A question from Nikolai. Why do black spots appear on pear leaves? Then the same spots are formed on the fruits, they become hard and tasteless in these places. Apple trees also have a similar disease. How to deal with it? (I attach a photo of sick trees and pears).
Black spots on pear leaves
Answer.
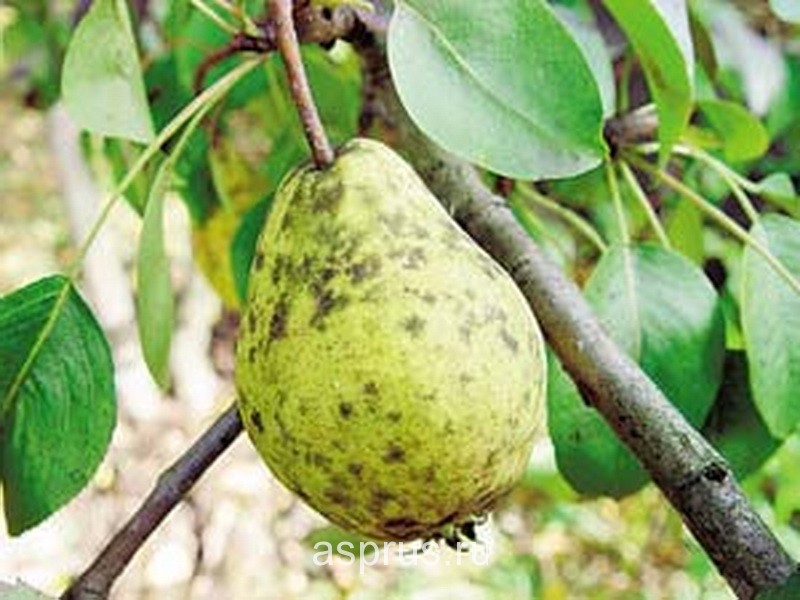
This disease is called scab (see the symptoms of this pear disease in the pictures from the atlas). The causative agent in pears is the mushroom Venturia pirina. After blooming, dark green spots appear on the leaves, then they turn brown, almost black, increase in size, sometimes completely merging. On fruits, scab also appears as velvety spots. At the same time, under the stain, the tissues of the fetus cork (harden). On an apple tree, scab is also caused by the fungus Venturia, only another species is inaegualis.

Diseases of pears in pictures
Spores of the fungus overwinter in fallen leaves, in spring with water (during rains) they spread and germinate, causing an outbreak of the disease. Such pear varieties as Severyanka, Belorusskaya late, Lyubimitsa Klappa, Bergamot Lvovskiy, Bergamot Donskoy, Josephine Mehelnskaya, Cheremshina, Dilbar, Melting Shadne are relatively resistant to scab.
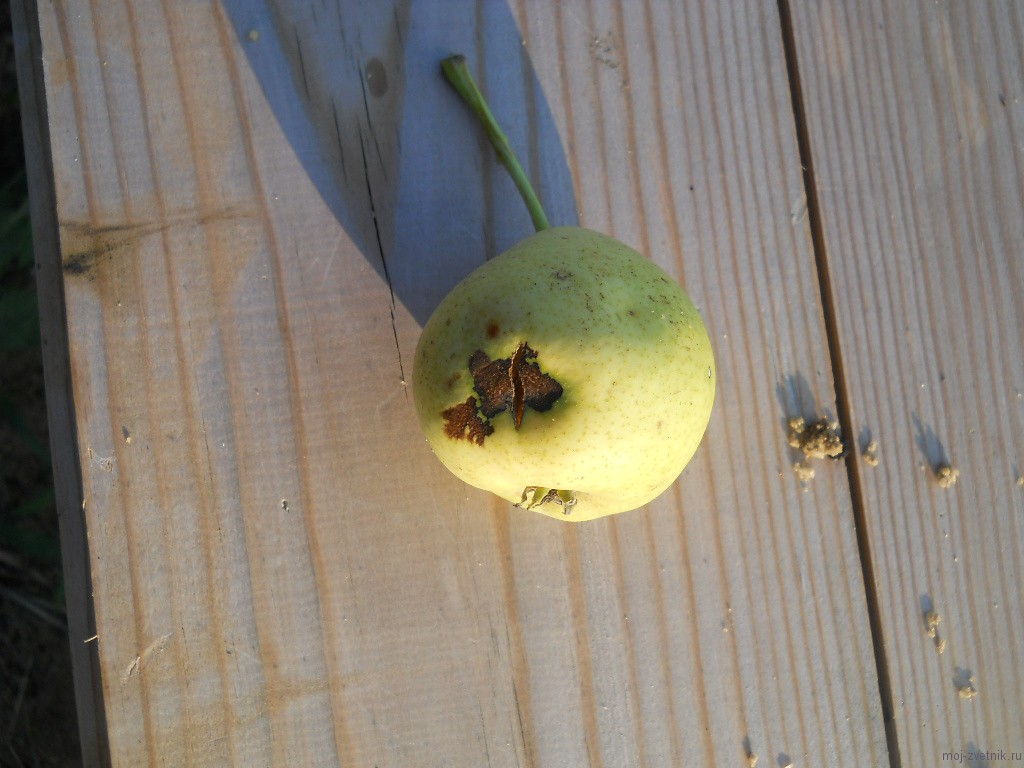

