Method of determination Immunoassay.
Study material Blood serum
Home visit available
Serological marker of unicameral echinococcosis.
Echinococcosis - tissue helminthiasis, the infection is caused by the larva of Echinococcus spp.
The main source of infection for the dog. Human infection occurs through contact with infested animals, when picking berries and herbs, drinking water from sources contaminated with helminth eggs. Due to the peculiarities of the epidemiology, the disease is more common in certain professional groups (slaughterhouse workers, shepherds, tanners).
With echinococcosis, deeply lying organs are usually affected and it is impossible to obtain material for microscopy by non-invasive methods. Therefore, serological diagnostics (detection of specific antibodies to antigens of an infectious agent) is of great importance. But the use of serological methods is limited by the fact that in some carriers of echinococcal cysts, the immune response may not develop and there may be no antibodies in the blood.
Literature
- Rakhmanova A.G., Neverov V.A., Prigozhina V.K. Infectious Diseases: Manual - 2nd ed. - 2001 - 576 p.
- Ayadi A, Dutoit E, Sendid B, Camus D 1995. Specificdiagnostic antigens of Echinococcus granulosus detected by western blot. Parasite, v .. 2 pp. 119 - 123.
Alveococcosis (lat. Alveococcosis) is a rare zoonotic helminthiasis in humans from the group, which is characterized by a severe course and causes tumor-like liver damage with metastases to other organs (mainly to the lungs and brain). In most cases, the disease ends fatally after years, it develops slowly, and delayed treatment can usually only slow down the process.
Synonyms: multi-chamber or alveolar echinococcosis.
According to ICD-10, the disease has a code B67.5 (liver alveococcosis), B67.6 (damage to other organs), B 67.7 (localization not specified).
Causative agent
In the left photo (A) an adult alveococcus, which lives in the intestines of foxes and other canines, reaching a length of 6 mm. But the disease of alveococcosis is caused by its larval stage, which forms around itself vesicles (cysts), which resemble balls up to 20 mm in diameter (photo B). Their number is constantly growing and they grow together.An adult worm usually does not exceed 4 mm in length. It belongs to the type of flatworms, the class of cestodes (tapeworms), the order (Cyclophyllidea). However, unlike such well-known relatives from the same order as or tapeworms, it has only up to 5 segments, and not thousands.
 Alveococcus life cycle (Echinococcus multilocularis)
Alveococcus life cycle (Echinococcus multilocularis) Alveococcosis in humans is much less common than unicameral (cystic) echinococcosis, caused by the larvae of several other species of worms from the genus Echinococcus (most often Echinococcus granulosus). The reason is that dogs are often carriers of the causative agent of echinococcosis, and alveococcosis is often carried by foxes and other wild canines. With unicameral (cystic) echinococcosis, a cyst is formed from the larva, which grows in size and can reach several kilograms. But it can be surgically removed, which is much more difficult to do with a huge number of small formations fused with the tissues of the organ, as in alveococcosis.
Infection routes
Man acts as an intermediate host. To sexually mature individuals, helminths grow in the body of wild (foxes, wolves, coyotes and others) and domestic animals (cats and dogs). They are the ultimate masters.
People become infected by swallowing helminth eggs, which occurs as a result of non-compliance with hygiene rules - contact with animal hair, and then eating without first washing their hands. Increased risk for hunters, menageries workers. You can get infected when cutting fox carcasses, rarely - when caring for pets.
Also, infection occurs when eating herbs and berries contaminated with feces of sick wild animals. Sometimes eggs can enter the human body even if the dust is inhaled.
People are not able to infect each other with alveococcosis, since the pathogen inside them does not become mature and cannot produce eggs.
In addition to wild animals, domestic dogs can also act as carriers and, accordingly, distributors of eggs, although this is rare due to the fact that they do not often eat such intermediate hosts as rodents. A dog is much more likely to contract unicameral echinococcosis.
