Typically, summer residents try not to choose chemical protection to combat pests and diseases, because they are afraid of the effects of chemicals. They are mainly used by farmers and agricultural companies to treat large areas when insect attacks become unbearable, or most of the plantings become diseased.
A little about the dangers of chemistry
The biggest problem that pesticides can cause in the soil is the extinction of native "residents" who are often beneficial, guarding or fertilizing your yard. For example, the following may be affected:
- hedgehogs (catching snakes and mice);
- birds (distribute seeds and destroy pests);
- pets (if any).
In order to litter your area with chemicals as little as possible, you need to understand what you are fighting against and what is the best way to do it.
It should also be noted that pests become accustomed to poisonous chemical elements, therefore, the means with which you treat the garden should be alternated.
Chemical pest control
The most dangerous living organisms for bushes and trees are all kinds of pests. They not only carry pathogenic bacteria, but also destroy huge plantings themselves. Because of them, sometimes a summer resident not only does not receive profit in the form of fruits from his garden, but also suffers huge losses because he cannot even harvest what he planted.
War on aphids, thrips, false scale insects and whiteflies
To protect against these insects, it is necessary to spray the areas where they accumulate. The treatment is carried out during the period when the plant is already infected with aphids or whiteflies. Depending on the degree of damage, the application is provided:
- to the focus of accumulation (at initial manifestation);
- on the entire surface (in case of severe infection, more than 20% of the surface);
- into the soil (if there is a systematic need for treatment).
- Aktara or VDG, which are a systemic insecticide. Effective chem. the protection has a fairly strong protective property and works on the basis of contact action with the intestines (that is, when eaten by pests);
- Fitoverm is an insectoacaricide that does not cause addiction to chemical protection because it is of biogenic origin. Recommended for use during the growing season. Effective against ticks;
- Fufanon - has the same properties as the previous chemical. protection. It is better to choose it for spraying during the growing season. It is an organophosphorus insectoacaricide and can have an effect on all gnawing and sucking pests.
To combat thrips, it is worth adding Vermitek to this list, which, like Aktara, is sprayed onto the area where insects accumulate. Its method of action is the same, but it also has an additional effect on the mining species, which will allow you to get rid of caterpillar pupae and spider mites.
If there are a lot of insects and they are of different types
There are times when the entire garden is simultaneously infested by various pests. Therefore, the sprayers described above to combat them will not help. What's the point of treating with two or three substances when you can handle it with one?
It is for these purposes that the universal chemical is used. protection. These include Fufanon, described above. All these products are used for processing during the growing season. You can process both mature trees and bushes and young shoots.
Universal chemical protection that can help in the destruction of several species includes:
- Actellik. Belongs to the class of pesticides - insecticides, very effective for the mass destruction of pests in fields;
- Decis Extra. As the name suggests, it is a top-class substance. It also has a very wide spectrum of action and is capable of destroying all winged insects in the garden, including scale-, equal- and coleoptera.
It’s important to remember! In order not to harm beneficial insects, you must follow the dilution conditions specified in the instructions. If you cannot remove one of the pests, you should not increase the dosage in the solution, it is better to change the substance.
Fighting diseases with chemical protection
How to get rid of powdery mildew and rust or spotting?
Surely, everyone who is even a little interested in growing crops is afraid of this “infection” like fire. In addition, this disease has a “viral hybrid” called downy mildew.
If you need chemical protection that can help against all of the listed infections at once, or you want to use it for prevention, try Fundazol. This drug is universal and can be combined with others, and a description of its action can be found in paragraph number 3.
How to treat pome and stone fruit trees?
First you need to answer the question, what is it? These crops, most often found in gardens, include:
- apples and pears (pome fruits);
- apricots and plums (stone fruit);
- sweet cherries and sour cherries (stone fruits).
Since, in addition to the plants themselves, the fruits are also susceptible to diseases, there are also medicines for them:
- Horus. It is a fungicide from the class of pesticides. It is recommended to treat trees during the growing season. Perfect for combating diseases such as monoloiasis, scab or Alternaria. Has strong protective properties, can be used as an anti-resistant agent for treatment;
- Polished. Best suited for controlling infestations of apple trees. Belongs to the same class as the previous protection. Most often used for preventive treatment of trees and helps protect fruits and leaves from scab, as well as powdery mildew.
Today we’ll talk about folk remedies for plant protection, which are preferable to other methods, if, of course, they help cope with the problems at hand.
