The tree peony (Paeonia x suffruticosa), or semi-shrub is a hybrid species belonging to the genus peony of the peony family. There are scientists who believe that they are not a species, but simply a group of different varieties and hybrid forms. To date, about 500 of them are known. Most of them can be found in China. The tree peony was created by breeders in China. But at the same time, breeders of Japan also began to grow this plant with great passion after it appeared on their islands during the Tang Dynasty. In European countries, this plant appeared in the 18th century, and it was appreciated by both professional flower growers and amateurs.
The tree peony is a deciduous shrub that ranges in height from 150 to 200 centimeters. Thick erect shoots are pale brown in color. Unlike a herbaceous peony, the stems of such a plant do not fade in autumn, but every year they grow more and more, and over time the bush acquires a hemispherical shape. Ornamental, openwork leaves are doubly feathery. The flowers are located at the ends of the stems and range in diameter from 12 to 20 centimeters or more. Such flowers are double, semi-double and simple. They can be painted in white, purple, yellow, pink, crimson, as well as bicolor. With age, flowering becomes more and more abundant. The flowering of such a peony begins 2 weeks earlier than the herbaceous one, and its duration is 14–21 days. Such peonies are resistant to cold.
Types and varieties of tree peonies with a photo
The various varieties of such plants are based on several species that are natural, namely: yellow, Potanin, Lemoine and Delaway, which are directly related to the group of semi-shrub peonies. Most of the registered varieties of these plants grow in China. These varieties are divided into 3 groups:
The flowers are very large and double. They weigh a lot and therefore are drooping. Flowers can be painted in various shades from fuchsia to light pink.
The flowers are not very large and light. They seem to float above the bush.
Created from Delaway peony and yellow peony - the most popular varieties are with yellow flowers.
The most popular varieties:
The pink-shaped inflorescences are painted in 2 colors, so, one half of it is dark red, and the other is creamy white. The flower reaches 16 centimeters in diameter.
The diameter of light pink flowers with a dark crimson center is 18 centimeters. About 50 flowers can open on a bush at the same time.
Crown flowers are painted in 2 colors: white and salmon at the same time. They reach no more than 20 centimeters in diameter.
The flower shape is very effective and unique. It is a pale green bud.
Landing rules
Experts advise planting a tree-like peony in open ground from mid-August to the last days of September. Before you start directly landing, you need to choose the most suitable place. For this plant, you should choose a well-lit place located on a not very high elevation. There should not be any buildings or trees in the immediate vicinity, as they will block the sun. Tree peonies prefer loamy soil. In the event that it is sandy, then this can be corrected by introducing humus, sod soil, clay, and also peat. If the soil is clayey, then organic fertilizers, as well as sand, need to be added to it. It is worth paying special attention to the choice of place and soil, because this type of peony can grow in the same place for several decades (about 100 years).
Autumn planting
In the case when the groundwater is low, the hole for the flower must be made in the form of a cone. At the same time, at the soil surface, the diameter of the hole should be 0.7 meters, its depth is also 0.7 meters. Make a drainage layer 25-30 centimeters thick at the bottom of the pit, gravel, broken brick or sand are perfect for this. Pour lime or bone meal from 200 to 300 grams into acidic soil. After that, soil is poured into a hole in the form of a cone and a peony is placed on it. Then a large amount of water is poured into the hole in order to properly straighten the peony roots. When the liquid is completely absorbed, such an amount of soil must be poured into the hole so that the root collar of the plant is located at the same level with its surface. The distance between the bushes should be about 150-200 centimeters.
Growing tree peonies from seeds
If a tree peony is grown from a seed, then its flowers can be seen only for 5-6 years of life. Since these seeds have an underdeveloped embryo, they must certainly be subjected to a stratification procedure. Seeds cannot be stored for a long time, as they lose their germination capacity. The stratification procedure has 2 stages. The first is warm and the second is cold. Subject to all the rules, not everyone succeeds in growing a peony from a seed anyway.
How to care
In the event that you do not know the rules for caring for this type of peonies, then you should take care of it in the same way as for a herbaceous one. So, it must be watered in a timely manner and after this procedure it is imperative to loosen the soil and remove weeds. Watering should be done once every 2 weeks, while 1 bush should take from 6 to 7 liters of water. If the weather is hot and dry, then the frequency of watering should be increased. Since August, it is necessary to water less and less each time until it stops completely. When the plant is watered, the soil near the bush within a radius of 50 centimeters must be thoroughly loosened (the depth of loosening is not more than 5 centimeters). Pull up all the weeds and sprinkle the soil with mulch (humus).
Fertilizer
These plants simply need a lot of nitrogen and potassium for normal growth and development. When the period of intensive growth is just beginning, such plants need nitrogenous fertilizers, and from the moment the budding begins until the growing season ends, tree peonies need a large amount of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers. When the flowering period begins, the plant will need both phosphorus and potassium, and nitrogen. But at the same time, do not forget that an excess of nitrogen in the soil can cause the development of gray rot. In order not to burn the root system with fertilizers, before applying them to the soil, it must be well watered.
Pruning features
Pruning must be done in the spring before the start of the intensive growth period. In this case, you need to cut off the dried stems. Old shoots must be cut off so that about 10 centimeters remain. Florists in China have learned to rejuvenate the tree peony. To do this, once every 20 years, they cut the bush almost to the surface of the soil. As a result of this, the adventitious buds awaken at the very base of the stems. In order for the flowering to be more abundant next year, you need to trim the stems to the upper axillary bud. How long your peony will live is influenced by the correct pruning. These plants can live to a very respectable age, usually up to a hundred years or even more. In China, there are copies that have already exceeded 500 years, while they are protected both by specialists and by law.
Such a peony is very negative about the transplant. So, it happens that a very strong transplanted plant can get sick for several years, because it is very difficult for it to recover. During the transplant procedure, you need to be very careful with the bush. So, it must be very carefully dug out together with a lump of earth, which is then gently washed off with a not very strong jet of water. Then you need to inspect the root system. If there are rotten roots, then they should be cut off, and too long are shortened at the same time. It is necessary to process the cut sites with a solution of potassium manganese (1%), and then sprinkle with chopped charcoal. If necessary, you can divide the rhizome, thereby multiplying the peony. To do this, you need to stretch the parts of the bush with your hands to the sides at the root collar. In the event that there are cuts on the rhizome, then they must be processed. Each of the divisions should have roots and replacement kidneys (several pieces). Before the delenki are planted in open ground, they must be immersed in a clay talker for 30 minutes.
How to propagate by dividing a bush
How to propagate a peony by dividing a bush is described above. It should be remembered that only the peony whose age is older than 5-6 years can be divided, and this procedure must be carried out in August.
How to propagate by cuttings
For cuttings, semi-lignified shoots are required. They need to be cut from mid-June. At the same time, the bud itself, the leaf and part of the stem wood should be present on the handle. The sheet plate should be shortened by ½ part. Prepare the container by filling it with peat mixed with sand. Then a stalk is stuck into it one and a half centimeter deep, and on top of the container it is necessary to cover the container with a transparent film or glass. The cuttings must be systematically watered, as well as humidified from a sprayer. In the last days of September, the cuttings should be transplanted into individual pots and placed in a greenhouse before the onset of spring. After the plants start growing, they are ready to be transplanted into open soil.
It will take a couple of years to propagate a tree peony by layering. On May days, before the bush begins to bloom, it is necessary to select well-developed stems and an incision should be made on the side that faces the soil. It is then treated with a root-growth agent and a peg is inserted into it. After that, the shoot must be bent to the surface of the soil and dug in to a depth of 8 to 10 centimeters. When watering the bush itself, do not forget to moisten the soil above the layer. In the month of September, small roots should already grow on the layer, and it can be carefully separated from the mother bush and planted in open soil in a permanent place.
For reproduction, you can also use air layers. To do this, you need to make an incision on the stem and wrap it with moistened moss, and on top with a film. It must be tightly fixed. As a rule, the roots grow towards the end of the summer period. This breeding method, although very simple, is ineffective.
How to propagate by vaccination
This method is the most highly effective, and it is widely used by specialists. But a gardener can also propagate this plant by grafting. For grafting, use the root system of a herbaceous peony. To do this, in the first days of August, you need to cut tree cuttings with 2 buds from a peony. From below, the stalk must be sharpened so that it takes on a wedge-shaped shape. Then, according to the shape of this wedge, a groove is made in the rhizome of the herbaceous peony and a stalk is inserted into it, which should fit very tightly. The vaccine must be wrapped tightly with foil. Then these rhizomes must be placed in a box, which must be filled with moistened sawdust. Place the box in the shade for storage. After 4 weeks, the grafted rhizomes must be planted in a container so that the peephole located below is at a depth of 5 to 7 centimeters. The container is then transferred to the greenhouse. Such a peony is grown from 1.5 to 2 years.
They are quite disease resistant. Most often, those peony bushes are sick that are old or have recently undergone a transplant. Gray mold can kill the plant. In order to get rid of it, you need to treat the bush with a solution of potassium permanganate (for 5 liters of water, 1.5 g of the substance). Also for this purpose, you can use a solution of copper sulfate (6-7%). However, before starting treatment, the affected shoots should be carefully cut and destroyed.
It happens that the bushes become infected with brown spot. Infected leaves should be torn off and destroyed in order to avoid further spread of the disease. Then the peony is treated with a solution of Bordeaux liquid (1%).
Arboreal peony after flowering
After the end of flowering, you need to cut off the faded stems to the upper axillary bud so that they do not take away the strength from the bush. In the autumn, before wintering, you need to feed. To do this, 200 grams of bone meal and 300 grams of wood ash must be added to the soil under each bush.
Preparation for wintering
As mentioned above, tree peonies are not afraid of frosts, but you still need to shelter them for the winter. The fact is that during the thaws in the spring, the buds that are in the open air wake up, and the peony begins to grow. However, frosts that follow a thaw can cause the death of this plant. In this regard, in October it is worth preparing the bush for wintering. To do this, you need to tie the stems and sprinkle the near-stem circle with a layer of mulch (peat). After the frosts begin, the bush must be covered by making over it a kind of hut of dry leaves, spruce branches and a fairly thick layer of fine bark. You can use jute bags for this.
Processing peonies in spring and summer from diseases and pests is a primary measure to combat these misfortunes. Most often, these plants are damaged by gray and root rot, rust and ring mosaics. Gall nematodes and ants do no less harm to peonies. To protect the crop from infections and pests or to cure already developed diseases, there are many drugs, and you will learn about the most effective of them from the table on this page.
Treatment of peonies from gray rot

