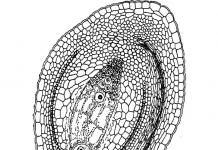
This lettuce pest can be wingless or winged. The body of the aphid can vary in different shades of green, the length of the insect is from 1.5 to 2.5 millimeters. It is not recommended to place beds with lettuce near currant plantings, since aphids migrate to the crop from this plant. The pest appears on currant leaves in early spring.
Destroy pests using chemicals not recommended, because lettuce leaves are constantly used as food by humans. Alternatively you can use folk remedies, 400 grams of dandelion leaves and stems per 10 liters of water or an infusion of potato tops (1-1.5 kilograms of green tops per bucket of water). Good results can be achieved by spraying lettuce leaves with a solution of onion peels, which will help destroy other pests. To prepare the infusion, 200 grams of husk are infused in a bucket of warm water for 24 hours, after which the liquid is filtered and the crops are sprayed.
Vegetable garden without pests Fatyanov Vladislav Ivanovich
Lettuce pests
Lettuce pests
Many pests feed on lettuce. Among them there are many polyphagous species, such as the cabbage cutworm and the gamma cutworm, which eat leaves. Cutworm caterpillars damage stems.
Lettuce seeds suffer from fly larvae. Even seeds can lose their viability due to the invasion of the light green leaf roller and the light green moth.
From the book Garden without pests author Fatyanov Vladislav IvanovichLettuce Pests Many pests feed on lettuce. Among them there are many polyphagous species, such as the cabbage cutworm and the gamma cutworm, which eat leaves. Cutworm caterpillars damage the stems. Lettuce seeds suffer from fly larvae. Even seeds can lose their viability
From the book The Golden Book of a Rich Harvest author Samsonov Sergey AnatolievichPests Whiteweed is a widespread pest of cabbage and other vegetable crops cruciferous family. Cabbage and turnip whites are known. The first is a butterfly with a body length of about 4 cm and a wingspan of up to 6 cm. The wings are white, with black corners. U
From the book Legumes. We plant, grow, harvest, heal author From the book Cabbage, lettuce, sorrel, spinach. We plant, grow, harvest, heal author Zvonarev Nikolai MikhailovichUse of lettuce in cooking Lettuce is one of the most popular green plants, which is especially valued in the spring, when the diet lacks vitamins and minerals. Lettuce is a delicious dietary vegetable and an essential component of the most delicious European dishes.
From the book Raspberries, blackberries. Varieties, cultivation, care author Zvonarev Nikolai MikhailovichUse of lettuce in medicine medicinal purposes They mainly use juice and infusion of lettuce. Lettuce juice refreshes and quenches thirst. Recommended for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, obesity, elderly and sedentary people, polio and others
From the book Woody Plants author Zgurskaya Maria PavlovnaGrowing lettuce Fresh greens of this popular vegetable plant can be easily grown in your garden. all year round. Salads in most of the European territory of the country can be grown all year round: in spring, summer and autumn in open ground, and in winter - in
From the book Growing Your Favorite Roses author Vlasenko Elena AlekseevnaTypes and varieties of lettuce Types of lettuce In total, more than 100 varieties of lettuce are known. Among them there are leafy and cabbage species of various shapes and colors - from soft green to dark burgundy. Leaf lettuce forms a rosette of leaves without a head, and in head forms at first
From the book A Million Plants for Your Garden author Kizima Galina AlexandrovnaLettuce varieties Leaf lettuce Ordinary leaf lettuce. Rosette of leaves of medium size, spreading. The leaves are light green, green, green-yellow, sometimes with purple-red pigmentation. The consistency is oily or crispy, the taste is delicate, with a bitterness. Early ripening varieties,
From the book Ploskorez Fokina! Dig, weed, loosen and mow in 20 minutes author Gerasimova NatalyaDiseases of lettuce Beach of all types of lettuce are gray and white rot, affecting plants at all phases of development. Sick plants are promptly cut and removed. To prevent diseases, it is important to maintain an appropriate moisture regime in the crops. The lettuce forms a compact