Get rid of all kinds of harmful insects and mites that swarm in hordes on garden beds, berry bushes and fruit trees, gardeners and gardeners can be helped by various herbal infusions, decoctions and others. True, their effectiveness is somewhat lower than that of pesticides (pesticides), and they do not affect all pests, but they are much safer than chemicals: they do not accumulate in plants, quickly lose their toxic properties, and do not harm the environment.
The toxic properties of plants used for this purpose depend on the following points: time of collection and weather conditions. The bulk of herbs should be collected in the flowering or budding phase. Plants whose raw material is root should be collected in early spring or autumn.
Herbs should be harvested in dry weather, when there is no dew on the plants. Only healthy plants should be collected. Bulbs and rhizomes used for decoctions and infusions are well cleaned and washed cold water. After collecting, the plants need to be thoroughly dried in a well-ventilated area, or better yet under a canopy, tied in small bunches and hung on a rope or spread out in a thin layer.
Dry herbs intended for pollinating plants are ground into powder, and to prepare infusions and decoctions, they are roughly crushed, poured with hot or warm water, and then infused for a certain time or boiled. Cooked infusions and decoctions can be stored by tightly sealing the container and placing it in a cool place (if properly stored, they can remain toxic for up to two months).
Infusions and decoctions are used, with rare exceptions, on the day of their preparation, preferably in cloudy weather, and even better in the evening. Their impact on pests intensifies when adding adhesives to them: soap, glue, molasses. Repeat the treatment of garden and vegetable crops after 5 - 7 days (as necessary). There are from 3 to 5 such treatments per season. Data on effectiveness folk plant protection products contradictory.
It should be remembered that freshly prepared plant mixtures used to protect plants have toxic properties and are dangerous for people and animals. When using infusions and decoctions, generally accepted precautions must be observed.
In folk practice, quite a few recipes have accumulated for the destruction of pests and pathogens without chemicals. Here are the most popular folk plant protection products:
 Aloe (Agave)– To prevent plant diseases, seeds are disinfected vegetable crops in aloe juice diluted half and half with water. The seeds are kept in it for 5 - 7 hours, washed clean water, dry.
Aloe (Agave)– To prevent plant diseases, seeds are disinfected vegetable crops in aloe juice diluted half and half with water. The seeds are kept in it for 5 - 7 hours, washed clean water, dry.
Marigold– Preparation of infusion: infuse half a bucket of dry plants in 10 liters of warm water for 2 days, then filter and add 35 – 50 g of laundry soap. Used to kill aphids on berries and vegetables. To protect strawberries from pests, it is recommended to plant plantations with marigolds.
Elderberry herbaceous– Used to protect vegetable stores from rodents. Elderberry branches are laid out in different places in the room or vegetable storage.
Mustard (powder)– Used to disinfect vegetable seeds from pathogens. They do it as follows. Prepare mustard slurry from two teaspoons of mustard and one tablespoon of warm water. The resulting slurry is placed at the bottom of a two-liter jar and the seeds are placed in a gauze bag at a height of 10–20 cm from the bottom and covered with a lid. The seeds are kept there for half an hour, then they are laid out in a thin layer for ventilation for 2 - 3 hours.
To protect berry bushes from gray rot, strawberry-raspberry weevil, currant bud moth, currant glass, gooseberry moth, sawfly larvae, prepare a solution: 100 g of dry mustard pour 10 liters hot water, leave for two days, then dilute in half with cold water and spray on the plants.
 Calendula (medicinal marigold)– Preparation of infusion: 200 g of dry inflorescences are poured into 10 liters of warm water and infused for 24 hours. Used to protect vegetable crops from mites and Fusarium root rot. To repel pests, calendula is sown around vegetable beds and, if possible, on them.
Calendula (medicinal marigold)– Preparation of infusion: 200 g of dry inflorescences are poured into 10 liters of warm water and infused for 24 hours. Used to protect vegetable crops from mites and Fusarium root rot. To repel pests, calendula is sown around vegetable beds and, if possible, on them.
Potatoes (tops)– Preparation of infusion: 1.2 kg of green tops are infused in 10 liters of warm water for 4 hours. For spraying, use a freshly prepared infusion with the addition of 35 - 45 g of laundry soap. Used to protect vegetable crops from aphids, mites, small cabbage white caterpillars, cutworms and moths.
Burdock– Preparation of infusion: Fill 1/3 of a bucket with crushed burdock leaves and fill it to the brim with warm water, leave for three days, filter and use for spraying without diluting with water. Used to protect cabbage and other vegetable crops from caterpillars.
Onion (husk)– Preparation of infusion: 1/4 of a bucket of husks is poured with hot water up to half the bucket, infused for 24 hours, filtered, the bucket is topped up and used for spraying. Used to protect vegetable crops from mites and aphids. To repel carrot flies, sow onions next to carrots or in the same bed (every other row).