Gray rot (Botrytis) — Botrytis paeonia Oud- the main and most widespread disease of peonies in our strip. As a rule, symptoms of gray rot appear on peonies either in spring (in central Russia - in the third decade of April, especially intensively - in the wet season), or in summer - in early autumn (when it rains and the air humidity is high, with increased soil acidity , excess nitrogen fertilizers, heavy clay soils, high groundwater levels, thickened plantings, unventilated areas).
The most dangerous for plants is the spring outbreak of the disease, at the time of active growth of shoots.
As you can see in the photo, with this disease at this time, shoots with very soft tissues are affected at the place where the stems emerge from the ground:


A rotten dark area appears on the side of the stem. Very soon the stem falls off. Black sclerotia are visible on decaying tissues.
In other years, at high temperatures during the period of active growth, the stems in the middle part are affected by the gray rot of peonies: the plant bends in this place, the top withers. If the soil is carefully shaved off, on the underground part of the damaged shoot there will be noticeable damage to the base of the stem with Botrytis. It is believed to be the result of a short spring that quickly turns into hot weather in May.
After sufficient regrowth and hardening of the stem tissues, in the third decade of May, the stunted and weak stems are mainly affected.
The second time the appearance of the disease can be observed in the summer-autumn period. Buds, sepals, petals (at the base) rot, brown spots with a gray bloom appear on the leaves, stems and leaves darken and dry out. Brown rings are visible when the diseased stem is cut.
We note once again that the cold season, rains and high humidity contribute to the external manifestation of Botrytis.Almost any adult plant, to one degree or another, in the underground part shows traces of damage by Botrytis: on the remains of last year's stems and in the zone of their transition to the rhizome, on old ones, starting to wither away, roots. But with the correct culture, its external manifestations will be absent or insignificant throughout the life of the plant.
For the treatment of gray rot of peonies, you must:
- compliance with the rules of planting and plant maintenance;
- periodic introduction of deoxidizing additives into the soil (bone, dolomite, limestone flour);
- removal and destruction of damaged parts of the plant;
- mandatory and timely full pruning of the stems in the fall;
- limited use of nitrogen fertilizers;
- the use of fungicidal preparations and agents for the prevention and suppression of the disease.
Most of the fungicides produced by the chemical industry are suitable for controlling botrytis. Among them are well-known and approved for a long time: all copper-containing, basezol, colloidal sulfur. Terms of their application: in spring, at the beginning of active growth of stems, in our strip in the third decade of April, and then another 1-2 times with an interval of 10-12 days, depending on the weather and the degree of damage to plants. It is necessary to strictly follow the recommendations for the dosage of drugs and observe safety measures.
To combat this disease of peonies, the following rules must be observed:
- It is better to alternate between different agents, this contributes to their more effective action and reduces the accumulation of hazardous drugs in the ground. For example, you can alternate: foundationol - 0.3% (or equivalent), oxychloride - 0.3% (copper sulfate - 0.5%) and a solution of potassium permanganate - 0.03%.
- The concentration of preparations with a burning effect (copper sulfate) in spring when spraying young plants should be half that for adults. At this time, young tissues are too soft and delicate, easily damaged. Aim to use a minimum of chemicals while protecting yourself, fauna and soil. Spray if possible, and when watering only moisten the topsoil above and around the plant using a small-hole watering can. Then you can limit yourself to the norm of 0.5-1.0 liters per peony. No watering of the plant from above!
These photos show the treatment of peonies for gray rot disease:


Fighting Peony Root Rot


Root rot. Peonies are also affected by pathogenic fungi from the genera Fusarium, Sclerotinia, Rhizoctonia, Phytophtora. According to my observations, diseases are rare and it is quite difficult to distinguish between different rot. Outwardly, the disease manifests itself in the sudden blackening of the stems and their wilting in the middle of summer. Excavated roots look brownish, softened to mucus, and give off an unpleasant odor. The affected bush is dug up and destroyed.
The causes of the disease are the same as in Botrytis: wet weather, flooding of the site with melt and rainwater, thickened plantings, unventilated areas, acidic soils and re-planting in a place previously occupied by peonies.
Control measures:
- using healthy planting material;
- correct fit;
- the use of phosphorus-potassium fertilizers and microelements;
- for the treatment of this disease of peonies, it is necessary to use fungicidal preparations: copper sulfate, Homa, foundationol (0.2%) and others indicated in the table.
Peonies treatment for rust and stains


Rust — Cronartium flaccidum (Alb. & Schw.) Wint... The disease manifests itself in the summer, usually after. Brown or purple spots become visible on the upper side of the leaves, orange-brown spots on the lower side. Later, the leaves dry up and curl. The stems look unharmed. The host of the causative agent is Scots pine.
Control measures:
- collecting and burning diseased leaves;
- spraying (wetting) the leaves with fungicidal preparations, the same as for gray rot. It is recommended to add a solution of laundry or green soap, a pinch of washing powder as a means of holding the preparation on sheet plates.


Spotting. A number of different and difficult to distinguish from each other diseases affecting peonies are known. They cause premature death of leaves and stems. Diseases develop actively at high humidity and temperature. Disease-causing fungi remain on plant debris.
Control measures:
- collecting and burning affected leaves and stems;
- spraying the entire plant with fungicidal preparations, as is the case with rust;
- thorough cleaning in autumn and burning of plant residues of peonies.
Peony disease mosaic: photos and videos of the fight against it


Ring mosaic virus (Ringsort virus) outwardly manifests itself in the summer after the regrowth of the stems, before flowering. Symptoms vary by cultivar and species. Most often, rings, half rings and stripes appear on the leaves, yellow or lighter than the main color of the leaf plate. The rest of the plant does not look depressed, it blooms normally.
The disease spreads when flowers are cut in summer and stems in autumn, as well as insects sucking the plant sap, in particular aphids. The disease is poorly understood and behaves rather mysteriously: it can disappear on the plant, and then reappear after a few years.
Opinions about the control measures are very contradictory: from immediate destruction of the plant at the slightest manifestation of the disease to the option “do not touch the plant even if it is completely infected”. It is suggested that the disease in a latent form exists in many varietal peonies, outwardly not manifesting itself for many years.
Control measures... Starting from the moment of regrowth, very carefully monitor the foliage of the peonies. Usually, signs of the disease appear before flowering of the bush, initially on only a few stems of the plant, the leaves of the remaining stems remain normally colored. The affected stems must be removed without residue (unscrewed), sprinkle the wounds with ash. Cut flowers and stems from the affected plant with a separate knife and burn. It often happens that further traces of the disease do not appear. If the next year the damage to the plant is insignificant, repeat the above procedure.
See how the fight against peony disease is carried out in these photos:


If the disease does not disappear, but has captured most of the plant, it is dug up and destroyed. In all cases, if the appearance of a disease has been noted on the peony at least once, in the future, when working with it, it is necessary to use a separate tool. Avoid varieties that are susceptible to disease.
The video "Diseases of peonies" demonstrates the most effective measures to combat ailments:
The following describes how to get rid of nematodes and ants on peonies.
How to get rid of nematodes and ants on peonies




