Functions additional education children in the context of a student-centered approach to education.
Additional education for children – an integral part of general education.
Purpose of additional education: Creation of a developing educational environment, which helps to identify and develop those inclinations and abilities of children that will ensure their sustainable self-development in life.
Additional education is based on the following priority principles:
free choice by the child of types and areas of activity;
focus on the child’s personal interests, needs, and abilities;
opportunityfree self-determination and self-realization of the child;
unity of training, education, development;
practical-activity basis of the educational process.
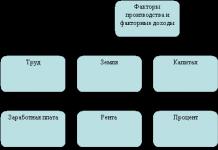
BASIC FUNCTIONS OF ADDITIONAL EDUCATION
value-oriented aimed at the child’s mastery of social, cultural, moral values through a system of personally significant activities;
communicative, allowing you to expand your circle of communication, learn the rules and forms of cooperation, respectful attitude towards partners, and the ability to conduct dialogue;
social-adaptive , providing the child with the ability to solve real life problems, become an active member of the community;
psychotherapeutic, creating comfortable relationships in a team where the child has the right to make mistakes, where he can experience a situation of success;
career guidance, allowing the younger generation to gain an early understanding of the world of professions and reduce the risk of incorrectly defining their professional work;
culture-forming , promoting the active inclusion of the child in a variety of layers of culture, allowing not only to expand their horizons, but also to master productive ways to enrich the cultural environment.
IN additional education the very specifics of children’s activities require the organization of the educational process withdevelopmental training positions . Here the educational process is less formalized compared to basic education, so it is closer to the natural foundations of child development. If in school during lessons learning is initiated by the teacher, then in the system of additional education of children - first of all by the child himself, who himself chooses an interesting type of activity.
Personality-oriented approach to teaching - concentration of the teacher’s attention on the holistic of a person, concern for the development of not only his intellect, civic sense of responsibility, but also his spiritual personality with emotional, aesthetic, creative inclinations and development opportunities.
The goal of personality-oriented education is to create conditions for the full development of the following functions of an individual:
human ability to ;
the ability to reflect and evaluate one’s life;
search, creativity;
formation of the image of “I”;
(in accordance with the wording “I am responsible for everything”);
autonomy of the individual (as it develops, it becomes increasingly freed from other factors).
Interaction between teacher and student in educational institutions
In student-centered education, the student is .
The teacher becomes not so much a “source of information” and “controller”, but rather a diagnostician and assistant in the development of the student’s personality. Organization of such educational process presupposes the presence of leadership, the formula of which may well be taken from - “help me do it myself.”
Methods and approaches of student-centered education
Personally-centered education implies a focus on the training, education and development of all students, taking into account their individual characteristics:
age, physiological, psychological, intellectual;
educational needs, orientation towards different levels the complexity of the program material available to the student;
identifying groups of students according to knowledge and abilities;
distribution of students into homogeneous groups: abilities, professional orientation;
treating each child as a unique individual.
The difference between LOP and traditional training
Traditional approach
Person-centered approach
Learning as a normally structured process (and strictly regulated at that)
Learning as an individual activity
student, its correction and pedagogical
support
The development vector is set
Education not only sets the vector of development,
how much creates everything necessary for this
Terms
A common, unified and obligatory line of mental development for all
Helping every student improve
your individual abilities,
Develop as a person, taking into account
his existing knowledge experience
The development vector is built from training to teaching
The development vector is built from the student
Towards the definition of pedagogical influences,
contributing to its development
The task of personality formation with given
properties
Security personal growth, developing
Abilities for strategic activities,
Creativity, criticality, meaning-making,
system of needs and motives,
Self-determination abilities
self-development, positive self-concept
Pedagogical technologies based on a student-centered approach
Personality-oriented learning (Yakimanskaya I.S.) 1
Technology of self-development training (Selevko G.K.) 2
Pedagogical technologies of adaptive school 3
Humane-personal technology Amonashvili Sh.A.4
Gaming technologies 5
Level differentiation technologies 6
Individual learning technology ( individual approach, individualization of learning, project method)7
Technology "Pedagogical workshops" 8
The following interrelated tasks are aimed at achieving the goal:
· improvement legislative framework in terms of additional education for children, bringing the regulatory framework of the system into compliance with Russian legislation;
· preservation and development of a network of institutions for additional education for children;
· ensuring state guarantees of accessibility and equal opportunities for students to receive additional education, achieving the effectiveness and quality of additional education for children;
· preservation of a unified educational space based on the continuity of the content of basic and additional education for children;
· maintaining the interdepartmental nature of the system of additional education for children;
· improving the content, organizational forms, methods and technologies of additional education for children;
· creation and development of new information technologies, including telecommunication projects and distance learning in institutions of additional education for children;
· improving the system of state certification and accreditation of institutions of additional education for children;
· guaranteed allocation of funds from budgets of all levels for material and technical support for the activities of institutions of additional education for children;
· development and approval of a block of resource support for additional education of children in accordance with the focus of educational programs;
· improving the social status and professional development of teaching and management personnel in the system of additional education for children, support All-Russian competition teachers of additional education “I give my heart to children”;
· development of socio-economic measures of regulatory legal regulation attracting extra-budgetary funds by institutions of additional education for children;
· development of additional education for children as an open state-social system based on the distribution of responsibilities between subjects of educational policy and increasing the role of all participants in the educational process - students, teachers, parents.

