Pharmacy No. 10 in Krasnoyarsk from the group of oral contraceptives contains the following low-dose drugs that do not cause side effects: Mercilon, Marvelon, Novinet, Regulon, Logest, Femoden, Lindinet, Exluton. These oral contraceptives belong to the combination and gestagen-containing “mini-pill” drugs. Determine the breadth, breadth and depth coefficients for this pharmacotherapeutic group.
Sample answer:
Stage 1. We identify the main product lines (assortment groups, subgroups and product names) in the product range under study at pharmacy No. 10 in Krasnoyarsk.
1.1. We identify the main product line by assortment group - oral contraceptives among contraceptives and enter it in the “name of assortment group” line of the table.
1.2. We select assortment subgroups and enter them in the “name of assortment subgroup” line of the table.
1.3. We select the name of the product (variant of the product unit) and enter it in the “trade name of the product” columns of the table.
Stage 2. We analyze the assortment in the pharmacy in terms of breadth, completeness and depth.
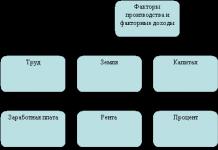
2.1. We determine the breadth of the assortment.
2.1.1. We establish the name and number of the studied product lines (assortment groups) available in the pharmacy’s trade assortment - Sh f, and their total number in the industrial assortment according to OKP or the State Register - Sh b.
Table 1. Product lines of the studied product nomenclature in the sales range of pharmacy No. 10 in Krasnoyarsk.
|
Name of assortment groups in the trade assortment 1. Oral contraceptives The industrial assortment includes 8 product groups |
|||
|
Name of assortment subgroups in the trade assortment 1. Combined oral contraceptives 2. “Mini-drink” The industrial assortment includes 3 product subgroups. |
|||
|
1. Combined |
2. “Mini-drink” |
||
|
Trade name of the product |
Trade name of the product |
||
|
Mercilon |
Exluton |
||
|
Marvelon |
|||
|
Lindinet |
|||
2.1.2. We calculate the latitude coefficient Kw using the formula:
K w = W f / W b = 1/8 = 0.13
We enter the results in column 2 of the second table.
2.1.3. Conclusion: the breadth of assortment is low.
2.2. Determine the completeness of the assortment:
2.2.1. We establish the number of assortment subgroups in the retail assortment of the pharmacy - P f according to the situational problem and the total number of assortment subgroups in the industrial assortment according to OKP or the State Register - P b.
K p = P f / P b = 2/3 = 0.67
Enter the results in column 3 of the second table.
2.2.3. Conclusion: the completeness of the assortment is satisfactory.
2.3. Determine the depth of the assortment.
2.3.1. We establish the number of product units for each assortment subgroup according to the situational problem in the pharmacy’s trade assortment (G f) and the total number of product units according to OKP or the State Register - G b.
2.3.2. We calculate the depth coefficients K g for combined OK and “mini-pill” using the formula:
For combined OK: K g = G f / G b = 7/29 = 0.24
For the “mini-pill”: K g = G f / G b = ½ = 0.5
We enter the results in column 4 of the second table.
Table 2. Results of analysis of the assortment of oral contraceptives in pharmacy No. 10 in Krasnoyarsk.
2.3.3. Conclusion: for combined oral contraceptives the depth coefficient is low, but for the “mini-pill” it is sufficient.
Stage 3. Conclusion: in order to individually select a drug according to a woman’s phenotype, it is necessary to introduce more oral contraceptives of different qualitative and quantitative composition into the assortment.
Abstract of the dissertationin pharmacology on the topic Marketing research on the consumption and demand of contraceptive medicines (using the example of the Caucasian Mineral Waters region)
As a manuscript
Ivchenko Olga Grigorievna
MARKETING RESEARCH OF CONSUMPTION AND DEMAND OF CONTRACEPTIVE MEDICINES (BASED ON THE EXAMPLE OF THE CAUCASIAN MINERAL WATER REGION)
Specialty 15.00.01 - drug technology and organization of pharmaceutical business
dissertation for the degree of candidate of pharmaceutical sciences
Pyatigorsk 2002
WORK WAS COMPLETED AT PYATIGORSK STATE PHARMACEUTICAL ACADEMY
RESEARCH SUPERVISOR: Candidate of Pharmaceutical Sciences, assistant professor
GATSAN V.V.
OFFICIAL OPPONITORS: Doctor of Pharmaceutical Sciences,
General Director of NPO Pulse L. M. KUZYAKOVA; Candidate of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of UEF FPO LAAS A. A.
LEADING ORGANIZATION: Kursk State Medical
university
The defense will take place on March 05, 2002 at 9:00 a.m. at a meeting of the dissertation council D 208.069.01 for the defense of dissertations at the Pyatigorsk State Pharmaceutical Academy (357532, Pyatigorsk-32, Kalinina Ave., 11)
The dissertation can be found in the library of the Pyatigorsk State Pharmaceutical Academy (Kalinina Ave., 11)
General characteristics of work
The relevance of the topic. In the public health system, recent decades have been characterized by increased attention to the problem of family planning. Since the adoption of the WHO Declaration of Alma-Ata (1978), maternal and child health, including family planning, has been considered an essential element of primary health care to ensure the preservation of public health. Family planning in its modern sense is the control of reproductive function for the birth of only desired children. Rational reproductive behavior takes into account the age, health status, financial capabilities of the parents, and optimal intervals between births. Family planning programs are involved in solving medical, demographic and social problems of our time.
The particular importance of the problem of family planning and birth control in the Russian Federation is associated with a general deterioration in the health of the population, poor medical and demographic indicators, and a decline in material well-being and living standards of some segments of the population. Recent years have been characterized by a low birth rate - about 33 births per 1000 women of fertile age per year. At the same time, the number of abortions exceeds the number of births by 1.8 times. Statistics on the number of abortions in Russia indicate that modern methods of contraception are currently used in Russia extremely insufficiently to ensure the existing level of fertility.
Family planning, as a targeted state program of the Russian Federation, began to operate in 1993. In 1992, the Russian Society for Contraception was created, which, together with the Russian Family Planning Association, is designed to solve national problems of family planning and contraception.
One of the necessary conditions for the implementation of a family planning program is the improvement of drug supply with modern contraceptives, especially hormonal contraceptives.
tives, which are the most common and common means of family planning in the world. The market nature of the supply of contraceptives requires a marketing approach and marketing research, as the most modern methodology for studying the drug market, in order to improve the drug supply to the population.
The Caucasian Mineral Waters (CMW) region, which is part of the Stavropol Territory, is influenced by the main factors of the economic, political, political and national policies of the Russian Federation. But at the same time, the geographical location of the region also determines the greater complexity of the social and economic problems facing the population of the Caucasian Sea. The way of life and thinking of the population of the region is influenced by the peculiarities of the national mentality of the neighboring republics of the North Caucasus, the diverse national composition, and a large number of mixed marriages. All this affects, among other things, reproductive behavior and the use of contraception and makes the CMS region unique and interesting for studying the level of development of the problem of family planning and contraceptive drug supply.
The theoretical foundations of marketing research of the drug market (JIC) were developed by scientists: L.V. Kobzarem, N.B. Dremovoy, P.S. Skulkova, S.G. Sboevoy, Z.G. Maksudova and others. Marketing research on family planning and contraception was carried out in various regions by O.I. Knysh, O.A. Vasnetsova, G.F. Lozovoy, A.Yu. Karimov, Zh.V Mironenkova, N.Yu. Baranova et al. However, an analysis of the available literature showed that no studies have been carried out on the demand and provision of contraceptive drugs to the population of the KMS region.
Thus, all of the above has determined the relevance of conducting a set of marketing studies of the pharmaceutical market of contraceptive JICs in the CMS region. This determined the main goal of our research and the formulation of specific tasks to achieve this goal.
Purpose and objectives of the study. The purpose of this study is to develop scientifically based methodological approaches to optimization of
distribution of contraceptive drugs to the population in the Caucasian Mineral Waters region using marketing methods.
To achieve this goal, the following tasks were identified:
■ study the current state of medical and drug support for the problem of contraception;
■ analyze methods for conducting marketing research in relation to the contraceptive market;
■ conduct a retrospective analysis of the reproductive behavior of the population of the Caucasus and the dynamics of the use of basic contraceptive drugs;
■ conduct sociological research among women of fertile age, as the main consumers of contraception;
■ study the supply of contraceptive drugs to the regional CMV market;
■ conduct an expert assessment of contraceptive drugs using two groups of experts (gynecologists and pharmacists), and carry out a scientifically based selection and compilation of a list of main drugs used for contraception;
■ make a forecast of the need for hormonal contraceptives in the CMS region for the period up to 2003;
Scientific novelty of the research. Methodological approaches have been developed for conducting comprehensive marketing research of the regional market of drugs used for contraception.
Using statistical and sociological methods, a study of consumers of contraceptives was conducted, which made it possible to determine
to divide consumer preferences and requirements for family planning products, segmented consumers by income and determined the characteristics of each segment.
Using content analysis and the comparison method, the assortment of contraceptives on the regional pharmaceutical market, its structure, completeness, and degree of renewal were studied. Using the method of expert assessments, we will determine the optimal range of drugs used for contraception.
A methodology for determining the future need for contraceptive drugs using a normative method has been proposed, standards for the consumption of hormonal contraceptives have been developed, and a demand forecast for the period up to 2003 has been compiled.
Practical significance of the work. The developed methodology for conducting marketing research of the contraceptive market allows us to determine the assortment structure, consumer preferences, demand trends and predict the future need for hormonal contraceptives. The results obtained during the study make it possible to improve the drug supply of contraceptives in the CMS region.
Implementation of work results. Based on the research conducted, “Methodological recommendations for conducting marketing research of the market of contraceptive medicines” were developed, which were introduced into the practical activities of family planning offices, antenatal clinics and other medical institutions, as well as wholesale and retail pharmacy enterprises of the Stavropol Territory, the Republic of Adygea, Karachaevo Circassian Republic, Rostov region, Krasnodar region.
Approbation of the obtained results. The main results of the dissertation research were reported and discussed at the 53, 54, 55, 56 regional conferences on pharmacy, pharmacology and personnel training of the Pyat State Physics Faculty (Pyat
Tigorsk, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2001). In general, the dissertation work was reported at the interdepartmental conference of the Pyatigorsk State Pharmaceutical Academy (Pyagishrsk, November 2001).
Provisions submitted for defense. The following provisions and research results characterized by scientific novelty are put forward for defense:
■ methodology for conducting marketing research on the regional market of contraceptive drugs;
■ results of analysis of the state of contraception in the territory of the CMS;
■ results of sociological studies of the main consumers of contraceptives (women of fertile age);
* results of expert assessments of the nomenclature of contraceptives;
Mathematical models that allow predicting the number of users of hormonal contraceptives;
■ forecast of the need for hormonal contraceptives for 2001 - 2003.
Volume and structure of the dissertation. The dissertation consists of an introduction, four interconnected chapters, conclusions, bibliography and appendices. The bibliographic index includes 200 literary sources, including 25 in foreign languages. The work is presented on 141 pages of typewritten text, contains 26 tables and 16 figures.
CHAPTER 1. ORGANIZATION OF MEDICAL AND DRUG PROVISION OF CONTRACEPTION
The study and synthesis of available literature data and departmental materials shows that currently in the public health system of the Russian Federation, the problem of contraception is of particular importance due to low birth rates and high abortion rates.
A significant impact on the birth rate is exerted by the difficulties of economic transformations, significant differentiation of the monetary incomes of the population.
leniya. However, it becomes obvious that there has been a “restructuring” of the reproductive behavior of the Russian population, which cannot be associated only with a reaction to the social and economic crisis. Therefore, it is expected that in the coming decades the total fertility rate will fluctuate only slightly, not exceeding 1.3 births per woman.
At the same time, in Russia to this day there is often a negative attitude towards the problem of family planning. This leads to the fact that the frequency of abortions in Russia is much higher than in most countries of the world. The high number of abortions leads to decreased reproductive health indicators, infertility, and high maternal and infant mortality rates, which are several times higher than in Western countries. The number of normal births in 1999 was 31%, the rest occurred with some kind of abnormality for the mother or child.