Scab on pear fruits
Measures to combat pear scab are as follows: harvesting fallen leaves and digging up the soil under the tree (plowing in gardens), in the spring it is very important to have time to carry out the first treatment of trees with copper-containing preparations in the green cone phase (leaf bud opening). The treatment is repeated before flowering (especially on susceptible varieties). It is very important to observe an interval of 10 - 12 days (no more) between these two first treatments.
If the disease develops weakly, then after flowering, treatment with a 0.5% urea solution with the addition of 0.5% potassium salt can be carried out. If the scab is rampant (cloudy and rainy weather contributes to this), then after flowering the trees are treated with systemic fungicides - fast, crayfish. In the fall, after harvesting, spraying with Bordeaux mixture is repeated.
Material prepared by:
Dorokhova E.V.,
specialist of the Association of Producers of Fruits, Berries and Planting Material
The main diseases of the pear
Pear scab
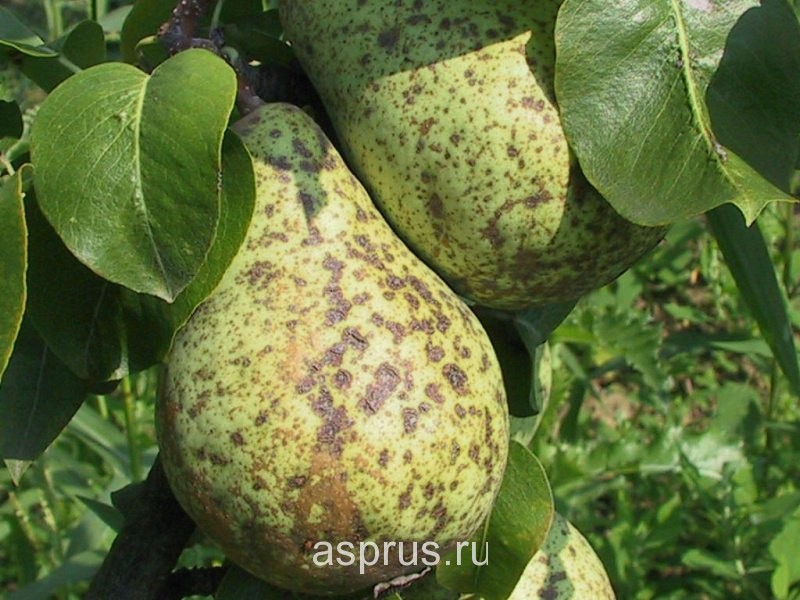 Scab on pear fruits
Scab on pear fruits
A common pear disease is scab. Leaves, flowers, fruits, shoots are affected. Premature shedding of leaves, cracking of fruits, penetration of spores into the fruit, hardening of the pulp are observed. The scab can also attack young shoots. In such cases, after detecting this disease on the shoots, it is better to remove the shoots. Fruits become infected with leaf scab. On them, rounded dark spots with a light rim are formed, covered with an olive-brown velvety bloom. The tissue of the fruit in places of spots becomes corky, becomes woody, becomes covered with cracks (very similar to a crust of clay soil cracked from the heat). Early infection of fruits, especially pears, leads to their deformation, fruits acquire irregular shape, become one-sided. On stalks, sepals and ovary, scab spots are small, dark, with a velvety bloom.
Control measures with a scab of a pear in the fall - destruction of fallen leaves, mechanical tillage, thinning of the thickened crown; early spring eradicating spraying of the garden with the annual development of the disease; spraying with protective fungicides: multiple spraying with 1% Bordeaux mixture, copper oxychloride; the first spraying is carried out during the period of advancement and the beginning of the separation of the buds; the second - immediately after flowering; the third - 15 days after the second; spraying against scab can be combined with spraying against a complex of pests.
Powdery mildew
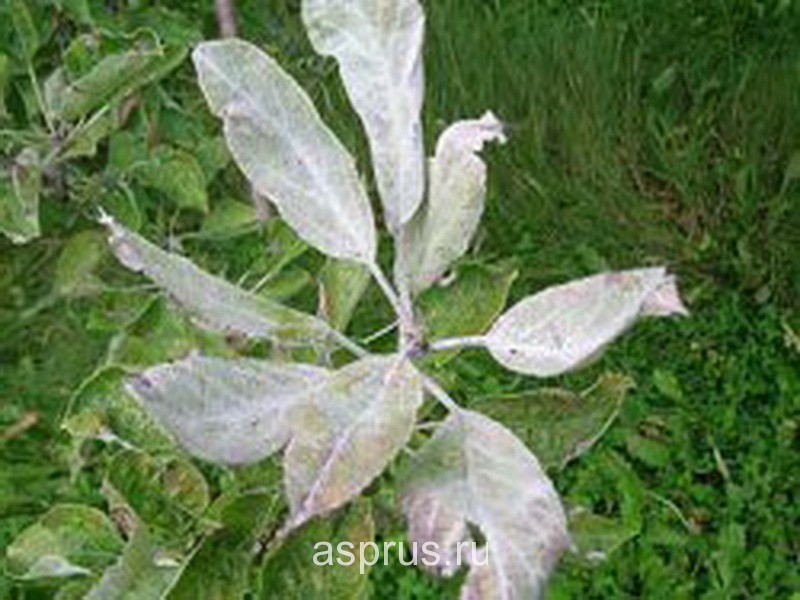 Powdery mildew on pear leaves
Powdery mildew on pear leaves
Control measures. For the prevention of powdery mildew, fallen leaves are destroyed, the tree is sprayed with the preparations "Fundazol" or "Sulfite". Fungal spores spread quickly in wet weather, so several treatments are carried out. Re-processing is done after flowering. It helps well with powdery mildew spraying with a mixture of antibiotics: terramycin 100 units / ml, penicillin 100 units / ml and streptomycin 250 units / ml in a 1: 1 ratio.
Pear rust
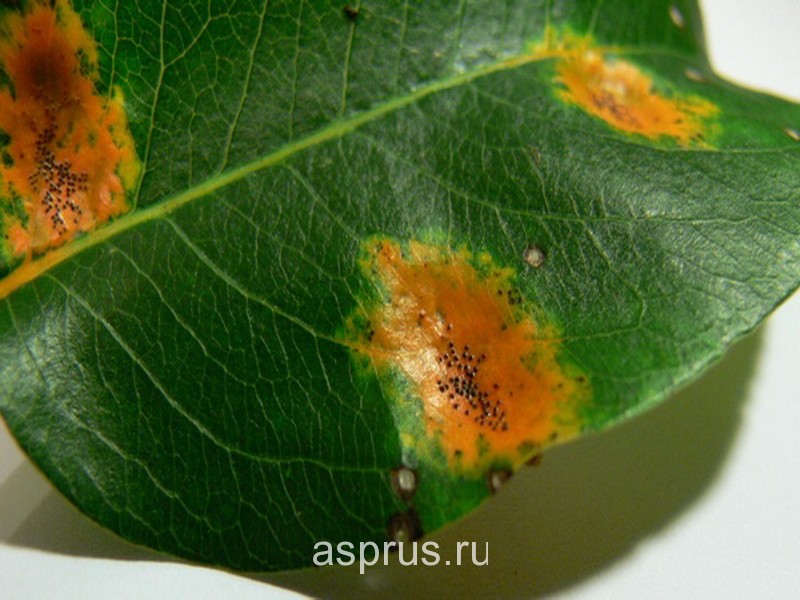 Rust on pear leaves
Rust on pear leaves
Rust. Signs: orange-dark spots on leaves and fruits. This disease is especially common in those areas in which the juniper grows, since it is in it that the rust pathogen is located. Affected fruits and leaves must be disposed of.
Control measures. During the budding period and after flowering, the tree must be treated with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid. In late autumn - harvesting and burning of fallen leaves of a pear, as well as shoots with obvious signs of rust damage. After leaf fall - abundant spraying of trees with a solution of urea (700 g per 10 liters of water).
Pear fruit rot
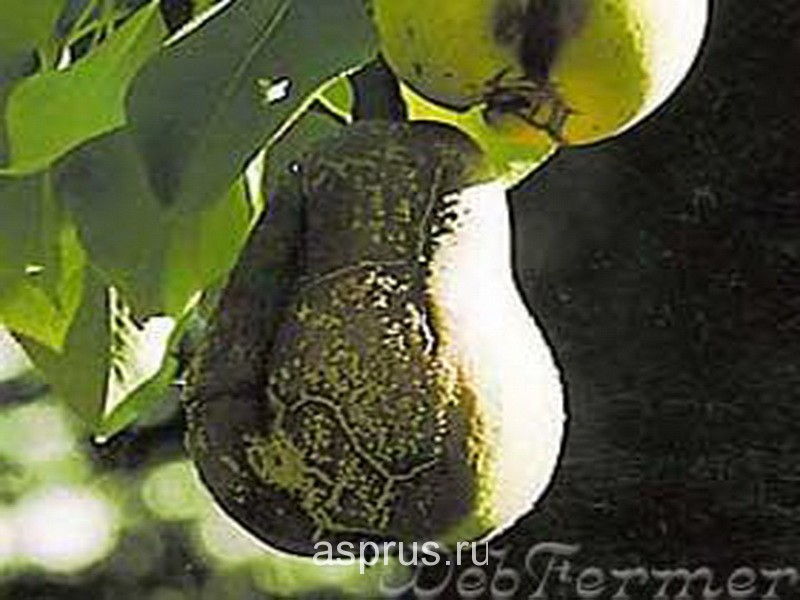 Pear fruit rot
Pear fruit rot
Fruit rot. It appears as brownish spots on the surface of the fruit. With the development of the disease, the spots increase, in a week the entire fetus can be covered with a brown spot. The pulp becomes loose, loses its taste. Large white growths (with fungal spores) appear on the fruits, located in concentric circles. The affected fruits fall off, those that remain hanging on the branches are mummified and can persist for up to two years, causing the spread of the disease. Mass spread of rot is observed in the second half of summer, especially when high temperatures and air humidity (above 75%). First of all, fruits with mechanical damage and wounds (from insects), cracks from apple and pear scab, fruits infected by a goose are affected.
Control measures- laying a garden in a well-ventilated area; collection and packaging, transportation of fruits without mechanical damage; destruction of diseased fruits; autumn or spring cutting and destruction of diseased branches, digging the soil in near-trunk circles; spraying trees with fungicides.
Black pear crayfish
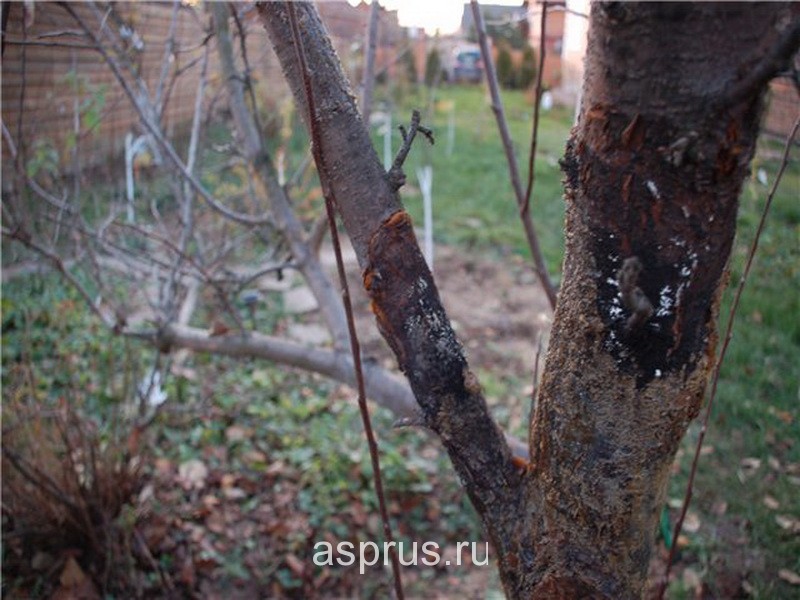 Black cancer on the bark of a pear
Black cancer on the bark of a pear
Black cancer affects the bark on the trunk and skeletal branches. Small, barely noticeable wounds form on the damaged areas, which gradually increase in size. Brown spots form around the wounds. On the leaves and fruits affected by cancer, reddish spots appear, the flowers curl up, the pistils darken.
Control measures. To prevent the appearance of this disease, fallen leaves are collected and burned. Sick fruits are removed, fresh wounds are treated with copper sulfate and covered with a mixture of clay and mullein.
Cytosporosis
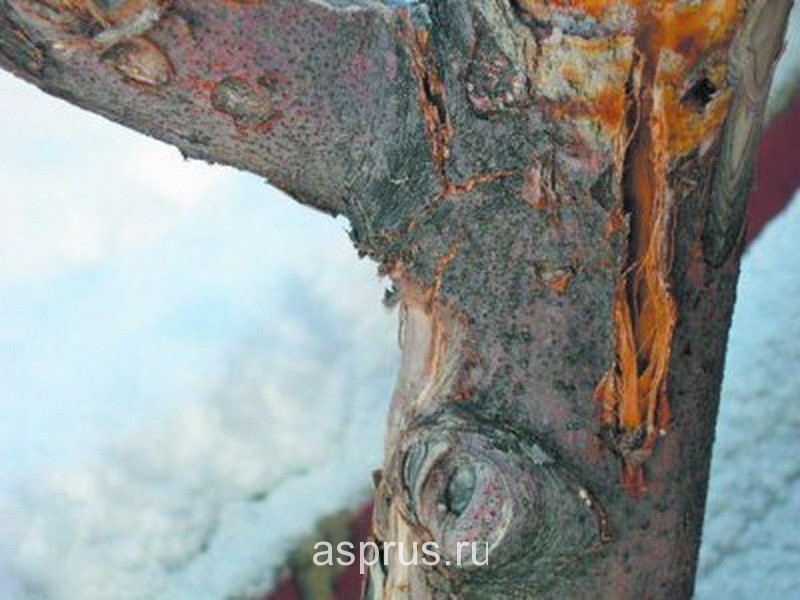 The manifestation of cytosporosis on the branches
The manifestation of cytosporosis on the branches
Cytosporosis manifests itself on the bark of a tree, which, when infected, changes its color to red-brown and dries up. Bulges or tubercles appear on the affected areas - an accumulation of sporangia of cytosporosis.
Control measures. The fight against the disease is carried out in the same way as with black cancer.
Pear bacterial burn
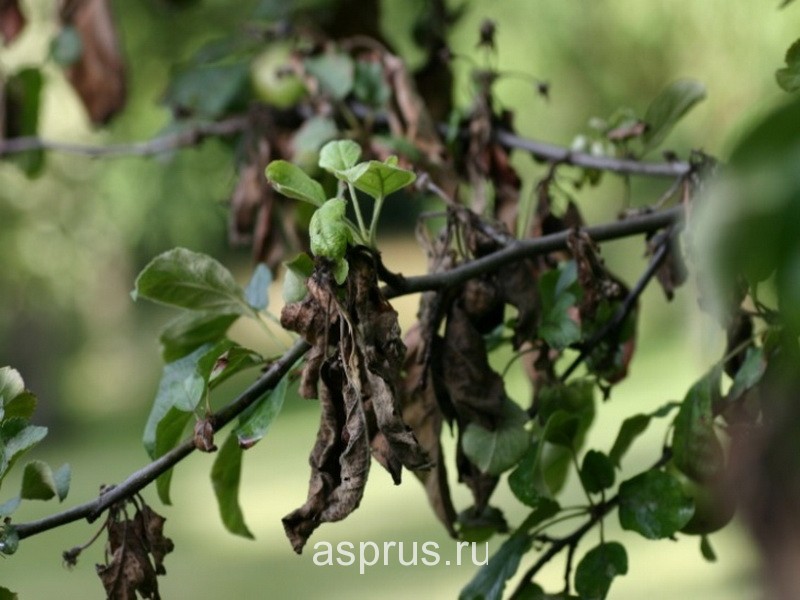 Pear bacterial burn
Pear bacterial burn
Bacterial burn develops very quickly. Disease-causing bacteria spread through the vessels of the tree along with the sap and contribute to the death of tissues. In most cases, this leads to the death of the plant, which is cut down and burned.
Control measures. In order to save the pear, measures are taken immediately. Leaves and flowers are abundantly sprayed with antibiotics every 5 days. With the subsequent trimming of the crown, the instrument is disinfected in a solution of boric acid. This helps to avoid the spread of the pathogen.
Mosaic disease
 Manifestation of mosaic disease
Manifestation of mosaic disease
The most dangerous viral disease is mosaic disease... The manifestation of this pear disease is angular spots of light yellow or pale green color, which become noticeable only when the leaves of the pear reach normal size. Infection with the virus occurs during vaccination.
Control measures. Obligatory careful selection and culling in nurseries of 2-year-old seedlings affected by mosaic. It is no longer possible to save diseased seedlings and young trees, they are burned so that the virus does not infect neighboring trees.
Sooty fungus on a pear
 Sooty fungus on a pear
Sooty fungus on a pear
Sooty fungus. A black bloom appears on the leaves and shoots of fruit trees. Blackening is the result of the development of a sooty fungus that settles on the surface of leaves, shoots, annelids and even fruits.
Control measures. It is necessary, first of all, to find out the cause of the appearance of the sooty fungus and eliminate it. Sprinkle the trees with a copper-soap solution (5 g of copper sulfate and 150 g of soap per 10 liters of water). You can treat trees with a solution of Bordeaux liquid or copper oxychloride, as in the case of scab. Avoid excessive soil moisture and thinning thickened tree crowns.


D.s.-kh. Doctor of Economics, Professor, Saratov State Agrarian University named after N.I. Vavilov "

