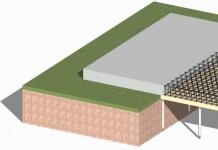
To put a greenhouse for year-round use, it is important to establish a foundation. There are several types of foundations. But before installing them, it is necessary to perform a number of preparatory work, which are the same for all types. It is also necessary to sensibly evaluate your own capabilities, because the installation of the foundation requires a lot of time and effort.
Many gardeners are interested in whether a foundation is needed for a polycarbonate greenhouse. There is no need for a foundation for a temporary structure. But if a long-term operation of the greenhouse is planned, then it is worth building the right foundation.

Benefits of using a foundation:
- The design becomes more durable and reliable. The greenhouse is affected by wind, weather precipitation and other adverse conditions. If you do not take care of the foundation, then the greenhouse can move.
- With the right choice of the type of base, it becomes possible to protect seedlings from pests and weeds.
- The necessary thermal insulation is created for growing crops in winter.
Thanks to the foundation, the greenhouse becomes stronger and more reliable. It is able to withstand heavy loads and provide comfortable growing plants. Be sure to install the base in winter greenhouses.
In order to properly equip the foundation, it is necessary to choose the optimal type of foundation. Each of them has its own characteristics, positive and negative points.
At the same time, for the seasonal construction of the foundation is not needed. This is just a waste of money, effort and time. Summer residents often build a small greenhouse only in the spring to breed seedlings, after which they dispose of it. But for long-term use of the greenhouse, a reliable foundation is required.
Types of foundation for a polycarbonate greenhouse
First you need to identify the purpose of building the foundation. Only then can you choose. It is necessary to take into account the term of operation of the greenhouse. For year-round use, you need a strong base. Sometimes only a protective barrier against insects and weeds is erected.

Foundation types:
- Tape made of concrete;
- Pillars;
- piles;
- Monolithic slab.
Each type has its own uses. The concrete foundation is the most popular among summer residents. Pillars and piles are a more economical type of foundation. A monolithic slab provides the most reliable foundation.
When choosing the optimal type of foundation, you need to take into account the type of soil, terrain, greenhouse area, climatic conditions and the period of construction.
Many species may require prior leveling of the soil. This is especially true for a monolithic slab. It is necessary to install such a foundation on the most even surface so that the greenhouse does not squint during operation.
Features: how to put a polycarbonate greenhouse without a foundation
If the greenhouse is installed only during the warm period, then the foundation is not needed and you can save on materials and time. But such an installation has its own characteristics. First you need to choose the right place to install the greenhouse.
It is necessary to study the soil and choose a well-lit area. If the soil is sandy, then this is a good basis for planting vegetables. If the earth is made of clay, then the top layer will need to be replaced. The place itself should be well lit. There is no need to build a greenhouse next to buildings that will shadow the greenhouse. If the soil is wet, you will have to equip the drainage system.

Installing a greenhouse without a foundation:
- Preparatory work. It is necessary to determine the perimeter of the greenhouse and mark it with pegs and ropes. Differences and irregularities on the ground no more than 5 cm.
- It is necessary to dig a trench 30 cm wide. The depth of the channel depends on the height of the support. The bottom must be well tamped. The trench must be covered with slate or roofing material to protect the earth from weeds.
- Frame assembly. You need to start with the end walls. You also need to fix the window and door frames. The wooden frame must be treated with antiseptics.
- Installation of polycarbonate. You need to start with the end walls. It is important to fix the layers with the right side so that the protective layer comes out.
You can do the installation of a frameless greenhouse with your own hands. It is important to ensure that the building does not go crooked. To do this, you need to use special tools.
Most often, frameless greenhouses are used for seedlings. You can read about their arrangement at the link:
How to make a foundation for a polycarbonate greenhouse: preparation
Any construction involves preparatory work. It is necessary to choose the right place and assess the condition of the soil. In some cases, the top layer needs to be replaced.

Preparatory work before installing the foundation:
- Territory cleaning. Clearing it from debris, stones, dry branches.
- It is necessary to measure the evenness of the surface. To do this, in several places you need to measure the ground with a building level. If necessary, it is necessary to level the soil. Somewhere to add earth, somewhere to remove. The top layer needs to be replaced.
- Create markup. Before work, you need to make drawings and, following them, you should place the pegs and pull the rope.
After that, it is necessary to dig a trench and mount reinforcement. The dimensions of the greenhouse depend on the frame itself. It is necessary to take into account its weight and material of manufacture. If this is a classic greenhouse with a metal profile frame with polycarbonate sheets, then the depth should be 50 cm and the width should be 30 cm.
For a winter greenhouse, you need to make a formwork for the basement, the size of which should be 30-60 cm in height. The trench itself must be covered with a waterproofing film.
To create a waterproofing, you can use a plastic film or geotextile.
You will also need to install an armored belt. It is simpler and looks lighter than the standard version for residential buildings. It is necessary to stick steel bars into the bottom. The length of one twig is 60 cm. 30 cm are dipped into the ground, and the rest of the height is on the surface of the soil. The rods must be connected with a thick wire.
Pouring the foundation for a polycarbonate greenhouse with your own hands
Filling the solution can take place in two scenarios. In the first option, a sand substrate should be made. It is necessary to pour 15 cm of sand and compact the soil well. After that, reinforcement is installed and cement mortar is poured. In the second option, it is necessary to fill in 10 cm of sand and 10 cm of crushed stone. After tamping and mounting the armored belt, you can pour the solution.

Grades of concrete for pouring the base for a polycarbonate greenhouse:
- M100. Together with sand and gravel, a solution is prepared that can withstand a load of up to 100 kg per 1 cm2.
- M200. With crushed stone and sand, a strong foundation is obtained that can withstand a weight of 200 kg per 1 cm2.
Most greenhouses are installed under the first brand of concrete. This turns out to be enough. The strength of the foundation depends on the proportions of all components of the solution.
We pour the solution into the trench, provided that 5 cm remains to the edge of the soil. An armored belt should also be covered by 5 cm. It is necessary to quickly pour concrete so that the solution does not have time to harden before it is evenly distributed over the trench. After that, it is necessary to cover the foundation with polyethylene.
On the foundation, you can install a finished polycarbonate greenhouse from the manufacturer. The criteria for choosing a quality product are described in our material:
How to install a polycarbonate greenhouse with a monolithic foundation
First you need to do the preparatory work. To do this, you need to clear the soil, make markings, remove the top layer of soil and dig a pit. Its depth should be 30-40 cm. It is also necessary to cover the bottom with polyethylene or geotextile.

