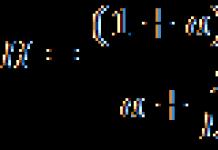GOST 10704–91. Electric-welded straight-seam steel pipes. Assortment. GOST 10705–80 Electric-welded steel pipes. Specifications
This standard applies to straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes.
The dimensions of the pipes must correspond to those indicated in the table. 12.
Table 1. Range and maximum deviations of small diameter pipes |
||
Outer diameter, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Limit deviations, diameter, mm |
0.8; 0.9; 1.0; 1.2 | ||
11; 12; 13; 14; 15 | 0.8–1.2; 1.4; 1.5; 1.6 | |
0.9–1.6; 1.8; 2.0 |
||
0.9–2.0; 2.2; 2.5; 2.8; 3.0 |
||
1.0–3.0; 3.2; 3.5 |
||
35; 36; 38; 40; 42; 45 | ||
1.2–3.5; 3.8; 4.0 |
||
60; 63.5; 70; 73 | ||
1.2–4.5; 5.0; 5.5 |
||
102; 108; 114; 121; | ||
127; 133; 140; 152 |
Notes:
Maximum deviations in wall thickness should not exceed +10% of the nominal value. For pipes Dн > 76 mm, a thickening of the wall at the burr by 0.15 mm is allowed.
Notes:
Maximum deviations of wall thickness should not exceed the requirements of GOST 19903–74 for the maximum thickness of a sheet of normal accuracy. Thickening of the wall at the burr by 0.15 mm is allowed.
Pipes are manufactured:
- unmeasured length:
At the customer's request, pipes of groups A and B with a diameter of over 152 mm must be manufactured with a length of at least 10 m; pipes of all groups with a diameter of up to 70 mm - a length of at least 4 m.
- measured length:
- multiple lengths of any multiple not exceeding the lower limit established for measuring pipes must have a total length not exceeding the maximum length of measuring pipes. In this case, the allowance for each multiple is 5 mm and is included in the ordered multiple.
Depending on the quality indicators, pipes of the following groups are manufactured:
A- according to mechanical properties in accordance with the requirements given in Table 3 for heat-treated and Tables 4, 5 for non-heat-treated pipes made of calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades St2, St3 and St4 (categories 1–3) according to GOST 380–88;
B- by chemical composition from calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades BSt2, BSt3, VSt4 according to GOST 380–88, as well as from calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades 08, 10, 15 and 20 according to GOST 1050–88 and steel 08Yu according to GOST 9045–70;
IN- according to mechanical properties in accordance with the requirements of table. 3–5 and the chemical composition of mild, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades VSt2, VSt3, VSt4 (categories 1, 2), semi-quiet and mild steel VSt3 (categories 3–6) according to GOST 380–88, as well as from calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades 08, 10, 15 and 20 according to GOST 1050–88 and steel 08Yu according to GOST 9045–70 for diameters up to 50 mm;
D- without standardization of chemical composition and mechanical properties, but with standardization of test hydraulic pressure.
Note:
With the consent of the consumer, the yield strength is not determined.
Table 4. Mechanical properties of non-heat-treated pipes with a diameter of 8–152 mm |
|||||||
steel grade | Wall thickness, mm | Tensile strength, MPa | Relative extension, % |
||||
63–152 | 63–152 |
||||||
08, 08ps, 08kp | |||||||
All thicknesses | |||||||
10, 10ps, 10kp, VSt2sp, VSt2ps, VSt2kp, St2sp, St2ps, St2kp | |||||||
All thicknesses | |||||||
15, 15ps, 15kp, 20, 20ps, 20kp | |||||||
All thicknesses | |||||||
St3sp, St3kp, St3ps, VSt3sp, VSt3ps, VSt3kp | |||||||
All thicknesses | |||||||
All thicknesses |
Note:
At the consumer's request, for pipes made of steel of all grades Dн=20Ў60 mm, Sє0.06 Dн and pipes Dн=20 mm, as well as Dн=20–60 mm, SЄ0.06 Dн, it is allowed to increase the minimum elongation value by 3% compared to standards given in table 4.
Yield strength standards are established by agreement of the parties.
Heat-treated pipes made of steel grades 08, 10, 15, 20, 08Yu and VSt3 with a wall thickness of at least 6 mm must withstand the impact strength test.
The impact strength of pipes made of VSt3 steel with SЄ6 mm should be Є784 kJ/m¤ at 20°C, Є392 kJ/m¤ at -20°C and Є392 kJ/m¤ after mechanical aging.
Table 5. Mechanical properties of non-heat-treated pipes with a diameter of 159–530 mm |
|||||
steel grade | Wall thickness, S, mm | Tensile strength, MPa | Relative extension, % |
||
not less for pipes with outer diameter, mm |
|||||
159–245 | 273–377 | 402–530 |
|||
08, 08ps, 08kp, 10ps, 10kp, 10, St2kp, VSt2kp | |||||
St2sp, St2ps, VSt2sp, VSt2ps | |||||
15ps, 15kp, 20, 20ps, 20kp | |||||
St3sp, St3ps, St3kp, VSt3kp, VSt3sp, VSt3ps | |||||
St4sp, St4ps, St4kp, VSt4sp, VSt4ps, VSt4kp | |||||
The impact strength of pipes made of steel grades 08, 10, 15, 20, 08Yu is not standardized, but the test results are recorded in the quality document.
Pipes Dн<102 мм должны выдерживать испытательное гидравлическое давление не менее 6.0 МПа, DнЄ102 мм - 3.0 МПа, Dн=402-530 мм и S=4.0-5.5 мм - не менее 2.0 МПа.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, hydraulic pressure testing may not be carried out.
With 100% quality control of the weld using non-destructive methods, hydraulic pressure testing is carried out on an additional 15% of pipes from the batch.
GOST 10705-80
INTERSTATE STANDARD
ELECTRIC WELDED STEEL PIPES
TECHNICAL CONDITIONS
Date of introduction 01.01.82
This standard applies to straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes with a diameter of 10 to 630 mm made of carbon and low-alloy steel grades used for pipelines, structures, as well as products for various purposes.
The standard does not apply to steel pipes used for the manufacture of thermal electric heaters.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 5,).
1. ASSORTMENT
1.1. The dimensions and maximum deviations of pipes must comply with GOST 10704.
2. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
2.1. Electric-welded steel pipes are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard and according to technical regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
2.2. Depending on the quality indicators, pipes are manufactured into the following groups:
A - with standardization of mechanical properties of calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades St1, St2, St3, St4 according to GOST 380;
B - with standardization of the chemical composition:
GOST 380;
GOST 1050;
Made from steel grade 08Yu according to GOST 9045;
Made from low-alloy steel grade 22ГУ with a chemical composition according to table 1a
GOST 19281 (pipes with a diameter from 114 to 630 mm inclusive);
B - with standardization of mechanical properties and chemical composition:
From calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades St1, St2, St3, St4 according to GOST 380;
From calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades 08, 10, 15, 20 according to GOST 1050;
Made from steel grade 08Yu according to GOST 9045;
From low-alloy steel grades in accordance with GOST 19281 and other regulatory documents with a standardized carbon equivalent of no more than 0.46% (pipes with a diameter from 114 to 630 mm inclusive);
D - with normalization of test hydraulic pressure.
Pipes are made from rolled products in accordance with GOST 14637 (categories 1 - 5), GOST 16523 (category 4), GOST 9045, GOST 19281 and other regulatory documents approved in the prescribed manner.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 7)
Table 1a
|
Steel grade |
Mass fraction of elements, % |
|||||||||
|
Manganese |
Aluminum |
|||||||||
|
no more |
||||||||||
|
Note: Permissible deviations in the mass fraction of elements from the standards given in the table must comply with GOST 19281 |
||||||||||
2.3. Pipes made of carbon steel grades are manufactured by heat treatment (throughout the entire volume of the pipe or along the welded joint), hot-reduced or without heat treatment. Pipes made from steel grade St1 are manufactured without heat treatment.
Pipes made from low-alloy steel grades are manufactured heat-treated (throughout the entire volume of the pipe or along the welded joint) or without heat treatment.
The type of heat treatment is chosen by the manufacturer. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the pipes are thermally treated in a protective atmosphere.
2.2, 2.3 (New edition, Amendment No. 6).
2.4. The mechanical properties of the base metal of heat-treated and hot-reduced pipes must comply with the standards specified in Table 1. The mechanical properties of pipes made of steel grade 22ГУ, as well as pipes made of low-alloy steel grades not listed in Table 1, are established by agreement of the parties.
|
steel grade |
Tensile strength s in, N/mm 2 (kgf/mm 2) |
steel grade |
Tensile strength s in, N/mm 2 (kgf/mm 2) |
Yield strength s t N/mm 2 (kgf/mm 2) |
Relative elongation d5,% |
||
|
St4sp, St4ps, |
|||||||
|
08, 08ps, 10kp |
|||||||
|
10, 10ps, 15kp, St2sp, St2kp, |
20F, 20-KSKH, 06GB |
||||||
|
20kp, St3ps, St3sp, St3kp |
09G2S, 09GSF, 13HFA, 17GS, 17G1S, 17G1S-U, 08ХМФЧА, 22ГФ, 26ХМА |
||||||
Note: At the request of the consumer, pipes with a wall thickness of 4 mm or more from steel grades St3sp, 15, 15ps are manufactured with a yield strength of 235 N/mm 2 (24 kgf/mm 2), a relative elongation of 23%; from steel grades St4sp, 20, 20ps - with a yield strength - 255 N/mm 2 (26 kgf/mm 2), relative elongation 22%.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 6).
|
steel grade |
Temporary tensile strength s in, N/mm 2 (kgf/mm 2), with the outer diameter of the pipes D, mm |
D, mm |
|||||||||||||
|
St. 19 to 60 |
St. 60 to 152 |
from 10 to 60 with wall thickness |
St. 60 to 152 |
||||||||||||
|
more than 0.06 D |
0,06 D or less |
||||||||||||||
|
St1ps, St1kp |
|||||||||||||||
|
10kp, St2kp |
|||||||||||||||
|
10ps, St2ps |
|||||||||||||||
|
St4kp, St4ps |
|||||||||||||||
|
20F, 20-KSKH, 06GB |
|||||||||||||||
|
09G2S, 09GSF, 13HFA, 17GS, 17G1S, 17G1S-U, 08ХМФЧА, 22ГФ, 26ХМА |
|||||||||||||||
Note: At the request of the consumer, for pipes of all grades of steel with a diameter from 10 to 60 mm, the relative elongation increases by 3% compared to the standards given in.