Danilova T.A.
Using material by Marcin Oleszczak
Factors affecting the degree of rustiness of apple fruits. Causes of the appearance of various types of leaf spots
The prevailing weather conditions in the spring of 2013 with severe drought during the first 6 weeks after flowering of the apple tree had a significant impact on the appearance of rustiness on the fruits of Golden Delicious, Gala and Aelis varieties. In addition, premature leaf fall was noted in some gardens, especially in the Golden Delicious variety.
Causes of fruit rustiness
This phenomenon occurs as a result of damage to the cells of the skin (epidermis) under the influence of external factors. This is the result of a natural process of tissue suberization in places where skin cells are damaged. They can be in the form of a sparse or solid grid, as well as in the form of continuous points. Often rustiness is manifested only in the deepening of the surface of the fruit - in the funnel. Sometimes it is so strong that it covers the fruit almost entirely, inhibits the growth of the fruit and leads to cracking. The degree of rust damage is genetically determined and manifests itself in different ways in different varieties.
An example of varieties, the fruits of which are easily subject to rusting, is Golden Delicious, while in Elstar, Gala and Champion varieties it is manifested to a lesser extent. In the Elstar variety, rustiness, as a rule, is uniform, and in the Gala variety, it is focal. The third group includes varieties, the fruits of which are covered with a brown net as a result of damage to plants by powdery mildew (Idared, Cortland, Paulared) or as a result of damage to the fruit (Jonagold and Rubin).
 The manifestation of powdery mildew on young leaves of an apple tree
The manifestation of powdery mildew on young leaves of an apple tree
It should be noted that on a tree, not all apples are affected by rusting to the same degree. More than others, the disease manifests itself in the most beautiful fruits, which are the most vulnerable to changes in weather, frost or hail, located at the periphery of the crown. Uneven browning of apples can be associated with the timing of flowering. Rust usually appears early in the growth of fruits, within 30-40 days after flowering, but the greatest susceptibility to this disease appears in the first 2-3 weeks after flowering.
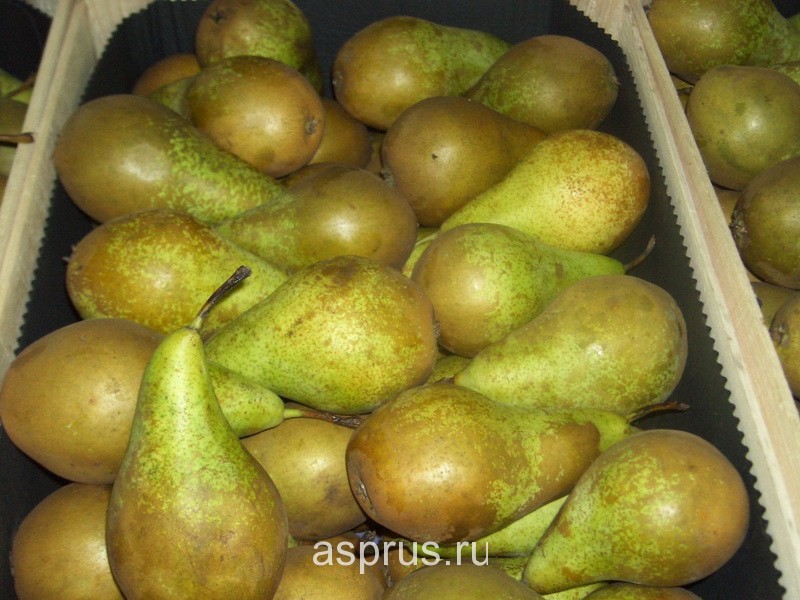 Rustiness on pear fruits Conference
Rustiness on pear fruits Conference
Evaluation of resistance to rustiness of pear varieties The conference showed that the period of browning of the fruits of this culture is longer than that of apple fruits and can take up to three months after flowering. During this time, the size of the fruit increases rapidly, and the thin layer of the cuticle inhibits the formation of spots.
Rustiness is often caused by disturbances in the synthesis of endogenous gibberellins. Apples with fewer seeds (hence producing few gibberellins) are more susceptible to this phenomenon. In turn, trees growing on slopes, in conditions of a high degree of insolation, produce less rusty fruits, because they produce more gibberellins. Among the climatic factors favoring the appearance of a net on fruits, the main ones are high humidity and precipitation. Even one drop of liquid at temperatures above 0 ° C in conditions of high activity of microorganisms will be favorable for the appearance of rustiness. Low temperatures in spring or early autumn damage the conductive tissues of the kidneys, impairing the supply of water to the future fetus, which also contributes to its browning.
 Grid on the fruits of the Golden Delicious variety
Grid on the fruits of the Golden Delicious variety
On heavy clay soils, with a high level of groundwater, apples suffer from rustiness to a greater extent. This phenomenon is also observed where the garden has been fertilized with high doses of nitrogen, which causes rapid growth of cells of the fruit with delicate skin. Browning is restrained by high doses of phosphorus-potassium fertilizers containing boron, as well as irrigation of gardens. Fruits are mostly covered with a rusty netting in dry conditions within six weeks after flowering.
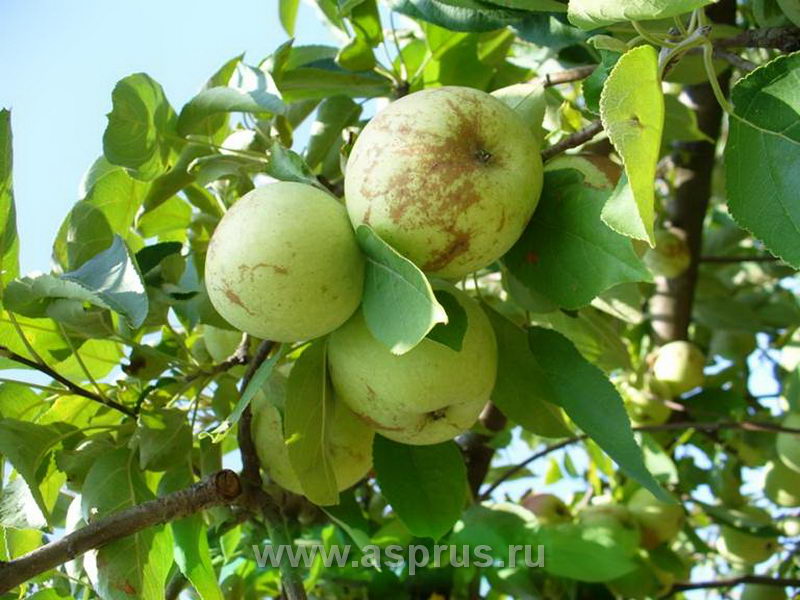 Netting on apple fruits due to powdery mildew
Netting on apple fruits due to powdery mildew
If we analyze the weather conditions in 2013 from May 16 to the end of June (the period of active cell division and growth of ovaries), the reasons for the rustiness of fruits in certain apple varieties become clear: a large number of precipitation, rapid weather changes, temperature fluctuations and intensive protection of the apple tree from scab. Unlike apple varieties that are not resistant to powdery mildew (for example, Idared), the appearance of a "net" on the fruits is the main consequence of this disease.
Necrotic leaf spot
This type of spotting is the result of fungal diseases (necrotic spots on the leaves and small dark spots around the edges), the signs of which should be detected in a timely manner. In publications devoted to this issue, there is information about the influence of various conditions (stress and precipitation after a hot dry period) on its occurrence. Such conditions mainly develop in July and August. Spotting can also occur as a result of physiological deviations - in conditions of magnesium deficiency and, judging by some publications, may be associated with a lack of manganese and zinc in the leaves. In the climatic conditions of Central Russia, the physiological basis of the disease is practically not found. The main factors, as a rule, are bad weather, a strong drop in temperature and prolonged rains. On the Internet, information can be found about root flooding as the cause of necrotic leaf blight. Such conditions cause stress in plants and associated hormonal disturbances - the appearance of ethylene or ABA (the aging hormone of plants). All of the above can be superimposed on a deficiency of magnesium and zinc in the soil (heavy rain leads to the leaching of magnesium, and the appearance of a large amount of manganese, a competitor of divalent ions, especially magnesium, also causes zinc deficiency). Observations have shown that the use of foliar feeding magnesium in combination with low doses of zinc (Zn once 40-50 g / ha) reduces the frequency of necrotic leaf spot. In the gardens where the observations were carried out, the signs of the disease were eliminated (or minimized) due to the use of manganese fertilizing. This conclusion is based on an analysis of the manganese content in soils and observations of the course of weather conditions, including, in particular, the presence of heavy rainfall over the past two years. Undoubtedly, the role of zinc is useful in reducing the disease, acting as an element responsible for the synthesis of the auxin precursor.
 Brown spot on the leaves of an apple tree
Brown spot on the leaves of an apple tree
Alternaria on an apple tree
Another disease, which potentially or theoretically can include such signs as rot and premature leaf fall, is Alternaria alternata. Lesions caused by this pathogen can appear on apple leaves in spring or early summer. Necrotic spots with a diameter of 1.5 mm to 5 mm are brown or black-brown in color. The border of the spot is black and purple. They can connect with each other and darken over time, acquiring a specific pattern called the "frog's eye".
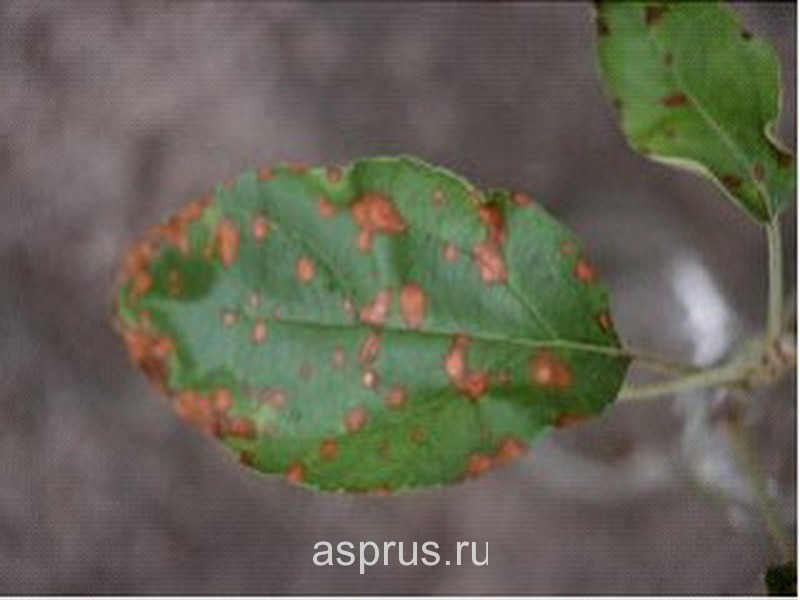 Manifestation of Alternaria on apple leaves (photo: Agrotech-Garant)
Manifestation of Alternaria on apple leaves (photo: Agrotech-Garant)
The result of the appearance of spots is the premature fall of leaves. Symptoms of the disease can also appear on fruits in the form of spots similar to spots of subcutaneous bitter pitting. However, these signs appear relatively rarely, more often premature leaf fall simply occurs. The fungus hibernates as a mycelium on fallen leaves. The spread of the fungus can occur even a month after leaf fall. Infection can occur even after a few hours at temperatures from 21 ° C to 27 ° C and the presence of drip-liquid moisture on the leaves. The optimum temperature for the development of the disease is 25 ° C. The spots usually appear two days after infection. As the disease progresses, large quantities of substances are produced that are toxic to susceptible varieties and lead to defoliation. The two most sensitive varieties Golden Delicious and Imperia are damaged especially often and with great intensity. The development of disease and defoliation of shoots is also facilitated by the presence of numerous ticks and their damage.
Unlike the spots described, small, irregular, oval, necrotic spots with a diameter of 6 mm may be present on the leaves of the apple tree, at first they are light brown with a darker outline, later gray-white. Black dots appear on the spots - pycnidia of the fungus.
Other potential pests
Spots on leaves and fruits can be caused by the fungus Mycosphaerella. Sphaeropsis malorum can give similar signs of manifestation. It is believed that bacteria, namely Pseudomonas syringae py, can also lead to leaf spot. Papulans. On the leaves, the disease manifests itself in the form of small dark brown spots... This season, the leaves of the Golden Delicious cultivar have been spotted with tiny specks, with the thin edging characteristic of Pseudomonas.
It is difficult to say the influence of which pathogens caused the leaves to fall off in this variety, since it is impossible to talk about the cause of the disease without actually determining the presence of a specific pathogen on the leaves in the form of bacterial cells, fungal hyphae, spores or fruit bodies.
 Quality fruits of the Golden Delicious variety grown in an intensive garden
Quality fruits of the Golden Delicious variety grown in an intensive garden
When diagnosing, it should be borne in mind that different pathogens can cause similar signs of the manifestation of the disease, just like the manifestation of the same disease can change.
Preliminary results prove the possibility of co-occurrence on leaves of necrotic spots caused by Alternaria and Pseudomonas.

Mukhanin I.V.
President of the Association of Russian Gardeners (APPYAPM), Chairman of the Association of Nursery Gardeners (ASP-RUS), Doctor of Agricultural Sciences

L.A. Schekotova
Candidate of Biological Sciences, Scientific Consultant of the ASP-RUS Association

Danilova T.A.
Specialist of the Association ASP-RUS, student of MichGAU
Using material from Professor Remigiusz W. Olszak
Harmfulness and spread of aphids
These small (2-3 mm long) insects are the most common and dangerous pests all fruit trees. Usually they massively populate and infect various parts of plants (buds, leaves, shoots), forming colonies from several to hundreds and even thousands of individuals. Those in colonies, as a rule, wingless individuals, suck sap from the tissues of leaves and shoots of plants. Every second generation of offspring gives rise to winged insects that spread to other trees. At the end of the aphid's abdomen there are juice tubes through which sticky insect secretions come out - pad. The body color, depending on the type of aphid, is dark green, yellow, brown or even black. Sometimes a waxy bloom on the surface of the cuticle of aphids gives them a whitish color (for example, in the root beet aphid) or it is long waxy threads (cotton aphid). Some pest species are found only on certain host plants (for example, apple aphid), other species can create different colonies (for example, peach aphid or potato aphid). Aphid secretions (honeydew, or honeydew) contain a large amount of sugar and cover parts of plants on which pests settle. Dark spots of sooty fungus appear on this pad, which is an excellent environment for the development of fungal organisms.
Apple aphid is widespread throughout Russia, first of all, it settles in nurseries and in young gardens, and on old trees - mainly on annual shoots. Depending on weather conditions, this pest can have from 10 to 16 generations during the growing season. During budding, the first generation larvae emerge from the wintering eggs, which penetrate the buds. The aphid has an intense green color with two black tubes at the end of the abdomen. Insects can completely cover non-lignified shoots, petioles and young leaves.
In weakened trees inhabited by aphids, winter hardiness sharply decreases. The apple aphid can carry viruses. Studies have shown that there are varieties with increased resistance to some types of aphids.
Red-gall apple aphid
It is found throughout Eastern Europe, inhabiting both young and old trees. The first larvae emerge from eggs in early spring - in early April, initially localized on vegetative buds, then on leaves, peduncles and even fruits. The larvae are light pink in color, and the adult insects are brownish-pink or gray-blue in color with a white powdery bloom. This type of aphid causes serious damage to plants - leaves curl and set fruits are deformed. The leaves turn yellow, turn brown, turn black and dry out. Buds do not develop, young leaves in the rosette are strongly curved. From deformed buds, small, very dense fruits develop. A strong spread of aphids can lead to the loss of 80% of the marketable crop. By the second half of August, from 6 to 10 generations can develop on an apple tree.
A large number of drugs have been registered to combat apple aphids. It is best to use the natural enemies of aphids that are selective for the fauna - aphidophages, which play an important role in reducing the number of these pests. Studies have confirmed that in the absence of aphidophages, it is extremely difficult to control aphids, and in some cases it is almost impossible. Treatment of plants with chemical preparations should be carried out when the economic threshold of harmfulness is reached, i.e. when the cost of pesticides is paid off by the profit from the saved crop. In this case, the profitability of growing a crop increases.
Cotton aphid
Another type of aphid, also dangerous in our conditions, is the cotton aphid. It is widespread throughout the country, slightly less in the northeastern regions. The larvae overwinter on the roots, which are located below the soil surface, and in "nooks" - cracks in the bark on the trunks and in the buds. Throughout the growing season, they feed on young tree roots, and also settle on trunks and branches or in holes from mechanical damage.
The reddish-brown body of the aphid is covered with long white waxy filaments. Places with pest colonies look like they are covered with cotton fibers. Trees inhabited by aphids form short growths, the leaves are covered with sooty mushrooms. It is important to take into account that damage to the bark facilitates the penetration of various pathogens, which weaken the plants, as a result of which the yield decreases.
To combat cotton aphids, first of all, selective preparations should be used to limit the influence of this pest. Important role play two types of beneficial insects-entomophages - a ladybug and a common earwig. To increase their number, you need to artificially transfer insects to the garden. The number of entomophages can be increased by providing them with various “dwellings”. For example, you can fasten pieces to trees corrugated paper or small bundles of straw.
Aphids in a pear garden
Aphids can be a problem for the pear garden too. Usually, the list of pear pests includes brown and green pear-umbrella aphids. Each of these species can have several generations. The greatest damage is caused by brown aphids. She settles and sucks juice from leaves, stalks, sometimes from young shoots. As a result - deformed leaves, slower growth of shoots.
Cotton aphid on a pear damages the roots of young plants and seedlings in nurseries, so you need to look at the roots of weakened and dying plants, aphids can also damage relatively large plants. To combat it, it is recommended to use selective plant protection methods for beneficial fauna. However, as with the apple tree, effective pesticides are also used.
Aphids on the drain
Due to the ability of aphids to spread the plum sharka virus, it is important to start fighting these pests as soon as possible after the first individuals appear. Therefore, it is important to inspect the plantings from the very beginning of the growing season - you need to look at the buds (before the plum blossom), and then the shoots and leaves.

