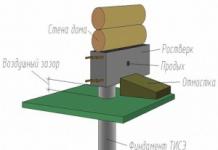
| Name of works | Explanations | Cost of work, rub. |
|---|---|---|
| Radiator heating, design work | per sq.m. | 75,00 |
| Water supply cold and hot (cold water and hot water), design works | per sq.m. | 35,00 |
| Sewerage, design work | per sq.m. | 45,00 |
| Underfloor heating water (underfloor heating), design work | The price is only for the square footage of areas where underfloor heating is used (not buildings). | 95,00 |
| Boiler room design | 245,00 | |
| Ventilation, design work | per sq.m. | 90,00 |
| Boiler room design | For 1 kW of boiler (boilers) power | 245,00 |
| Design of external networks | PC. | from 9000.00 |
The quality of the water we use directly affects the quality of our lives. It does not matter if it is a city water supply, or water from an artesian well or a well. In any situation, the HEATING.RU company will make a project for a reliable water supply for your building. Whether it is a residential building, a cottage, an office, a warehouse or an enterprise. Stable water supply is the result of our design.
Designing water supply systems. Where to start?
The installation of water supply systems is best carried out on the basis of preliminary calculations of the consumption of hot and cold water. It is especially important to do this if the water will be used for production needs. In buildings with an extensive system of water supply pipelines and a large number of consumers, it is necessary to carry out design work on the water supply system.
Water supply design. Collector or tee?
There are two types of designs of modern water supply systems. The first is based on one or more collectors, the so-called collector (or fan) wiring system. The second design is based on reducing tees, when a branch departs from the thick supply pipe to each water supply point. Both water supply systems have strong and weak sides. With a collector system, it is easy to achieve a uniform pressure at once more than two points of water intake. If there are shut-off inserts or taps on the manifold, it is possible to turn off one consumer without turning off the others. But when wiring on tees, well-placed valves provide the same effect. Installation of water supply on the basis of collectors allows you to lay pipeline branches from the collector to the place where the water outlet is installed in whole pieces, avoiding such a large number connections, as in wiring on tees. The most economical cost will be tee wiring from polypropylene pipes. When using Rehau cross-linked polyethylene, any water distribution system is reliable. The water supply collectors themselves are installed in special collector cabinets.
Laying pipelines in a water supply project
Water supply pipelines, according to the type of their wiring, can be divided into hidden and open. Open wiring of water supply pipelines is becoming less and less common. With open wiring, special requirements arise, both for appearance pipes and how they are laid. Open piping is used in the design of water supply in small apartments and houses, in the reconstruction of old buildings. Also in the case of using fittings that are not allowed to be embedded in the screed or to hide access to them. Sometimes, open wiring of water supply pipelines is used for design purposes.
More often, in modern water supply projects, we use hidden pipe laying. Most often, when installing water supply, pipes are hidden behind plasterboard walls or in a floor screed. In brick walls, pipes are laid in strobes, then the places where they pass are covered with mortar, then tiles can be laid. Concealed water piping fits perfectly into the modern concept of bathrooms. Everything should be concise and neat, a minimum of places where dust can accumulate. After all, sticking pipes need constant care! Concealed wiring needs more detailed water supply design. With a hidden wiring of water supply pipelines, it is important to decide in advance on the placement of plumbing. Before starting work, it is necessary to stock up on technical cards for all purchased plumbing. These cards contain instructions for fixing and connecting the device, as well as the geometric dimensions of the device and its seats.
