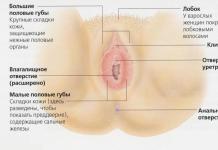
Gunstige Shishas kaufen
Unsere Mitarbeiter werden Sie gerne beim Kauf einer Shisha Online oder telefonisch beraten. Haben Sie sich im Shisha Shop beraten lassen, aber Sie hätten es lieber ein wenig günstiger, dann lohnt sich ein Blick in unserem Auf der suche können Sie sich mit den Schlagworten: "Shisha billig online kaufen" einen Überblick verschaffen, welche Shishas, zu welchen Preisen angeboten werden. Bitte beachten Sie, dass es auch bei günstigen Shishas zu Preisunterschieden kommen kann. Um eine Shisha in einer passenden Preisklasse zu finden, setzen Sie Prioritäten:
Nutzen Sie die Shisha zuhause oder unterwegs?
Für unterwegs: Die Shishas, die Sie bequem unterwegs verwenden können haben eine Göße von ca. 25-45 cm und passen somit in eine Reisetasche. Sie sind perfekt, um sich mit Freunden im zu Park treffen, oder sich einen Tag am Strand zu versüßen. Dazu kommt, dass sie preislich mit €10 – €50 recht günstig und somit für jedermann erschwinglich sind.
Wie oft verwenden Sie die Wasserpfeife?
Wenn sie öfter eine Shisha verwenden möchten empfiehlt es sich, darauf zu achten das Die Shisha leicht zu reinigen ist, es gibt auch extra Zubehör die das Reinigen erleichtert.
Ist Ihnen die Qualität wichtiger, oder der Preis?
Gute Shishas die eine Ordentliche Größe und Volumen aufweisen und Qualitativ hochwertig Verarbeitet sind haben einen stolzen Preis. Dagegen Stehen billige Asia Importe die aus Minderwertigen Materialien Gefertigt werden. Ein Fachhandler kann sie diesbezüglich gut beraten.
Wie viele Personen sollen mitrauchen?
Wenn Regelmäßig mehrere Personen gleichzeitig die Wasserpfeife Rauchen möchten, sollte man darüber nachdenken, sich Wasserpfeifen mit mehreren Schläuchen zu kaufen. Es schadet auch nicht, wenn die Shisha ein gewisses Volumen bietet. Diese Fragen gilt es zu beantworten, bevor Sie sich erkundigen welche Shisha Sie kaufen können.
Aber welche Arten von günstigen Shishas können sie kaufen?
Es gibt Reiseshishas, die Sie bequem unterwegs nutzen können Der Klassiker sind die Shishas, die Sie stationär, z.B. zuhause verwenden Die E-Shisha wird mit Liquid gefüllt, eng verwandt mit E-Zigaretten. Ideal fur Unterwegs. Für Anfänger Empfiehlt sich eher eine kleine Shisha, somit ist der Wertverlust, falls diese bei Ungeschicktheiten kaputt geht, nicht ganz so hoch.
Bester Shisha Tobacco
Bei der Suche nach den Besten Shisha Tabak kann es vorkommen das sie sich von dem Angebot erschlagen fühlen. Es ist empfehlenswert sich etwas durch zu testen bis sie den richtigen Wasserpfeifen Tabak Für sich gefunden haben.
Mit guter Qualität und Hochwertigkeit bestechen folgende Tabak Marken: Aqua Mentha Tabak mit Sorten wie Aqua Blubry (Minze & Blaubeere) oder Aqua Chrry (Minze und Kirsche). Ebenfalls stark gefragt sind die Sorten von Adalya zum Beispiel Tabaksorte Love 66 (Honigmelone, Maracuja, Minze & Wassermelone) oder Adalya Tabak Mng Tango Ice. Auch sehr beliebt ist Chaos Tabak – Medusa (schwarze Traube, Blaubeere und Menthol) und Aqua EXOTIC von Aqua Mentha Tabak. Von Al Waha Tabak stehen unter anderem die Sorten Grap Min (Geschmack nach Traube, Minze) und Amor (Geschmack nach Kiwi und Minze) zur Auswahl. Weitere Hersteller und Sorten aus unserem Sortiment sind zum Beispiel Chaos Tabak mit Adios Amigos (Apfel, Maracuja), 187 Tabak mit California Love (Ananas, Mango, Zitrone) und 7 Days Tabak mit Sour Bomb Classic (saure Apfelringe) zur Auswahl.
Shishakohle: Holzkohle & Naturkohle fur Wasserpfeifen?
Es ist bei Shisha Raucher Kreisen verpönt selbstentzündende Kohle zu nehmen. Wer sich nicht total blamieren möchte sollte sich schnell dafür entscheiden seine Shisha nur mit Naturkohle für Wasserpfeifen zu beheizen. Diese überzeugt durch 100% natural Zutaten, meist werden Kokosschalen verwendet. Obwohl das Anzünden der Sishakohle etwas schwieriger als bei selbstentzündender Kohle ist, besticht die Naturkohle hat viele Vorteile. Neben einer langen Brendauer bis 90 Minuten überzeugt die Kohle mit einer hervorragenden Hitzeentwicklung und verbrennt während des Rauchens vollständig. Als Reines, unbehandeltes Naturprodukt verbrennt die Naturkohle geschmacksneutral, ohne den Shisha Geschmack des Tabaks zu verfälschen. Wenn Sie öfter Shisha rauchen ist es empfehlenswert einen Kohleanzünder zu kaufen, zur Auswahl stehen Elektrische oder Gas Kohleanzünder.
Was ist eine Shisha bar?
Eine Shisha Bar ist eine Gastronomie, in der als Service das Wasserpfeifen Rauchen angeboten wird. Sie führen meist die beste Auswahl an Getränken, diversen Kaffee- und Teespezialitäten, Softdrinks, Mixgetränke mit oder ohne Alkohol, und bieten kleine Köstlichkeiten. Sie ist ein idealer Treffpunkt nach der Arbeit, Uni oder Ausbildung, nach dem Ausgehen. Auch fur einen entspannenden Zwischenstopp bietet sich eine Shisha Bar an. Viele möchten aber auch einfach nur eine hervorragende und authentische, aromatische Wasserpfeife genießen. Die einen möchten dort in Gruppen feiern und für andere kann das Shisha Bar als Rückzugszone dienen. Viele Bars können für Partys und Veranstaltungen angemietet werden. Sportübertragungen und Medienpräsentationen sind dort üblich. Zu beachten ist, dass der Verkauf und Konsum in Deutschland ab 18 ist. Es ist dementsprechend anzunehmen – und zu hoffen, unter 18-Jährigen der Aufenthalt in Shisha-Bars verwehrt wird. Lassen Sie sich in die Welt der Shisha & Wasserpfeifen entführen und besuchen Sie unseren Shisha Shop!