Makhorka– Preparation of infusion: 200 g, pour 10 liters of hot water, leave for two days. For better adhesion to plant leaves, add 35–45 g of laundry soap to the infusion. It is used to protect vegetable crops from small caterpillars, sawfly larvae, aphids, and mites.
Dandelion officinalis– Used to combat copperheads, mites, and aphids on plants. Preparation of infusion: 400 g of leaves or 250 - 300 g of crushed roots are poured into 10 liters of warm water (up to 40 degrees) and infused for 3 - 4 hours, filtered and immediately used for spraying.
 Tansy– Used to control aphids on apple and currant trees. Preparation of infusion: 0.8 - 1.0 kg of crushed dry plants or 2.5 kg of freshly collected during the flowering period, pour 10 liters of water, infuse for two days. After this, the infusion is boiled for 25 - 30 minutes, cooled, filtered and the same amount of water is added. For better adhesion to the leaves, add 25–35 g of laundry soap per 10 liters of infusion.
Tansy– Used to control aphids on apple and currant trees. Preparation of infusion: 0.8 - 1.0 kg of crushed dry plants or 2.5 kg of freshly collected during the flowering period, pour 10 liters of water, infuse for two days. After this, the infusion is boiled for 25 - 30 minutes, cooled, filtered and the same amount of water is added. For better adhesion to the leaves, add 25–35 g of laundry soap per 10 liters of infusion.
Tomatoes (tops, stepsons)– Used to combat caterpillars, mites, aphids, cruciferous flea beetles, rapeseed sawfly larvae on vegetable crops. Preparation of the infusion: 400 - 500 g of fresh tops or stepsons are passed through a meat grinder, infused for 4 hours in 10 liters of water, filtered. To increase the effectiveness of the infusion, add 35–45 g of laundry soap.
Wormwood– Used to control caterpillars on fruit trees. Preparation of the decoction: 1 kg of plants collected during flowering is slightly withered and boiled in an equal volume of water for 15 - 20 minutes, cooled, filtered and topped up with water to 10 liters.
pharmaceutical camomile– Used to combat caterpillars, aphids, spider mites, apple blossom beetle, plum and cherry slimy sawfly on fruit trees. Preparation of infusion: 1 kg of dried inflorescences with leaves are finely crushed, pour in 10 liters of water, leave for 12 - 14 hours, then filter and add another 30 liters of water. For better adhesion to plant leaves, add 35–45 g of laundry soap for every 10 liters of infusion.
Pine and spruce– Used to repel codling moth butterflies, white moths, cabbage aphids, cabbage and carrot flies. Preparation of infusion: 200 g of annual growth needles or 100 g of fresh cones, pour 600 - 800 ml of rain or river water, stirring daily, leave for a week in a dark place. Before spraying, the infusion is diluted 10 times.
Tobacco dust– Used to combat small caterpillars, mites, aphids, and sawfly larvae. Preparation of infusion or decoction: 400 - 500 g of tobacco dust are infused for 24 hours in 10 liters of water or boiled in the same amount of water for 2 hours. The broth is cooled, filtered and brought to 10 liters. For better adhesion to plant leaves, add 35–45 g of laundry soap to the decoction.
Yarrow– Used to combat small caterpillars, spider mites, thrips, copperheads, and aphids. Preparation of the infusion: 800 - 900 g of dried and finely crushed herb is poured with boiling water, infused for 30 - 40 minutes, the volume of liquid is brought to 10 liters and continued to infuse for another 45 - 50 minutes, filtered. To increase efficiency, add 35–45 g of laundry soap to the infusion.
Citrus fruits (peels)- Used to combat spider mites, thrips, and melon aphids. Preparation of infusion: 0.5 - 0.6 kg of peels are ground in a meat grinder, placed in a glass container, 2 liters of water are added and, tightly closed, infused for 5 - 6 days in a dark place, then filtered and squeezed well. The infusion is well sealed. For spraying, take half a glass of infusion and dilute it to 10 liters. To increase efficiency, add 35–45 g of laundry soap to the infusion.
Garlic– Used to prevent diseases of vegetable crops, as well as to combat currant bud mites, spider mites, and aphids.
Preparation of an infusion for disinfecting vegetable seeds: Take one tablespoon of ground garlic, pour half a glass of water, stir. The seeds in a gauze bag are immersed in this mixture and kept in a tightly closed jar for 1 - 1.5 hours, after which they are washed in water and dried.