The only reliable and effective means of preventing unwanted pregnancy and reducing the number of induced abortions is the use of modern methods of contraception. A study of world statistics shows that the frequency of abortions is inversely proportional to the frequency of use of modern contraceptives.
Contraceptives are a special type of pharmaceutical product. The main consumers of these drugs are not sick people, but those who show a desire to consciously approach family life, have children and maintain health. The need for contraceptives depends on the general culture and culture in the field of reproductive behavior and is formed through health education work with the population. In recent years, there have been slight positive changes in the attitude of doctors and consumers to the problem of contraception. The consumption of hormonal contraceptives, the most promising means of family planning, is growing.
Study of existing methods for conducting marketing research of contraceptives and regional characteristics of reproductive
This behavior on the CMS necessitates the development of methodological approaches to conducting comprehensive marketing research of the regional market of contraceptive drugs, during which the main aspects of the pharmaceutical market are studied - consumers, goods and the market itself (sales).
CHAPTER 2. Marketing research studies
consumers of contraceptives The study of consumers of contraceptives consisted of an analysis of medical and demographic indicators and sociological studies. The analysis of medical and demographic indicators was carried out over 7 years (1994-2000). In table Table 1 presents the main indicators of reproductive behavior and the use of contraception in the studied region.
Table 1
Indicators of reproductive behavior and the use of basic means of coitracception! residents of the KMS region (per 1000 f.w.)
Indicators 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000)
Fertility 43.0 44.3 40.0 40.1 39.9 37.0 39.2 |
Claim abortions 65.0 69.1 63.0 55.8 56.6 55.3 48.8 1
Application of KS 188.4 202.5 216.9 207.6 206.3 190.1 182.9
VT. including Navy; 146.2 149.5 151.8 138.8 123.6 105.0 91.1
GCS 42.2 53.0 65.1 68.8 82.7 85.1 91.8 |
As follows from the data in table. 1, the birth rate in the studied region tends to decrease. In 1996-2000 per 1,000 women of fertile age in the region there were about 40 births per year. In 1999, there was a decrease in the birth rate, which can be explained by the reaction to the economic crisis in August 1998. The highest birth rates were observed throughout the entire study period in the city of Essentuki (in 2000 - 57.0 births per 1000 women of fertile age). And, on the contrary, the lowest birth rate was noted in the city of Mineralnye Vody (27.1 births per 1000 women of childbearing age
age). In the CMS region, the birth rate is higher than in the Russian Federation as a whole (by 18%), but lower than in the North Caucasus region (by 7% according to 1998 data).
Analysis of statistical data showed that in the CMS region, as in the country as a whole, induced abortions are widespread. About 60% of all pregnancies in CMS end in induced abortion. The largest number of induced abortions is typical for the city of Essentuki, the smallest for Kislovodsk and Zheleznovodsk. During the studied period, there was a decrease in the number of abortions in all cities of the KMS region, especially in the city of Zheleznovodsk (2.6 times). But in the region as a whole, the number of abortions decreased during this period by only 23%. Abortion rates in the Kavminvodsky region are higher than similar indicators throughout the North Caucasus region (by 5%), but lower than the average for the Russian Federation (8%).
It has been established that the main contraceptive methods taken into account - intrauterine devices (IUDs) and hormonal contraceptives (HCS) - are used by about 18.3% of women of childbearing age, which is a low figure. During the studied period, the ratio of these two methods changed in favor of hormonal contraception The use of IUDs in the CMS region decreased by 1.57 times, and the use of GCS increased by 2.22 times. In 2000, the use of IUDs and GCS was approximately equal. The total number of women using modern contraceptives decreased slightly due to a decrease in the use of IUDs. .
For the purpose of sociological research of consumers of contraceptives, we developed a special questionnaire and conducted a survey of women of fertile age living in urban and rural areas of the CMS region. A total of 500 women's responses were used for analysis.
The study found that the most popular contraceptive method is the condom, followed by the IUD and GCS. A large number of respondents used traditional methods of contraception, the reliability of which is low. The results of the analysis of the attitude of interviewed women towards hormonal contraceptives are shown in Fig. 1.
Attitude towards the GCS of residents of the KMS
Decided negatively to take GCS
It should be noted that there is a large proportion of women who have a negative attitude towards GCS. However, in recent years there has been an increase in the popularity of this type of contraception, especially among young people. In addition to those who already use GCS, 23% of women surveyed intend to use them in the future. This segment may become even larger due to those who have not decided on their attitude towards hormonal contraceptives. In Fig. 2 presents the results of an analysis of the reasons preventing the use of GCS.
Prnchshp.1, preventing the use of GKS
0 high price 0 individual, contraindications
Sh insufficient choice in pharmacy 0 others
As shown in Fig. 2, the most frequently cited concerns were fear of side effects, lack of information, and high cost.
When combining the main demographic characteristics of respondents with their attitude towards the Civil Code, we identified the following patterns:
1) with increasing income, the use of GCS increases; they are most often used by women whose monthly income per family member exceeds the subsistence level;
2) the level of patients using corticosteroids among urban residents is higher than in rural areas;
3) with an increase in the level of education, women’s awareness of modern contraceptives and the proportion of GCS use increases;
4) women over 35 years of age are more conservative in their views on hormonal methods of contraception. In contrast, women under 25 years of age are much less susceptible to prejudice in this area and are more likely to express their intention to use this method of contraception.
In order to determine typological models of consumer behavior in the contraceptive market, consumers were segmented by income and the characteristics of the selected segments were determined. Segments with an average monthly income of 1 to 2 subsistence minimums per family member per month are the most promising in terms of creating the need for civil society, which is due to their large population, optimal age composition and sufficient purchasing power. The main barriers to using hormonal contraception are lack of information and fear of side effects. In these segments, we consider it advisable to carry out more intensive information work on the use of GCS.
CHAPTER 3. ANALYSIS OF THE NOMENCLATURE OF MEDICINES USED FOR CONTRACEPTION
To study the range of contraceptive drugs presented on the pharmaceutical market of the region under study, we used direct sample observation using the main array method. Unit per-
Observation was the assortment of pharmacies and wholesale intermediary organizations. The range of contraceptive drugs actually present on the pharmaceutical market of the CMS region is significantly narrower than the list of this group of drugs officially registered in Russia. For the marketing characteristics of the assortment, the assortment completeness coefficient was calculated. In the Russian Federation, 41 drugs are registered and approved for use as GCS. There are 23 types of GCS in KMV pharmacies, so the assortment completeness coefficient was only 0.56.
The entire available range of GCS consists of 78% combined estrogen-progestin drugs, mono-, two- and three-phase; 13% - drugs containing microdoses of progestogens (shshi-pndi), 4% - postcoital drugs, 4% - injectable and implantable depot drugs.
Almost the entire range is represented by imported drugs. The main manufacturers represented on the regional GCS market are shown in Fig. 3:
The main manufacturers of GCS in the pharmaceutical market of the CMV region
Other 18%
Jenaferm (Germany) 13%
Organon (Holland) 13%
Gedeon Richter (Hungary) 30%
Schering (Germany) 26%
The clear leaders of the GCS market are the companies Gedeon Richter and Schering. The number of companies supplying 1 type of GCS each includes Searle (USA), Silag (Switzerland), Upjohn (Belgium), Leiras (Finland).
To characterize the dynamism of the contraceptive drugs market, an assortment renewal index was determined. For 3 years (1998-2000) it amounted to
0.26, which is quite high. The pharmaceutical market in the region is actively introducing new contraceptives and rapidly updating the range.
At the next stage of research, an expert assessment of the competitiveness of available contraceptives was carried out to determine the preferred composition of the range, guaranteeing high quality of drug services to the population. Two groups of experts were involved: gynecologists and pharmacist specialists who assessed contraceptive drugs from different professional positions. Assessments of contraceptives by two groups of specialists should complement each other, although due to the fact that GCS are prescription drugs, the opinion of doctors is more significant.
To increase the reliability and validity of the method, the competence of each expert was determined according to the methodology we developed. For this purpose, the responses of potential experts to the first group of questions (about professional data) were used. The methodology for determining the competence of experts is presented in Table 2.
Table 2
Determining the competence of experts _____
Coefficient Method of determination
Kdaf. using the nomenclature Kk 2 A+B K = - N N
Expert awareness coefficient Co A+C co=- and N
Coefficient of acquired experience Kop - work experience less than 3 years - K0p = 0.1; - work experience from 3 to 5 years - K0p = 0.3; - work experience from 5 to 8 years - K0p = 0.5; - work experience from 8 to 10 years - Cop = 0.8; - work experience over 10 years - Cop = 1.0
Qualification level coefficient Kkv - second category - Kkv = 0.1; - first category - Kkv = 0.2; - highest category - Kkv = 0.3.
General competence coefficient Kk Kk = Kn + Ko + Kop + Kkv
where A is the number of drugs used by the expert most often; B - the number of drugs rarely used by the expert; N is the total number of contraceptive drugs present on the pharmaceutical market of the region.
C is the number of new contraceptive drugs introduced by the expert into practice over the past 3 years.
Quantitative assessment of competence is carried out on the following scale:
Kk< 1,5 - малокомпетентные эксперты;
Kk from 1.5 to 2 - competent experts;
Kk > 2 - highly competent.
Only competent and highly competent experts were used for expert assessments. The average competence coefficient was 2.18.
The study of assessments by experts of different groups of the weight of the parameters of the competitiveness of contraceptives was carried out using the ranking method. The results of the analysis are compared with the data of a sociological survey and are presented in table. 3.
Table 3
Ranks of competitiveness parameters of cotraceive drugs for various groups of experts and consumers
No. Competitiveness parameters rank by degree of importance
for the public for experts
pharmacists
1. High efficiency 1 1 1
2. Ease of use 3 3 2
3. Side effects and contraindications 2 2 3
4. Release form 7 7 6
5. Directions for use 5 5 5
b. Brand prestige -- 10 9
7. Price 4 4 4
8. Interaction with other drugs - b 8
9. Conditions of use (doctor's help) 6 8 7
10. The need for honey. control - 9 10
For all groups of respondents, the main property of contraceptives is their high efficiency in use. Second and third places were shared by minimal side effects and ease of use. Price ranks only 4th.
In order to determine the optimal range of contraceptive drugs, estimates of the frequency of prescription (for doctors), supply and demand (for pharmacists) and consumer properties of available contraceptives were studied. For statistical analysis of the obtained data, the method of “weighting expert assessments taking into account the competence of experts” was used.
Determining the optimal range of drugs used for contraception, which is given in Table. 4, we took into account, first of all, high estimates of frequency of appointment, demand, and consumer properties.
Table 4
Optimal nomenclature of drugs used for contraception
Group Medicine
Monophasic drugs first- 1. Non-ovlon
th generation
Monophasic drugs second- 2. Ovidon 1
th generation 3-4. Rigevidon (Microgynon) |
Biphasic drugs 5. Anteovin I
second generation
Three-phase drugs 6. Triquilar
second generation 7. Tri-regol
8. Trnziston
Monophasic drugs third- 9. Marvelon
th generation 10. Mercilon
11. Femoden
12. Diana-35
13. Silest
14. Egestrenol
Postcoital drugs 15. Postinor
Progestogen drugs 16. Norkolut
Injectable and implanted - 17. Depo-Provera
washable depot preparations 18. Norplant
Spermicidal agents 19. Pharmatex
At the same time, the unique properties of some drugs were taken into account. Thus, Postinor received low ratings from expert doctors due to the severity of side effects, but since it is the only drug for emergency contraception registered in our country, it is not advisable to abandon it.
Preparations of the 1st and 2nd generations, despite the fact that oral contraceptives with a new progestogen component and a lower content of hormones appeared, have not lost their importance. Due to their higher content of active substances, they are more often prescribed for therapeutic purposes. In addition, they are in demand among consumers with low purchasing power due to their relatively low price.
The optimal range includes one drug from the group of spermicides - Pharmatex, which is available in several dosage forms and is in high demand. We consider it expedient to exclude Coptractin T, which received low expert ratings, since it is inferior in terms of the most significant parameter of competitiveness - reliability.
CHAPTER 4. FORECASTING PROSPECTIVE DEMAND FOR HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES
Currently, the ability to quickly determine needs using a small number of indicators is relevant. The accessibility and simplicity of the normative method allow it to be used at the level of medical and pharmacy institutions by persons who do not have special mathematical training. The advantage of this method is also the ability to take into account changes in factors influencing demand. Therefore, the normative method is the most appropriate for quickly determining the need for GCS.
