The device of the mansard roof allows you to significantly increase the usable area and rationally organize the space of a low-rise building. However, its construction often frightens home craftsmen with an overly complicated and time-consuming process.
You should not be afraid, because the result will provide a beautiful roof and comfortable additional rooms. And in order for the result of the work to please the owner and household, you need to know according to what rules the truss system of the attic roof is built, in what way it is easier and better to arrange it.
At the mention of mansard roofs, we instantly recall a pentagonal gable structure of impressive size over a log house, concrete or brick walls. Visual memory suggests that its slopes must certainly have a bias of different sizes, i.e. the bottom of the roof simply has to be much steeper than the top. Due to the difference in the angles of inclination, a convex fracture is formed, which gave the roof the popular name "broken". The term reasonably migrated to the technical definitions of attic structures. It reflects the essence of the usual standard in the device, but often has nothing to do with the configuration. Despite the fact that the design of all mansard roofs necessarily includes two parts, visually their presence cannot always be determined.
Purely by external indicators, the predominant number of attic structures can be divided into:
- Triangular roofs, the lower and upper parts of which have an equivalent slope. Outwardly, they resemble traditional gable structures without kinks in the plane of the slopes.
- Pentagonal roofs with slopes having convex corners. This category clearly shows the presence of two docked parts in the design.
In both of these varieties, the truss system consists of two tiers stacked on top of each other. The lower structure forms a usable space of a residential attic with a height of 2 to 2.5 m, so that it is not difficult to move inside it. The second tier creates the shape of the top of the roof, it is allowed to be of arbitrary height.

By varying the angle of inclination of the upper and lower rafter legs, you can get the roof shape that is optimal in your own opinion. It is believed that a pentagonal attic looks best, the corners of which are in contact with an imaginary circle.

Note that the principle of building a broken roof is suitable not only for gable truss systems. By interpreting the basic method, the attic can be arranged in hip, shed, tent and other roof structures.
Sometimes an existing structure is remodeled into an attic, in the construction of which “broken” technology was not used. However, these roofs a priori cannot be attributed to the attic category. True, with sufficient power of the rafter legs, no one bothers to use the crossbars of the pitched truss systems as ceiling beams, and the supports of additional runs as a beam for attic sheathing.

We found out that the main feature of a mansard roof is the presence of two adjacent truss structures connected in a triangle or pentagon of a shape that is nice to the owner. In their construction, typical ones are used:
- Layered, according to which the lower tier of the attic is built and used in the device of the upper part.
- Hanging. In accordance with it, only the upper part of the structure is built.
If, for simplicity, the section of the mansard roof is divided into two halves, a trapezoid will be obtained below, and a triangle at the top. The inclined sides of the trapezoid are allowed to be exclusively layered, and the sides of the triangle are layered and hanging.

Basic schemes of truss systems
The "classic of the genre" is rightfully considered the pentagonal scheme of the mansard roof truss system with props that form the walls of the interior. Its section is conditionally divided into the simplest geometric shapes. In the center is a rectangle, on the sides of which there are two mirror-image right-angled triangles, on top is an equilateral triangle.
Standard attic design
The rafters of the lower part of the structure rest on the Mauerlat below, and with the upper heel on the right or left run. Part of the frame of the mansard roof, crowning the structure, is made by hanging truss arches. They are supplemented with a hanging headstock in the middle if they are intended to cover a span of more than 3m. The headstock cannot be connected to the arch tightening with a notch, like a support post. Her job is to prevent sagging of the puff - this is not a support, but a suspension.
Supports-racks of the layered rafters of the lower part are supported through the bed on the ceiling. If necessary, to increase the stability under the props, struts are mounted. The racks are connected to the bed and girders with cuts, the junctions are duplicated by metal corners and toothed plates. If the ceiling is concrete, bituminous waterproofing is laid under the bed. The bed can be laid not on the ceiling, but on brick posts or on leveling boards. When installing an attic on a wooden floor, you can generally do without a bed and cut the racks directly into the beams.

The rather steep lower parts of the mansard roof slopes are practically not affected by the snow load, because precipitation does not linger on them. However, steeply installed rafters have another problem - gusty winds will tend to turn over and tear off the roof. Therefore, fastening the system to the Mauerlat must be taken very seriously. In the attic situation, each rafter is tied to the walls with twists, and not through one, as in conventional pitched structures.
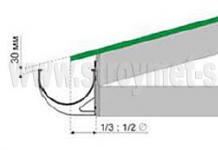
The way to take out the rafters for the wall line
It often happens that the planned attic structure forms too narrow an interior space. It can be expanded by extending the rafter legs outside the walls. Those. the rafter leg will rest not on the Mauerlat, but on the beams of the upper floor. This case, in theory, does not need a Mauerlat at all. But reinforcing struts in the scheme with the removal of rafters are used without question, because there is no support at all under the extreme part of the side triangles.
The Mauerlat installation can be abolished, but pouring a monolithic reinforced concrete belt for attaching beams to brick walls is highly desirable. Floor beams are attached to the monolithic belt with anchors, support posts are cut into them by a maximum of 1/3 of the beam thickness. An important point: the removal of the rafters beyond the wall is simply obliged to form a cornice for wooden houses with a width of at least 0.5 m, for concrete and stone at least 0.4 m.

Technology for the construction of a truss structure with the removal of the rafter leg beyond the wall:
- We install the extreme floor beams that define the contour of the cornice overhangs. Because the ceiling will be loaded, the cross section of the beams is taken from 150 × 200 mm. If, when laying the starting beam, it turns out that the walls do not form a perfect rectangle, we strive to correct the flaws by changing the position of the beams.
- On the laces stretched between the fixed extreme beams, we lay and fix the remaining bars. We control the height and step of laying the beams before fastening. The distance between the floor elements is equal to the step between the rafter legs. For insulated roofs, the optimal installation step for rafters is 0.6 m, because it is equal to the width. If the rafters are mounted with a similar frequency, they can be made from a 50x150mm board.
- From the left and right edges, set aside a distance equal to the length of the short leg of a right triangle. At the marked points, carefully select the nests with a chisel to a third of the height of the beam under the extreme supports.
- Let's make supports by cutting out spikes. They need to be made according to the size of the selected nests. For the manufacture of corner supports, a bar with a section of 100 × 150 mm is suitable, and two bearing supports for the gable sides of the roof should be made from it. Under ordinary racks, a beam of 50 × 100 mm is sufficient. The material for the support elements should be longer than the design height by the length of the tenon, but better by 10 cm in case of errors when stacking.
- We install the corner posts and fasten them with temporary struts. We connect the racks with a cord.
- Using a cord with a plumb line, we align in the beams the sampling points of nests for ordinary supports and select the indicated holes.
- We install ordinary racks and two bearing supports in the centers of the attic gables.
- We lay runs on the installed supports - boards with a section of 50 × 150 mm. We fasten the runs with corners. It is not necessary to use as many nails as in the corners of the holes. Enough two or three for each plane. As a result of laying the board, the frame of the walls of the future attic is obtained.
- We connect the supports installed against each other with bars, attaching them to the girders with corners. These elements will act as tensile crossbars. Therefore, for their manufacture, lumber of the 1st grade with a section of 100 × 150 mm is required. Under each installed crossbar, a temporary support from an inch 25 × 150mm is needed.
- From above, we temporarily fasten the crossbars with the same inch, stepping back from the edges of the frame 20-30cm. A temporary rare flooring of one, two or three boards is needed for ease of installation of the upper part of the truss system.
- We make a template for the rafters of the lower row from an inch. To do this, we apply a blank board to the end of the run and the beam. Then we outline the lines of the grooves along which we have to cut off the excess. We try on, if necessary, trim the excess.
- We make rafter legs according to the template. If there is any doubt about the impeccability of the construction, then it is better to cut only the upper groove for a start. By placing the rafter in its proper place, it will then be possible to adjust the lower groove after the fact without unwanted damage to the material.
- We install the end rafter legs, which will need to be connected again with a cord.
- Focusing on the lace, we mount the rafter legs of the lower tier of the attic.
- Similarly, we make a template for the upper part of the truss system. In order to find the line of the upper cut, we temporarily sew a board onto the gable support.
- We make a mirror counterpart for the previous template. The rafters of the upper tier will lean against each other.
- Trying both templates on the roof. If everything is in order, we make the required number of upper rafters from a 50 × 150mm board using them.
- We are constructing the upper tier of the truss system.
- In order for the crossbars not to sag, we mount headstocks of the required size to each upper truss. We firmly sew them only to the ridge zone, the bottom should not be rigidly fixed.
Further, the rafter legs are screwed to the walls with wire bundles. Then the pediment frame is installed, along which it needs to be sheathed. At the end, the crate is mounted with a step corresponding to the characteristics of the roofing material.