|
steel grade |
Wall thickness, mm |
Tensile strength s in, N/mm 2 (kgf/mm 2), |
Yield strength s t, N/mm 2 (kgf/mm 2) |
Relative elongation d s,%, with outer diameter of pipes D, mm |
||||||
|
St. 152 to 244.5 |
St. 244.5 to 377 |
St. 377 to 630 |
||||||||
|
08.08ps, 08kp |
||||||||||
|
10, 10ps, 10kp, St2kp |
||||||||||
|
St2sp, St2ps |
||||||||||
|
15, 15ps, 15kpp, 20, 20ps, 20kpp |
||||||||||
|
St3sp, St3ps, St3kp |
||||||||||
|
St4sp, St4ps, St4kp |
||||||||||
|
All thicknesses |
||||||||||
|
20F, 20-KSKH, 06GB |
All thicknesses |
|||||||||
|
09G2S, 09GSF, 13HFA, 13GS, 17GS, 17G1S, 17G1S-U, 08ХМФЧА, 22ГФ, 26ХМА |
All thicknesses |
|||||||||
|
All thicknesses |
||||||||||
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 7)
2.5. The mechanical properties of the base metal of pipes with a diameter of 10 to 152 mm inclusive without heat treatment and with heat treatment of the welded joint must comply with the standards specified in Table. 2. Mechanical properties of the base metal of pipes with a diameter of over 152 to 630 mm inclusive. without heat treatment and with heat treatment, the welded joint must comply with the standards specified in. The mechanical properties of pipes made of low-alloy steel grades not listed in tables and are established by agreement of the parties.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 5, , ).
2.6. Cracks, spots, dents, flaws and risks are not allowed on the surface of the pipes.
Ripples, nicks, dents, small scratches, a layer of scale and traces of stripping are allowed provided that they do not take the wall thickness and diameter of the pipe beyond the maximum deviations. Edge displacement up to 10% of the nominal wall thickness is allowed.
The surface of pipes heat-treated in a protective atmosphere should be free of scale. The presence of an oxide film is allowed.
Lack of penetration in seams must be welded, and the welding area must be cleaned. By agreement with the consumer, on pipes with a diameter of 159 mm or more, in places where seams are repaired by welding, a displacement of the welded edges is allowed by no more than 20% of the nominal wall thickness and the height of the reinforcement bead is not more than 2.5 mm.
Repairs by welding the base metal of pipes are not permitted.
In the case of repair by welding of pipes that have undergone heat treatment, they are subjected to repeated heat treatment (respectively throughout the entire volume or along the welded joint).
2.7. On pipes with a diameter of 57 mm or more, one transverse seam is allowed.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, one transverse seam is allowed on pipes with a diameter of less than 57 mm.
2.6, 2.7.
2.8. External beads on pipes must be removed. At the deburring site, the wall may be thinned by 0.1 mm above the minus tolerance.
At the request of the consumer, on pipes with an internal diameter of 33 mm or more, the internal burr must be partially removed or flattened, while the height of the burr or its traces should not exceed 0.35 mm - with a wall thickness of less than 2 mm; 0.4 mm - with a wall thickness of 2 to 3 mm; 0.5 mm - for wall thickness over 3 mm.
The height of the internal flash or its traces for pipes with an internal diameter of less than 33 mm is established by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
2.9. The ends of the pipes must be cut at right angles and cleared of burrs. The formation of a chamfer is allowed. The cutting angle for pipes with a diameter of up to 219 mm should not exceed 1 mm, and for pipes with a diameter of 219 mm or more - 1.5 mm. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, pipes are made cut in the mill line.
2.10. At the consumer's request, the ends of pipes with a wall thickness of 5 mm or more should be chamfered at an angle of 25 - 30 ° to the end of the pipe and an end ring with a width of (1.8 ± 0.8) mm should be left. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the bevel angle and width of the end ring can be changed.
2.11. The pipes must withstand the test hydraulic pressure. Depending on the test pressure, pipes are divided into two types:
I – pipes with a diameter of up to 102 mm – test pressure 6.0 MPa (60 kgf/cm 2) and pipes with a diameter of 102 mm and more – test pressure 3.0 MPa (30 kgf/cm 2);
II - pipes of groups A and B, supplied at the request of the consumer with test hydraulic pressure calculated according to GOST 3845, with a permissible stress equal to 90% of the standard yield strength for pipes made of this steel grade, but not exceeding 20 MPa (200 kgf/cm 2).
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
2.12. At the request of the consumer, heat-treated throughout the entire volume of pipes made of carbon steel with a wall thickness of at least 6 mm and low-alloy steel with an outer diameter of at least 219 mm and a wall thickness of at least 6 mm of the grades given in the table must withstand impact bending tests of the base metal. Impact strength standards are indicated in the table.
Standards for the impact strength of pipes made of steel grade 22ГУ are established by agreement of the parties.
2.13. Heat-treated pipes with a diameter of up to 152 mm inclusive, hot-reduced pipes without heat treatment with a diameter of more than 20 to 152 mm inclusive and a wall thickness of 0.06D n or less, as well as pipes with heat treatment of the welded joint must withstand the flattening test.
Flattening of heat-treated pipes should be carried out to the distance between the flattening planes N, mm, calculated by the formula

Where A– the coefficient for pipes made of steel grades 08Yu, 08kp, 8ps, 08, 10kp, St2kp is 0.09, and for pipes made of other steel grades it is 0.08;
S– nominal wall thickness, mm;
D n – nominal outer diameter of the pipe, mm.
Flattening of pipes without heat treatment should be carried out to a distance equal to 2/3D n . Flattening of pipes with heat treatment of the welded joint should be carried out to a distance equal to 1/2D n.
At the request of the consumer, flattening of heat-treated pipes with a diameter of over 152 to 530 mm should be carried out to a distance equal to 2/3D n.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
2.14. Pipes with a diameter of up to 108 mm must withstand the expansion test.
Pipes with a diameter of up to 108 mm made of carbon steel grades listed in Table 5 must withstand the expansion test.
The increase in the outer diameter of heat-treated pipes during distribution must comply with the standards specified in.
The increase in the outer diameter of pipes without heat treatment during distribution should be at least 6%.
At the request of the consumer, the increase in the outer diameter when distributing heat-treated pipes with a wall thickness of up to 4 mm from steel grades 10kp, St2kp should be at least 12%.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3, 4,).
2.15. At the request of the consumer, pipes must withstand the tests provided for in paragraphs. - .
The tensile strength of a welded joint of pipes without heat treatment with a diameter of 50 mm or more must comply with the standards specified in and.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3,).
2.19. Pipes must be sealed.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
3. ACCEPTANCE RULES
3.1. Pipes are accepted in batches. The batch must consist of pipes of the same size, one steel grade, one type of heat treatment and one manufacturing group, accompanied by one quality document, in accordance with GOST 10692 with the addition of the chemical composition of the steel in accordance with the quality document of the manufacturer of the workpiece.
The number of pipes in a batch should be no more than, pcs.:
1000 - with a diameter of up to 30 mm;
600 - with a diameter of St. 30 to 76 mm;
400 - with a diameter of St. 76 to 152 mm;
200 - with a diameter of St. 152 mm.
3.2. In case of disagreement in assessing the quality of the chemical composition, at least one pipe from the batch is selected for testing.
3.3. Each pipe is subjected to control of the dimensions and quality of the pipe surface. It is allowed to control dimensions and surfaces selectively on each batch with a one-stage normal level of control in accordance with the requirements of GOST 18242 *. Control plans are established by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
* GOST R 50779.71-99 is in force on the territory of the Russian Federation **.
3.6. If unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one of the indicators, repeated tests are carried out on a double number of pipes selected from the same batch.
The results of repeated tests apply to the entire batch.
3.7. The welding places of pipes of groups A, B, C must be checked by non-destructive methods, and the repaired pipes must be tested with hydraulic pressure in accordance with the requirements of this standard.
Places where seams are welded in pipes of group D must be tested using non-destructive methods, or pipes after repair must be tested with hydraulic pressure.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
4. TEST METHODS
4.1. For quality control, one sample is cut from each selected pipe for each type of test, and for impact strength testing, three samples are cut for each test temperature.
4.2. The chemical composition of steel is determined according to GOST 22536.0 - GOST 22536.6, GOST 12344 - GOST 12354. Samples to determine the chemical composition are taken according to GOST 7565.
Metal carbon equivalent ( WITH e) low alloy steel grades are calculated using the formula
Where WITH, MP, WITH r, Mo, V,Si, Ni- mass fraction of carbon, manganese, chromium, molybdenum, vanadium, copper, nickel in steel, %.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 6).
4.3. Inspection of the pipe surface is carried out visually. The depth of defects is checked by filing or another method.
It is allowed to control the surface and dimensions of pipes using non-destructive methods according to technical documentation.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
4.4. Pipes measure:
outer diameter and ovality - with an adjustable measuring clamp according to GOST 2216 or a caliper according to GOST 166, or a micrometer according to GOST 6507;
internal diameter - with a plug in accordance with GOST 14810 or with a caliber in accordance with GOST 2015, or by subtracting two wall thicknesses from the outer diameter;
curvature - with a straight edge according to GOST 8026 and a feeler gauge;
wall thickness, thickness difference and height of the internal burr - with a micrometer according to GOST 6507 or a wall gauge according to GOST 11358;
displacement of the edges - using a template according to technical documentation or a micrometer according to GOST 6507 or a depth gauge according to GOST 162;
The cutting angle is ensured by the design of the equipment for processing pipe ends, the chamfer angle is ensured by a goniometer in accordance with GOST 5378. In case of disagreement in quality assessment, the cut angle is checked with a charcoal cutter and a probe;
the end ring at the ends of the pipes - with a ruler in accordance with GOST 427;
depth of surface defects - using a depth gauge according to GOST 162. The outer diameter of the pipe is measured at a distance of at least 15 mm from the end of the pipe for pipes with a ratio of the outer diameter to the wall thicknessD n/ S n equal to 35 or less; at a distance of at least 2/3D n - for pipes with ratioD n/ S n over 35 to 75; at a distance of at leastD n - for pipes with ratioD n/ S n over 75.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3).