Ants. Often these insects are considered pests of peonies. They refer to the fact that ants suck the juice from the buds and, having settled under the peony, destroy the plant. But many pinovodists believe that if there is harm from ants, then it is very small. During the budding period, the ants feast on the nectar that is on the bud. If this annoys you, wash the buds with warm water. However, in recent years, a new population of ants has appeared, which settle on the buds and severely deplete them, interfering with flowering.
To get rid of ants on peonies as quickly as possible, you need to spray the buds with a fufanol solution. As for the settlement of ants under the peony, this means that the plant is seriously hurt and badly rotted. And ants are not a cause, but a clear signal of trouble. Ants do not settle under a healthy peony. We'll have to dig up such a plant and sort it out on the spot.
Preparations for processing peonies in spring and summer against diseases and pests
From the table below you will find out.Further you will learn how to treat peonies in spring and summer against diseases and pests.
Preparations for the fight against diseases and pests of peonies
| A drug | Diseases and pests of peonies | Condition and processing time | Processing method | Norm application |
| Copper oxychloride (HOM) | Botrytis, root rot | With the manifestation of symptoms of botrytis; when root rot appears | Watering under the base of the bush |
0.5% solution with repetition of treatment after 10 days |
| Copper vitriol |
Botrytis | When symptoms of botrytis appear | Watering under the base of the bush; spraying the plant itself | 0.5% solution (no more!) Repeated after 10 days |
| Alirin | Root and root rot, late blight | Before boarding | Application to the planting hole and 2-3-fold watering during the growing season | 1 tablet / 1 l of water |
| Powdery mildew, late blight, anthracosis, septoria, gray rot | During the growing season | Spraying (2-3 times) until the symptoms of the disease disappear | 2-3 tablets / 1 liter of water. Effective at temperatures above 7 ° C |
|
| Maksim | Gray rot, root rot | Front landing |
Soaking the cut (for 30 min) | 2 ml / 2 l of water |
| During the growing season | Watering the soil | 2 ml / 1 l of water | ||
|
Fitosporin M |
Fungal and bacterial diseases: rot, rust, powdery mildew |
Before boarding |
Soak |
10 drops / 200 ml of water |
|
During the growing season |
Spraying |
20 drops / 200 ml of water |
||
|
Powdery mildew, spots, botrytis |
Before boarding |
Tillage |
3-5 g / 1 l of water |
|
|
During the growing season |
Spraying |
1-3 g / 1 l of water |
||
|
Root and root rot, late blight |
Before boarding |
Tillage |
1 tablet / l l of water |
|
|
Bacterial spots, late blight, powdery mildew, rot |
During the growing season |
2 tablets / 10 l of water |
||
|
Preventive spraying before and after flowering |
2 tablets / l l of water |
|||
|
Fungal diseases |
At the beginning of the growing season |
Preventive |
2-4 ml / 10 l of water |
|
|
With a strong defeat |
Spraying |
10 ml / 10 l of water |
||
|
Rust, powdery mildew, black spot, rot |
During the growing season |
Spraying |
Prevention 5 ml / 10 l of water |
|
|
Leaves processing on both sides |
10 ml / 10 l of water |
|||
|
Insect pests In contact with |
The most common diseases of pions are gray rot (botrytis), rust and annular mosaic of leaves.
Gray rot(pathogen - Botrytis paeonie, B. cinerea). This is one of the most dangerous and most common peony diseases. In our floriculture zone, gray rot affects the stems, buds, leaves, and the underground part of the plant. Young shoots are most often affected in the spring during the regrowth period. A gray bloom appears at the base of the stem, then the stem here darkens, breaks and falls. Large brown spreading spots appear on the tips of the leaves. The leaves become deformed and dry out. Small buds turn black and dry out too. Larger buds open halfway, only on one side, the edges of the blossoming petals turn brown and dry, the flowers are disfigured. The disease develops especially actively in damp and cold spring. During the budding period, gray rot often affects the upper part of the stems, buds and leaves.
Spores of the fungus overwinter on plant debris, peony rhizome, in the upper soil layer near the bush. It develops more intensively on heavy, clayey soils and in areas with close groundwater flooding, in thickened, poorly ventilated plantings, as well as in areas flooded with spring melt water. An excess of nitrogen fertilizers contributes to the development of the disease. The early-flowering forms of the medicinal peony and many hybrids are especially strongly affected. If severely damaged, the entire plant may die.
The fight against the disease is carried out in two directions. The first direction provides for the correct agricultural technology: non-thickened planting; regular loosening of the soil; exclusion of overfeeding with mineral fertilizers; removal and burning in the fall, immediately after pruning, of all plant residues and the aerial part of the peony bushes on the site; drainage of the site in case of close occurrence of groundwater. Another direction is preventive measures for the destruction of fungal spores using chemical antifungal drugs - fungicides. The use of fungicides does not replace the complex of agrotechnical measures, but only supplements it. With poor agricultural technology, fungicides do not save from disease, since weakened plants, as a rule, are not able to resist the disease.
There are a large number of fungicidal preparations. Most of them are toxic and require great care when applied. Only the least toxic drugs can be used on household plots. At the time of germination, the spores of the fungus are quite easily vulnerable even to non-toxic fungicides - copper oxychloride, copper sulfate, Bordeaux liquid, etc. The only condition for their successful use is compliance with the exact processing time.
Usually, two or three preventive treatment is carried out with an interval of 10-12 days: the first is watering the bushes with one of the fungicide solutions at the beginning of the growing season when buds appear above the ground (2-Zl solution per bush); the second and third - spraying plants with one of the fungicide solutions. In the future, when gray rot appears on the stems, they are immediately cut out to the rhizome and the site of the lesion is poured with one of the fungicides (1 liter of solution per bush).
Least toxic fungicides:
copper sulfate (50-70 g per 10 liters of water);
copper oxychloride (60-70 g per 10 liters of water);
colloidal sulfur (60-100 g per 10 liters of water);
Bordeaux liquid (100 g of copper sulfate and 75 g of quicklime); the components are dissolved separately, then a solution of copper sulfate is poured into the lime solution and the mixture is added with water to 10 liters;
Burgundy liquid - prepared in the same way as Bordeaux, but instead of lime, take soda in the same amount;
potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) - 3 g per 10 liters of water;