Skeleton method
The technology differs from the previous method in that not separate supports are installed on the ceiling, but modules-blocks of the side walls of the future attic are fully prepared for fastening.
The block method of arranging the truss system allows you to optimize the construction of the mansard roof, because the construction of modular elements is carried out on the ground. In calm conditions without a sense of height, it is easier to achieve the accuracy of nodal connections.

The process of installing a block mansard roof:
- According to a pre-made project, we manufacture frames for the walls of the attic. Longitudinal bars according to this method play the role of runs and beds. We lay them out together with the racks on a flat area and mark with the help of a square the nests for the supports of the side walls. We make cuts along the measured lines.
- We cut spikes on the racks, the size of which must correspond to the size of the nests.
- We connect the longitudinal beam with vertical posts, we get two modular frames - these are the walls of the attic.
- We raise the frames up, install them in the intended place. We temporarily fix the position of the walls with spacers, then attach them to the floor beams with brackets.
- With a chisel, we select nests on the edges of the beams for installing the lower row of rafters. You need to place them in one line. In order to observe the geometry, it is easier to first outline them with a chainsaw, then refine them with a chisel.
- We carry out the upper truss tier of the attic on the ground, having previously tried on blanks for the installed elements. For accuracy of fitting to the end of the future roof, we temporarily nail the board so that one of its edges clearly repeats the central axis of the truss system. The base of the upper attic triangle performs the function of stretching. Its length is equal to the distance between the outer vertical planes of the installed frames. We select nests along the edges of the stretch, and spikes on the lower heels of the rafters.
- We assemble the roof trusses of the upper tier, for reliability we mount an additional crossbar, we reinforce the ridge knot with a triangular wooden lining.
- Until we moved to the roof, we make blanks for rafter legs. We try them on the frames laid out on the ground. It is more convenient to “cut” them in one fell swoop, grabbing a few pieces with a clamp. We cut out only the upper bevel, taking into account the fact that it will rest partly on the wall rack, partly on the stretching of the upper truss trusses.
- We try on the lower rafter to the end. We draw in the area of her lower heel the shape of a spike, repeating the configuration of the nest in the beam. We cut out the spikes.
- We move to the roof of the farm of the upper tier and the rafter legs of the lower tier. We mount the trusses first, attaching them to the upper wall trim with brackets, then the rafters of the lower part, attaching them to the floor beams with the same brackets.
The subsequent stages of roof construction are carried out according to standard rules. The drawings for the mansard roof, which clearly represent the structure, will be introduced in detail to the described principles of the construction of the truss system. Thanks to the production of connections by cutting in half a tree, the strength and rigidity of the frame as a whole increases, which will allow not to mount additional struts.

The disadvantage of the method is that the finished modules are quite difficult to transport to the roof. To transfer the assembled blocks there without the use of lifting equipment, a minimum of 4 people will be required.


Plank and nail truss system
It is not advisable to build a powerful attic over small country houses, but you still want to save space on a small plot. For the owners of small buildings, there is an excellent option - a light board-and-nail layered structure. The method should appeal to adherents of economy, because the whole timber is not used in the construction.
For the manufacture of each of the supporting elements, two boards are used, between which spaced pieces of the bar are installed. The bar-shaped cavity explains why the system is lightweight compared to solid counterparts. To ensure spatial rigidity, wind contractions are installed that connect the supports to the rafter legs. The crate, in turn, will contribute to the strengthening of the structure.

People's way of designing a layout
For a successful result of the work, the project is very desirable. It is not a fact that the presented drawings with dimensions are suitable for arranging a particular house. Typology in construction is now not at all welcome. If there is no documentation at all, it is better to make at least a sketch of the future roof, not forgetting the height of the ceilings in the attic room. Wherein:
- Proportions should be observed, because too large an attic can turn a small house into an awkward, mushroom-like building.
- It must be remembered that the lower part of the mansard roof is built using layered rafter legs, and they optically underestimate the overhang and block the upper part of the high windows. There will be no tangible effect of overhanging when constructing an attic according to the scheme with the removal of rafters.
- Do not forget that the height of the attic room must ensure freedom of movement. It is this landmark that is required to correctly determine the height of the racks of the attic walls.
You can choose the best proportions of the roof in a folk template-layout way. According to it, bars or boards are laid out on a flat, spacious area, repeating the contour of the building in real size. By changing the angles, moving the components, you can achieve the optimal configuration. Elements need to be fixed with nails and immediately measure the lengths of beams, rafters, puffs, racks. The resulting dimensions will help in the manufacture of templates.

Calculations and planning of the truss system under the mansard roof will be demonstrated by the video:
The basic options and diagrams of the attic truss structure given by us will help determine the choice of the optimal type of truss structure.
Use the entire possible area, give the house originality and significantly reduce heat loss through the roof - these are the tasks that the attic solves. If there is a certain margin of safety at the foundation, in this way it is possible to turn a one-story house into a two-level one. It is also attractive that a do-it-yourself mansard roof can be built even without special building skills. It is important not to make a mistake with the choice of materials and do everything according to the rules.
Windows in the usual floor are located in the walls. There are no or almost no walls in the attics. Roofing replaces them. That is why windows are made special: they not only have to let in enough light, but also withstand wind and snow loads, which are much more on the roof than on the walls.
Skylights
When planning an attic, it is worth considering the recommendations of SNiP. They recommend that the window area be at least 10% of the floor area. So if the attic is divided into several rooms, each should have a window.
Of all the methods shown in the photo for arranging skylights with an attic, the inclined installation is the easiest to implement. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure the proper degree of waterproofing of the junction, as well as to use special models with a reinforced frame and reinforced glass - the load on the surface can be significant.
Benefits of a sloped roof window:
- more light, not so sharp borders of light and shadow;
- the roof surface remains flat, its relief is not complicated;
- relatively easy installation.
When planning such a window, it must be remembered that its area increases with an increase in the angle of inclination. At what height is it more convenient to install such a window and how its height in centimeters increases depending on the slope, see the photo.

The steeper the slope relative to the floor, the lower the height of the window should be.
The width of the window frame should be 4-6 cm less than the pitch between the rafters. Then it can be easily installed without disturbing the structure of the frame. If the window is wider, it is necessary to make a reinforced beam above it, calculate the load.
If you need to have a larger window, it is easier to put two narrow ones side by side. They look no worse than one big one, and there will be fewer problems.

When installing a dormer window, the geometry of the roof becomes more complicated: a valley appears on top and on the sides. Because of this, the truss system becomes more complex in both planning and assembly. The complexity of laying roofing also increases. All valleys are the places where leaks are most likely to occur. That is why it is necessary to do everything very carefully. In regions with a lot of snow, it is advisable to install snow retainers above such windows: so that they are not blown away during a sharp descent.

The device of a vertical window-dormer in the mansard roof
The advantage of such a window: near it you can stand in full growth. But they let in less light, the terrain becomes more difficult and the roof becomes more problematic.
A recessed window is usually used if an exit to a balcony is made through it. In other cases, this method of arrangement is not the best option: there is little light, the shadows are very deep, which is tiring for the eye, the geometry also becomes more complicated, although not to the same extent as in the previous version.
The easiest way is to make a window in the end part of the attic. In this case, a reinforced frame or reinforced glass is not needed. Quite simply high-quality glasses are enough. It is this option that can most often be seen in country attics: this is the most inexpensive option, which is easily implemented with your own hands.
truss system
With the independent construction of private houses with an attic, usually a sloping roof is chosen. It allows you to get a room of a significant area, larger than under the gable.