Sun Microsystems, a world-renowned manufacturer of server solutions, software, networking, and SPARC architecture, was founded in 1982 to provide affordable workstations for CAD/CAM applications.
Currently, the company's clients in Russia are the largest banks, government agencies, telecom operators and industrial enterprises.
Sun Microsystems represents a wide range of software and hardware products.
Hardware and software solutions from Sun Microsystems
The portfolio of software and hardware products from Sun Microsystems allows you to create information systems of any scale and complexity: from user workstations to computer centers, from operating systems and office suites to application servers.
entry level servers. High performance, reliability, rack-mountability, combined with a low price, have made these servers extremely popular both in large data centers and in small companies and workgroups. The range of offered servers extends from one to eight-processor servers running OS Solaris or Linux - now you have the opportunity to choose exactly what you need. The latest update to this family is the latest Sun Fire V20z server, a two-socket server based on AMD Opteron processors: high performance, easy administration, new architecture - at a competitive price.
More information: http://ru.sun.com/products/servers/entry

Enterprise departmental and midframe servers. Representatives of this class have long and firmly gained a leading position where reliable operation of business-critical applications is required - server consolidation, data storage, data mining, online transaction processing (OLTP) systems, databases of a significant volume, as well as production management systems. The latest update to this family is the Sun Fire E2900, E4900, and E6900, the first UltraSPARC IV-based servers to use on-chip multi-threading technologies. According to various studies, their performance is twice the performance of their predecessors - servers based on the UltraSPARC III processor.
More information: http://ru.sun.com/products/servers/midrange

Data center servers. Servers in this class provide the highest level of reliability and scalability and are built for networked computing, such as business-critical applications such as server consolidation, application migration from mainframes to open architecture systems, HPC, decision support systems, systems data storage, structured information storage systems.
This family is represented by both servers based on UltraSPARC IV and UltraSPARC III processors - the customer can choose what best suits his business needs. Two of the latest UltraSPARC IV-based servers, the Sun Fire E25K and Sun Fire E20K, offer twice the performance of their UltraSPARC III-based predecessors.
More information: http://ru.sun.com/products/servers/highend

Storage systems. For reliable storage and operational operation, Sun Microsystems designs and manufactures disk arrays and tape libraries of the StorEdge family. StorEdge disk arrays allow you to build a wide range of storage solutions for data centers of any size. A wide range of tape libraries allows you to create archiving and backup systems.
More information: http://ru.sun.com/products/storage
Workstations and thin clients. Built on SPARC architecture processors, Sun Ultra's high-performance workstations are ideal for software development, imaging, and engineering work. Ultra-thin clients provide mobility, ease of use and secure storage. In addition, they have a wide range of upgrade options.
More information: http://ru.sun.com/products/workstations
Sun Java System. The Sun Java System platform is a radical new approach to how businesses acquire, develop, and manage software. Currently, only Sun has the expertise and product line to deliver this unique and industry-revolutionary strategy. With the Java System, network services and critical business applications are deployed and run faster, easier, and at lower cost than ever before. Now our customers can spend more time innovating and achieving better results in their work.
More information: http://ru.sun.com/products/products/javaenterprisesystem
Software from Sun Microsystems. Sun Microsystems is committed to providing the most complete solution to ensure web service continuity at the lowest complexity and cost. Sun Microsystems software, including Java technologies, the Solaris operating system, Sun Java System middleware, and N1 data center management solutions, is industry-leading and delivers added value to users.
Today, the conceptual slogan once proclaimed by the company Sun, "The network is a computer" is already taken for granted, and yet less than two decades ago, when the first workstations only appeared on the market Sun-1, the validity of this motto was not so certain. At the time when the ideology of centralized information processing based on mainframes dominated, the company Sun proposed a new approach to the development of computer technology based on four principles:
- Open and compatible with a wide range of application software operating system Unix network-oriented hardware architecture.
- distributed network file system NFS
- specialized network administration tools.
Over time, these components developed and transformed, and by the beginning of the 90s, the basis of the technical concept Sun took shape in a solid design from the hardware RISC- platforms with architecture SPARC, operating system Solaris, network file system NFS and network administration platforms SunNet Manager, which was later replaced by software Solstice. But the initially chosen strategy, concentrating in the slogan<Сеть - это компьютер>, remained practically unchanged, and its fidelity was reflected in the statement Sun position as a strong leader in the production of workstations, servers and networking software and was characterized by a rise in product sales Sun in the early 90s.
When talking about successful companies in business, they often characterize their years of operation as key events in their history: big deals, important product announcements, profitable years. However, in order to track the stages of development of the company Sun, it is best to pay attention first to how the strategies adopted at an early stage affected the entire computer industry and how the Sun new technologies have become an integral part of the modern life of the computer industry.
Company Sun was established in 1982 at Stanford University, one of the world's leading educational institutions in the field of computer technology. Abbreviation SUN meant Stanford University Network- Network of Stanford University, thus, already in the very name of the company the idea of network computing was incorporated. It all started when an undergraduate student from Germany Andreas Bechtolsheim decided to build his own computer from available inexpensive components. In promoting the resulting product, he was assisted by a student in the field of economics Vinod Khosla who had the business acumen to understand the economic potential of the job Bechtolsheim and quickly raise funds among representatives of Silicon Valley. Soon in Sun came and Bill Joy who led the development UNIX at the University of California at Berkeley. And, finally, a friend took over to lead the work of the company Vinoda from the School of Business Scott McNealy. In 1984, Vinod left Sun, and Scott McNeely became president.
The founders of the company shared a common opinion about the need to use the ideas of open systems and networked computing as standards for their work. The decisions made at the first stage set the tone for the development of the company itself Sun with its innovative projects, and the entire computer industry as a whole. The combination of off-the-shelf components, a standardized and accessible operating system, and uncomplicated design has allowed the company to Sun Microsystems quickly enough to bring to market a powerful and affordable workstation for technicians. Wherein Sun also tried to use those new graphics and network technologies that were previously available only in more expensive and<закрытых>devices.
Initially, the firm's strategy was focused not so much on quick profits, but on expanding the market and conducting basic research and development. Thereby, Sun has benefited not only itself, but the entire industry as a whole, turning the operating system Unix into its core technology by offering the industry the network file system model NFS and licensing architecture SPARC and the Solaris operating environment, paving the way for safe investments for thousands of companies.
Today Sun, a company from the list Fortune 500, has a strong reputation in the business community as a market leader in workstations, servers, and Internet and Intranet technologies. Just a few years ago the company Sun proposed technology Java, which has now received mass recognition and the widest distribution. Sun is actually driving the evolution of Java technology, which is now a key player in Intranet/Internet and networking in general.
