Zebrafish refers to the so-called model organisms of developmental biology. Thanks to the ease of maintenance, reproduction, and the high rate of embryo development, it has become a kind of laboratory white mouse for ichthyology. This is one of the few living organisms that have visited space orbit.
Lat.: Danio rerio.
English: Zebrafish.
Synonyms: brachydanio rerio.
The first description dates back to 1822. Described by Hamilton.
Zebrafish- inhabitant of rivers and streams of the eastern coast of Western India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Myanmar, Bhutan. Russian aquarists first saw the fish around 1905-1906. It was re-imported into the territory of the USSR around 1950.
In addition to the main name, aquarists gave the fish a number of other affectionate nicknames such as “ladies' stockings,” “stripes,” “danya,” and “zebra.”
Description
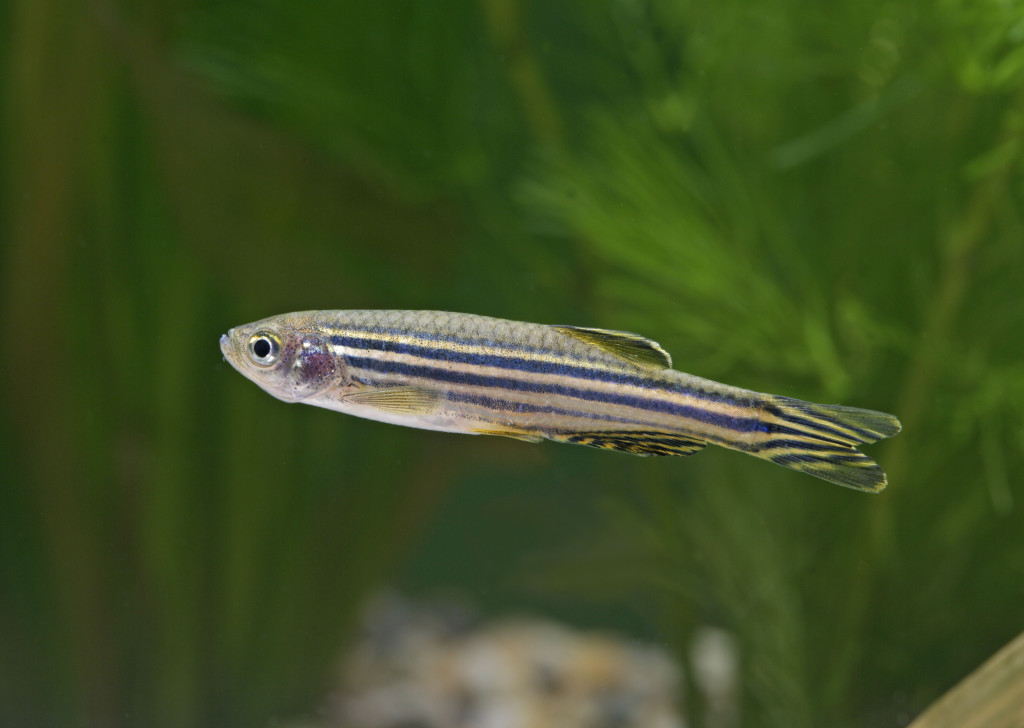
The zebrafish has an oblong body shape, along which there are yellow-green stripes alternating with dark blue. At one time there was quite a lively debate about which color was the main one and which was the additional one.
Now it is believed that the color is yellow-green with a metallic sheen, and there are 4-5 dark blue stripes along the body. This statement is confirmed by the existence of the leopard variety.
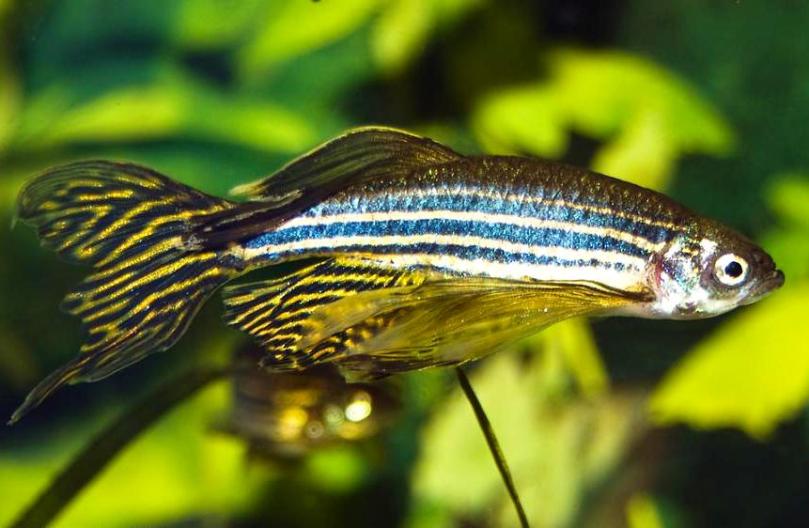
Young representatives have short fins. But as they grow, they become veiled. The fins give their owners an enchanting look. The edges of the veil fins may have a yellow color.