From what to design water supply? What materials are used to create a water supply system in modern buildings?
For water supply systems, pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene, copper or polypropylene are traditionally used. We will select the best option for you in terms of price / quality ratio within the desired budget.
Water supply design? Smart Savings!
A faucet was opened in the adjacent shower room, and cold water went into your warm place. Or very hot? Residents of some houses are already accustomed to responding to such changes instantly. Add hot or cold! An incorrectly executed water supply project can lead to a loss of pressure in the pipes below a comfortable level.
Therefore, when choosing a contractor for the design and installation of engineering systems, it is worth taking into account not only the initial costs, but also how much money will be spent on maintaining the system and reworking it.
HEATING.RU - extensive experience in engineering design
Since 2003, OTOPLENIE.RU has been working in the field of design, installation and operation of internal engineering systems various buildings. To understand all the intricacies of designing water supply during the construction of your facility, it is better to entrust specialists who successfully solve these issues every day.
We will try to find an answer to your questions. Absolutely free of charge, we will provide a detailed estimate for the design of water supply. If necessary, our specialist will come to you and offer his solution!
Photos of works
-
Heating and underfloor heating.
- 2nd floor plan." href="/upload/iblock/1b8/1b8903216d587757d64d6e9c8240335d.JPG" class="modal solutions-slider-item">
Heating. Plan of the 2nd floor.
- Bath plan.
Axometric scheme." href="/upload/iblock/4fd/4fde2d6a79daa0128b8bbfcd24e60e3d.JPG" class="modal solutions-slider-item">Water supply. Bath plan. axometric diagram.
- Hardware location." href="/upload/iblock/586/586fbf3d12ba2c9cab8b4af88344c859.JPG" class="modal solutions-slider-item">
Thermal mechanical part. Equipment location.
- Hydraulic piping diagram." href="/upload/iblock/358/3585c335ca2de914898c6876199c5751.JPG" class="modal solutions-slider-item">
Thermal mechanical part. Hydraulic scheme of pipelines.
- Hydraulic circuit heating point baths." href="/upload/iblock/dec/dec3ecc78903b131d3ed3438620ce1ca.JPG" class="modal solutions-slider-item">
Thermal mechanical part. Hydraulic scheme of the thermal point of the bath.
- Apartment plan.
Radiator heating layout." href="/upload/resize_cache/iblock/dd8/1200_848_1afe264dcf853fb13ffaff4b372df94c6/dd8ddd55b51267081df2315d0404a492.jpg" class="modal solutions-slider-item">
Heating. Apartment plan. Distribution of the radiator heating system.
- Ground floor plan М 1:100.
Layout of the underfloor heating system." href="/upload/resize_cache/iblock/716/848_1200_1afe264dcf853fb13ffaff4b372df94c6/716be205fcf762191a0039c1a81fc67f.jpg" class="modal solutions-slider-item">
Heating. Ground floor plan М 1:100. Distribution of the underfloor heating system.
- Attic floor plan.
Distribution of the heating system and underfloor heating." href="/upload/resize_cache/iblock/720/1200_848_1afe264dcf853fb13ffaff4b372df94c6/72041f93c45e4971fab681c7f11f7231.jpg" class="modal solutions-slider-item">
Heating. Attic floor plan. Distribution of the heating system and underfloor heating.
- Plan of the first floor M 1:100.
Layout of underfloor heating contours." href="/upload/resize_cache/iblock/77b/1200_848_1afe264dcf853fb13ffaff4b372df94c6/77b7626f4bea3d0a6a4c01baef20de99.jpg" class="modal solutions-slider-item">
Heating. Plan of the first floor M 1:100. Layout of the contours of the warm floor.
- Schematic diagram of the boiler room." href="/upload/resize_cache/iblock/c6e/1200_848_1afe264dcf853fb13ffaff4b372df94c6/c6ede3fa178456a159ab64d56f7fbeeb.jpg" class="modal solutions-slider-item">