Sun Microsystems was a pioneer in the workstation market with its concept of open systems. Continuing this direction, the company is now focusing on building and managing enterprise networks. Having announced a new series of enterprise-scale servers a few years ago Sun Enterprise 3000-6000(systems 3500-6500 are now being produced), Sun, in addition to the workstation market, gained recognition in the Unix-based server market. The result was consolidated by the release in 1997 of a server with the capabilities of mainframe class systems - Sun Enterprise 10000, also known as StarFire. But computers based on Unix and in the lowest price range. At prices comparable to processor-based systems Intel, Sun Microsystems offers customers 2 and 4 processor workgroup servers Sun Enterprise 250 And Sun Enterprise 450, as well as workstations: Sun Ultra 5,Sun Ultra 10 providing users with the power and functionality Unix PC prices. At the same time, a feature of the systems of the family Ultra is that the same hardware components are often used in different classes of machines, that is, in fact, the systems have a modular architecture, which makes it possible to simplify and unify the development of software for them.
One of the most important branches of the company's development in the field of software is the operating system Solaris. In 1991 Sun announced the release of a new version of the operating system Unix-Solaris, which was based on two varieties Unix: Berkeley 4.2/4.3 (BSD) And AT&T System V. grown out of Sun OS, the Solaris operating system, conforming to numerous industry standards ( X/Open UNIX 95, various sections POSIX 1003.1, X11R6), has one of its important properties a high degree of scalability. The same operating system is used on single-processor workstations, workgroup-scale servers, and 64-processor servers Sun Enterprise 10000, an enterprise scale server. Solaris provides an almost linear increase in performance as the number of processors connected to the system increases.
Now Sun also engaged in the development of cluster architectures. By combining separate servers Ultra into the overall system, users can achieve significant improvements in performance and reliability of computing systems. Sun offers two options for cluster solutions. First, it is a system of increased reliability HA (High Availability), where all the elements that form the cluster are duplicated. Thus, when a machine fails, the most critical application is launched on the standby cluster node. Second, it is a system PDB (Parallel Database), which is designed to ensure parallel operation of relational databases on the computers that make up the cluster.
One of the ways to implement the dominant concept Sun"The network is a computer", the meaning of which is to use for information computing not only a single computer with limited resources, but also practically unlimited network resources to which this computer has access, was embodied in the idea of creating a network computer. According to her, all large tasks should be solved on powerful servers, and the client should only have access to data input and results.
The start-up costs of a networked computer are low, and other costs, such as maintenance and upgrades of hardware and software, are also significantly lower than those of a conventional workstation or personal computer. Low prices are due to the fact that network computers do not need special administration. Since, for example, most networked computers will be left without their own permanent storage devices, all user data and configuration information will be stored on servers. Thus, when upgrading software or installing new applications, all replacements occur in only one place - on the server. Centralized administration and configuration can provide significant savings for businesses with thousands of client machines. Java technologies allow you to host applications on a server and make them available to any client, regardless of its platform. This is faster than traditional ways of distributing software and is much cheaper than upgrading a large number of personal computers.
The concept of a network computer is very closely related to the company's Sun language Java And Java technologies generally. When calculating according to the model Java administrative and modernization tasks are moved from the client level to centralized servers. To support working with Java, servers must support interaction with clients. Java and application launch Java. For example, Sun releases servers Netra And Ultra Enterprise that meet these requirements. Since the bulk of the calculations when working with a thin client, which is a network computer, is performed on a server, it is necessary to take care of increasing the throughput of servers and their scalability in terms of performance and capacity.
Currently Sun offers a new network computer option sunray, which should gradually replace conventional PCs, although this time the company is ready for the indifferent attitude of potential customers. This is not the first time Sun: the first networked computer designed Sun, -JavaStation- was introduced about two years ago, but then it was ruined by the global decline in prices for personal computers, numerous delays in the release of the product itself and slow work Java. Now there is a lot of new: the concept Hot Desk, which allows you to run applications on servers Sun, and also supports the work with Windows NT, office suite Staroffice from Star Division as well as support smart card for remote work and administration. In addition, the strategy itself for the distribution of networked computers has changed. Now Sun is going not to sell, but to rent out new network computers for about $10 a month.
In 1995 the company Sun Microsystems coined the term , denoting a corporate network infrastructure built on the principles of technology Internet and in particular www. The emergence of this new technology stemmed from a project to develop a universal interface for household appliances. The initial goal was never achieved, but from this project a lot of things were born, without which it is now difficult to imagine Internet technologies. Thus, the proposed concept Intranet largely based on technology Java, which was created to develop mobile applications for www.
So the language Java was born in the course of a project to create advanced software for various household appliances. At first, the project was implemented on C++, however, at some point, the developers realized the need to change the programming tool itself to deal with the problems that arose during the work. It became obvious that a platform-independent programming language was needed that would allow programs to be written that would not require compilation on every new hardware architecture and that could be used on different processors on different operating systems.
Birth of language Java preceded by an interesting incident. Software developer Patrick Naughton, one of the employees of the company, realized that he was no longer able to support hundreds of different interfaces of programs used in the company, and informed the executive director Sun and to your friend Scott McNeely that is going to leave the company. In response to this McNeely asked noton make a list of the reasons forcing him to take this step, as well as suggest possible ways to solve the problems that have arisen. Naughton did not expect his letter to receive at least some response, nevertheless he wrote it, criticizing many software developments in Sun, in particular the software architecture being developed at that time NeWS. However, this letter was sent to all the leading engineers Sun Microsystems, who immediately responded, supporting the ideas of their colleague. The appeal received approval from the top management Sun: Bill Joy, one of the founders Sun Microsystems, And James Gosling, chief noton. As a result, it was decided to start developing something new and unusual. This was done by a development team codenamed Green, which has chosen as the application of its forces the study of household devices, such as Nintendo Game Boys and remote control devices. It was necessary to find a means by which it would be possible to establish an interaction between these heterogeneous devices, given that all of them - VCRs, laser disc players, stereos and other equipment - are implemented on different processors. Therefore, when developing software for such devices, it would be necessary to take into account the specific hardware features of each of them, to be squeezed within the provided hardware. These factors stimulated the emergence of a new approach to software programming, which would smooth out the existing differences in architectures and which was to become the leader in the consumer electronics market. And the developers of the group Green started to create a new program development tool, an object-oriented programming language, which was named oak in honor of the oak that grew under the window Gosling. Soon Sun transformed the team Green to the company First person. The company had an interesting concept, but still could not find a use for it. After a series of failures, the eyes were turned to the recently born World Wide Web - world wide web. Then it was suggested to use the language oak to create Internet applications. So oak became a product in its own right, breaking away from the world of consumer electronics. A special Oak browser, named webrunner. In 1995 Sun Microsystems announced the release of a new product, renaming oak in Java, the explanation for which can only be found in the special love of programmers for coffee, and the browser webrunner has been renamed to HotJava.