In the wild, adult individuals reach 6-7 cm. Aquarium inhabitants, as a rule, 4.5 - 5 centimeters. It is advisable to keep schools of at least seven to ten fish.
Males are somewhat slimmer than females, and also have more saturated colors. Females have a more rounded abdomen, especially after puberty.
Stays most of the time in the middle, upper layers. Life expectancy is about three years. Sometimes, with good care, they live up to five years. They become sexually mature when they reach six to eight months of age.
Breeding forms
with veil fins
A variety with longer pectoral and caudal fins than the natural form. Breeders managed to fix this mutation at the genetic level.
leopard color
U leopard variety the body is covered with dark spots. The spots resemble the coloration of a leopard. This coloration gave the name to this breed. Although some ichthyologists are inclined to consider this species a separate species. But among the inhabitants wildlife she's not there. At least according to the data that I was able to find. It is more likely, therefore, that the leopard color is the result of the work of breeders.
Fluorescent transgenic "GloFish"
In 2003, a genetically modified breed - fluorescent - appeared on the world market. The first fluorescent “” was obtained by implanting a fragment of jellyfish DNA with the ability of biofluorescence into the DNA of a danio rerio embryo.
The first GloFish had green. Today the following varieties are known: “Starfire Red”, “Electric Green”, “Sunburst Orange”, “Cosmic Blue”, “Galactic Purple”. All these varieties were developed using genetic engineering.
In Canada and the countries of the European Union, keeping, breeding, selling, and exchanging genetically modified objects (organisms) is prohibited!
Conditions of detention
Zebrafish– unpretentious, peaceful, freshwater fish.
Water hardness does not matter much. It is better for the pH reaction to be closer to neutral. Withstands temperature fluctuations from 15 to 30 degrees Celsius.
They are not demanding on the volume of the vessel. Even three liter jar will nice home three to four individuals. Although, of course, a three-liter bottle should be considered only as a temporary replacement for an aquarium. It is better for a flock of ten individuals to equip a normal permanent dwelling with a volume of ten to fifteen liters. It will take up a little more space than a jar, but it will look much better. In addition, it will be easier to care for your pets.
The bottom must be covered with a layer of granite chips or small stones. The soil can be coarse river sand. It is better that the soil is dark in color.
The preferred plants are long-leaved ones - Heleocharis, Sagittaria, Cabomba, Myriophyllum. Plants should be planted along the back and side walls, making sure to leave room for swimming.
Danio rerio is a restless, very fast creature. Sometimes, having accelerated properly in the upward direction, she, having played too much, can jump out of the aquarium. It must be fun to have fun like this in the wild. Jump higher and fly a little, then plop down again in your native element.
In the room, such flights end in failure with a hard landing on the floor. If there is no person nearby who can correct pilot errors in time, things will end very badly. Therefore, the vessel with these fish must be equipped with a lid or at least covered with glass of suitable sizes.
It is advisable to contain at least 7-10 pieces. Danio rerio fish are compatible with almost any other peace-loving fish with similar conditions of detention (other representatives of the genus zebrafish, guppies, swordtails, rasboras, tetras, barbs).
Feeding
They eat any food, but prefer live food. Small crustaceans are better, for example, daphnia, cyclops. A small one will do just as well. A delicacy for them is also scraped meat. It is permissible to feed dry, medium-sized food, after lightly rubbing it with your fingers. Feed danio rerio It’s easier to take from the surface of the water or fish in its thickness.
Danio rerio reproduction
Reproduction also takes place without any particular difficulties. But this fish is a spawning fish. Therefore, it is impossible to do without preliminary preparation.