Boiler room. Schematic diagram of the boiler room.
- Plan of the first floor M 1:100.
Heating layout." href="/upload/resize_cache/iblock/d88/1200_848_1afe264dcf853fb13ffaff4b372df94c6/d8807f642ad891daffd56a2ebc89dcc9.jpg" class="modal solutions-slider-item">
Heating. Plan of the first floor M 1:100. Distribution of the heating system.
The design of water supply and sewerage (water disposal) systems is one of the main and most important sections of engineering design. Its implementation is necessary both in the construction of a country house, and in the repair of an apartment. To no lesser extent, it is necessary to open a cafe or restaurant, a beauty salon or a fitness center.
Design of water supply systems and networks
The design of water supply networks is very important for builders, since the water supply and sewerage project has already resolved issues that save money and time during installation work. Finished project already has detailed and detailed answers to questions about:
- what should be the thickness of the screed so that the water pipes fit in the floor;
- which pipes should be chosen to avoid leaks;
- what water supply system should be accepted for the object;
- how to properly connect a water heater for a hot water supply system;
- how much material and equipment for the installation of water supply and sewerage needs to be purchased.
 Water supply plan
Water supply plan
Not only builders rely on a quality water supply and sewerage project. If during cosmetic repairs you can do without it, then with a major overhaul - no. Water supply design in last case is mandatory in case of changes in the volume of water consumption, to connect to external networks and make changes to network engineering. In addition, water supply design will be required to obtain permission to start construction work from the operating organization.
Installation sewerage systems And water supply , of course, you can produce without a project, but in this case, the imaginary savings will cost much more.With absence designing water supply networks, you may encounter a number of problems, among which the overrun of water supply pipes will not be the worst, the wrong choice of water supply pipes will be much worse, as a result of which leaks and, as a result, flooding of neighbors are possible. Competent design of water supply, subject to the high-quality implementation of design decisions, is a guarantee of trouble-free and long-term operation of the entire water supply system.
 Water heater connection
Water heater connection
Difficulties in designing water supply and sewerage
When designing water supply and sewerage systems, many factors should be considered. First of all, it is worth noting that all projects must be completed in compliance with the relevant rules and regulations. Among them:
- - for external water supply networks;
- "- for internal water supply networks.
- Drawings must be carried out in accordance with and.
Designing water supply and sewerage of a country house or apartment in accordance with the requirements and wishes of customers requires before starting design work taking some important steps. The first step is to collect the initial data. To do this, you should find out what the volume of water consumption will be (how many people will live in the house), whether there is additional equipment that needs to be connected to the water supply. Next, the balance of water supply and sanitation is calculated, which is based on Appendix 2 of SNiP 2.04.01-85 * ".
Water consumption depends on the number of water users and on the purpose of the building. The appendix lists the water supply costs for each type of building, including for each appliance. For example, one administrative worker consumes 16 liters of tap water per day, and a resident of a residential building - 150-300 liters, depending on the water supply system and the type of residential building. When calculating the balance of water supply, it is necessary to take into account the probabilities of opening the device, depending on how many people fall on one plumbing fixture. Well, the main thing is the source of water supply. As such, central city networks or an autonomous well can act.
In addition, when designing water supply, it is necessary to determine the source of receipt or method of preparation. hot water. Hot water can come from central networks, be prepared centrally in the heat exchanger of the ITP of the building, or in an individual gas or electric water heater. When designing water supply and sanitation systems, it is necessary to plan the premises with plumbing fixtures, equipment and other water consumers applied to them. It is possible to significantly speed up and reduce the cost of designing water supply and sewage systems by providing layouts in electronic form - in dwg format. If the operating organizations (ZHEU, DEP, UK, etc.) have their own special requirements, they should also be known before the start of design work on the water supply system.
The initial data for the design of external water supply networks are technical conditions for connection, general plan, geology And topography site. Existing communications should be applied to the master plan.
After the initial data have been collected, it is necessary to form the terms of reference for the design of the water supply system. Our experts will help you do it. You can complete the task yourself by downloading the file or . Well, when the task is drawn up, the design contract is signed, the design process begins.