4.5. The impact bending test is carried out on longitudinal samples of type 3 according to GOST 9454, cut from a section of the pipe located at an angle of about 90° to the weld.
Impact strength is determined as the arithmetic mean value based on the test results of three samples. On one of the samples, a decrease in impact strength by 9.8 is allowed× 10 4 J/m 2 (1 kgf × m/cm 2).
The temperature of the impact bending test is specified by the customer in the order for the supply of pipes.
4.6. The tendency of the base metal of pipes to mechanical aging is determined according to GOST 7268. It is allowed to edit samples with a static load.
4.7. The tensile test is carried out according to GOST 10006 on a longitudinal proportional short sample.
When testing on segment-section samples, the latter is cut out from a section located at an angle of about 90° to the weld and is not straightened in the calculation part.
Instead of tensile testing, it is allowed to monitor the tensile strength, yield strength and relative elongation of pipes using non-destructive methods.
If disagreements arise, pipe testing is carried out in accordance with GOST 10006.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1,).
4.8. The flattening test is carried out according to GOST 8695.
4.9. The expansion test is carried out according to GOST 8694 on a mandrel with a taper of 30°. It is allowed to use mandrels with a taper of 1:10 and remove burrs in the distribution area.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
4.10. The bend test is carried out according to GOST 3728. Pipes with a diameter of 114 mm are tested on cut longitudinal strips 12 mm wide.
4.11. The boarding test is carried out according to GOST 8693. In the flanging area, deburring is allowed.
4.12. Determination of the temporary resistance of a welded joint is carried out on ring samples according to technical documentation.
On pipes with a diameter of 219 mm or more, it is allowed to carry out testing in accordance with GOST 6996 on type XII samples with removed reinforcement of the welded joint, cut perpendicular to the pipe axis, using a static load when straightening the samples.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 7).
4.13. Hydraulic testing of pipes is carried out in accordance with GOST 3845 with a pressure exposure of 5 s.
4.14. Inspection of the weld is carried out using non-destructive methods (ultrasonic, eddy current, magnetic or x-ray equivalent methods) according to technical documentation.
5. LABELING, PACKAGING, TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
5.1. Labeling, packaging, transportation and storage - in accordance with GOST 10692.
INFORMATION DATA
1. DEVELOPED AND INTRODUCED by the USSR Ministry of Ferrous Metallurgy
2. APPROVED AND ENTERED INTO EFFECT by Resolution of the USSR State Committee on Standards dated December 25, 1980 No. 5970
Change No. 5 was adopted by the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (Minutes No. 13 of May 28, 1998)
Registered by the Technical Secretariat of the IGU No. 3166
|
State name |
Name of the national standardization body |
|
The Republic of Azerbaijan |
Azgosstandart |
|
Republic of Armenia |
Armgosstandard |
|
Republic of Belarus |
State Standard of the Republic of Belarus |
|
The Republic of Kazakhstan |
Gosstandart of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
|
Republic of Kyrgyzstan |
Kyrgyzstandard |
|
The Republic of Moldova |
Moldovastandard |
|
Russian Federation |
Gosstandart of Russia |
|
The Republic of Tajikistan |
Tajikgosstandart |
STATE STANDARD OF THE USSR UNION
ELECTRIC WELDED STEEL PIPES
TECHNICAL CONDITIONS
GOST 10705-80
Publishing house of standards
Moscow
STATE STANDARD OF THE USSR UNION
Date of introduction 01.01.82
This standard applies to straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes with a diameter from 10 to 530 mm made of carbon and low-alloy steel, used for pipelines and structures for various purposes.
The standard does not apply to steel pipes used for the manufacture of thermal electric heaters.
1. ASSORTMENT
1.1. The dimensions and maximum deviations of pipes must comply with GOST 10704 -91
2. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
2.1. Electric-welded steel pipes are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard and according to technical regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
2.2. Depending on the quality indicators, pipes are manufactured into the following groups:
A - with standardization of mechanical properties of calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades St1, St2, St3, St4 according to GOST 380-94 (category 4 according to GOST 16523-89, category 4 according to GOST 14637-89);
B - with standardization of the chemical composition from calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades St1 St2, St3, St4 according to GOST 380-94 and GOST 14637-89, from calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades 08, 10, 15 and 20 according to GOST 1050- 88, made of steel grade 08Yu according to GOST 9045
B - with standardization of mechanical properties and chemical composition of calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades St1, St2, St3, St4 according to GOST 380-94 (category 4 according to GOST 16523-89 and categories 2-5 according to GOST 14637-89), from calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades 08, 10, 15 and 20 according to GOST 1050-88, from steel grade 08YU according to GOST 9045-93, from low-alloy steel grade 22GYu with the chemical composition given in (pipes with a diameter of 140 to 426 mm) ;
D - with normalization of test hydraulic pressure.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 4, Amendment No. 5).
2.3. Pipes are manufactured by heat treatment (throughout the entire volume of the pipe or along the welded joint), hot-reduced and without heat treatment.
The type of heat treatment throughout the entire volume of the pipe is chosen by the manufacturer. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the pipes are thermally treated in a protective atmosphere.
Pipes made from steel grade 22GYu are produced by heat treatment along the welded joint or throughout the entire volume, pipes made from steel grade St1 are produced without heat treatment.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, Amendment No. 5).
2.4. The mechanical properties of the base metal of heat-treated and hot-reduced carbon steel pipes must comply with the standards specified in. The mechanical properties of heat-treated pipes made of steel grade 22ГУ are established by agreement of the parties.
|
steel grade |
Tensile strength sв, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2) |
Yield strength st N/mm2 (kgf/mm2) |
Relative elongation d5, % |
|
08, 08ps, 10kp 10, 10ps, 15kp, |
196 (20) |
||
|
St2sp, St2kp, St2ps 1 5, 15ps, 20kp, |
|||
|
St3sp, St3ps, St3kp |
|||
|
St4sp, St4ps, St4kp, |
|||
Note. At the request of the consumer, pipes with a wall thickness of 4 mm or more from steel grades St3sp, 15, 15ps are manufactured with a yield strength of 235 N/mm2 (24 kgf/mm2), relative elongation of 23%; from steel grades St4sp, 20, 20ps - with a yield strength - 255 N/mm2 (26 kgf/mm2), relative elongation 22%.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 2, Amendment No. 3, Amendment No. 4 Amendment No. 5).
2.5. The mechanical properties of the base metal of pipes with a diameter of 10 to 152 mm inclusive without heat treatment and with heat treatment of the welded joint must comply with the standards specified in Table. . The mechanical properties of the base metal of pipes with a diameter of over 152 to 530 mm inclusive without heat treatment and with heat treatment of the welded joint must comply with the standards specified in.
|
Steel grade |
Temporary resistance rupture sв, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2), with outer diameter of pipes D, mm |
fluidity st, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2) |
with outer diameter of pipes |
||||
|
from 10 to 60 with wall thickness |
|||||||
|
more than 0.06 D |
0,06 D or less |
||||||
|
no less |
|||||||
|
08ps, 08kp, St1ps, St1kp |
|||||||
|
10kp, St2kp |
|||||||
|
10ps, St2ps |
|||||||
|
St4kp, St4ps |
|||||||
Note. At the request of the consumer, for pipes of all grades of steel with a diameter from 10 to 60 mm, the relative elongation increases by 3% compared to the standards given in table. .
|
Steel grade |
Wall thickness, |
Temporary resistance gap sв, |
Yield strength st, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2) |
Relative elongation ds, %, with outer diameter of pipes D, mm |
||||||
|
St. 152 to 244.5 |
St. 244.5 to 377 |
St. 377 to 530 |
||||||||
|
no less |
||||||||||
|
08.08ps, 08kp |
||||||||||
|
10, 10ps, 10kp, St2kp |
||||||||||
|
St2sp, St2ps |
||||||||||
|
15, 15ps, 15kp, |
||||||||||
|
20, 20ps, 20kpp |
||||||||||
|
St3sp, St3ps, |
||||||||||
|
St4sp, St4ps, |
||||||||||
|
All thicknesses |
||||||||||
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, Amendment No. 3, Amendment No. 4, Amendment No. 5).
2.6. . Cracks, spots, dents, flaws and risks are not allowed on the surface of the pipes.
Ripples, nicks, dents, small scratches, a layer of scale and traces of stripping are allowed provided that they do not take the wall thickness and diameter of the pipe beyond the maximum deviations. Edge displacement up to 10% of the nominal wall thickness is allowed.
The surface of pipes heat-treated in a protective atmosphere should be free of scale. The presence of an oxide film is allowed.
Lack of penetration in seams must be welded, and the welding area must be cleaned. By agreement with the consumer, on pipes with a diameter of 159 mm or more, in places where seams are repaired by welding, a displacement of the welded edges is allowed by no more than 20% of the nominal wall thickness and the height of the reinforcement bead is not more than 2.5 mm.
Repairs by welding the base metal of pipes are not permitted.
In the case of repair by welding of pipes that have undergone heat treatment, they are subjected to repeated heat treatment (respectively throughout the entire volume or along the welded joint).
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, Amendment No. 4, Amendment No. 5).
2.7. On pipes with a diameter of 57 mm or more, one transverse seam is allowed.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, one transverse seam is allowed on pipes with a diameter of less than 57 mm.
2.8. External beads on pipes must be removed. At the deburring site, the wall may be thinned by 0.1 mm above the minus tolerance.
At the request of the consumer, on pipes with an internal diameter of 33 mm or more, the internal burr must be partially removed or flattened, while the height of the burr or its traces should not exceed 0.35 mm - with a wall thickness of less than 2 mm; 0.4 mm - with a wall thickness of 2 to 3 mm; 0.5 mm - for wall thickness over 3 mm.