About a week before spawning, it is necessary to separate the males from the females and keep them separate from each other. Females can be distinguished from males by their more rounded abdomen and less saturated color of yellow-green stripes. Before spawning, spawners need to be fed generously, preferably with bark.
An aquarium with a volume of 10 liters can serve as a spawning ground (in extreme cases, an ordinary three-liter jar). Cover the bottom with glitter or fontinalis. I also had positive results with the regular one. The plants are lightly pressed down with small stones so that they do not rise to the surface. You can also use a mesh that has cells of such a size that the eggs can pass through them freely. But its cells must be tight for producers.
The water must be fresh, standing for at least 2 days. Temperature 24 - 26 degrees Celsius. It is poured in a layer of about 5 centimeters above the plants.
In the evening, two males (three are possible) and one female are placed in the spawning tank prepared in this way. The female's readiness to reproduce is indicated by a thickened abdomen near the anal fin. Place the container on a well-lit window. Danio rerio breeding begins in the morning when the first rays of the sun fall on the spawning ground. The female can lay from 50 to 400 eggs at a time.
If spawning does not occur on the first morning, the spawners need to be kept in the spawning area for another day and fed with small bloodworms. If even now there was no spawning. Then the males need to be separated from the females and after 3-4 days put back into spawning.
There is one peculiarity - if the spawned female is not put back into spawning after 7-10 days, then she may lose her ability to reproduce.
After the end of spawning, the spawners should be removed, and half of the water should be replaced with fresh, settled water of the same composition and the same temperature.
After about 3-4 days, larvae emerge from the eggs and hang on the glass of the jar for several days. They look like threads with thickened heads. After a few days the fry begin to swim. As soon as the fry swim, they need to be given ciliates, rotifers, and Artemia nauplii. If the situation with food is very tense, you can feed it with hard-boiled egg yolk diluted with water. You just need to give it very carefully in small portions, as it greatly spoils the aquatic environment. The results will be somewhat worse.
As the fry grow, the food for them can and should be increased. Grown-up fry can be given small crustaceans - daphnia, cyclops. As they grow, older fry must be transferred to a larger vessel.
As you can see, this representative of the underwater kingdom can become a worthy decoration for the general aquarium of a novice aquarist. A flock of these fidgets can enliven any underwater landscape. Danio rerio fish are disease resistant. If you do not create extreme conditions, they will delight your eyes for a long time with their endless play.
Danio rerio (lat. Brachydanio rerio, today - Danio rerio) is a freshwater fish that belongs to the Cyprinidae family. The species received a scientific description in 1822. These days, zebrafish are popular aquarium fish that can be kept at home. In zebrafish natural environment Habitats: water bodies of Southeast Asia. They prefer rivers, lakes and canals with slow currents.
They swim in the upper layers of water, cruising between the stems of aquatic plants and grasses that hang into the water. Danio rerio here feed on small invertebrates and insect larvae. Spawning occurs with changes in water temperature during the rainy season. The eggs of the fish fall on the thickets of aquatic vegetation; this is a safe place for them.

Quickly navigate to the article
External characteristics of fish
Wild and aquarium danios Rerios look the same - a striped pattern is visible on their body. The symmetry of the body is narrow, flattened on the sides, length 4-5 cm. Along the body there are horizontal stripes of a yellowish-green and violet-blue hue, which alternate with each other. In females these stripes are wider than in males. During the spawning period, the stripes on the body of males become bright. The color of the fins is yellow-white, the dorsal fin has a dark edge. Females have a round body with a full abdomen. Males are slightly smaller and have an angular body.
There are varieties of zebrafish with different options scale color and fin color. Nowadays, aquarium Danios with veil fins, albino, red, pink, green, artificially colored specimens are common. There are genetically modified fish that have a jellyfish or coral gene introduced into their bodies. They have fluorescent scales in pink, orange, green, blue colors(Glofish). Such aquarium pets look beautiful, but there is no evidence for them yet. negative impact on the environment.
Watch a video about keeping and breeding zebrafish.
Not so long ago, geneticists from Southeast Asia bred a genetically modified breed of zebrafish with a red tint of scales, and called it “Red zebra”. Although it differs in appearance from the ordinary Brachydanio rerio, it is just as easy to maintain; the behavior style and habits of the fish are identical. Bright body color is a consequence of changes at the genetic level that are inherited. The use of dyes or special injections is unacceptable.