Water supply and sewerage design
Typical composition of a water supply and sewerage project (VC section):
- Title page
- General data on the project
- The composition of the water supply and sewerage project
- Balance of water consumption and sanitation
- Explanatory note
- Floor plans with sewer networks, storm sewers, industrial sewers
- Floor plans with hot and cold water networks
- Axonometric diagram of sewerage, storm sewerage, industrial sewerage
- Axonometric diagram of hot and cold water supply
- Assemblies and parts of water supply and sewerage systems, if necessary
- Scheme of the water meter unit
- Sewer system specification
In addition to the quality of the project, the timing and cost of design are no less, and sometimes even more important for the customer. For our clients, we are ready to perform and constantly perform labor feats. In exceptional cases, the design time is from two days. The typical turnaround time for a water supply and sewerage project is one to two weeks. For small facilities, the cost of a water supply and sewerage project is 9-12 thousand rubles. For more details on the prices for water supply and sewerage projects, for the design of water supply and heating, as well as other systems, you can find in a special
No modern home is complete without hot water and automatic heating. This has become the minimum necessary for a comfortable life. To feel confident in your home and not be afraid due to constantly popping up malfunctions, we recommend that you trust hot water supply design and installation of hot water supply is better for professional specialists.
The specialists of our company have all the necessary skills and abilities to competently draw up hot water project, taking into account all the features of the structure and the allocated financial resources. After drawing up the project, the masters of the company carry out the installation of hot water supply according to the design of hot water systems, using the latest technologies and modern materials.
When installing hot water systems, galvanized steel pipes are used, which are then covered with thermal insulation to reduce heat loss. The pipeline is laid in such a way that it is easy to repair and replace it.
Drafting DHW project and their installation is carried out in compliance with certain accepted standards. The risers of the DHW system are in most cases located on the right side of the risers of the cold water supply (when viewed from the side of the room). Hot water pipelines are laid above the cold water supply, which is done to reduce water heating.
If it is required to measure the flow of water, then this is taken into account when DHW design and further counters are installed.
In progress hot water system design our specialists strive to take into account all the wishes of the customer, so that the end result fully meets his requirements. This is a priority task of the GALEX Group of Companies. With a creative approach to DHW system design can find the most suitable option for a specific home. The subsequent installation of a hot water supply system is already a proven process that allows you to carry out work in the shortest possible time.
In each case, the installation of hot water supply is carried out with the most suitable equipment. So, for example, for dachas, electric water heaters are mainly preferred, which is associated with their efficiency.
In our company, the client can always count on receiving qualified assistance from our employees. The customer at each stage of work is informed about the implementation of certain works. If any malfunctions occur after the installation of the DHW system, the specialists eliminate them as soon as possible.
Heat and the presence of water in a person's home are one of the main components of comfort. It is impossible to imagine a modern residential building that would not have such amenities of civilization as heating and a hot water supply system (DHW).
Design features of hot water supply
To create a project for a hot water supply system, it is better to turn to professionals, to specialized organizations. Only qualified specialists will be able to choose the right scheme and types of equipment that will allow optimal heating of water in the building. Mainly used in water supply systems gas boilers, since they are more economical than electric models in terms of operating costs for heating the same volume of water. There are also boiler systems that allow you to get hot water in large volumes. Such installations will be convenient in large buildings with many hot water consumption points (showers, bathtubs, kitchens, bidets, sinks, etc.). Boilers can also be included in a single heating system at home, providing an integrated approach to creating comfortable conditions for people to live.
In modern houses, combined equipment is more often used, which makes it possible to simultaneously solve 2 tasks at once: heating the building and heating water for domestic needs. For this, special double-circuit boilers are used, which make it possible to effectively perform these tasks. Such modern equipment has the necessary built-in automation that maintains the desired temperature level in the heating system, as well as heating elements for preparing hot water.
When choosing heating devices, it is necessary to take into account the features of the building architecture and provide for the possibility of laying a chimney to ensure the removal of gas combustion products. When drawing up a project, it is necessary to carefully calculate the power of the heating equipment, taking into account the configuration, length and diameter of pipelines. To ensure that all end points of consumption receive water at the right pressure and the right temperature level. The choice of a model of heating equipment depends not only on the characteristics of the building itself, but also on the specific conditions of the area, the possibility of supplying centralized gas supply or the availability of the required power supply, as well as various other factors affecting the choice of the model of the boiler unit.
Types of heating equipment
For heating water in buildings can be used:
- Instantaneous water heaters
In these devices, water is heated only after the tap is turned on, while heat is consumed only in the amount that is needed for consumption. Hot water can be used indefinitely without compromising system performance. This type of installation includes electric heaters, geysers and plate heat exchangers.
- Storage water heaters
Such installations include boilers or boilers with an internal capacity. The main components of such units are: a heating element, an external tank, a thermostat, thermal insulation, and a control system. In reserve tanks, water is heated in advance, and in this state it is always there. When the tap is turned on, hot water is consumed through the pipes, and an appropriate portion of cold liquid enters the boiler, which is heated there to the desired temperature. When designing storage-type hot water supply schemes, an expansion membrane tank is also included in the equipment kit, which compensates for the thermal expansion of the liquid in the system. There are different models of such boilers (with built-in coils, with a double casing, tank-in-tank type), which allow solving the problems of heating and water heating.
An integrated approach to the design of DHW systems
The creation of a hot water supply system must be considered in conjunction with other communications and systems in the house: sewerage, cold water supply, heating. In such a project, it is necessary to take into account the type of pipeline and pipe laying locations, fastening taps and switchgears, installing bathtubs or sinks, laying sewer channels, as well as filters, membrane tanks, fittings, and other parts and controls of heating and communication equipment.
It is better to entrust the choice of the final version to specialists who will be able to take into account all the factors and objective conditions, and will perform a comprehensive qualitative calculation of the hot water supply system. Only professionals with many years of experience will be able to create individual DHW projects that fully meet building standards, as well as modern safety and energy saving requirements.
Our topic today is hot water supply: SNiP (building codes and regulations) will help you figure out how to design hot water systems, what fittings and materials should be used during their installation.
Can you see everyone
We will be familiar with two documents:
- SNiP II-34-76. This document was introduced back in 1977 and is no longer valid, however, even now it can serve as a source of valuable information;
- In 1986, a new SNiP 2.04.01-85 was introduced, containing design standards for internal engineering systems of buildings - sewerage, hot and cold water supply.
He replaced the previous set of rules and is still in effect; however, the document has undergone a number of changes to reflect the current rebar and material market. The most recent edition is known as SP 30.13330.2016.