From the book The Grapevine. Growing experience author Krasnikov Petr AlekseevichPests The raspberry beetle is one of the main pests of raspberries. Beetles and larvae damage berries and flowers. The berries become unsuitable for sale in fresh and processing. The body of the beetle is oblong-oval, grayish-yellow, less often red, 2.5–3 mm long. Larva
From the book Vegetable Garden at Your Home author Kalyuzhny S.I.Pests It must be remembered that preventing pests is better than treating the plant. Therefore, the main pest control measures are preventive: to prevent diseases, it is necessary to correctly follow cultivation techniques. Plants for which
From the author's bookPests Spider mites This insect is found in almost every garden and affects any plants: fruit trees, grapes, flowers, berries, vegetables; Roses are no exception. Thus, of all insect pests, spider mites are the most common. He
From the author's book From the author's bookDifferent types lettuce and beets (Fig. 3) The width of the bed is 1 m. First, we plant the lettuce seedlings. The distance between plants is 30 cm. In this way, we plant four rows of lettuce. We thin out the lettuce and in its place, between the bushes of the remaining lettuce, we plant 2–30-day-old beet seedlings
From the author's bookPests Felt, spider mites and the little-described, but increasingly widespread, humpback leafhopper. The felt mite strikes grape leaves from the inside. On the outer side there are small, distinct tubercles. From the inside in these
From the author's book3.15. Lettuce seedlings Name: lettuce sativum. Family: Asteraceae. Seed class: dicotyledonous. Type of root system: branched. Leaves: light green wavy. Life expectancy: annual. Period from germination to first harvest: 20–60 days. Lettuce has a lot
Green crops are usually used soon after germination, so the use of pesticides on them should be limited.
Vegetating plants can only be processed if they are cultivated for roots or seeds.
Pests
Aphids- small insects that inhabit singly, or more often in colonies, leaves and peduncles of watercress, spinach, rhubarb and sorrel. Aphids suck plant juices. The green leaves are deformed, and they themselves are depressed and bear little fruit.
Control measures. Treating plants with soap and soda solution. Dissolve 50 g of soap and 50-100 g of soda ash in 10 liters of water. Take twice as much baking soda. The testes are sprayed with karbofos or decoctions of insecticidal plants.
Fleas- very small jumping bugs. Most dangerous for seedlings and young plants. They feed on watercress, mustard and other cruciferous vegetables, and rhubarb. Fleas chew out many small sores on the leaves. Severely damaged plants with the growing point eaten away die, and the remaining ones become very sick and lag behind in development.
Control measures. Pollination of plants with dry ash, road and cement dust, possibly mixed with tobacco.
Naked slugs live in damp areas. They can be detected by eaten leaves, on which a silvery trace of dried mucus remains. Lettuce is damaged more often, other crops less often.
Control measures. Scatter superphosphate or lime around the beds. Among the chemicals, metaldehyde is effective. You can catch slugs under shelters - wet, damp boards, especially in areas with sparse vegetation. The planks are placed between the rows on the soil. During the day, the slugs gathered under the board are destroyed.
Diseases
Mosaic. The causative agents of mosaics are viruses. The disease appears on leaves as white and yellow spots or discolored stripes along the veins. The leaves are deformed and underdeveloped. Viruses are spread mechanically by crops and aphids. Celery, parsley, and spinach are affected.
Control measures. Removing and burning diseased plants. Fighting aphids.
Leaf spot caused by fungal diseases. What is common is that round or angular spots of varying colors appear on the leaves. Sometimes they are limited by a dark red rim or a light brown border. The disease spreads by wind and mechanically during the growing season. It persists in the soil on affected plant debris. Spots affect celery, parsley, parsnips, lettuce, spinach, and sorrel.
Control measures. Collection and destruction of plant residues, weed control. Spraying the testes with 1% Bordeaux mixture or copper oxychloride.
Powdery mildew- fungal disease. A white powdery coating forms on the leaves, petioles, stems, and inflorescences. The disease usually develops in dense crops. The pathogen persists in the soil on plant debris. Celery, parsley, parsnips, dill, caraway seeds, lettuce, and mint are affected.