Pralia Ivan Ivanovich
Doctor S.-kh. sciences, gen. Director of LANDSCAPE LLC.
Brief description of the main diseases of the apple tree
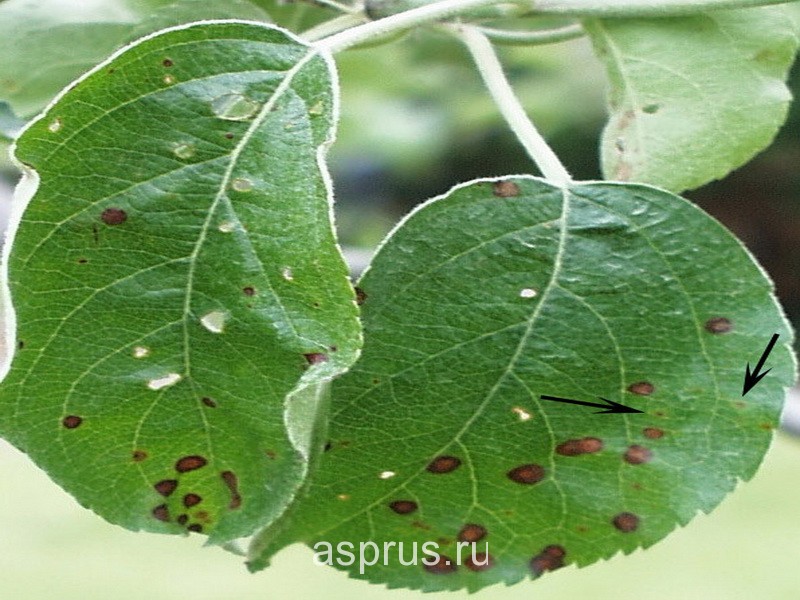
Apple scab(Venturia inaequalis Wint.) (Photo 1) is the most aggressive apple disease. It is widespread everywhere, but most severely damages in areas of intensive horticulture in the Trans-Volga, Central Forest-Steppe, Volga-Don and Azov-Black Sea zones. The vast majority of apple varieties are affected. Only a few varieties of this crop are relatively resistant to scab - Prima, Florina, Interprise, Golde Resisten, Liberty and Berkutovskoe.
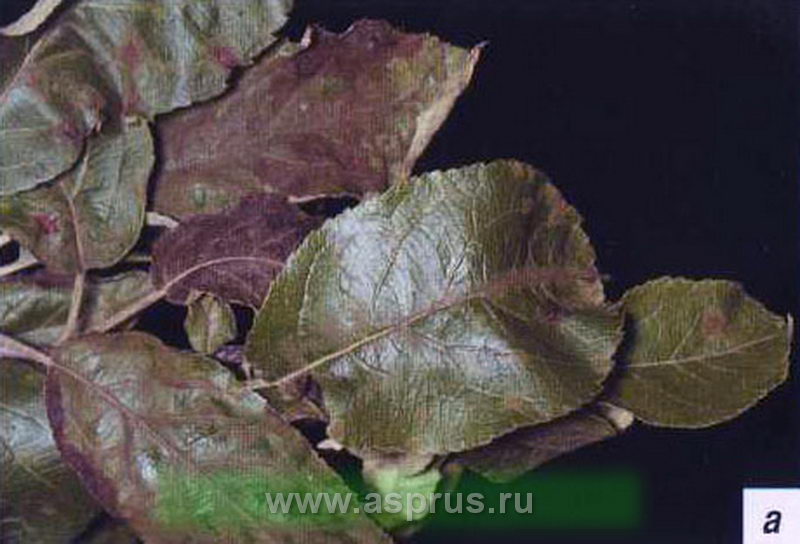 |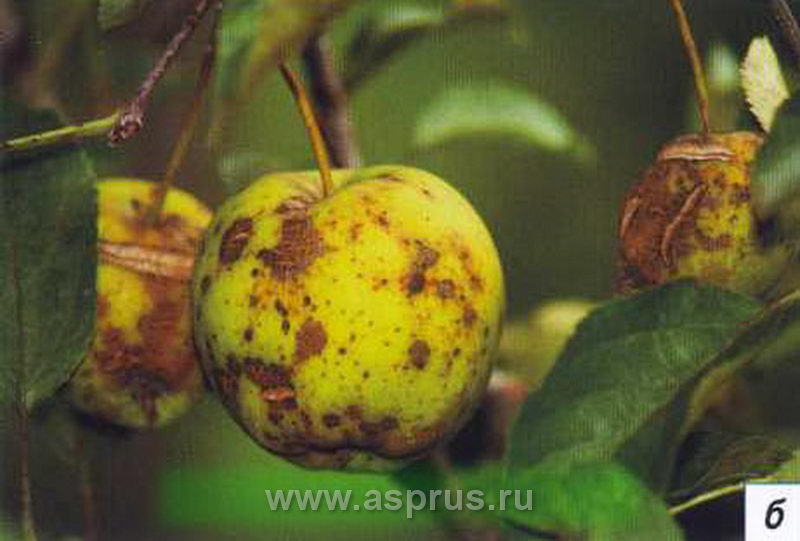  |
Photo 1. Apple scab: a - scab on leaves; b - scab on fruits.
The source of infection are fruiting bodies (perithecia), wintering on fallen leaves.During the growing season, infection of leaves and fruits with scab occurs both as a result of the dispersion of spores (ascospores) from overwintered leaves and conidiospores from leaves infected during the growing season, flowers and fruits ...
The most favorable conditions for the development of scab are air temperature and the duration of leaf wetness. The optimum temperature for germination of scab spores is considered to be the temperature range of 13-21 ° C, and the period of leaf wetness is about 8-9 hours. It has also been proven that the increased (82%) air humidity plays a significant role for the scab aggressiveness. Even in the absence of a combination of such conditions, in some hot periods of summer, there is a strong infection of leaves and fruits with scab.
Damage to the pedicels and stalks with scab leads to the loss of flowers and young ovary, and damage to the fruits leads to a loss of their quality. Severe damage to the leaf apparatus of a tree affects not only the harvest of the previous year, but also frost resistance. This is the harmfulness of scab. Symptoms of scab on leaf blades are initially chlorotic and then oily spots, which are then covered with a gray-green dense bloom. On the affected fruit, dark spots with a velvety bloom are formed. The tissue under the spots becomes corky, which blocks the development of the fetus and deforms it.
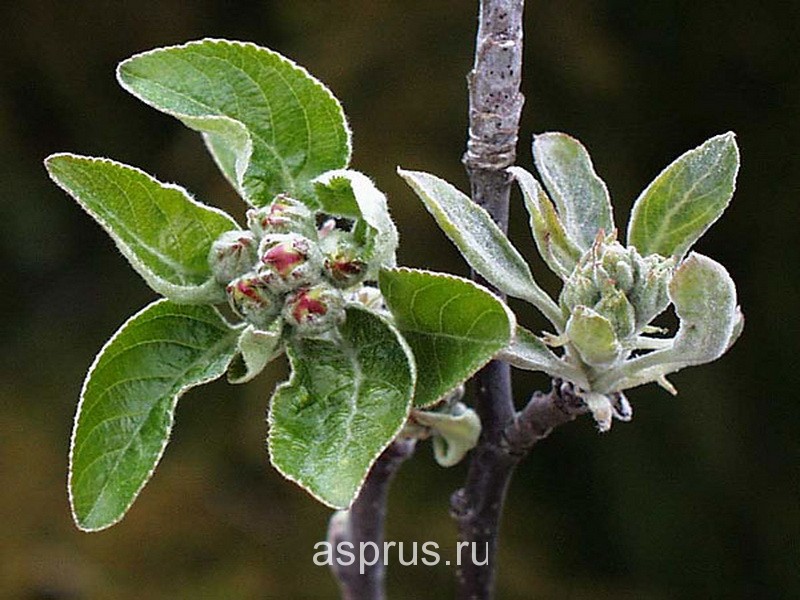
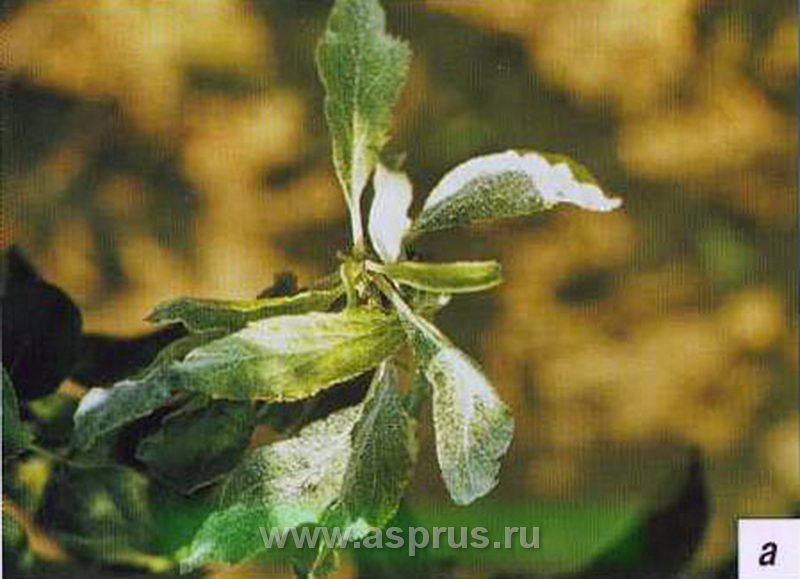
Apple powdery mildew(Podosphaera leucotricha Salm.) (Photo 2) - the second most important disease in the garden. It affects numerous apple varieties, but prefers the following zoned varieties - Jonathan, Renet Simirenko, Idared, Boyken, Aprelskoe, Berkutovskoe and Kortland.
 |
||
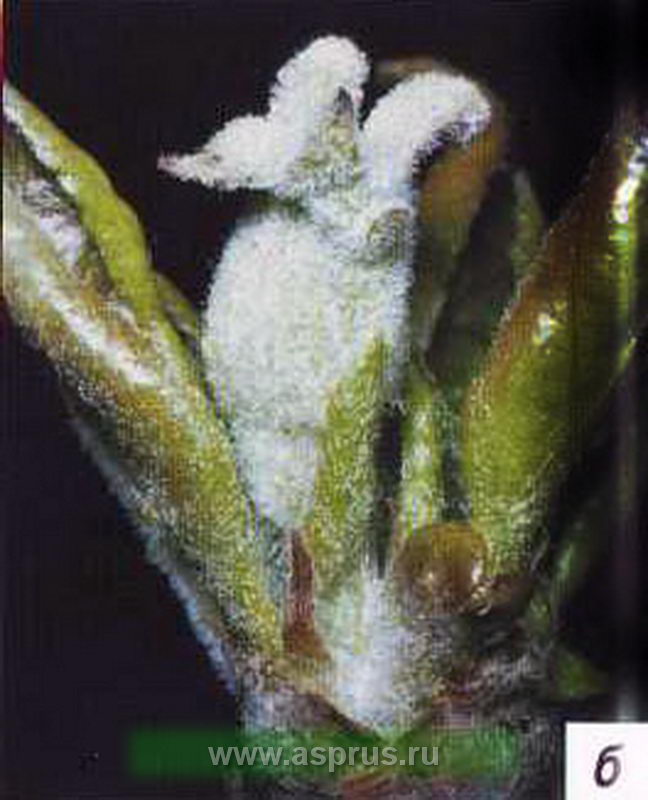 | 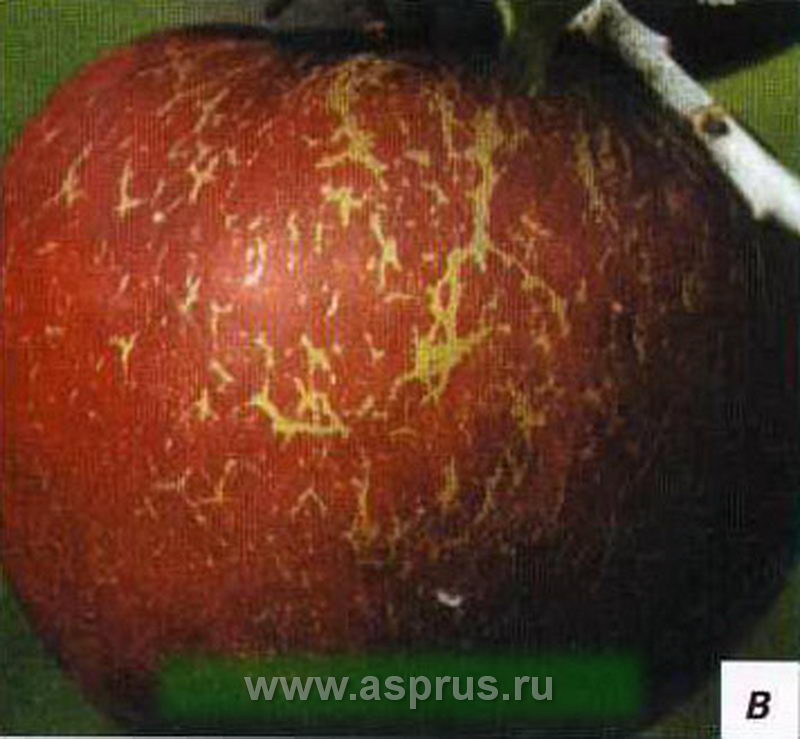 |  |
Photo 2. Powdery mildew of an apple tree: a - plaque on the leaves; b - kidney damage; c - damaged fetus; d - necrosis on the leaves.
The source of infection is the overwintering mycelium under the covering scales of diseased vegetative and generative buds. The primary infection of the disease appears at the beginning of the green cone phenophase. Secondary infection is noted on the 10-15th day after the manifestation of the primary. Affected shoots have shortened internodes. The organs of the flower are strongly deformed and do not form an ovary. The affected parts of the plant are covered with a dense white song, which then darkens. As a result of lesions in susceptible apple varieties, the mass of leaves and the growth of shoots are reduced by 2-3 times, the occupation is crumbled by 50-60%. This is the harmfulness of powdery mildew. In addition to leaves and shoots, powdery mildew also affects fruits, forming spots on them in the form of a rusty mesh. Powdery mildew is especially harmful in nurseries, which reduces the yield of planting material by more than 20%.
The greatest harmfulness of powdery mildew is manifested in mild winters in combination with low relative humidity in the spring and summer. V cold winter(especially in the northern zones) buds infected with powdery mildew freeze and fall off, so here in the spring the disease manifests itself to a lesser extent.
Bacterial burn(Erwinia amylovora (Burrill) Com,) (photo 3) dangerous quarantine object. In our country, the disease is present in all areas of horticulture, damages more than 150 plant species, but most often it occurs on pear, apple and sweet cherry. The source of infection is a hibernating bacterium - gram-negative, aerobic, movable bacillus, difficult to diagnose. The pathogen persists in infected plant debris or under the bark of infected trees.
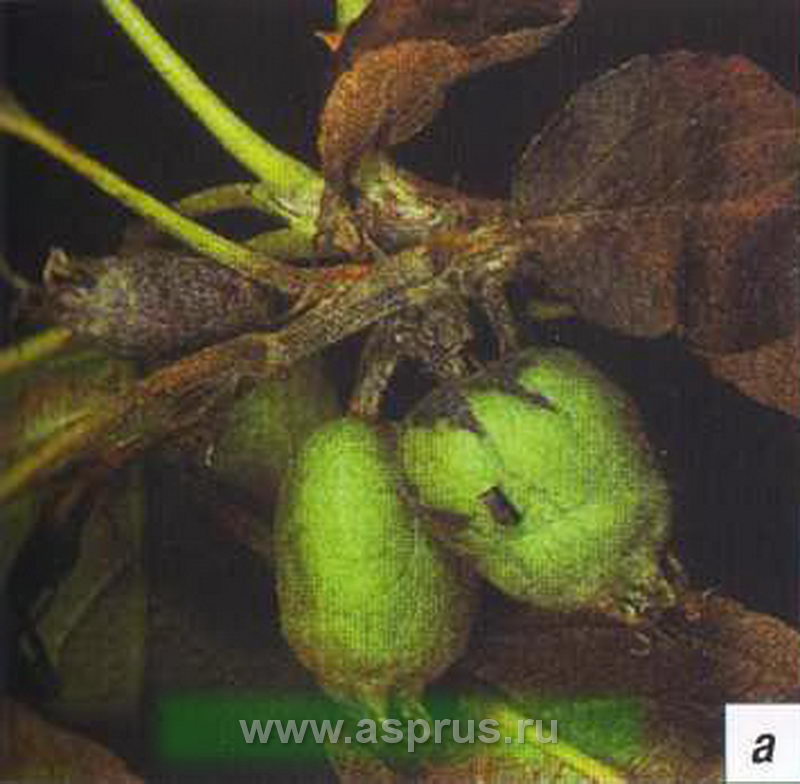 |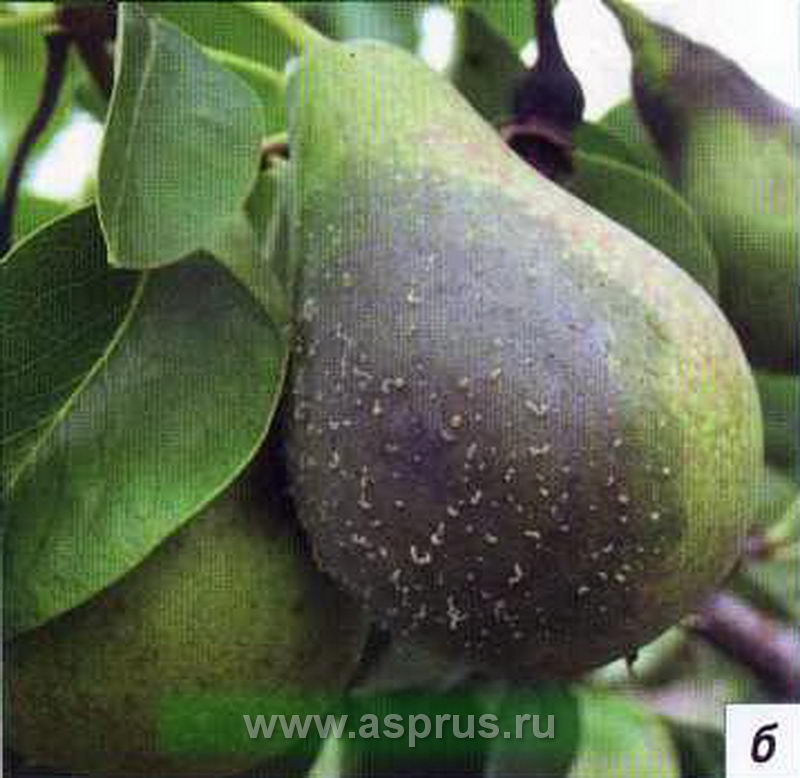  |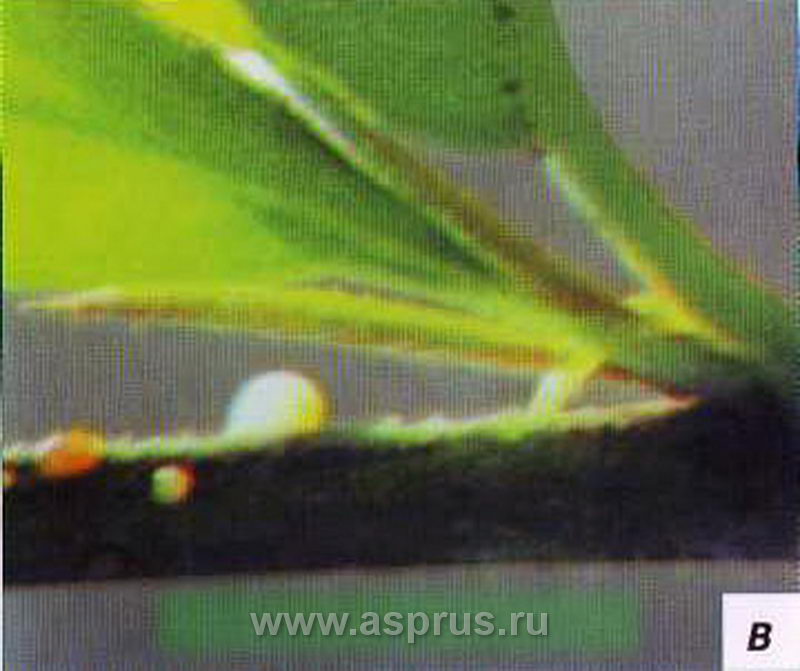  |
Photo 3. Bacterial burn: a - damage to ovaries and leaves; b - damage to pear fruits; c - exudate on the escape.
The bacterium is spread mechanically during pruning, as well as by insects, in particular bees, during flowering. Over long distances, the causative agent of the disease. Transferred by cuttings or planting material. During flowering, bacteria penetrate into the pistils and stamens, and from there into the wood of the fruit branches.
Signs of the disease: sudden wilting of flowers and tops of young shoots. The damaged parts of the plant do not fall off, but remain on the branches. Bends and swells and fills with liquid, which then flows out in wet weather. Dents form on infected wood. In these places, the bark softens, becomes watery, drops of colorless and yellowish liquid appear on the surface of the wood and fruits - exudate. This is the main (a characteristic sign of a bacterial burn from other bacterial diseases - Xanthomonas and Pseudomonas. In addition, the infection proceeds very quickly, the fruits immediately wilt, and the shoots dry out. With a strong infection, the disease penetrates into the skeletal branches, then into the stem and can cause the complete death of the tree or a whole garden in two to three months, which is the danger and harmfulness of a bacterial burn.