The sequence of installation of a monolithic foundation:
- Footing installation. It is necessary to pour the solution on the sandy layer and smooth everything thoroughly.
- Formwork creation.
- Covering walls and footings with roofing material or slate.
- Reinforcement. It is necessary to install steel rods and wrap them with thick wire.
- Pouring concrete solution. You need to do this procedure quickly enough so that it does not have time to freeze.
All operations are similar to the installation of a strip foundation, only the scale will be larger. The coating of a monolithic slab must be moistened periodically. After a day or two, you need to install the anchor and leave the surface in this form until it dries completely. After the final drying, it is necessary to install roofing material on top of the slab.
The drain inside the greenhouse must be taken care of before pouring concrete.
You can do all the work yourself. But at the same time, you need to understand that installing the foundation requires a lot of effort, finances and time. In this case, it is impossible to pour concrete gradually. You need to do it in one go.
Installing a polycarbonate greenhouse on a foundation (video)
There are different types of greenhouse foundations. Which option will be better depends on the desires of the owner and the purpose of the base. It is imperative to mount the foundation for winter construction and with significant loads on the soil. For a temporary greenhouse, you can not install the base.
Examples of a foundation for a polycarbonate greenhouse (photo ideas)


















Greenhouses for growing greens and vegetables are made of lightweight materials. But, like other overall structures, they require the arrangement of a reliable and durable foundation, which will evenly distribute the load exerted on the supporting frame of the greenhouse.
Why do you need a foundation for a greenhouse
The foundation for the greenhouse plays the role of a supporting structure, which gives the supporting frame of the structure strength, reliability and safety. Plants planted in greenhouses built on various types of foundations are more protected from the harmful effects of moisture, insects and small rodents.
The presence of a foundation makes the greenhouse structure more stable and durable
In addition, the presence of a foundation avoids such problems as:
- windage of the building - overall greenhouses sheathed with polycarbonate and polyethylene film, with strong gusts of wind, can move relative to their original position. When constructing the foundation, the frame of the greenhouse is attached to the strapping of the supporting base, which eliminates any displacement of the greenhouse;
- poor thermal insulation - a greenhouse built on a foundation will be located 15–30 cm above ground level. Even a slight rise helps to save up to 15% of thermal energy;
- short service life - the foundation isolates the support frame of the greenhouse and the covering material from contact with the ground. This reduces the risk of moisture absorption from the surface of the earth and the formation of rot on the wooden structures of the greenhouse, which in turn increases the life of the structure.
Despite many clear advantages, the bearing base is not always made in the form of a foundation. For example, for greenhouses and small greenhouses made of plastic pipes, building a foundation is unjustified. In autumn, these structures are easier to disassemble and put away for storage until the next season.
In fact, the foundation for the greenhouse is built only in cases where the structure is large and stationary. For greenhouses made of polycarbonate or old window frames, the construction of a foundation is mandatory, since these structures are large and cannot be dismantled for the winter. Without a reliable supporting base, the supporting frame of these greenhouses can lead. Especially during the snowmelt period, when the soil is mobile and oversaturated with moisture.
Base types
The foundation for greenhouses of various designs practically does not differ from the bearing foundations that are used for the construction of low-rise residential buildings, small-sized residential buildings, technical premises, etc. The main difference between the foundation for a greenhouse is that its depth is much higher than the level of soil freezing.
Point type type of foundation made of bricks and timber
For the North-Western region of Russia, the freezing depth varies from 100–130 cm, and the depth of laying foundations for greenhouses rarely exceeds 80 cm. This applies to both medium-sized structures for growing greenery and flowers, and large-sized polycarbonate greenhouses.
As a foundation for greenhouses, such types of bases are used as:

For the construction of load-bearing bases for greenhouses, similar materials are used, as well as for the construction of foundations for one- or two-story buildings. As a rule, a wooden beam, concrete mix, brick, foam blocks, steel poles are used.
When erecting tape and point types of foundation, both one material and a combination of several are used. For example, when constructing a columnar foundation made of reinforced concrete, a wooden beam of the appropriate section can be used to construct a grillage. When arranging a strip base, a strapping of thick edged boards or timber is often used.
A monolithic foundation for a greenhouse is built quite rarely - it is expensive, time-consuming and inefficient. A monolithic concrete slab completely covers the fertile soil layer, which is not suitable for the tasks for which greenhouses are being built. Usually, a monolithic foundation is used for flower greenhouses, when the plants already have soil and are in separate boxes, baskets and racks.
What type of foundation to choose
The most popular type of foundation for a greenhouse is a strip foundation. But its use is not always rational, since different areas, even within the same dacha farm, can have different types of soil and groundwater levels.
When choosing a foundation for a greenhouse, one should take into account the type of soil and the level of groundwater.
Therefore, when choosing a foundation for a greenhouse, it should be borne in mind that:
- a shallow strip foundation is used in conditions where groundwater is low on the site. At the same time, the soil is not prone to heaving and is mostly represented by sand and gravel deposits, which quickly absorb and filter a large amount of storm water. If there is clay soil at the place where the greenhouse will be erected, then before laying the foundation it must be replaced with a sand and gravel cushion;
- columnar and pile foundation types with a wooden grillage are erected in areas where there is a high level of groundwater and excess moisture in the soil. This is determined quite simply: if after precipitation there are puddles on the site for a long time, and water accumulates in a newly dug hole, then the soil is oversaturated with moisture. And also point types of bases are erected on heaving soils when it is planned to build an overall greenhouse. For example, on a site with clay soil during the construction of a greenhouse 10 m long, 3 m wide and 2 m high;
- a monolithic or slab type of bearing base is constructed during the construction of greenhouses on unstable soil types. These types of soil include: loam, sandy loam, clay, peat. A heavy and monolithic base will dampen uneven heaving and mobility of the soil, while maintaining the supporting structures and greenhouse cladding intact.
From a financial point of view, the most affordable type of foundation is a columnar foundation made of concrete with a wooden grillage. If desired, concrete can be replaced with cobblestone or brick, but this will only increase the cost of the structure. In addition, working with brick is somewhat more difficult than with concrete mix.
A strip foundation made of concrete or block tape is ideal in terms of price to quality ratio. When building small greenhouses, concrete mix or blocks can be replaced with wooden beams treated with bituminous varnish or mastic.
A monolithic foundation is the most expensive, since a large amount of steel reinforcement and concrete mixture is used to fill it. If we take into account the pace of construction, then a monolithic base will also require more time - the complete drying of the concrete mixture occurs after 28 days.
Polycarbonate base for greenhouse
Polycarbonate greenhouses are a support frame made of a galvanized pipe 20x20 or 25x25 mm and covering material in the form of cellular polycarbonate. Typically, this type of greenhouse is manufactured in the factory, but if desired, a polycarbonate greenhouse can be designed and built with your own hands. The weight of the structure and the choice of foundation directly depend on the size of the greenhouse.
A concrete strip base is the optimal type of foundation for polycarbonate greenhouses.
For example, let's take a typical polycarbonate greenhouse from a random manufacturer. The weight of the frame of the greenhouse measuring 6×3 m, excluding polycarbonate, does not exceed 68 kg. Greenhouse 8 × 3 m has a supporting structure weight of not more than 76 kg. The total weight of polycarbonate sheets for sheathing, even taking into account the stock, will not exceed 20 kg.
From these data, we can conclude that for the construction of polycarbonate greenhouses, which will be built in typical suburban areas, you can use a columnar, block or strip foundation. If the owner of the site has enough funds, then you can build a greenhouse on a pile foundation.
If necessary, to save money, it is allowed to build a greenhouse on a shallow wooden belt made of timber, treated with an antiseptic or hydrophobic composition.
It is better to build large-sized greenhouses with a length of more than 10 m on a tape insulated base, especially if artificial heating of the soil is supplied for year-round use of the structure. To insulate the foundation, extruded polystyrene foam or foam plastic of the appropriate density is used.
Detailed instructions on how to equip a strip base for a polycarbonate greenhouse will be described in the section below.
From a bar
Greenhouses based on wooden frames made of edged boards or bars are rarely large, so a columnar base made of concrete, brick or foam block is used as a foundation.
For greenhouses made of window frames, it is better to use a point type of foundation with timber strapping
The main task of the foundation in this case is to raise the grillage above ground level in order to protect the wooden frame from the harmful effects of moisture. The grillage, as a rule, is made from a bar of the corresponding section. For additional protection of the grillage and the frame of the greenhouse, a wood preservative is used. If the size of the greenhouse exceeds 8 × 3 m, then it is better to fill in a shallow strip foundation 25–30 cm wide as a base.
If we are talking about greenhouses from window frames, then it is better to use the simplest and most affordable types of foundations that can be quickly built without significant financial costs. For example, for winter greenhouses made of frames, a columnar foundation made of bricks with a strapping of timber is ideal.
If the window frames are old, then even after restoration their service life will not exceed 3-5 years. In this case, it is recommended to completely abandon the columnar base and build a greenhouse only on a wooden belt. This will be enough so that the design of the greenhouse does not lead to dampness and moisture. The main thing is to prepare a good place on the site where the structure will be located.
How to make a foundation for greenhouses with your own hands
Before proceeding with the manufacture of the foundation and the construction of the greenhouse, preparatory work should be carried out. To do this, you will need to do the following:

After carrying out preparatory measures, purchasing and delivering materials to the territory of the land plot, you can proceed to the construction of the foundation and the construction of the greenhouse.
The technology of installing a supporting base from a bar
For the manufacture of a wooden base, a beam of 20 × 20 or 20 × 25 cm will be used. As fasteners, it is better to use galvanized self-tapping screws 70 mm long, a reinforced corner 150x150x65 mm and reinforced plates 180 × 65. The metal thickness of fasteners is at least 2 mm.
For the manufacture of a point foundation for a greenhouse, you can use a wooden beam 20 × 20 cm
As a tool, you will need to prepare a hacksaw for wood, a screwdriver and a building level. If a columnar foundation is being built, then a bayonet shovel and a hand drill will be needed.
If only the manufacture of a wooden frame is required, which will be laid on a prepared piece of land, then for this it is necessary to prepare 2 long and short blanks. The workpieces are fastened at the corners with the help of self-tapping screws and reinforced corners.
For example, we will describe the technology of building a columnar foundation with a wooden frame made of timber as a grillage. The technology for building a point foundation from a bar consists of the following:
- Marking of the prepared site is carried out. For this, wooden pegs and nylon thread are used. The pegs are driven in around the perimeter of the greenhouse, after which a thread is pulled between them.
- At the corners and length of the greenhouse, the places of the pit for the supports are indicated. The step between the supports is 2 m. If necessary, a place is marked for an intermediate support along the width of the greenhouse on each side.
The depth of the pits for the installation of supports should be no more than 2/3 of the length of the support.
- With the help of a drill and a shovel, a hole is formed for the supports at the corners and length of the greenhouse. The depth of the pits should be equal to 2/3 of the length of the buried support. For example, for a support of 90 cm, the depth of the pit should be at least 60 cm.
- At the bottom of each pit, fine-grained sand is poured with a layer of 7–10 cm and is well compacted to obtain a dense sand cushion. If necessary, the sand is slightly moistened.
A reinforced corner is used to assemble the grillage
- In the pits, support from a bar is installed, which are prepared in advance in the right amount. The voids between the support and the walls of the pit are filled with sand, crushed stone or gravel. After installation, each support is checked for level.
- A U-shaped fastener 160x70x160 mm is mounted on the end part of the supports to fix the grillage. After that, taking into account the dimensions of the greenhouse, the preparation of blanks from the timber is carried out for assembling the belt over the point supports.
The wooden beam is connected using reinforced plates and self-tapping screws 70 mm long
- Prepared blanks from a 20 × 20 mm beam are laid on supports and fixed with self-tapping screws 70 mm long. If it is necessary to connect the grillage on weight, then a reinforced plate or edged board 50–60 cm long is used. A reinforced corner is used to connect the beam at the corners.
At the end of the work, the assembled structure is checked for level. If there are any shortcomings, then they should be eliminated before the greenhouse frame is built. Before assembling the supporting frame of the greenhouse, the wooden foundation is treated with an antiseptic.
Concrete strip foundation pouring technology
To build a strip foundation, you will need a ready-made concrete mix M300. If you want to save money, then you can use dry mixes from the manufacturer of the appropriate brand.
For mixing, it is better to use a concrete mixer or a construction mixer for concrete. In addition, you will need steel reinforcement with a cross section of 8–12 mm and a welding machine. To assemble the formwork, you can use an edged board. The main thing is that it be strong. As fasteners, any nails or self-tapping screws 40-50 mm long are suitable.
The technology for pouring a strip foundation for a greenhouse consists of the following steps:
- The site for the construction of the greenhouse is marked out with the help of pegs and a thread that is stretched between them. Taking into account the markings, a trench is dug up to a depth of 80 cm. The width of the trench is no more than 30 cm. The bottom of the trench is carefully leveled.
The depth of the trench for the foundation of the greenhouse can reach 60-80 cm
- 2 layers of roofing material are laid at the bottom of the trench. Crushed stone of fraction 20–40 and fine-grained sand are poured onto the laid insulation. The thickness of each layer is no more than 10 cm. The sand and gravel cushion must be well compacted.
Reinforcement of the foundation is carried out using steel reinforcement with a cross section of up to 12 mm
- A reinforcing frame is formed from steel reinforcement, consisting of an upper, middle and lower belt, 2 rods each. The distance between parallel rods is no more than 20 cm. Vertical ligaments are used to connect them, which are installed in increments of 30–50 cm. A detailed frame knitting scheme is shown in the photo above.
When installed, formwork panels are pulled together with bars
- Edged board shields are installed in the trench with a reinforcing belt. If there is plywood or metal sheets, then they can also be used as formwork. From the outside of the shields, spacers from a board or edged bar are installed. When installing, it should be borne in mind that the foundation will rise 30–40 cm above ground level.
25-28 days after pouring the foundation, you can start building a greenhouse
- They begin to prepare the concrete mixture and its gradual pouring from any corner of the trench. After pouring 30-40 liters of concrete mixture, it is carefully rammed with a special tool or a reinforcement bar. Subsequent pouring then continues until all formwork segments are filled.
Having finished with pouring, the foundation is covered with plastic wrap and left to dry for 25-28 days. After 4 weeks, you can remove the formwork and prepare the supporting base for the construction of the greenhouse.
For this, the foundation is treated with bituminous mastic 2 times. If necessary, foam plastic or expanded polystyrene is glued to the mastic, on top of which roofing material is glued. It is optimal if the joints between the sheets of roofing material are glued with mastic and heated with a blowtorch.
Video: spot foundation for a pipe greenhouse
The foundation for the greenhouse allows not only to extend the service life of the structure, but also helps to avoid problems associated with the breakdown of the supporting frame due to its mobility under the action of the load. It does not matter what size of the greenhouse the foundation will be built for. Even a bearing base made of timber, laid on the ground, will help to avoid many problems during the operation of the greenhouse.
Despite the fact that the greenhouse is a lightweight structure, it requires a reliable and solid foundation. Indeed, in the absence of a good foundation, there is a risk that it will “walk” around the site, and young plants may die from frost and wind. So, what kind of foundation is needed for a greenhouse and how to build it correctly?


The foundation for the greenhouse is a reliable foundation for the structure, which extends its service life, as well as protecting plantings from negative factors. Many summer residents have a question: is it possible to build a greenhouse without a foundation for the sake of saving money and time?

Of course, this is possible, but arranging the base for a greenhouse has a number of advantages:
- the foundation firmly attaches the greenhouse to the ground, so that even the strongest winds will not be afraid of it;
- the structure will be above ground level - this will save about 10% of the heat inside;
- insects, moles and other pests will not be able to get to the landings;
- plants will be protected from frost, precipitation and other adverse factors.