Preparation of infusion for pest control: 50 - 70 g of garlic cloves or 100 - 130 g of green plants with leaves and arrows are finely chopped, pour in 10 liters of water, infuse for 24 hours, then filter. Plants are sprayed 2 - 3 times with an interval of 6 - 8 days. Tomatoes are treated with the same infusion to prevent late blight in the phase of setting the second cluster, and two more treatments are carried out at intervals of a week.
Blackroot– Used to control rodents in garden plots and vegetable stores. To do this, plant blackroot around the perimeter of the site or hang fresh plants or dry ones scalded with boiling water in storage in bunches.
 – Used to combat onion flies, caterpillars, copperheads, and aphids. Preparation of infusion: 200 - 250 g of dry crushed raw materials are poured into 10 liters of warm water and infused for 24 hours. To increase efficiency, add 35–45 g of laundry soap to the infusion.
– Used to combat onion flies, caterpillars, copperheads, and aphids. Preparation of infusion: 200 - 250 g of dry crushed raw materials are poured into 10 liters of warm water and infused for 24 hours. To increase efficiency, add 35–45 g of laundry soap to the infusion.
Horse sorrel– Used to combat spider mites, thrips, and melon aphids. Preparation of infusion: 300 - 350 g of finely chopped plant roots, pour 10 liters of warm water, leave for 3 hours, filter. To increase efficiency, add 35–45 g of laundry soap to the infusion.
Wood ash– Used to combat beet and cruciferous flea beetles. To do this they pollinate wood ash young plants of radish, radish, cabbage, beets (5 - 10 g per 1 sq. m).
Ash-soap solution– Used to control pests on fruit bushes (aphids, gooseberry sawfly, moth, currant bud moth, glass beetle). Preparation of the decoction: sift 300 - 350 g of ash, pour in 10 liters of water, put on fire and bring to a boil. The cooled and settled broth is poured through a fine sieve and 35–45 g of laundry soap is added. For spring (March - May) spraying, add 25 - 30 g of urea per 10 liters, for summer - an extract from nitrophoska - 55 - 60 g. Such spraying is a good fertilizer for plants and reliably protects against pests.
Laundry soap– Used to control aphids on various vegetable crops. The solution is prepared as follows: A piece of soap is crushed and thoroughly dissolved in 10 liters of water.
Soda ash– Used to combat cherry mucous sawfly and prevent powdery mildew of gooseberries and currants. A solution for combating the cherry mucous sawfly is prepared as follows: 70 g is dissolved in 10 liters of water and 35 - 45 g of laundry soap are added. To prevent diseases, take 50 g of soda.
Table salt– Used to combat onion fly larvae and late blight of tomatoes.
To combat onion flies, grooves are made at a distance of 3–5 cm from the rows, into which they are watered with a 2% salt solution (200 g of salt per 10 liters of water). Then the grooves are covered with earth. The first watering is carried out when the feather length is 5–7 cm, the second after 20–25 days.
When the first signs of late blight on tomatoes appear (brown spots on the leaves), the tomatoes are sprayed with a 10% salt solution. The plant and fruits are covered thin film salt, which protects the fruit and prevents the spread of disease throughout the plant. After treatment, some loss of leaves on tomatoes is observed.
Popularity organic farming is growing from year to year. Many summer residents completely or partially refuse to use chemical plant protection products. In many cases, even those who like to spray their plantings with chemicals are forced to use the experience of our grandmothers and turn to biological methods of plant protection.
Relevance folk recipes increases in cases where the mass infestation of vegetable and fruit crops by dangerous insect pests or the onset of disease development coincides with the period of flowering and intensive formation of ovaries. At this time, chemical insecticides are generally contraindicated for use.
Adherents of the principles of organic farming have been using synthetic pesticides intended for pest and disease control, folk remedies. They are absolutely harmless to the plants themselves, humans, animals, birds and beneficial insects (bumblebees, bees, and other pollinating arthropods). Besides use of formulations based on natural remedies guarantees environmental friendliness and absolute safety of grown fruits.
Proven recipes for pest and disease control
Pine concentrate
To prevent the appearance of pests in the garden use a solution of 2 tablespoons of concentrate per bucket of water. To destroy existing pests:
- slowpoke,
- gooseberry moth,
- codling moth
For 10 liters of water, take a double dose of pine concentrate (4 tablespoons). To enhance the effect of the solution, add grated soap to it. In combination with infusions of wormwood and chamomile, the effectiveness against pests increases sharply.
Soap solution
Treatment with a solution of laundry or green soap helps in the fight against such pests:
- spider mite,
- larvae and adults of the pear honeydew,
- aphids of all kinds.