With an equal width of the base (house), the attic room under a sloping roof is larger than under a conventional gable. The truss system is getting more complicated, but a gable roof with an attic under a sloping roof is still more popular.
The design of the sloping mansard roof is such that the overhangs can be lowered quite low, giving the house an interesting look. But the long overhang of the roof is not only a decorative role. They also cover the upper part of the wall from precipitation and divert the bulk of the water away from the foundation. Although when planning, you need to keep in mind that in strong winds they increase the windage. Because of this, it is necessary to use more powerful boards and beams. Therefore, the size of the roof overhang is chosen based on several considerations, the main of which is weather conditions.
Tilt angle
It depends on the roofing material, but most of all - on the region and weather conditions. The classic version is shown in the figure: the lower slopes in relation to the plane of the attic floor are inclined by 60 °, the upper ones by 30 °. Based on these data and the parameters of your building, all lengths can be calculated. Just keep in mind that according to SNiP, the ceiling height in the attic cannot be less than 2 m. Then, by definition, this is an attic. A person will feel comfortable if the ceiling is raised to a height of at least 2.2-2.3 m. Based on this, according to the rules of geometry, calculate the required lengths.

In the classic version, the load from precipitation on the side surfaces may not be taken into account. Precipitation can only be held on the upper part, the angle of inclination of which is less than 45 °.
In general, the slope of the side surfaces usually ranges between 45° and up to 80°. The steeper the slope, the greater the windage it has, this must be taken into account: in regions with strong winds, it is better to make flatter roofs. Then the wind loads will be perceived much better.
Types of rafter systems of broken roofs

The design of a broken mansard roof is one of the options for the truss system (the most common)
For the manufacture of a sloping roof frame with their own hands, pine lumber is most often used, the grade is not lower than 2. The choice of the section of timber and boards depends on the size of the roof, the selected roofing (its weight), wind and snow load in the region, the installation step of the rafters. All these parameters are taken into account in the calculation. The technique is prescribed in SNiP 2.08.01-89 and TCP 45-5.05-146-2009.

One of the options for building a frame with hanging rafters
Above in the figure is a drawing of a frame with hanging rafters. It can only be implemented if the base of the upper triangle is no more than 4.5 meters (in this case, this is the width of the attic room). If more, you will have to make layered rafters, which should rest on the load-bearing wall in the middle (the attic will turn out to be divided into two parts by a row of beams).
Another version of the upper part is shown in the photo below (the picture is clickable). In this case, the side rafters are reinforced with struts. They significantly increase the rigidity of the system.
There is a second way to achieve a similar effect - to set contractions - in the figure they are only outlined with barely visible lines. The length of the side rafter leg is divided into three, contractions are set in these places. They will be needed if the roofing will have a solid weight.

A variant of the rafter system of a sloping roof - with struts that increase the rigidity of the system
For a building that is small in size, the roof frame can be generally simple: at the top there are two hanging rafter legs, a puff, floor beams, racks and side rafters (pictured below).

The device of the truss system of a broken mansard roof for a small house
How to calculate a sloping roof
The mansard sloping roof of a small house (width no more than 6-7 meters) has been built so many times that, based on experience, we can say what materials should be used. Many parameters are dependent on other materials. For example, the installation step of the rafters is tied to the parameters of the insulation. To ensure that there is as little waste as possible during insulation, installation is easier, it is necessary that the distance from one rack to another is slightly less than the width of the insulation (by 20-30 mm). So, if you are going to use mineral wool, its width is 60 cm. Then the racks must be installed so that the clearance between two adjacent ones is 57-58 cm and no more.
The width of the board for the rafter leg is again determined based on the insulation. For the central zone of Russia, the required thickness of basalt wool is 200-250 mm. That's not all. In order for the thermal insulation to dry out, a ventilation gap of 20-30 mm is required (without it, the condensate will gradually rot the wood and render the mineral wool unusable). In total, it turns out that at a minimum the width of the rafter leg should be 230 mm. The thickness of the board is at least 50 mm. This is in regions with mild winds and not very heavy snowfalls. Summing up, for all rafters - ridge and side - a board of 230 * 50 mm is required.
If lumber with such characteristics turns out to be too expensive, it will be possible to make insulation in two directions: part along the rafters, part, stuffing the crate, across. You can lay a minimum of 100 mm of basalt wool, therefore, you can take a standard board 50 * 150 mm and leave it on the ventilation gap of 50 mm, or order a non-standard 130 * 50 mm. See what is more profitable in terms of money.
For racks and beams, it is better to take a beam of at least 80 * 80 mm, better - 100 * 100 mm. Especially in areas with difficult weather conditions - with heavy snowfalls or strong winds.
For a more accurate estimate, ask the experts. This is a long process, consisting of the collection of loads from the roofing material, the structural elements themselves, wind and snow loads. After that, according to a certain formula, the elements are selected. For more information on how the calculation is carried out, see the following video.
Do-it-yourself mansard roof: installation procedure
The Mauerlat device on mansard roofs is no different from the standard version. If or logs, you can use the upper crown as a Mauerlat. It is only pre-treated with impregnation with high protective properties.
If the wall is made of foam blocks, a reinforced monolithic belt is arranged on top of it. On a brick wall or made of shell rock, other similar materials, the device of such a belt is optional. Waterproofing is laid on the wall in two layers, and on top - a timber treated with an antiseptic - 150 * 150 mm or a log. It is fixed with embedded studs.

When assembling all elements, long nails are used - at least 150 mm long. In the most critical places, it is better to connect three or more elements with bolts or studs with double-sided threads. It is desirable to strengthen all joints with steel plates or corners.
First way
The installation of mansard roof rafters is done in two ways. First: parts are assembled on the ground, then they are lifted up in finished form. There, the first to expose the extreme structures that will become the gables. They are placed vertically, fixed. It is often more convenient to fix them with long bars nailed to the wall (temporary). The following assembled structures are inserted into the prepared recesses in the Mauerlat (they are made with the required step). They are set strictly vertically, carefully fixed. If necessary, install additional temporary spacers that fix them in the desired position. Side rails are installed.
How to build a sloping roof in this way, collect nodes, see the video below.
Second way
The second method - the construction of a sloping roof is carried out by sequentially collecting elements right on the spot. This method is more convenient if the structure is large and when assembled it can only be lifted using special equipment (crane).
First, floor beams are laid. Racks and puffs are attached to them, temporary struts are placed to hold them in the vertical direction. Next, the rafters of the upper and side legs are assembled, puffs and jibs are installed.
During installation, the following sequence of actions is observed: first, the extreme elements are installed and set in the desired position, securely fixed. If necessary, use temporary spacers. Between them, a fishing line, rope, lace is stretched, which will serve as a guide for the installation of all subsequent elements. This simple move allows you to get the perfect geometry (do not forget to check the slope angle, verticality or horizontality).
Puffs are attached over the racks - bars, to which the side rafters are then fixed and on which the puff of the upper triangle is installed. Puffs are attached with metal corners. Since the beams are long, they sag. This is further eliminated - after the installation of the upper rafter legs - using vertical beams of a fixed or adjustable height. And temporarily they can be propped up with racks (so as not to pull the entire system).

To make it easier to maintain the desired angle when installing the side rafter legs, templates are made according to which the cuts are made. But since the geometry of DIY buildings is rarely perfect, adjustments may be needed. To check the resulting angle of inclination from several boards, another template is knocked down, which checks the correct installation.
If the standard length of lumber - 6 meters - is not enough, either order the required length (expensive) or increase it. When building up, two boards with a size of at least 0.6 meters (30 cm on each side of the junction) are nailed to the junction. They are nailed on both sides or bolts are used.

A reliable way to build rafters. The length of the "patch" - at least 60 cm
After installing the side rafters, it remains to install the top ones. A template is also made for them, it is first sawn on the ground, and installed at the top.

The top part can be done in different ways. Its structure depends on the width of the base. See the photo below for how to make it.

Since the device of the mansard sloping roof does not provide for the presence of a ridge, a beam is stuffed in the middle, to which the slopes are attached, fixing the triangle in the required position.

Nodes and their drawings
When installing the truss system, questions may arise regarding the assembly of nodes - the intersection and connection of several structural elements. In the photo you see drawings of key connections.

The second option is to connect the side rafters and the upper triangle. Bolts are used for more secure fastening.