The height of the internal flash or its traces for pipes with an internal diameter of less than 33 mm is established by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3).
2.9. The ends of the pipes must be cut at right angles and cleared of burrs. The formation of a chamfer is allowed. The cutting angle for pipes with a diameter of up to 219 mm should not exceed 1 mm, and for pipes with a diameter of 219 mm or more - 1.5 mm. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, pipes are made cut in the mill line.
2.10. At the request of the consumer, the ends of pipes with a wall thickness of 5 mm or more should be chamfered at an angle of 25-30° to the end of the pipe and an end ring with a width of 1.8 mm ± 0.8 mm should be left. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the bevel angle and width of the end ring can be changed.
2.11. The pipes must withstand the test hydraulic pressure. Depending on the test pressure, pipes are divided into two types:
I - pipes with a diameter of up to 102 mm - test pressure 6.0 MPa (60 kgf/cm2) and pipes with a diameter of 102 mm and more - test pressure 3.0 MPa (30 kgf/cm2);
II - pipes of groups A and B, supplied at the request of the consumer with test hydraulic pressure calculated according to GOST 3845-75, with a permissible stress equal to 90% of the standard yield strength for pipes made of this steel grade, but not exceeding 20 MPa (200 kgf /cm2).
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, Amendment No. 5).
2.12. Heat-treated pipes made of steel grades St3sp, St3ps (categories 3-5), 10, 15 and 20 with a wall thickness of at least 6 mm must withstand the impact bending test of the base metal. In this case, the standards of impact strength must correspond to those specified in.
The impact bending test of the base metal of heat-treated pipes made of steel grade 22ГУ is carried out at the request of the consumer, the standards of impact strength are established by agreement of the parties.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, Amendment No. 4, Amendment No. 5).
2.13. Heat-treated pipes with a diameter of up to 152 mm inclusive, hot-reduced pipes without heat treatment with a diameter of more than 20 to 152 mm inclusive and a wall thickness of 0.06 Dn or less, as well as pipes with heat treatment of the welded joint must withstand the flattening test.
Flattening of heat-treated pipes should be carried out to the distance between the flattening planes H, mm, calculated by the formula
Where A- the coefficient for pipes made of steel grades 08Yu, 08kp, 8ps, 08, 10kp, St2kp is 0.09, and for pipes made of other steel grades it is 0.08;
S - nominal wall thickness, mm;
Dn - nominal outer diameter of the pipe, mm.
Flattening of pipes without heat treatment should be carried out to a distance equal to 2/3 Dn. Flattening of pipes with heat treatment of the welded joint should be carried out to a distance equal to 1/2 Dn.
At the request of the consumer, flattening of heat-treated pipes with a diameter of over 152 to 530 mm should be carried out to a distance equal to 2/3 Dn.
(Changed version of Amendment No. 1, Amendment No. 3, Amendment No. 4, Amendment No. 5).
2.14. Pipes with a diameter of up to 108 mm must withstand the expansion test.
Pipes without heat treatment with a diameter of up to 20 mm, as well as with a diameter of 20-60 mm with a wall thickness of more than 0.06 DN, are not tested for expansion.
Increasing the outer diameter of heat-treated ones. pipes during distribution must comply with the standards specified in.
The increase in the outer diameter of pipes without heat treatment during distribution should be at least 6%.
At the request of the consumer, the increase in the outer diameter when distributing heat-treated pipes with a wall thickness of up to 4 mm from steel grades 10kp, St2kp should be at least 12%.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3, 4).
2.15. At the request of the consumer, pipes must withstand the tests provided for in paragraphs. -
The tensile strength of a welded joint of pipes with a diameter of 219 to 530 mm, which has undergone heat treatment throughout the entire volume of the pipe or heat treatment of the welded joint, must comply with the standards specified in. The tensile strength of a welded joint of pipes with a diameter of 50 to 203 mm, which has undergone heat treatment throughout the entire volume of the pipe or heat treatment of the welded joint, must be at least 0.9 of the standards specified in.
The tensile strength of a welded joint of pipes without heat treatment with a diameter of 50 mm or more must comply with the standards specified in table. And .
2.19. Pipes must be sealed.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
3. ACCEPTANCE RULES
3.1. Pipes are accepted in batches. The batch must consist of pipes of the same size, one steel grade, one type of heat treatment and one manufacturing group, accompanied by one quality document, according to GOST 10692-80
with the addition of the chemical composition of the steel in accordance with the document on the quality of the manufacturer of the workpiece.
The number of pipes in a batch should be no more than, pcs.:
1000 - with a diameter of up to 30 mm;
600 - with a diameter of St. 30 to 76 mm;
400 - with a diameter of St. 76 to 152 mm;
200 - with a diameter of St. 152 mm.
3.2. In case of disagreement in assessing the quality of the chemical composition, at least one pipe from the batch is selected for testing.
3.3. Each pipe is subjected to control of the dimensions and quality of the pipe surface. It is allowed to control dimensions and surfaces selectively on each batch with a one-stage normal level of control in accordance with the requirements of GOST 18242-72. Control plans are established by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
3.3a. Welded seams of pipes of groups A, B and C must be subjected to 100% testing using non-destructive methods.
When carrying out non-destructive testing along the perimeter of the entire pipe, hydraulic testing of Type I pipes is permitted not to be carried out.
It is allowed, instead of non-destructive testing of type I pipe welds, to test each pipe with increased hydraulic pressure, calculated in accordance with the requirements of GOST 3845-75 at an allowable stress equal to 85% of the yield strength for pipes with a diameter of 273 mm or more and 75% of the yield strength for pipes with a diameter of less than 273 mm, but not exceeding 12 MPa (120 kgf/cm2).
Group D pipes must be subjected to hydraulic pressure testing or weld inspection using non-destructive methods.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 3). (Changed edition, Amendment No. 5). (Amendment,).
3.4. To check the height of the internal flash, 2% of the pipes from the batch are selected.
3.5. To test for flattening, expansion, beading, bending, impact strength, the tendency of the base metal of pipes to mechanical aging, tensile strength of the base metal and weld, two pipes are selected from the batch.
The yield strength of the base metal of pipes is determined at the request of the consumer.
At the request of the consumer, impact strength is not determined.
Pipes subjected to the flattening test are not subjected to the expansion test.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
3.6. If unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one of the indicators, repeated tests are carried out on a double number of pipes selected from the same batch.
The results of repeated tests apply to the entire batch.
3.7. The welding places of pipes of groups A, B, C must be checked by non-destructive methods, and the repaired pipes must be tested with hydraulic pressure in accordance with the requirements of clause 3.3a of this standard.
Places where seams are welded in pipes of group D must be tested using non-destructive methods, or pipes after repair must be tested with hydraulic pressure.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 1, Amended edition, Amendment No. 5).
4. TEST METHODS
4.1. For quality control, one sample is cut from each selected pipe for each type of test, and for impact strength testing, three samples are cut for each test temperature.
4.2. The chemical composition of steel is determined according to GOST 22536.0 -87; GOST 22536.1 -88; GOST 22536.2 -87; GOST 22536.3 -88; GOST 22536.4 -88; GOST 22536.5 -87; GOST 22536.6 -88 GOST 12344-88; GOST 12345-88; GOST 12346-78; GOST 12347-77, GOST 12348-78; GOST 12349-83; GOST 12350-78; GOST 12351 -81; GOST 12352-81; GOST 12353-78; GOST 12354-81. Samples to determine the chemical composition are taken according to GOST 7565-81.
4.3. Inspection of the pipe surface is carried out visually. The depth of defects is checked by filing or another method.
It is allowed to control the surface and dimensions of pipes using non-destructive methods according to technical documentation.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
4.4. Pipes measure:
length - tape measure according to GOST 7502-89.
outer diameter and ovality - with an adjustable measuring clamp according to GOST 2216-84 or a caliper according to GOST 166-89 or a micrometer according to GOST 6507-89;;
internal diameter - with a plug in accordance with GOST 14810-69, or with a caliber in accordance with GOST 2015-84, or by subtracting two wall thicknesses from the outer diameter;
curvature - with a straight edge according to GOST 8026-92 and a feeler gauge;
wall thickness, wall thickness and height of the internal burr - with a micrometer according to GOST 6507-90 or a wall gauge according to GOST 11358-89;
displacement of the edges - using a template according to technical documentation or a micrometer according to GOST 6507-90 or a depth gauge according to GOST 162-90;
The cutting angle is ensured by the design of the equipment for processing pipe ends, the bevel angle is ensured by a goniometer in accordance with GOST 5378-88. In case of disagreement in quality assessment, the cut angle is checked with a charcoal cutter and a probe;
end ring at the ends of the pipes - a ruler in accordance with GOST 427 -75;
depth of surface defects - using a depth gauge according to GOST 162-90. The outer diameter of the pipe is measured at a distance of at least 15 mm from the end of the pipe for pipes with a ratio of the outer diameter to the wall thickness D H/ S H equal to 35 or less; at a distance of at least 2/3 DH - for pipes with a ratio D H/ S H over 35 to 75; at a distance of at least DH - for pipes with ratio D H/ S H over 75.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3).
4.5. The impact bending test is carried out on longitudinal samples of type 3 according to GOST 9454-78, cut from a section of pipe located at an angle of about 90° to the weld.
Impact strength is determined as the arithmetic mean value based on the test results of three samples. On one of the samples, a decrease in impact strength by 9.8·104 J/m2 (1 kgf·m/cm2) is allowed.
The temperature for impact bending testing of pipes made of steel grades 08, 10, 15 and 20 is selected by the consumer.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
4.6. The tendency of the base metal of pipes to mechanical aging is determined according to GOST 7268-82. It is allowed to edit samples with a static load.
INTERSTATE STANDARD
ELECTRIC WELDED STEEL PIPES
TECHNICAL CONDITIONS
Official publication
Standardinform
UDC 669.14-462.2:621.791.7:006.354
Group B62
INTERSTATE STANDARD
ELECTRIC WELDED STEEL PIPES
Specifications
Electrically welded steel tubes. Specifications
MKS 23.040.10 OKP 13 7300 13 8100 13 8300
Date of introduction 01/01/82
This standard applies to straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes with a diameter from 10 to 530 mm made of carbon and low-alloy steel, used for pipelines and structures for various purposes.