In short, then Java is not only a language, but an application development platform that includes a simple, portable, interpreted, high-performance and object-oriented programming language, as well as a runtime environment.
One of the basic principles Java is that the operating system is separated from application development. In other words, developed with Java the code should not depend on the platform on which it is developed and executed. And the more platform independent the code is, the more mobile and portable it is. To ensure platform independence, a virtual Java machine, on which the Java programs, its architecture, command system and data representation are defined. Source texts Java programs translated into the codes of this machine. These are not machine codes like those produced by language compilers C, and the so-called bytecodes are high-level machine-independent codes for an abstract machine that consists of an interpreter Java and the execution system. Bytecode set Java not only easy to interpret, but also quite efficient to compile<на лету>into the machine codes of the platform on which the virtual machine is running Java. At the same time, bytecodes contain redundant information that allows you to check them for execution safety. The concept of a virtual machine ensures that when a new hardware and software platform appears, only Java machine, and all programs written in Java, no changes are required. Standard Java also defines that when editing the external links of the program in a transparent way for the user, the necessary objects can be searched not only on the local machine, but also on other computers available on the network.
At first, many considered Java just as a means of revitalization Web pages. However, there are other ways to diversify content. www, e.g. animated GIFs, programs JavaScript, specially designed for browsers plug-ins. A skate Java the possibility of mobile computing began to be considered. Programs that run on any platform and are freely transmitted over the network have proven to be very convenient. It should be noted that the ideas of mobile code on the web Internet existed for a long time, but there was no suitable environment for their implementation. The role of such an environment was seriously claimed by the system X Window, however, it did not have the generic interface required for this. Nevertheless, the mobile code also has a number of significant drawbacks, the main of which are the security of the transmitted code. First, the source program may initially contain<программные закладки>, viruses or just errors. Secondly, there is a danger of unauthorized access when using a mobile code. In order to get rid of possible problems associated with errors in the program code, in Java removed address arithmetic and introduced a special mode of working with memory. In this case, the program is launched in a separate, virtual machine with its own address space. In addition, tracking the process of allocating and freeing dynamic memory in Java no longer the programmer, but the environment itself. The programmer does not need to worry about the timely release of the part of dynamic memory that is no longer used by him, the garbage collector will take care of this; virtual cars. The main task of these measures was to combat the most common errors: fixed-length string constant overflows, stack overflows when calling subroutines, memory allocation and deallocation during program operation. Of course, this approach could not but affect the efficiency of the code. However, this disadvantage is compensated by the potentially greater stability of the system. To ensure security related to the possibility of unauthorized access when using a mobile code, the specification Java restrictions on the use of code on the network were introduced. First of all, this applies to the development and use of distributed information systems. Restrictions are placed on receiving and transmitting data and code to hosts other than the one from which it is launched Java applet, which leads to the need to use special proxy servers (proxy) to link all the necessary components.
Java technologies are especially widely used in network infrastructure Intranet. Term Intranet used to refer to the use of technology Internet in internal corporate networks. At the same time, on the basis Intranet lies the idea of efficient sharing of information through a single type of user interface - the browser Internet. Using the Browser Paradigm Internet simplifies the work of users on the network, avoids problems associated with updating software at user workstations, improves the internal interaction of systems in the corporate network as a whole. Used in Intranet The principles of web navigation and search make it easier for users to collect and analyze information. One of the advantages of using Java technologies in corporate networks is to allow users to log in from anywhere Intranet and still have access to their native working environment. In this centralized information management model, the cost of system administration is greatly reduced.
So, at the core Java Computing lies the client/server model, in which the program code Java loaded dynamically from the server at the request of the client. Applications Java can work anywhere where the virtual machine software is installed Java. This achieves platform independence and portability of the code. Java. So, for example, they can be executed in any Java-enabled browser. It is this property that makes it possible to achieve a gradual migration to thin and, therefore, easier to manage clients - special devices like JavaStation or a newly announced company Sun stations sunray.. Such devices - network computers - instead of a traditional OS contain a simple system, for example Java OS, which powers the Java Virtual Machine. Java OS and the Java virtual machine can be stored on the client in flash memory or downloaded from the network. User data and configuration information for clients are stored on servers, which provides centralized administration and the ability to access the necessary data from anywhere in the corporate network. Architecture Java OS is a collection of microkernel and memory manager, device drivers, Java virtual machine, system Java OS Graphics And JavaOS Windowing, network classes and support for all application programming interfaces (API) Java. Client-side applications communicate with servers using standard network protocols, but more complex protocols can also be used, such as the JDBC, which provides SQL-oriented connection to databases. More complex, layered applications can be built using distributed objects that have the ability to communicate using protocols. CORBA. It should be noted that the platform independence of Java allows you to use Java technologies not only in traditional desktop environments, but also in numerous devices such as smart phones with built-in displays, digital assistants (PDA) such as, Palm Pilot, in various consoles, cash registers, etc.
Java technology is guided by the motto "Write Once, Run Anywhere"("Write once, use everywhere"), setting the standard for cross-platform compatibility. This principle of software development allows you to optimize the process of creating and implementing applications, and allows you to shorten the cycles of developing new products. Language Java and modular application programming interfaces JavaBeans do not tie developers and users to any one platform. However, it should be noted that Java allows you to insert code written in other languages, such as C++. Therefore, in order to guarantee the portability of programs to Java, company Sun proposed an initiative 100% Pure Java(100% pure Java). This initiative defines a set of APIs that provide maximum cross-platform compatibility for Java applications developed with them. Java natively maintains a high level of platform independence, code security, ease of loading remote classes, and<сборку мусора>. However, when trying to link Java code to source platform code, these features can be lost. When using platform-specific methods, there is no longer a guarantee that the code will be safe and will not violate the stability of the system. Sometimes it may be necessary to include native platform methods to access system resources that are not supported by Java. In such cases, you can create an interface for communication between platform-specific codes and codes Java, however, such an application can no longer be considered 100% compliant with the Java cross-platform compatibility standards. To support maximum portability, the program code should be written entirely in Java only, without any inserts in other languages, for example C++. Applications claiming 100% definition pure java must undergo special certification. Parts of applications that are written using Java codes and other codes can also be certified. In this case, those parts of the application that meet the definition of 100% can be certified. pure java. Such, for example, are client/server applications, the client part of which is written entirely in Java.
The most important basis for the development of applications on Java is an application programming interface Java API. It provides interaction between Java components, applets, and applications, and defines a set of key interfaces that developers use to write applications. Java API consists of two components: basic interface Java Core API and interface of standard extensions Java Standard Extension API. Standards Compliant Applications 100% Pure Java, must fully comply with the basic specifications of application programming interfaces Java (Java Core API).