How to make a do-it-yourself fastening of the upper triangle and rafter leg on a mansard roof
The methods for attaching the rafter legs to the Mauerlat or, as in this case, to the side beam are shown in the figure below. To make it easier to mount a heavy element, a stop board (bar) is nailed to the rafter from below, which limits its movement: the board rests against the edge and prevents it from falling lower.

There are several options for roofs under which you can place a comfortable living space. In order to ensure the maximum volume of the under-roofing attic space, it is necessary to choose the optimal angle of inclination of the slopes and not to forget about the snow and wind load on the roof. We will consider the most popular designs of the attic truss system in the middle lane.
Mansard roof truss system design
The mansard roof makes it possible to obtain additional usable space with a relatively small financial investment, so this architectural solution has gained great popularity. So what is an attic?
Attic (from French mansarde) - an exploited attic space (both residential and non-residential premises), formed on the top floor of the house, or the top floor of a part of the house, with a mansard roof.
Wikipedia
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Attic
The attic is located within the bearing walls of the building and rests on them through the Mauerlat, horizontal beams (puffs) and rafters. The larger the attic space, the greater its useful volume, which is achieved by increasing the angle of inclination of the slopes and is formed by a more complex truss system. The location of the mansard roof rafters depends on the design, which can be of different types, namely:
- Hipped or pyramidal design with a minimum amount of under-roof space.
The slopes of the tent structure rest on the side rafters and the central post, so the amount of under-roof space is minimal here.
- Hip or semi-hip roof, in which the main living space is located under the trapezoidal slopes.
Hip roof rafters form two triangular and two trapezoidal slopes
- Gable construction, which is a symmetrical gable roof with gables cut at a right angle, which provides a significant amount of attic space.
A multi-gable roof allows you to equip a full-fledged attic floor
- A gable symmetrical roof with a mansard is a classic option that is easy to install and resistant to wind due to its rigid structure.
A gable roof requires the least amount of working time and a small consumption of building materials
- The rafter system of the mansard sloping roof, providing the maximum amount of living space at a relatively low cost.
A sloping roof is the best solution in terms of the ratio of the cost of construction to the volume of useful attic space
The rafter system must withstand constant loads, which consist of the weight of structural elements, insulation and roofing. In addition, there are variable loads that depend on the strength of the wind and the weight of snow on the roof. The choice of the section of the bearing elements and the method of their connection should be aimed at creating the most durable and rigid structure that evenly distributes the load on the walls of the building.
Depending on the width of the building, different types of attic truss systems are used, which are divided into hanging, layered and combined.
- Hanging rafters are called, which rest on the walls of the building through the Mauerlat and puff, and form a ridge in the upper part. With this method of connection, there is no intermediate support, and the bursting pressure on the walls of the house is reduced with the help of crossbars, racks and struts. The hanging rafter system is usually used with a building width of no more than 6 m.
To compensate for bursting forces in hanging truss structures with a span of up to 6 m, puffs and crossbars are used
- Rafters are called rafters with an intermediate support on the inner wall of the house. They are used when the width of the building is from 6 to 16 m. The larger it is, the more elements are used to evenly distribute the load.
Rafter rafters have one or more supports inside the house
- The combined type of truss system is used in mansard roofs with a variable angle of inclination of the slopes. The most characteristic example is a broken mansard roof, where the lower rafter legs are layered, supported by a rack and mauerlat, and the upper ones are mounted as hanging rafters, supported by a puff and headstock. When building mansard roofs, all types of truss systems are used, and their choice depends on the design in which they are used.
In the construction of a sloping roof, the upper rafters are hanging, and the lower ones are layered.
Scheme of the truss system of the mansard roof
To build a roof, you must have a project that indicates the list and size of structural elements, as well as the method of their connection. To understand the principle and sequence of installation, you need to know the purpose of the elements of the rafter group and the way the roof fits to the walls of the building. The mansard roof consists of the following elements:
- the connecting element between the wall of the building and the rafter group is the mauerlat, which is attached to the walls of the house with studs, brackets or anchors;
- puffs are attached to the Mauerlat parallel to the short wall of the building, and beds are installed along the long side;
- vertical racks are mounted on the central bed;
- the ridge run rests on the racks;
- the upper part of the rafters rests on the ridge run, and the lower part is connected to the puff, forming a cornice overhang;
- rafter legs in the upper part are connected by crossbars;
- on hip roofs, diagonal rafters and shortened sprigs are used;
- Sprengels serve as an additional support for the diagonal rafters;
- racks and struts are used for intermediate fastening of rafters;
- if necessary, the rafters are lengthened with fillies.
The main load-bearing elements of the mansard roof are rafter logs, beds and puffs, as well as vertical racks and a ridge run.
The diagram indicates the dimensions of the elements of the truss system, their location, angles of inclination and methods of tie-in at the connection nodes. Be sure to also provide information about the location of the double rafters, the presence of additional supports, the dimensions of the eaves and gable overhangs.
The scheme is the main document for assembling the rafter system, it reflects all the necessary parameters. However, before cutting the material, it is necessary to check the calculations again and create templates for the main parts. In the absence of a project, you need to carry out calculations and create a scheme yourself.
Mansard roof rafter step
Before starting work, you need to choose the pitch of the mansard roof rafters. The distance between the rafters and the joists (in the case of a hip roof) depends on several factors:
- building size;
- type of truss system;
- constant and variable load on the roof;
- sections of rafters, racks and slopes;
- type of roofing;
- type and step of the crate;
- heater dimensions.
For rafters, battens and counter battens, coniferous material is selected in accordance with SNiP II-25, and the load on the rafters is calculated according to SNiP 2.01.07 and ST SEV 4868. Based on the building codes and regulations, we can say that for rafters less than 9 m, the beam section is applicable from 50X150 to 100X250 mm at a step from 60 to 100 cm. The size of the building affects the design of the farm and the presence of racks, struts and crossbars, the use of which increases the strength of the rafter legs and allows you to increase the step between the rafters to 120 cm or more . Usually, reference tables are used to select a step, which contain recommendations, taking into account the length of the rafters and the cross section of the timber.
Table: dependence of the step between the rafters on the cross section of the beam and the length of the rafters
The type of roofing used also affects the choice of rafter pitch, because different materials have different weights:
- tile, depending on the type, weighs from 16 to 65 kg / m 2, slate - 13 kg / m 2. Such heavy coatings imply a decrease in the pitch of the rafter legs to 60–80 cm;
- the weight of metal coatings and ondulin does not exceed 5 kg / m 2, so the pitch of the rafters can be increased to 80–120 cm.
On hip roofs, in any case, the spacing of the sprigs is chosen to be 50–80 cm to make the slope more rigid.
In addition, the installation step of the rafters depends on:

The length of the rafters and lathing of the mansard roof
With independent calculations, the dimensions of some structural elements of the roof have to be calculated according to the existing dimensions of the building and the angle of inclination of the slopes. The length of the rafters sometimes has to be adjusted for different types of mansard roof, choosing the optimal dimensions of the entire structure as a whole.
Suppose that the main dimensions of the building are known and it is necessary to calculate the length of the rafter logs for several proposed options for the angle of inclination and the type of roof. Let half the width of the building L be 3 m, the size of the cornice slope be 50 cm.