Among the most important characteristics that a greenhouse base should have are strength, resistance to environmental influences and compliance with the design features.
- Reliability. The stability of the base plays a special role during the end of winter, as melting snow and water can destroy the entire structure.
- Resistance to negative factors. For the sake of economy, some summer residents build a foundation from improvised means (for example, plastic bottles or old tires) or low-quality material, which can be a big mistake - due to the influence of groundwater and temperature changes, such a foundation can quickly collapse.
- Compliance with the size, shape and material of the greenhouse. If the technical features of the design differ significantly from the features of the foundation, the greenhouse will quickly deform and may even collapse.

Summing up, we can say that not only the appearance and functionality, but also the “health” of plantings and the future harvest depend on the correct choice of the type and material of the base of the greenhouse.
The base for the greenhouse is selected depending on the material from which the structure is made (for example, silicate glass requires a more rigid base than), financial and time costs, as well as the climatic conditions of the region. The types of foundations that are used for arranging greenhouses include tape and surface (small or shallow). The principles of their construction are almost identical, with the only difference being that a deeper pit is needed for the tape base.

As for building materials, in this case, you can take wood (timber), brick, concrete mix, as well as ready-made concrete slabs or blocks. Each of the options has its own advantages and disadvantages that must be considered when choosing a foundation.

Prices for concrete slabs
concrete slab foundation
Table. Advantages and disadvantages of different types of foundations.
| foundation type | pros | Minuses |
|---|---|---|
| Wood | Cheap, light and simple both in work and in operation (the design can be easily transferred to another place). Good thermal insulation characteristics. | Low strength, therefore suitable for polycarbonate greenhouses and other lightweight structures. A short service life compared to other materials, and in conditions of high humidity it will rot even after treatment with special compounds. |
| Concrete-brick | It is light in weight, easy to arrange, well resists loads and deformations, therefore it is suitable for heated greenhouses. | The material has the ability to accumulate moisture and quickly collapse. At low temperatures, additional insulation is required. |
| Concrete tape | Reliable, durable, well resists high humidity and other negative factors. | Requires considerable investments, has low thermal insulation properties and a large mass. Quite complicated to set up. |
| Blocky | Easy to install, relatively inexpensive, environmentally friendly. | It does not hold heat well and has low strength. |
| Columnar | Reliable, strong, durable, relatively cheap. | The design features of the foundation require additional work - rigid piping and basement insulation. |
| pile | The design is extremely easy to install, if necessary, it can be easily transferred to another place. Work can be carried out in any weather, suitable for moving soils and areas with difficult terrain. | The disadvantages are similar to those of a columnar foundation. In addition, the metal piles from which the frame is made are prone to corrosion. |
| slab | Durable and durable, provides rigid fixation and stability of the structure on any soil. Well isolates the interior of the greenhouse from negative factors and pests. | Expensive to install, has a lot of weight and requires additional insulation. Since the plantings will be isolated from ordinary soil, it will be necessary to equip the greenhouse in the greenhouse and carefully monitor the microclimate. |


In order to choose the right base design for the greenhouse, the following rules must be observed.
- It is not recommended to build a greenhouse on a deep foundation, as it can collapse due to swelling of the soil.
- The base should not be heavier than the entire structure, otherwise the greenhouse will deform or warp over time.
- Foundation insulation is required only for those greenhouses that are planned to be used in winter: for this, expanded polystyrene or expanded clay is used, which fills the gaps between the base structure and the trench.


Important! Another important point is that the reliability and strength of both the foundation and the entire greenhouse depend on strict adherence to the construction instructions and the correct execution of all work.
Step by step instructions for laying the foundation for the greenhouse
Each type of foundation has its own peculiarities of laying, but in any case, you must first make the appropriate calculations (depending on the dimensions and design of the room). After that, the site is cleared of debris, trees and shrubs, and, if necessary, leveled.

Tools and materials
Materials for arranging the foundation are selected in advance, it can be a wooden beam, concrete mix, blocks, etc.
In addition, the following tools will be needed to complete the work:
- rope or fishing line;
- wooden stakes;
- building level;
- roulette;
- hacksaw;
- hammer;
- nails;
- shovel shovel and bayonet;
- anchors for fixing the main structure.
It should be noted that this is not a complete list of tools and improvised materials necessary for arranging the foundation. Depending on the type of base chosen, you will need to add a hand drill (for a pile foundation), formwork boards (for laying a strip base), etc. to the list.
A polycarbonate greenhouse, like any other structure, requires regular maintenance and sometimes repairs. He will tell you about the proper care of the greenhouse, as well as techniques and methods of repair.
Laying the foundation from a bar
A timber foundation is the best option for economical summer residents who plan to use the greenhouse exclusively in the warm season.

The timber must be clean and dry (moisture content not more than 20-22%), without signs of decay or damage by pests, and the cross section depends on the size of the greenhouse - logs with a large cross section will be needed for a large-sized structure. The best option is larch material that has been previously treated with antiseptic compounds (otherwise, you will have to do it yourself, because the foundation will quickly rot or be damaged by pests).

The basis of the timber can be made in several ways, and the simplest consists of the following steps.

Step 1. On the selected site, make markings with wooden stakes and ropes, and you should make sure that each corner is 90 degrees.

Step 2 Remove the top layer of soil (later it can be used for beds).
Step 3 Dig a trench along the perimeter of the marking, the depth of which is determined depending on the section of the beam (for example, for a material with a section of 100x100 mm, a trench 150 mm deep will suffice), and the width should be 70-80 mm more than the thickness of the logs.

Step 4 Lay out the bottom and walls of the trench with roofing felt, which will play the role of a waterproofing material. It is necessary to lay the material with an overlap - so that the beam is in a kind of "envelope".
Prices for roofing material
ruberoid
Step 5 Lay the timber on the roofing material and fasten the corners together in any way that is used for the construction of wooden houses (for example, “in a paw” or “half a tree”).


Step 6 Fasten the structure with metal corners, which have holes for nails or self-tapping screws.
Step 7 Align the base to the spirit level using wooden wedges or scraps. Minor deviations are eliminated by adding sand or gravel.

This solution is suitable for areas with a simple relief and low groundwater. On wet soils or areas with difficult terrain, it is recommended to install the frame on low point supports. The frame for such a foundation is made as indicated above, but does not fit into a trench, but is installed on rods previously driven into the ground - one support on the inside of each corner and every 1-1.5 m along the perimeter of the future greenhouse. As a building material, you can use trimmings of reinforcement, screw supports or wooden stakes (length no more than 70 cm). The timber frame is nailed or screwed to the supports.

Brick foundation laying
A brick foundation is much more reliable and durable than a timber foundation, but its laying will require more time and labor, since the frame is installed on a special cushion of concrete and gravel. This cushion protects the foundation from deformation due to heaving of the soil, so that the structure will be reliable and durable. It is better to use not silicate, but ordinary red brick, since it is less susceptible to destruction due to the influence of negative factors. The algorithm for laying a brick foundation is as follows.

Step 1. Make markings on the site of the future greenhouse.
Step 2 Remove the top layer of soil to a depth of 20-25 cm.
Step 3 Pour well-washed gravel into the bottom of the resulting trench and tamp it thoroughly, and the layer should be at least 5 cm. When building a brick foundation on a pillow, you can do without gravel, making the base only of concrete, but the gravel will give the structure more rigidity and stability.

