of the first stage therapy, as well as to exclude, which could develop during antibiotic treatment.
Vaginal suppositories Acylact, Lactobacterin, Lactonorm are used locally. Sometimes the doctor prescribes the intake of drugs containing lactobacilli, inside (Lactobacterin, Lactonorm plus).
During treatment, it is recommended to follow a diet that excludes spicy and fried foods, spices, and alcoholic beverages. It is necessary to eat foods containing lactic acid bacteria (biokefirs, bifido yoghurts, homemade kefir prepared with "Narine" -type starter cultures).
Usually, in parallel with the treatment of bacterial vaginosis, the treatment and prevention of intestinal dysbiosis is carried out. Women are prescribed drugs containing prebiotics (Linex, Normoflorin, Bifidumbacterin).
Do not forget that often in the occurrence of gardnerellosis, a weakening of the body's immune defenses plays an important role. In order to correct immunodeficiency, immunomodulatory agents, multivitamins (biomax, vitrum), natural immunostimulants (echinacea, lemongrass) are prescribed.
During treatment, it is advisable for a woman to refrain from sexual intercourse or use barrier contraception.
Evaluation of the effectiveness of the treatment is carried out a week after the completion of the course of taking the drugs and the disappearance of the symptoms of the disease. Re-examination is recommended 1-1.5 months after the first.
Which doctor to contact
If signs of gardnerellosis appear, you should consult a gynecologist. Since this disease does not belong to sexually transmitted infections, a visit to a venereologist is not required. Additionally, you should visit a gastroenterologist and consult with him about the treatment of concomitant intestinal dysbiosis.
Gardnerella - what is it? This type of microorganism is called Gardnerella vaginalis; it is normally present in small quantities in the microflora of women.
Gardnerellosis
Gardnerella is anaerobic, i.e. actinobacterium developing in the absence of air. Its size is slightly more than a gonococcus. Under certain conditions, gardnerella begin to actively multiply and displace the normal microflora of the vagina and urethra. The disease develops gardnerellosis. This disease does not belong to STIs (Sexually Transmitted Infections). What is this bacterium - gardnerella? Photos of this microorganism can be found in medical sources and on multiple sites dedicated to women's health.
Men do not suffer from this disease; gardnerella does not develop in their bodies. But in 10% of cases, they can become the spread of this disease, and with a decrease in immunity, these microorganisms can cause some complications associated with male health:
- Ureaplasmosis.
- Epididymitis.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Cystitis.
The reasons for the development of gardnerellosis

Gardnerella - what is it, and under what circumstances does this microorganism become the cause of the disease? Among the factors contributing to the development of gardnerellosis, the most common are:
- Sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, and other STIs.
- Hormonal disruptions - These can be caused by various factors, such as pregnancy. Gardnerella during pregnancy, like thrush, is often found in smears, and this condition requires certain treatment.
- Diet disorders. So, one of the reasons for the development of this disease may be insufficient consumption of lactic acid products.
- Some contraceptives containing hormones, 9-nonoxynol or spermicidal condoms, as well as the use of antibacterial suppositories and ointments can lead to an imbalance in the vaginal microflora and provoke the development of gardnerellosis.
- Frequent change of sexual partners.
- Decreased immunity and immunodeficiency states.
- Chronic infections leading to an imbalance of the intestinal microflora and the genitourinary system.
- Stress and severe physical and emotional overload.
Symptoms
This disease can be acute or chronic. In the chronic course of this pathology, symptoms may be completely absent. In this case, gardnerella is found in a smear by chance, usually during routine examinations.
In the acute course of the disease, women are concerned about pathological pasty vaginal discharge with an unpleasant "fishy" odor. They are grayish-white in color, the consistency is uniform. During intercourse and urination, itching and burning are disturbing. During a gynecological examination, changes of an inflammatory nature in the vagina, urethra and in the cervical region are noticeable.

Complications
Gardnerellosis, if left untreated, can cause complications such as endometritis (inflammation of the uterus) and adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages). These inflammatory processes in this disease can provoke menstruation, artificial termination of pregnancy, childbirth, as well as intrauterine devices.
Diagnostics
Usually, the diagnosis of gardnerellosis does not cause difficulties. Examination by a gynecologist and the woman's complaints of discomfort, as well as laboratory data (these microorganisms are clearly visible in stained gynecological smears) confirm this diagnosis. When evaluating laboratory data, attention is paid not only to the presence of the pathogen in the smear, but also to its quantity - this is what makes it possible to make a diagnosis. The ratio of microorganisms in the obtained vaginal secretion is also assessed.
Gardnerella during pregnancy. What threatens the baby?
These microorganisms can cause inflammation in the body of a pregnant woman. As mentioned above, this can be facilitated by a change in hormonal levels during pregnancy.
Gardnerella - what is it, and how can this microorganism threaten the fetus?
If a similar disease develops during pregnancy, then while the child is in the womb, he is not in danger, because it is protected by the placenta. Infection of the baby occurs during labor during the passage of the birth canal. But gardnerella is not a highly pathogenic microorganism, moreover, it can carry out its vital functions only without access to air, therefore, after hygienic treatment of a newborn, such infection, as a rule, passes without a trace and complications. But this disease, with an untreated, advanced form, can lead to the birth of a baby with a lack of weight or provoke the development of pneumonia and other pathologies in him after birth.

What is the danger of gardnerellosis for the expectant mother?
Gardnerella - what is it, and how is it dangerous for a pregnant woman? For the health of the expectant mother herself, this microorganism is not so harmless. It is capable of causing an inflammatory process of the genitourinary system, abnormal uterine bleeding, premature rupture of the membranes during childbirth and complications in the postpartum period, such as the development of endometritis and possible infertility in the future.
Treatment
With gardnerellosis, treatment is mandatory. The causative agent of this disease is resistant to sulfonamides, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides and tetracycline drugs. The disease is treated with Metronidazole (Trichopolum). It is prescribed for oral administration, one tablet per day for 7-10 days. In addition, vaginal tablets or Metrogyl or Flagil gel are used.
Men do not need to treat gardnerellosis. But if a woman (sexual partner) is planning a pregnancy, then both need to be treated.
Prophylaxis
Violation of the vaginal microflora often occurs due to a decrease in immunity, therefore, it is recommended to take vitamins and eat properly during pregnancy.

When treating serious diseases with antibiotics, one should not forget about immunostimulation. Permanent parterres are a reliable way to protect yourself from STIs. Compliance with basic hygiene rules is also an important step in prevention.