lime-sulfuric broth (200 g of sulfur and 100 g of lime per 10 liters of water); quicklime is slaked in a little water and then sulfur powder is added. Add water to 10 liters and boil for 1 hour; the resulting mother liquor is diluted before use in the ratio of 200 g of solution to 10 liters of water.
Good results in the prevention of combating gray rot are obtained by spraying peonies in autumn with a solution of nitrafen at a concentration of 200 g per 10 liters of water after cutting and burning the aboveground part of the plants. Of the methods of plant protection that are harmless to humans and animals, more often than others, amateurs use the treatment with an infusion of garlic (3-5 g of minced garlic per 1 liter of water).
Rust. A dangerous fungal disease, very common in some years. After flowering (in the middle zone - the first half of July), yellowish-brown spots with a purple tint appear on the leaves. The spore pads of the fungus are visible on the back of the leaves. Spores are carried by the wind and infect new plants.  The disease spreads quickly - in two to three days, especially in humid warm weather, peony bushes on large areas can be affected. Leaves curl and dry out. The accumulation of nutrients in old roots and the growth of new ones stop, which negatively affects the establishment and development of renewal buds, and, consequently, the flowering of the next year. Plants are weakened, the likelihood of their being affected by other fungal diseases, in particular gray rot, increases.
The disease spreads quickly - in two to three days, especially in humid warm weather, peony bushes on large areas can be affected. Leaves curl and dry out. The accumulation of nutrients in old roots and the growth of new ones stop, which negatively affects the establishment and development of renewal buds, and, consequently, the flowering of the next year. Plants are weakened, the likelihood of their being affected by other fungal diseases, in particular gray rot, increases.
The fungus, the causative agent of rust, develops on a pine tree in the second half of summer, in the branches of which the mycelium remains and hibernates. For the prevention of rust, like other fungal diseases, the complex of agrotechnical measures given above is of great importance. Plants are prophylactically sprayed with fungicides after flowering at intervals of seven to ten days, as well as immediately when signs of disease appear. You can use the fungicides listed above to prevent gray mold control. Such preventive spraying, combined with a complex of agrotechnical measures, allows minimizing plant damage. At the first sign of illness, the leaves should be trimmed and burned.
According to long-term observations, different varieties of peonies are unequally affected by rust. All varieties, according to their tendency to be affected by this disease, can be conditionally divided into three groups:
strongly affected by rust (massive leaf damage, wilting of the entire bush - Albatr, Graziella, Duchesse de Nemours, Marcella, Cornelia Shaylor, Phase Top, all forms of officialis;
moderately affected varieties (presence of a heel, damage to a small number of leaves) - Argentina, Anshantress, Iceberg, Akron, Blush Queen, White Parus, Gladys Hodson, Dr. Bretour, Inspector Lavsrny, Lady Keith, Le Sin, Masere Choice, Nadezhda, Nick Shaylor , Torch Song, Felix Suprim;
not amazed - A. E. Kundred, Amalia Olson, Arkady Gaidar, Alice, Anne Cousins, Ballerina, Belle Doisier, Beat Red, Boomer Suner, Bowl of Cream, Beat Ben, Varenka, Evening Moscow, Gardenia, Glory Hallelujah, JC , Dixie, John G. Widgell, Dandy Dan, Jensign Mariarty, The Fleece, Kansas, Carl Rosenfield, Casablanca, Lillian Gamm, Linnaeus, Lady Orchid, Marilla Beauty, Margaret Clarke, Mont Blanc, Myrtle Gentry, Miss America, Eli Monsieur Jiet Mary Brand, Neon, Opost Desser, Orlando Roberta, Otens Red, Memory of Paustovsky, Memory of Gagarin, Peppermint, Pink Lemonade, Victory, Princess Margaret, Rayon Line, Red Red Rose, Red Cap, Red Dandy, Sarah Berry Sandy, Seedling. 310/59, Sinbad, Solange, Sir John Franklin, Solveig, Walter McIns, Felix Kruss, Festival Maxima, Philippe Rivoir, Florence Ellis, Evangjeian Newhall, Helen Cowley, Edwin C. Bills.
Using the above list, amateur flower growers may not carry out preventive spraying against rust of all plantings of peonies, but choose only those varieties that are susceptible to this disease, or exclude such varieties from the collection. Most varieties of domestic selection are not affected by rust or are affected to an insignificant extent.
Circular mosaic of leaves(pathogen - Paeonia virus). Viral disease.  On the leaves between the veins, light green and yellowish stripes, rings, half rings are formed, which reduces the decorative effect of the bushes, but does not reduce the growth and abundance of flowering. Disease can be spread by using a single knife to cut flowers or cut stems from diseased and healthy plants without intermediate thermal disinfection of the instrument. Both sick and healthy shoots grow on the bushes at the same time. During the budding period, diseased shoots should be cut to the rhizome and burned. In case of severe damage or re-manifestation of the disease, the plant is destroyed entirely.
On the leaves between the veins, light green and yellowish stripes, rings, half rings are formed, which reduces the decorative effect of the bushes, but does not reduce the growth and abundance of flowering. Disease can be spread by using a single knife to cut flowers or cut stems from diseased and healthy plants without intermediate thermal disinfection of the instrument. Both sick and healthy shoots grow on the bushes at the same time. During the budding period, diseased shoots should be cut to the rhizome and burned. In case of severe damage or re-manifestation of the disease, the plant is destroyed entirely.
Brown spot, or septoria(pathogen - Septoria macrospora). The disease manifests itself on the leaves in June - July in the form  bilateral brownish-brown, rounded or elongated spots with a darker rim. First, single spots appear, then they merge. First of all, the lower, older leaves are affected, then the disease spreads higher along the stem, and all leaves can dry out. The disease weakens the plant, affects its winter hardiness and blooms next year.
bilateral brownish-brown, rounded or elongated spots with a darker rim. First, single spots appear, then they merge. First of all, the lower, older leaves are affected, then the disease spreads higher along the stem, and all leaves can dry out. The disease weakens the plant, affects its winter hardiness and blooms next year.
Brown spot, or cladospariosis.(pathogen - Cladosporium paeoniae).
 The disease manifests itself in the form of large brown spots, growing, they merge and cover the entire leaf, which looks like burnt. Elongated reddish-brown spots are formed on young shoots. The entire stem darkens and becomes covered with smoky sporulation of the fungus.
The disease manifests itself in the form of large brown spots, growing, they merge and cover the entire leaf, which looks like burnt. Elongated reddish-brown spots are formed on young shoots. The entire stem darkens and becomes covered with smoky sporulation of the fungus.