The most favorable conditions for the development of fire blight are the following conditions: warm and humid weather in autumn, frost-free and snowy winters, wet and warm spring (temperature - about 18 ° C), especially during the flowering period. To maximize the potential for infestation, intense fog and moisture retention on the leaves are required for 9-12 hours a day.
Brown spot of apple tree leaves(Mycosphaerella pomi Lind) (photo 4) is ubiquitous. Almost all varieties are affected. According to the type of manifestation of spots on the leaves, two groups of the disease are distinguished - physiological and infectious. The first manifests itself as a result of a violation of the conditions for plant growth, the second - as a result of an infectious infection (phylostictosis). The development of the first (non-infectious) type is facilitated by dry winds and a sharp change in temperature during the day. The development of the second (infectious) type is facilitated by high and prolonged air humidity and heavy rainfall.
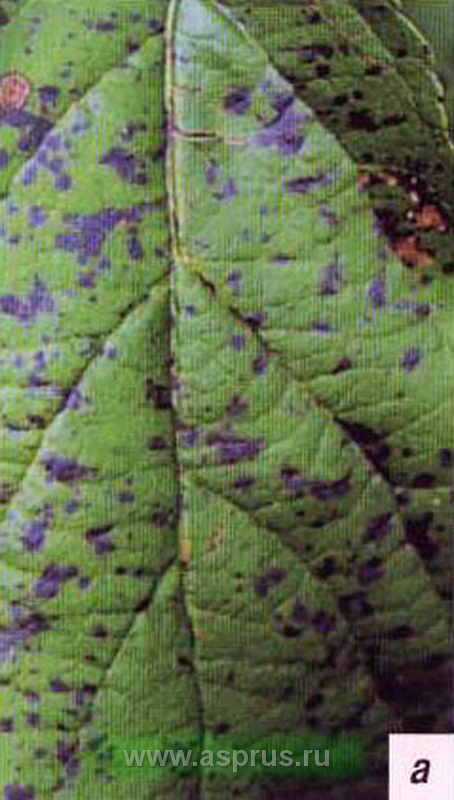 | 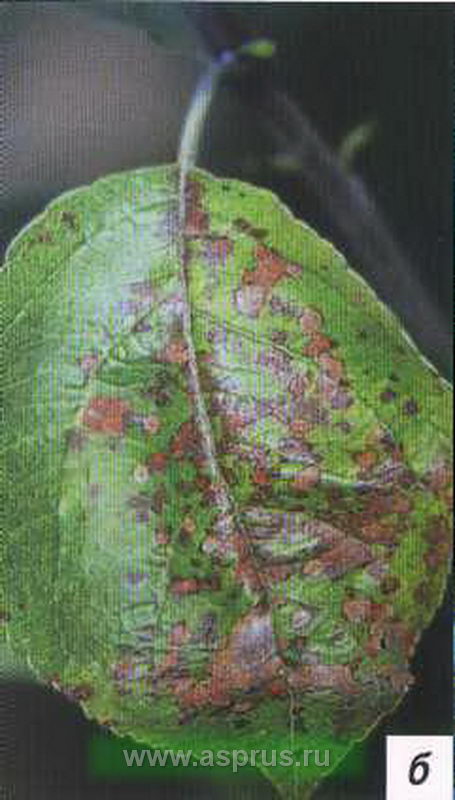 |
Photo 4. Philostiktosis: a - the beginning of development; b - severe defeat.
The causative agent of brown spot overwinters in the imperfect conidial stage on fallen leaves. Distribution occurs due to the expansion of conidiospores. The primary infection appears in May, but the disease develops most intensively in July-August.
The harmfulness of brown spot is manifested in the defeat of the leaves (from the presence of several small spots to the appearance of holes) and their premature shedding, which leads to a decrease in the setting of the crop for the next season.
Apple moniliosis(Monilinia fructigena Schr., Monilinia cinerea Pers.) (Photo 5) is widespread. It manifests itself in two forms - "mushroom burn" and "fruit rot". The first appears on the flowers, in the form of their death, the second - on the fruits, in the form of small brown spots, which then grow and cover the entire surface of the fruit. They form yellow-white or ash-gray sporulation pads of the fungus, scattered over the entire surface or arranged in concentric circles. At high or low air temperatures, spore neck does not form. In these cases, the fruits acquire a blue coloration and glossy appearance. Most often they remain missed on a tree.
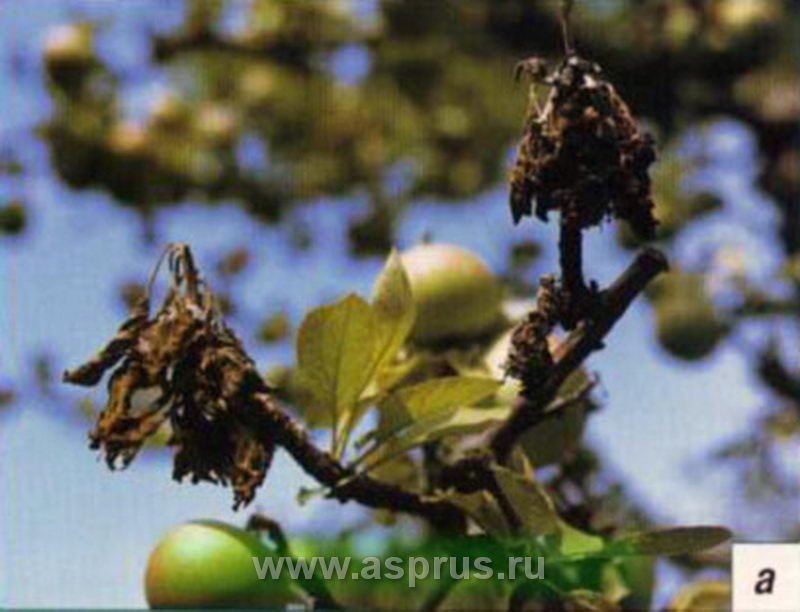 |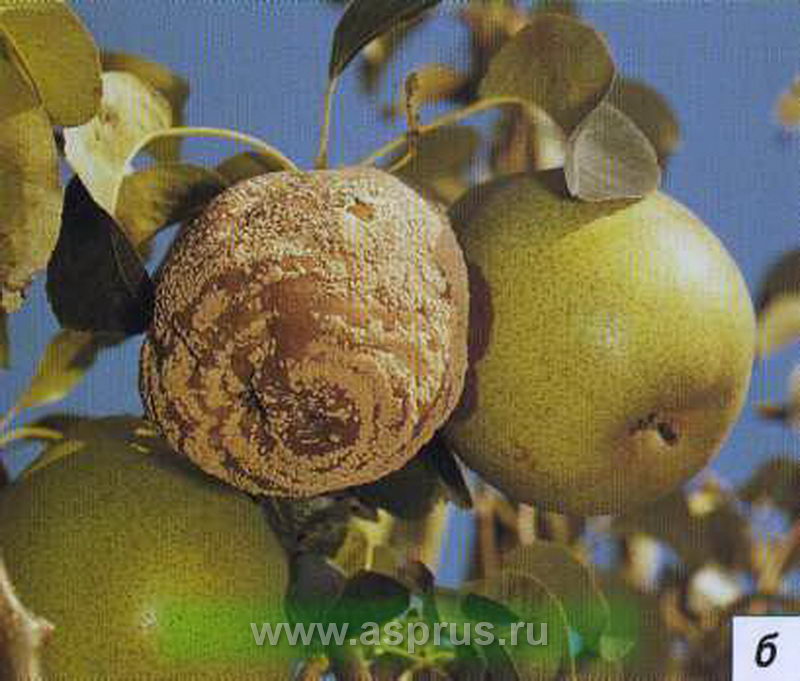  |
Photo 5. Moniliosis: a - monilial burn of shoots; b - monilial fruit rot.
The causative agent of moniliosis hibernates on the affected branches, shoots and mummified fruits in the form of mycelium, on which conidia form in spring. Moniliosis increases its harmfulness at temperatures of 24-27 ° C in combination with prolonged rains. Such conditions not only promote the spread of conidia, but are also necessary for their germination. Stone fruits suffer the most from "fungus burn", and pome crops suffer from "fruit rot". In some years, against the background of mass reproduction of the pathogen, complete death is noted Photo 6. Common cancer: a - on the shoot; 6 - on the trunk. harvest immediately after flowering.
Common cancer(Dialonectria (Nectria) galligena Bres) (photo 6) is ubiquitous. In the development cycle, it has marsupial and conidial stages. It penetrates into plant tissues through various damage to the bark. Therefore, most often the symptoms of the disease are manifested in places of frostbites, pruning of branches or in places of damage to the bark by mechanical or other means. The pathogen hibernates in places where plants are affected by mycelium and perithecia. Wet or rainy weather is essential for dispersing spores. Most common cancer spreads in the spring or fall. Cancer affects the conducting system - and this is its main harmfulness. In the affected areas, metabolism is disturbed and the water balance deteriorates. As a result, growths with open wounds are formed (open form), in the middle of which darkened wood is visible. If the wounds are closed by growths and influxes (closed form), then only deep cracks are visible on the bark.
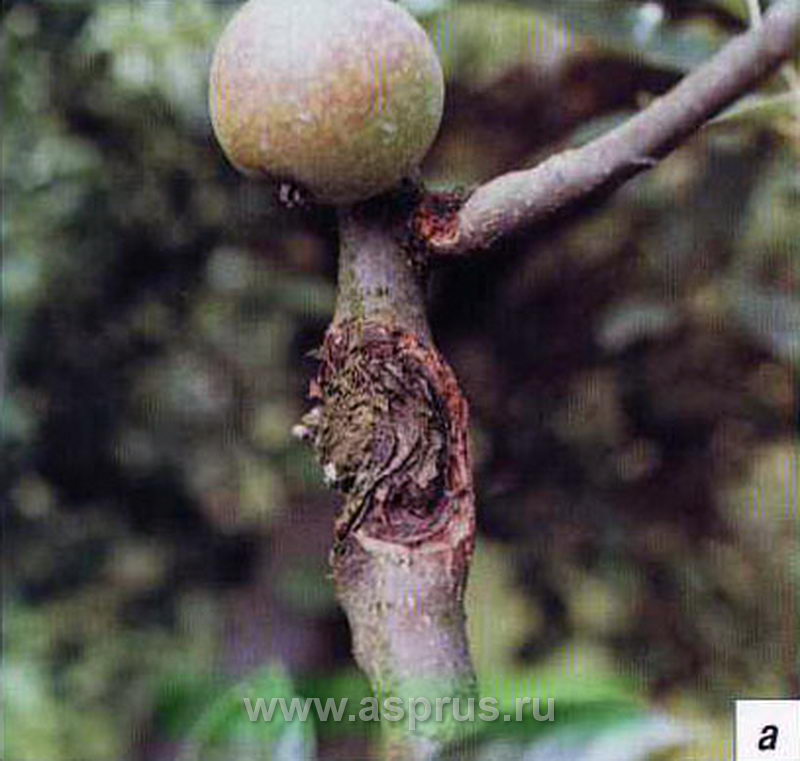 |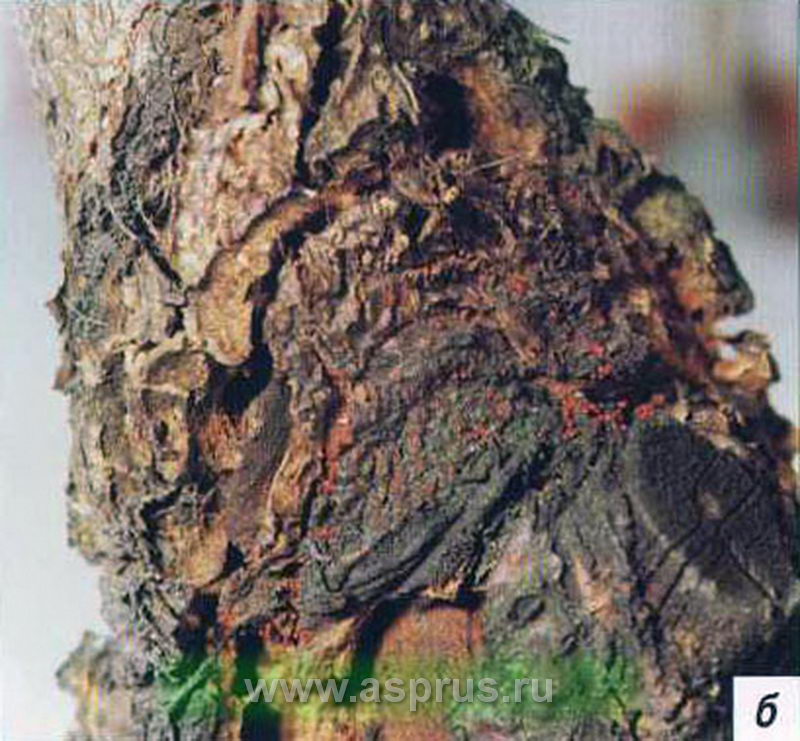  |
Photo 6. Common cancer: a - on the shoot; 6 - on the trunk.
Black cancer(Shpaeropsis malorum Peck.) (Photo 7) is distributed everywhere, but most strongly in old gardens. For an optimal cycle of disease development, a temperature of 25-27 ° C is required. The incubation period lasts 15-27 days. Indirect factors that contribute to the development of the disease: weakened trees, sun and sun-frost bark burns. On glorious trees, black crayfish develops more strongly.
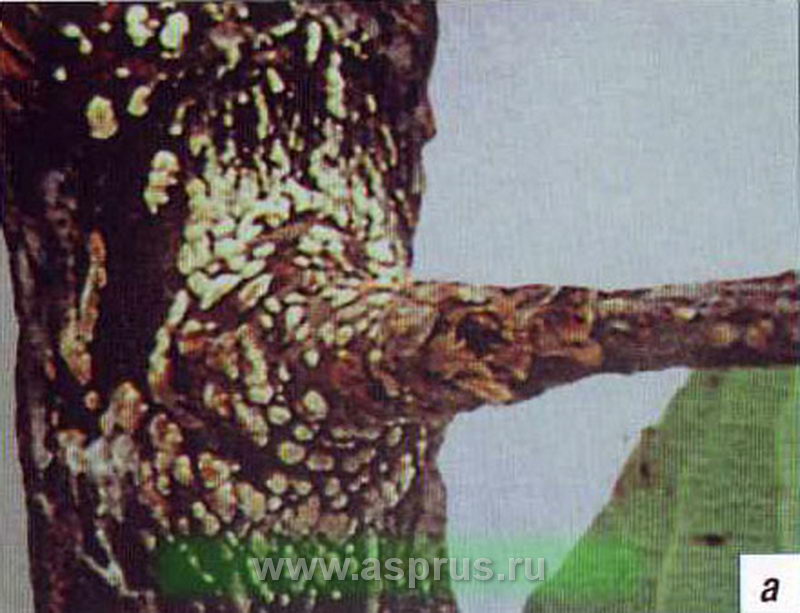 |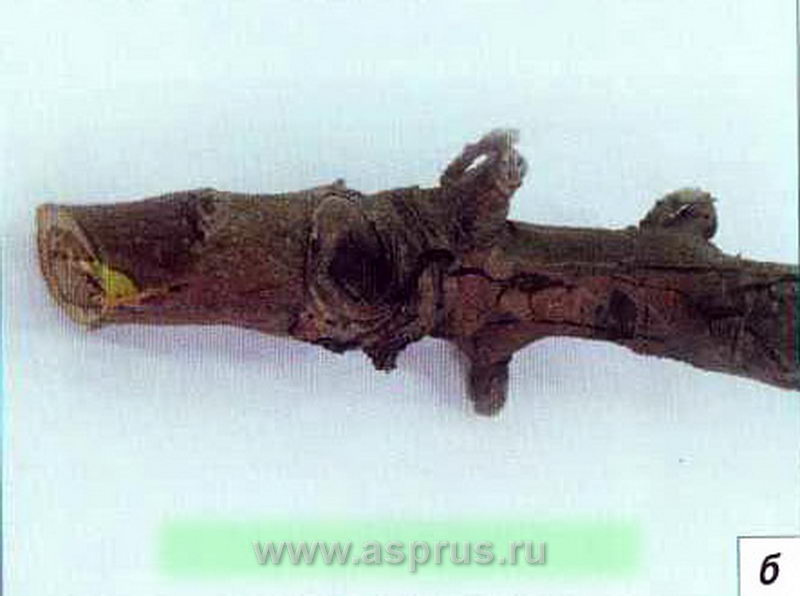  |
Photo 7. Black cancer: a - fruiting bodies on the trunk; b - affected shoot.
The disease hibernates in the form of mycelium on the affected tissues of the bark. The disease can be diagnosed by the brownish-violet spots formed on the branches and boles, in the form of dents on the surface. Over time, the bark turns black and cracks, forming a network of longitudinal and transverse cracks. This is one of the typical signs of this disease. Second characteristic feature devils about cancer - the formation of black tubercles under the epidermis of the cortex - the pycnidia of the pathogen. On young growing branches, the bark first turns red, then swells, stagnates and then breaks. The branches quickly dry up, the leaves on them turn brown and sag, the fruits shrivel and dry up, the affected branches look like those burned by fire, and therefore they often confuse black cancer with a bacterial burn. Depending on the year, the proportion of affected branches reaches 25-35%, and flowers and fruits - 35-40%. Unlike fruitlets affected by moniliosis, fruits affected by black cancer have not a shiny, but a dark gray matte rough surface. Pycnidia are visible under the skin.
APPLM members