Additional calculations show that an increase in the angle of inclination of the lower slope from 60 to 70 ° will increase the width of the attic by 10%.
The length of the sheathing connecting the rafter legs is determined taking into account the gable overhangs that protect the walls of the facade from precipitation. The length of the gable overhang depends on the height of the building and is selected in the range from 40 to 60 cm. Therefore, the total length of the slope will be equal to the length of the house, increased by twice the length of the overhang.
Suppose that the length of the house is 10 m, and the gable overhang is 0.6 m. Then the dimensions of the crate must be calculated taking into account the length of the slope, equal to 10 + 0.6 ∙ 2 = 11.2 m.
The parameters of the lathing should be calculated taking into account the length of the gable and eaves overhangs
Any adjustment of the project requires a careful recalculation of the parameters of the truss system, taking into account the changes that have occurred.
Video: mansard roof calculation
The nodes of the truss system of the mansard roof
The nodes of the roof truss system are the junction of individual elements into a single structure, which allows you to evenly distribute the load on the walls of the building. The connection is made with nails, self-tapping screws or bolts using overhead wooden elements or metal squares and plates, as well as by connecting into a groove. For the construction of a gable roof, the following main components are used:
- A ridge knot that connects the rafter legs to each other and to the ridge run.
- Places where the crossbar connects the rafters to give greater strength and rigidity to the truss trusses.
- Attachment points for struts and struts that give additional support to the rafters.
- A cornice assembly in which rafters are attached to a puff or mauerlat, forming a cornice overhang.
The nodal connections of the truss system must be carried out in such a way as to ensure the most rigid fastening of the elements to each other.
For a gable sloping roof, the node is characteristic, where the upper and lower rafter logs, a vertical post, a crossbar and a run are connected. Such a complex connection requires the use of tie-ins, bolts, steel plates and building brackets.
In the most complex node of a broken mansard roof, five truss elements are connected
The most complex node of the hip mansard roof is the junction of the lateral or diagonal rafter legs with the Mauerlat. The side rafter in the lower part rests on the corner beam of the Mauerlat and on the embedded beam; in another version, a vertical stand or sprengel is placed between the embedded beam and the rafter leg. The upper part of the hip rafters is attached to the ridge run with bolts or nails.
The corner rafters of the hip roof carry the greatest load, so the knot of their connection with the Mauerlat must be thought out most carefully
The nodes described are most often used in the installation of truss systems of various designs and allow the installation of load-bearing elements on their own. For efficient and high-quality assembly, drawings and the manufacture of templates with verified angles of joints and tie-ins are necessary.
Video: nodes of the truss system
Calculation of the truss system of the mansard roof
The truss system is the basis of the roof, so it is important to choose the design that best suits the climatic conditions of the region and the existing requirements for the size of a residential attic. After choosing the design, the angle of inclination of the slopes and the height of the ridge are calculated for the required dimensions of the attic room. Calculations are made taking into account the size of the cornice according to the following formulas:

The meaning of trigonometric functions can be found in the reference tables.
Table: values of trigonometric functions for various slope angles
The hardest part of designing mansard roofs is counting the lumber. Calculating the number of rafters needed and linking them to a standard length of 6 m can sometimes be quite difficult. Let's say that we have chosen the hip roof, the most difficult in calculations, with a size of 10X13 m, taking into account the cornice overhangs 80 cm long and the angle of inclination of the slopes is 45 °. Then the side rafters will have a length of 5 / sin 45 o = 7.04 m. Therefore, the standard six-meter beam will have to be lengthened. Usually, for rafters a little more than 6 m long, a 100X200 mm beam or a 50X250 mm board is used.
If the building is large, then it requires rafters longer than the standard size of 6 m, so the timber has to be lengthened
As for the horizontal floor beam, since the width of the building is 10 m, the puffs should consist of two parts, which either rest on the inner wall of the building, or are joined together by reinforcing elements and rely on the run. For puffs and runs, a beam with a cross section of at least 50X200 mm is used. A mauerlat runs along the perimeter of the building, for which a beam of 150X150 mm or 200X200 mm is used. According to the scheme we have chosen, the perimeter of the building is 39.6 m, so seven six-meter bars will be required to install the Mauerlat. The dimensions of all other elements of the truss system will not exceed 6 m.
The weight of the lumber of the truss system is calculated by summing up the lengths of all elements with a certain section and converting their number into cubic meters. This is necessary to determine the mass of the entire roof, and is also necessary when purchasing and transporting material. The calculation is made according to the table, and then the obtained values \u200b\u200bare multiplied by the weight of 1 m 3 of lumber.
Table: calculation of the amount of lumber in 1 m 3 and the volume of one unit of material
Pine lumber weighs 505 kg/m 3 at 12% humidity, and 540 kg/m 3 at 25% transport humidity. Here are some examples of calculations:
- If 1 m 3 of material with a section of 50X200 mm contains 16.6 boards, then the weight of one board will be 540/16.6 = 32.5 kg.
- If 25 m 3 of lumber is purchased, then it will weigh 25 ∙ 540 = 13,500 kg.
- If 100 boards 25X200 are required, then you need to buy 100 / 33.3 = 3 m 3 of wood, which will weigh 3 * 540 = 1,620 kg.
It is important to note that it is advisable to purchase edged lumber with the lowest moisture content so that after installation it does not warp or crack, especially for large-section timber. For the construction of the truss system, the moisture content of the wood should not exceed 18%.
Installation of the attic truss system
Installation of a truss system with a residential under-roof space requires careful preparation. It is necessary to mount convenient scaffolding, decking and ladders, as well as provide workplaces with safety ropes. Workers must be provided with overalls, protective equipment and serviceable equipment. On the ground, you need to choose a flat place for pre-assembly of trusses, marking corners and making templates. All wooden elements must be treated with antiseptic and fire-fighting compounds.
After that, you can begin work, which takes place in the following sequence:
- On walls with walled studs, a Mauerlat is mounted around the perimeter. If there is a load-bearing wall inside the building, we lay a bed or run of the same height with a Mauerlat on it.
If the house is being built from building blocks, then it is most convenient to lay the Mauerlat on threaded studs that are immured into the wall during its laying
- Puffs with eaves extensions are attached to the Mauerlat parallel to the short wall.
- On the puffs, vertical racks are set, limiting the attic room.
- The racks are connected to the puff, which serves as the ceiling of the attic room. The trusses installed in this way are interconnected by horizontal runs.
Vertical racks, top puffs and horizontal runs form the frame of the attic space
- The lower and then the upper rafters are installed, which are attached to the ridge part.
- To strengthen the lower and upper rafters, struts, grandmas and surfs are used.
- The crate and frontal board are mounted on the cornice overhang.
After installing all the rafters, it remains to lay the crate and nail the frontal board
We examined the assembly of the truss system using the example of a broken mansard roof. The construction of other structures consists of similar operations and mainly consists in performing work according to the design installation diagram, which reflects the methods of connecting the elements of the truss system. In the presence of carefully calculated drawings, a team of four people is able to mount a roof with a truss system of any complexity.
Video: installation of a mansard roof
We examined the truss group of the mansard roof, its design, calculation, as well as the diagram and description of the main components. They offered a variant of step-by-step installation of the supporting structures of the attic, attached illustrations and videos that explain the assembly procedure for the structural elements of the attic roof. Now its successful erection depends only on the thoroughness of the implementation of the requirements of instructions and technologies and the availability of certain skills for the performers of construction work. We wish you success.
A house with an attic is not only an additional living space, but also a respectable view of the entire building. Even if the room under the roof is made unheated and is used only in the summer, it still creates a powerful "air cushion" that helps to retain heat inside the entire capital building.
And about, then - read on our portal.
Attic project
When drawing up a scheme for building an attic, it is best to do this in different projections in order to see and understand the placement of all elements of the truss system. It is very important to correctly calculate the height of the roof ridge, since the size of the area under it will directly depend on it.

When drawing up a scheme-project for the construction of a mansard roof, you need to calculate the height of the ridge, the ceiling and the total area of \u200b\u200bthe room.
The minimum height from the floor to the ridge should be 2.5-2.7 m, if this distance is less, then the room is not an attic, it can only be called an attic. This parameter is set by the norms of SNIP.

In order for all elements to be drawn accurately and have the desired location in the overall system, it is necessary to start from a figure with right angles, that is, a rectangle or square - a section of the created attic room. Based on the sides (height and width of the future room), it will be almost impossible to make a mistake with the angles at which roof slopes are located, with the location of the ridge, rafters and all retaining elements. Determining these parameters, they must immediately be entered into the drawing.
First you need to find the middle of the width of the front wall. Starting from this point, the parameters of the height of the ridge, the future ceiling of the attic, the location of the rack-walls and the size of the cornice overhang are determined.
Due to the fact that each of the structures has a certain number of connecting nodes that have different configurations, it would be nice to draw each of these ligaments separately in order to understand their features of conjugation among themselves of all elements connecting at this point.