The standard does not apply to steel pipes used for the manufacture of thermal electric heaters.
1. ASSORTMENT
1.1. The dimensions and maximum deviations of pipes must comply with GOST 10704.
2. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
2.1. Electric-welded steel pipes are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard and according to technical regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
2.2. Depending on the quality indicators, pipes are manufactured into the following groups:
A - with standardization of mechanical properties of calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades St1, St2, StZ, St4 according to GOST 380 (category 4 according to GOST 16523, category 1 according to GOST 14637);
B - with standardization of the chemical composition from calm, semi-calm and boiling steel grades St1, St2, StZ, St4 according to GOST 380 and GOST 14637, from calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades 08, 10, 15 and 20 according to GOST 1050, from steel grade 08Yu according to GOST 9045, from low-alloy steel grade 22GYu with the chemical composition given in table. 1a (pipes with a diameter from 140 to 426 mm);
B - with standardization of mechanical properties and chemical composition from calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades St1, St2, StZ, St4 according to GOST 380 (category 4 according to GOST 16523 and categories 2-5 according to GOST 14637), from calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades 08, 10, 15, 20 according to GOST 1050, from steel 08Yu according to GOST 9045, from low-alloy steel grade 22GYu with the chemical composition given in table. 1a (pipes with a diameter from 140 to 426 mm);
D - with normalization of test hydraulic pressure.
2.3. Pipes are manufactured by heat treatment (throughout the entire volume of the pipe or along the welded joint), hot-reduced and without heat treatment.
The type of heat treatment throughout the entire volume of the pipe is chosen by the manufacturer. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the pipes are thermally treated in a protective atmosphere.
Pipes made from steel grade 22GYU are produced by heat treatment along the welded joint or throughout the entire volume, pipes made from steel grade St1 - without heat treatment.
Official publication
Reproduction is prohibited
Publishing house of standards, 1981 5) STANDARDINFORM, 2005 5) STANDARDINFORM, 2008
Table 1a
2.4. The mechanical properties of the base metal of heat-treated and hot-reduced carbon steel pipes must comply with the standards specified in Table. 1. The mechanical properties of heat-treated pipes made of steel grade 22ГУ are established by agreement of the parties.
Table 1
|
steel grade |
steel grade |
Tensile strength a b, N/mm 2 (kgf/mm 2) |
Yield strength o t, N/mm 2 (kgf/mm 2) |
Relative elongation 6 5,% |
|||
|
20kp, StZsp, | |||||||
|
08, 08ps, Yukp |
StZps, StZkp | ||||||
|
10, Jups, 15kp, | |||||||
|
St2sp, St2ps, |
St4sp, St4ps, | ||||||
Note. At the request of the consumer, pipes with a wall thickness of 4 mm or more from steel grades StZps, 15, 15ps are manufactured with a yield strength of 235 N/mm 2 (24 kgf/mm 2), a relative elongation of 23%; from steel grades St4sp, 20, 20ps - with a yield strength of 255 N/mm 2 (26 kgf/mm 2), relative elongation of 22%.
table 2
|
Temporary tensile strength about in, N/mm 2, (kgf/mm 2), with outer diameter of pipes D, mm |
Yield strength o t, N/mm 2, (kgf/mm 2) |
Relative elongation 6 5, outer diameter of pipes D, |
%>, at mm |
||||
|
steel grade |
from 10 to 60 with wall thickness |
St. 60 to 152 |
|||||
|
St. 19 to 60 |
St. 60 to 152 |
more than 0.06 D |
0.06 D or less |
||||
|
St1ps, St1kp | |||||||
|
Yukp, St2kp | |||||||
|
Yups, St2ps | |||||||
|
St4kp, St4ps | |||||||
Note. At the request of the consumer, for pipes of all grades of steel with a diameter from 10 to 60 mm, the relative elongation increases by 3% compared to the standards given in table. 2.
Table 3
|
steel grade |
Thickness, walls, mm |
Tensile strength a b, N/mm 2 (kgf/mm 2) |
Yield strength with t, N/mm 2 (kgf/mm 2) |
Relative elongation 6 5,%, with pipe diameter D, mm |
||
|
St. 152 to 244.4 |
St. 244.5 to 377 |
St. 377 to 530 |
||||
|
08, 08ps, 08kp | ||||||
|
YuDOps, Yukp, St2kp | ||||||
|
St2sp, St2ps | ||||||
|
15, 15ps, 15kp, 20, 20ps, 20kp | ||||||
|
StZps, StZps, StZkp | ||||||
|
St4ps, St4ps, St4kp | ||||||
|
All thicknesses | ||||||
2.5. The mechanical properties of the base metal of pipes with a diameter of 10 to 152 mm inclusive without heat treatment and with heat treatment of the welded joint must comply with the standards specified in Table. 2. The mechanical properties of the base metal of pipes with a diameter of over 152 to 530 mm inclusive without heat treatment and with heat treatment of the welded joint must comply with the standards specified in table. 3.
2.6. Cracks, spots, dents, flaws and risks are not allowed on the surface of the pipes.
Ripples, nicks, dents, small scratches, a layer of scale and traces of stripping are allowed if
provided that they do not take the wall thickness and pipe diameter beyond the maximum deviations. Edge displacement up to 10% of the nominal wall thickness is allowed.
The surface of pipes heat-treated in a protective atmosphere should be free of scale. The presence of an oxide film is allowed.
Lack of penetration in seams must be welded, and the welding area must be cleaned. By agreement with the consumer, on pipes with a diameter of 159 mm or more, in places where seams are repaired by welding, a displacement of the welded edges is allowed by no more than 20% of the nominal wall thickness and the height of the reinforcement bead is not more than 2.5 mm.
Repairs by welding the base metal of pipes are not permitted.
In the case of repair by welding of pipes that have undergone heat treatment, they are subjected to repeated heat treatment (respectively throughout the entire volume or along the welded joint).
2.7. On pipes with a diameter of 57 mm or more, one transverse seam is allowed.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, one transverse seam is allowed on pipes with a diameter of less than 57 mm.
2.2-2.7. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
2.8. External beads on pipes must be removed. At the deburring site, the wall may be thinned by 0.1 mm above the minus tolerance.
At the request of the consumer, on pipes with an internal diameter of 33 mm or more, the internal burr must be partially removed or flattened, while the height of the burr or its traces should not exceed 0.35 mm - with a wall thickness of less than 2 mm; 0.4 mm - with a wall thickness of 2 to 3 mm; 0.5 mm - for wall thickness over 3 mm.
The height of the internal flash or its traces for pipes with an internal diameter of less than 33 mm is established by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
2.9. The ends of the pipes must be cut at right angles and cleared of burrs. Admission
chamfer formation is repented. The cutting angle for pipes with a diameter of up to 219 mm should not exceed 1 mm, and for pipes with a diameter of 219 mm or more - 1.5 mm. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, pipes are made cut in the mill line.
2.10. At the consumer’s request, the ends of pipes with a wall thickness of 5 mm or more should be chamfered at an angle of 25°-30° to the end of the pipe and an end ring with a width of (1.8 ± 0.8) mm should be left. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the bevel angle and width of the end ring can be changed.
2.11. The pipes must withstand the test hydraulic pressure. Depending on the test pressure, pipes are divided into two types:
I - pipes with a diameter of up to 102 mm - test pressure 6.0 MPa (60 kgf/cm 2) and pipes with a diameter of 102 mm and more - test pressure 3.0 MPa (30 kgf/cm 2);
II - pipes of groups A and B, supplied at the request of the consumer with test hydraulic pressure calculated according to GOST 3845, with a permissible stress equal to 90% of the standard yield strength for pipes made of this steel grade, but not exceeding 20 MPa (200 kgf/cm 2).
2.12. Heat-treated pipes made of steel grades StZsp, StZps (categories 3-5), 10, 15 and 20 with a wall thickness of at least 6 mm must withstand the impact bending test of the base metal. In this case, the standards of impact strength must correspond to those indicated in the table. 4.
Table 4
The impact bending test of the base metal of heat-treated pipes made of steel grade 22ГУ is carried out at the request of the consumer, the standards of impact strength are established by agreement of the parties.
2.13. Heat-treated pipes with a diameter of up to 152 mm inclusive, hot-reduced pipes without heat treatment with a diameter of more than 20 to 152 mm inclusive and a wall thickness of 0.06 Z) H or less, as well as pipes with heat treatment of the welded joint must withstand the flattening test.
Flattening of heat-treated pipes should be carried out to the distance between the flattening planes H, mm, calculated by the formula
(1 + a) ■ s s
where a - coefficient for pipes made of steel grades 08Yu, 08kp, 8ps, 08, Yukp, St2kp is equal to 0.09, and for pipes made of other steel grades it is equal to 0.08; s - nominal wall thickness, mm;
Z) H - nominal outer diameter of the pipe, mm.
Flattening of pipes without heat treatment should be carried out to a distance equal to 2/3 D H. Flattening of pipes with heat treatment of the welded joint should be carried out to a distance equal to 1/2 Z) H.
At the request of the consumer, flattening of heat-treated pipes with a diameter of over 152 to 530 mm should be carried out to a distance equal to 2/3 Z) H.
2.11-2.13. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
2.14. Pipes with a diameter of up to 108 mm must withstand the expansion test.
Pipes without heat treatment with a diameter of up to 20 mm, as well as with a diameter of 20-60 mm with a wall thickness of more than 0.06 Z) H are not tested for expansion.
The increase in the outer diameter of heat-treated pipes during distribution must correspond to the standards specified in table. 5.
Table 5
The increase in the outer diameter of pipes without heat treatment during distribution should be at least 6%.
At the request of the consumer, the increase in the outer diameter when distributing heat-treated pipes with a wall thickness of up to 4 mm made of steel grades Yukp, St2kp must be at least 12%.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3, 4).