When determining the need, the following indicators were calculated:
■ forecast of the number of GCS consumers;
■ coefficients of consumption intensity for each drug;
■ consumption of each drug for 1 year of use by one consumer.
The forecast for the number of consumers was made based on an analysis of the dynamics of GCS consumption by extrapolating existing trends. Anastic alignment was used, the task of which is to determine, on the basis of actual data, the type of function that describes the systematic component (trend) of the time series. The parameters of the demand function were found using the least squares method.
To select optimal equations for trends in time series, several types of correlation equations were considered. The obtained functions were assessed by the certainty indicator A", which reflects the proximity of the aligned trend line values to the actual data. Qualitative assessment of regression models was carried out by calculating the approximation coefficient, which characterizes the average relative value of the model error. The results of constructing regression models and their qualitative assessments are presented in Table 5 .
Table 5.
Regression equations for time series and their estimates
Time series Equation & calrox
Pyatigorsk city, = 273D86+ 39639-/ 0.903 8.6%
Min-Water y, = 116R0+272.86-/ 0.952 14.2%
Essentuki city, = 283471+ 372D4-1 0.938 6.9%
Kislovodsk city, = 283533*- 8938-1 - 67.55-^ + 19.44-g 0.867 6.5%
Lermontov u, =392.0+ 47.29-1 0.892 8.2%
Zheleznovodsk ~у, = 1335.95 +5.93-/-44.56-12 + 9.75 0.870 4.8%
The highest level of certainty was obtained with a linear trend form for the time series of the number of GCS consumers in the cities of Pyatigorsk, Mineralnye Vody, Essentuki, and Lermontov. For the cities of Kislovodsk and Zheleznovodsk, the most optimal was a polynomial approximation of the third degree with two extrema. All models have a high level
great certainty, and a satisfactory average error.
After selecting the regression equations, a forecast was made for 2001-2003. To do this, the values of / corresponding to the years of the forecast (point forecast) were substituted into the found equations. When extrapolating trends, the pattern of changes in deviations of actual levels from the leveled ones was also taken into account by calculating the average error, or confidence interval, of the forecast. An example of actual and forecast dynamic series, as well as prospective dynamics with confidence intervals, is presented in Fig. 4.
Analysis and forecast of the number of GCS consumers in Pyatigorsk
Number of people 7000
1 994 1 9 96 1991 2000 2002
Analysis of the dynamics series and the forecasts made from them allow us to conclude that the number of GCS consumers in all CMS cities will increase.
In order to determine consumption intensity coefficients, outpatient cards and prescription sheets of women using GCS were analyzed. To increase the reliability of the results, a comparative assessment of the consumption structure was carried out for two time periods and a comparison with the results of an expert assessment of the frequency of prescription and demand and a questionnaire-based survey.
th consumer survey. The calculated values of the correlation coefficients indicate a high correlation between the data. Thus, the data from studying the frequency of GCS prescriptions according to patients’ outpatient records are justified and significant.
Calculation of the consumption of each drug per year of use per person was carried out according to the use pattern. For tablet preparations: 1 cycle - 28 days, 13 cycles a year, in 1 package of tablets for 1 or 3 cycles of administration. For injectable drugs - 1 injection every 3 months, 4 injections per year.
Taking into account the fact that the annual increase in the number of consumers is planned, the calculation of the need for GCS was carried out using the following formula:
L, =4, ■КгХ^Чг-Кг- or П^^+Ш-К.-Х, (1)
where N1 is the number of probable regular consumers;
Chh - the number of probable new consumers;
TO\. - coefficient of consumption intensity of drugs;
Xj is the consumption of the drug for 1 year of use by one consumer.
As data from a sociological survey showed, in addition to the real need for GCS, there is a hidden need - 23% of women of fertile age would like to use GCS, but there are certain obstacles to this. These women can be considered as potential consumers. According to our calculations, the potential need is the most significant in segments with low incomes and decreases with increasing income, turning into real demand, supported by purchasing power. Thus, for a segment with an income of up to 0.5 subsistence minimums, potential consumers in 3.3 times more than real ones; for the segment 0.5-1 subsistence level - already 1.9 times, and for other segments with income above the minimum subsistence minimum, the notional need does not exceed the real one.
The reasons preventing the use of GCS are also different. D; segments with incomes up to 1 subsistence level - this is, first of all, a high price. Introduction of benefits or subsidies for the purchase of contraceptives
these segments could significantly increase the number of CS users and reduce the number of abortions. For segments with income above the subsistence level per family member, the main obstacles are lack of information and fears of side effects. Information and outreach efforts will help increase the consumption of contraceptives in these segments. Thus, the practical use of the research results will improve the drug supply of the population with contraceptive drugs.
2. An analysis of medical and demographic indicators in the CMS region was carried out, the dynamics of the use of basic contraceptives - intrauterine devices and hormonal contraceptives - was studied. Fertility rates have been found to be about 40 births per 1,000 women of childbearing age per year. The main trend in the use of family planning is an increase in the use of hormonal contraceptives and a decrease in the use of intrauterine contraception. The total number of women using modern contraceptives is small - 19% of women of fertile age, and with low fertility there is a high rate of abortion.
3. Sociological studies of women of fertile age - actual and potential consumers of contraceptives - have been conducted. Issues of public awareness and consumer preferences in the field of contraception have been studied. We segmented consumers by income and established typological models of behavior of the selected segments. This
made it possible to identify and characterize the most promising segments for the introduction of modern contraceptive methods.
4. The range of contraceptive drugs on the pharmaceutical market of the CMS region has been studied, its structure, completeness, and degree of renewal have been determined. The pharmaceutical market in the region under study contains 56% of hormonal contraceptives and 80% of spermicidal agents officially registered in the Russian Federation. Among them are drugs of all pharmacotherapeutic subgroups of 1, 2 and 3 generations. There is a high dynamism of the regional contraceptive market.
5. Based on the method of collective expert assessments using two groups of experts - gynecologists and pharmacist specialists - the nomenclature of contraceptive drugs most often used in the CMS region was studied, their functional properties and competitiveness were assessed. Based on the drugs that received the highest ratings from experts, an optimal range of contraceptive drugs was formed, including 19 types of hormonal and spermicidal drugs.
6. Based on a retrospective analysis of time series of the number of consumers of hormonal contraceptives in CMS cities for 1994-2000. Dynamic models have been compiled to predict the number of consumers by extrapolating existing trends. Calculated for the forecast of the number of users of hormonal contraceptives for the period up to 2003.
7. A methodology has been developed for determining the future need for hormonal contraceptives using a normative method. The coefficients of consumption intensity and consumption of each drug for the 1st year were calculated; application by 1 consumer. A forecast of the future need for hormonal contraceptives in the cities of the CMS region for the period up to 2003 has been compiled.
1. Gatsan V.V. Research on the consumption of drugs used for contraception / V.V. Gatsan, O.G. Ivchenko // Region, conf. on pharmacy, pharmacology and personnel training (53; 1998; Pyatigorsk): Materials... - Pyatigorsk, Pyatigorsk, Pyatigorsk, 1998. -P.126.
2. Ivchenko O.G. Results of a sociological survey on the use of family planning means / O.G. Ivchenko, V.V. Gatsan // Region. conf. on pharmacy, pharmacology and personnel training (54; 1999; Pyatigorsk): Materials... - Pyatigorsk, PyatGFL, 1999. -P.105.
3. Ivchenko O.G. Analysis of the range of contraceptive drugs / O.G. Ivchenko, V.V. Gatsan //Region, conf. on pharmacy, pharmacology and personnel training (55; 2000; Pyatigorsk): Materials... - Pyatigorsk, Pyatigorsk, Pyatigorsk, 2000. -S. 162-163.
4. Ivchenko O.G. Analysis of contraceptive activity of residents of the KMV / O.G. Ivchenko, V.V. Gatsan // Region, conf. on pharmacy, pharmacology and personnel training (55; 2000; Pyatigorsk): Materials... - Pyatigorsk, Pyatigorsk, Pyatigorsk, 2000. -S. 163-164.
5. Smirnov A.B. Development of databases for entering and processing the results of sociological research / A.B. Smirnov, O.G. Ivchenko // Region, conf. on pharmacy, pharmacology and personnel training (55; 2000; Pyatigorsk): Materials... -Pyatigorsk, PyatGFA, 2000. -S. 169-170.
6. Ivchenko O.G. Study of consumers of contraceptive drugs in the Caucasian Mineral Waters region / O.G. Ivchenko, V.V. Gatsan // Man and Medicine: Proc. report 7 Ross. national congr. April 10-14 2000 - M., 2000. - P.580.
7. Ivchenko O.G. Results of collective expert assessments of the nomenclature of contraceptives / O.G. Ivchenko, V.V. //Region, conf. on pharmacy, pharmacology and personnel training (56; 2001; Pyatigorsk): Materials... - Pyatigorsk, Pyatigorsk, Pyatigorsk, 2001. - P. 150-151.
8. Ivchenko O.G. Application of the method of collective expert assessments in the study of the nomenclature and consumption of contraceptives / O.G. Ivchenko, V.V. Gatsan - Pyatigorsk, 2001.-26 p. -Dep. in VINITI 09/05/2001, No. 1930-B2001.
Ivchenko Olga Grigorievna
Marketing research of consumption and demand
contraceptive medicines (on the example of the Caucasian Mineral Waters region)
Signed for printing: 3-/-Format 60*84-1/16. Book-magazine paper. Rotaprint printing. Us. oven l. 1.0. Circulation 100 copies. Order No. 1ChG
Pyatigorsk State Pharmaceutical Academy 357532, Pyatigorsk, Kalinina Ave., 11.
Rotaprint PyatGFA, Pyatigorsk, Kalinina Ave., 11.
CHAPTER 1. ORGANIZATION OF MEDICAL AND DRUG PROVISION OF CONTRACEPTION.
1.1. Characteristics of medical problems of family planning
1.2. Review of consumer properties of contraceptives.
1.3. Methodological approaches to conducting marketing research of family planning products.
Conclusions on the chapter.
CHAPTER 2. MARKETING RESEARCH STUDY
CONSUMERS OF CONTRACEPTIVE DRUGS.
2.1. Analysis of medical and demographic indicators in the Caucasian Mineral Waters region.
2.2. Characteristics of the state of contraception in the territory of the Caucasian Mineral Waters.
2.3. Results of a sociological survey of the population on the use of family planning means.
Conclusions on the chapter.
CHAPTER 3. ANALYSIS OF THE NOMENCLATURE OF MEDICINES USED FOR CONTRACEPTION.
3.1. Studying the range of contraceptives on the pharmaceutical market of the Caucasian Mineral Waters.
3.2 Analysis of the results of expert evaluation of contraceptive medicines.
Conclusions on the chapter.
CHAPTER 4. FORECASTING PROSPECTIVE DEMAND FOR
HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES.L """.- .ISH.4D-i - ".MC1.SHTs.
4. 1, Analysis of time series and forecasting of the number of consumers of hormonal contraceptives in the Caucasian region
Mineralnye Vody.
4.2. Determination of standards and calculation of the need for hormonal contraceptives.
Conclusions on the chapter.
Introduction of the dissertationon the topic "Drug technology and organization of pharmaceutical business", Ivchenko, Olga Grigorievna, abstract
Relevance of the topic. In the public health system, recent decades have been characterized by increased attention to the problem of family planning. Since the adoption of the WHO Declaration of Alma-Ata (1978), maternal and child health, including family planning, has been considered an essential element of primary health care to ensure a healthy population. Family planning in its modern understanding consists not only of limiting the birth rate, but, more importantly, of controlling a woman’s reproductive function in order to give birth to only desired children. Rational reproductive behavior takes into account the age, health status, financial capabilities of the parents, and optimal intervals between births. Family planning programs are involved in solving medical, demographic and social problems of our time.
The particular importance of the problem of family planning and birth control in the Russian Federation is associated with a general deterioration in the health of the population, poor medical and demographic indicators, and a decline in material well-being and living standards of some segments of the population. Recent years have been characterized by negative natural population growth. In 1999 it was -6.3 per 1000 population. Birth rates are almost 2 times less than those required for positive population growth. At the same time, the number of abortions exceeds the number of births by 1.8 times. At the same time, in Russia, until now, there is often a negative attitude towards the problem of family planning; insufficient attention is paid to the medical and social aspects of this problem.