Any truss system consists of basic elements and additional ones, which may not be in every design. The main components of the mansard roof are.
- Floor beams, which are the basis for the rest of the elements of the truss system. They are laid on the main walls of the building.
- Rafter leg, straight in a gable roof system or consisting of two sections - in a broken pattern. In this case, the upper rafter is called the ridge rafter, as it forms the highest point of the roof - and the rafters that form the walls of the attic are called side rafters.
- A ridge board or beam is an indispensable element for a gable roof, but is not always used when constructing a broken roof model.
- Mauerlat - a powerful bar, fixed to the main side walls of the building. Rafter legs are installed on this element.
- Racks are supporting elements necessary to strengthen a gable and broken structure. In the latter case, a ridge and side rafters are attached to it, and in the first case, the stand is a reliable support for a long rafter. In addition, the racks serve as a frame for insulation and sheathing of the attic walls.
- Diagonal braces or bevels additionally hold the posts or stringers and rafters together, making the structure more durable.
- Attic floor beams are used in all attic options - they connect the racks, and they are also the frame for the ceiling device.
- Interrafter runs are installed in a broken form of the roof for structural rigidity.
To be sure that the prepared project is developed correctly, you need to show it to a specialist. Only he can determine whether the attic parameters are correctly selected for the width and length of the walls of the building.
Video: professional mansard roof calculation using special software
Parameters of materials for the construction of a mansard roof
If the graphic project is ready, then, starting from the dimensions marked on it, you can calculate the amount of materials needed to build a mansard roof. Materials must be selected according to their characteristics, which must meet the requirements of fire and environmental safety. For wood, it is necessary to provide special treatment with fire retardants, which will reduce the combustibility of the material. So, for the construction you will need:
- Boards for rafter legs. Their cross section is selected according to the results of special calculations - this will be discussed in more detail below.
- A beam having a cross section of 100 × 150 or 150 × 200 mm - for floor beams, depending on the selected truss system and the width between the bearing walls, as well as for girders, diagonal legs or valleys - if they are provided for by the design.
- Beam with a section of 100 × 150 mm or 150 × 150 mm for laying Mauerlat.
- For racks, a beam of 100 × 100 or 150 × 150 mm is usually used.
- Unedged board for subflooring and some fasteners.
- Annealed steel wire with a diameter of 3-4 mm - for fastening together some parts.
- Nails, bolts, staples of various sizes, corners of various configurations and other fasteners.
- Metal sheet with a thickness of at least 1 mm - for cutting overlays.
- Lumber for battens and counter battens for roofing material - depending on the type of roofing chosen.
- - for thermal insulation of the roof.
- Waterproofing and vapor barrier membranes.
- Roofing material and fasteners for it.
What section are required rafters
Rafters are roofing elements that will perceive the main external loads, therefore, the requirements for their cross section are very special.
The size of the required lumber will depend on many parameters - on the step between the rafter legs, on the length of these legs between the support points, on the snow and wind load that falls on them.
The geometric parameters of the design of the truss system are easy to determine in the drawing. But with the rest of the parameters - you will have to refer to the reference material and carry out some calculations.
Snow load is not the same for different regions of our country. The figure below shows a map on which the entire territory of Russia is divided into zones according to the intensity of the snow load.

There are eight such zones in total (the last, eighth, is more likely to be extreme, and it can not be considered for the construction of a mansard roof).
Now you can accurately determine the snow load, which will depend on the angle of the roof slope. For this, there is the following formula:
S = Sg × μ
Sg- tabular value - see the map and the table attached to it
μ — correction factor depending on the steepness of the roof slope.
- If the slope angle is less 25° then μ=1.0
- With a steepness from 25 to 60 ° - μ=0.7
- If the roof is steeper than 60 °, then it is considered that the snow does not linger on it, and the snow load is not taken into account at all.
It is characteristic that if the mansard roof has a broken structure, then for its different sections the load can have different values.

The angle of the roof slope can always be determined either by a protractor - according to the drawing, or by a simple ratio of the height and base of the triangle (usually - half the width of the span):
The wind load also mainly depends on the region of construction of the building and on the characteristics of its environment and roof height.

And again, for the calculation, the initial data on the map and the table attached to it are first determined:
The calculation for a specific building will be carried out according to the formula:
Wp = W × k × c
W- tabular value, depending on the region
k- coefficient taking into account the height of the building and its location (see table)
The following zones are indicated in the table with letters:
- zone A - open areas, steppes, forest-steppes, deserts, tundra or forest-tundra, open to the winds of the coast of the seas, large lakes and reservoirs.
- zone B - urban areas, wooded areas, areas with frequent obstacles to the wind, relief or artificial, at least 10 meters high.
- zone IN- dense urban development with an average height of buildings above 25 meters.
With- coefficient depending on the predominant wind direction (wind rose of the region) and on the angle of inclination of the roof slopes.
With this coefficient, the situation is somewhat more complicated, since the wind can have a double effect on the roof slopes. So, it has a direct, overturning effect directly on the roof slopes. But at small angles, the aerodynamic effect of the wind takes on special significance - it tries to raise the slope plane due to the emerging lifting forces.

In the drawings, diagrams and tables attached to them, the sections of the roof that are subject to maximum wind loads are indicated, and the corresponding coefficients for calculation are indicated.
It is characteristic that at slope angles up to 30 degrees (and this is quite possible in the section of ridge rafters), the coefficients are indicated both with a plus sign and negative, that is, directed upwards. They somewhat extinguish the frontal wind load (this is taken into account in the calculations), and in order to level the effect of lifting forces, it will be necessary to very carefully fix the truss system and roofing material in this area using additional connections, for example, using annealed steel wire.
After the wind and snow loads are calculated, they can be summed up, and, taking into account the design features of the system being created, determine the cross section of the boards for the rafters.
Please note that the data are given for the most commonly used coniferous material (pine, spruce, cedar or larch). The table shows the maximum length of the rafters between the support points, the cross section of the board depending on the grade of the material, and the step between the rafters.
The value of the total load is indicated in kPa (Kilopascals). It is not difficult to bring this value into more familiar kilograms per square meter. With quite acceptable rounding, you can accept: 1 kPa ≈ 100 kg/m².
The dimensions of the board along its section are rounded up to the standard sizes of sawn timber.
| rafter section (mm) | Distance between adjacent rafters (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 600 | 900 | 300 | 600 | 900 | ||
| 1.0 kPa | 1.5 kPa | ||||||
| higher | 40×89 | 3.22 | 2.92 | 2.55 | 2.81 | 2.55 | 2.23 |
| 40×140 | 5.06 | 4.60 | 4.02 | 4.42 | 4.02 | 3.54 | |
| 50×184 | 6.65 | 6.05 | 5.28 | 5.81 | 5.28 | 4.61 | |
| 50×235 | 8.50 | 7.72 | 6.74 | 7.42 | 6.74 | 5.89 | |
| 50×286 | 10.34 | 9.40 | 8.21 | 9.03 | 8.21 | 7.17 | |
| 1 or 2 | 40×89 | 3.11 | 2.83 | 2.47 | 2.72 | 2.47 | 2.16 |
| 40×140 | 4.90 | 4.45 | 3.89 | 4.28 | 3.89 | 3.40 | |
| 50×184 | 6.44 | 5.85 | 5.11 | 5.62 | 5.11 | 4.41 | |
| 50×235 | 8.22 | 7.47 | 6.50 | 7.18 | 6.52 | 5.39 | |
| 50×286 | 10.00 | 9.06 | 7.40 | 8.74 | 7.66 | 6.25 | |
| 3 | 40×89 | 3.06 | 2.78 | 2.31 | 2.67 | 2.39 | 1.95 |
| 40×140 | 4.67 | 4.04 | 3.30 | 3.95 | 3.42 | 2.79 | |
| 50×184 | 5.68 | 4.92 | 4.02 | 4.80 | 4.16 | 3.40 | |
| 50×235 | 6.95 | 6.02 | 4.91 | 5.87 | 5.08 | 4.15 | |
| 50×286 | 8.06 | 6.98 | 6.70 | 6.81 | 5.90 | 4.82 | |
| total snow and wind load | 2.0 kPa | 2.5 kPa | |||||
| higher | 40×89 | 4.02 | 3.65 | 3.19 | 3.73 | 3.39 | 2.96 |
| 40×140 | 5.28 | 4.80 | 4.19 | 4.90 | 4.45 | 3.89 | |
| 50×184 | 6.74 | 6.13 | 5.35 | 6.26 | 5.69 | 4.97 | |
| 50×235 | 8.21 | 7.46 | 6.52 | 7.62 | 6.92 | 5.90 | |
| 50×286 | 2.47 | 2.24 | 1.96 | 2.29 | 2.08 | 1.82 | |
| 1 or 2 | 40×89 | 3.89 | 3.53 | 3.08 | 3.61 | 3.28 | 2.86 |
| 40×140 | 5.11 | 4.64 | 3.89 | 4.74 | 4.31 | 3.52 | |
| 50×184 | 6.52 | 5.82 | 4.75 | 6.06 | 5.27 | 4.30 | |
| 50×235 | 7.80 | 6.76 | 5.52 | 7.06 | 6.11 | 4.99 | |
| 50×286 | 2.43 | 2.11 | 1.72 | 2.21 | 1.91 | 1.56 | |
| 3 | 40×89 | 3.48 | 3.01 | 2.46 | 3.15 | 2.73 | 2.23 |
| 40×140 | 4.23 | 3.67 | 2.99 | 3.83 | 3.32 | 2.71 | |
| 50×184 | 5.18 | 4.48 | 3.66 | 4.68 | 4.06 | 3.31 | |
| 50×235 | 6.01 | 5.20 | 4.25 | 5.43 | 4.71 | 3.84 | |
| 50×286 | 6.52 | 5.82 | 4.75 | 6.06 | 5.27 | 4.30 | |
Tools
Naturally, during work, one cannot do without tools, the list of which includes:
- Electric drill, screwdriver.
- Building level and plumb line, tape measure, square.
- Axe, chisel, chisel, hammer
- Circular saw, jigsaw, hacksaw.
- Carpentry knife.
Installation will be accelerated if the tools for work are of high quality, and the work is carried out with competent mentors, with assistants, carefully and in stages.
Installation steps
It is necessary to strictly observe the sequence of work - only under this condition the design will turn out to be reliable and durable.
Mauerlat mount
The installation of any truss system begins with fixing a powerful supporting structure at the end of the side walls of the structure. timber - Mauerlat on which it will be convenient to install rafter legs. Mauerlat is made from a high-quality bar with a cross section of at least 100 × 150 mm. It must be laid on the roofing material waterproofing laid along the upper end of the wall (regardless of the material).
Due to the Mauerlat, the load will be evenly distributed along the walls and transferred to the foundation of the building.