2.15. At the request of the consumer, pipes must withstand the tests provided for in paragraphs. 2.16-2.18.
2.16. Heat-treated pipes with a diameter of up to 530 mm inclusive must withstand the bend test. The bend radius for pipes with a diameter of up to 60 mm must be at least 2.5 A” for the base metal of pipes with a diameter of over 60 to 530 mm - in accordance with GOST 3728. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the bend radius can be reduced.
2.17. Heat-treated pipes with a diameter from 30 to 159 mm with a D/s ratio equal to
12.5 and more must withstand the flange test. The width of the bent side, measured from the inner surface, must be at least 12% of the internal diameter of the pipe and not less
1.5 wall thickness.
The flange angle should be:
90° - for pipes made of steel grades 08, 10, 15, St2;
60° - for pipes made of steel grades 20, StZ, St4.
2.18. Pipes with a diameter of 50 mm or more of groups A and B must withstand the tensile test of the welded joint.
The tensile strength of a welded joint of pipes with a diameter of 219 to 530 mm, which has undergone heat treatment throughout the entire volume of the pipe or heat treatment of the welded joint, must comply with the standards specified in Table. 1. The tensile strength of a welded joint of pipes with a diameter of 50 to 203 mm, which has undergone heat treatment throughout the entire volume of the pipe or heat treatment of the welded joint, must be at least 0.9 of the standards specified in table. 1.
The tensile strength of a welded joint of pipes without heat treatment with a diameter of 50 mm or more must comply with the standards specified in table. 2 and 3.
(Changed edition, Amendment 1.3).
2.19. Pipes must be sealed.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
3. ACCEPTANCE RULES
3.1. Pipes are accepted in batches. The batch must consist of pipes of the same size, one steel grade, one type of heat treatment and one manufacturing group, accompanied by one quality document, in accordance with GOST 10692 with the addition of the chemical composition of the steel in accordance with the quality document of the manufacturer of the workpiece.
The number of pipes in a batch should be no more than, pcs.:
1000 - with a diameter of up to 30 mm;
600 - with a diameter of St. 30 to 76 mm;
400 - with a diameter of St. 76 to 152 mm;
200 - with a diameter of St. 152 mm.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
3.2. In case of disagreement in assessing the quality of the chemical composition, at least one pipe from the batch is selected for testing.
3.3. Each pipe is subjected to control of the dimensions and quality of the pipe surface. It is allowed to control the dimensions and surface selectively on each batch with a single-stage
normal level of control in accordance with the requirements of GOST 18242*. Control plans are established by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
**3.3a. Welded seams of pipes of groups A, B and C must be subjected to 100% testing using non-destructive methods.
When carrying out non-destructive testing along the perimeter of the entire pipe, hydraulic testing of Type I pipes is permitted not to be carried out.
It is allowed, instead of non-destructive testing of type I pipe welds, to test each pipe with increased hydraulic pressure, calculated in accordance with the requirements of GOST 3845 at an allowable stress equal to 85% of the yield strength for pipes with a diameter of 273 mm or more and 75% of the yield strength for pipes with a diameter of less than 273 mm, but not exceeding 12 MPa (120 kgf/cm2).
Group D pipes must be subjected to hydraulic pressure testing or weld inspection using non-destructive methods.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 5, Amendment).
When monitoring the quality of a seam using non-destructive methods, additional control with hydraulic pressure is carried out on 15% of the pipes from the batch.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, hydraulic pressure testing of pipes is not carried out.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 3).
3.4. To check the height of the internal flash, 2% of the pipes from the batch are selected.
3.5. To test for flattening, expansion, beading, bending, impact strength, the tendency of the base metal of pipes to mechanical aging, tensile strength of the base metal and weld, two pipes are selected from the batch.
The yield strength of the base metal of pipes is determined at the request of the consumer.
At the request of the consumer, impact strength is not determined.
Pipes subjected to the flattening test are not subjected to the expansion test.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
3.6. If unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one of the indicators, repeated tests are carried out on a double number of pipes selected from the same batch.
The results of repeated tests apply to the entire batch.
3.7. The welding places of pipes of groups A, B, C must be checked by non-destructive methods, and the repaired pipes must be tested with hydraulic pressure in accordance with the requirements and. 3.3a of this standard.
Places where seams are welded in pipes of group D must be tested using non-destructive methods, or pipes after repair must be tested with hydraulic pressure.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
4. TEST METHODS
4.1. For quality control, one sample is cut from each selected pipe for each type of test, and for impact strength testing, three samples are cut for each test temperature.
4.2. The chemical composition of steel is determined according to GOST 22536.0 - GOST 22536.6, GOST 12344 - GOST 12354. Samples to determine the chemical composition are taken according to GOST 7565.
4.3. Inspection of the pipe surface is carried out visually. The depth of defects is checked by filing or another method.
It is allowed to control the surface and size of pipes using non-destructive methods according to technical documentation.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
4.4. Pipes measure:
length - tape measure according to GOST 7502;
outer diameter and ovality - with an adjustable measuring clamp according to GOST 2216 or a caliper according to GOST 166, or a micrometer according to GOST 6507;
* GOST R 50779.71-99** is in force on the territory of the Russian Federation.
internal diameter - with a plug in accordance with GOST 14810 or with a caliber in accordance with GOST 2015, or by subtracting two wall thicknesses from the outer diameter;
curvature - with a straight edge according to GOST 8026 and a feeler gauge;
wall thickness, wall thickness and internal burr height - with a micrometer according to GOST 6507 or a wall gauge according to GOST 11358;
displacement of the edges - using a template according to technical documentation or a micrometer according to GOST 6507, or a depth gauge according to GOST 162;
cutting bevel - this parameter is ensured by the design of the equipment for processing ends
chamfer bevel angle - with a goniometer according to GOST 5378. In case of disagreement in quality assessment, the cut angle is checked with a square and a feeler gauge;
the end ring at the ends of the pipes - with a ruler in accordance with GOST 427;
depth of surface defects - depth gauge according to GOST 162. The outer diameter of the pipe is measured at a distance of at least 15 mm from the end of the pipe for pipes with a ratio of outer diameter to wall thickness Z) H /s H equal to 35 or less; at a distance of at least 2/з Ai - for pipes with a ratio D u /s u over 35 to 75; at a distance of at least D, - for pipes with a ratio D H / s H over 75.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3).
4.5. The impact bending test is carried out on longitudinal samples of type 3 according to GOST 9454, cut from a section of pipe located at an angle of about 90 ° to the weld.
Impact strength is determined as the arithmetic mean value based on the test results of three samples. On one of the samples, a decrease in impact strength by 9.8 10 4 J/m 2 (1 kgf m/cm 2) is allowed.
The temperature for impact bending testing of pipes made of steel grades 08, 10, 15 and 20 is selected by the consumer.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
4.6. The tendency of the base metal of pipes to mechanical aging is determined according to GOST 7268. It is allowed to straighten samples under a static load.
4.7. The tensile test is carried out according to GOST 10006 on a longitudinal (in the form of a strip or a piece of pipe) proportional short sample.
When testing on segment-section samples, the latter is cut out from a section located at an angle of about 90° to the weld and is not straightened in the calculation part.
Instead of tensile testing, it is allowed to monitor the tensile strength, yield strength and relative elongation of pipes using non-destructive methods.
If disagreements arise, pipe testing is carried out in accordance with GOST 10006.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
4.8. The flattening test is carried out according to GOST 8695.
4.9. The expansion test is carried out according to GOST 8694 on a mandrel with a taper of 30 °. It is allowed to use mandrels with a taper of 1:10 and remove burrs in the distribution area.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
4.10. The bend test is carried out according to GOST 3728. Pipes with a diameter of 114 mm are tested on cut longitudinal strips 12 mm wide.
4.11. The flanging test is carried out in accordance with GOST 8693. In the flanging area, deburring is allowed.
4.12. Determination of the tensile strength of a welded joint of pipes with a diameter of 50-530 mm is carried out on ring samples according to technical documentation.
On pipes with a diameter of 219 mm or more, it is allowed to carry out testing in accordance with GOST 6996 on type XII samples with the welded joint reinforcement removed, cut perpendicular to the pipe axis, using a static load when straightening the samples.
4.13. Hydraulic testing of pipes is carried out in accordance with GOST 3845 with a pressure exposure of 5 s.
4.14. Inspection of the weld is carried out using non-destructive methods (ultrasonic, eddy current, magnetic or x-ray equivalent methods) according to technical documentation.
5. LABELING, PACKAGING, TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
5.1. Labeling, packaging, transportation and storage - in accordance with GOST 10692.
INFORMATION DATA
1. DEVELOPED AND INTRODUCED by the USSR Ministry of Ferrous Metallurgy
2. APPROVED AND ENTERED INTO EFFECT by Resolution of the USSR State Committee on Standards dated December 25, 1980 No. 5970
Change No. 5 was adopted by the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (Minutes No. 13 of May 28, 1998)
Registered by the Technical Secretariat of the IGU No. 3166 The following voted for the adoption of the change:
|
State name |
Name of the national standardization body |
|
The Republic of Azerbaijan |
Azgosstandart |
|
Republic of Armenia |
Armgosstandard |
|
Republic of Belarus |
State Standard of the Republic of Belarus |
|
The Republic of Kazakhstan |
Gosstandart of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
|
Republic of Kyrgyzstan |
Kyrgyzstandard |
|
The Republic of Moldova |
Moldovastandard |
|
Russian Federation |
Gosstandart of Russia |
|
The Republic of Tajikistan |
T adzhikgosstandart |
|
Turkmenistan |
Main State Inspectorate "Turkmenstandartlary" |
|
State Standard of Ukraine |
3. INSTEAD GOST 10705-63
4. REFERENCE REGULATIVE AND TECHNICAL DOCUMENTS
|
Item number |
Item number |
||
|
GOST 11358-89 | |||
|
GOST 12344-2003 | |||
|
GOST 380-94* |
GOST 12345-2001 | ||
|
GOST 12346-78 | |||
|
GOST 1050-88 |
GOST 12347-77 | ||
|
GOST 2015-84 |
GOST 12348-78 | ||
|
GOST 2216-84 |
GOST 12349-83 | ||
|
GOST 3728-78 |
GOST 12350-78 | ||
|
GOST 3845-75 |
2.11; 3.3a; 4.13 |
GOST 12351-2003 | |
|
GOST 5378-88 |
GOST 12352-81 | ||
|
GOST 6507-90 |
GOST 12353-78 | ||
|
GOST 6996-66 |
GOST 12354-81 | ||
|
GOST 7268-82 |
GOST 14637-89 | ||
|
GOST 7502-98 |
GOST 14810-69 | ||
|
GOST 7565-81 |
GOST 16523-97 | ||
|
GOST 8026-92 |
GOST 18242-72* | ||
|
GOST 8693-80 |
GOST 22536.0-87 | ||
|
GOST 8694-75 |
GOST 22536.1-88 | ||
|
GOST 8695-75 |
GOST 22536.2-87 | ||
|
GOST 9045-93 |
GOST 22536.3-88 | ||
|
GOST 9454-78 |
GOST 22536.4-88 | ||
|
GOST 10006-80 |
GOST 22536.5-87 | ||
|
GOST 10692-80 |
GOST 22536.6-88 | ||
|
GOST 10704-91 |
5. The validity period was lifted by Gosstandart Decree No. 1247 dated July 12, 1991
6. EDITION (November 2005) with Amendments No. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, approved in December 1986, December 1987, June 1989, July 1991, April 1999 (IUS 2-87, 3-88, 10-89, 10-91, 7-99); Amendment (NUS 5-2005)
Reprint (as of March 2008).