Control measures. Thin out plants in a timely manner, fight weeds, and treat plantings with a 1% sulfur suspension.
False powdery mildew . Yellow spots are visible on the upper side of the leaves irregular shape, bounded by veins. They gradually enlarge and merge, the tissue turns brown and dies. A white or gray powdery coating forms on the spots on the underside of the leaf. In young plants, all organs can be affected and die. Lettuce, spinach, and sorrel get sick. The infection persists on plant debris.
Control measures. Trimming and burning diseased leaves. Spraying the testes with 1% Bordeaux mixture.
Gray rot. First, brown spots form on the lower, then on the upper leaves. A gray or brown fluffy coating appears on the rotting tissue of leaves, stems and inflorescences. Affected inflorescences wither. The development of the disease is facilitated by high air humidity and thickened crops. Lettuce, spinach, and parsnips are affected.
Control measures. Removal of diseased plants from crops, destruction of plant residues.
Blackleg affects the root collar of plants. It turns brown and rots, a constriction appears on the stem, and it becomes bent. The plant lays down and dies. Increased soil moisture promotes the development of the disease. The infection persists on plant debris. Celery, parsley, lettuce, watercress, and spinach are affected.
Control measures. Thinning the crops, loosening the soil, collecting and removing affected plants and treating the remaining ones with 1% Bordeaux mixture or copper oxychloride.
Rust. In late spring or early summer, orange spots are visible on the leaves or stems. Later, dark powdery pads form on them. Diseased stems die rapidly. The pathogen persists on plant debris. Sorrel, asparagus, coriander, cumin, and mint are affected.
Control measures. Cutting and burning diseased organs, spraying healthy plants with 1% Bordeaux mixture. Destruction of plant residues,
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.
The salad is healthy, relatively easy to grow and has... But this crop also has a lot of pests and diseases.
Lettuce pests
Lettuce is often damaged naked slugs.
There are several types of this pest. In some species, eggs overwinter, while in others, adults.
Slug hatching begins in May. And after two months they become adults. At the end of summer, females lay eggs under lumps, in cracks in the soil, at the base of plants and under various shelters in damp places.
Slugs are most active in the evening and at night. During the day they hide in damp, cool places, in cracks in the soil, under plants, among leaves.
How to fight
You can fight slugs on lettuce using the same methods as on.
Salad fly
This pest is dangerous for lettuce seeds. Adult flies are ash-gray in color. But the males still have a black-velvety back. The size of flies is up to 4-8 mm. The false cocoon has a dirty yellow color. It is in the stage of false cocoons that the lettuce fly overwinters in the soil. Usually the depth of wintering is 6-10 cm. Hatching of flies occurs in late June and early July. Females lay eggs and larvae hatch from them. They are the ones who do the damage. tender leaves salad
How to fight
Cut and destroy damaged plants.
Wingless aphids and winged aphids are grayish-green in color. In early spring they settle on black currants, less often on gooseberries. And then they move on to the salad.

Aphids inhabit shoots, leaves, flowers and stems of plants. And they feast. It should be added that it is aphids that transmit various viral diseases.
How to fight
Helps great onion peel. Infusion of 200 g of husk per 10 liters of water. You can make an infusion of 1.3 kg of green potato tops per 10 liters of water. You can take green dandelion leaves: 400 g per 10 liters of water.
Lettuce diseases
This disease is caused by a soil fungus.

The manifestation of the disease begins near the surface of the soil and at the base of the leaves, where they come into contact with the soil. Brown spots appear first. Then the infection spreads up the stem and penetrates into the plant, affecting the leaves.
If the weather is damp, a gray fluffy coating appears on rotten fabrics. The disease develops quickly at high air humidity.
How to resist this disease: promptly remove diseased leaves and destroy plant debris.
White rot
The causative agent is a fungus. This disease affects not only lettuce, but also many others. cultivated plants. In mature lettuce plants, diseased leaves appear first. These are the leaves that lie on the ground. The disease also appears on the stem in the moist axils of large leaves, closer to the soil.