What are the main values and functions of additional education for children?
The concept of modernization of additional education for children Russian Federation until 2010 (6.10.2004 No. PK-2)
...Additional education of children is based on the following principles: humanization, democratization of the educational process, individualization, pedagogy of cooperation. The most important principle of additional education for children is the child’s voluntary choice of a subject (type) of activity, a teacher and an association of interests. It is in demand by children, parents, teachers and society as a whole, as it allows one to satisfy various cognitive interests of the individual in the informal educational process. Institutions of additional education for children create equal “starting” opportunities for each child, sensitively responding to the rapidly changing needs of children and their parents, provide assistance and support to gifted and talented students, raising them to a qualitatively new level of individual development. Each institution of additional education for children should become an organizational and methodological center for the development of additional education for children educational institutions various types and views of your neighborhood, municipality, region. Government institutions additional education for children (federal, republican, regional, regional) must carry out coordinating, informational, organizational, programmatic and methodological functions to support the development of additional education for children at the subject level.
...Additional education for children is essentially practice-oriented. It is largely carried out by specialists, professionals, “masters of their craft”, which ensures its versatility, attractiveness, uniqueness and, ultimately, effectiveness. Additional education for children is the “zone of proximal development” of the child’s personality, which he chooses himself or with the help of an adult in accordance with his desires and needs. The flexibility of additional education for children as an open social system makes it possible to provide conditions for the formation of leadership qualities, the development of social creativity, and the formation of social competencies. The system of additional education for children is developing on an interdepartmental basis and acts as a guarantor of the support and development of gifted children. Expenditures from budgets of all levels on additional education of children are long-term investments in the future development of Russian society and the state, human resources for the intellectual, scientific, technical, creative and cultural development of society; neglect and prevention of juvenile delinquency and other antisocial manifestations in children and adolescents. In institutions of additional education for children, socio-pedagogical models of activity are more effectively introduced, since the traditions, style and methods of work of these institutions take into account the characteristics of society as much as possible. The consequence of this is that children accumulate experience in civic behavior, the foundations of democratic culture, personal self-worth, conscious choice of profession, and receive qualified assistance in various aspects of social life, which affects the social adaptation of children and youth to changing living conditions.
Methodological recommendations of the Department of Education and Additional Education of Children and Youth of the Ministry of Education of Russia on the development of additional education for children in general education institutions (Appendix to the letter of the Ministry of Education of Russia dated January 1, 2001 No. /16)
The interdepartmental program for the development of the system of additional education for children over the years, approved by order of the Ministry of Education of Russia dated January 1, 2001 No. 193, considers the development of additional education for children as one of the priority areas of educational policy.
Additional education for children is a purposeful process of upbringing, personal development and learning through the implementation of additional educational programs, the provision of additional educational services and information educational activities beyond the boundaries of basic educational programs in the interests of the individual and the state.
Additional education for children cannot be considered as some kind of appendage to basic education that performs the function of expanding opportunities educational standards. Its main purpose is to satisfy the constantly changing individual sociocultural and educational needs of children. In science, additional education for children is considered as a “particularly valuable type of education”, as a “zone of proximal development of education in Russia.”
The modern system of additional education for children provides the opportunity for millions of students to engage in artistic and technical creativity, tourism, local history, environmental and biological activities, sports and research work– in accordance with your desires, interests and potential capabilities.
Important changes have occurred in the software and methodological support for additional education for children: additional education teachers are developing original additional programs, trying to create conditions for the development of children's creative activity, while realizing their own professional and personal potential.