The water for preparing the composition must be soft (melt, rain). If you are using tap water or well water, then baking soda (100 grams per bucket) will help soften it; after dissolving, the liquid is boiled. For a standard bucket of water, take 250 grams of liquid or 300 grams of laundry soap, grated on a grater with large holes.
Washing green shoots inhabited by aphid colonies with a soapy solution gives good effect without risk to the environment. The most convenient way is to dip the affected branches and young shoots directly into a bucket of soapy mixture.
This recipe is advisable to use in areas where the use of pesticides is unacceptable for some reason, for example, located between trees or during the ripening period of berries on bushes. To prevent foliage burns, treatment is carried out in dry weather after sunset.
Ash-soap solution
Effective against:
- aphids,
- cruciferous flea beetle,
- gooseberry powdery mildew.
Garlic
Traditional recipes using all parts(bulbs, arrows, leaves), as well as husks have proven themselves in the fight against dangerous pests and vegetable garden. Garlic helps with:
- aphids,
- slowpoke,
- spider and kidney mites,
- sawflies,
- gooseberry moth,
- bud moth,
- gall midge
It is also effective in combating pathogens of many crop diseases, especially those of fungal origin, in particular against:
- rust,
- leaf spotting,
- brown rot,
- scabs,
- fusarium gladioli.
Garlic infusion recipe
Crush 5 cloves of garlic or pass through a press, fold into 2 liter jar, pour 1.5 liters of warm (38-40) water, close the lid tightly and leave for 5 days. Dilute the strained garlic concentrate with water (1:5) and use it to spray plants affected by pests or diseases.
Garlic decoction
Finely chop 0.7 kg of unpeeled heads or pass through a meat grinder (blender), add a bucket of hot water, boil for an hour under the lid, strain and dilute in half with clean water. The composition is used for watering beds against pests living in the soil at the rate of half a liter per square meter. meter of land. The procedure is repeated once a week.
All kinds of diseases and insect pests cause considerable damage to our gardens and vegetable gardens. Fighting them with chemicals is an effective method, but not harmless to health. Biological means of protection can fight pests and plant diseases no less successfully. These funds, their benefits and advantages will be discussed in the article.
To rid plants of pests and diseases, use the following plant protection methods:
- chemical Insecticides and fungicides are used for control;
- mechanical. This means creating all sorts of obstacles from the invasion of harmful insects in the form of adhesive rings on trees, barrier grooves. Using it over large areas is difficult;
- biological. Their natural enemies are used as assistants in the fight against pests;
- agrotechnical. This method is used for prevention. Conditions are created that prevent the development of pests and diseases;
- physical. Used when the crop is stored. They destroy pests living in the soil using steaming, which is suitable for closed ground;
- quarantine the plants.
Advantages of biological plant protection products
The most effective method of pest control is chemical. Pests really die en masse, but useful living creatures disappear along with them, and there is no need to talk about the usefulness of insecticides and fungicides for the human body. Another thing is biological plant protection products:
- absolutely harmless to humans;
- do not have a harmful effect on the environment;
- destroys only pests;
- they can always be used, even when harvest time approaches;
- they do not accumulate in plants and insects do not get used to them.
With this method of protection, pests are controlled using:
To understand what means to protect plants, let’s look at diseases caused by microorganisms, using vegetable crops as an example. These are the ones we most often grow in our dachas.
What diseases do plants suffer from?
So, there are diseases:
- bacterial. Bacterial diseases include root rot, spotting, and growths.
- fungal. This is the most common type of disease when growing vegetables. These diseases occur due to pathogenic fungi. They primarily infect seeds, soil, and plant waste. The disease is transferred to neighboring plants. Such diseases include powdery mildew, rust, downy mildew, blackleg, and late blight. It is almost impossible to completely remove the source of infection from the site, but it is quite possible to reduce its strength with the help of biological protection;

- viral. These include mosaic and leaf yellowing.