See notes from FSUE “STANDARTINFORM” (p. 9).
NOTES FSUE "STANDARTINFORM"
1 Specified in the section “Information data” to GOST 10705-80:
GOST 380-94 was replaced by GOST 380-2005;
GOST 18242-72 was replaced by GOST R ISO 2859-1-2007.
2 An amendment was published in the information index “National Standards” No. 5-2005
to GOST 10705-80 Electric-welded steel pipes. Specifications [see Edition (June 2001) with Amendments No. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and the collection “Metal pipes and connecting parts for them. Part 3. Welded pipes. Profile pipes" (Edition 2001)]
Editor R.G. Goverdovskaya Technical editor V.N. Prusakova Corrector V.I. Barentseva Computer layout I.A. Naleykina
Signed for publication on April 29, 2008. Format 60 x 84 1/s. Offset paper. Times typeface. Offset printing. Uel. pech.l. 1.40. Academician-ed.l. 1.10. Circulation 97 copies. Zach. 428.
FSUE "STANDARTINFORM", 123995 Moscow, Granatny per., 4.
Typed into FSUE "STANDARTINFORM" on a PC
Printed in the branch of FSUE "STANDARTINFORM" - type. "Moscow Printer", 105062 Moscow, Lyalin lane, 6.
Electrically welded steel tubes. Specifications
GOST 10705-80
OKP 13 7300, 13 8100, 13 8300
Date of introduction 01/01/82
This standard applies to straight-seam electric-welded steel pipes with a diameter from 10 to 530 mm made of carbon and low-alloy steel, used for pipelines and structures for various purposes.
The standard does not apply to steel pipes used for the manufacture of thermal electric heaters.
1. ASSORTMENT
1.1. The dimensions and maximum deviations of pipes must comply with GOST 10704.
2. TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
2.1. Electric-welded steel pipes are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard and according to technical regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
2.2. Depending on the quality indicators, pipes are manufactured into the following groups:
A - with standardization of mechanical properties of calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades St1, St2, St3, St4 according to GOST 380 (category 4 according to GOST 16523, category 1 according to GOST 14637);
B - with standardization of the chemical composition from calm, semi-calm and boiling steel grades St1, St2, St3, St4 according to GOST 380 and GOST 14637, from calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades 08, 10, 15 and 20 according to GOST 1050, from steel grade 08Yu according to GOST 9045, from low-alloy steel grade 22ГУ with the chemical composition given in table. 1a (pipes with a diameter from 140 to 426 mm);
B - with standardization of mechanical properties and chemical composition from calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades St1, St2, St3, St4 according to GOST 380 (category 4 according to GOST 16523 and categories 2-5 according to GOST 14637), from calm, semi-quiet and boiling steel grades 08, 10, 15.20 according to GOST 1050, from steel grade 08Yu according to GOST 9045, from low-alloy steel grade 22ГУ with the chemical composition given in table. 1a (pipes with a diameter from 140 to 426 mm);
D - with normalization of test hydraulic pressure.
2.3. Pipes are manufactured by heat treatment (throughout the entire volume of the pipe or along the welded joint), hot-reduced and without heat treatment.
The type of heat treatment throughout the entire volume of the pipe is chosen by the manufacturer. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the pipes are thermally treated in a protective atmosphere.
Pipes made from steel grade 22GYU are produced by heat treatment along the welded joint or throughout the entire volume, pipes made from steel grade St1 - without heat treatment.
Table 1a
2.4. The mechanical properties of the base metal of heat-treated and hot-reduced carbon steel pipes must comply with the standards specified in Table. 1. The mechanical properties of heat-treated pipes made of steel grade 22ГУ are established by agreement of the parties.
Table 1

Note: At the request of the consumer, pipes with a wall thickness of 4 mm or more from steel grades StZsp, 15, 15ps are manufactured with a yield strength of 235 N/mm 2 (24 kgf/mm 2), relative elongation 23 %; from steel grades St4sp, 20, 20ps - with a yield strength of 255 N/mm 2 (26 kgf/mm 2), relative elongation of 22%.
Table 2

Note: At the request of the consumer, for pipes of all grades of steel with a diameter from 10 to 60 mm, the relative elongation increases by 3% compared to the standards given in table. 2.
Table 3

2.5. The mechanical properties of the base metal of pipes with a diameter of 10 to 152 mm inclusive without heat treatment and with heat treatment of the welded joint must comply with the standards specified in table. 2. The mechanical properties of the base metal of pipes with a diameter of over 152 to 530 mm inclusive without heat treatment and with heat treatment of the welded joint must comply with the standards specified in table. 3.
2.6. Cracks, spots, dents, flaws and risks are not allowed on the surface of the pipes.
Ripples, nicks, dents, small scratches, a layer of scale and traces of stripping are allowed provided that they do not take the wall thickness and diameter of the pipe beyond the maximum deviations. Edge displacement up to 10% of the nominal wall thickness is allowed.
The surface of pipes heat-treated in a protective atmosphere should be free of scale. The presence of an oxide film is allowed.
Lack of penetration in seams must be welded, and the welding area must be cleaned. By agreement with the consumer, on pipes with a diameter of 159 mm or more, in places where seams are repaired by welding, a displacement of the welded edges is allowed by no more than 20% of the nominal wall thickness and the height of the reinforcement bead is not more than 2.5 mm.
Repairs by welding the base metal of pipes are not permitted.
In the case of repair by welding of pipes that have undergone heat treatment, they are subjected to repeated heat treatment (respectively throughout the entire volume or along the welded joint).
2.7. On pipes with a diameter of 57 mm or more, one transverse seam is allowed.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, one transverse seam is allowed on pipes with a diameter of less than 57 mm.
2.2—2.7. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
2.8. External beads on pipes must be removed. At the deburring site, the wall may be thinned by 0.1 mm above the minus tolerance.
At the request of the consumer, on pipes with an internal diameter of 33 mm or more, the internal burr must be partially removed or flattened, while the height of the burr or its traces should not exceed 0.35 mm - with a wall thickness of less than 2 mm; 0.4 mm - with a wall thickness of 2 to 3 mm; 0.5 mm - with a wall thickness of over 3 mm.
The height of the internal flash or its traces for pipes with an internal diameter of less than 33 mm is established by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
2.9. The ends of the pipes must be cut at right angles and cleared of burrs. The formation of a chamfer is allowed. The cutting angle for pipes with a diameter of up to 219 mm should not exceed 1 mm, and
for pipes with a diameter of 219 mm and more - 1.5 mm. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, pipes are made cut in the mill line.
2.10. At the request of the consumer, the ends of pipes with a wall thickness of 5 mm or more should be chamfered at an angle of 25-30° to the end of the pipe and an end ring with a width of (1.8 +0.8) mm should be left. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the bevel angle and width of the end ring can be changed.
2.11. The pipes must withstand the test hydraulic pressure. Depending on the test pressure, pipes are divided into two types:
I - pipes with a diameter of up to 102 mm - test pressure 6.0 MPa (60 kgf/cm 2) and pipes with a diameter of 102 mm or more - test pressure 3.0 MPa (30 kgf/cm 2);
II - pipes of groups A and B, supplied at the request of the consumer with test hydraulic pressure calculated according to GOST 3845, with a permissible stress equal to 90% of the standard yield strength for pipes made of this steel grade, but not exceeding 20 MPa (200 kgf/cm 2 ).
2.12. Heat-treated pipes made of steel grades St3sp, St3ps (categories 3-5), 10, 15 and 20 with a wall thickness of at least 6 mm must withstand the impact bending test of the base metal. In this case, the standards of impact strength must correspond to those indicated in the table. 4.
Table 4

The impact bending test of the base metal of heat-treated pipes made of steel grade 22ГУ is carried out at the request of the consumer, the standards of impact strength are established by agreement of the parties.
2.13. Heat-treated pipes with a diameter of up to 152 mm inclusive, hot-reduced pipes without heat treatment with a diameter of more than 20 to 152 mm inclusive and a wall thickness of 0.06 D H or less, as well as pipes with heat treatment of the welded joint must withstand the flattening test.
Flattening of heat-treated pipes should be carried out to the distance between the flattening planes H, mm, calculated by the formula

where a is the coefficient for pipes made of steel grades 08Yu, 08kp, 8ps, 08, 10kp, St2kp equal to 0.09, and for pipes made of other steel grades equal to 0.08; s is the nominal wall thickness, mm;
D H - nominal outer diameter of the pipe, mm.
Flattening of pipes without heat treatment should be carried out to a distance equal to 2/3 D H. Flattening of pipes with heat treatment of the welded joint should be carried out at a distance equal to 1/2 D H.
At the request of the consumer, flattening of heat-treated pipes with a diameter of over 152 to 530 mm should be carried out to a distance equal to 2/3 D H.
2.11—2.13. (Changed edition, Rev. No. 5).