Relatively recently the company Sun released a new version of the platform Java - Java 2, formerly named Java 1.2. This version significantly improves the performance of the application runtime, implements a new flexible security model, and includes an expanded set of programming interfaces. (API). Now interface Java Core API consists of fifteen class libraries covering core technologies Java: applet, awt, beans, io, lang, math, net, rmi, security, sql, text, util, accessibility, swing, corba. The previously existing sandbox security model, i.e. isolating an application running in a virtual machine from a real operating system, has been extended so that developers, administrators and users can define their own flexible security policy, or a set of rules that provide control over the actions of applications and applets. The permissions of Java programs can vary depending on the source of the Java program, which determines the level of access that program has to system resources. Java 2 also includes the implementation of a set of programming interfaces JFC - Java Foundation Classes, which allow you to solve a large number of standard application programming problems. IN Java 2 the integration mechanism with a number of existing network programming technologies is also included. So, for example, V Java 2 enabled module Java IDL, which enables remoting according to CORBA standards.
One of the branches of a sprawling tree Java technologies from Sun- technology JavaBeans, which implements the concept of a platform-independent modular software architecture for the development environment Java. module JavaBeans almost any part of a software system can, from a graphical user interface element to a large application program element with a large number of functions. Technology advantage JavaBeans is based on the principle of modularity, which means that the same code can be reused in different applications. So, for example, a text editor implemented as JavaBeans component, can be used in a wide range of developing applications without rewriting its code. Following the principles of Java, technology JavaBeans platform independent, so solutions based on it can be used on both traditional computers and other architectures, such as cell phones or microcomputers such as "personal assistant".
Modular software JavaBeans can be integrated into other modules, such as ActiveX. This compatibility is provided through the company-developed Sun controls ActiveX (JavaBeans Bridge for ActiveX). This tool makes it possible JavaBeans work in traditional shells ActiveX, such as Microsoft office And VisualBasic.
One of the new technologies that Sun has high hopes and in which, perhaps, he sees the foundation of network computing for the next century, is called jini. Fundamentally jini is a software architecture based on a language Java, which allows operating system services to be distributed throughout the network. In other words, jini is part of the software environment Java which runs on a virtual machine Java and allows devices to dynamically connect to the network and take advantage of the capabilities of all other devices in it, if they have specially registered their services and agree to provide them to the network community. In the future, Sun sees the ability to connect devices to the network and instantly establish communication with other devices on the network without the use of any additional drivers. To start free communication of the device with its<коллегами>it will be enough just to plug it into the network.
Project jini began to develop in parallel with the growth Java technologies, originating in 1994, when it was announced Java. The main goal of the project was to create a network infrastructure that would allow easy integration of dissimilar devices in the network. It is not surprising that many companies involved in consumer electronics, computer peripherals, network services, computer systems, and generally related to the use of advanced computer technologies immediately showed interest in this project, since the market demand for technology that simplifies the operation of devices in a computer network and makes this network more functional, is obvious. Many companies are now partnering with Sun to develop and test technology jini, analyzing and testing it in solving their problems.
At the heart of the technology creation concept jini the following idea lay: the work of most modern information and computing systems is based on computer networks, which are now being created and developed everywhere. At the same time, the equipment operating on the network, as well as network software, can be difficult to get to work smoothly without additional financial costs. This gives particular inconvenience to the user who needs a simple and reliable network that does not require constant care and support for its operation, and does not force you to spend a lot of effort on connecting new devices. For example, the advantages of the developed company Sun technology jini can be illustrated as follows: when a device is connected to the network, for example, Palm Pilot, this immediately becomes known to other devices operating on the network: the PDA will automatically become part of it. At the same time, the computer can obtain information about other network devices and the services they provide. For example, the user will be able to easily access data on some computers, process it with programs on others, and then print the information on a nearby printer without using any additional drivers, but simply accessing the services provided by devices connected to the network and using technology jini. Such automatic integration should be implemented for all electronic devices, from a personal computer to a cell phone.
Technical principles of the technology jini consist of the following actions: when the device is connected to the network, it is automatically registered in the search service lookup service using discovery and join services Discovery and Join Service, thereby the device enters the so-called<федерацию>. The interaction of network objects is carried out using the mechanism of Calling Remote Methods (Remote Method Invocation, RMI)- a high-level way to support distributed computing by the Java platform. The RMI specifications allow remote devices to advertise the set of services they can provide (this is called a remote object interface declaration in Java terms). When a client system wishes to use a service registered with a search service, the search service tells that client system the address of the device where the service is directly available (in Java terms, returns a reference to a remote object that implements the desired interface). The Leasing leasing model defines the principles for removing lists of registered services from the bulletin board and for contracting, and the list of access rights Access Control List of this service determines who can use it.
True, this concept of distributed computing architecture is hardly something completely new. David Gelernter, professor at Yale University, once put forward the idea of distributed architecture in the project Linda. Similar ideas were later developed in Lucent Technologies within technology Inferno, at IBM in the project T Space, in the national laboratory Oak Ridge in project Parallel Virtual Machine. Microsoft is also making plans to develop a distributed operating system called Project Millennium.
Theoretically technology jini can be applied to any devices or programs running on the network. Jini is not a new network operating system, but a network infrastructure built on technology Java and making an attempt to bring distributed network computing to a new level. jini solves the problem of incompatibility of network equipment, and also provides an effective mechanism for the interaction of computing devices and applications in the network.
Now Sun moves to a new stage in the development of network technologies and, in particular, electronic business and commerce, putting forward the concept<.com>. <.Com>is a more global concept than a simple transfer of operations to the network. According to Sun, using the principles<.com>will allow companies to improve contacts with their customers, suppliers, partners and employees. The relative novelty of this idea is that now computer companies, and primarily Sun, intend to offer their services in an even more integrated way, in order to save their customers from having to configure and adjust purchased hardware and software on their own. The user needs to receive services, and this is the main thing. The main attention of the user will be focused exclusively on his immediate tasks, whether it is the provision of any services through computer technology, trade, production. In this vision, the computer industry is shaped more like a telephone network, where service users are very loosely connected to the mechanism for providing their connection, and all they need is to pick up the phone, hear the dial tone and dial the number. In essence, the concept<.com>was a natural stage in the development of services Sun Microsystems, especially given the significant development of network business and commerce in recent years. As they say, now comes a new era of invisible computing, leaving behind personal computers.
One of the foundations<.com>has become a recently released new version of the operating system Solaris - Solaris 8. Operating environment Solaris 8- a potential standard of the era ".com" is a product built using a flexible and scalable architecture and having extended functionality compared to previous versions of the system. This version of the system allows you to significantly increase the performance of Web servers through the use of NCA (Network Cache Accelerator). According to the Sun application Java in some cases increase productivity several times due to the use of the subsystem Java hotspot. Database performance Oracle increases by 40% according to Sun. With the release of a new version Solaris Sun introduces a new business model that includes free access to the operating system Solaris, including the OS source code, and free software licenses for end users.