CONTROL MEASURES: spraying with one of the preparations: 0.6-0.7% copper oxychloride solution, 1-2% Bordeaux liquid solution or 0.2-0.3% foundation. The first spraying is right after flowering. As needed - every 10-12 days.  Powdery mildew. Peonies are amazed by it on the slope of summer. A rare cobweb bloom forms on the upper part of the leaves. This disease on peonies, fortunately, does not bring much harm and does not occur very often. CONTROL MEASURES: it is possible to spray the plants when the first signs of the disease appear with a solution of soda ash and soap.
Powdery mildew. Peonies are amazed by it on the slope of summer. A rare cobweb bloom forms on the upper part of the leaves. This disease on peonies, fortunately, does not bring much harm and does not occur very often. CONTROL MEASURES: it is possible to spray the plants when the first signs of the disease appear with a solution of soda ash and soap.
Phylostictosis... Initially, small brown spots with a dark purple rim are formed on the leaves.  Later, the spots increase in size, become rounded or oblong, brighten in the center and are covered with numerous convex dark dots. The disease with a strong development causes premature drying of the leaves.
Later, the spots increase in size, become rounded or oblong, brighten in the center and are covered with numerous convex dark dots. The disease with a strong development causes premature drying of the leaves.
CONTROL MEASURES: the main measure has always been prevention - the elimination of the causes of the disease. Therefore, do not plant peonies on too heavy, excessively moist soils with high acidity; do not allow thickened landings that impede air circulation; cut out the diseased parts of the plant in time and cut off the faded flowers, preventing them from shedding on the leaves; for the winter, prune peonies to ground level and remove the weight of plant debris; systematically carry out preventive spraying of plants at least three times - at the beginning of the growth of shoots and the appearance of leaves, during the budding period and after flowering with one of the following preparations: 0.6-0.7% copper oxychloride solution, 1-2% Bordeaux solution liquid or 0.2-0.3% foundation.
Peonies delight in spring with bright flowering. In the Middle Kingdom, where the flower comes from, the plant is cultivated as a medicinal and is used in landscape design. It is believed that the peony protects from evil spirits and has magical qualities. The light-loving plant is easy to care for, but it is important to monitor its health.
Diseases of peonies
Often, peonies are exposed to viral or fungal phyto-diseases.
Common infections that cause fungus include:
- rust;
- gray rot;
- types of spots.
The ring mosaic of foliage belongs to viral pathologies.
On a note. Flower crops are usually infected with multiple viruses, making therapy difficult.
Among the harmful insects that like the peony are:
- ants;
- caterpillars;
- bronze.
Causes
The increased humidity of the air provokes fungal diseases of peonies. Infection of peonies with gray rot occurs during unfavorable weather during the spring and summer seasons. Humidity and heat can cause rust to appear. Excessive nitrogen and thickening of plantations increase the danger of fungus.
Diseases of peonies
The meteorological conditions do not play a special role on the growth of viral ailments.
It is generated by:
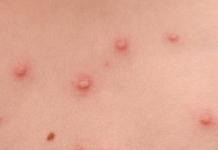
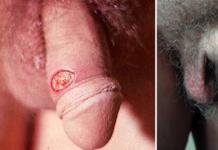
Gray rot is a dangerous fungal disease that completely affects the flower. They are found early on sluggish young branches in early spring. Later, the formation of gray plaque on various organs of the culture and brownish spots on peonies around the peduncle in the zone of the root collar are added to the symptoms.
Disease symptoms
They recognize rust on peonies by brown or reddish spots on the foliage, which consist of fungal spores. Powdery mildew is indicated by a white bloom at the top of the leaf plate of adults.
On a note! Viral diseases are manifested by specks, light stripes, necrotic blotches.
Treatment
It is important to start the therapy of infected plants on time. Rust is dangerous because the spread of fungal spores occurs with the movement of the wind and causes infection of other crops. Timely removal and elimination of diseased foliage, spraying bushes with 1% Bordeaux mixture are appreciated. The liquid is used to spray the peonies in the spring to prevent gray mold infestation. For prevention, they fight against ants - carriers of the disease. If an infected area is found on the bush, it is immediately cut out and destroyed, the peony is sprayed with a suspension of Tiram (0.6%).
Powdery mildew is resisted by spraying plants with sodium carbonate solution (0.5%). Peonies are processed twice, observing a 10-day break between procedures. Figon's solution (0.2%) is effective in the fight against powdery mildew.
Spraying peonies
Diseases for which viruses are responsible are not cured. Affected peonies or areas are removed from the flower bed and destroyed. In such a situation, the main method of struggle is prevention. It is required during the growing season to weed out weeds in the front garden - the focus of infection. It is necessary to keep garden tools clean: be sure to disinfect with a solution of potassium permanganate after cutting off diseased flowers.
It is important to remember about pests, which are the cause of the development of viral pathologies. Therefore, timely preventive measures are taken and the plants are treated with pesticides.
Peony disease
Like garden plants, peonies get sick. Sometimes phyto-diseases have a viral or fungal breed. It is important for flower growers to understand the diseases of peonies and their treatment, especially when rolling the leaves.
Watching the video will allow amateur flower growers to understand the causes of the ailments of peonies and take adequate measures to heal them.
Gray rot
The development of gray rot usually occurs at the end of spring. In the process of illness, foliage loses its freshness, mold appears everywhere.
Gray rot on peonies
Manifestations
- brown spots on peony leaves, wilting and drying of plants;
- the appearance of a grayish coating on dark spots in conditions of warmth and humidity;
- the acquisition of a bloom of a black shade at the bottom of the stem and its break-off and fall;
- decay of buds, flowers, shoots.
Causes
- separation of fungal spores by color;
- excessive humidity, shaded plantings, poor ventilation;
- excess nitrogen fertilization.
The disease threatens the entire plant: branches, leaves, buds are infected. The sick flower sneezes and dies. Damp bad weather conditions the rapid spread of gray rot.
Treatment
The affected areas are immediately excised and destroyed. At the onset of the spring season, the bush is treated with 1% Bordeaux mixture.
Bordeaux mixture
Ways to preserve flower health include prevention:
- choose varieties that are not susceptible to harmful microorganisms for cultivation;
- planted on a lighted flower bed with permeable and loose soil away from trees and shrubs;