SNiP II-34-76
So, what should be the hot water supply according to SNiP 11-34-76:
- The choice of centralized or local water supply is determined by the mode and volume of hot water consumption;
- In some cases (for example, at consumer services enterprises), it is allowed to combine household and drinking water and technological water pipes for hot water supply;
- When designing the hot water supply of enterprises, the possibility of using the heat generated by the equipment during operation should be considered.
Important: when in contact with process equipment, the quality of water supplied for household and drinking needs must remain unchanged.
Centralized DHW
- With a centralized supply of hot water, the heat carrier of the heating systems should be used to heat it. For this purpose, water-water (in steam-heating systems - steam-water) heat exchangers are used;
- Direct selection of hot water from the heating network is allowed. In this case, the DHW system must be connected to both the supply and return pipelines;

- The water heating point should be located as close as possible to the center of the district, the water supply of which it provides;
- For buildings above 50 meters, it is necessary to zone the DHW system in height;
Author's note: this implies a separate supply of water to the lower and upper floors with different pressures in each group of risers. Zoning allows you to meet the pressure standards at the points of water intake. The current joint venture recommends the use of pressure reducers installed in front of consumer groups on the lower floors for this purpose.
- In DHW systems, continuous circulation of water should be provided. Dead-end water supply is permissible if the water temperature without circulation does not fall below 60 ° C (50 degrees for DHW systems connected to closed heat supply systems);

- In bathrooms and shower rooms, it is necessary to install heated towel rails, and they must be connected according to a scheme that provides for their continuous heating;
Captain Evidence suggests: without circulation in the hot water supply system, continuous operation of heated towel rails is impossible by definition. In Khrushchev houses with dead-end water supply systems, dryers were placed in the break of the hot water supply lines and, accordingly, heated up only when water was flowing through one of the mixers in the apartment.

- It is allowed to connect heated towel rails to a year-round functioning heating system;
- DHW should be designed with a lower wiring (when bottling passes through the basement, subfloor or technical floor). Upper wiring (DHW bottling in the attic) is allowed for buildings with vertical zoning of the water supply system, and for buildings with water supply by gravity;
- In 9-story and higher buildings, DHW risers are combined into groups with ring jumpers. Each group is connected to a circulation riser. Water intake from the circulation riser is prohibited;
Note: the author has repeatedly encountered the combination of jumpers of a pair of risers laid in one apartment (through the kitchen and bathroom). Plumbing fixtures were attached to both looped risers. The circulation was not interrupted.
- In showers with three or more points of water intake, the DHW pipeline should be looped in order to avoid a drop in water pressure when it is consumed. One-way hot water supply is allowed only for collector wiring;

- DHW water meters are installed at the cold water inlet to the heat exchanger, and in houses with open heat supply - on the supply and general circulation pipelines.
Local DHW
Local hot water supply is organized in buildings that are not connected to the heating network.
SNiP suggests using the following types of heaters:
- Water-water;

- Steam-water;
- Gas;
- solid fuel;
- Diesel;
- Electrical.
As a rule, there is no circulation in local DHW pipelines.
Author's note: in practice, with a significant size of the cottage, looping the DHW circuit is fully justified. It allows you to significantly save water: in a fairly large dead-end system, every time you open a tap, it has to be drained in liters in anticipation of heating.