Epidemiology
Alveococcosis occurs on all continents with the exception of Antarctica. Although alveococcus is very common among animals (in some regions, up to 50% of foxes are infected), humans rarely become infected.
The highest incidence rate was recorded in the Northern Hemisphere, where a cold-temperate climate prevails. Cases of alveococcosis are more often recorded in Central Europe (Germany, France, Switzerland, Austria), northern and central Asia, China, North America, including Canada.
Over the past decades, there has been an expansion of areas where alveococcosis occurs. Back in the 1980s, many of the eastern European countries had no or very rare cases, and in the early 2000s their statistics changed dramatically. This is primarily caused by the migration of foxes. It is assumed that there will be changes in the future. The increase in infection cases is not hindered by the increase in the level of development of the countries of Central Europe or the United States, since they have only become more frequent in recent decades. Nevertheless, alveococcosis remains a relatively rare disease - with 1982 to 2000, a total of 559 cases were reported all over Europe.
In the Russian Federation, the disease occurs in most of the territory, but mainly in the Republic of Sakha, Khabarovsk, Krasnoyarsk, Altai Territories. Also, cases of infection were recorded in the Kirov region.
Pathogenesis
Helminth eggs enter the human intestine. Oncospheres (the first stage of the larva) are introduced into the wall of the small intestine. With the bloodstream, they reach the right lobe of the liver within three to four hours, where they settle in at least 90% of cases compared to other organs (according to some sources, it is always initially only in the liver). In the future, damage to any other organs due to metastasis is possible, in which the infection from the liver spreads through the blood (hematogenous) and the lymphatic system.
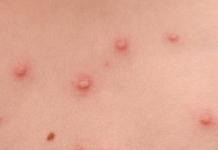
Alveococcosis in humans can be asymptomatic for many years. After that, the first general symptoms appear, such as headache, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, rarely jaundice. An important more specific symptom is also present - hepatomegaly (enlargement of the liver).
The clinical picture is similar to that of cancer. Without treatment for ten years, more than 90% of alveococcosis leads to death. The incubation period is 5-15 years.
The development of alveococcosis occurs in several stages:
- early;
- the height;
- stage of severe manifestations;
- terminal.
Each of them is accompanied by characteristic features.
Alveococcosis of the liver
In most cases, at an early stage of the development of the disease, they are completely absent. Even after many years of the course of alveococcosis, only nonspecific signs appear: lethargy, abdominal discomfort, decreased appetite. At this stage of the disease, larvocysts have already reached a fairly large size.
At the height of the disease, the disease begins to progress. There is soreness in the right hypochondrium, epigastric region, digestion is disturbed, belching appears, upset stool, weakness.
At the stage of severe manifestations, obstructive jaundice develops. Feces become light, and urine, on the contrary, dark. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity becomes yellowish. As the disease progresses, the limbs, face, and trunk acquire the same color. Patients complain of itching on the back, arms and legs.
If the nodes grow into large veins, portal hypertension may develop. In this regard, there are edema of the lower extremities, varicose veins and there is a risk of bleeding.
The terminal stage of the disease is accompanied by irreversible processes. Weight drops sharply, immunodeficiency occurs, complications appear. As a rule, the patient dies.
Alveococcosis of the lungs
Basically, the lungs are affected secondarily as a result of the formation of metastases. They germinate through the diaphragm from the liver. Alveococcosis of the lungs is accompanied by chest pains, cough with the release of purulent contents or sputum with blood impurities. Empyema of the pleura (purulent lesion) often develops. In children, echinococcosis, including alveolar echinococcosis, usually develops faster in the lungs than in the liver, which is most likely due to certain physiological features that facilitate the growth of nodes.
Alveococcosis of the kidneys
This type of disease is rare. As with the lungs, kidney damage is secondary. In this case, signs similar to necrosis appear.