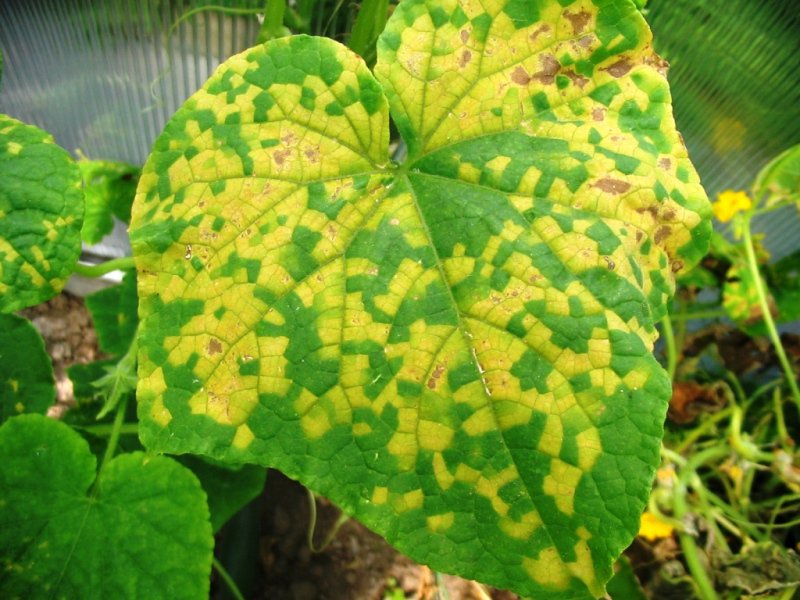

How to protect plants from diseases?
Of course, to combat plant diseases, you do not need to breed beneficial microorganisms yourself, because biological products can be bought ready-made. For example, the drug “Baktofit”, produced by Sibbiopharm. Has an international certificate.
"Baktofit". How is it used and why?
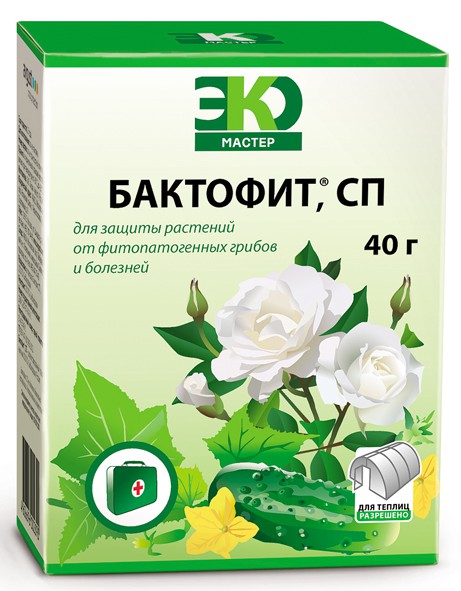

This drug is universal:
- it is used to process planting material;
- if plants need to be replanted, the roots are treated with it. Treatment of roots with bactofit is also useful for seedlings;
- Bactofyte is sprayed and watered at the roots of the plants;
- in particularly advanced cases, it can be used together with herbicides.
Advantages of "Baktofit":
- it contains everything that is necessary to nourish plants;
- used as a prophylactic and as protection;
- makes plants more resistant to diseases;
- increases productivity up to 20%;
- a large group of harmful microorganisms stops growing and stops developing;
- safe for humans, animals, birds and beneficial insects;
- already 1 day after its use, you can collect vegetables or fruits;
- no accumulation in plants and soil;
- When used, beneficial microflora develops in the soil.
"Fitosporin" in the fight against plant diseases

Many fungal and bacterial diseases are suppressed by the biological product “Fitosporin”. It contains natural bacteria in a preserved form, which destroy pathogenic bacteria or prevent their penetration. And besides this biofungicide:
- stimulates plant immunity;
- accelerates growth;
- increases productivity;
- reduces the likelihood of re-infections.
“Fitosporin”, produced by LLC Scientific and Implementation Enterprise “BASHINKOM”, is irreplaceable:
- when soaking cuttings, seeds, bulbs - as a growth stimulator;
- when spraying potatoes, cabbage, tomatoes, cucumbers, home and garden flowers;
- to speed up the compost preparation process;
- for watering when digging an area, as it is also a good soil fertiliser. When there is severe frost, the predatory bacterium dies, but the fertilizer remains.
Growth stimulating biofungicide – AGAT – 25K
This drug does:
- plant treatment;
- feeding;
- stimulates root growth and seed germination.
Effective for:
- root rot;
- powdery mildew;
- septoria;
- fusarium and other diseases dangerous to plants.
It differs favorably from similar drugs in that it can significantly inhibit the development of particularly harmful diseases:
- pepper;
- cucumbers;
- potatoes;
- tomatoes;
- carrots.
Other benefits:
- is used sparingly;
- can be stored for a long time;
- retains properties at temperatures from -15 to +20 degrees C;
- can be combined with chemotherapy and fertilizers.
AGAT-25K is produced by BIO-BIZ LLC.
Plant protection from pests

Growing a good harvest is accompanied by fighting hordes of pests. Biological plant protection will help you to survive this struggle and not poison the plants, and at the same time yourself, with pesticides and nitrates.