Combining its hardware platforms and software technologies such as Java And jini as well as a new operating system Solaris 8, and calling the updated integrated approach to service delivery the concept<.com>, Sun is trying to take a new step in the development of the network business in particular and the provision of network services in general.
Development of the company Sun Microsystems keeps pace with the evolution of network computing. Having laid the foundation for the explosion of networking technology, Sun remains one of the leading companies in this sector of the market. Now no one doubts the fact that a modern computer is unthinkable without a network, which confirms the slogan put forward at the founding of Sun<Сеть - это компьютер>. Today, Sun continues its research and brings to the computer market technologies that will allow users of not only computers, but also a wide variety of electronic devices, to access the power of modern networked computing systems with simplicity worthy of the technologies of the next millennium.
In preparing this article, materials from the company's web servers were used Sun Microsystems: http://www.sun.com/ , http://www.sun.ru/ , as well as publications of journals ComputerWorld, LAN, Networks and etc.
The site reviewer studied the history of Sun Microsystems, one of the fastest growing US companies in the 80s, which developed the SPARC processor architecture and the Java programming language, but due to the dot-com crisis and management errors, suffered losses for almost a decade and was sold to Oracle.
Sun Microsystems ceased to exist in 2010 after it was taken over by Oracle. Despite this ending to the company's history, Sun Microsystems is remembered for its products, intense growth, and extraordinary founders. For two decades, Sun was considered one of the most successful computer companies in the United States. Then her position was undermined by the dot-com crisis, the departure of the founders and the controversial decisions of the leadership.
Sun Microsystems office
Andy Bechtolsheim. Founding of Sun Microsystems
The history of Sun Microsystem must begin with the brilliant engineer Andy Bechtolsheim, thanks to whose developments the company was created. Andreas von Bechtolsheim was born in 1955 in Germany. His father was an elementary school teacher and his mother was a housewife. Andy was the second child in the family.
The childhood of the future entrepreneur took place on a farm in the Alps. The family did not have a TV, the closest neighbors lived a few kilometers from the Bechtolsheim house, and therefore Andy was not distracted by anything. He was an inquisitive boy, asked his parents questions about everything in the world, read a lot and was interested in electronics, in which he had rather an applied interest, trying to figure out how this or that device works, and he also made various devices on his own.
In 1963, the Bechtolsheim family moved to Rome, where they lived for five years. There is no information about the reasons for the move. In 1968 they returned to Germany in the small town of Nonnenhorn. It was here that Andy spent his teenage years. At school, he was famous for his success in physics, including helping the teacher during laboratory work. There is information that Andy had to replace the teacher from time to time.
However, the development that preceded it began much earlier - in 1983, when Sun was engaged in the Sunrise project to produce a coprocessor that performs computational operations with floating point numbers. Following the conclusions made by Bechtolsheim, Sunrise was finalized to a full-fledged processor.
The first workstation to use this processor was the Sun-4. The SPARC architecture was officially introduced in 1987. The company itself did not produce microprocessors, relying on third-party manufacturers, of which there were already four by 1988.
In 1989, for promotional purposes, the company dropped the Sun name from its product lines, using SPARC instead. The first SPARCstation was presented to the public in 1989. It was released to compete with the Macintosh and IBM PC. Despite the fact that it was not possible to achieve impressive success, SPARCstation lasted on the market for six years, and about 35 thousand units were sold in the first year.
The non-profit organization SPARC International was formed to trade licenses for the SPARC Sun architecture. Everyone can get membership in it, but you still have to pay for a license. SPARC International also sells finished products. The creation of this organization was connected with the desire to repeat the success of IBM and, trading licenses for their own equipment, enter the market for hundreds of clones.
In 1987, the company surpassed Apollo in sales and took the lead in the market. In 1988, the company's sales amounted to one billion dollars. There was nothing unusual about such success. Sun entered the workstation market during their popularization. In addition, the company was one of the pioneers in the industry and was able to quickly acquire the best people, from Bechtolsheim and Joy to talented university graduates.
In addition, Sun was right in its open systems orientation, defeating Apollo with it. In its first ten years of existence, Sun went from being a small company to being the market leader in its industry, producing more than 10 million workstations, and becoming a Fortune 500 company.
In 1987, Sun partnered with AT&T to further develop the UNIX operating system into standard workstation software. It should be noted that until that moment, Sun used its own UNIX-based operating system, SunOS, on workstations. During the collaboration, AT&T acquired 20% of Sun. Together they released Unix System V Release 4. Sun would eventually adapt this development for its own products, and it would become known as Solaris.
In response, several workstation companies fearful of Sun's reign, including Hewett Packard and IBM, formed the OSF consortium. Together they were going to develop and distribute open source software systems. They created an operating system based on UNIX - OSF/1.
AT&T and Sun did not stand aside and, having teamed up with Data General and Unisys, launched a competing organization - Unix International. The two consortiums competed for some time to define a commercial UNIX standard for the entire industry.
These and subsequent events became known as the UNIX wars, and the struggle between the consortia prevented UNIX from gaining market leadership. AT&T sold its stake in Sun in 1991 and exited the operating system market in 1993. This date is considered to be the end of the UNIX wars, and soon a common standard was defined, known as the Single UNIX Specification. However, its appearance did not change the situation - Windows has already achieved market supremacy.
Despite being actively involved in all these endeavors, in 1989, Sun ran into some problems - by launching the SPARCstation 1 on the market, management was simultaneously trying to support two other product lines that were losing their relevance. The situation was exacerbated by rapid growth and active staff growth, which in turn led to managerial difficulties. Demand for SPARCstation was also clearly underestimated, which resulted in the inability to fully meet the needs of the market. In addition, due to the fact that Hewlett Packard acquired Apollo in 1989, the company lost its leadership for some time.
Sun Microsystems in the 90s. Creating Java
Sun management had to deal with all this already in the new decade, and it turned out relatively easily. First of all, the product line was reduced, in which only SPARC-based products remained. Revenues for 1990 increased by 40%, and the market position was restored.
In the early 1990s, competition in the workstation market became increasingly fierce. Sun's competitors released several successful products, which kept the company from falling behind.
Good financial performance allowed Sun to expand its product line in different directions. The company started with the production of workstations for the insurance business, air carriers, brokerage companies. However, entering the market of office computers cannot be called too successful because of the large number of competitors. Then it was decided to launch a line of budget products. A cheaper $5,000 workstation was soon introduced.