The first program in Russia, “Women’s Health through Birth Control,” was developed in 1991 for Moscow and the Moscow region. Family planning, as a targeted state program of the Russian Federation, began to operate in 1993. In 1992, the Russian Society for Contraception was created, which, together with the Russian Family Planning Association, is designed to solve national problems of family planning and contraception.
One of the necessary conditions for the implementation of a family planning program is the improvement of drug supply with modern contraceptives, primarily hormonal contraceptives, which are gaining increasing promise thanks to the successes of a relatively new branch of medical science - reproductive endocrinology. The market nature of the supply of contraceptives requires a marketing approach and marketing research as the most modern methodology for studying the drug market in order to improve the drug supply to the population.
The Caucasian Mineral Waters region, which is part of the Stavropol Territory, is influenced by the main factors of economic, political, demographic and national policy of the Russian Federation. But at the same time, the geographical location of the region also determines the greater complexity of the social and economic problems facing the population of the Caucasian Sea. The status of the KMS - as one of the largest resorts in Russia - is the reason for the large number of people coming to the region from various parts of the country. In addition, the lifestyle and thinking of the population of the region are influenced by the peculiarities of the national mentality of the neighboring republics of the North Caucasus, the diverse national composition, and a large number of mixed marriages. The situation in the North Caucasus region is characterized by low per capita income, but at the same time there is a relatively high birth rate. Thus, at the end of the 90s, the number of births per 1000 women of childbearing age exceeded the same figure for the Russian Federation as a whole by about 30%. The number of abortions was at a lower level - 10-12% lower. More favorable indicators of reproductive behavior are typical for the national republics of the North Caucasus. According to the above indicators, the CMS region occupies an intermediate place between the entire North Caucasus and the Russian Federation as a whole. All this has an impact, including on reproductive behavior and the use of contraception, and makes the CMS region unique and interesting for studying the level of development of the problem of family planning, as well as the drug provision of contraception.
Drug provision with contraceptives should be carried out taking into account the current state of the problem of family planning from the perspective of the pharmaceutical market and market mechanisms for solving this problem. The theoretical foundations of marketing research of the JIC market were developed by scientists: JI.B. Kobzarem, N.B. Dremova, E.V. Lazareva, S.G. Failure, Z.G. Maksudova and others. Comprehensive marketing research in matters of family planning was carried out by O.I. Knysh, O.A. Vasnetsova in the Tyumen region. Separate studies of the contraceptive market in various regions were carried out by G.F. Lozovoy, A.Yu. Karimov, Zh.V. Mironenkova, N.Yu. Baranova et al. However, an analysis of the available literature showed that no studies have been carried out on the demand and provision of contraceptive drugs to the population of the KMS region.
Thus, all of the above determined the relevance of conducting a set of marketing studies of the pharmaceutical market of contraceptive drugs in the CMS region. This determined the main goal of our research and the formulation of specific tasks to achieve this goal.
Purpose and objectives of the study. The purpose of this study is to develop scientifically based methodological approaches to optimizing the drug supply of the population with contraceptive drugs in the Caucasian Mineral Waters region using marketing methods.
To achieve this goal, the following tasks were identified: to study the current state of medical and drug support for the problem of contraception; analyze methods for conducting marketing research in relation to the contraceptive market; conduct a retrospective analysis of the reproductive behavior of the KMS population and the dynamics of the use of basic contraceptives; conduct sociological research among women of fertile age, as the main consumers of contraception; to study the provision of the regional CMV market with contraceptive JICs; conduct an expert assessment of contraceptive JICs using two groups of experts (gynecologists and pharmacists), and carry out a scientifically based selection and compilation of a list of the main JICs used for contraception; make a forecast of the need for hormonal contraceptives in the CMS region for the period up to 2003; develop scientifically based recommendations for improving the drug supply of contraception.
Relation of research objectives to the problem design of pharmaceutical sciences. The dissertation work was carried out in accordance with the scientific research plan of the Pyatigorsk State Pharmaceutical Academy (state registration number 01.2.00 101054) within the framework of the “Pharmacy” problem of the Scientific Council No. 38 of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
Scientific basis, objects and methods of research. The scientific basis was the modern concept of marketing research, the methodology of system analysis and scientific forecasting of economic phenomena.
The objects of research were the performance indicators of pharmacies and medical institutions and enterprises of the CMV in the medical and drug provision of contraception.
The source information was: departmental materials of the health departments of the cities of the KMS for the period 1994-2000; data from the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation, statistics departments under the administrations of CMS cities; statistical accounting and reporting documents of medical institutions in the cities of the Caucasus Minsk (antenatal clinics, family planning rooms, maternity hospitals); questionnaires from a sociological survey of the population on the use of contraceptives; data from expert assessment of contraceptives; materials of documentary observation on outpatient cards and prescription sheets for contraceptives for 1998-2001; assortment of contraceptive JICs in retail and wholesale intermediary pharmaceutical enterprises of the KMS region for 1997-2001.
During the research process, a systematic approach was used using the following methods: grouping, comparison, graphic, mathematical and statistical, content analysis, methods of applied sociology (questionnaire survey, expert assessments).
The research results were processed on a PC using licensed software - Windows 95 and Office 97.
Scientific novelty of the research. Methodological approaches have been developed for conducting comprehensive marketing research of the regional JIC market used for the purpose of contraception.
Using statistical and sociological methods, a study of consumers of contraceptives was carried out, which made it possible to determine consumer preferences and requirements for family planning products, segmented consumers by income and determined the characteristics of each segment.
Using content analysis and the comparison method, the range of contraceptives on the regional pharmaceutical market, its structure, completeness, and degree of renewal were studied. The optimal nomenclature of JICs used for contraception was determined using the method of expert assessments.
Mathematical models have been developed to predict the number of consumers of hormonal contraceptives for each city in the CMS region.
A methodology for determining the future need for contraceptive drugs using a normative method has been proposed, standards for the consumption of GCS have been developed, and a forecast of demand for the period up to 2003 has been compiled.
Practical significance of the work. The developed methodology for conducting marketing research on the contraceptive market allows us to determine the assortment structure, consumer preferences, demand trends and predict the future need for hormonal contraceptives. The results obtained during the study make it possible to improve the drug supply with contraceptives in the CMS region.
Implementation of work results. Based on the research conducted, “Methodological recommendations for conducting marketing research on the market of contraceptive medicines” were developed, which were introduced into the practical activities of family planning offices, antenatal clinics and other medical institutions, as well as wholesale and retail pharmacy enterprises of the Stavropol Territory, the Republic of Adygea, Karachay-Cherkessia Republic, Rostov region, Krasnodar region.
Approbation of the obtained results. The main results of the dissertation research were reported and discussed at the 53, 54, 55, 56 regional conferences on pharmacy, pharmacology and personnel training Pyatigorsk (Pyatigorsk, 1998,1999, 2000, 2001).
In general, the dissertation work was reported at the interdepartmental conference of the Pyatigorsk State Pharmaceutical Academy (Pyatigorsk, November 2001).
Provisions submitted for defense. The following provisions and research results, characterized by scientific novelty, are put forward for defense: methods of conducting marketing research of the regional market of contraceptive J1C; results of analysis of the state of contraception in the CMS territory; results of sociological studies of the main consumers of contraceptives (women of fertile age); results of expert assessments of the nomenclature of contraceptives; mathematical models that allow predicting the number of users of hormonal contraceptives; forecast of the need for hormonal contraceptives for 2001 - 2003.
Scope and structure of the dissertation. The dissertation consists of an introduction, four interconnected chapters, conclusions, bibliography and appendices. The bibliographic index includes 200 literary sources, including 25 in foreign languages. The work is presented on 141 pages of typewritten text, contains 26 tables and 16 figures.
Conclusion of the dissertation researchon the topic "Marketing research on the consumption and demand of contraceptive medicines (on the example of the Caucasian Mineral Waters region)"
General conclusions
1. Literature data on the problem of contraception and the provision of modern contraceptives, as well as existing research methods for analyzing and forecasting the market of contraceptive medicines, have been studied and summarized. Low birth rates, high abortion rates and positive changes in attitudes towards the issue of contraception determine the relevance of conducting comprehensive marketing research on consumption and demand for contraceptive medicines.
2. An analysis of medical and demographic indicators in the CMS region was carried out, the dynamics of the use of basic contraceptives - intrauterine devices and hormonal contraceptives - was studied. It is shown that birth rates have stabilized since 1997, and amount to about 40 births per 1000 women of childbearing age per year. The main trend in the use of family planning is an increase in the use of hormonal contraceptives and a decrease in the use of intrauterine devices. The total number of women using modern contraceptives is small - 19% of women of fertile age, and with low birth rates there is a high rate of abortions.
3. Sociological studies of women of fertile age - actual and potential consumers of contraceptives - were conducted. Issues of public awareness and consumer preferences in the field of contraception have been studied. Consumers were segmented by income and typological models of behavior of the selected segments were established. This made it possible to identify and characterize the most promising segments for the introduction of modern contraceptive methods.
4. The assortment of contraceptive JICs on the pharmaceutical market of the CMS region has been studied, its structure, completeness, and degree of renewal have been determined. In the pharmaceutical market of the studied region there are 56% of GCS, and 80% of spermicidal agents officially registered in the Russian Federation. Among them are drugs of all pharmacotherapeutic subgroups of 1, 2 and 3 generations. There is a high dynamism of the regional contraceptive market
5. Based on the method of collective expert assessments using two groups of experts - gynecologists and pharmacist specialists - the nomenclature of contraceptive drugs most often used in the CMS region was studied, their functional properties and competitiveness were assessed. Based on the drugs that received the highest ratings from experts, an optimal range of drugs used for contraception was formed, including 19 types of hormonal and spermicidal drugs.
6. Based on a retrospective analysis of time series of the number of GCS consumers in six cities of the KMS for 1994-2000. Dynamic models have been compiled to predict the number of consumers by extrapolating existing trends. The forecast for the number of consumers of hormonal contraceptives for the period up to 2003 has been calculated.
7. A method has been developed for determining the future need for hormonal contraceptives using a normative method. The coefficients of intensity of consumption of GCS in the CMS region and the consumption of each drug for 1 year of use by 1 consumer were calculated. A forecast of the future need for hormonal contraceptives in the cities of the CMS region for the period up to 2003 has been compiled.
List of used literaturein pharmacology, dissertation 2002, Ivchenko, Olga Grigorievna
1. Abortion in the fate of a woman // Women’s health. - 1996. - No. 1(7). - P. 9.
2. Abortion as a remedy for pregnancy // Med. news. - 1996. No. 11 (26). - P. 4.
3. Abramova, G.P. Marketing: questions and answers / G.P. Abramova. - M.: Agropromizdat, 1991.- 159 p.
4. Academy of the Market: Marketing / Deyan A., Buquerel F., Lankar R. et al. - M.: Economics, 1993. - 572 p.
5. Aleksina, I.L. Experience of the Russian Family Planning Association in organizing the work of youth centers / I.L. Aleksina // Medicine for You - 1996. - No. 18. P. 22-25.
6. Apazov, A.D. Social and legal aspects of drug provision / A.D. Apazov, N.I. Sosina, N.Ya. Kulchik // Pharmacy. 1996. - T.45, No. 4. -P.9-14.
7. Safety of oral contraceptives: a modern view of common concerns // Point of view. - 1993. - No. 3.-S. 6.
8. Beshelev, S.D. Mathematical and statistical methods of expert assessments / S.D. Beshelev., F.G. Gurvich - M.: Statistics, 1980. - 263 p.
9. Bisset, A.M. The use of progestin oral contraceptives / A.M. Bisset //Family planning.-1993.-No.3.-P.27-28.
10. Biteryakova, A.M. Marketing research of regional markets of medicines / A.M. Biteryakova, E.L. Kuzubova // Man and Medicine: Abstract. report 4 Ross. national congress April 8-12 1997 M., 1997, - P.310.
11. Borovikov, V.P. Statistica - statistical analysis, data processing in the Windows environment/ V.P. Borovikov, I.P. Borovikov M.: Filin, 1998 -608 p.
12. Boyarsky, A.Ya. General theory of statistics / Boyarsky A.Ya., Gromyko G.L. - M.: Moscow State University Publishing House, 1985. - 375 p.
13. Bruinix, N.P. Improving oral contraceptives: results of 35 years of work / N.P. Bruinix //Rus. Honey. magazine - 1992. T.1, No.2. -P.43-46.
14. Bykov, A.V. Form as the basis of rational pharmaceutical management / A.V. Bykov, A.P. Zagorsky // Pharmacy 1996. - T.45, No. 3.- P. 9-14.
15. Vaganov, N.N. The role of family planning in protecting women’s health / N.N. Vaganov, J.I.B. Gavrilova // Vestn. obstetrician-gynecologist. - 1992. -No. 2. -P.12.
16. Vasnetsova, O.A. Marketing in pharmacy / O.A. Vasnetsova - M.: Book World, 1999 -334 p.
17. Vasnetsova, O.A. Marketing research in the creation of family planning clinics in Russia / O.A. Vasnetsova, O.D. Knysh // Man and Medicine: Proc. report 4. Ross. national congr. April 8-12 1997 M., 1997. - P.312.
18. Vasnetsova, O.A. Situational analysis of the population's provision with contraceptives / O.A. Vasnetsova, O.I. Knysh, N.Yu. Baranova // Man and Medicine: Abstract. report 4 Ross. national congr. April 8-12 1997 M., 1997. - P.312.
19. Volkova, N.V. Study of consumer assessments of the assortment and quality of goods / N.V. Volkova - M.: Finvest, 1991. - P. 48.
20. Issues of providing contraceptives. MFPS. // Family planning. - 1995, - No. 3, - S. 23.
21. Gerasimenko, I.F. Health care reform: some results and prospects / I.F. Gerasimenko// Health Economics. -1997.-No. 1. -P.5-7.
22. Golubkov, EJI. Marketing. Choosing the best solution. / E.JI. Golubkov, E.N. Golubkova, B.D. Sekerin. - M.Economics, 1993.--85 p.
23. Hormonal contraception with tablets. // Pharm. Vestn. - 1996. -No. 5-S. 6.
24. Hormonal contraceptives (chemical plant Gedeon Richter). Budapest, 1997. - 79 p.
25. State report on the state of health of the population of the Russian Federation in 1998 // Healthcare of the Russian Federation. Federation.-2000.-No.4.-S.Z-15.
26. Grechikhin, V.G. Lectures on the methodology and technology of sociological research / V.G. Grechikhin - M.: MSU, 1988. - 232 p.
27. Gromyko, G.L. Statistics/ G.L. Gromyko. - M.: Moscow State University Publishing House, 1981. - 408 p.
28. Gusarova, G.I. Improving the quality of services for the protection of reproductive health of the population of the Samara region / G.I. Gusarova, O.I. Lineva, E.V. Finogenova // Family planning. - 1995. - No. 3. - P. 36-39.
29. Data on contraceptives injected once a month: WHO meeting memorandum // Bulletin. V03.-1993.-No.6.-S. 18-30.
30. Dementieva, Z.S. Basic conceptual approaches to optimal forecasting and formation of the drug market / Z.S. Dementieva, L.V. Kobzar // Sat. scientific tr. All-Russian Research Institute of Pharmacy. M., 1993.-T.XXXI. - P. 46-54.
31. Dementieva, Z.S. Solving the problem of scientifically based planning of the need for medicines / Z.S. Dementieva, M.V. Shugaleva // Modern aspects of drug provision to the population: Sat. scientific works - M., 1989. - T. 32. - P. 80-83.
32. Dichtl, E. Practical marketing / E. Dichtl, X. Hershgen. - M.: Higher. school.- 1995, -255 p.
33. Dremova, N.B. Concept of marketing research for analysis and forecasting of the drug market / N.B. Dremova, E.V. Lazareva //Pharmacy.-1996.-T. 45, No.>1.-P.27-29.
34. Dremova, N.B. Modeling the consumption of medical goods based on the method of group accounting of arguments / N.B. Dremova, I.N. Laskina, M.V. Artemchenko //Pharmacy.-1992. T.42, No. 2. - P.20-24.
35. Dremova, N.B. Main directions of research in scientific forecasting of drug consumption / N.B. Dremova, L.V. Kobzar //
36. Pharmacy.-1992.- T.41, No. 3.- P.73-79.
37. Dremova, N.B. Problems and opportunities of marketing research of the drug market / N.B. Dremova // Med.-farm. Vestn. 1996.-No. 9-10.- SZ-8.
38. Dremova, N.B. System of marketing research of medicines as a product / N.B. Dremova, E.V. Lazareva //Pharmacy.- 1996.-T.45, No. 3.-S14-16.
39. Dremova, N.B. Modern pharmaceutical market: state and development trends (literature review) / N.B. Dremova // Pharmacy. -1998. -T. 47, No. 4. -WITH. 57-59.
40. Dremova, N.B. Statistical analysis and regression modeling of consumption of medical goods / N.B. Dremova, I.N. Laskina, S.V. Straw //Pharmacy, - T.42, 1992.-No.2.-S. 15-19.
41. Dubnitskaya, L.V. The influence of hormonal contraceptives on menstrual and generative function of women / L.V. Dubnitskaya, E.I. Sotnikova // Obstetrics and gynecology. - 1990. -№4.-S. 57-60.
42. Dubnitskaya, L.V. Acceptability of hormonal contraceptives with low steroid content / L.V. Dubnitskaya // Obstetrics and gynecology. - 1990.-№8,-S. 10-12.
43. Duke, V. Data processing on a PC in examples / V. Duke. SPb. Liter, 1997. 240 p.
44. Egorov, V.N. Complex analysis in the system of marketing activities /V. N. Egorov, - M.: JV "All Moscow", 1994. - 256 p.
45. Eliseeva, I.I. General theory of statistics / I.I. Eliseeva, M.M. Yuzbashev -M.: Finance and Statistics, 1999. 480 p.
46. Erofeeva, S.V. On the experience of sex education and education in foreign countries / S.V. Erofeeva // Medicine for you. 1996. - No. 20 - P. 12.
47. Zhuravleva, K.I. Statistics in healthcare./ K.I. Zhuravleva-M.: Medicine, 1981.-176 p.
48. Health of the population of Russia and the activities of healthcare institutions in 1997 // Healthcare of Russia. Federation.- 2000 No. 1.-P.22-36.
49. Ivchenko, O.G. Analysis of the range of contraceptive drugs / O.G. Ivchenko, V.V. Gatsan // Region, conf. on pharmacy, pharmacology and personnel training (55; 2000; Pyatigorsk): Materials. Pyatigorsk, 2000. -S. 162-163.
50. Ivchenko, O.G. Analysis of contraceptive activity of residents of the KMV / O.G. Ivchenko, V.V. Gatsan // Region, conf. on pharmacy, pharmacology and personnel training (55; 2000; Pyatigorsk): Materials. Pyatigorsk, 2000. -P.163-164.
51. Ivchenko, O.G. Study of contraceptive JIC consumers in the Caucasian Mineral Waters region / O.G. Ivchenko, V.V. Gatsan // Man and Medicine: Proc. report 7 Ross. national congr. April 10-14 2000 M., 2000. - P.580.
52. Ivchenko, O.G. Application of the method of collective expert assessments in the study of the nomenclature and consumption of contraceptives / O.G. Ivchenko, V.V. Gatsan Pyatigorsk, 2001. - 26 p. -Dep. in VINITI 09/05/2001, No. 1930-B2001.
53. Kant, V.I. Mathematical methods and modeling in healthcare / V.I. Kant. - M.: Medicine, 1987, - 223 p.
54. Kareva, Marketing in the pharmaceutical market / N.N. Kareva, I.A. Hunting // Pharmacy. 1995. - T. 45, No. 6.-P.28-29.
55. Carlos, M. X. A manual for the provision of services in the field of family planning. / M. Huso Carlos, Catherine Briggs - M.: MFPS, 1992. - 174 p.
56. Kiryushchenkov, A.D. Hormonal contraception / A.D. Kiryushchenkov, E.V. Nesterkin // Doctor.-1994.-No. 8.-P.5-8.
57. Knysh, O.I. Methodological foundations of pharmaceutical marketing in matters of family planning / O.I. Knysh, O.A. Vasnetsova. - Tyumen: Softdesign, 1998 - 350 p.
58. Knysh, O.I. Model of a complex of marketing research to study the demand for contraceptives / O.I. Knysh, O.Yu. Grigoshina // Med.-farm. Vestn. - 1997. -T.46, No. 2.-S. 8-12.
59. Kobzar, JI.B. Marketing research, assessment and forecasting of the Russian pharmaceutical market / JI.B. Kobzar // Pharmacy.-1993. -T.42, No.6.-P.30-33.
60. Kobzar, JI.B. Features of the development of the drug market in Russia / L.V. Kobzar // Pharmacy. 1999. - T.48, No. 2. - P. 9-12.
61. Kobzar, L.V. Development of an assortment of medicines and methodological principles of its analysis / L.V. Kobzar, Z.G. Maksudova // Pharmacy. - 1996. -T. 44, No. 3,-S. 9-12.
62. Konovalov, O.E. Family, marriage, health / O.E. Konovalov // Healthcare of Russia. Federation. - 1994. -No. 6, -S. 27-30.
63. Contraceptive effectiveness and contraceptive choice. Materials of the International Federation of Family Planning // Family Planning. - 1995. -№3.-S. 20-23.
64. The concept of state family policy in the Russian Federation // Healthcare of Russia. Federation-1994-No. 2.-S. 3-6.
65. Korsunskaya, M.P. Implementation of approaches to drug provision in market conditions / M.P. Korsunskaya // Medical Market.-1994,- No. 2.-P.4.
66. Korkhov, V.V. Three-phase contraceptives / V.V. Korkhov, G.E. Lupanova.//Pharmacology and toxicology.-1989.-No.5.-p.115-119
67. Kotler, F. Fundamentals of Marketing: Trans. from English / F. Kotler.-M.: Progress, 1990.-736 p.
68. Kulakov, V.I. Medical and social significance of family planning / V.I. Kul akov.//Family planning. -1994. -No.2 .-p.3-1.
69. Kulakov, V.I. Medical and social aspects of family planning / V.I. Kulakov, O.G. Frolova, V.F. Volgina // Obstetrics and gynecology.-1994.- No. 3.-S. 10-12.
70. Lakhnit, U. Current state of oral contraception / U. Lakhnit // Pharmateka.-1994.-No. 2.-P.35-36.
71. Lebedev, A.A. The use of marketing philosophy in the activities of medical institutions of the state healthcare system in a market economy / A.A. Lebedev // Healthcare Economics." 1997, - No. 7. - P. 31-37.
72. Lindström, L. Norplant implantation: a contraceptive method convenient for a woman / JI. Lindstrom //Family Planning.-1993.-No.3.-P.21-23.
73. Maksimkina, E.A. Competitiveness of pharmaceutical organizations in market conditions / E.A. Maksimkina, E.E. Loskutova, V.V. Dorofeeva. M.: MCFR, 1999.-256 p.
74. Malakhov, V.Yu. Pharmaceutical market of oral contraceptives in Russia/V.Yu. Malakhov, O.A. Vasnetsova //Pharmacia.-1994.-No.1-p.27-30.
75. Manuilova, I.A. Current problems of family planning / I.A. Manuilova //Pharmacy and hospital. -1996. No. 2-3 - pp. 18-21.
76. Manuilova, I.A. Benefits and risks of hormonal contraception / I.A. Manuilova//Med. pharm. Vestn.-1996.-No.1.-P.39-46.
77. Manuilova, I.A. Femoden is a new optimal hormonal contraceptive / I.A. Manuilova //Pharmacy and hospital.-1996. -No. 2-3 -P.27-28.
78. Manuilova, I.A. Current problems of family planning / I.A. Manuilova, L.V. Dubitskaya. - M.: Medicine, 1990. 125 p.
80. Manuilova, I.A. Modern methods of preventing pregnancy / I.A. Manuilova, P.N. Krutkovskaya //Health for everyone. - 1990. - Issue 3. - P. 3-16.