Content Rules
Danio rerio are unpretentious aquarium pets, suitable for beginners. The character is peaceful, agile, playful. They swim quickly, have a high reaction speed, thanks to which they quickly hide from danger. They can live in small aquariums. Schooling fish, it is advisable to immediately place 6-8 fish in the aquarium. They swim in the upper and middle layers of water.
The tank must be covered with a lid - these fish are jumping and can easily end up outside the reservoir. Male fish are playful and can periodically catch up with each other, or “intimidate” females, thus establishing hierarchical relationships within the school. You can put 4 fish in a 10-liter tank, but it is better to install a spacious aquarium and put a flock of more fish there.


Plant plants in the aquarium: sagittaria, cabomba, vallisneria, echinodorus, cryptocoryne, heleocharis, myriophyllum, Java moss or ferns. They will saturate the water with oxygen in case of problems with aeration. Leave a clear space at the front glass of the tank so that the fish can swim freely there. Intense lighting is recommended, 10-12 hours a day fluorescent lamps. Sunlight is allowed for several hours a day. Aeration inside the reservoir must be constant, filtration - due to internal filter with weak water flow.
Permissible water temperature: 22-25 o C, although zebrafish can tolerate more wide ranges temperatures Warm water reduces the level of oxygen in the water, but it promotes the rapid development of eggs and fry. Also elevated temperature the aquatic environment serves as a stimulation for spawning.
See how the zebrafish spawns.
Once a week, replace 20% of the water in the aquarium with fresh and clean water, do not forget to infuse it and measure the parameters with a water thermometer and an indicator of acidity and hardness. Recommended water hardness is 5-15 o, acidity is 6.5-7.5 pH. Brachydanio rerio eaten different types feed: live, plant, artificial. Food must be chopped. Bloodworms, tubifex, coretra, daphnia, cyclops, insect larvae, ciliates are mandatory food containing protein. You can feed it with crushed egg yolk, branded food in the form of flakes and granules. Aquarium fish will not refuse finely chopped plant foods - lettuce, nettles, dandelion, spinach.
IN general aquarium Brachydanio rerio easily gets along with small fish, which have a calm and peaceful character. Corydoras catfish (speckled, panda), tetras, minors, rasboras, neons, and ternets are suitable as neighbors. Cannot be kept with goldfish, barbs, large cichlids, swordtails, large catfish.
What types of Brachydanio rerio are there?
Due to the hardiness of zebrafish embryos, they are used as material in the field of genetic engineering. The result is the emergence of new forms of fish with different fins and body colors. The most famous breeding forms are “Glofish”, with veil fins and a leopard print color. There are also other breeds.


Danio rerio with a mutant body color (Bleached blond) were obtained after manipulations by insertional mutagenesis. The hybrid form of the fish has lost its standard color with black pigment in melanocytes due to the inability to produce melanin. Wild Danio rerio in the first days of life (fry) have a dark body color, and hybrids of this form are born translucent.
Danio rerio Glofish are genetically modified fish whose bodies glow thanks to bioluminescence genes. The first hybrids appeared in 2003, and now they are found in many aquariums around the world. Thanks to the introduction of jellyfish DNA, the fish emit a glow. The forms of such fish with different shades of skin have been developed.
Danio kyathit (orange-finned) is a modified form of zebrafish, a model object for research. The color of the fins is yellowish, the edges have an orange edging. The fish is small, up to 5 cm in length. The body color is orange with horizontal blue stripes. The tail fin is translucent, with a blue shimmer.
Family Cyprinidae
Habitat
In the wild, zebrafish live in the upper layers of coastal standing ponds or slow-flowing rivers in Southeast Asia. Usually this fish swims between the stems of aquatic plants or shore grasses hanging into the water. Here it is easiest for zebrafish to find their favorite prey - small invertebrates. Here the fish spawn, laying eggs in dense thickets of coastal plants.
Body size and shape
The narrow body of zebrafish reaches about 5 cm in length. At the corners of the mouth there is a pair of small antennae directed towards the bottom. Females differ from males in having a fuller abdomen.