A white flake-like coating of mycelium appears. It spreads quickly along the stem and leaf bases. The entire plant immediately falls down and turns into a soft, watery mass. Later the mass turns black and dries out.
The pathogen persists in the form of sclerotia for a long time in the soil, on post-harvest residues.
How to fight:
1) do not swamp or over-moisten the soil directly under the plant;
2) alternate crops;
3) the same methods of struggle as with gray rot.
Black leg (rotting of seedlings)
And this is where soil fungi work. Lettuce shoots have appeared. They become infected with mycelium and the stems and roots of the lettuce begin to rot. The lower part of the stem near the root collar turns black, spots appear, the affected part of the stem becomes thinner, bent, the seedlings fall and die. On heavy and wet soils, seed germination slows down and the danger of blackleg increases.
Deep planting of seeds and soil compaction after rainfall or watering also contribute to the development of blackleg. The infection persists in the soil and on plant debris.
How to fight
1) alternate crops;
2) do pre-sowing watering and finely plant the seeds;
3) remove affected plants. And spill the soil with a solution of potassium permanganate (3 g per 10 liters of water). After watering, add a layer of sand (2-4cm).
4) thin out the lettuce seedlings.
Downy mildew
This disease is caused by a fungus. First, light green spots appear on the upper surface of the leaves, and then they acquire a brown tint.

The shape of the spots is angular. After a few days, loose formation can be observed on the lower surface of these spots. white coating. The development of the disease occurs at any above-zero temperature and at air humidity of 80-100%.
How to fight
2) keep the garden beds clean.
3) remove plant debris at the end of the season.
Jaundice (mosaic)
This is a viral disease. It affects lettuce plants in the 5th to 10th leaf phase. Light yellow spots appear on affected young plants, they are small, but then they grow, and the leaf becomes wrinkled, yellowish-green in color. Later the leaves turn brown and dry out. The infection persists in the soil.
How to fight
1) destroy weeds. It is on them that viruses rest.
2) promptly remove all plant debris.
Marginal burn
Dying tissues dry out, then fungi or bacteria develop in them, and mucus appears in the affected area. And so the entire plant becomes infected, which then dies.
Surplus nutrients, increased soil moisture - these are the factors that cause the development of the disease.
What to do?
Do not apply too much nitrogen fertilizer. Do not overwater, especially in a greenhouse or greenhouse.
When preparing the text, information was used from the book “Plant Protection in personal plot" Publishing house "Kolos".
Alexandra Sobolevskaya, website
Thus, the stem of lettuce is gnawed by the caterpillars of the cutworm, the leaves are eaten by the caterpillars of the cabbage cutworm and the gamma cutworm. In wet years, lettuce leaves are damaged by naked slugs. Of the sucking pests, lettuce is damaged by the stem lettuce aphid, the lettuce seeds are damaged by the larvae of the lettuce fly, and damage to immature lettuce seeds by the larvae of the lettuce moth and lettuce budworm has also been noted.
Salad fly damages lettuce seeds.
Flies are 7-8 mm long, females are ash-gray in color, with red, widely spaced eyes, males with a black-velvety back.
IN middle lane flies fly out in the first half of June, females lay white, elongated oval eggs on inflorescences or between open lettuce flowers. The larvae hatched from the eggs, white, 7-8 mm long, bite into the seeds and destroy their contents. Damaged baskets do not open and turn brown. To pupate, the larvae go into the soil, where they overwinter in a false cocoon. False cocoon brown, up to 6 mm long.
Control measures. When the first larvae appear in the lettuce buds, it is effective to spray the testes with 40% a.e. phosphamide at a concentration of 0.2%. In areas where lettuce seeds grew, it is necessary to carry out autumn plowing.
Stem lettuce aphid widespread everywhere.