General Director of the company "FitoMag" LLC, Moscow
The main areas of work of the APPLPM
Are you planning to get a large harvest of pears? Then you must pay special attention to the trees. Diverse and insects try to live on the pear. The spots on the leaves are evidence of this. You must be able to provide prevention and treatment. First, you need to find out what each disease looks like and what symptoms appear.
Infections
Consider the most common diseases that can affect your orchard, including a pear. To be able to fight the disease, let's face it:
- Opens up our list of known scab infections. This is a fungal disease that kills fruits, shoots and leaves. Most often, the microorganism is located under the bark of a diseased tree or in fallen leaves. If you notice black spots on the leaves of a pear, then most likely this is a scab that has manifested itself. Diseased fruits crack and fall off.
- Next on the list is fruit rot. This is another representative of a fungal disease. It manifests itself after the tree is already infected with scab. Most often, the fetus suffers from the infection. If brown-black spots appear on them, this is one of the signs of fruit rot.
- Next on the list is another equally popular disease. It is called powdery mildew. It, like its predecessors, is a fungal infection. Most often, the disease lurks in infected kidneys. Everything suffers from it: fruits, flowers, buds, branches. If yellow spots are found on the leaves of a pear, then these are the first manifestations of powdery mildew. Constant dry weather contributes to its early spread.
- The disease, no less known to summer residents, takes the next place in our list. And the name of the disease is rust. It is also considered one of the varieties of the fungus. Orange spots on the leaves of a pear indicate the presence of a disease. If the tree is not cured in time, then next year it will not bear fruit.