Water quality
The composition and quality of water must meet the requirements of GOST 2874-73. Direct supply of geothermal waters to the hot water supply system is allowed only if they meet the requirements of the standard.

In a house with a closed heat supply and water supply to heat exchangers or other water heaters from the cold water system, the pipes must be coated to prevent corrosion and scale formation. The coating must not impair the quality of the water supplied to consumers.
The reagents present in the hot water supplied directly from the heating system should also not reduce its quality.
As anti-corrosion measures can be used:
- Water deaeration(removal of air dissolved in it);

- Sodium silicate additive;
- Addition of magnomass(last roasted dolomite).
To combat scale, water must be magnetically treated.

If the house has hot water supply, the SNiP water temperature is set equal to:
- 60-75 °C for open heat supply;
- 50-75 °С for closed heat supply;
- 60-75 °C for local water supply.
However: in preschool institutions, schools and orphanages, the maximum allowable water temperature is 37 °C.

Batteries
Storage tanks can be used for:
- Increasing the efficiency of water treatment against scale and corrosion;
- Equalization of water consumption. Its reserve allows to ensure peak consumption, having a heat source limited in power;
- Water pressure limits. If it comes from the tank by gravity, the pressure cannot exceed the height of the tank above the draw-off point.
Tanks can be open and pressure. In the latter case, they work on the principle of displacing hot water with cold water. Open tanks cannot be used in buildings with open heating systems (with the exception of laundries, baths and showers).

Tanks should be located in a lighted and ventilated room with a temperature above zero. Their location should provide free access for repair and inspection. Thermal insulation of storage tanks for hot water supply is mandatory.

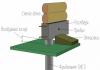
The non-pressure tank is supplied with:
- A supply pipe with a tap or valve and a float valve (or several valves);
- Pipe for water flow;
- Overflow at the level of the maximum possible water level;
- Downpipe connected to the bottom of the tank and overflow;
- Drain pipe connecting the tank tray with overflow;
- Circulation pipe (if it is necessary to maintain the temperature of the water in the accumulator);
- Water level indicators (if possible - with data transfer to the control panel).
Fittings and pipes
The DHW pipeline should generally be designed from galvanized steel pipes.

However, there are a couple of nuances:
- It is allowed to use pipes without zinc coating with a water pipe diameter of more than 150 mm;
- Plastic pipes (or steel pipes with a heat-resistant plastic inner lining) can also be used if their composition is approved by the Ministry of Health.
When designing a DHW system, thermal expansion of pipelines should be taken into account and measures should be taken to compensate for them.
Horizontal pipelines are mounted with a slope of at least 0.002. At the lower point of the water supply, a vent must be provided for draining water, and at the top - an air vent. It is allowed to use water folding fittings as the last one.

Location DHW pipelines must be accessible for visual inspection for leak detection and repair. The piping to plumbing fixtures can, however, be laid in the floor, under wall cladding or in strobes.
DHW risers and bottlings must be thermally insulated. Connections to individual devices do not need to be isolated.

However: risers passing through heated rooms can also do without insulation.
The shut-off valve must be:
- At the outlet to the riser section;
- At the water inlet to a separate structure;
- At the entrances to separate rooms;
- On the basis of risers (with a house height of three or more floors).
Attention: if it is possible to change the direction of the water flow, the shut-off valves must allow this possibility. Simply put, screw valves cannot be used in areas with a changing direction of flow; gate valves, plug and ball valves can be used.

For pipeline sizes up to 50 mm, fittings made of brass, bronze or heat-resistant plastics should be used.