Color
Danios have an original striped coloration. Throughout the body, starting at the gill covers, they alternate from straw-yellow or yellow-green to black-blue and extend to the caudal and anal fins. The widest stripes on the zebrafish's body are located in the middle part of the body, they are especially pronounced in females. Towards the head and tail the stripes become narrower. The zebrafish's fins have a light yellow tint, and the rear end of the dorsal fin has a dark stripe along the edge.
Danio rerio is one of the most commonly found fish in private aquariums. It is very mobile and unpretentious fish, able to live comfortably even in small aquarium. A 5-6 liter container can comfortably accommodate 3-5 fish.
As in natural conditions, in an aquarium zebrafish usually stay in the middle and upper layers of water. They can often jump out of fright, and therefore it is better to cover the aquarium with a tight lid. Typically, zebrafish live in a school of about 8-10 fish. Male zebrafish constantly playfully chase each other, moving quickly around the aquarium. Due to the fact that these fish need to constantly move, you should choose an aquarium that is slightly elongated in length. And it is also better to plant it densely along the edges with vallisneria, sagittaria, myriophyllum, heleocharis, cabomba and other plants. On the side of the aquarium from which it is most convenient to watch the fish, you should leave a free area where the fish can frolic. You should also give them food there. Due to the dense vegetation, the aquarium should be equipped with good lighting.
Requirements
Danios are extremely indifferent to changes in water temperature, and can easily tolerate its gradual decrease to 15°C and increase to 30°C. However, for keeping breeders, as well as for fry, a temperature of 21-25°C is recommended. With further heating of the aquarium, the ability of the fish to reproduce increases, but the amount of oxygen in the water greatly decreases, therefore, at this temperature, regular strong ventilation of the aquarium is required. For a comfortable life for zebrafish, a weekly change of 10-15% of the water volume is necessary. pH 6-7.5; dH 3-15°. This fish feeds mainly on small live and dry food.
Reproduction
Puberty in Daneo rerio occurs at 3-6 months, given the lifespan of these fish is 2-3 years. However, it is quite difficult to achieve spawning in them, although zebrafish are able to reproduce at any time of the year. To begin with, you should separate the males and females for several days, placing them in spacious aquariums (from 10 liters) with a water temperature of 20 °C and feeding them generously with bloodworms or live red daphnia. The female's readiness for spawning is determined by the shape of the abdomen - when the eggs mature, it becomes very thick not only in the anterior part, but also in the part adjacent to the anal fin.
Directly for spawning, you should choose small containers with a transparent glass bottom (for example, glass jars or aquariums of 3-10 liters). It is better not to put sand on the bottom, so that it is convenient to observe the hatching and development of eggs. If the selected vessel has a flat bottom, then it should be covered with well-washed topnyak or fontinalis, carefully pressed down with pebbles. In jars or vessels with a concave bottom, moss is placed in a ring along the outer edge of the bottom, also carefully pressed with stones. The spawning area is filled with water from a clean aquarium, passed through a siphon, or with fresh, settled water. The water level in the spawning area should be at least 5-8 cm, so that 3-4 cm of free space above the moss remains. The vessel itself is best placed on a windowsill or near a window. Producers (usually 2-3 males and one female) are planted in the spawning area in the evening.
The water temperature is not particularly important, but it should not be too low. Overnight the fish will get used to the new “nest”, and when the next morning the spawning area is well lit and the plants begin to actively release oxygen, spawning should begin. The fish begin to move very quickly, rushing around the aquarium with lightning speed. The males chase the female, trying to hit her in the abdomen, knocking out the eggs and releasing milk on them. The tags follow one after another with breaks of no more than 5 minutes, and the whole process usually takes about an hour.
The amount of eggs spawned from one female depends on its size and degree of preparedness for spawning, and reaches 400 eggs. After marking is completed, the males should be removed, but after 7-10 days it will have to be repeated, otherwise the eggs will become overripe and fry will not be produced. It happens that the female refuses to spawn at all, but usually one female zebrafish can give birth to 5-6 litters in a row.
Sometimes, after landing for spawning, the female hides and does not respond to males. This may mean either that the caviar is underripe, or vice versa. If the abdomen of a non-spawning female is not too large, it is better to remove her and feed her generously for several days. In a plump female that refuses to spawn, you have to squeeze out the eggs by wrapping the fish in wet cotton wool and gently pressing with your fingers. If everything is done correctly, after 4-5 days the female will collect new eggs and can be spawned again. In the opposite case, when males do not begin rutting in front of an active female within 2 days, the producers should be placed in a container with more high temperature water and feed intensively until they begin to actively chase each other.
To ensure that the eggs do not overripe, during the periods between spawnings, keep the zebrafish intended for tags in water at a temperature of no more than 17-19°C, feeding them a small amount of food.
Caviar usually matures in 30-36 hours at 26-28 °C; at lower temperatures, ripening can take up to 7 days. The hatched fry hang for several days, attached to plants or the walls of the aquarium, and then gradually begin to swim. In the first days, zebrafish fry are fed ciliates or “live dust”, then as they grow they can be switched to more large feed and move to a larger aquarium. Optimal temperature water for good development of young zebrafish - 26-27 °C with plenty of feeding. After 2.5-3 months in such conditions, the fish reach sexual maturity.
Danio rerios belong to the Karpov family. In their natural habitat, they live in rivers and streams on the east coast of India, Bangladesh and Nepal. Russian aquarists first became acquainted with this fish in 1905. They came up with other names for it: “ladies’ stockings” and “stripes,” “danya” and “zebras.”
Danio rerios have an elongated body. Along it are yellow-green and dark blue stripes. They alternate with each other.
Young representatives of this fish species have short fins. As the fish grow, the fins become veiled and give an enchanting appearance to their owners. The edges of the fins are yellowish in color.
The body length of Danio rerio in nature reaches 6-7 cm. And in an aquarium they grow up to 5 centimeters.
Males are much slimmer than females and more attractive with their rich colors. Females have a thicker abdomen. These fish live up to five years and become sexually mature at 6 months of age.
By the way, in 2003, a genetically modified breed of Danio rerio was developed - fluorescent. This is a glowing fish that was injected with a fragment of jellyfish DNA.
Danio rerio fish are quite peaceful and unpretentious. As for the requirements for the water in which they are kept in the aquarium, it is better that its hardness is neutral. The temperature can be from 15 to 30 degrees.
The fish are not picky about the volume of the aquarium. Even a three-liter jar will suit them, but better, of course, is a 15-liter aquarium. Since these are schooling fish, it is recommended to keep them at least in groups of four.
It is better to cover the bottom of the fish house with a layer of granite chips or small stones. Large river sand will do as a soil.
It is better to take long-leaved plants. For example, Vallisneria or Heleocharis, Sagittaria or Cabomba.
It is advisable to cover the aquarium with a lid, because these are quite jumping and active fish.
Danio rerios get along with all types of peace-loving fish: Guppies and Swordtails, Rasboras and Tetras, Barbs and Neons.
The feeding of these fish is normal. They are omnivores, but love live food. Suitable food for them is daphnia and cyclops, small bloodworms. A particularly favorite delicacy for Danio rerio is scraped meat.
Reproduction
Reproduction of these fish is hassle-free. A week before spawning, you need to separate the males and females. They should be fed generously, and it is advisable to use coretra.
The spawning ground can be a 10-liter container, the bottom of which must be covered with pinnate or fontinalis. It is recommended to press down the plants with pebbles so that they do not rise from the bottom of the spawning tank. It is mandatory to have a net to prevent the female and male from eating the eggs. Water for spawning should be left for two days.
It is better to plant one female and 2-3 males in the spawning area. The female's readiness for spawning is her thickened abdomen.
Spawning occurs in the morning with the first rays of the sun. On average, the female lays up to 400 eggs.
After spawning, the spawners are removed as usual. After 3-4 days, the eggs turn into larvae. They hang on the walls of the spawning tank for several days. Then the larvae become fry. Young Danio rerios need to be fed with ciliates, rotifers, and nauplii. A hard-boiled egg yolk will also work. Adult fry can already be given daphnia and cyclops. As the fry grow, the Danio rerio should be transferred to a larger aquarium.
Important point! After spawning, the spawned female should be replanted for spawning after 10 days. If this is not done, she may lose her reproductive functions.
Zebrafish are small and very active pets that prefer to live in schools. This species was one of the first to be introduced into home aquariums. The fish are easy-going, unpretentious, interesting to watch, and even a beginner can cope with breeding.