In parallel, the company was negotiating with software manufacturers to adapt it for SPARC. In 1991, she managed to negotiate with the developers to adapt programs to SPARC 2,800. The company continued to actively work with external contractors, while retaining the assembly and testing of products.
At the same time, Sun became active in the software market. Two subsidiaries were created - SunSoft, which sold the company's operating system to other computer manufacturers, and Sun Technology Enterprises, which supplied software to SPARC. The main areas of work of Sun Microsystems were also separated into subsidiaries. Each subsidiary operated autonomously, with its own developers, production, and independent marketing and sales.
In 1992, Sun had 21 subsidiaries around the world. Half of the company's income was provided by the external market. However, already during this period, analysts, who had previously admired the rapid growth of Sun, predicted a slowdown.
Especially the opinion of Sun experts did not bother. The company, through the efforts of Bechtolsheim, continued to improve its own technologies in the field of multiprocessors. Of course, there have been successful innovations in other areas as well. In 1991, a project was launched to create a computer for ordinary users, called Green.
At the head were Bill Joy, Patrick Naughton and James Gosling. The development had to have reliable and convenient functionality. As the project progressed, it became clear to the project leaders that they would need a new programming language. The development was called Oak, which will eventually be finalized and will receive a new name Java.
However, this is a shorter version of events. Usually, the history of the creation of Java begins with a story about the programmer Patrick Noughton. He informed management of his decision to leave for NeXT because he was tired of adapting software to Sun's vast number of operating systems and architectures. There is an opinion that Noughton was completely at odds with Sun's development approach. McNeely, who was friends with Noughton, suggested that he clearly identify and put in writing the reasons for dissatisfaction, as well as ways to solve existing problems.
A letter written by Naughton to the management and engineers of the company, in which he sharply criticized Sun Microsystems and its development approaches, had an unexpected effect. Bill Joy and James Gosling drew attention to him and supported Naughton's ideas. This story ended with the proposal of the management to the developers and to Noughton himself to create something extraordinary and revolutionary. This is how the Green project was launched.
As a result, his team set about creating some kind of tablet, with which it was possible to control various equipment that had computer chips. At that time, according to Gosling's observation, it became more and more. During the development process, it became clear that the Green team would need a new programming language to create software with a minimum focus on certain platforms.
At first, Gosling tried to redesign C++ for this purpose. However, little came of this idea. Gosling soon had to admit that a completely new programming language was needed, which he undertook to create. The development was called Oak. Gosling managed to make the first version of Oak in just a few months.
 James Gosling
James Gosling
Bechtolsheim has invested in a large number of companies, but his most famous and successful investment came in 1998. It was then that two graduate students from Stanford University, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, turned to him. At that time, Brin and Page had already received several refusals to invest, but Bechtolsheim was interested in their idea.
By all accounts, he almost immediately agreed to invest $100,000 in the company, not really listening to the programmers' presentation. According to one version, Andy was just in a hurry and made a quick decision. In any case, the meeting ended successfully for Page and Brin and set the stage for the creation of one of the largest conglomerates of our time.
By the way, some sources believe that the meeting of Brin and Page with Bechtolsheim caused another interesting consequence. Andy incorrectly entered the name on the receipt - instead of Googol - Google. Page and Brin had to put up with it. However, there are other versions of the origin of the name Google.
- Sun is a leader in x64 and UltraSPARC processor innovation and delivers high-performance, scalable systems that make better use of data center physical space.
- Sun provides many system design innovations, from the processor, server, and operating system to data center management software and integrated middleware.
- Sun provides more choice, from processor to operating system.
- Sun combines servers and services into one solution, and offers unique remote connection and network upgrade services that save time and money.
- Sun provides continuous investment protection and compatibility with the Solaris 10 OS. The multi-threading capabilities of Java software, operating system, and processors help you outperform the competition, provide faster speed, higher performance, and lower costs.
Storage systems
Sun Microsystems combines server and storage expertise (StorageTek) with technologies and techniques to simplify the structure of customer data, secure it, manage identity, improve data recovery and archiving, and expand the use of that data.
- Sun offers its customers additional options in the field of information storage and data archiving:
- Benefit: An attractively priced data management solution gives you a competitive edge.
- Access: the ability to obtain the necessary information at any time and in any form, regardless of its structure, format or placement.
- Simplicity: An environment that is easy to manage.
- Reliability: constant confidence in the integrity of the data, that is, that it has not been modified, corrupted or read in an unauthorized way - from the moment of creation to deletion.
- Sun's advantage lies in its unique approach to data and storage systems. Sun and StorageTek provide a single, most complete offering of enterprise storage, data management systems and services, including a heterogeneous system of disk, tape and IT infrastructure optimization software and services.
- Sun's disk storage systems outperform the competition (Sun StorageTek 6920 outperforms HP by more than 140% and IBM by more than 70% in the SPC-1 benchmark test) and is backwards compatible with our NAS, unlike NetApp products. Sun Microsystems has a unique track record in building identity-enabled ILM solutions and implementing systems approaches to information security. Our competitors, on the other hand, focus on point-to-point products (EMC and NetApp) and expensive custom-made systems (IBM Corporation).
- Sun is committed to providing world-class innovative services, including:
- Sun simplifies management with a single Web-based platform.
- Sun offers more secure approaches to in-host (host), in-band (over the network), and in-device (device) data encryption.
- Sun leverages its full range of content and archive management solutions to leverage the best policy-based software tools for data migration and archiving, providing the industry's only truly end-to-end identity solution for content delivery, monitoring, compiling reports, data transfer and archiving.
- Sun Microsystems' StorageTek 5320 NAS appliance delivers record low total cost of ownership and excellent price/performance using Sun x64 systems.
- Sun offers Sun Managed Operations for Storage and Sun Host-based Data Migration Service.
Software
Sun offers an open, fully integrated software platform on a non-commercial basis or at predictable prices. Companies using the Sun platform as the core of their infrastructure can take advantage of Sun's comprehensive service support.
- The advanced Solaris 10 operating system can serve as the backbone of a customer's IT infrastructure.
- Broad Choice: Hundreds of x64 and UltraSPARC based systems support this OS; 6 million registered users.
- Lots of innovations: Solaris ZFS file system, DTrace dynamic tracing, Solaris containers, high performance network computing, secure execution, predictive self-diagnostics combined with enterprise quality.
- Non-Commercial Open Source: The OpenSolaris.org community takes an innovative approach to the Solaris OS.
- Sun has made the Java platform open source under the terms of the GPL license (November 2006).
- The Java Enterprise System is an open, freely available, fully integrated software platform at predictably low prices with world-class support for customers who use it as the core of their infrastructure.
- The Java System Identity Manager is the only complete user service and metadirectory solution on the market that simultaneously enhances enterprise security while significantly reducing the return on investment.