- when planting, check the roots and remove rotten roots with a sharp disinfected device, grease the wounds with brilliant green or sprinkle with charcoal;
- warm up the root system of peonies for 10-12 minutes in water heated to +60 .. + 70 ºC, dry, then plant in holes, sprinkled with ash;
- avoid the introduction of nitrogen after the flowering of the plant;
- carry out a short pruning of peony shoots for the winter;
- periodically loosen the soil.
In the fight against peony rot, they resort to fungicides:
- Soon and Pure Blossom;
- Mikosan and Maxim;
- Vectre and Planrizu.
Rust
If the leaves on the peony turn red, and a bloom has appeared, the plant suffers from rust.
Rust
Manifestations
- damage to the leaves: the formation of brown uneven spots, and on the underside of the leaf - pads with fungal spores;
- reddening of the leaves;
- premature bushes turn yellow and dry;
- winter badly;
- grow poorly next year.
If measures are not taken, the disease is quickly transmitted to other cultures. With the flowering of peonies, the disease progresses. Fungi of this type have enhanced cold resistance. With the arrival of spring, rust doubles its activity and can destroy the entire flower garden.
Causes
The rust fungus is responsible for why the leaves of peonies turn red. It develops in the middle of summer on a pine tree, where it stays on its legs and hibernates.
With the flowering of peonies, the disease progresses
Treatment
It is useful for summer residents to know why the peony has red leaves and what to do in this case. The following measures are taken:
- remove the affected leaves;
- collecting and burning vegetation waste;
- dig deep into the soil;
- in early spring, when shoots appear, the upper 2-3 cm layer of earth is removed and fresh soil is poured, which is mixed with sand;
- sprayed with a solution of ammonia or tar soap: for 10 liters of liquid 3 tbsp. l. funds.
If the disease intensifies, they use fungicides:
- Bordeaux liquid, which is prepared from 10 liters of water with the addition of 100 g of lime and copper sulfate;
- colloidal sulfur (100 g per 10 liters of water);
- copper chloride (for a 10-liter bucket of 40 g).
Copper oxychloride
Rolling the leaves
Peony bushes react sharply to watering. Lack of moisture or excess has a negative effect on the culture: the leaves of the plant may curl, or root rot develops.
Causes
- insufficient illumination;
- potassium deficiency in the ground or soil voids;
- damage to the roots by harmful insects;
- exposure to viruses and fungi.
Rolling the leaves
Treatment
Sometimes it is difficult to figure out why the leaves of peonies suddenly curl and what to do. If foliage curls in the absence of damage and stains, the reason lies in improper care of the plant. You should not use chemicals, it is enough to tweak the care of the peony.
If you twisted the leaves of a peony, and the rhizome turns black as a result of the disease, then:
- when transplanting bushes in September, the diseased roots are removed, carefully cut off the decayed areas of the roots;
- sprinkle the places of the cuts with coal powder, which is mixed with Fundazol or sulfur in a 2: 1 ratio;
- carry out a 30-minute sanitization of the root system using chemicals: 1% copper sulfate, 1% TMTD, 2% Fundazole or a mixture of 0.6% TMTD and 0.2% Fundazol;
- when planting, they try not to deeply deepen the rhizomes and cuttings, spilling it with a mixture of Tsineb and Fundazol or TMTD;
- during the growing season, Fitosporin-M and Alirin-B, Gamair and Aktofit are used.
Peony pests and control
When peonies are left unattended, the bushes are attacked by harmful insects. Photos will help establish how to deal with pests and improve peonies.
Bronze beetles
Bronzovik beetle on a peony
What to do
To get rid of bronzers requires:
Pests are characterized by predominant damage to plant roots. Nematodes are recognized by nodular swellings where small worms are located.
What to do
- eliminate and burn infected peonies;
- disinfect the soil with Formalin (1%);
- carefully choose the material for planting;
- dig deep into the ground before planting flower bushes;
- dispose of the remnants of vegetation when cleaning the garden.
Gall nematodes
Turf ant
Harmful insects with a yellowish-reddish body will surely appear on peonies due to the sweet syrup, which attracts ants. Pests gnaw the edges of the petals together with the leaves.
What to do
In opposition to ants, flower crops are sprayed with repellents, as well as the soil around the bush.
Sod ant on a peony
Summer residents practice spraying with decoctions of aromatic crops:
- wormwood and tansy;
- mint and lavender;
- bay leaf and anise;
- needles and parsley.
Processing peonies in the spring from diseases and pests
In order to prevent, with the arrival of spring, a number of measures are carried out in a comprehensive manner, which are aimed at protecting against pests and phyto-diseases.
0.1% Topaz;
To spray one plant, 2-3 liters of solution are consumed.
On a note. After the snow melts, many gardeners water the soil with a solution of potassium permanganate, using 1-2 g per 5-6 liters near the peony to protect against fungal infection.
Folk remedies
The celandine recipe is popular among folk remedies. For cooking, you need 0.5 kg of fresh grass, which is placed in 5 liters of boiling water and insisted for 2 hours. Sick peonies are sprayed with the filtered tincture, the procedure is repeated at intervals of 5 days.
Celandine for the treatment of peonies
If necessary, spraying with antifungal drugs is carried out every 10 days until the symptoms of the disease disappear.
Biological preparations
Biological products are distinguished by their productivity in the battle against phyto-diseases of the peony:
- heals rust with Extrasol-55;
- protects against gray mold Glyocladin;
- fights rust, annular sheet mosaic, gray mold Alirin-B.
The drug "Glyocladin"
Prevention of diseases and pests of peonies
To prevent phyto-diseases of peony, it is recommended to adhere to preventive measures:
- observe agrotechnical rules for watering and loosening, fertilizing and weeding;
- use healthy seedlings for planting;
- acquire varieties of peonies that are resistant to diseases;
- process the bushes 3 times with chemicals per season;
- keeping garden tools clean.
Peonies are not particularly demanding in care, therefore many owners of personal plots prefer these flowers for their decorative properties. However, sometimes plants are affected by harmful insects and diseases. In the fight against pests, flower growers will be helped by a description of the symptoms of diseases, as well as the means used that will solve the problem and make the flower garden even more beautiful.
Peonies are the undisputed kings of the garden. The beauty and scent of their chic flowers sets the tone for the entire summer. These flowers bring a lot of joy, especially if you cope with the problems that no, no, but arise with them. Using the example of users of our portal, we will consider the diseases and subtleties of agricultural technology of these plants and understand what to do with them.
Insufficient feeding
A rare, but still found on FORUMHOUSE story: small buds appear on the bushes of peonies, which never bloom.