Step 4 Prepare a concrete mixture of cement, gravel and sand, the recommended proportions are one part cement, three parts sand and five parts gravel.
Step 5 Pour the prepared mixture into the trench, and then wait at least two weeks for the concrete to completely harden.
Step 6 To waterproof the foundation, lay a layer of roofing material on the pillow.
Step 7 Lay bricks, and the number of rows depends on the dimensions of the greenhouse - for a small structure, one row will be enough. Strengthen the anchors between the bricks, which will serve as fasteners for the future greenhouse, while focusing on its design features. Bricks should be laid as evenly as possible, using the building level for checking, and the space between them should be well filled with mortar to avoid cold air entering the interior of the greenhouse.


After the solution hardens, you can proceed to the construction of the greenhouse, which is attached to the anchors fixed in the foundation.

Strip foundation laying
The strip foundation is the simplest, but at the same time the cheapest and most reliable option for the basis for the greenhouse, which will provide the structure with all the necessary characteristics and protect the planting from the influence of negative factors. This is the optimal solution for polycarbonate structures, which today is one of the most popular materials for the construction of greenhouses and hotbeds. The principle of laying such a foundation is similar to laying a brick foundation.

Step 1. Dig a trench 30-50 cm deep and 15-20 cm wide at the site of the future foundation according to the marking. If the greenhouse is planned to be used in winter, the trench must be dug deeper - approximately to the depth of soil freezing.

Step 2 Build formwork (can be made from old boards), if necessary, strengthen with supports and screeds.
 Formwork for pouring (example for large greenhouses)
Formwork for pouring (example for large greenhouses)
Step 3 Fill the bottom with sand (a layer of about 20 cm) or gravel (at least 5-10 cm), then tamp.
Step 4 Prepare a concrete solution (proportions: one part of cement, three parts of fine gravel, three parts of well-washed river sand) and pour it. It is better to do this in one step, otherwise the concrete will harden unevenly, and in the future cracks will appear in the foundation.

It will take at least 20 days for the mixture to completely solidify, after which you can proceed to the construction of the main structure.

Block foundation laying
Of all types of foundation, block foundation has one of the highest strength indicators and good waterproofing properties, so it is recommended to equip it in places with high humidity and in low-lying areas. For the foundation, you can use FBS blocks, which are reinforced concrete structures, or hollow foam concrete blocks.


Step 1. With the help of a rope and wooden stakes, make markings on the site of the future greenhouse.
Step 2 Dig a trench so that the rope runs in the middle. The width should be approximately 25 cm, and the depth is determined depending on the depth of soil freezing.
Step 3 Pour gravel at the bottom of the trench with a layer of 10 cm thick and compact well.
Step 4 Prepare a concrete solution and fill it with the prepared bottom of the trench.

Step 5 Until the solution has hardened, press the blocks into the corners of the future structure and align them horizontally and vertically. The surface of the masonry should be approximately flush with the ground.
Step 6 Lay blocks in the same way along the entire perimeter of the trench.
Step 7 It is good to fill all the voids between the blocks with mortar, and compact the masonry on the sides, adding earth. Smooth the surface with a trowel to make it as smooth as possible.

Important! To make the construction as reliable as possible, several rows of bricks can be laid out on top of the foundation, having previously laid the waterproofing material, and then let the entire masonry “grab” well.
Laying a columnar (pile) foundation
The column base is an inexpensive and simple solution for light greenhouses that are planned to be used in the warm season.

For large-sized heavy structures, such a base is not the best option due to an insufficient level of rigidity, therefore it is recommended to additionally make a strong strapping. To build a columnar base structure, you will need small concrete or wooden posts - usually 6-8 supports are enough for a medium-sized greenhouse.

Step 1. Mark the future foundation, install the pillars at the corners of the greenhouse and along the perimeter with an interval of 70-90 cm. On peat soils, the supports must be driven into the soil until they reach denser layers and are securely fixed.

Step 2 With a garden drill, make a trench about a meter deep between the supports (it is desirable that its bottom be approximately at the level of the freezing depth of the soil).
Step 3 Lay roofing material on the bottom of the well, which will play the role of formwork and protect the foundation from moisture.
Step 4 To give the base rigidity, you need to make a frame - tie 2-3 reinforcing pins together, and then lay them too.

Step 5 Lay a wooden formwork around each pile, otherwise, after pouring with concrete, they may change their position or warp (it is not required to remove it after the concrete has dried).
Step 6 Prepare the concrete mixture, pour it into the well.
Similarly, you can equip the foundation of special screw piles; Compared to concrete supports, they have a number of advantages:
- installation does not require the use of special tools or equipment;
- the design does not require concrete pouring, due to which the entire greenhouse is assembled in just a few hours;
- screw piles are completed with heads, on which the main structure is easily and quickly installed;