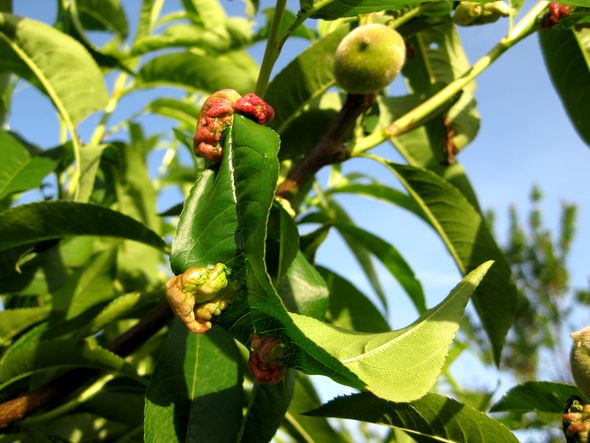

Plant protection from pests involves the use of microorganisms that, once in the enemy’s body, cause it to die. For example: for all vegetable crops, the nematode is a great danger, but it has a natural enemy - the predatory fungus Arthrobotris oligospora. It was this that was the basis of the drug created to combat it.
Nematophagin
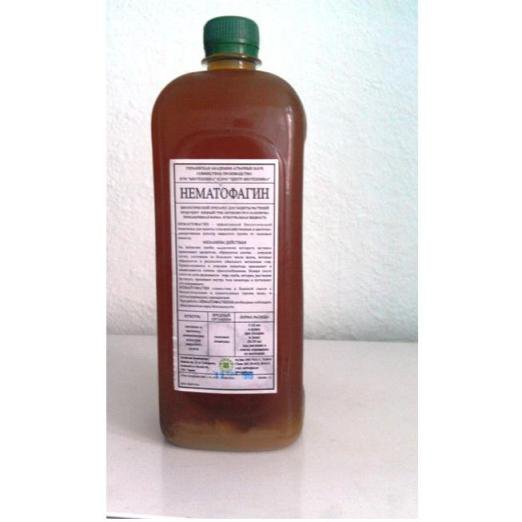

The manufacturer of Nematophagin is Center Biotekhnika LLC. This drug works in this way:
- on the mycelium of the main active substance, i.e. mushroom, traps are formed in the form of numerous rings;
- as soon as the nematode touches these nets placed for it, it is captured by them;
- After this, the predator fungus absorbs the pest.
These predatory fungi live for a long time in the soil and on plant debris.
Fitoverm

Its spectrum of action includes 20 types of pests, including:
- Colorado potato beetle;
- leaf rollers;
- spider and fruit mites;
- thrips;
- codling moth, etc.
This miracle drug is produced by NCB Fabriomed LLC. Its advantages:
- versatility;
- high efficiency;
- Availability of packages of various sizes. If you need to get rid of diseases from indoor flowers, then a small “Fitoverma” package in the form of glass ampoules is specially provided for this.
"Bitoxibacillin"

Provides biological protection of plants, destroying many harmful insects. At the same time, other insects do not suffer. Destroys:
- Colorado potato beetle larvae;
- cabbage scoop;
- fire;
- cabbage moth;
- bunch budworm on grapes;
- fruit moth, etc.
Advantages:
- lack of phytotoxicity;
- guaranteed receipt of environmentally friendly products;
- the ability to process plants 5 days before the expected fruit harvest.
The manufacturer is the production association “SIBBIOPHARM”.
You will learn about other biological plant protection products by watching this video:
Building an environmentally friendly garden on a small personal plot always involves risks. After all environment is open, and if there is some explosion in the insect population in the region, then losses cannot be avoided even where the plants are healthy. But you can’t help pests with your unreasonable agricultural technology: you need to eliminate monoplantings, use crop rotation, and increase soil fertility. And, of course, protect your garden from pests. So, we select folk remedies for protecting plants from pests and diseases.
Protecting plants from pests and diseases: folk remedies
Due to their fungicidal and insecticidal properties, herbs are in great demand in natural farming. Of course, the desired effect of plant components when processing a garden is not as pronounced as when using chemicals. But they do not harm plants, soil, or humans. To extend the validity of “home” plant protection products against pests Soap must be added to the working solution: it improves the adhesion of the solution to fruit and vegetable crops, retains essential substances on the leaves, which confuses pests.
Unlike pheromone and beer traps, infusions and decoctions of herbs do not attract, but repel pests. And this is an obvious advantage for the garden. After all, it is better for insects to avoid unfamiliar, frightening odors than to leave their offspring in unknown conditions. Here are some verified folkplant protection products against pests and diseases, which can be alternated with each other.