- The Java Composite Application Platform Suite provides everything a customer needs to develop and deploy a service-oriented architecture that enables application reuse, provision of new services, and rapid integration of legacy and packaged applications.
- Customers can pilot their core applications using Sun's software for free, reducing cost and risk. When deploying these applications, the benefits are enhanced because Sun provides subscription support, warranties, and compensation.
- For system administrators and IT leaders looking to accelerate implementation and capitalize on experience gained from pilot projects, Sun software is the easiest way to prepare, negotiate, implement pilot projects, and deploy applications.
- Sun pre-installs and tests its software on various platforms; applications similar to those optimized for the Solaris OS can be implemented for other operating systems such as Linux, Windows, and HP-UX.
- Sun provides its developer communities with a wide range of fully integrated state-of-the-art tools that can be downloaded for free:
- NetBeans Software: A full-featured tool for developing multi-platform Java applications.
- Sun Java Studio Creator Integrated Development Environment: Visual programming tool for Web applications.
- Sun Java Studio Enterprise Software: A complete solution for developing, testing, and deploying applications.
- Sun Java Studio Mobility Pack: Emulation and development tools to help you create applications for mobile devices.
- Sun Studio Software: Full native application support + C/C++/Fortran language compilers for UltraSPARC and x86 processors.
Services
Sun promotes the automation and simplification of IT services, thereby reducing the costs associated with their provision. Sun Microsystems works with its customers to help them grow their business with technology, not with more people, so they can focus on business success without IT distractions and keep IT costs under control.
- Sun provides an innovative approach to ongoing subscription services that help customers, partners, and developers stay connected to Sun Microsystems remotely and access the latest information and updated applications.
- Sun simplifies its portfolio and integrates Sun's computing, storage and software services to provide competitively low prices.
- SunSpectrum Support is Sun's most important customer service.
- Sun Professional Services is a suite of Sun's proven, highly reliable professional services that speed solution selection and deployment.
- Sun Managed Services - these services allow you to create a variety of flexible heterogeneous IT infrastructures and provide management tools.
- Learning Services are training and certification services that are useful at all stages of the life cycle of an IT project.
- Sun Grid (network.com) allows you to use high-performance computing resources on a processor/hour or GB/month basis.
- The key to Sun Microsystems' success is customer satisfaction and loyalty. That is why we constantly analyze the opinions of customers and strive to improve the work of our service support.
Facts and figures
Servers
- The Sun Fire X4200 and Sun Fire X4600 servers received InfoWorld's Technology of the Year awards. The Sun Fire X4200 server was named Best Server and the Sun Fire X4600 was named Best High Performance Server (InfoWorld, 01/01/2007).
- Sun Fire V490, V890, E2900, E4900, E6900, E20K, and E25K servers and 1.8 GHz UltraSPARC IV+ processors:
- World record performance and industry-leading investment protection for midrange and data center servers.
- Accelerate applications up to 8x faster than servers based on previous generation UltraSPARC II processors.
- Double the amount of RAM for the US IV+ 1.5 GHz processor and up to 33% more I/O bandwidth.
- An ideal choice for enterprise applications, consolidation projects, and application migration from mainframes.
- Sun Fire X2100 M2 and Sun Fire X2200 M2 servers with next generation AMD Opteron processors (1.8-2.6 GHz); best performance and power savings among x64 servers for Solaris, Linux and Windows applications. Both servers are ideal for large scale HPC and Web infrastructure deployments.
- The Sun Fire X4500 is the world's first 4-core hybrid data server that combines the industry's highest throughput with 24TB of storage for up to 5 times the density of traditional solutions at about half the price. (as low as $2/GB).
- The new Sun Fire X4600 server is the world's first x64 server with 16 processor cores in a 4 RU chassis, delivering more than double the performance of systems based on the Intel Xeon MP processor.
- With 10 world performance records, the Sun Fire T1000 server outperforms all 1RU systems. The Sun Fire T2000 server delivers 5x the performance, 4x less space and 5x less power than competitive 4-socket systems.
- Sun x64 servers and UltraSPARC processor-based systems have set over 175 world records for 25 workloads and outperform competing solutions in performance and price/performance.
Storage systems
- The Sun StorageTek 6140 Storage System won China InfoWorld's 2006 Editor's Choice Award. China InfoWorld, 12/18/2006.
- Sun Microsystems topped the rankings for enterprise-wide tape library support. Storage Magazine, "Quality Awards II: Leading Libraries", 01/15/2007.
- The Sun StorageTek FlexLine 6000 Series systems were ranked #1 in the Diogenes Labs Storage Magazine Quality Award for Supplier Competence and overall #2 for Initial Product Quality, Reliability, Features and Support, ahead of HP, IBM, Dell and EMC in the " Information arrays of the middle class. Storage Magazine, Quality Awards II: EqualLogic Named Top Midrange Array, 12/14/2006.
- ILM Provider of the Year Award 2006 (at The Storries annual awards ceremony held in the UK).
- Sun StorageTek Business Analytics storage system won Byte and Switch's "Big Bytes" award for "Best Storage Management Software". 09/13/2006.
Software
- Solaris Cluster Software is the world's only integrated cluster solution. It supports all major open source applications from other vendors and provides 24/7 access to all services running on SPARC and x86/x64 systems. CXOtoday, 01/10/2007.
- NetBeans 5.5 won InfoWorld's Technology of the Year Award for Best Innovative Java IDE. InfoWorld, 01.01.2007.
- Solaris OS: 125 world records, over 5,000 applications, over 800 supported platforms, 6.8 million registered users - more than the number of OS copies shipped by all competitors together in the last 24 months.
- Sun Microsystems Corporation is the largest contributor to open source software development - three times more than IBM and five times more than Red Hat, according to the Economic Impact of Open Source Software on Innovation and the Competitiveness of the Information study. and Communication Technologies (ICT) Sector in the EU” (Economic Impact of Open Source Software on Innovation and Competitiveness of European ICT Companies). UNU-MERIT, 20.11.2006.
- Sun Microsystems ranked #1 in the Forrester Wave: Integration-Centric Business Process Management Suites for Q4 2006 through its acquisition of SeeBeyond Technologies. Forrester Research, 12/20/2006.
- In Gartner's recent User Provisioning Magic Quadrant, Sun Microsystems was ranked in the Leaders quadrant; in the report "E-APS Magic Quadrant 2005" (Platforms for launching enterprise-level applications) - to the Visionary quadrant ("Innovative companies"); in the report "Integration Software Gartner Magic Quadrant 2005" (Integration software for backbone systems) - to the "Leaders" quadrant; in the report "Web Services Platforms Gartner Magic Quadrant 2005" (Platforms for Web services) - to the Visionary quadrant.
- 2006 CRN Channel Champions: Best Network Operating System Award (Solaris OS).