Complications
Possible complications include various lesions of the liver tissue (purulent, necrotic, fibrosis), the spread of larvae in the patient's body and damage to other organs. Most often there is inflammation of the biliary tract (cholangitis), jaundice (due to impaired outflow of bile from the liver), gallstones (cholelithiasis), sepsis, thrombosis of the inferior vena cava, glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys), chronic and acute liver failure, increased venous pressure etc. As the disease progresses, one or more complications may occur.
Diagnostics
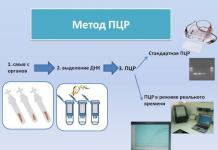
At the initial stage of the disease, serological tests are used, which make it possible to establish a diagnosis before the first symptoms appear. In this case, they are more effective than with unicameral echinococcosis. Includes analysis for antibodies, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), immunochromatographic analysis (ICA).
Imaging techniques play an important role. It is possible to determine the presence of nodes and tissue damage on an ultrasound scan, complementing the methods of computer (preferably) or magnetic resonance imaging.
Diagnostics also includes laboratory methods of research, such as a general analysis of blood and urine. When examining a sputum smear under a microscope, the causative agent of the disease can be identified. Differential diagnosis is based on the exclusion of unicameral echinococcosis, cirrhosis and polycystic liver disease, cancers.
A biopsy of the site may be done to detect the pathogen. But at the same time, it is worth initially excluding unicameral echinococcosis, in which this procedure exposes the patient to a high risk of the contents of the cyst entering the abdominal cavity due to its size and puncture.
Treatment
Therapy is usually carried out in a hospital setting. Early diagnosis and timely treatment can lead to full recovery after surgical removal, but there is a high risk of incomplete disposal of the lesions and further growth.
Even with proper treatment and after a successfully performed surgical intervention, recurrence of the disease is not excluded. Patients should undergo examinations at least 2 times a year and take anthelmintic drugs for long courses to avoid the re-development of alveococcosis.
Prophylaxis
The rarity of the disease and the long incubation period complicate individual and community prevention measures. First of all, you must follow the rules of personal hygiene. Do not eat with dirty hands after contact with the fur of a wild animal. Do not eat unwashed berries and herbs. If the professional activity of a person suggests the possibility of contaminated dust entering the respiratory tract, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment (masks). People from risk groups should undergo regular examinations.
According to the recommendations of the Office of the International Epizootic (OIE) for effective destruction of eggs, processing is required at a temperature of 85 ° C or 70 ° C, but already for 12 hours. She also gives recommendations for processing at low temperatures, but they are not applicable in everyday life - (-80 ° C) in within 48 hours or -70 ° C inwithin 4 days. But it can be assumed from this that freezing at a temperature of -24 ° C for a longer period can also kill eggs. Chemical disinfection is considered unreliable.
We will find out the causes and symptoms of this serious illness. Consider the methods of diagnosis and treatment of this disease.
What is the disease and what are its causes
Alveococcus belongs to the category of biohelminths
Pathogenesis of the disease
Oncospheres that have entered the human gastrointestinal tract are carried by the bloodstream into the liver, where they develop. Damage to the lungs, brain, spleen and peritoneum occurs due to metastasis. Mostly in the right lobe of the liver, nodes of a whitish color of cartilaginous density are formed, resembling cheese with holes. Finns grow outward, so it grows like a tumor. Alveolar nodes ranging in size from 1 to 30 cm, as they increase, reach the surface of the liver and germinate adjacent organs - the kidneys, bones and diaphragm.
The accession of a bacterial infection is accompanied by the formation of a liver abscess.

Helminth eggs from the intestines of animals fall on the ground and mix with the grass. Human invasion occurs:
- while working in garden plots;
- through unwashed contaminated fruits and vegetables;
- during contact with infected animals;
- when cutting carcasses and processing the skins of invaded animals.
In the human stomach, a larva is released from the egg - a Finn. Once in the human intestine, the larva pierces its wall and spreads through the blood and lymphatic vessels throughout the body. In most cases, the Finn enters the liver through the portal vein, where it settles and develops. In some cases, the larva enters the lungs and other organs of a person through a small circle of blood circulation.