81. Manuilova, IA. Modern contraceptives / I.A. Manuilova.- M„ 1993.-198 p.
82. Matyushichev, I.Yu. Creation of an expert system for forecasting the need for medicines / I.Yu. Matyushichev, B.V. Passet // Pharmacy.-1995.-T.44, No. 2.-P.27-29.
83. Mashkovsky, M.D. Medicines: In 2 volumes/M.D. Mashkovsky -Kharkov: Torsing, 1997.-T.2.-P.49-51.
84. Medical and social characteristics of young people at the stage of creating a family // Healthcare of Russia. Federation. - 1991. -№1.-S. 13-16.
85. Medical and social problems of abortion // Medicine for you. - 1996. - No. 22.-S. 9.
86. Method of expert assessments in the study of drug consumption / N. B. Dremova, V. V. Kuleshova, V. A. Lizun, A. V. Lazareva // Sociology in medicine: theoretical and scientific-practical aspects.- M. , 1990. - Issue. 3.-S. 189-192.
87. Meshkovsky, A.P. On national drug policy / A.P. Meshkovsky // Pharmateka.-1995.-No.1.-P.35-41.
88. Mintser, O.P. Methods for processing medical information./ O.P. Mintser,
89. B.D. Ugarov, V.I. Vlasov - Kyiv: Vysh. school - 1991. - 271 p.
90. Moiseev, B.C. On the problems of forming the drug market in
91. Russia / B.C. Moiseev // Medical Market.-1996. No. 1. - P.20.
92. Morris, R. Marketing: situations and examples: Trans. from English / R. Morris1. M., 1994. 207 p.
93. Moshkova, L.V. Pharmacy in the conditions of the pharmaceutical market L.V. Moshkova, V.E. Torosyan, O.A. Bakhtina //News of medicine and pharmacy. Yarinvest medical.-1995.-No.2.-P.28-30.
94. Moshkova, L.V. Scientific research in pharmacy abroad / L.V.
95. Moshkova, E.A. Korzhavykh//Pharmacy.-1993.-T.42, No. 2.-P.61-63.
96. Nazarova, N.M. Contraceptive and therapeutic effectiveness of triregol / N.M. Nazarova, V.N. Prilepskaya // Med.-farm. Vestn.-1996.-No. 2,-P.15-17.
97. Nazarova, N.M. Tri-Regol: experience of use in gynecological practice /
98. N.M. Nazarova, V.N. Prilepskaya // Medical Market.-1996.-No.3.-P.65-66.
99. Nechaev, E.A. Scientific concept of drug supply to Russia E.A.
100. Nechaev // Pharmacy. - 1994. -T.43, No. 1.-S. 7-9.
101. Nozdreva, R.B. Marketing: how to win in the market / R.B. Nozdreva, L.I.
102. Tsygichko. M.: Finance and Statistics, 1991.-305 p.
103. On the development of demographic processes in the Russian Federation in 1998 // Healthcare of Russia. Federation 2000 - No. 2.-S. 13-28.
104. On the main trends in the development of the demographic situation in Russia until 2015 // Healthcare of Russia. Federation 1999 - No. 2.-P.27-32.
105. General theory of statistics / Ed. A. M. Golberg, V. S. Kozlova M.: Finance and Statistics, 1985. - 367 p.
106. Olgin, M. Forming an assortment: contraceptive drugs / M. Olgin // Remedium, 1998.- No. 7.-P.42-43
107. Fundamentals of applied sociology / Ed. F. E. Sheregi, M. K. Gorshkova. -M.: Interprax, 1996.-184 p.
108. Panchenko, E.I. Determination of current and future needs for medicines / E.I. Panchenko, JI.B. Kobzar // Pharmacy. 1983. - T. 32, No. 1. -WITH. 11-15.
109. Perminova, S.G. Some aspects of social and reproductive behavior based on the results of a sample study / S.G. Perminova, E.I. Sotnikova // Obstetrics and gynecology. - 1993. - No. 3.-S. 23-25.
110. Perfilyeva, G.N. Automated remote expert system for family planning service / G.N. Perfilyeva, S.P. Chudova // Healthcare of the Russian Federation. - 1993. -№11.-S. 23-24.
111. Family planning is a state matter //Med. news. - 1996. - No. 1.-S.2.
112. Family planning - scientific foundations //Med. newspaper. - 1994. -No. 40.- P. 1.
113. Side effects of contraceptives: help with characteristic manifestations that cause concern among clients // Point of view. - 1994. -№3 - P. 8.
114. Pollack, Amy E. Female and male voluntary sterilization: Modernization of contraceptive techniques / Amy E. Pollack // Family Planning. 1995. -No. 3.-S. 27-30.
115. The situation in global health care: analysis and forecast, 1950-2025 // South Russian Medical Journal.-1997.-No. 2.-P.6-16.
116. PZ.Proude, V.R. Marketing: Current issues in theory and practice / V.R. Proude. - Riga: “Avots”, 1991. - 58 p.
117. Prilepskaya, V.N. Intrauterine contraception, prevention and treatment / V.N. Prilepskaya, S.I. Rogovskaya, E.A. Mozhevitinova //Rus. honey. magazine -1996. -No. 1.-S. 44-49.
118. Prilepskaya, V.N. The influence of various hormonal contraceptives on the condition of the cervix / V.N. Prilepskaya, N.M. Nazarova, N.I. Kondrikov // Chem.-farm. magazine. 1993. - No. 2. - P.8-9.
119. Prilepskaya, V.N. Contraceptives / V.N. Prilepskaya, E.A. Mozhevitinova, N.M. Nazarova. M., 1990. - P. 3-9.
120. Prilepskaya, V.N. Hormonal contraception / V.N. Prilepskaya //Obstetrics and gynecology. - 1991. -№12.-S. 63-67.
121. Prilepskaya, V.N. Hormonal contraception with tablets / V.N. Prilepskaya //Farm. messenger - 1996. - No. 5.-S. 6.
122. Prilepskaya, V.N. Clinical aspects of the use of the drug Femoden/ V.N. Prilepskaya, V.A. Burlev, A.A. Kuzemin //Family planning. -1995.-No.3.-S. 30-33
123. Prilepskaya, V.N. Contraception with the long-acting injection drug "Depo-Provera" / V.N. Prilepskaya, N.I. Kondrikov, T.T. Tagieva // Obstetrics and gynecology.-1995.-No.3-P.7-10.
124. Prilepskaya, V.N. Oral hormonal low-dose contraceptives of a new generation / V.N. Prilepskaya, V.A. Burlev, A.A. Kuzemin // Bulletin of obstetrician-gynecologist.-1996.-No.4.-P.45-49.
125. Prilepskaya, V.N., Sotnikova E.I. Contraception in family planning / V.N. Prilepskaya, E.I. Sotnikova //Obstetrics and gynecology. - 1994. -4. - P. 60-62.
126. Project. Concept of development of healthcare and medical science in the Russian Federation // Healthcare Economics.-1996. -No. 3. -8-19.
127. Puradova, N.V. Assessing the competitiveness of products / N.V. Purado-va, E.M. Tobacco // Marketing. - 1993. - No. 1. - P. 133-140.
128. Puchinina, T.N. Analysis of the contraceptive market / T.N. Puchinina, S.V. Sinotova // Pharmacy in the 21st century: innovations and traditions. / Abstract. Dokl. Intl. conf. April 7-8, 1999. -S.-P6.D999. -WITH. 116.
129. Rachev, E. Clinical observations of the use of the three-phase contraceptive drug Tri-regol / E. Rachev // Richter-news.-1995.-No.2.-P.22-23.
130. Revolution in birth control //Business world. - 1993. - No. 7, -S. 9.
131. Register of Medicines of Russia-96: Addition/ Sub. ed. Yu.F. Krylova. - M.: Remako. - 1996. - 672 p. - Register-96.
132. Reichart, D.W. Pharmaceutical market: its features, problems and prospects / D.V. Reichart, W.A. Sukhinina, Yu.V. Shilenko. - M.: Slavic dialogue. - 1995. - 304 p.
133. Ross, D. National family planning programs efforts and achievements / D. Ross, P. Mauldin // World Health Forum.-1994.-vol.15.-No.3.-pp.40-45.
134. Guide to family planning / Kulakov V.I., Serov V.N., Vaganov N.N. and others. M.; Rusfarmamed, 1997.-298 p.
135. Safta, V.N. Analysis of consumption and planning of the need for medicines from the perspective of a systems approach / V.N. Safta //Healthcare. -1980. -No. 1. -P.34-36.
136. Sboeva, S.G. Methodological approach to studying the demand for medicines using sociological research methods / S.G. Sboeva, L.A. Sukhanova, V.G. Medvedev // Pharmacy. 1986. - T. 35, No. 3. - pp. 12-16.
137. Sevostyanov, V.A. Marketing research, an integrated approach / V.A. Sevostyanov, A.A. Lysikov // Marketing. - 1992. - No. 4. - P. 141153.
138. Serov, V.N. Maternal mortality from abortions and ways to prevent it /
139. V.N. Serov, G.M. Burduli, O.V. Manannikova //Family planning.- 1993.-No. 3.-S. 12-15.
140. Smetanin, V.N. On the characteristics of the reproductive health of urban teenage girls / V.N. Smetanin, V.I. Shvachkina // Healthcare of Russia. Federation. -2001. -No. 1. -WITH. 31-32.
141. Smolyar, N.Ya. Family as an object of research on consumer behavior in the pharmaceutical market / N.Ya. Smolyar, E.E. Loskutova, M.K. Ilyukhina // Pharmacy. 1997. - T. 46, No. 3. - pp. 39-40
142. Modern marketing / Ed. V.E. Khrutsky. M.: Finance and Statistics, 1991.-256 p.
143. Solovyov, B. Consumer behavior / B. Solovyov //Business.-1992.-No. 7.1. P.13-15.
144. Solovyov, B. Price in the system of marketing means/ B. Solovyov //Business. - 1994. -№1 - pp. 10-11.
145. Sotnikova E.I. Modern hormonal contraceptives / E.I. Sotnikova // Pharmateka. - 1995. - No. 2. - P. 30-33.
146. Sotnikova, E.I. Acceptability of modern methods of contraception in adolescents / E.I. Sotnikova, L.V. Dubnitskaya, S.G. Perminova
147. Obstetrics and gynecology. - 1993. -№3.-S. 26-29.
148. Sociology in medicine: theory. and scientific-practical. aspects / N. B. Dremova, V. A. Lizun, V. V. Kuleshova and others - M., 1990 Issue. 3.- pp. 119-129.
149. Vidal Directory: Medicines of Russia. M.: Astra-PharmService. - 1996. - 1296 p.
150. Directory of medicines from foreign companies in Russia. - M.: AstraPharmServis, 1993. 790 p.
151. Handbook of obstetrics and gynecology / Ed. G. M. Savelyeva. - M.: Medicine. - 1992. - P. 318-322.
152. Emergency contraception: Materials of the International Federation of Family Planning //Family Planning. - 1995. - No. 3.-S. 26-27.
153. Sterlina, N.B. Foreign companies on the Russian drug market / N.B. Sterlina // Pharmateka. -1995. -No. 1. -S. 15-17.
154. Stroganova, I.V. Modern contraceptive drugs / I.V. Stroganova // Avicenna.-1997.-No.6.-S. 11.
155. Tatarova, G.G. Methodology of data analysis in sociology / G.G. Tatarova. M.: Strategy, 1998. - 224 p.
156. Tausend, S. Outdated views hinder the spread of oral contraception / S. Tausend // Family Planning. - 1994. - No. 2. - P. 18-22.
157. Tokova, 3.3. Maternal mortality in Russia, regional features/3.3. Tokova, O.G. Frolova //Healthcare of Russia. Federation. 1994. - No. 4.-S. 21-25.
158. Tyurin, Yu.N. Statistical analysis of data on a computer / Yu.N. Tyurin, A.A. Makarov. M., 1998. - 528 p.
159. Uzdenikov, A.N. Organization of trade in medicines in a market economy / A.N. Uzdenikov // Pharmacy.-1995.-T.44, No. 2.-P.13-14.