Description
The zebrafish was first described in 1822. Its homeland is the reservoirs of Asia, Nepal and Budapest. The fish has many color options and fin shapes. From the photo you can understand how diverse this species is.
The zebrafish body has an elongated shape, flattened on both sides. There are four whiskers around the lips. Distinctive feature are blue and white stripes that begin at the gill covers and end at the caudal fin. The anal fin is also decorated with stripes, but the rest are completely colorless. Maximum length especially for adults - 6 cm, but they rarely reach such sizes in aquariums. Life expectancy is short - up to 4 years. It is recommended to keep at least 5 individuals in one aquarium.
Varieties
After looking at the photo, you can guess that these fish have many varieties. However, only the zebrafish has been genetically modified. Such representatives are also called GloFish. A fluorescent element was introduced into the genes of these fish. This is how pink, green and orange zebrafish appeared. They are distinguished by their bright color, which becomes more intense under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The content and behavior of this variety is no different from the classic one.
The red color was obtained by introducing coral DNA, green fish became thanks to the genes of the jellyfish. And representatives possessing these two DNAs turn out yellow-orange.
Be sure to include plants, but place them in one corner to give the zebrafish plenty of room to swim. Provide good lighting.
Water requirements:
- Temperature – from 18 to 26 degrees.
- Ph – from 6.6 to 7.4.
In their natural environment, fish feed on plant seeds that fall into the water, small insects and their larvae. At home they become almost omnivores. Any live, frozen or artificial food will suit them. Preference is given to brine shrimp and tubifex. Please note that they only catch pieces of food from the surface of the water. Everything that sinks to the bottom will remain there.

Who should you choose as your neighbor?
The aquarium fish zebrafish is not at all aggressive, so it can get along with almost any neighbors. In a flock they can chase each other, but this is a manifestation of hierarchical relationships that do not extend to other species. Danios are perfect for keeping in a community aquarium. They will not cause any harm even to slow and calm species. The main thing is that there are no predators among the neighbors who could perceive small fish as food. It is noticeable in the photo that zebrafish are extremely miniature, but, thanks to their speed and non-conflict nature, they can get along even with such aggressive neighbors as cichlids (small ones), gourami, and angelfish.
They go well with small fish - guppies, macropods, rasboras. Ternetias, cardinals and nanostomuses are also suitable as neighbors.
Preparing for spawning
Breeding zebrafish is a simple process that even a beginner can handle. The fish reach sexual maturity at 4-6 months. And you can start breeding them at any time of the year.
Before spawning begins, zebrafish are moved to large aquarium(from 10 liters), the water temperature should be above 20 °C. You need to feed the fish abundantly. Red daphnia and bloodworms are excellent for these purposes. The food must be live.

Soil in the spawning tank is optional. Many aquarists specially select containers with a transparent bottom in order to monitor the spawning and formation of larvae. But you can’t leave it completely empty. The bottom is covered with topsoil or fontinalis, which is necessarily pressed down with something. Water for the spawning tank is taken from a common aquarium where the fish constantly live. Be sure to install a siphon in the container. It is better to place the aquarium on a windowsill so that there is access to direct sunlight.
Several males and one female are selected for breeding. It is better to place them in the spawning tank in the evening. During the night they will be able to get used to the new place, and in the morning, when it dawns, spawning will begin.
Breeding
Let’s continue the topic “zebrafish – reproduction”. It is very interesting to watch the spawning process. The fish move extremely quickly around the aquarium, literally fly. When the male manages to catch up with the female, he hits her in the belly, from which eggs fly out, and releases milk himself. Spawning lasts about an hour. During this time, several marks may occur with intervals of 6-8 minutes. During this time period, the female can lay from 60 to 400 eggs.
You can also place two females in a spawning tank, but then you will get fewer offspring. Therefore, if you want to get more fry, prepare several breeding tanks.
When spawning is over, males and females are removed from the “nest” and seated in different containers. The mark is repeated after a week, otherwise the caviar will become overripe. For one female it is normal to have up to 6 litters. If during spawning she hides from the male, then her eggs are not yet ready or are already overripe. In any case, the fish are left in the spawning tank for another two days.
The incubation period lasts two days. Then the fry are born, they can be seen in the photo below. They are very small, so you need to be extremely careful when cleaning the aquarium. At first, the cubs are fed ciliates and egg yolk. As babies grow, they are switched to more food.