Recipe 1 – tobacco-garlic mixture
Fill a liter jar with 2/3 of the cigarette butts and squeeze out 2 cloves of garlic. Pour boiling water over it. Leave for 24 hours. Add 200-300 ml of the resulting solution to a 10-12 liter sprayer. Processing should be carried out weekly in the evening. Tobacco-garlic infusion against pests is used to treat trees and roses against sucking pests: aphids, weevils, spider mites, scale insects. The solution can be stored for a long time, part of it can be poured into a spray bottle and when aphids attack garden crops (cabbage, for example), spot spray any plants to protect the garden from pests.
Recipe 2 – infusion of cilantro and calendula
Pour four teaspoons of cilantro seeds (coriander) and 1 glass of calendula seeds into 1 liter of boiling water and let it sit for 24 hours. Add 200-300 ml of the resulting solution to a 10-12 liter sprayer. Processing should be carried out weekly in the evening. The infusion is useful for protecting the garden from diseases and pests in the spring, and reduces leaf curl in peach.
Recipe 3 – citrus peels
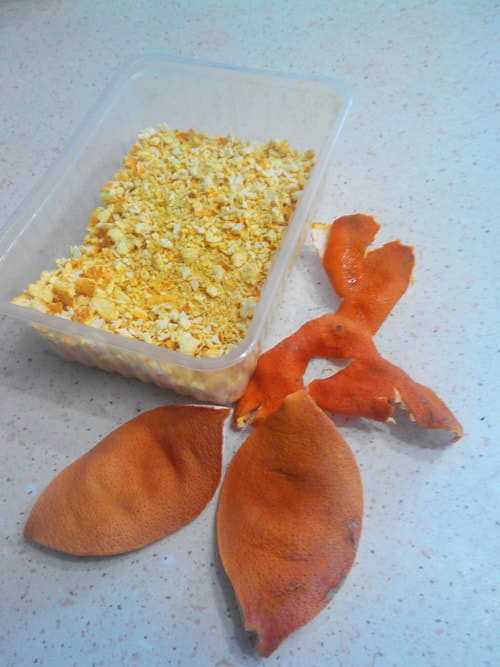 Protecting your garden from pests and diseases using citrus peels accumulated over the winter is also quite affordable and effective method. The crusts are dried on a heating radiator and then ground with a blender or electric meat grinder. Over the winter, we accumulate 3 plastic containers from salads, and they are stored in the toilet room, simultaneously refreshing the air without any chemicals. We scatter the ground peels under fruit trees in the summer; worms happily swallow them when the lumps of peels swell. Haven’t tried brewing citrus peels - a lot essential oils, you may not guess the proportion and severely burn the foliage. Citrus fruits do not grow in our region and insect pests avoid such strong aromas.
Protecting your garden from pests and diseases using citrus peels accumulated over the winter is also quite affordable and effective method. The crusts are dried on a heating radiator and then ground with a blender or electric meat grinder. Over the winter, we accumulate 3 plastic containers from salads, and they are stored in the toilet room, simultaneously refreshing the air without any chemicals. We scatter the ground peels under fruit trees in the summer; worms happily swallow them when the lumps of peels swell. Haven’t tried brewing citrus peels - a lot essential oils, you may not guess the proportion and severely burn the foliage. Citrus fruits do not grow in our region and insect pests avoid such strong aromas.
Recipe 4 – marigold infusion
If you don’t plant marigolds in your garden, you can make an infusion from them to protect against many types of nematodes. For 5 liters of solution you need about 200 grams of dry marigold herb (if bought at a pharmacy). The solution should be used on the same day, after cooling. The solution can be added to a barrel of irrigation water in combination with EM-preparations and humates
Without marigolds, protecting strawberries from pests and diseases is unthinkable. They are also very useful for potatoes, clematis and roses - they perfectly inhibit the development of the nematode population. An infusion of marigolds also protects cabbage from cutworms and cabbage whites. This universal insecticide from fresh plants is prepared simply: a bucket is filled 1/3 with chopped tops (along with flowers) and filled with lukewarm water (45-50 degrees). Cover the bucket with a lid and place it in the shade for 48 hours. Before use, the infusion is diluted 2 times.
Recipe 5 - pine extract solution
Well, and of course, spraying against pests with herbal infusions can and should be combined with fertilizing, growth stimulants and biological products. Read about the so-called tank mixtures for biological treatment of gardens and vegetable gardens in the following articles. We hope protection of plants from pests and diseases folk remedies are also more to your taste than the use of pesticides, and with joint efforts we can gradually improve our ecological environment (at least in a single garden in a particular state).