160. Standard of living and income of the population of the Stavropol Territory in 1998 //
161. AiF Northern Caucasus. -1998. -No. 35.--P.4.
162. Federal target program "Safe Motherhood" for 1995-1997 //Vesta. obstetrician-gynecologist.-1995.-No.1.-P.37-59.
163. Femoden and contraception in adolescents //Pharmacy and Hospital. -1996. -No.2-3 -P.31-33.
164. Feoktistova, E.M. Marketing: theory and practice / E.M. Feoktistova, I.N. Krasnyuk. - M.: Higher. school, 1993. - P. 79.
165. Finger, U. Modern intrauterine devices are safe and effective contraceptives / U. Finger // Family Planning. - 1993. - No. 3. - P. 25-27.
166. Fomina, A.V. Features of family consumer behavior in the pharmaceutical market / A.V. Fomina, D.I. Kicha, T.P. Lagutkina // Pharmacy.-2000. - T.49, No. 3. -WITH. 28-29.
167. Formation of a system of criteria for segmentation of drug consumers /Dremova N.B., Lazareva E.V., Oleynikova T.A. and others // Man and Medicine: Proc. report 2 Ross. national congr. April 21-25 1998 - M., 1998. -WITH. 683
168. Frolova, O.G. Controversial issues of contraception in women after childbirth / O.G. Frolova, V.F. Volgina, T.N. Pugacheva //Obstetrics and gynecology. - 1996. -No. 6, -S. 43-46.
169. Frolova, O.G. Contraception in the postpartum period / O.G. Frolova, V.F. Volgina, T.N. Pugacheva //Family planning. 1995. - No. 3. - P. 33-35.
170. Frolova, O.G. Reproductive losses: New methods of analysis and assessment / O.G. Frolova, T.N. Pugacheva, S.V. Glinyanaya //Healthcare of Russia. Federation - 1994. -No. 2.-S. 25-27.
171. Khomasuridze, A.G. Features of hormonal contraception in women with hyperandrogenism / A.G. Khomasuridze, N.I. Ipatieva, B.V. Gorgoshidze //Obstetrics and gynecology. - 1993. -№5.-S. 42-45.
172. Khomasuridze, A.G. Side effects of oral contraceptives / A.G. Khomasuridze //Obstetrics and gynecology. - 1983. - No. 2. - pp. 27-29.
173. Khrutsky, V.E. Modern marketing / V.E. Khrutsky, I.V. Korneeva, E.E. Avtukhova. - ML: Finance and statistics. -1991. - 256 s.
174. Chernov, V.M. Drug pricing and market. / V.M. Chernov // Pharmac. Vestn. - 1996. -№6.-S. 14.
175. Shevchenko, Yu.L. On the progress of implementation of the concept of development of healthcare and medical science, tasks for 2001-2005. and for the period until 2010 / Yu.L. Shevchenko // Healthcare of Russia. Federation. 2001. - No. 4. -WITH. 3-9.
176. Sharing goes into action//Med. newspaper.-1996.-No. 88.-P.9.
177. Shtemberg, M. et al. Prevention of pregnancy / M. Shtemberg. -Chisinau: Central Printing House. - 1995. - 100 p.
178. Evans, J.R. Marketing / J.R. Evans., B. Berman - M.: Economics, 1990.-351p.
179. Experts approve the use of injectable contraceptives //Family Planning.-1994.-No.2.-P.23-24.
180. Effective work with Excel 7.0 for Windows 95 / Dodge M., Kinata K., Stinson K. et al.: Trans. from English St. Petersburg: Peter, 1996. - 1040 s.
181. An expert system for information on pharmacology and drag interactions / J. Roach, S. Lec, G. Wilcks, M. Echrich // Comput. Biol. Med. - 1985,- Vol. 15, No. 1, -P. 11-23.
182. Bakker, A. Methodologie van geneesmiddelen-gebruikonderzock / A. Bakker // Pharm. Wbl, 1990, - V. 125, No. 4. P. 96-99.
183. Banwell, S.S. The search for Meaning: Ru-486 and the law of abortion./ S.S. Banwell, T.M. Paxman // Am Y. Public Health. 1992. -82. - No. 10.-P.25-28.
184. Baulieu, E. Ru-486 as an Antiprogesterone steroid. From receptor to contragestion aid beyond / E. Baulieu // J. Amer. med. Ass. 1989. - Vol. 262, No. 13. - P. 1808-1814.
185. Belfield, P. Problems of compliance in contraception./ P. Belfield // Br.Y. Seznal med. 1992. - P 56-60.
186. Busy, F. Marketing in a Goal-Oriented organization / F. Busy // Business horizons.- 1988 - Vol.29, No. 4.- P. 11-18.
187. Cady, G. Drags on the Market / G. Cady-Lexington, 1975 275 p.
188. Carson, D. Gotterdammering for marketing? / D. Carson // J. of market-ing.-1988 No. 3 - P. 11-18.
189. Derman, R. Oral contraceptives a reassessment. / R. Derman // Gynecol. Surv. 1989. - Vol. 44, No. 9.-P. 662-668.
190. Elam, N., Pally E. Marketing for the non-marketing executive / N. Elam, E. Pally // Business horizons - 1987-Vol.29. -№2 - P.30-40.
191. Elsten, M. Advances in oral hormonal contraception / M. Elsten, Hilary A. Furniss //Zbl. Gynakol.- 1995.- Vol. 117, No. 11.- P. 559 565.
192. Goldrieher E.Y. Pharmacology of the contraceptive steroids./ Eds Yoseph Goldrieher and Kenneth Fotherby. Kaven Press. New York: Kaven Press. 1994.--P.5.
193. Harnden, D. The managment of pharmaceutical R&D, - The keys to success; Richmond/ D. Harnden, D. McArthur UK, 1990.--25 p.
194. Kinney, E. Expert system detection of drag interactions: Results in consecutive inpatients / E. Kinney // Comput. Biol. Med. - 1986- Vol. 19, No. 5, -P. 462-467.
195. Quillebaund Y. Oral contraceptive compliance. Churchill Livingstone, 1994.
196. Rosenberg, M.J. Unintended pregnancies and usi, misuse and discontinuation of oral contraceptives / M.J. Rosenberg, M.S. Waugh, Sh Long.// J. Reprod. Med.- 1995.- Vol. 40, No. 5, - P.355 360.
197. Rowe, P.M Investigations into long acting contraceptives/ P.M. Rowe // Lancet.- 1995.-No. 8976.- P.693.
198. Runnebaum, B. New gestagene in oral horomonal contraceptive./ B. Runnebaum, Th. Rabe.//Arch. gynecol. 1989. - Bd. 245, No. 1-4 - P 1000-1005.
199. Skouby, S., Petersen K. et all. The influence of New Low-doss oral contraceptives on Metabolic variables. / S. Skouby, K. Petersen // J. Advances in Contraception.- 1991.- No. 7.- P. 77-88.
200. Smith, M.C. Pharmaceutical Marketing: strategy and cases. /Mickey C. Smith - New York: Pharmaceutical press, 1991. - 405 p.
201. Stern, L. Marketing Channels/ L. Stern // Business horizons.- 1990.- Vol.47, No. 3.- P.129-135.
202. Walther, H.P. Philosophic eines strategischen pharma Marketing N.R./ Walther //Pharm. Industr. - 1989.- Bd.51, No. 2.-S. 145-148.
203. Webster, F. Social aspects of marketing / F. Webster // J. of marketing-1989-№1.- P. 10-13.
204. Westhoff, C. Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate contraception. Metabolic parameters and mood changes/ Corolyn Westhoff // J. Reprod. Med. 1996-Vol. 41, No. 5- P. 401-406.
205. Winikoff, B. Women’s health: an alternative perspective for choosing interventions/ B. Winikoff//. Stutt. Fam. Plan. -1988.- Vol.19, No. 4.-P. 197-214.-214.
Studying the range of contraceptives at the Pharm-Leader pharmacy
The pharmaceutical market currently has a very wide range of contraceptives, which are divided into groups.
Each group of contraceptives has a number of advantages that play a role in the choice for different consumers (young people, middle-aged people, elderly people, parous and nulliparous women, and others). At the same time, each group of contraceptives has features and undesirable side effects that reduce their attractiveness to consumers.
Contraceptives general provisions
Contraceptives- these are means that can prevent the onset of unwanted pregnancy, as well as for the prevention of sexually transmitted infections.
All contraceptives can be divided into the following groups:
- 1. Hormonal contraceptives
- 2. Contraceptive IUDs
- 3. Barrier contraception
- 1. Hormonal contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives - these are products that contain sex hormones - estrogens and gestagen. They are prescribed not only as contraception, but also as a means of replacement therapy for the prevention and treatment of menopausal disorders.
Their action is based on the suppression of ovulation and thickening of the mucous secretion secreted by the cervix. Thick mucus prevents sperm from entering the uterine cavity, and the supply of sex hormones from the outside prevents the production of one’s own sex hormones, so the egg does not mature.
Combined oral contraceptives(COCs) contain 2 hormones estrogen and gestagen. Depending on their composition they are divided into:
- 1. Monophasic oral agents contain the same doses of estrogens and gestagens throughout the cycle.
- · high-dose - estrogen content more than 35 mcg (Tri-regol, Triquilar, Triziston, Ovidon, Non-Ovlon)
- low-dose - estrogen content less than 35 mcg (Yarina, Yarina Plus, Midiana, Tri-Mercy, Lindinet-30, Femoden, Silest, Janine, Siluet, Janetten, Miniziston, Regulon, Marvelon, Microgynon, Rigevidon, Belara, Diane-35, Chloe, Belluna-35, Demoulin)
- microdosed - estrogen content less than 20 mcg (Zoeli, Qlaira, Jess, Jess plus, Dimia, Miniziston 20 fem, Lindinet-20, Logest, Novinet, Mercilon)
- 2. Biphasic ones contain different doses of estrogens and gestagens throughout the cycle.
- 3. The first 11 tablets containing one dose of estrogen and gestagen, then 10 tablets in which the estrogen content remains the same, and the gestagen content increases. (Anteovin)
- 4. Three-phase ones contain different doses of estrogens and gestagens, the content of which changes three times during the entire cycle. (Tri-mercy, Triquilar, Tri-regol, Triziston)
Progestin-based oral contraceptives(mili-pili) are drugs containing only one hormone - gestagen (Exluton, Charozetta, Micronor, Microlut, Ovret). Microdoses of progesterone provide effective contraception in women without suppressing ovulation due to their effect on the viscosity of the cervical fluid. They have fewer side effects and quickly restore fertility after stopping use.
In recent years, parenteral contraceptive drugs (injectable, implantation, intrauterine) have become quite widespread.
Progestin-based parenteral contraceptives are indicated for women who do not tolerate oral administration of combined hormonal drugs well enough, or who are not attentive enough to strictly adhere to the daily regimen of taking the drug.
The advantages of parenteral contraceptives include the possibility of using them in lower doses than when taken orally.
Vaginal rings(NovaRing) are flexible contraceptive rings containing the hormones estrogen and progestogen in microdoses. Inserted into the vagina, the effect lasts for three weeks. Hormones do not pass through the liver, which reduces side effects. The negative point is prolapse, as well as side effects associated with the presence of a foreign body in the vagina - increased vaginal discharge.
Contraceptive patch(Evra) is a transdermal contraceptive system. Apply once a week, stick to the skin of the body (except for the mammary glands). In terms of the amount of hormones entering the blood, Evra corresponds to low-dose oral contraceptives. The drug does not pass through the liver and, therefore, there are no side effects from the gastrointestinal tract, and has virtually no effect on body weight or blood pressure.
Implant(Norplant) are 6 thin silicone capsules containing the hormone levonorgestrel, which enters the bloodstream for 5 years. It is inserted under the skin of the shoulder through a small incision under local anesthesia and removed after 5 years. A side effect is uterine bleeding.
Hormonal injections(Depo-Provera) - consists of an aqueous fine-crystalline suspension that contains high doses of gestagen, administered intramuscularly once every 3 months. Easy to use, long-lasting. The negative point is the need to see a doctor for an injection, and the inability to stop contraception at any time.
Hormonal intrauterine system(Mirena) is a plastic spiral with a container containing the hormone levonorgestrel (progestogen). It is installed in the uterine cavity, where it operates for 5 years. Mirena combines the benefits of intrauterine devices and hormonal contraceptives. Does not cause inflammatory reactions in the endometrium and significantly reduces the intensity of menstrual bleeding. Levonorgestrel, which is part of the drug, protects women from osteoporosis.