How proudly we demonstrate the rows of preserves and jams in our basement, made from our own grown tomatoes, peppers, berries. But our climate likes to throw surprises. Therefore, in order to achieve a harvest in a cold and rainy summer, greenhouses or greenhouses will be needed in the garden. A greenhouse is an unreliable structure, poorly resisting unexpected summer hail and rain, and dismantled for the winter. Therefore, a greenhouse with a hard coating is preferable in such conditions. You can buy a complete greenhouse (which is quite expensive) or build it yourself. But in any case, for a stable, solid greenhouse, you will have to make a foundation.
What greenhouses need a foundation
A greenhouse is a squat and long structure made of a light removable frame and a thin film coating. It is assembled from bending plastic or metal pipes inserted into the ground. Therefore, the foundation of the greenhouse is not needed.
Long greenhouses made of metal arcs can be installed in endless rows and in different directions
The greenhouse is a more serious building. Its base is assembled from expensive and durable materials: reinforced plastic or metal pipes of a larger diameter, a metal profile or a wooden bar. There are buildings made of double-glazed windows, reminiscent of a greenhouse or a winter garden. They provide additional heating and water. Greenhouses come in different shapes and sizes.
For a lightweight greenhouse - made of plastic pipes covered with a film - a foundation is not needed. To prevent the structure from moving in strong winds, you can build stretch marks on pegs or clamps in the ground. But it is desirable to put such a structure on a frame made of timber.
Photo gallery: types of greenhouses
 A small double-glazed greenhouse with ceiling windows can be used as a flower greenhouse
A small double-glazed greenhouse with ceiling windows can be used as a flower greenhouse  A huge greenhouse made of plastic double-glazed windows is a modern version of a winter building for growing vegetables
A huge greenhouse made of plastic double-glazed windows is a modern version of a winter building for growing vegetables  A greenhouse made of PVC pipes can also be covered with a reinforced film and used without a foundation, dismantled for the winter
A greenhouse made of PVC pipes can also be covered with a reinforced film and used without a foundation, dismantled for the winter  A spherical greenhouse made of wood and film will decorate any personal plot
A spherical greenhouse made of wood and film will decorate any personal plot  A greenhouse in the form of a tower with a gable roof, assembled from polycarbonate, does not require snow removal
A greenhouse in the form of a tower with a gable roof, assembled from polycarbonate, does not require snow removal  A greenhouse made of plastic bottles is a fun and practical invention that does not require large financial investments.
A greenhouse made of plastic bottles is a fun and practical invention that does not require large financial investments.  Greenhouse vegetarian attached to the wall of the house on the sunny side
Greenhouse vegetarian attached to the wall of the house on the sunny side
A foundation is needed if the greenhouse:
- solid and heavy;
- works also in winter;
- attached to the house;
- can warp when the ground moves;
- stands on a slope;
- light, but large - can move in strong winds;
- wooden - may begin to rot.
Foundation Benefits:
- increase in strength and rigidity of the structure;
- protection of wood from moisture;
- convenience in the construction of the greenhouse, since the base is even and solid;
- prevention of subsidence and destruction of a large and heavy greenhouse.
Foundation Disadvantages:
- the impossibility of moving the building to a new location (excluding the foundation-frame made of timber);
- requires money and labor.
To build a greenhouse with a foundation, you need to choose the right place.
Photo gallery: polycarbonate greenhouses on different foundations
 A greenhouse on a strip foundation of cinder blocks is easy to build, but you need to follow the laying technique
A greenhouse on a strip foundation of cinder blocks is easy to build, but you need to follow the laying technique  The greenhouse on a monolithic reinforced concrete foundation looks like a real mansion
The greenhouse on a monolithic reinforced concrete foundation looks like a real mansion  On a slope, it is more convenient to put a greenhouse on a foundation made of timber, leveling the horizontality of the building according to the level
On a slope, it is more convenient to put a greenhouse on a foundation made of timber, leveling the horizontality of the building according to the level  A greenhouse on a screw pile foundation is placed in case of heavy weight and unfavorable soil
A greenhouse on a screw pile foundation is placed in case of heavy weight and unfavorable soil  A greenhouse on a foundation made of timber, if desired, can be moved to another place
A greenhouse on a foundation made of timber, if desired, can be moved to another place  The strip foundation is laid quickly, which saves time and effort
The strip foundation is laid quickly, which saves time and effort
Do I need a foundation for an arched greenhouse? There are known varieties of arches made of pipes put on rods concreted into the ground. But usually an arched greenhouse is a strong and heavy structure, and it needs a foundation. And its appearance depends on the mass, dimensions and purpose of the building.
The arched greenhouse is suitable for all types of plants: from heat-loving berries to vegetables
Types of foundations for greenhouses:
- A - tape: it can be monolithic (made of concrete or cement mortar) or prefabricated - made of bricks or blocks of different weights;
- B - slab: always monolithic;
- B - columnar: monolithic from concrete or mortar, prefabricated from blocks or bricks;
- G - pile: piles are concrete, metal screw, from a bar or pipes (asbestos-cement, metal).
A specific foundation option is selected for each greenhouse: tape, slab, pile or spot on various supports
Greenhouses, varying in weight and design, require different types of bases.
- If the greenhouse is squat, with good rigidity, but light (made of PVC pipes, covered with a film), then it can budge in strong winds. And it needs at least a foundation-frame: it is made of long and thick wooden beams.
- If the greenhouse is heavier (metal profile and polycarbonate), then a serious foundation is needed: tape (non-buried or shallow columnar, monolithic or prefabricated from small blocks) or piled from metal or asbestos-cement pipes. If desired, you can use a folk invention - from car tires filled with concrete or old iron barrels.
- If the building is large and heavy, and the soil is loose, then a shallow columnar foundation (monolithic concrete or prefabricated from blocks) or a shallow strip foundation (made of concrete, blocks or panels), or an unburied / shallow monolithic slab, or screw piles will do.
- If the frame of the greenhouse is wooden, then any foundation is made with waterproofing.
It is important to choose the type and material of the foundation, correlating it with the model of the greenhouse, the conditions of the site, the budget for construction, your skills and the desired time frame.
There is a difference between "summer" and "winter" foundations. Since the greenhouse is a simple building, it can be installed at any time of the year. But with the foundation for a greenhouse built in winter, the situation is more complicated.
Pouring the foundation in winter is an expensive undertaking
In addition to the fact that any type of winter foundation will cost 20 percent more, during its construction there will still be a lot of pitfalls and dangers:

Table: setting of concrete at different temperatures
| Concrete grade M200 - M300 (mortar mixed with Portland cement M400 - M500) | Average daily external temperature for concrete, deg. Celsius | Hardening interval, days | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 14 | 28 | ||
| Compressive strength of concrete (percentage of brand value) |
||||||||
| -3 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 25 | |
| 0 | 5 | 12 | 18 | 28 | 35 | 50 (n) | 65 | |
| +5 | 9 | 19 | 27 | 38 | 48 (n) | 62 | 77 (b) | |
| +10 | 12 | 25 | 37 | 50 (n) | 58 | 72 (b) | 85 | |
| +20 | 23 | 40 | 50 (n) | 65 | 75 (b) | 90 | 100 (P) | |
| +30 | 35 | 55 (n) | 65 | 80 (b) | 90 | 100 (P) | - | |
Table note:
- (n) - normative-safe concrete strength for a certain day of hardening;
- (b) - safe strength of concrete for a certain day of hardening;
- (p) - the full strength of concrete for a certain day of hardening.
You need to know exactly the required depth of the foundation. Under the greenhouse, it is laid shallow: above the freezing point of the soil. Usually the depth of the foundation is 20-30 centimeters.
Before starting the construction of a greenhouse with a polycarbonate coating, you need to select the appropriate type of base.
Preparing to build the foundation
To begin with, it is important to choose the right place for the greenhouse, determine its size and choose the appropriate type of foundation, based on all the data on the future building and the soil on the site. Next, you should draw up a plan-drawing for pouring the foundation, making accurate measurements and calculations into it. Based on this plan, the necessary building material will be selected and its quantity calculated.
A greenhouse made of HDPE or PVC pipes, covered with polycarbonate, is rarely heavier than a centner. Therefore, a shallow and narrow “tape” (monolithic or prefabricated), columnar, pile or pile-grillage foundation is suitable as a basis for it.
It is also possible to use metal pins, which must be concreted into the concrete foundation pillars, but pouring the pillars individually is a long and laborious task, although it saves mortar.
A greenhouse made of pipes on concreted rods is a rather complicated and impractical solution.
The materials for the foundation will depend on the functionality, labor intensity, and cost of the foundation. Consider all types of foundations that are suitable for a polycarbonate greenhouse:
- The foundation-frame is made of timber, which is joined at the corners end-to-end or “in a paw” and placed on a sand-gravel cushion (filled into a recess from the removed fertile layer) and waterproofing. Pros: It's quick and easy to make. Cons: even with good antiseptic and hydrophobic impregnation, it is short-lived.
Large cross-section timber is connected and laid on crushed stone and waterproofing
- Monolithic "tape" - is poured into the formwork on a sand-gravel drainage mixture either on the soil with the fertile layer removed (unburied foundation), or in a shallow trench (shallow foundation), waterproofing is attached on top. Ready-made concrete or self-mixed cement mortar is used. The most versatile and fastest base to build: can be used in almost all soils. But takes a long time to harden.
Tape monolithic foundation: concrete is poured into the formwork from boards, reinforcement is used inside
- A prefabricated "tape" of blocks connected by a mortar is laid on a sand-gravel drainage mixture either on the soil with a fertile layer removed (unburied foundation), or in a shallow trench (shallow foundation), waterproofing is attached on top. It is quickly constructed and relatively inexpensive: the price depends on the type of blocks - expanded clay and cinder blocks are cheaper, foam and aerated concrete blocks are more expensive. It is applied at any soils.
A strip foundation of blocks is placed in a shallow trench on a cushion of rubble
- It is more difficult to lay a prefabricated "tape" of bricks. Such a foundation will cost more than a block one. He needs a screed-concrete (concrete base), which complicates the process and lengthens the construction time. But it is beautiful and does not need plastering. Waterproofing is placed on top. It is laid in any soil.
The red brick foundation requires an additional concrete base, it is very beautiful and durable
- A shallow columnar foundation of blocks connected by mortar is built quickly. It'll be cheap. But under it you need to dig a large number of identical neat marked holes. The blocks are placed in the pits on the drainage mixture and connected with a grillage (a wooden grillage from a bar will be enough for a greenhouse). Waterproofing is placed on top. It is applied practically at any soils, but it is more preferable at marshy and quicksand.
A columnar shallow foundation of blocks is placed in pits on crushed stone pillows and connected with a wooden grillage
- A shallow columnar foundation made of bricks on mortar is similar to that of blocks, but more expensive, and its laying is technically more difficult.
A shallow columnar foundation made of bricks is placed in pits on crushed stone pillows and connected with a wooden grillage
- An unburied columnar foundation made of concrete blocks is the easiest to manufacture from the above: blocks one by one or two / four (connected with a mortar) are laid on a sand-gravel mixture on the ground with a fertile layer removed or simply on the ground, connected with a grillage or strapping. Waterproofing is placed on top. Used on hard soils.
Columnar non-buried foundation of concrete blocks - the blocks are simply laid on a cushion of crushed stone directly on the ground
- A pile foundation made of pipes (metal and asbestos-cement) needs to be connected with a strong grillage, which complicates its construction. The number of supports and pits here is much greater. Waterproofing is placed on top. It is preferable to apply on swampy soils and quicksand.
A pile foundation made of asbestos-cement pipes requires a solid grillage and the accuracy of the horizontal level of construction
- A strip prefabricated foundation of heavy concrete panels connected with a mortar is put up quickly, but only with the help of heavy equipment. If it is shallow, then the walls of the greenhouse will have to be additionally insulated. Waterproofing is placed on top. It is applied at any soils.
The foundation of concrete panels is best used for a greenhouse with a large area
- Metal screw piles are reliable, but expensive. When screwing them, skills and special devices are needed. Such a foundation needs a serious strong grillage. If it is made of metal, then it will cost even more, and welding will be required for installation. Waterproofing is placed on top. It is preferable to use on swampy soils and quicksand.
The foundation of screw piles must be connected with a reliable grillage
- A monolithic slab is the most labor- and material-intensive foundation. For a shallow slab, a large pit is dug, and for a shallow slab, a fertile layer is removed. A sand-gravel cushion is made, reinforcement is laid. The top is waterproofing. It is applied on any soils. Cons: completely covers the layer of the earth. The fashion for a monolith came from the West - they always arrange floors and capital shelves in greenhouses.
A monolithic slab always requires reinforcement and long drying
For a small polycarbonate greenhouse, it is better to choose a shallow monolithic strip foundation. It is easier to dig a shallow trench by marking than deep separate pits for concrete "pillars". If you plan to use the greenhouse in winter, it is advisable to insulate the foundation.
You will need the following materials:

Material calculation and necessary tools
To calculate the foundation of the greenhouse, you can choose a simple online calculator from the Internet:
- We fill in the columns depending on the size of the greenhouse and the desired parameters of the foundation: brand of concrete, dimensions of the greenhouse, thickness and depth of the foundation. We put a tick - we want to calculate the reinforcement. "Concrete preparation" - a pre-poured thin screed at the bottom of the trench - will not be needed. We put "no".
Online foundation calculator - fill in the main columns by materials and sizes
- The calculation of reinforcement will be done depending on the reference values.
The calculation of the reinforcement will be done depending on the reference values of the materials and all the characteristics of the laying
- Entering data on formwork boards. Click on "Calculate".
Formwork is calculated according to the dimensions of the boards
- We receive data on the "tape".
The result of the calculation for the "tape" foundation is given in the main numbers for each material
- Go to the window "concrete volume" - "online concrete calculator". There are automatically inserted data on the dimensions of the foundation. We insert the selected type of cement, select the type of crushed stone and sand.
The calculation of the composition and proportions of concrete is also calculated automatically
- We do a "marketing research" on the Internet and enter the average cost of cement, sand and concrete.
The calculator will calculate the cost of all components for the volume of concrete you need
- We enter the type of seal and the characteristics of the materials (medium, that is, ordinary). Click on "Calculate".
We enter the type of seal and the characteristics of the materials - the calculation will be carried out according to average indicators
- We get the calculation by the amount of cement and the proportions of the mixture.
Calculation by the amount of cement and the proportions of the mixture - how much you need to buy components for concrete in a particular case
- And estimated cost.
The calculation for the approximate cost of the entire required amount of concrete shows the numbers based on the data laid down
- We return to the calculation data for reinforcement.
Reinforcement calculation with the number and cross section of rods is a very important stage in foundation planning
- To make it clear, a drawing is attached.
The drawing of the online calculator will show the location of the reinforcement in concrete: it was it that was used in the calculations
- Next comes the calculation for supports and formwork boards.
Calculation for formwork with lumber volume is given as recommended for a given foundation size
- To calculate the insulation of the foundation, we enter the brand of insulation and its average cost. Click on "Calculate".
We enter all the data for the calculation and get the final figures in the next window of the calculator
- We get the calculation of the heater with the price.
We get the result according to the required quantity and the total price of insulation for the foundation
We need tools:
- electric mixer (or container) for mixing cement mortar;
- shovels (shovel for mortar and bayonet for digging trenches);
- manual metal wheelbarrow;
- tamping device;
- hammers are different;
- pliers are different;
- grinder (cut rebar);
- circular saw for boards (or hacksaw);
- electric drill (drill boards);
- screwdriver (to collect boards on self-tapping screws);
- ticks;
- hydraulic level;
- roulette.
Step by step instructions for laying the foundation
- Choose the right place for the greenhouse.
The heating and duration of natural lighting of the greenhouse will depend on the correctly chosen place.
- Take into account the slope of the territory, the location of the house and trees: there are certain rules that are spelled out in the relevant SNiP.
You need to choose the optimal place for the location of the greenhouse
- The chosen place should be flat and convenient for water supply. And you need to take into account that the finished greenhouse looks organically in the landscape of the site.
If the greenhouse fits into the surrounding landscape, then it will become a real decoration of the site, and not just a place to harvest
- Prepare a site for construction: weed the grass, remove stumps, if necessary, remove the fertile layer, level the soil.
- Mark the future "tape" with a tape measure, level, pegs and rope. Corners should be marked not with stakes, but with the intersection of strings.
Marking for digging trenches under the "tape" is done strictly according to the drawn up drawing and is measured at the horizontal level
- Dig trenches of the intended section with a small margin in width for the formwork.
- Lay a draining mixture of sand and gravel (or gravel) at the bottom by 10 centimeters.
- Moisten and compact the mixture.
- Saw the boards for the formwork, assemble it according to all the rules and check the horizontalness of the upper edges with a hydraulic level.
The formwork is assembled on self-tapping screws to the height of the plinth of the future greenhouse
- Lay the reinforcement in the formwork according to the calculation and connect it in the right places with wire.
The reinforcement in such a foundation must be connected with wire so that the reinforcement turns out to be movable.
- Knead in a mixer a solution of sand, cement, gravel and water. Pour it into the formwork in several stages. It is necessary to fill the entire formwork with mortar during the day, otherwise the “monolith” will consist of unbound layers due to different hardening times.
- Smooth the surface with a trowel until cement laitance appears.
It is important to carefully level the surface of the concrete pour with a trowel with slightly vibrating movements, achieving the appearance of a light liquid on the surface.
- Close the foundation with a film, daily moistening the surface of the concrete screed.
- Remove the formwork after 1-2 weeks. But the entire structure will fully gain the calculated hardness only after 28-30 days.
- Lay roofing material on top for waterproofing.
Roofing material must be laid on top of the concrete to provide good waterproofing for the greenhouse.
- Outside, insulate the foundation with XPS boards (using special glue or anchor bolts).
To prevent the floors in the greenhouse from freezing in winter, it is necessary to insulate the foundation from the outside
- Facing should be done after the construction of the greenhouse.
To make the brickwork of the foundation look beautiful without finishing, you need to embroider the seams between the bricks
Jointing is done inside the masonry or brought out. For this, there are special tools - expanders.
In fresh brickwork, jointing is done with special tools - jointers (convex or concave)
Any foundation with a high plinth can simply be smoothly plastered with cement mortar.
The basement of the foundation of concrete blocks is coated with cement plaster to protect the structure from destruction by moisture.
The cement mortar can be applied unevenly, imitating stone.
Cement plaster under a stone can also be very beautiful, especially if you then mark the borders of a convex pattern with colored paint
But you can also simply prime the surface of the foundation with plaster and paint it. For concrete, primers are used:
- epoxy;
- polyurethane.
The primer is applied to the plastered surface in order to prepare it for painting.
Facade paints are:

There are also facade plasters - two in one. They consist of a binder - acrylic or silicone - and a textured filler.
Facade plaster combines protective and aesthetic functions
To insulate the foundation, you can use a non-removable insulating polyurethane foam formwork during pouring. But such a design is expensive for a greenhouse.
Fixed formwork for pouring the foundation also serves as a heater
It is better to sheathe the already frozen foundation with panels of extruded polystyrene foam (EPS), which is 90 percent air and does not allow moisture to pass through, therefore it serves as both a heater and an additional side waterproofing layer.
Extruded polystyrene foam - the best solution for protecting and insulating the foundation
Even easier - to foam the foundation with polyurethane foam composition.
The better the foundation is protected from the outside, the warmer and drier it will be in winter inside the greenhouse
And on top - veneer the foundation with something beautiful. The design can be very diverse, but you should take into account the design of the greenhouse and not make it visually heavier. Types of external cladding:
- brickwork is too heavy for a conventional greenhouse foundation, so it is rarely used;
Complex brick cladding is used only for very heavy greenhouses built on a high foundation.
- clinker tile masonry - used more often, since clinker has a lower weight than conventional bricks;
Clinker brick is a great way to finish: beautiful and fast
- masonry is also a heavy material for small greenhouses. Minus: it does not hold on to the insulation;
It is difficult to decorate the strip foundation of the greenhouse on top of the insulation with rubble stone: you must first build a reinforcing mesh into it and glue the stone onto the plaster over it
- siding - composite or plastic panels that perfectly imitate any masonry.
Plastic siding panels are light, easy to use and ideally imitate any masonry, but they can burst in frost
Video: construction of a tape monolithic foundation for a greenhouse
Laying even the most labor-intensive foundation for a polycarbonate greenhouse is a great way to apply your skills and practice before tackling more difficult construction tasks.
The construction of the foundation is a crucial stage, the strength and stability of the structure largely depends on it. A greenhouse without a foundation is a structure that some summer residents build on their plots of polycarbonate. Let's try to figure out how justified this construction option is.
A reliable foundation will be needed both for a finished structure purchased on the market, and for a do-it-yourself building made from improvised materials.

The article explains why a foundation is needed. In it you will find a photo of the foundation for the greenhouse.

The article raises the question of what kind of foundation the construction will need, depending on the chosen building material. There is a detailed instruction on how to make a foundation for a polycarbonate building.
Why is a foundation required to build a greenhouse?
As a rule, a foundation is needed for a permanent building, such as a house. As for light structures in the country, they are erected temporarily. Land owners cannot but be interested in the question of whether a foundation is needed for a greenhouse at all.

Only one answer is possible here - you can’t do without building a base. The foundation performs the following tasks:
- Provides reliable fixation of the frame, which is not afraid of strong gusts of wind or precipitation.
- Does not allow the structure to come into contact with the ground, thereby increasing the service life. The base allows you to save approximately 10% of heat.
- The base does not allow cold air and fog to penetrate inside.
- Protects the building with the crop from pests and rodents.
What are the foundations for greenhouse structures?
There are 4 types of foundations:
- tape;
- pile;
- columnar;
- slab.

Knowing the specific features of the soil, topography, climate, and the dimensions of the building will help the owner of the site decide which foundation to make for the greenhouse.
Tape
The strip base is considered suitable for the vast majority of structures. According to the principle of construction, several types are distinguished:
- Unburied. It lies on a solid layer of soil. To make it, you need to remove the fertile soil. Such a foundation serves as a grillage for the foundation on piles.
- Shallow. They dig a trench to a depth of 70 or 80 cm. A special pillow is prepared in advance for the base. This option is not suitable when groundwater is located close to the site.
- Buried. It is sunk to a considerable depth. On average, the indicator varies from 1.2 m to 1.4 m.

It is necessary that the value of the height of the cross section exceed the value of the thickness or width. The proportional ratio of the length of the structure in relation to the width is 1.5 - 2:1.

The optimal proportion for depth with height is considered to be 0.7: 0.3-0.4 m. Concrete blocks, stone, clay, brick, foam blocks, concrete can serve as materials for the construction of a strip foundation.

If the greenhouse needs a foundation that is cheap, then it should be built from timber. Special protective compounds will help to make the base more durable, to prevent the process of decay.

pile
A stilt foundation is a great option for building a greenhouse in wetlands or uneven areas.

- driving;
- screw.

The installation of a pile foundation takes less time than the construction of a strip foundation. The distance between the piles is from 1.5 to 2 m. The grillage of the building can be cast-in-place concrete. It can also be built from beams or sleepers.

Columnar
The columnar base is a budget solution suitable for small buildings. Such a foundation for a greenhouse with your own hands will need to be deepened by 0.7-0.8 m.

For the construction of a columnar base, the following materials may be needed:

- brick;
- rubble stone;
- T-shaped concrete pillars;
- pipes made of metal, asbestos or roofing material;
- foam blocks;
- wooden stumps.

To prevent cold from penetrating inside the structure, the gap between the ground level and the base of the structure is sewn up with boards.

slab
A slab base is a suitable solution for sites with unstable ground or high groundwater levels. There are 2 types of plates:
- floating;
- base with stiffeners.
A trench is dug under the slab to a depth of 0.3-0.7 m. Sand and gravel are poured into the bottom, the pillow is leveled and covered with geotextile and roofing felt.

The thickness of the foundation is calculated depending on the purpose of the building. For a light greenhouse, 100 mm is enough, and for a large stationary type greenhouse, 200 or 250 mm is required.

Building a polycarbonate greenhouse
The building has its own characteristics. So, a strip foundation for a polycarbonate greenhouse is the best choice.
- You need to create a project. The drawing indicates the dimensions of the future structure and the main components. At this stage, you need to decide on building materials and their quantity.
- We choose a place for the construction of a greenhouse. Clears the construction site of stumps and debris.
- We set up the foundation.
- It is recommended that the base rises 1/3 above the ground.
- attached to the base with anchor bolts.
After installing the greenhouse, it is important to seal the gap between the base of the structure and the foundation.


Photo of the foundation for the greenhouse