The first signs and manifestations of the disease
Alveococcosis in comparison with echinococcosis is characterized by a malignant course. But at the beginning of the disease, subtle symptoms appear.
The disease may not manifest itself even for many years.
Throughout the disease, as the alveolar nodes increase, the following symptoms of alveococcosis appear:
- pain in the right hypochondrium and epigastric region;
- nausea, belching;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- losing weight;
- heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- decreased appetite;
- itchy skin;
- weakness and general fatigue.
The progression of alveococcosis is accompanied by increased pain in the right half of the abdomen and dyspeptic disorders. Bile colic attacks appear. Allergic reactions become more pronounced.

The causative agent of the disease is alveococcus (Alveococcus multilocularis)
At the stage of enlargement and germination of the node into other organs, the following symptoms appear:
- obstructive jaundice;
- inflammation of the bile ducts (cholangitis);
- enlargement of the spleen;
- yellowing of the sclera.
In case of infection of the bile ducts, the temperature rises, chills and fever appear. The liver is enlarged, pain in the projection of the liver intensifies. Palpation of the liver becomes painful. At this stage, the disease can be complicated by a liver abscess.
Compression of the portal vein by liver nodes is accompanied by ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity). Symptoms of portal hypertension are also manifested by the expansion of veins in the skin of the chest and abdomen. Due to the compression of the vessels, the veins of the esophagus and stomach dilate, which can be complicated by esophageal and gastric bleeding.
Liver nodes can disintegrate to form cavities that become inflamed. In this case, the patient's condition worsens, the temperature rises. Symptoms of intoxication appear in the form of headache and weakness.
Alveococcosis examination
Diagnosis of alveococcosis is based primarily on the clinical picture of the disease and anamnesis data. Hunters and fur farm workers are at risk of invasion.
Laboratory examination includes the following methods:
- Serum immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and RNGA (indirect agglutination reaction), the reaction of enzyme-labeled antibodies with alveococcal diagnosticum.
- Sputum microscopy.
- General blood analysis. In the peripheral blood, eosinophilia and an increase in ESR are noted.

Ultrasound of the liver is used to diagnose alveococcosis
Specific instrumental examination methods are carried out:
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) detects a cyst in the liver and lungs in 100% of cases;
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound).
Modern examination methods make it possible to detect the disease at an early stage. But the lack of a screening system leads to late diagnosis.
Alveococcosis treatment methods
Treatment of alveococcosis is surgical. At an early stage of the disease, a node in the liver is excised within healthy tissue. Radical liver resection allows treating a patient with good long-term results.
If a node in the liver reaches a huge size and compresses or grows organs, it is impossible to carry out radical treatment by surgery.
In this case, palliative liver resection is performed. The remaining parts of the node are treated with antiglase agents or subjected to cryodestruction. In most cases, alveococcosis is diagnosed late. Therefore, a radical operation can be performed only in 20% of cases.

After the operation, you can apply prophylactic treatment of alveococcosis with folk remedies. Healers use home remedies to treat worms. For these purposes, they use onions, garlic, pumpkin seeds and wormwood. These foods also boost immunity. However, it is at least unwise to use folk remedies as a basic treatment for alveococcosis.
Prevention of alveococcosis
Disease prevention comes down to following the rules of personal hygiene after working in the garden, when dealing with dogs and cats. It is important for prevention to carry out deworming of domestic dogs and cats. In order to prevent invasion, regular preventive examinations and examination of persons at risk are required. These include livestock breeders, hunters and those working in carcass butchery and fur processing.
As a result, we will highlight the main thoughts of the article. Alveococcosis is characterized by a severe course with the formation of single or multiple cysts in the liver. The disease has a tendency to metastasize to the lungs and other organs. Alveococcosis is similar to echinococcosis, but differs in a more aggressive course and severe complications. Treatment of alveococcosis is only surgical.