The enemies of pears are not only fungal diseases, but also insects, which are also recommended to get rid of. Let's consider them in more detail and find out what harm they bring to trees.
Pests
On the pear, spots (on the leaves) appear not only from infectious diseases... There are several main enemies of this culture that you should know by sight. So, here they are:

- If you find orange spots on the leaves of a pear, it is possible that the tree is under the influence of hawthorn. She has a remarkable appearance... In length, it reaches 40 mm. There are three multi-colored stripes on the back.
Now we have found the reason, as a result of which spots are formed on the pear (on the leaves). Such signs appear suddenly, so it is worth learning about the methods of their treatment.
Against scab
Getting rid of an infection is easy. In early spring, be sure to spray the pear, as well as its buds, foliage and bark. For this, a solution is prepared from Bordeaux liquid and copper oxychloride. If it rains after spraying, the procedure must be repeated. In this case, you need to maintain a pause of two weeks. Diseased leaves should be disposed of, and the soil should be additionally treated with Nitrofen.
Removing fruit rot
If such a disease has taken root on your pear, then it can be removed using a special spraying. To do this, use diluted bordeaux liquid... Before that, you must remove all bad fruits and leaves.
Getting rid of powdery mildew
It is difficult to eliminate such a fungal disease. But if you want to get a rich harvest of pears, then use our recommendations:
- normalize watering, preferably daily;
- Spray with colloidal sulfur every week;
- it is also recommended to use soapy water for washing the barrel;
- constantly clean the tree of affected branches and leaves.

If you carry out all these procedures regularly, it will go away.
Spray treatment is also carried out for rust. To do this, use a solution of Bordeaux liquid and copper oxychloride. The procedure should be carried out strictly in early spring, when the buds begin to bloom.
Insect treatment
We have learned how to remove stains on pear leaves from fungal diseases. Now you need to treat trees from insects. Each caterpillar has its own weak points, so the preparations will be different. Let's consider each case separately.
From a tick
- spraying with a solution of colloidal sulfur and mitaka;
- diluted "Nitrofen" in the amount of 300 grams is suitable for young trees;
- after flowering, processing with "Karbofos" in the amount of 90 g is allowed.
Against the honeydew
You can get rid of this insect in the most unusual ways. Let's consider each of them separately:
- Catch ladybugs and release them in your fruit garden;
- carry out additional spraying with "Nitrofen" and "Karbofos".

If you want to get rid of, then here you need to try. To do this, you need to do the following:
- inspection of the tree and removal of caterpillars and larvae from it;
- spraying with tobacco and wormwood;
- treatment with various biological preparations, for example, a suspension of "Endobacterin", is allowed.
Now you know not only what caused spots on the leaves of the pear, but also how to deal with them. Treatment is a good thing, but it’s still better that yours do not get sick.
Prophylaxis
To prevent diseases from appearing and returning, it is worth paying special attention to prevention. To do this, you need to carry out regular activities, which are as follows:
- Keep the soil around the tree clean. Remove fallen fruits and leaves regularly.
- Prune the tree. Remove all old and diseased shoots in time.
- Additional treatment with fungicides is allowed. They will help get rid of insects once and for all.
- The tree needs constant feeding mineral fertilizers and salts.
- Dig up the soil every year at the beginning and end of the season.

Do prophylaxis, and you will never know why spots on the leaves appear on the pear. The tree will thank you with a delicious and ripe harvest.
Today we invite you to familiarize yourself with the catalog of all pear diseases, with photos and descriptions, as well as tips for combating them. In the article we will talk about various methods of prevention, as well as about alternative methods of treatment. This fruit tree, unfortunately, is sensitive to many pathogens, both bacterial and viral or fungal. Therefore, if you want your orchard to be in excellent condition, you must carefully monitor it, and not only for the pear, but also for it a lot, but first things first.
Often, to determine what ailment struck a pear, its leaves can begin to turn black, curl to dry, at the very beginning of spring, which is not at all characteristic of it, and such a move can leave the gardener without a crop.
Often, one type of fungus, infecting one fruit tree in the garden, can spread to others, while being just as dangerous for all varieties and species. Therefore, if you find one of the pathogens on a pear, plum or peach, it is necessary to treat all other trees growing on your site in order to prevent it.
The main diseases of the pear with a photo:

As it became clear from the text above, timely detection of pathogens of ailments can save your entire garden, so take the study of the symptoms seriously.
Scab.
![]()
The fungus Fusicladium pirinum affects not only the pear, but also many other cultivated plants.
Symptoms: the foliage suffers first, a speck of dark green color can be observed on the bottom of the plate, plaque will be noticeable on these spots, these are mushroom colonies. As the fruit progresses and ripens, the scab spreads onto them. The peel becomes covered with spots, after which it begins to crack, the pulp in this place, on the contrary, acquires an uncharacteristic hardness, which reduces the taste. Deformation of the fetus occurs, they also lose their presentation.
Prevention:
Bordeaux liquid is a reliable remedy, it is necessary to process the pear three times in order to avoid scab:
- As soon as greenery appears on the tree.
- Spray the second time when the buds turn pink.
- After flowering.
The trunk's access to fresh air also significantly reduces the risk of scab. Therefore, be sure to thin out the crown, remove unnecessary branches, and be sure to coat the cut with garden pitch. For air to enter the roots, it is necessary to loosen the soil near the trunk circle. Also, do not forget to constantly remove fallen fruits and branches, foliage.
After leaf fall, all biological waste is burned away from plants. Those pears, which are heavily infected with scab, are treated with "Dnock" or with the help of "Nitrafen" paste in autumn. The systemic fungicide "Skor" shows excellent results, but it must be applied with extreme caution, acting strictly according to the instructions.
Do not give in to scab: "Muratovskaya", "Rusanovskaya", "Yanvarskaya".
Fruit rot or Moniliosis of apple and pear trees.

This disease harms not only the pear, but also many other fruit and stone fruit trees in the garden. Moniliosis can cause significant yield damage. It is especially dangerous during the fruiting period. But even after you have taken the harvest, the disease does not go away, but remains on the fruits, where it continues its destructive effect.
It manifests itself in two forms:
- Fruit rot... The causative agent is a harmful fungus. It is widespread in all regions where stone fruits are grown. This is a very dangerous enemy, because after its action, the fruits become completely unusable. The first manifestation will be the formation of a brown spot on the pear, which quickly grows throughout the fruit. Taste qualities are completely lost along with the presentation. Light spots appear on the rot, these are spores of fungal colonies. They are easily carried by rain or wind, and insects can also be carriers. The rapid development of events makes moniliosis a dangerous enemy for the entire garden, the incubation period lasts only a few days, and after a week the spores are ready to go to another tree. They penetrate through small cracks and damage. Optimal weather - temperatures from +16 to +30 С and high air humidity. If it is too dry, or hot, cold spores are not tolerated, but become bluish and mummified, this process most often occurs on fruits during storage. Therefore, it is important to remove them, especially if they have fallen from the tree. The fungus can remain in them until spring, wait for suitable conditions and start infecting healthy plants.
- Monilial burn... In this case, inflorescences and flowers, ringlets, fruit branches and twigs remain affected. This condition is also caused by the mushroom, which is stored in the mycelium, on damaged branches, and in the spring, upon awakening, begins its vigorous activity. The awakening temperature is approximately +14 C, and high humidity, in the form of rains and fogs, will also be a prerequisite for propagation. This fungus is especially dangerous in the Far East.
Methods of control and prevention:
Collect fallen fruits constantly, if they show signs of infection, destroy them away from the garden. Pluck sick, mummified fruits from the branches. Protect the pear and apple tree from scab, because at this time it creates cracks into which moniliosis penetrates, it is also necessary to protect the garden from birds, they can also peck fruits, damaging them, and opening the way for harmful fungi.
Infected plants can be treated with fungicides. At the first lesions, you can start working with the moth, repeat the procedure after 15-20 days. In the case of processing pears from scab and powdery mildew, processing from fruit rot can be omitted. The following fungicides have proven themselves well: "Horus", "Strobi", "Bordeaux liquid", "Abiga-Peak".
Remove the affected branches and fruits from the tree, because the causative agent of monilial burn usually hibernates there.
Sooty fungus, pear leaves turn black, what to do.

Blackening of pear leaves is the surest sign of the appearance of a sooty fungus on a tree. It manifests itself already from mid-July, in the form of a black bloom on leaf plates, in appearance it is very similar to soot. The main targets for the pest are weakened plants, with a lack of minerals, or on which pests or other diseases have settled.
The best habitat for the fungus is considered to be sugar secretions from insects, for example, aphids, in addition, it damages the structure of the tree, and soot bloom penetrates through these cracks. Insects also weaken the immune system of the pear. The fungus hibernates under the bark, or in dry foliage, and begins to act in the spring.
Fight and prevention:
Insecticide - "calypso" is used to prevent blackening of pear leaves, it destroys insect vectors. To contain the spread of the fungus in the complex, the fungicide "fitover" is used.
Resistant variety: "Cathedral".
Leaf diseases:
Due to leaf or root diseases, the bark of a pear can completely cease to bear fruit. These diseases are very harmful, they must be eliminated in time in order to preserve your harvest. The causative agents are fungi, viruses, bacteria.
Powdery mildew of apples and pears.

The carrier of powdery mildew is the marsupial mushroom. The symptoms are very vivid and difficult to confuse with other diseases. Already at the very beginning of spring, on young and not only shoots that have blossomed, you can notice a bloom white... Over time, it changes its shade to red, over time, the affected leaves or inflorescences begin to dry and fall off. Young shoots are worst of all, as a rule, whole mushroom colonies settle on them.
Fight and prevention:
Dry and damaged branches, shoots should be removed and burned away from the garden. From time to time, pears and apple trees must be sprayed with preparations: "foundation" or "sulfite".
Folk methods of dealing with powdery mildew on trees.
As a fight against powdery mildew using folk methods, you can process the garden with a solution: soda ash 50 grams, 10 grams of liquid soap, all this for 10 liters of water. Sometimes a 1% solution of potassium permanganate is used for spraying a tree.
Resistant varieties: Moskvichka, Dukhmyanaya, Yanvarskaya.
Rust of leaves.