The Mauerlat is fixed to the wall with metal studs, which are pre-embedded in a concrete belt or a crown running along the upper edge of the wall, or with anchor bolts with a diameter of 12 mm. They must go deep into the wall by at least 150 — 170 mm. If the Mauerlat is installed on a wooden wall, then the bars are attached to it with the help of wooden dowels.
Installation of the truss structure
- Installation of the truss system begins with the installation of floor beams. They can be mounted on the Mauerlat from above if the beams are planned to be taken out of the perimeter of the building and thereby increase the attic area. In this design, the rafter legs are fixed to the floor beams.
 Floor beams fixed on top of the Mauerlat (Fig. A)
Floor beams fixed on top of the Mauerlat (Fig. A) - Otherwise, they may fit into waterproofed walls and fastened with corners or staples to the inner edge of the Mauerlat. This option is used when the rafter legs are planned to be fixed directly to the Mauerlat.
 Another option - only rafter legs are attached to the Mauerlat
Another option - only rafter legs are attached to the Mauerlat - Next, you need to find the middle of the floor beam, since this mark will become a guideline for determining the location of the support posts and the ridge.
- Racks should be located at the same distance from the marked middle of the floor beam. In the future, they will begin to determine the location of the walls of the attic room, that is, its width.
- Bars for racks should have a cross section equal to the size of the floor beams. Construction sites are attached to the beams with the help of special corners and wooden linings. However, to begin with, they are first baited with nails, then carefully leveled with the help of a building level and a plumb line, and only then they are fixed thoroughly, with the expectation of future loads.

- When the first pair of racks is installed, they are fastened together from above with a bar, which is called a puff. This puff is also connected to the racks using special metal corners.

- After fixing the puff, you get a U-shaped design. Layered rafters are installed on it on the sides, which are attached to the floor beam with their second end or are laid on the Mauerlat.
- A special notch (groove) is cut out on the installed supports for the timber or in the rafters. With its use the rafters are tightly installed on the mauerlat beam, and fastened with metal brackets.

- For structural rigidity, struts can be additionally installed from the base of the rack to the middle of the installed side rafter. If this seems not enough, and saving material is not in the foreground, then you can strengthen the overall design with additional racks and contractions (they are indicated in the drawing in Fig. A by translucent lines).
- Further, the middle is calculated on the puff - a headstock will be attached to this place, supporting the ridge connection of the upper hanging subsystem of the rafters.
- The next step is to install ridge rafters, which can be fastened together with different connections - this can be a metal lining or powerful bolts with metal plates or washers.

- After their installation, a headstock is attached to the ridge and the middle of the puff.
- Having completed work on one part of the truss system, you need to make all the rest according to the same principle. The distance between adjacent rafters in such a system should be no more than 900 — 950 mm, but the interval of 600 mm will probably still be optimal - this will give both the necessary rigidity and stability of the structure, and will be convenient for insulation using standard mineral wool mats. True, this makes the structure heavier and requires more materials.

- First, the side parts of the complete system are installed, and then the intermediate ones. Between themselves, they are connected by runs, which are installed between the upper ends of the racks and act as spacers. Thus, a rigid structure of the attic rafters will be obtained, in which the frame for wall cladding will already be ready.
Prices for various types of fasteners for rafters
Fasteners for rafters
Mansard roof waterproofing
When the truss system is built, you can proceed to finishing it and their accompanying materials.
- The first coating to be fixed immediately on top of the rafters will be waterproofing and windproof film. it is attached to the rafters with staples and a stapler, starting from the eaves. Cloths are overlapped by 150 — 200 mm, and then the joints are glued with waterproof tape.
- On top of the waterproofing, a counter-lattice is stuffed onto the rafters, which will more reliably fix the film on the surface and create the necessary ventilation distance between the windproof and roofing material. The counter-lattice is usually made of boards with a width of 100 — 150 mm and 50 thick — 70 mm.

- A crate is fixed perpendicular to the counter-lattice, on which the roofing material will then be laid. The step between the rails must be calculated depending on the type and size of the sheet roofing material, taking into account the overlap required for it.
- If a soft roof is chosen, then plywood sheets are most often fixed to the counter-lattice.
Roofing installation
Roofing material is fixed on the prepared crate or plywood. Its installation usually starts from the roof eaves and runs in order, from one of the edges - depending on the type of roof. Roofing sheets are mounted with an overlap. If a metal profile or metal tile is used for coating, then such material is fixed with special self-tapping screws with elastic gaskets. Fasteners are usually matched in color to the roofing material.