Wingless aphids are 1.4-2.5 mm long, winged aphids are 1.4-2 mm long, dark or grayish green in color. In spring it lives on black currants, and in June it migrates to lettuce. Aphids inhabit shoots, leaves, flowers and stems of plants. As a result of damage, the leaves curl, become discolored, the lower leaves acquire a yellow mosaic color, and the plant is stunted in growth. In autumn, the aphids again fly to the currants, where they lay overwintering eggs.
Control measures. Lettuce seed plants can be effectively sprayed with 40% a.e. phosphamide. Lettuce crops cannot be sprayed with chemicals, since the young leaves are directly eaten. Lettuce plants can be sprinkled with an infusion of onion peels (200 g of onion peel per 10 liters of water), an infusion of green potato tops or dandelion leaves (400 g per 10 liters of water).
Lettuce diseases
The most harmful diseases of lettuce are gray and white rot, powdery mildew, downy mildew, and viral mosaic. Plant death, especially in wet years, reaches 50% or more.
Gray rot affects leaves, stems, heads of cabbage, testes and seeds. Brown spots form on leaves located near the soil surface, often the spots are located along the edge of the leaf, then the disease spreads to the leaf axils, causing rotting of the leaves, heads and stems.
Control measures. The most important measure is to maintain crop rotation, remove affected leaves and diseased plants, and destroy post-harvest residues. It is necessary to avoid growing lettuce in heavy acidic soils with the application of excessive doses of nitrogen fertilizers. Less susceptible varieties of lettuce should be grown - Khrustalny, Maysky, Moscow Greenhouse and moderately susceptible varieties from the Kamennaya Head variety type.
White rot affects all above-ground organs of lettuce plants. Initially, the infection penetrates leaves lying on the ground or in contact with the ground, and then spreads through the petioles of the leaves to the stem, forming watery light spots. A white flake-like coating of mycelium forms on the affected tissues.
The development of the disease is promoted high temperature-24-27° C and excess humidity.
Control measures. A prerequisite in the fight against white rot is strict rotation of crops. Affected leaves and diseased lettuce plants should be promptly removed and post-harvest residues should be deeply plowed. Avoid growing lettuce in heavy acidic soils with high doses of nitrogen fertilizers. Less susceptible varieties should be grown: Maisky, Moscow Greenhouse.
Powdery mildew affects leaves, stems, and heads of lettuce. The affected plant becomes chlorotic, growth and development slow down. Lettuce seeds are especially affected during the periods of flowering and seed ripening.
The most favorable condition for the development of the disease is sharp fluctuations in temperature at night and during the day. The infection persists on post-harvest residues.
Control measures. Strict adherence to crop rotation. Removal of affected leaves and plants during the growing season. Destruction of post-harvest residues.
Cultivation of less susceptible varieties: Moscow greenhouse, Berlin.
Downy mildew (peronospora) affects leaves, heads of cabbage, seed branches and inflorescences. On the upper side of the leaf, light green to yellow spots of a vague or angular shape are formed, and on the lower side there is a white coating of sporulation of the fungus. With severe development of the disease, the spots turn brown and the leaf dries out.
Favorable conditions for the development of the disease are high air humidity - 80-100%, the presence of droplet-liquid moisture, and poor ventilation.
The infection persists on post-harvest residues, as well as on self-sown plants. Transmission of infection through seeds is possible.
Control measures. Strict adherence to crop rotation. Collect seeds from healthy plants. Treating seeds with 80% TMTD.
Avoid dense crops and carry out weed control in a timely manner. Remove and destroy post-harvest residues.
Grow lettuce varieties less affected by peronosporosis: Bettner and some of the Romaine variety.
Marginal burn. The rot gradually spreads to the entire plant and it dies.
Plant diseases are caused by excess nutrients in the soil.
Control measures. Strict adherence to crop rotation. Optimal application of organic and mineral fertilizers, and especially nitrogen. Regular watering schedule.
During the period of technical ripeness, watering should be limited.
In greenhouses and film structures, avoid sudden fluctuations in temperature and humidity.
Removal and destruction of affected plants and post-harvest residues.
Growing the least affected varieties: Valentina, Profos, Noran, Oztipata.