A very dangerous disease that can lead to death of a pear. Caused by the fungus Gymnosporangium sabinae. An interesting fact is that for a successful life the fungus needs two plants: a pear and a juniper. It hibernates in a juniper, and in the spring it migrates to a fruit tree. It can destroy the entire crop, so fighting rust is very important.
Symptoms: on a juniper, the fungus spreads throughout the plant, infecting everything in its path, the disease is usually chronic. On it you can observe swelling and wounds, as well as orange jelly processes, which represent the mycelium. And in the spring, in wet weather, the spores begin their journey to the nearest pear, infecting young foliage and fruits.
Rust appears as rounded yellow spots, such spots appear after flowering, as a rule, at the end of April. Already in the middle of summer, rust appears on most leaves, and black dots also appear on the spots. The peak of the disease falls already in the fall, the red spots swell, processes appear on them, they contain spores that are transferred to the juniper, so that in the spring the circle will repeat again.
Prevention:
The first method of preventing rust on a pear is, oddly enough, pruning diseased branches on a juniper, they must be burned immediately, away from the garden.
Rust fighting:
- Infected branches must be cut, 10 centimeters lower, capturing the healthy part. Clean the lesions with a knife up to healthy wood, disinfect them with a solution of copper sulfate (5%), the last step will be to process the cut site with garden pitch.
- At the very beginning of spring, spray the pear with Bordeaux liquid 1%, it can be replaced with copper oxychloride. The second time spraying is carried out at the beginning of flowering, the third time shortly after the second, the fourth after another week and a half. Sometimes copper sulfate is used 50 milliliters of substance per 10 liters of liquid.
- To protect the garden from various diseases, such as scab, rust, you can use the preparation "scorch" 2 milliliters per 10 liters of water. Spray at least three times - before the leaves appear, before flowering, and after.
- By means of "triadimefon" processing is carried out 6 times a year, stirring 10 grams of the substance in 10 liters of liquid. Use the substance for the first time as soon as you see the manifestation of the disease, the rest every three weeks.
- Tincture wood ash- Dissolve half a kilogram of ash in 10 liters of liquid, let stand for 48 hours.
Resistant varieties: Gordzala, Gulabi, Nanaziri, Sailo, Sakharnaya, Souniani, Chizhovka.
Diseases of the trunk and roots, photos and treatment:
This group is the most difficult to detect and therefore the most difficult to treat. Since, pear leaves can turn black, and the reason will not be in them, but somewhere deep underground in the root system.
Black cancer (Antonov fire).

Black cancer develops slowly, over 2-3 years, first a crack appears on the bark, over time it grows, and the cambium is exposed. At the edges of the cracks, characteristic spots appear, brown in color, these are nothing but wounds into which spores of fungi, viruses and pathogenic bacteria are taken.
Struggle: Cut off the affected areas with a knife, with healthy tissue. Further, the resulting damage should be treated with the help, the clay should be mixed with the mullein, and applied on top of the wound. Always remove foliage and fruit by burning them away from the planting.
Resistant varieties: "August dew", "Samaryanka".
Cytosporosis (stem rot).

A fungal disease affecting the trunk, hence the second name. At the site of the lesion, the bark changes its color to red with a distinct brown tint; it soon begins to dry out. The fungus penetrates inside through sunburn and areas of the trunk damaged by frost.
The treatment is similar to the treatment of black cancer, it is necessary to remove the damaged area, up to healthy tissue, clean it with a knife. The operation site is covered with clay. For preventive purposes, it is necessary to constantly carry out sanitary, and also be sure to whitewash for the winter.
Resistant varieties to cytosporosis: "Moskvichka", "Yanvarskaya".
Bacterial burn.

The most common reason why the leaves of pears turn black is a bacterial burn of pome fruits. This is a rather dangerous disease, it can only be cured by applying an integrated approach. The causative agent is a bacterium that is carried both by insects and by the elements (rain, wind).
Symptoms: the first manifestations can be seen during flowering, you need to look at the inflorescences, they begin to fade rapidly, their color changes, and the pear leaves begin to turn black, curl, the inflorescences turn brown, the bark peels off and die.
The blight spreads rapidly throughout the tree and weak and susceptible plants die. Resistant plants will lose the ability to bear fruit for several seasons, after which their functions will be restored.
Control methods:
The infected shoot is immediately removed, and you need to cut it in a lively way, capturing a healthy area by about 20 centimeters. The branches should be burned, away from the garden. The tools that were used to manipulate the infected tree must be disinfected.
Folk remedies:
Some craftsmen and experts recommend, after cutting, smear the wounds with a solution (2.5 tablets of an antibiotic (rifampicin, gentamicin) diluted in one liter of water), the remaining preparation is suitable for spraying an entire pear affected by a bacterial burn. With the beginning of the growing season, all fruit trees on the site are sprayed with Bordeaux liquid. The number of procedures is about 8-9 per agricultural year.
Can also be treated after cutting with fungicides: copper sulfate 1%, and ferrous sulfate 0.7%.

Resistant varieties: "Moscow", "January", "March".
Root cancer.

The causative agent of root cancer is the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Most often, the pathogen remains in the roots of an untreated seedling, it can live underground for 2-3 years. This is a dangerous condition that can lead to the death of the plant. Therefore, carefully inspect the roots before planting, and if you see strange growths, as in the photo, be sure to remove them. Buy seedlings only in proven places, and be sure to process them before planting.
Pests:

But not only diseases are harmful to the pear, there are also a lot of pests that can ruin the life of a gardener. Therefore, at the peak of the season, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures.
Tick (galovy).

These small, creatures can do a lot of harm. They are carried in different ways, by wind, insects and even by a gardener, having sown on his clothes. After that, whole colonies of the settlement are formed on the leaves, you can recognize them by the swellings on the leaves. These are the places of poisoning, thanks to which the ticks suck the juices from the tree, further pear leaves start to turn black and fall off.
Prevention methods:
- Always collect and burn fallen leaves.
- Choose resistant varieties.
- The trunk circle must be dug up with the arrival of autumn.
Chemical fight:
Sulfur and phosphate preparations are used, such as the Vertimek insecticide. When working with these drugs, be sure to wear a protective suit.
Hawthorn butterfly.

You have probably noticed mummified leaves on the tree, but it may not have occurred to you that very harmful creatures hibernate in them. The hawthorn butterfly lays its larvae in them, which with the onset of spring will begin to destroy your plantings. In addition to the pear, apple trees, hawthorn and even bird cherry can also suffer from it. Therefore, be sure to cut them off in winter and burn them away from the site.
Sawyer.

During the opening of the buds, this insect penetrates them and lays its eggs in each of them. After the caterpillar is born, it rapidly destroys the foliage that grows next to its incubator.
The offspring live in cocoons from the web, so they must be detected and destroyed. Dig up the trunk circles.
In order not to lose the harvest, you need to know all the pear diseases in person, so we supplemented the material with a photo and description, we hope that what you read will help you cope with any problems that arise on your site. And remember that it is better to prevent an ailment than later, it is long and difficult to treat it, so take all preventive measures, cut trees, spray them with Bordeaux liquid, fight weeds and pests, and then you can enjoy the taste of your favorite fruits.
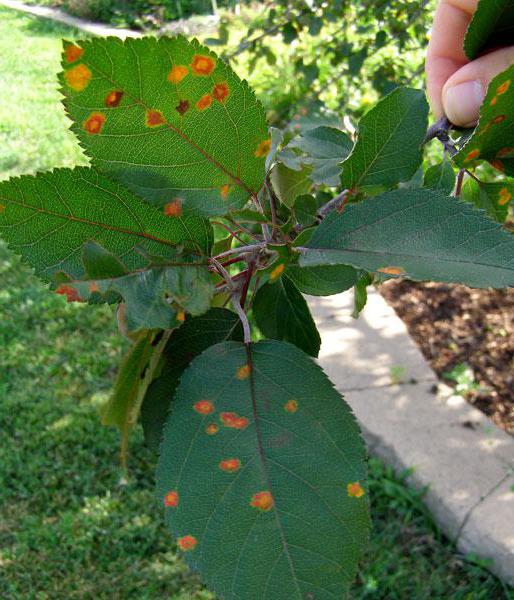
Being a dangerous disease - rust on a pear, it affects the culture mainly in spring (in April), in wet weather. The main source of the disease is juniper. After the rain, the basidia of the fungus dry out, detach from the growths and spread by the force of the wind over long distances (up to 50 km).
The leaves of the pear are covered with red spots with black dots (spermogonia), and cone-like outgrowths form on the underside. Both shoots and fruits are infected. Novice gardeners often have questions, "Why does pear have rusty spots and what to do in such cases?" To understand how to deal with the disease, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with its features.
Symptoms of a dangerous defeat
The first signs of the presence of basidia on the fruit crop are clearly visible already in July. The outer side of the leaf is covered with yellow or red spots with black dots up to 1.5 cm in diameter; a crimson border can stand out. After some time, a change in the color of the spots is observed, they acquire a brown color, and the growths turn brown. With deep damage to pear rust, peculiar horns form on the growths.
Leaves begin to fall off from rust on the pear, the fruits lose their presentation, decrease in mass. Infected shoots are covered with greenish-yellow spots, which inhibits their growth and development. They thicken and become short, and as a result, they dry out. If the disease is moderately developed, the shoots can continue to grow, but after 2-3 years the bark and wood cracks.
When planting, it is advisable to choose pear varieties that are resistant to rust. Disease-prone varieties can be noted:
- Bere Boek, Kure, Favorite Klappa, Bere Ardanpon, Winter Dikanka (strongly susceptible);
- Bere Gardi, Bere Ligel, William, Bere Giffard, Ilyinka, Skorospelka from Trevu (moderately affected);
- Suniani, Nanaziri, Gulabi, Sakharnaya, Gordzala, Sailo (relatively stable).
To prevent rusty spots from appearing on the leaves of the pear, you should periodically inspect the coniferous bushes located nearby the orchard. If its branches are covered with fungal spores, they must be cut and burned immediately.
Control measures should be aimed at carrying out the following measures:
- overly infected shoots, branches must be cut 5-10 cm before bud break;
- infected areas need to be cleaned to healthy wood and treated with a solution of copper sulphate 5%, then covered with garden varnish;
For information! For a better and faster recovery of the fruit crop, you can disinfect the wound with heteroauxin at the rate of 0.5 g per 10 l of water.
Treatment of pear disease can be carried out by spraying with copper and sulfur-containing compounds or agents from the category of dithiocarbamates. Before flowering work well on basidiospores:
- Bordeaux solution 1% or Kuproksat, Kuprosil, Champion, Blue Bordeaux, copper oxychloride;
- colloidal sulfur or Cumulus DF, Tiovit jet;
- Poliram DF.
After flowering of the fruit crop, the following spraying is performed with one of the proposed  fungicides. After three weeks, treat the garden again to prevent rust on the pear leaves. It is important to know that if you do chemical treatments for scab, then you do not need to additionally spray trees from a fungal disease.
fungicides. After three weeks, treat the garden again to prevent rust on the pear leaves. It is important to know that if you do chemical treatments for scab, then you do not need to additionally spray trees from a fungal disease.
In the fall, after picking up the fruit, it is advisable to use:
- Soon at the rate of 2 ml of the drug per 10 liters of liquid;
- Delanne at the rate of 7 grams per bucket of water;
- Terselom in the amount of 25 g, diluted in one bucket of liquid.
In order not to develop resistance in the causative agent of the disease, one fungicide cannot be used twice if yellow spots on the leaves appear on the pear.
After the leaves fall off, the trees must be treated with a urea solution, for which you need to measure 700 g of the product and dilute in 10 liters of water. The fallen leaves are burned or placed in a compost pit for two years.
How to get rid of with folk methods? Orange spots on pear leaves, as many gardeners assure, can be treated with an infusion of wood ash, marigolds, horsetail or organic fertilizer.
A good result is given by preventive measures, since the disease can again appear on the cured culture. It is necessary to observe the tree for at least a couple of years, given that it is quite difficult to deal with rust. If the leaves on the pears turn red, it is urgent to take measures to treat it.
What preventive actions should be taken?
Experienced summer residents say that preventive measures against rust on the pear are better than treating it. For this it is recommended:
- Establish wind-shelter plantations around the orchard. This is a kind of planting made from natural plants, especially a fir hedge. It not only protects from strong winds, but also from the spread of diseases. Such plantations allow to extend the life of fruit trees, protecting them from drying summer and frosty winter winds, as well as from spores from wild-growing juniper bushes.
- If it is not possible to abandon the cultivation of conifers near fruit trees, you need to carefully examine them in the spring for damage by fungus spores. If the affected parts of the tree are identified, they are cut off and burned.
- Regular pruning of nutrients and spraying with appropriate fungicides will help to increase the tree's resistance to damage by harmful spores.
- In the spring - autumn period it is recommended to use copper oxychloride, Bordeaux liquid 1%, effective drug Cuproxat.
- Another highly effective method in the fight against rust on a pear is considered to be four times spraying with Fitosporin - M. This drug is of biological origin, it should be used in the budding phase, after flowering and at the stage of ovary formation, when it grows to the size of a hazelnut, and after at the size of a walnut.
- If the foliage is covered with characteristic specks, it must be collected and burned without fail.
Rust on fruit crops causes many problems for gardeners, depriving them of a tasty and aromatic harvest. In addition, spores of the disease can spread throughout the garden, infecting both apple and quince. When the first symptoms of a lesion appear, it is recommended to process it as soon as possible. And the implementation of preventive measures will avoid relapse and preserve the plantings.