Alveococcosis is a relatively rare disease that affects young and middle-aged hunters. Natural foci of this helminthiasis are found in some regions of Russia (the Volga region, Western Siberia, Chukotka, Kamchatka, Yakutia), Asia, Europe (Switzerland, France, Austria, Germany), the USA and Canada.
Causes and risk factors
A person can also become an intermediate owner of an alveococcus. Infection occurs when eating herbs and berries contaminated with helminth eggs, communicating with pets, cutting animal carcasses during hunting.
Fur farm workers, hunters, herders and others at increased risk of infection should be regularly screened for alveococcosis.

Stages of the disease
During alveococcosis, several stages are distinguished:
- Asymptomatic (preclinical). Can last up to 10 years. The disease is detected as an accidental diagnostic finding during the examination of a patient for another reason.
- Uncomplicated. The pathological process is localized in the liver, that is, the location of the primary tumor. Patients complain of digestive disorders.
- Complicated. It is characterized by the presence of metastatic tumors, significant dysfunction of a number of internal organs.
Symptoms

As the tumor grows in the liver, the following symptoms appear:
- nausea, vomiting;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- deterioration in appetite;
- heaviness in the epigastrium;
- pain in the liver;
- growing weakness;
- weight loss;
- uneven abdominal enlargement associated with hepatomegaly (enlargement of the liver);
- frequent attacks of hepatic colic.
When examining the liver, a dense tumor-like formation with a tuberous uneven surface is palpated.
With metastasis to the brain, the patient develops cerebral and focal symptoms:
- Strong headache;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- hemiparesis;
- Jacksonian seizures (Jacksonian epilepsy).
Diagnostics
Examination of patients with suspected alveococcosis begins with a thorough collection of an epidemiological history (occupational risk, living in an endemic area, processing carcasses and skins of wild animals, hunting).
In the initial stage, which can last for many years, alveococcosis clinically does not manifest itself in anything.
At an early stage of the disease, positive allergic tests (for example, Casoni's reaction with an echinococcal antigen) play a diagnostic role, as well as an increase in the level of eosinophils in the blood. Specific tests for laboratory diagnosis of alveococcosis are different types of immunological reactions (ELISA, RLA, RIGA), PCR.

To identify the possible presence of metastatic tumors, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, MRI of the brain, and chest X-ray are performed.
Primary liver alveococcosis requires differential diagnosis with a number of other focal lesions of this organ:
- echinococcosis;
- cirrhosis;
- polycystic;
- hemangioma.
Treatment
Without appropriate treatment for alveococcosis, about 90% of patients die within 10 years.
Possible complications and consequences
The most common complications of alveococcosis are:
- obstructive jaundice associated with compression of the tumor of the biliary tract;
- liver abscess resulting from the ingestion of pyogenic microflora into the cyst;
- portal hypertension, the development of which is explained by compression of the growing tumor of the liver gate;
- peritonitis;
- purulent cholangitis;
- empyema of the pleura;
- ascites;
- gastric and esophageal bleeding;
- amyloidosis;
- chronic renal failure.
Infection with alveococcosis occurs when eating herbs and berries contaminated with helminth eggs, communicating with pets, cutting animal carcasses during hunting.
Forecast
The prognosis for alveococcosis is always serious. Without appropriate treatment, about 90% of patients die within 10 years. Lead to death:
- distant metastasis to the brain;
- infiltration of a tumor into neighboring organs with a violation of their functions;
- profuse bleeding;
- liver failure;
- purulent complications.
Prophylaxis
Prevention of alveococcosis consists in careful veterinary supervision, deworming of domestic animals and extensive sanitary and educational work with the population of endemic areas.
Fur farm workers, hunters, herders and others at increased risk of infection should be regularly screened for alveococcosis.
YouTube video related to the article:
Alveococcosis (lat. Alveococcosis) is a zoonotic helminthiasis, one of the many types of cestodosis, rarely found in humans. For medical reasons, it is considered dangerous, as it causes a tumor of the liver with metastases, a tumor of the lungs and brain. The disease develops slowly, generally delayed therapy does not contribute to treatment, but only slows it down and after a few years leads to a fatal case.