The material of glands and seals must be approved by the Ministry of Health. Materials that change the color, transparency of water or give it a smell are prohibited.
Throttle washers should be made of brass or stainless steel.
Note: the washers provide a pressure drop between the hot water tie-ins in one thread of the elevator assembly, which ensures water circulation.

In circulation risers, it is not recommended to reduce the diameter of the pipe in the direction of water movement. To connect galvanized pipes, it is allowed to use cast iron or steel fittings, electric welding and flanges. When welding, the ends of the pipes must be pre-cut.

The design standards proposed by SNiP seem strange to the author: in practice, it is better to assemble hot galvanized water supply (as well as cold water supply) only on threads. Welding will inevitably burn the zinc coating. That is why the first fistulas on galvanized risers appear precisely at the welds.

SP 30.13330.2016
What information can be gleaned from the second document we are about to study? Let's focus on its differences from its predecessor.
Temperature
The water temperature on plumbing fixtures should be within the range of 60-65 ° C. Concessions for closed heating systems have been removed, the upper temperature threshold has been reduced by 10 degrees.

Water heating
Direct water supply from the heating network is now not directly prohibited, but recognized as undesirable. In priority - heat exchangers and local water heaters.

Pressure
The water pressure in front of the mixers is limited to 4.5 kgf/cm2. It is permissible to increase it to 6 kgf / cm2 if a house with central hot water supply is built in the conditions of an existing multi-storey building.
In high-rise buildings, instead of vertical zoning, reducers should be used to normalize pressure.

Circulation
Hot water supply must be circulating. Dot. Dead-end systems are forever in the past.
The joint venture proposes to combine 3-7 risers into looped sections. Jumpers between them can pass:
- Through the warm attic;
- Through a cold attic (in areas with winter temperatures below -40 degrees - in isolation);
Author's Note: Installing jumpers in an unheated attic is an extremely bad idea. If the circulation stops for any reason, the water turns to ice within an hour. When an ice plug is thawed, the pipe often breaks along the weld and floods the room under the attic.
- With the lower DHW distribution - under the ceiling of the premises on the upper floor;
- With the upper wiring - in the basement.

With the upper location of the jumpers, they are supplied with air vents.
Towel dryers
Towel dryers can be connected to DHW supply risers or circulation risers through shut-off valves. A bypass that maintains circulation when the device is turned off is mandatory.

However, instead of a water heated towel rail, you can install an electric one.
Note: electrical appliances of this type consume only 30-150 watts. They perfectly fulfill their direct functions, but, of course, they do not provide any effective heating of the bathroom.

Pipes
Fittings and pipes still need to have hygiene certificates.

The minimum allowable service life of pipes for hot water supply at a temperature of 75 ° C and a pressure of 6 kgf / cm2 is half a century. Steel water and gas pipes (not excluding galvanized ones) do not meet these requirements: according to VSN 58-88, they serve on hot water from 10 to 20 years.
By the way: when installing a hot water supply system with your own hands in a house with open heat supply, the author strongly advises using only metal pipes (copper or stainless steel). The instruction is related to the instability of plastics to simultaneous exposure high pressure and temperatures over 100-120 degrees. Such an excess of temperature standards is quite possible in case of malfunctions of the shut-off valves at the supply of the elevator unit.


Expense accounting
A separate water meter for hot water supply is not needed in an apartment or other premises with one owner only when preparing hot water in an autonomous water heater (geyser, boiler, etc.). In other cases, metering devices are mounted at the DHW inlet to the house (in circulation systems - on both threads) and at the inlets to separate rooms.
Before the counter there should be a dirt collector or a mechanical (as an option - a magnetic-mechanical) filter. If the room (apartment, office, etc.) has cold water and hot water inlets, they are equipped with check valves, which should prevent the reverse movement of the impeller due to the pressure difference in the water supply systems.

Reference: some types of faucets (for example, with a ball switch for a shower) allow you to create a kind of short circuit between cold and hot connections. With a pressure difference between water pipes, the readings on one mechanical meter will increase, on the other - decrease.

Conclusion
We hope that the study of SNiP on hot water supply will help the reader in designing the engineering systems of his housing. As usual, a lot of useful thematic information can be found in the video in this article. Good luck!