Emergency contraception is a way to prevent unwanted pregnancy and its development after fertilization of the egg in case of unprotected sexual intercourse or ineffective use of methods of permanent contraception. The drugs are used immediately after unprotected sexual intercourse no later than 12-24 hours, after 12 hours the dose is repeated.
- · Postinor is a contraceptive, antiestrogenic and progestogenic agent, the basis of which is the artificial hormone levonorgestrel.
- · Ginepreston (Zhenale, Agest) is a drug that prevents egg fertilization.
- · Escapelle is a modern medical product based on the hormone levonorgestrel.
- 1. Contraceptive IUDs
Intrauterine device(IUD) is an intrauterine contraceptive, which is a small device made of plastic with copper, which inhibits the advancement of sperm into the uterine cavity, reduces the lifespan of the egg and, first of all, prevents the attachment of the fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus. They are recommended for older women who have given birth. The ability to conceive is restored immediately after removal of the intrauterine contraceptive device.
2. Barrier contraception
Barrier methods of contraception is a method of contraception aimed at mechanically preventing sperm from entering the cervical canal and their movement through the woman’s genital tract, as well as protecting against sexually transmitted diseases. They are less effective, but very reliable if used in conjunction with spermicides.
Among them are:
- mechanical means of barrier contraception
- chemical methods of barrier contraception
Mechanical means of barrier contraception - are special products that serve as an obstacle to sperm entering the uterus.
- 1. Male Mechanical Barriers- these are condoms (condoms). Provides protection against sperm entering the woman's genital tract, and also protects against infections. (Contex long love, durex, simplex, viva, favorite condoms)
- 2. Female barrier methods of contraception:
Female condoms- protect against unwanted pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections. (Female condoms Female Condom FC2)
Diaphragm- This is a cap made of thin latex, around the circumference of which there is a spring ring. The diaphragm is placed over the cervix before sexual intercourse.
Contraceptive sponge- retains sperm, preventing it from entering the cervical canal, and, at the same time, releases a spermicidal substance. Inserted into the vagina immediately before sexual intercourse and placed in front of the cervix. (Today Sponge)
Chemical methods of barrier contraception - these include specific substances.
Spermicides- these are substances that partially or completely inactivate or destroy sperm. The active ingredients included in their composition destroy sperm, reduce their motility and ability to fertilize.
Cream, vaginal gel - inserted into the vagina immediately before sexual intercourse. (Cream Delfen, Benatex gel)
Suppositories and vaginal tablets inserted into the vagina 10-20 minutes before sexual intercourse. (Vaginal suppositories Conceptrol, Pharmatex, Erotex, vaginal tablets Ginekotex, Benatex)
Studying the range of contraceptives at the pharmacy
When studying the assortment of contraceptives at the Pharm-Leader pharmacy, it was found that not all contraceptives are available in the pharmacy. The following types of contraceptives are not available in the pharmacy:
- 1. Hormonal contraceptives:
- · Vaginal rings (Nova Ring)
- Contraceptive patch (Evra)
- Implant (Norplant)
- 2. Barrier contraceptives:
- · Female condoms
- Contraceptive sponge
A very small quantity in the pharmacy’s assortment (only 1-2 items):
- 1. Vaginal suppositories:
- Pharmatex
- Conceptol
- 2. Vaginal tablets:
- · Gynekotex
The absence of the above-mentioned contraceptives in the pharmacy assortment can be explained by insufficient knowledge of the population about these contraceptives and the lack of demand for them.
Over the past period, the Group’s drug sales volumes amounted to $180 million and 27 million packs. The weighted average price of one standard package, therefore, amounted to 6.7 dollars. At the end of 2006, the share of contraceptive drugs in the total sales of all drugs was 3.9% of dollars and 0.8% of packing units.
Table 1. TOP 10 trade names
| No. | Cost rating | Natural rating | ||
| Trade name | %,Doll. | Trade name | %, pack. | |
| 1 | POSTINOR | 11,9 | POSTINOR | 21,6 |
| 2 | LOGEST | 10,3 | REGULON | 9,0 |
| 3 | YARINA | 8,0 | NOVINET | 8,1 |
| 4 | NOVINET | 7,0 | RIGEVIDON | 7,0 |
| 5 | REGULON | 7,0 | TRI-REGOL | 6,8 |
| 6 | MARVELON | 6,3 | LOGEST | 6,3 |
| 7 | JANINE | 5,5 | MARVELON | 4,5 |
| 8 | NOVARING | 4,9 | FARMATEX | 4,2 |
| 9 | TRI-MERCY | 4,6 | YARINA | 3,9 |
| 10 | MERSILON | 4,2 | LINDINET 20 | 3,3 |
TOP-10 pharmacy sales by trade name are presented in Table 1. Of the 45 titles participating in sales, the first three lines are occupied by Postinor, Logest And Yarina, which account for 30.2% of the value volume and about 32% of the natural volume. These are oral contraceptive drugs - Logest and Yarina - combined monophasic drugs, Postinor - a drug containing only progestogens, used for emergency contraception after sexual intercourse.
Table 2. TOP-10 manufacturing companies
| No. | Cost rating | Natural rating | ||
| Manufacturing company | %,Doll. | Manufacturing company | %, pack. | |
| 1 | GEDEON RICHTER | 37,8 | GEDEON RICHTER | 58,4 |
| 2 | SCHERING AG | 31,4 | SCHERING AG | 18,1 |
| 3 | ORGANON | 23,1 | ORGANON | 14,1 |
| 4 | 3,6 | LABORATOIRE INNOTECH INTERNATIONAL | 4,2 | |
| 5 | JANSSEN PHARMACEUTICA N.V. | 1,3 | MERZ CO GMBH | 2,0 |
| 6 | MERZ CO GMBH | 1,2 | JANSSEN PHARMACEUTICA N.V. | 1,0 |
| 7 | PFIZER | 0,7 | NIZHFARM OJSC | 1,0 |
| 8 | LEIRAS | 0,4 | PFIZER | 0,6 |
| 9 | NIZHFARM OJSC | 0,2 | 0,2 | |
| 10 | AMCAPHARM PHARMACEUTICAL GMBH | 0,2 | LEIRAS | 0,2 |
During this period, there were 17 manufacturers of the studied group of drugs on the Russian pharmaceutical market. Of these, the absolute sales leaders are: GEDEON RICHTER - 37.8% of dollars (manufacturer of the drugs Novinet, Postinor, Lindinet, Tri-Regol, etc.), SCHERING AG with a share of 31.4% of dollars (Zhanin, Non-Ovlon, Logest, Femoden, etc.) and ORGANON - 23.1% dollars (Mersilon, Marvelon, Charozetta, etc.). About 60% of the natural volume belongs to GEDEON RICHTER (due to sales of the drug Postinor).
TOP-5 nonproprietary names (NN) of the group of contraceptives are shown in Fig. 1. The most popular among consumers are drugs with the NN “ethinyl estadiol + desogestrel”, which accounted for 29.2% of the value volume and 27.5% of the natural one. These are drugs with the trade names Novinet, Marvelon, Tri-Mercy, Mercilon, etc.
The drugs of the study group belong to three groups of ATS of the 3rd level: “Contraceptives for local use”, “Hormonal oral contraceptives” and: “Progestogens” (Figure 2). About 90% of sales in value and volume are occupied by oral contraceptives.
Many modern contraceptives, in addition to their pregnancy-preventing effect, are used to treat many gynecological diseases; drugs with antiandrogenic activity have a beneficial effect on the condition of the skin and hair. The Group’s wide range of drugs allows you to choose the right drug, taking into account the characteristics of each woman.
The article uses data from a retail audit of the Russian pharmaceutical market by DSM Group; the QMS complies with the requirements of ISO 9001:2000.
The pharmaceutical market currently has a very wide range of contraceptives, which are divided into groups.
Each group of contraceptives has a number of advantages that play a role in choice for different consumers (young people, middle-aged people, elderly people, parous and nulliparous women, and others). At the same time, each group of contraceptives has features and undesirable side effects that reduce their attractiveness to consumers.
1.1 Contraceptives, general provisions
Contraception(from novolat. “contraceptio” - lit. - exception) - prevention of pregnancy by mechanical (condoms, cervical caps, etc.), chemical (for example, vaginal balls, gramicidin paste) and other contraceptives and methods.
Contraceptives- these are means that can prevent the onset of unwanted pregnancy, as well as for the prevention of sexually transmitted infections.
Contraceptives are divided into several types:
Barrier contraceptives,
Chemical contraceptives,
Hormonal (including mechanical hormone releasers),
Contraceptive coils,
Sterilization.
1.Barrier contraceptives
Barrier contraception is a method of contraception aimed at mechanically preventing sperm from entering the cervical canal and their movement through the woman’s genital tract, as well as protecting against sexually transmitted diseases. They are less effective, but very reliable if used in conjunction with spermicides.
There are two classifications of barrier methods of contraception:
By method of use:
mechanical means of barrier contraception;
chemical methods of barrier contraception.
By purpose:
male and female condoms;
vaginal diaphragms and cervical caps.
Let's consider the first classification of barrier methods of contraception:
Mechanical means of barrier contraception- are special products that serve as an obstacle to sperm entering the uterus.
Male Mechanical Barriers- these are condoms (condoms). Provides protection against sperm entering the woman's genital tract, and also protects against infections. (Contex long love, durex, simplex, viva, favorite condoms).
Female barrier methods of contraception:
Female condoms- protect against unwanted pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections. (Female condoms FemaleCondom FC2).
Diaphragm- This is a cap made of thin latex, around the circumference of which there is a spring ring. The diaphragm is placed over the cervix before sexual intercourse.
Contraceptive sponge- retains sperm, preventing it from entering the cervical canal, and, at the same time, releases a spermicidal substance. Inserted into the vagina immediately before sexual intercourse and placed in front of the cervix. (TodaySponge).
Chemical methods of barrier contraception - these include specific substances.
Spermicides- these are substances that partially or completely inactivate or destroy sperm. The active ingredients included in their composition destroy sperm, reduce their motility and ability to fertilize.
Cream, vaginal gel- inserted into the vagina immediately before sexual intercourse.
Suppositories and vaginal tablets inserted into the vagina 10-20 minutes before sexual intercourse.
Let's consider the second classification of barrier methods of contraception:
1.Male condom It is a thin oblong latex shell. It is put on the erect penis and protects the mucous membranes of partners from direct contact.
A condom is the most important means of contraception at the moment, since when used correctly it reliably prevents not only pregnancy, but also the transmission of infections, including HIV and hepatitis.
Flaws: requires a stable erection; may tear.
The use of a condom is under the control of the man, while the negative consequences of improper use - unwanted pregnancy - mainly fall on the woman. Both partners are at risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
Many men refuse to use condoms, believing that they reduce the intensity of sensations, obviously without comparing them with the intensity of sensations a woman experiences during an abortion. In fact, there are condoms with special surfaces that improve the sensation of both partners, which are recommended even for men who have difficulty achieving orgasm.
Condoms are also used to protect against the transmission of infections during oral and anal sex.
Reliability: 98%
Female condom- a polyurethane tube with a diameter of 8 cm and a length of 15 cm. Placed in the vagina and protects the mucous membranes of partners from direct contact.
Like the male condom, it prevents pregnancy and the transmission of infections. Can be used for weak erections. May remain in the vagina for several hours.
Flaws: Currently not sold in Russia.
Reliability: 95%
2.Vaginal diaphragms and cervical caps.
Caps and softer elastic diaphragms made of various materials (silicone, latex) are used in conjunction with spermicidal ointments. They are placed in the vagina so as to prevent sperm from entering the uterus, and are removed no earlier than 6 hours after the last ejaculation. Reduce the risk of transmission of certain infections. Does not prevent HIV infection. Can be used repeatedly (usually for 1-2 years). To choose the appropriate cap or diaphragm size, you need to consult a gynecologist.
Disadvantages of caps: less effective for women who have given birth. You need to re-size after giving birth. May cause inconvenience to partners.
Disadvantages of diaphragms: You need to reselect the size after childbirth and with a significant (from 5 kg) change in weight. May increase the risk of certain infections and inflammation of the cervix.
Reliability: 85-95%.