Synonyms: multi-chamber or alveolar echinococcosis.
According to ICD-10, the disease has a code B67.5 (liver alveococcosis), B67.6 (damage to other organs), B 67.7 (localization not specified).
The fact is that pathogens are carried by dogs, and alveococcosis is mainly carried by wild animals such as foxes and other canines. In a single-chambered (cystic) larva, the larva passes into a cyst, which grows and over the years can fill with liquid up to several kilograms. It can be removed surgically, but in the case of a disease of alveococcosis, in which a huge number of nodules grow together with the patient's organ, it is much more difficult to do something.
Infection routes
In this disease, a person is an intermediate host. Wild animals (fox, wolf, coyote and many others) are considered the final owners of the disease, and domestic animals (cats and dogs) are no exception. In animal organisms, they reach sexual maturity.
 It is possible to get infected by eating unwashed berries, herbs that have been contaminated with the feces of various wild animals. In rare cases, eggs enter the human body through inhalation of dust.
It is possible to get infected by eating unwashed berries, herbs that have been contaminated with the feces of various wild animals. In rare cases, eggs enter the human body through inhalation of dust.
The disease of alveococcosis is widespread throughout the world, with the exception of Antarctica. A person rarely becomes infected, and in a number of animals this is a common disease. There are areas where infection among foxes is 50%.
A higher level of disease in animals of the Northern Hemisphere, where the climate is more comfortable (cold-temperate). Alveococcosis is widespread in Central Europe (Germany, Australia, France, Switzerland), in northern and central Asia, China, North America, and also in Canada.
If in the last century the disease of alveococcosis was a rarity, then in recent decades it has covered various areas. Not so long ago, in the 1980s, many eastern countries had no idea about this disease, or it was extremely rare, but the statistics have changed dramatically since 2000. This is primarily due to the migration of foxes.
It can be assumed that in the future the situation will only worsen. Infection cases are only growing, and no one is preventing infection, so the disease is increasingly common in Central Europe and the United States.
But even based on this information, we can say that alveococcosis is considered a fairly rare disease - from 1982 to 2000, only 559 cases were recorded throughout Europe.
In our country, the disease occurred in the Republic of Sakha, in the Khabarovsk Territory, in the Krasnoyarsk Territory and in Altai. In the Kirov region, cases of infection were also recorded.
Pathogenesis

The pathological effect is manifested in the following:
- the waste products of helminths (toxic-allergic effects) have a detrimental effect on the body;
- oppression of the organs of the larva (larvae) growing by the conglomerate, this disrupts the work of the body;
- metastases spread to all organs;
- immunodeficiency, autoimmune reactions.
Symptoms of Alveococcosis
Alveococcosis is a latent disease and is asymptomatic in humans for many years
The first signs of the disease appear in the form of a headache, a malfunction in the gastrointestinal tract, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and in rare cases, jaundice. One of the important symptoms is hepatomegaly (enlarged liver).
Medical indications are similar to cancer. The incubation of the disease occurs from 5-15 years. In case of failure to undergo therapy for 10 years, 90% of patients with alveococcosis are fatal.
Alveococcosis develops in several stages:
- early;
- the height;
- stage of severe manifestations;
- terminal.
Each of them has characteristic features.
Alveococcosis of the liver
Basically, at the initial stage of the disease, the symptoms are not at all noticeable. For many years, alveococcosis has lived in the body with the manifestation of nonspecific symptoms: decreased appetite, lethargy, abdominal discomfort. With such ailments, Larvocysts are already huge in size.
 The disease progresses at the second stage of the peak. A painful condition appears in the right hypochondrium, in the epigastric region, the digestive tract fails, belching begins, digestion is disturbed, and general weakness.
The disease progresses at the second stage of the peak. A painful condition appears in the right hypochondrium, in the epigastric region, the digestive tract fails, belching begins, digestion is disturbed, and general weakness.
Obstructive jaundice develops at a difficult stage. During this period, the urine becomes dark in color, and the feces, on the contrary, are light. In the oral cavity, the mucous membrane turns into a yellowish tint. In the course of the disease, other organs of the arms, legs, trunk and face acquire this color. Patients suffer from severe itching that occurs on the back, arms, legs.
The manifestation of portal hypertension is possible, in cases where the nodes grow into large veins. Because of this, the lower extremities swell, varicose veins develop, there is a risk of bleeding.
In the future, the terminal stage of the disease passes with irreversible forms. Various complications appear, there is an immunodeficiency, an abruptly patient loses weight. The result is sad - the patient dies.
Alveococcosis of the lungs
Metastases are insidious, they penetrate from the liver through the diaphragm, and as a result, they affect the lungs. Disease  Alveococcosis of the lungs occurs with pain in the chest, cough with sputum, in which blood clots are present, purulent contents are released. Empyema of the pleura (purulent lesion) develops. In childhood, echinococcosis develops much faster in the lungs than in the liver, including alveolar, this can be explained by certain physiological features that facilitate the growth of nodes.
Alveococcosis of the lungs occurs with pain in the chest, cough with sputum, in which blood clots are present, purulent contents are released. Empyema of the pleura (purulent lesion) develops. In childhood, echinococcosis develops much faster in the lungs than in the liver, including alveolar, this can be explained by certain physiological features that facilitate the growth of nodes.
Alveococcosis of the kidneys
Kidney disease with alveococcosis is a rare type of disease. But, as with the lungs, kidney disease is secondary. The symptoms are very similar to necrosis.
Complications
With various complications, a large load falls on the liver tissue from various lesions (purulent, necrotic, fibrous), the larvae spread in the patient's body, affecting other organs. The bile ducts become inflamed more often than other organs (cholangitis), jaundice appears (during the course of the disease, the outflow of bile from the liver is disturbed), cholelithiasis is possible, sepsis is possible, venous thrombosis is possible, the kidneys become inflamed (glomerulonephritis), chronic and hepatic failure develops, venous pressure is significant increases and a number of other complications arise. In the course of the development of the disease, one or more complications are possible.
Diagnostics
At the initial stage of alveococcosis, the tests performed are more effective, in contrast to the single-chamber one. The studies included analyzes:
- for antibodies;
- enzyme immunoassays (ELISA)
- immunochromatographic analyzes (ICA).
Medical research also includes laboratory tests, it includes a general blood test and urine tests. The causative agent of the disease can be easily detected by examining the bacterial culture of sputum under a microscope. Differential diagnosis is prescribed to exclude unicameral echinococcosis, cirrhosis, polycystic liver, cancer.
In some cases, a biopsy of the node is prescribed to determine the pathogen. Be sure to exclude unicameral echinococcosis during this procedure, so as not to expose the patient to a high risk of fluid from the cyst entering the abdominal cavity, such a result is possible due to the size of the cyst during puncture.
Alveococcosis treatment
This disease is treated in medical institutions. Surgical intervention leads to complete recovery, with early diagnosis and timely treatment, but the risk of incomplete removal of nodes and their further development is not excluded.
No one is immune from recurrent disease, even with successful surgery and competent treatment. Re-disease of alveococcosis can be avoided only under the supervision of doctors and if all recommendations are followed. This is a test twice a year and a long course of medication.
Prophylaxis
The disease is rare, a long incubation period significantly complicates the prevention of the disease.  First of all, it's important to pay attention to personal hygiene. Communication with wild animals must necessarily end with washing hands with soap. Unwashed berries and herbs can be sources of infection. Regular examination is recommended for all people at risk. In cases where workers can become ill from contaminated dust, individual masks are used.
First of all, it's important to pay attention to personal hygiene. Communication with wild animals must necessarily end with washing hands with soap. Unwashed berries and herbs can be sources of infection. Regular examination is recommended for all people at risk. In cases where workers can become ill from contaminated dust, individual masks are used.