According to experienced users of our portal, who have been growing pythons for many years, this is most likely due to insufficient feeding. Up to three years, caring for peonies is reduced to loosening and watering, then the plants need to be fed. Usually peonies are "fed" with mineral fertilizers three times: in early spring, during budding and after flowering, about a week later. But on an excursion in the botanical garden of Moscow State University, a FORUMHOUSE user MiLeDi told that they were fed five times. Complex fertilizers are used for feeding - Kemiru or Fertik. And in the fall, experts recommend mulching peonies with compost, this gives very good results.
Root rot
But root rot is a common, even ubiquitous disease of peonies. The roots begin to rot even in peonies, which are looked after by the most experienced growers. This can manifest itself in different ways. This is how it was with Lory495: first, the tips of the leaves darkened, then quickly, literally in a week, the whole bush dried up. Little by little, the plant revived and even bloomed sluggishly, but then the same story repeated itself.
The hive mind of our portal has diagnosed root rot in Laura's peonies. In this case, it is better to wait until the end of August or the beginning of September, dig up and examine the roots. Clean the rotten areas with a sharp instrument to a healthy tissue, hold in the "Maxima" solution. Sprinkle the damaged areas with ash mixed with foundation in a 2: 1 ratio. If the bush is old, by the way, you can divide it. Then plant in open ground, not excessively wet and non-acidic. Plant, observing all the conditions: in a large pit, at least 60x60 cm, into which about two buckets of a mixture of compost with humus, 300 grams of ash and 300 grams of bone meal are poured. If the soil is clayey, it will be necessary to add sand, and if it is acidic, lime it. To deepen the rhizome by 4-5 cm.