The most difficult thing in covering a mansard sloping roof is the transition from layered side rafters to hanging ridge rafters. There may be certain difficulties in the event that ledges are provided on the roof for roofing over balconies or windows.
In addition, if a chimney pipe enters the roof, it requires a separate opening inside the rafter system and the insulation layer, and on the roof, a reliable waterproofing device around the pipe.
How and what is better to cover the roof, you can find out in detail on our portal, there is a whole section in which you can find answers to many questions, including recommendations for reliable insulation of the attic room.
Prices for popular types of corrugated board
Decking
Video: a detailed video tutorial on building a mansard roof
It should be noted that the work on the construction of any roof, and even more so complex as an attic, is not only responsible, but also quite dangerous, it requires special, increased security measures. If there is no experience in carrying out such construction processes, then it is better to entrust their implementation to professionals or to perform all actions under the supervision of an experienced craftsman, and with the utmost care and accuracy.
The rafter system is one of the final stages of building a house. The durability of the building itself and the comfort of living in it depend on how correctly it is executed. Ease of execution allows you to do the work yourself with the assistance of an assistant.
Rafter systems under the attic
Today there is a real boom in the use of various architectural elements in suburban construction, which, in the conditions of industrial construction, would seem to be forever gone. We are talking about such devices as bay windows, attics, mezzanines and the like. They allow you to significantly increase the area of \u200b\u200buseful space and give the building an original beautiful look.
Attics are especially popular, allowing you to arrange a full-fledged living space in the under-roof space. For this, special truss systems are used, designed to ensure the possibility of creating such a room, subject to sufficient structural strength.
The device of a broken mansard roof allows you to get a full-fledged living space on the second floor
Types of truss systems
The main types of truss systems for the attic device are represented by two options:
- gable;
- broken truss system.
Photo gallery: what is an attic
A sloping roof allows you to get the optimal combination of roof slope and usable area under it. It is possible to increase the volume of the attic in a structure under a gable roof only due to the high height of the ridge. The attic can be “completed” with a remote structure with a balcony under a separate roof.
However, in practice, the roofs of a country house are so diverse that it is almost impossible to classify them. The design uses a variety of elements:
- hip bevels;
- birdhouses;
- awnings;
- semi-embedded translucent structures (greenhouses);
- lanterns and other architectural solutions in the most original and sometimes unexpected combinations.
Photo gallery: projects of houses with a gable roof and an attic
A gable roof can be decorated with an elegant “birdhouse”, which will also increase the attic area. In large houses, a gable structure can be used as one of the elements of the roof composition. The main idea of such a house is to combine simplicity of execution with perfectly matched finishing elements
Elements and nodes of the mansard roof truss system
Obviously, the most durable construction is a gable roof. But in order to obtain a sufficiently spacious room with such a rafter arrangement, it is necessary to reduce the angle between the slopes, and this leads to an increase in wind loads on the roof. A reasonable way out is to create a semi-attic, when racks are installed from floor to ceiling to a height of 1.3–1.8 meters, and rafters are already attached to them. Such a device requires the installation of low crossbars to compensate for bursting loads from rafter legs on racks.
 To increase the useful volume of the attic, the crossbars that form its ceiling are installed as close as possible to the ridge knot
To increase the useful volume of the attic, the crossbars that form its ceiling are installed as close as possible to the ridge knot The use of a sloping roof allows you to simplify the shape of the attic room and get more living space.
 The construction of a sloping roof allows you to get a much larger attic than a conventional gable roof.
The construction of a sloping roof allows you to get a much larger attic than a conventional gable roof. The main elements of the truss system are:

When installing the truss system, additional parts are widely used to strengthen the fastening of structural elements.
 The use of modern fasteners will effectively strengthen the structure and significantly reduce installation time.
The use of modern fasteners will effectively strengthen the structure and significantly reduce installation time. Calculation of the truss system
The initial data for the calculation are taken from a previously developed project. For example, consider the scheme of the roof device in the presence of an attic.
 The design drawing indicates the dimensions, installation locations and material of all elements of the roofing system
The design drawing indicates the dimensions, installation locations and material of all elements of the roofing system The main indicator, calculated in the first place, is the pitch of the rafters, depending on the planned finish. So, to install ceramic tiles, the pitch of the rafters should be no more than 60 centimeters, and if you plan to install a plastic coating or a soft roof, this figure can be increased to 120–150 centimeters. Again, you need to take into account the nature of the loads - a combination of the effects of wind and snow - and set the optimal angle between the roof slopes.
The procedure for calculating the number of rafters
For example, consider the installation of roofs for a house 10 meters long. As a first approximation, we take the distance between the rafter legs equal to 80 centimeters. Then they will be needed: 1000: 80 + 1 = 13.5. Since the number of rafters must be an integer, we round the result to 13. In this case, the exact distance between them will be 1000: 13 = 769 (millimeters). This is the exact value of the gap between the axes of the rafter legs.
When calculating the need for materials, their cutability must be taken into account. In the case of wood materials, their length can be 4 or 6 meters. In the design process, it is necessary to select the dimensions of parts, taking into account the formation of the least amount of trim . Softwood cuttings are unsuitable even for firewood for stoves.
Materials for roof construction
The traditional material for rafters in Russia is wood. Larch is considered the best option, however, for the price and availability, it can not always be used. Therefore, bars made of coniferous wood are used. The size of the section depends on the design of the building.
Composite profiled wood materials are becoming more and more common. These include:

The device of the truss system of a gable roof with an attic
At the heart of the truss system with a gable roof is a triangle - the most rigid figure.

Only the main elements of the truss system are listed. Additional parts can be used to increase the strength of the structure.
Installation of the roof truss system, taking into account the formation of the attic
The gable roof truss system can be formed in two ways:
- Assembly of the main structure below, followed by lifting to the floor and installation on the Mauerlat.
- Installation of rafter legs in detail directly at the installation site.
A more productive and convenient way is the first option.
Bottom truss assembly
This work is done in the following order:

Video: assembly of roof trusses "on the ground"
Installation of truss elements
Rafters, as the main load-bearing element of the roof skeleton, must be securely interconnected. For this, many different methods have been invented, including specific ones designed for certain types of buildings. The rafter system of a wooden house requires special attention. The beam is attached to the Mauerlat with a sliding device, and the ridge connection is made on a hinge. This is due to the constant seasonal shifts of the log house, which must be compensated.
Photo gallery: ways to connect rafter legs
The rafter legs are attached to the Mauerlat using metal corners The rafters are connected on the ridge end-to-end or through a gash The critical nodes of the rafters are connected using metal connecting plates The rafter legs are connected using special swivel joints that provide freedom of movement of the structure during seasonal deformations of the building The joint in the ridge can be reinforced with bolts
Installation of support posts and girders
This is a responsible operation, because at this stage the surface of the front finish of the walls and ceiling of the attic is formed. Therefore, the order of execution is the same as when installing rafters:

For the manufacture of all parts of the truss system, a beam of the same size is used, as a rule, 50x150 or 40x150 millimeters in size.
Video: quick installation of the truss system
crate
This is an essential element of the truss system. In the case when a warm attic room is formed in the under-roof space, the crate is made twice:
- The outer lathing is carried out for fixing the finishing coating of the roof. In addition, if each of its boards is attached to the rafters with two nails, it serves as a fastening element of the frame. In addition, an insulating and moisture-proof roof cake is formed under the crate.
- The inner crate serves as a frame for insulating the attic and installing a fine finish on walls and ceilings.
In addition, counter-lattices are also installed, with the help of which the ventilation system of the under-roof space is organized.
 The counter-lattice is placed parallel to the rafter legs and provides a gap for ventilation of the under-roof space.
The counter-lattice is placed parallel to the rafter legs and provides a gap for ventilation of the under-roof space. For the crate, a board with dimensions of 25x100 millimeters, edged or unedged, is used. Unedged board must first be sanded. A board wider than the specified size is not recommended. When warped, it can deform the finish coating or damage the roofing cake.
The batten boards are fastened with nails at least 70 mm long and at least two pieces for each intersection. This method increases the resistance of the structure to wind loads.
The step of the lathing depends on the material of the finishing coating - for ceramic tiles and soft roofs, it should be minimal (about five centimeters), for metal tiles or corrugated boards, a distance between boards of up to 70 centimeters is allowed.
 A properly laid roofing cake necessarily contains a ventilation gap between the insulation and the roofing material, which helps to quickly remove moisture.
A properly laid roofing cake necessarily contains a ventilation gap between the insulation and the roofing material, which helps to quickly remove moisture. Video: crate truss system
Rafter finish
The truss system after installation of all roof elements becomes practically inaccessible for inspection and maintenance. Therefore, before installing each part in place, it must be carefully treated with protective compounds. There are enough special products on the building materials market to protect wooden structures from bacteria and rot, as well as various fire-fighting impregnations.
 Before installing the details of the truss system, they must be treated with special protective compounds.
Before installing the details of the truss system, they must be treated with special protective compounds. At the same time, it should be taken into account that carrying out protective operations on the finished structure is not always effective, since hidden surfaces remain untreated.
Any wood protection products are certified by state authorities, so when buying, you need to ask the seller for a certificate of conformity. It is issued by the sanitary authorities and the fire inspectorate. First of all, the safety of the composition for humans and its compliance with the declared qualities are guaranteed.
Which of them to choose, the consumer decides, depending on their financial capabilities. In principle, you can always run into a fake, but it turns out only after many years of operation.
Impregnations can be applied with a wide seam brush or roller, but an airbrush is also often used.
Video: installation of a gable roof truss system with an attic
A reliable roof largely determines the duration of the life cycle of a building. Properly arranged roof provides comfort and value of living in the house. In the conditions of Russia, when heating is needed most of the year, a properly arranged insulated roof retains up to 30% of heat. And high-quality insulation is possible only with a high-quality truss system.