When organizing additional education for children in general education institutions, one should rely on the following priority principles:
1. The child’s free choice of types and areas of activity.
2. Focus on the child’s personal interests, needs, abilities,
3. The possibility of free self-determination and self-realization of the child.
4. Unity of training, education, development.
5. Practical activity basis of the educational process.
 The listed positions constitute the conceptual basis of additional education for children, which corresponds to the main principles of humanistic pedagogy: recognition of the uniqueness and self-worth of a person, his right to self-realization, the personally equal position of the teacher and the child, focus on his interests, the ability to see in him a person worthy of respect.
The listed positions constitute the conceptual basis of additional education for children, which corresponds to the main principles of humanistic pedagogy: recognition of the uniqueness and self-worth of a person, his right to self-realization, the personally equal position of the teacher and the child, focus on his interests, the ability to see in him a person worthy of respect.
Education, as a top priority in education, should become an organic component of pedagogical activity, integrated into the overall process of learning and development. The most important tasks of education are the formation in schoolchildren of civic responsibility and legal self-awareness, spirituality and culture, initiative, independence, tolerance, the ability for successful socialization in society and active adaptation in the labor market.
Download:
Preview:
Municipal Educational Institution of Children's Education "Rakityan Children's Creativity House"
Article topic:
“Goals, objectives and functions of additional
education of children in the Russian educational system"
Methodist at the Children's Creativity House:
Shapovalova Ksenia Valerievna
Rakitnoye village - 2014
Goals, objectives and functions of additional education for children in the Russian educational system
Education, as a top priority in education, should become an organic component of pedagogical activity, integrated into the overall process of learning and development. The most important tasks of education are the formation in schoolchildren of civic responsibility and legal self-awareness, spirituality and culture, initiative, independence, tolerance, the ability for successful socialization in society and active adaptation in the labor market.
By “additional” we mean motivated education beyond the framework of basic education, which allows a person to acquire a stable need for knowledge and creativity, to realize himself to the maximum, to self-determinate himself objectively, socially, professionally, personally.
The main objectives of the institution of further education:
- providing the necessary conditions for personal development, health promotion, professional self-determination and creative work of children aged mainly from 6 to 18 years;
- their adaptation to life in society;
- formation of a common culture;
- organization of meaningful leisure;
- meeting children's needs for activities physical culture and sports.
The goal of modernizing additional education for children is to create conditions and a mechanism for the sustainable development of the system of additional education for children in the Russian Federation; ensuring modern quality, accessibility and effectiveness of additional education for children based on preserving the best traditions of out-of-school education and additional education in various areas of educational activity. Additional education for children is based on the following principles: humanization, democratization of the educational process, individualization, and pedagogy of cooperation. The most important principle of additional education for children is the child’s voluntary choice of a subject (type) of activity, a teacher and an association of interests. It is in demand by children, parents, teachers and society as a whole, as it allows one to satisfy various cognitive interests of the individual in the informal educational process.
Institutions of additional education for children create equal “starting” opportunities for each child, sensitively responding to the rapidly changing needs of children and their parents, provide assistance and support to gifted and talented students, raising them to a qualitatively new level of individual development. Each institution of additional education for children should become an organizational and methodological center for the development of additional education for children for educational institutions of various types in their microdistrict, municipality, and region. State institutions of additional education for children (federal, republican, regional, regional) must carry out coordinating, informational, organizational, program and methodological functions to support the development of additional education for children at the subject level. Additional education for children is essentially practice-oriented. It is largely carried out by specialists, professionals, “masters of their craft”, which ensures its versatility, attractiveness, uniqueness and, ultimately, effectiveness. Additional education for children is the “zone of proximal development” of the child’s personality, which he chooses himself or with the help of an adult in accordance with his desires and needs. The flexibility of additional education for children as an open social system makes it possible to provide conditions for the formation of leadership qualities, the development of social creativity, and the formation of social competencies. The system of additional education for children is developing on an interdepartmental basis and acts as a guarantor of the support and development of gifted children. Expenditures from budgets of all levels on additional education of children are long-term investments in the future development of Russian society and the state, human resources for the intellectual, scientific, technical, creative and cultural development of society; neglect and prevention of juvenile delinquency and other antisocial manifestations in children and adolescents.
In institutions of additional education for children, socio-pedagogical models of activity are more effectively introduced, since the traditions, style and methods of work of these institutions take into account the characteristics of society as much as possible. The consequence of this is that children accumulate experience in civic behavior, the foundations of democratic culture, personal self-worth, conscious choice of profession, and receive qualified assistance in various aspects of social life, which affects the social adaptation of children and youth to changing living conditions.
The modern system of additional education for children provides the opportunity for millions of students to engage in artistic and technical creativity, tourism, local history, environmental and biological activities, sports and research - in accordance with their desires, interests and potential capabilities.