Gray rot
Gray rot is the nastiest and most common disease of peonies, the nightmare of any grower. It affects all parts of the plant, from rhizomes to flowers. Usually early varieties of peonies are affected, but others are not insured: as soon as the shoots grow, ring spots appear on them, at the very base, then the stem in this place rots, breaks and falls. The stems may die off and not in the spring, but then the rings are formed higher, 10-15 cm from the base. The leaves are covered with brown spots, the flowers become ugly and dry out. The disease develops very quickly.
This is what peonies look like Tatham that she shared last year.

IgorM, a great authority on the topic "Peonies", diagnosed the initial stage of gray mold damage and recommended cutting off diseased plant areas below the injury site, not waiting for the infection to descend to the roots, spray all the peony bushes in the garden with fungicides, for example, foundation, and alkalize the soil.
Ring mosaic
And here are the other peonies Tatham. See this marble pattern? This is a ring mosaic, a disease of peonies, common in many regions of the Non-Black Earth Region.

This disease is fought mainly with preventive measures: it is necessary to choose healthy planting material. Especially valuable rhizomes are kept in warm water for about 20 minutes for 20 minutes. If the lesion is not too severe, it is recommended to cut it out to the root and stimulate the immune system of the peony with feeding and immunostimulants. A separate instrument is used for all operations with a diseased plant! If the peony variety is not particularly valuable or the damage is too strong, the bush can be completely destroyed.
Rust
Typically, peonies begin to rust soon after flowering. Spots appear on the leaves, the leaves curl, dry out. The disease is very contagious and can infect all peonies in the area in a few days. What rusty leaves look like, we can see on the example of peonies of the user of our portal Zimorodok:

Dark spots appeared on one peony, I immediately cut off the stems with such leaves. The rest of the bushes are still in excellent condition.
In general, cutting off the stems was optional. The roots need nourishment, and it was enough to remove and burn the affected leaves. And, of course, preventive treatments are needed: they are carried out two or three times, immediately after flowering. The period between treatments is 7-10 days. Peonies are sprayed with copper-soap liquid, colloidal sulfur solution and other low-toxic fungicides.
Spotting
What is it and how to deal with it?

This is brown spotting, a common disease in peonies. Such brown-yellow-brown spots usually appear at the beginning of summer: first on the lower leaves, and then "creep" higher and higher. Diseased leaves are cut and burned, peonies are sprayed with some remedy for fungal diseases. The problem is that the spotting weakens the plant, it becomes less winter-hardy, and blooms worse next year. As in other cases, the best treatment for the disease will be prevention - in the spring and during the budding period, spraying with Bordeaux mixture, phytospirin-M, etc. is carried out.
First bloom
Many are worried about whether it is necessary to pinch the buds of first-year peonies. It is believed that the first flowering takes away from young bushes their already weak strength, let it be better to build up the root system. Therefore, it is recommended to pinch peonies, especially in bushes that have grown from weak sections with two or three buds. Put the bud in water, let it make you happy in the room, but in the second year there will be more buds, and in the third bush it will bloom with a lush bouquet.

Division
There were precedents at Forumhouse when 20-year-old and even 60-year-old bushes were shared.
Why I believed it: during the war, my mother, a seven-year-old girl, brought a bouquet from the ruins of a manor house near Kashira. And the great-grandmother said that such flowers grew in the lady's garden. Nobody courted, and they bloomed even during the war!
On average, if good conditions are created during planting, peonies can grow in one place for 20-30 years. But by the age of five to six years, the root system of a peony reaches 60-70 centimeters in diameter and goes to the same length. Therefore, sharing old peonies is a dubious pleasure. magari w once shared 20-year-old peonies. In place of two bushes, such a crater formed that "a couple of sheep would have drowned."
Galija He recalls his story with a 20-year-old bush as a bad dream: the rhizome has gone deep into almost a meter, branched out like an octopus, overgrown. Many of the roots were old, many were rotten. Leaving such an ugliness in the ground was scary, so I had to dig everything completely and spill the soil with a foundation. Several divisions were left, cleaned and processed, the rest were thrown away. The new bush bloomed the next year. In general, there is no need to wait for 10-20 years: the peony is divided and transplanted when it starts to “bloom not so well”.

Peonies can be planted in the old place, the main thing is to pour fresh soil into the hole. And it is better to plant not large roots, but medium ones.
vitrage-service:
- If you look at the stars through a large root, then at best you can see one star. Growing, the roots often intertwine, such a heap is small. Nothing good, many small flowers can grow at best.
The optimal division is considered to be 4-7 eyes, with two to four thick roots. It is better to powder the places of the cuts obtained during division with ash. By the way, delenki without eyes also sprout - at FORUMHOUSE such cases are not uncommon.

Read how to build a diamond-shaped lattice from twigs to support peonies. Here is a heated discussion of the varieties and agricultural technology of peonies, with a demonstration of photographs and a detailed description of the entire growing process.