2.14. Pipes with a diameter of up to 108 mm must withstand the expansion test.
Pipes without heat treatment with a diameter of up to 20 mm, as well as with a diameter of 20-60 mm with a wall thickness of more than 0.06 D H, are not tested for expansion.
The increase in the outer diameter of heat-treated pipes during distribution must correspond to the standards specified in table. 5.
Table 5
The increase in the outer diameter of pipes without heat treatment during distribution should be at least 6%.
At the request of the consumer, the increase in the outer diameter when distributing heat-treated pipes with a wall thickness of up to 4 mm from steel grades 10kp, St2kp should be at least 12%.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3, 4).
2.15. At the request of the consumer, pipes must withstand the tests provided for in paragraphs. 2.16-2.18.
2.16. Heat-treated pipes with a diameter of up to 530 mm inclusive must withstand the bend test. The bend radius for pipes with a diameter of up to 60 mm must be no less than 2.5 D H, for the base metal of pipes with a diameter of over 60 to 530 mm - in accordance with GOST 3728. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the bend radius can be reduced.
2.17. Heat-treated pipes with a diameter from 30 to 159 mm with a D/s ratio equal to
12.5 and more must withstand the flange test. The width of the bent side, measured from the inner surface, must be at least 12% of the internal diameter of the pipe and not less
1.5 wall thickness.
The flange angle should be:
90° - for pipes made of steel grades 08, 10, 15, St2;
60° - for pipes made of steel grades 20, St3, St4.
2.18. Pipes with a diameter of 50 mm or more of groups A and B must withstand the tensile test of the welded joint.
The tensile strength of the welded joint of pipes with a diameter of 219 to 530 mm, which have undergone heat treatment throughout the entire volume of the pipe or heat treatment of the welded joint, must comply with the standards specified in table. 1. The tensile strength of a welded joint of pipes with a diameter of 50 to 203 mm, which has undergone heat treatment throughout the entire volume of the pipe or heat treatment of the welded joint, must be at least 0.9 of the standards specified in table. 1.
The tensile strength of a welded joint of pipes without heat treatment with a diameter of 50 mm or more must comply with the standards specified in table. 2 and 3.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3).
2.19. Pipes must be sealed.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
3. ACCEPTANCE RULES
3.1. Pipes are accepted in batches. The batch must consist of pipes of the same size, one grade steel, one type of heat treatment and one manufacturing group, accompanied by one quality document, in accordance with GOST 10692 with the addition of the chemical composition of the steel in accordance with the quality document of the manufacturer of the workpiece.
The number of pipes in a batch should be no more than, pcs.:
1000 - with a diameter of up to 30 mm;
600 - with a diameter of St. 30 to 76 mm;
400 - with a diameter of St. 76 to 152 mm;
200 - with a diameter of St. 152 mm.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
3.2. In case of disagreement in assessing the quality of the chemical composition, at least one pipe from the batch is selected for testing.
3.3. Each pipe is subjected to control of the dimensions and quality of the pipe surface. It is allowed to control sizes and surfaces selectively on each batch with a single-stage
normal level of control in accordance with the requirements of GOST 18242.* Control plans are established by agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
3.3a. Welded seams of pipes of groups A, B and C must be subjected to 100% testing using non-destructive methods.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, hydraulic pressure testing of pipes is not carried out.
When carrying out non-destructive testing along the perimeter of the entire pipe, hydraulic testing of Type I pipes is permitted not to be carried out.
It is allowed, instead of non-destructive testing of type I pipe welds, to test each pipe with increased hydraulic pressure, calculated in accordance with the requirements of GOST 3845 at an allowable stress equal to 85% of the yield strength for pipes with a diameter of 273 mm or more and 75% of the yield strength for pipes with a diameter of less than 273 mm, but not exceeding 12 MPa (120 kgf/cm2).
Group D pipes must be subjected to hydraulic pressure testing or weld inspection using non-destructive methods.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
When monitoring the quality of a seam using non-destructive methods, additional control with hydraulic pressure is carried out on 15% of the pipes from the batch.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, hydraulic pressure testing of pipes is not carried out.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 3).
3.4. To check the height of the internal flash, 2% of the pipes from the batch are selected.
3.5. To test for flattening, expansion, beading, bending, impact strength, the tendency of the base metal of pipes to mechanical aging, tensile strength of the base metal and weld, two pipes are selected from the batch.
The yield strength of the base metal of pipes is determined at the request of the consumer.
At the request of the consumer, impact strength is not determined.
Pipes subjected to the flattening test are not subjected to the expansion test.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
3.6. If unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one of the indicators, repeated tests are carried out on a double number of pipes selected from the same batch.
The results of repeated tests apply to the entire batch.
3.7. The welding places of pipes of groups A, B, C must be checked by non-destructive methods, and the repaired pipes must be tested with hydraulic pressure in accordance with the requirements of clause 3.3a of this standard.
Places where seams are welded in pipes of group D must be tested using non-destructive methods, or pipes after repair must be tested with hydraulic pressure.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
4. TEST METHODS
4.1. For quality control, one sample is cut from each selected pipe for each type of test, and for impact strength testing, three samples are cut for each test temperature.
4.2. The chemical composition of steel is determined according to GOST 22536.0 - GOST 22536.6, GOST 12344 - GOST 12354. Samples to determine the chemical composition are taken according to GOST 7565.
4.3. Inspection of the pipe surface is carried out visually. The depth of defects is checked by sawing or another method.
It is allowed to control the surface and size of pipes using non-destructive methods according to technical documentation.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
GOST R 50779.71 - 99 is in force on the territory of the Russian Federation.
4.4. Pipes measure:
length - tape measure according to GOST 7502;
outer diameter and ovality - with an adjustable measuring clamp according to GOST 2216 or a caliper according to GOST 166, or a micrometer according to GOST 6507;
internal diameter - with a plug in accordance with GOST 14810 or with a caliber in accordance with GOST 2015, or by subtracting two wall thicknesses from the outer diameter;
curvature - using a straight edge according to GOST 8026 and a feeler gauge;
wall thickness, thickness difference and internal burr height - with a micrometer according to GOST 6507 or a wall gauge according to GOST 11358;
offset of the edges - using a template according to technical documentation or a micrometer according to GOST 6507, or a depth gauge according to GOST 162;
cutting bevel - this parameter is ensured by the design of the equipment for processing ends
chamfer bevel angle - with a goniometer according to GOST 5378. In case of disagreement in assessing the quality, the bevel of the cut is checked with a square and a feeler gauge;
the end ring at the ends of the pipes - with a ruler in accordance with GOST 427;
the depth of surface defects - with a depth gauge according to GOST 162. The outer diameter of the pipe is measured at a distance of at least 15 mm from the end of the pipe for pipes with a ratio of outer diameter to wall thickness D H / s H equal to 35 or less; at a distance of at least 2/3 D H - for pipes with a D H / s H ratio of over 35 to 75; at a distance of at least D H - for pipes with a ratio D H / s H over 75.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3).
4.5. The impact bending test is carried out on longitudinal samples of type 3 according to GOST 9454, cut from a section of pipe located at an angle of about 90° to the weld.
Impact strength is determined as the arithmetic average of the test results of three samples. On one of the samples, a decrease in impact strength by 9.8-10 4 J/m 2 (1 kgf-m/cm 2) is allowed.
The temperature for impact bending testing of pipes made of steel grades 08, 10, 15 and 20 is selected by the consumer.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
4.6. The tendency of the base metal of pipes to mechanical aging is determined according to GOST 7268. It is allowed to straighten samples under a static load.
4.7. The tensile test is carried out according to GOST 10006 on a longitudinal (in the form of a strip or pipe section) proportional short sample.
When testing on segment-section samples, the latter is cut out from a section located at an angle of about 90° to the weld and is not straightened in the calculation part.
Instead of tensile testing, it is allowed to monitor the tensile strength, yield strength and relative elongation of pipes using non-destructive methods.
If disagreements arise, pipe testing is carried out in accordance with GOST 10006.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
4.8. The flattening test is carried out according to GOST 8695.
4.9. The expansion test is carried out according to GOST 8694 on a mandrel with a taper of 30°. It is allowed to use mandrels with a taper of 1:10 and remove burrs in the distribution area.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
4.10. The bend test is carried out according to GOST 3728. Pipes with a diameter of 114 mm are tested on cut longitudinal strips 12 mm wide.
4.11. The flanging test is carried out in accordance with GOST 8693. In the flanging area, deburring is allowed.
4.12. Determination of the tensile strength of a welded joint of pipes with a diameter of 50-530 mm is carried out on ring samples according to technical documentation.
On pipes with a diameter of 219 mm or more, it is allowed to carry out testing in accordance with GOST 6996 on type XII samples with removed reinforcement of the welded joint, cut perpendicular to the pipe axis, using a static load when straightening the samples.
4.13. Hydraulic testing of pipes is carried out in accordance with GOST 3845 with a pressure exposure of 5 s.
4.14. Inspection of the weld is carried out using non-destructive methods (ultrasonic, eddy current, magnetic or x-ray equivalent methods) according to technical documentation.
5. LABELING, PACKAGING, TRANSPORTATION AND STORAGE
5.1. Labeling, packaging, transportation and storage - in accordance with GOST 10692.
INFORMATION DATA
1. DEVELOPED AND INTRODUCED by the Ministry of Ferrous Metallurgy of the USSRDEVELOPERS
M. M. Bernstein, N. F. Kuzenko
2. APPROVED AND ENTERED INTO EFFECT by Resolution of the USSR State Committee on Standards dated December 25, 1980 No. 5970
Change No. 5 was adopted by the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (Minutes No. 13 of May 28, 1998)
Registered by the Technical Secretariat of the IGU No. 3166

3. INSTEAD GOST 10705-63
4. REFERENCE REGULATIVE AND TECHNICAL DOCUMENTS

5. The validity period was lifted by Gosstandart Decree No. 1247 dated July 12, 1991
6. EDITION with Amendments No. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, approved in December 1986, December 1987, June 1989, July 1991, April 1999 (IuS 2-87, 3- 88, 10-89, 10-91, 7-99)
GOST R 50779.71-99 is in force on the territory of the Russian Federation.