Important changes have occurred in the software and methodological support for additional education for children: additional education teachers are developing original additional programs, trying to create conditions for the development of children's creative activity, while realizing their own professional and personal potential.
When organizing additional education for children in general education institutions, one should rely on the following priority principles:
- free choice by the child of types and areas of activity;
- focus on the child’s personal interests, needs, and abilities;
- the possibility of free self-determination and self-realization of the child;
- unity of training, education, development;
- practical-activity basis of the educational process
The fundamental difference between additional education and general education is that, due to the absence of strict educational standards, teachers working in its system have the opportunity to transform the methods of activity (knowledge-abilities-skills) transmitted to students from the purpose of learning into a means of developing students’ abilities - physical, cognitive, personal, spiritual and moral The goal in this case is to create a developing educational environment that would ensure that each student demonstrates the creative principle inherent in him by nature, i.e. gain the ability to be a creative subject of your own development
Social function aimed at satisfying:
a) social demand (requirements of society, formed at the intersection of culture, education and public health);
b) parental demand (ideas about what their child needs or what is lacking: time commitment, pre-vocational training, education in additional subjects, solving problems of single-parent families, prestige of occupations, health),
c) children's demand - meeting the needs of cognitive and personal development, communication, leisure and pastime. Children's demand is dynamic, since it changes during the child's development, as well as depending on age and the corresponding type of leading activity;
d) economic demand - the opportunity to earn money (main, additional, part-time, etc.) for adults and pre-vocational training for children.
e) law enforcement demand - prevention of deviant and antisocial, including illegal, behavior of children.
Psychological function:
A) developing - creation of an educational environment that provides conditions for the physical and mental development of children (realization of children's interests, acquisition of skills. A child, not having the opportunity to express himself in a family and school environment, can prove himself in a pre-school education both in terms of development and self-affirmation , and in terms of self-actualization;
b) compensatory - psychological compensation for failures in the family, at school,
V) relaxation - an opportunity to take a break from the strict regulation of behavior in the family and at school;
G) consulting - for teachers, parents and children.
Educational function:
a) education in additional subjects, i.e. subjects additional to the standard list of academic subjects in general education institutions. For example, ship and aircraft modeling, sports sections, choreography, etc. These can also be “school” subjects, if for some reason there are no teachers in nearby schools in these subjects,
b) propaedeutics vocational education(for example, a design studio or a children's television studio);
c) professional self-determination;
d) training that satisfies the cognitive interest of a given child,
e) socializing - communication with peers, self-affirmation, self-determination, including - try to find yourself in different types activities, enrichment with social experience, development of the child as an individual, acquisition of the opportunity and ability to be not only an object, but also a subject of social influences and interactions,
Concept for the development of additional education for children in the Russian Federation ORDER of September 4, 2014 N 1726-r
Additional education functions as a “social elevator” for a significant portion of children who do not receive the required volume or quality educational resources in family and general education.
Additional education thus compensates for their shortcomings or provides alternative opportunities for the educational and social achievements of children, including such categories as children with developmental disabilities and children in difficult life situations. Additional education is implemented in child-adult communities and at the same time shapes them, ensuring intergenerational solidarity.
Additional education is characterized by obvious relevance for students, since it is associated with the implementation of personal needs and life plans. In the system of additional education, the cognitive activity of students always goes beyond the educational environment itself into the sphere of a wide variety of social practices. By becoming members of highly motivated child-adult educational communities, students receive a wide social experience of constructive interactions and productive activities. IN creative environment additional education, which provides opportunities for the disclosure and effective development of abilities, creates a creative, socially mature and active personality, striving for constant self-education, self-improvement and self-realization throughout life.
The competitive advantages of additional education in comparison with other types of formal education are manifested in its following characteristics: free personal choice of activities that determine individual development person; variability of content and forms of organization of the educational process; accessibility of global knowledge and information for everyone; adaptability to emerging changes.
Penetrating the levels of preschool, general, and vocational education, additional education becomes a semantic sociocultural core for a maturing individual, the key characteristic of which is cognition through creativity, play, work and research activity.
The fundamental difference between additional education and general education is that, due to the absence of strict educational standards, teachers working in its system have the opportunity to transform the methods of activity (knowledge-abilities-skills) transmitted to students from the purpose of learning into a means of developing students’ abilities - physical, cognitive, personal, spiritual and moral The goal in this case is to create a developing educational environment that would ensure that each student demonstrates the creative principle inherent in him by nature, i.e. gain the ability to be a creative subject of your own development
You can also find the information you are interested in in the scientific search engine Otvety.Online. Use the search form: